Heimler's History: APUSH Unit 1, APUSH Period 1 Review (1491-1607)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
How were tribes in the Americas described?
Diverse, as they did many different things and had different ways of life.
Some farmed, created cities, were nomads, etc.
Who were the Aztecs? Where did they live? What are some characteristics of their society?
Civilization in Mexico (at its peak had 300,000 people).
Capital city at Tenochtitlan.
Had written language, complex irrigation systems, and human sacrifice.
Who were the Mayans? Where did they live? What are some characteristics of their society?
Civilization in Yucatan Peninsula Mexico
Had large cities, complex irrigation systems, and large stone temples for rulers/gods.
Who were the Inca? Where did they live? What are some characteristics of their society?
Civilization in Andes Mtns of Peru (at height ruled 16 million people and covered 350,000 square miles.
Had fertile mountain valleys and irrigation systems that were great for farming.
Which crop did the Aztecs, Mayans, and Inca grow? How did this affect their society?
Maize.
This supported them economically, socially, politically, this was their cash crop that made their civilization grow.
What are the similarities of the civilizations of the Aztecs, Mayans, and Inca?
All located in Central/South America and Mexico.
Maize was the cash crop.
All had complex cities, irrigation systems, writing, and lots of technological advancements along with great infrastructure.
Who were the Pueblo? Where did they live? What are some characteristics of their society?
Lived in present day Arizona and New Mexico.
Sedimentary farmers that built their homes in the open and in sides of cliffs (remember Pueblo National Park).
Highly organized society.
Maize
Corn
Where was maize popular?
Present day Mexico northward to Southwest
How did maize transform society?
Less emphasis on hunting and gathering, increase in population, est. permanent villages with socially diverse societies
What was the main type of lifestyle in the Great Plains and the Great Basin?
Hunting and gathering because of the aridity and lack if natural resources
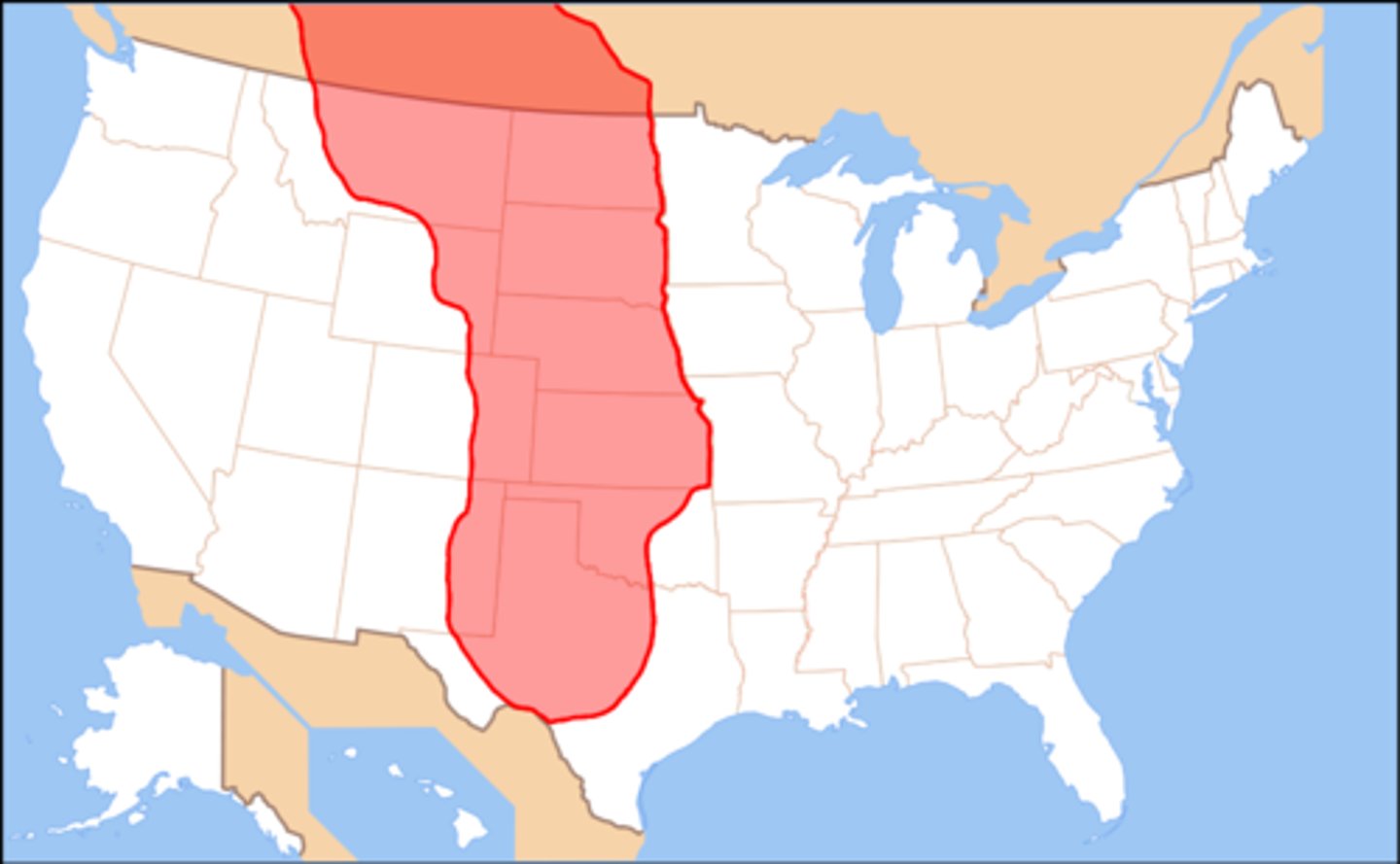
Arid
Dry
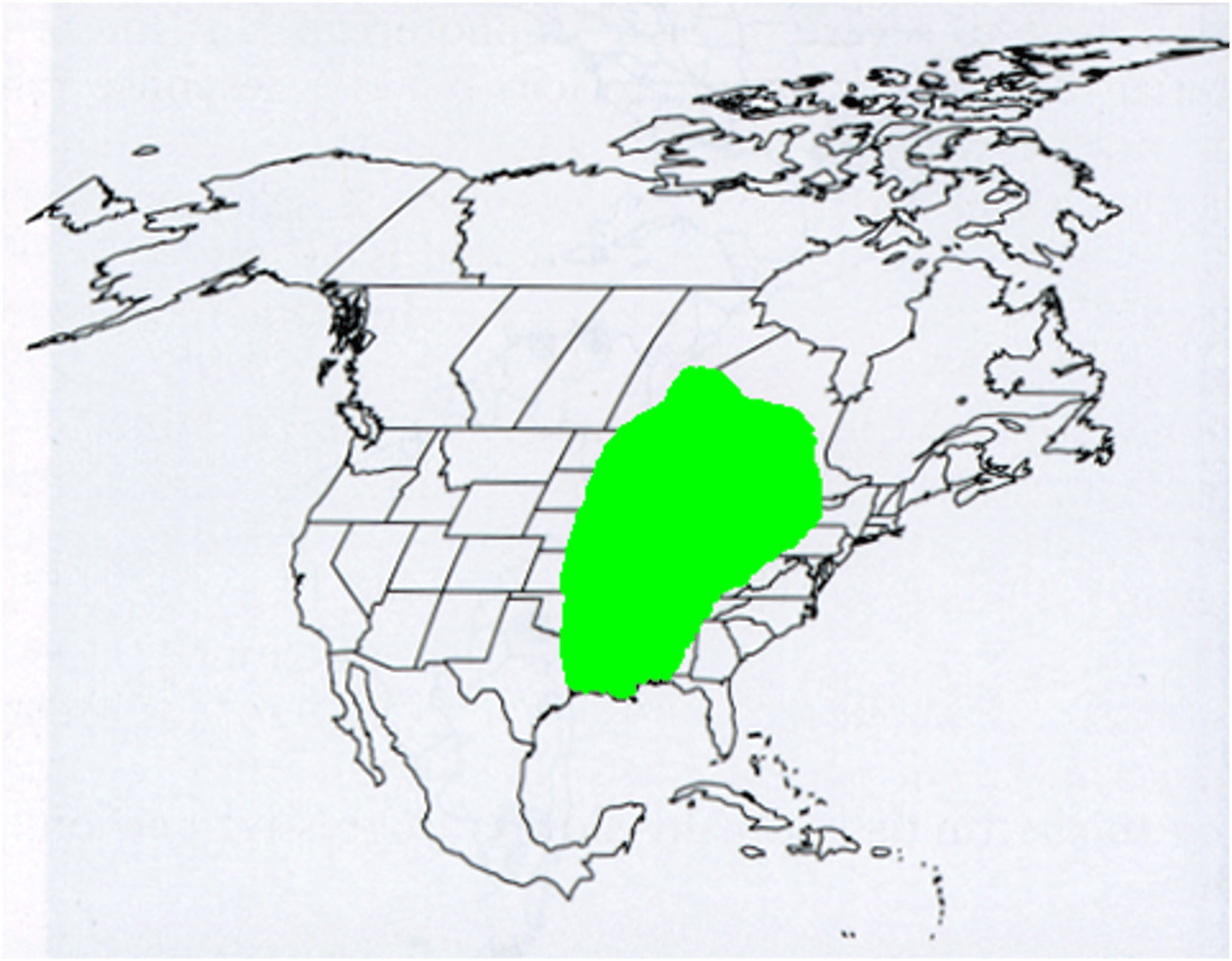
What type of lifestyle was found in the Northeast, Mississippi River Valley and along the Atlantic?
A mix of agricultural and hunter gatherer economies that favored the development of permanent villages.
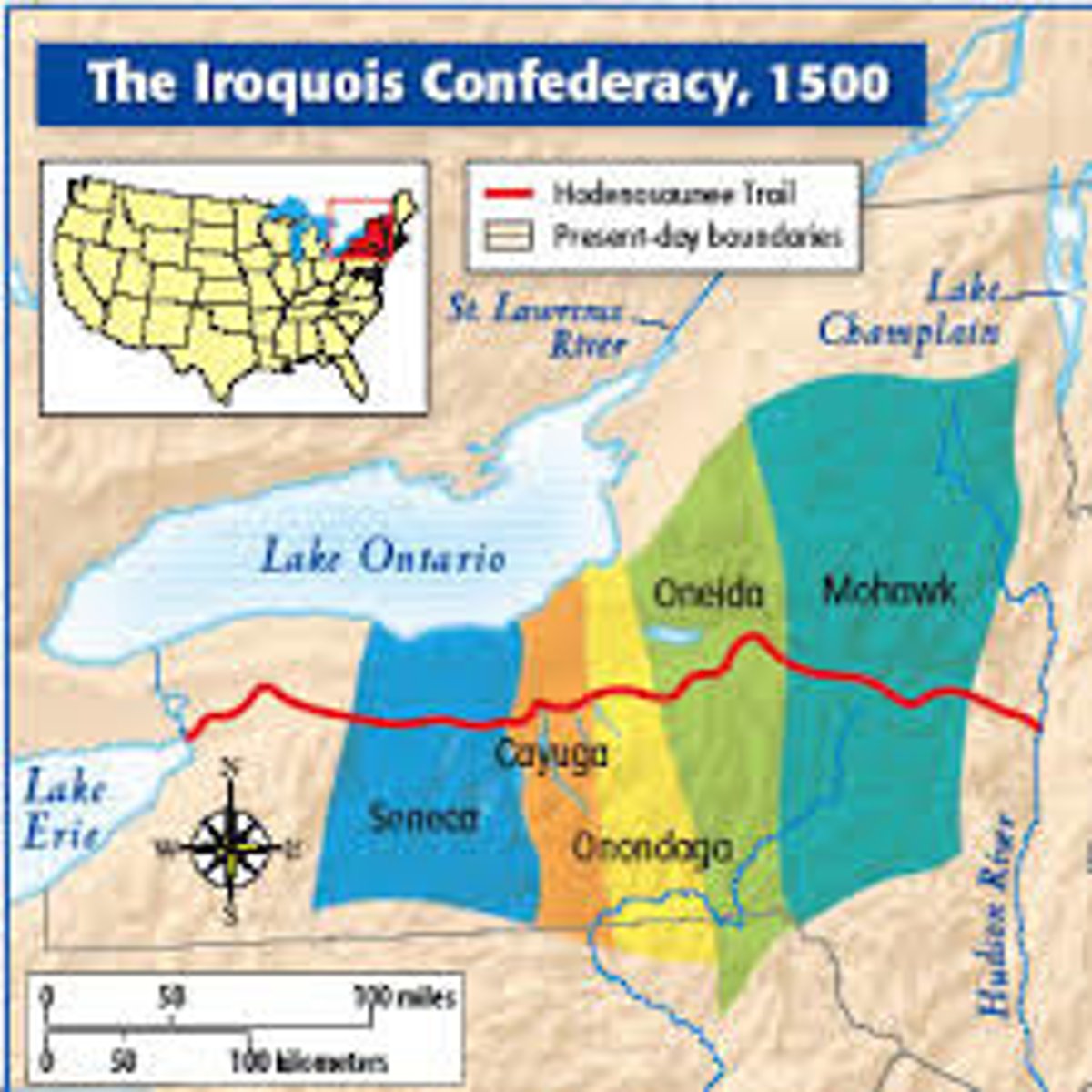
What is an example of a society being influenced by the economy?
The Iroquois were a matriarchal society because they were hunter gatherers. Women oversaw the crops and community affairs while the men were off hunting.
What were the societies of the Northwest and California based on?
Hunting, gathering and foraging
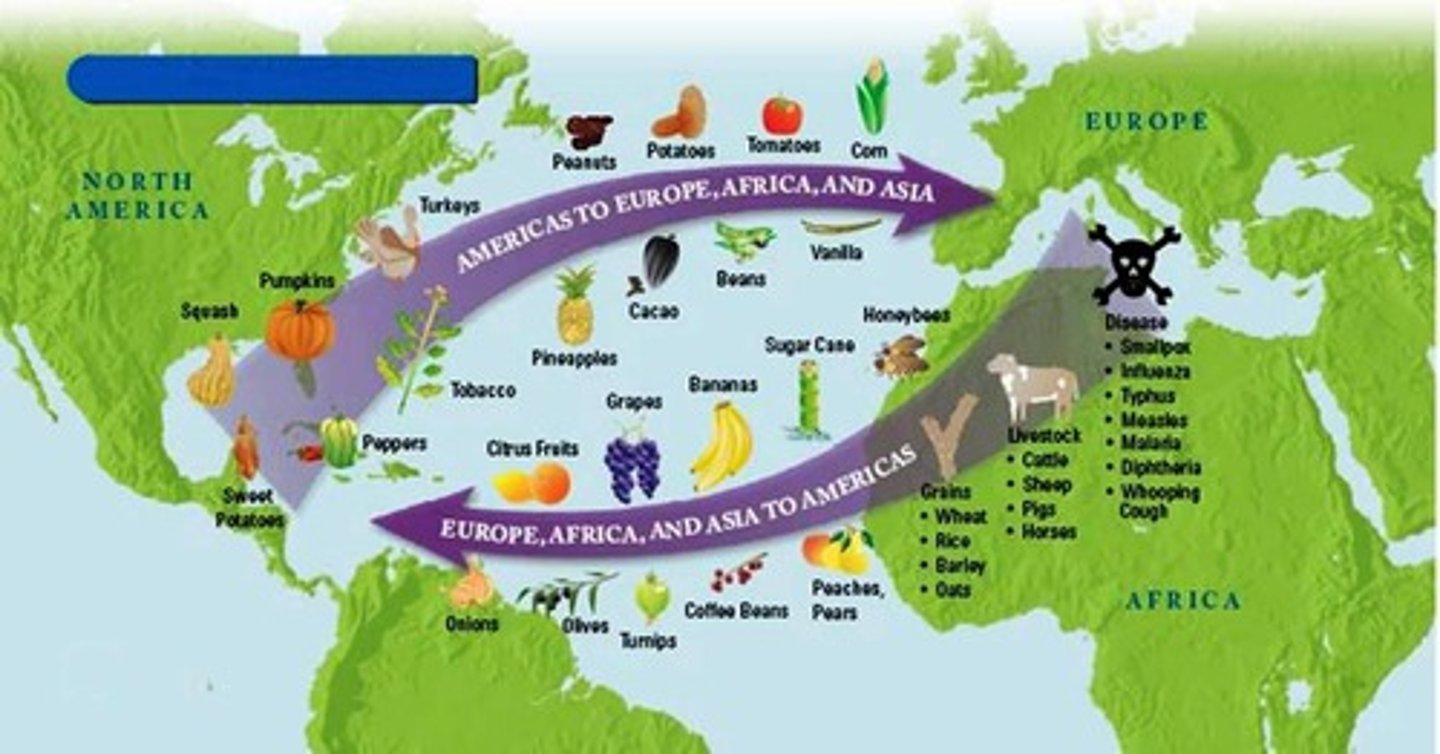
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, cultures, resources, languages, diseased and ideas between the Americas, Europe and Africa.
What triggered European nations' efforts to explore and conquer the New World?
3 gs: gold, glory (fame), god
Christopher Columbus
Italian mariner who in 1492 sailed west across the Atlantic Ocean in search of the Indies.
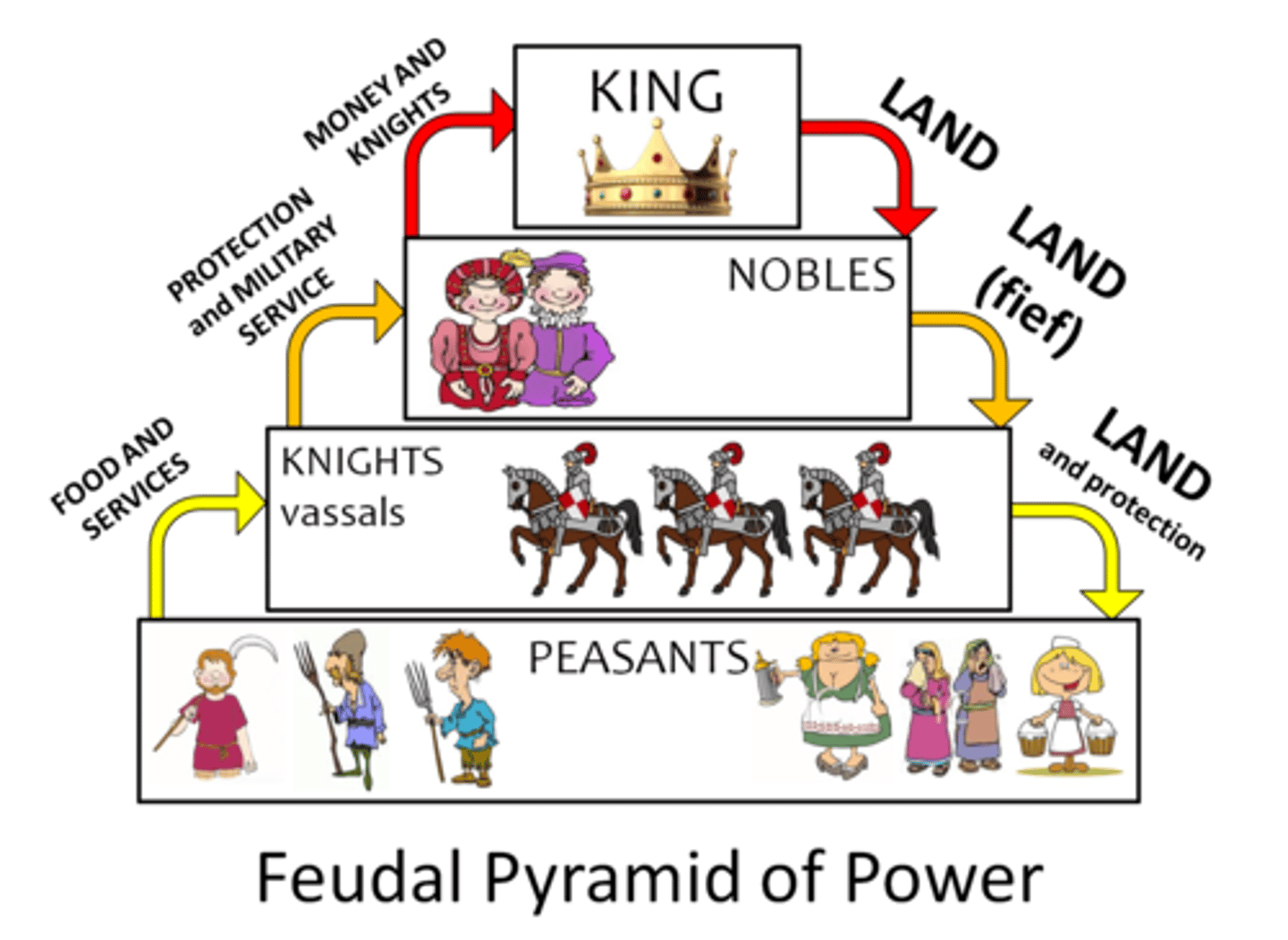
Feudalism
Political and economic system in medieval Europe, in which lesser lords received lands from powerful nobles in exchange for service.
Sextant
A piece of technology that could be used to find the exact position on earth that allowed for more precise sailing.

Caravel ship
Developed by the Portuguese that allowed for faster travel.

Joint Stock Company (with an example)
People would pool their money to raise money for explorations and would share the profits and losses of colonies. Ex. Jamestown in 1607

True or False: Spanish exploration and conquest of the Americas were accompanied by the deadly diseases and killed up to 90% of natives in some places.
True
How did the introduction of horses impact life on the Great Plains?
1) Some tribes became horse nomads
2) Hunting became more important as ranges increased
3) More frequent contact with other tribes caused an increased likelihood of competition and conflict
4) Wealth was sometimes measured by ones horses
5) could carry larger loads

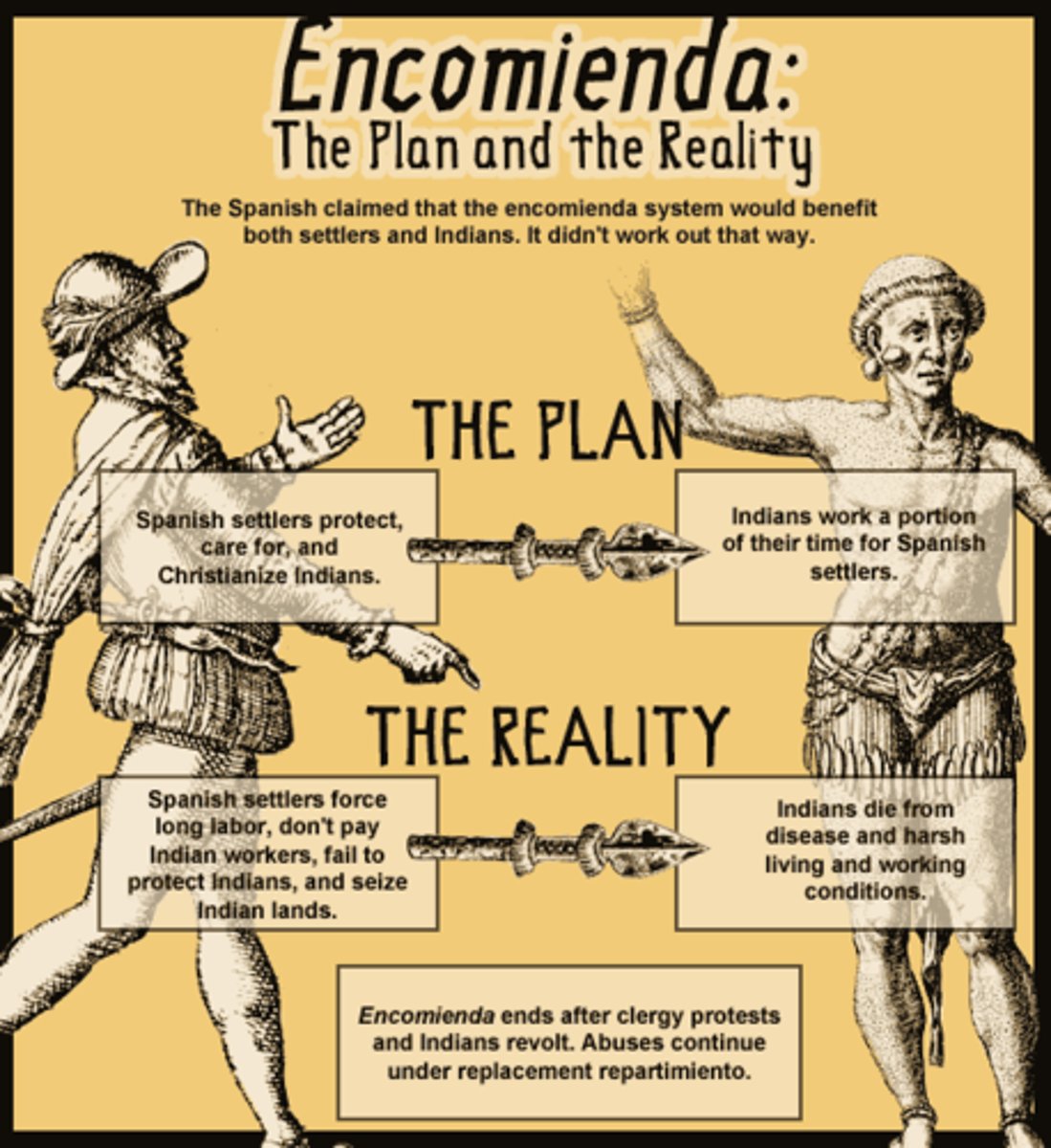
Encomienda System
Native American labor was marshaled (arranged, assembled) on plantations or in mines. It was later replaced by African slave labor.
When did the Atlantic slave trade being and by whom?
~1526 by the Portuguese
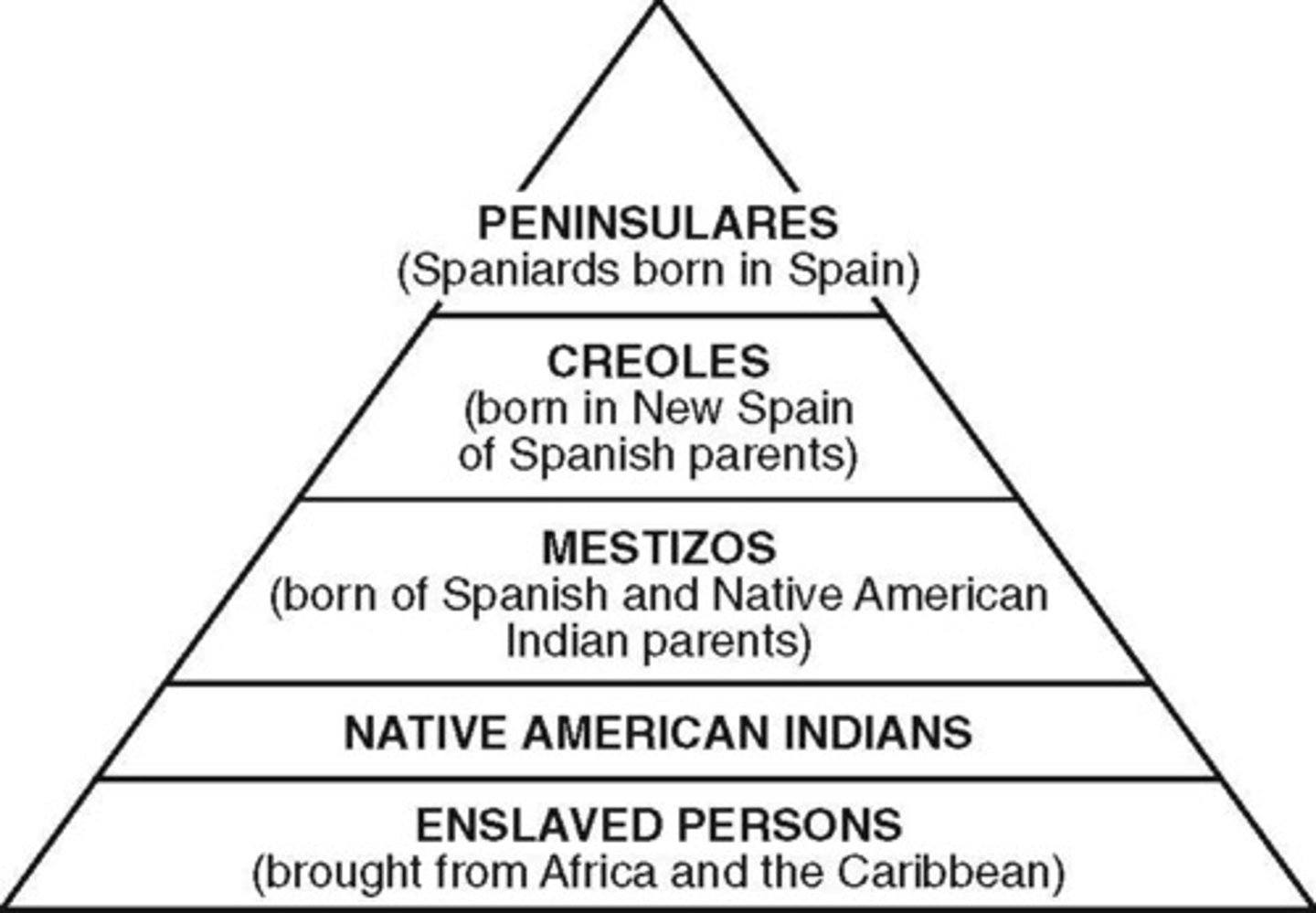
Caste System
Europeans from Europe (Peninsulares), Europes born in Central America (Creoles), Mixed (Mestizo, mulatos)
True or False: Columbus was the first European to America.
False, the Vikings were there first.
Black Legend
Propaganda to challenge the treatment of natives by the Spanish in the colonies.
Juan de Sepulveda
Advocated for the harsh treatment of natives and stated that slavery was justified in Christianity.
Bartoleme de Las Casa
Advocated for better treatment of natives and contributed to the Black Legend.

What were some ways that poor treatment of Africans and Natives was justified?
Racism, religious (spread of Christianity), seen as barbaric
Protestant Reformation 1517-1685
Started by Martin Luther's 95 Theses it was the challenging of Catholicism and the beginning of Protestant Christianity.

Hacienda
A great farm or ranch
Hernando Cortes
The leader of the Spanish conquistadors, he invaded and destroyed the Aztecs
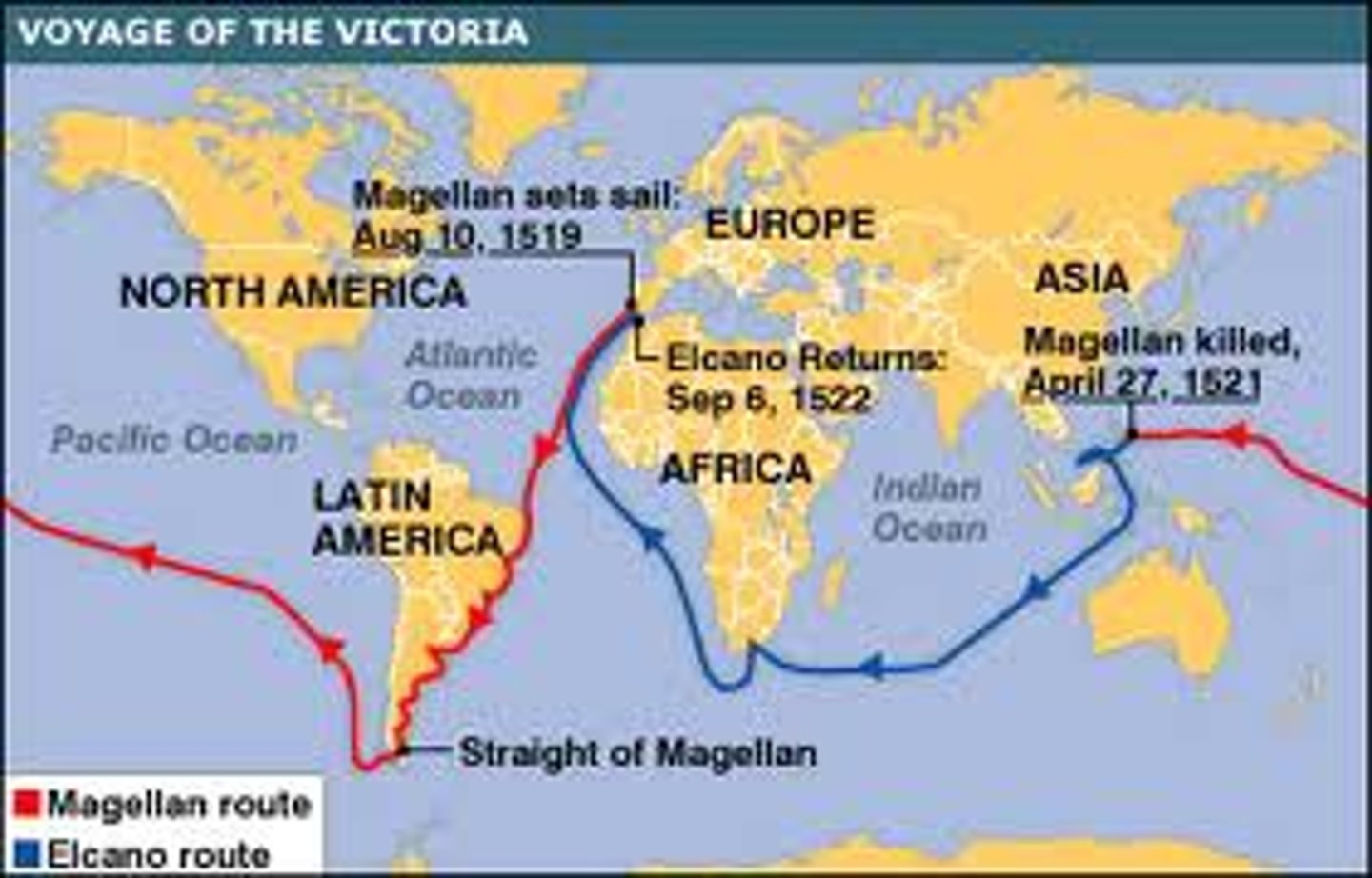
Ferdinand Magellan
Portuguese seaman, who in the employ of Spain set out to find passage through or around South America, and consequently led the first voyage around the globe.
Amerigo Vespucci
Italian explorer who first suggested that South America was a new continent.
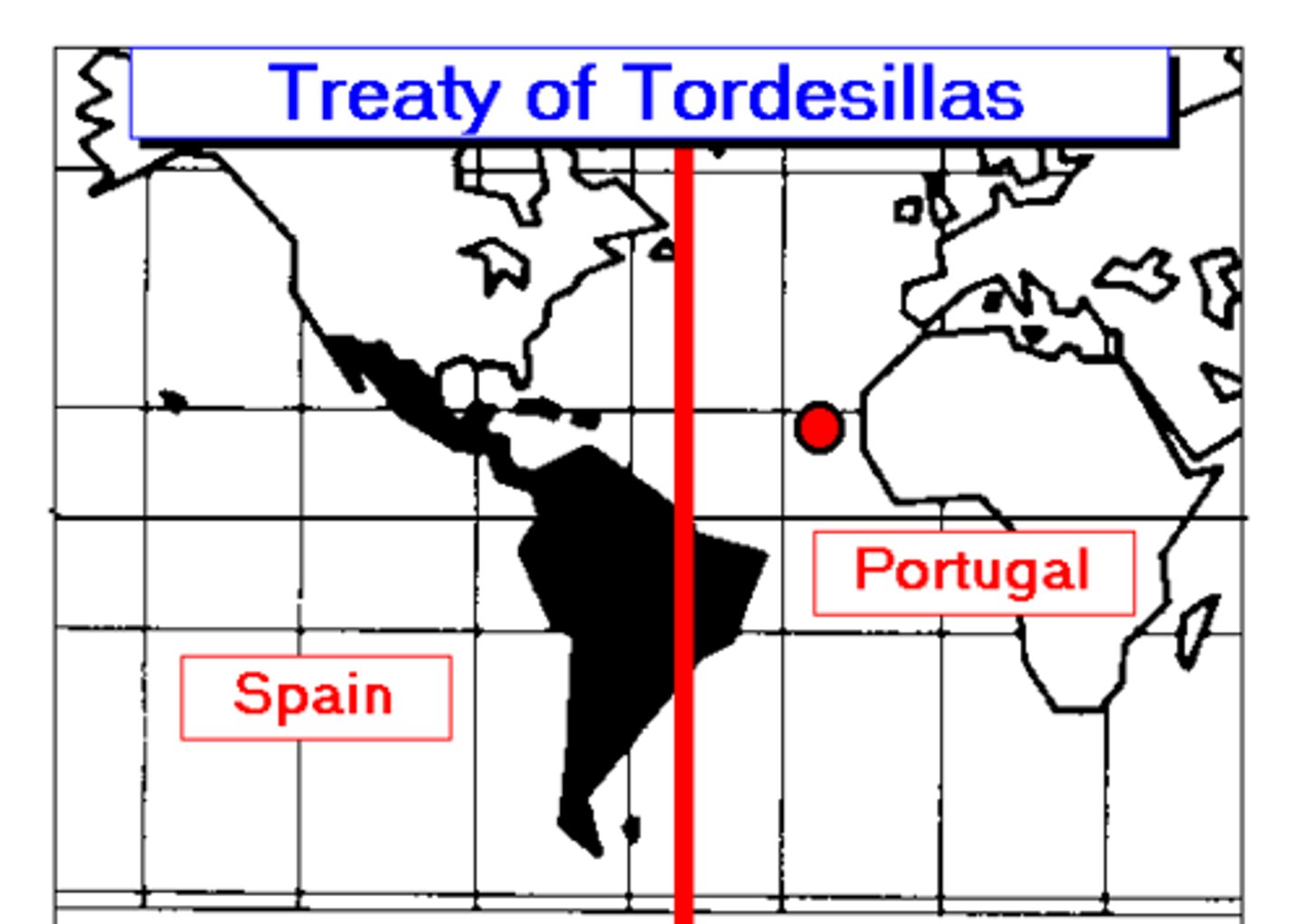
Treaty of Tordesillas
Treaty between Spain and Portugal defining the Spanish claim on exploration and settlement west of the Cape Verde Islands in 1494.
Reniassance
Period in European history from 12th C AD through the 16th C AD distinguished by its spirit of inquiry and return to secular learning.
Aztecs
Also known as Mexica, they created a powerful empire in central Mexico (1325-1521 C.E.). They forced defeated peoples to provide goods and labor as a tax.

Incas
A Native American people who built a notable civilization in western South America in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries. The center of their empire was in present-day Peru. Francisco Pizarro of Spain conquered the empire.

Maya
Mesoamerican civilization concentrated in Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula and in Guatemala and Honduras but never unified into a single empire. Major contributions were in mathematics, astronomy, and development of the calendar.

Atahualpa
Last ruling Inca emperor of Peru. He was executed by the Spanish.
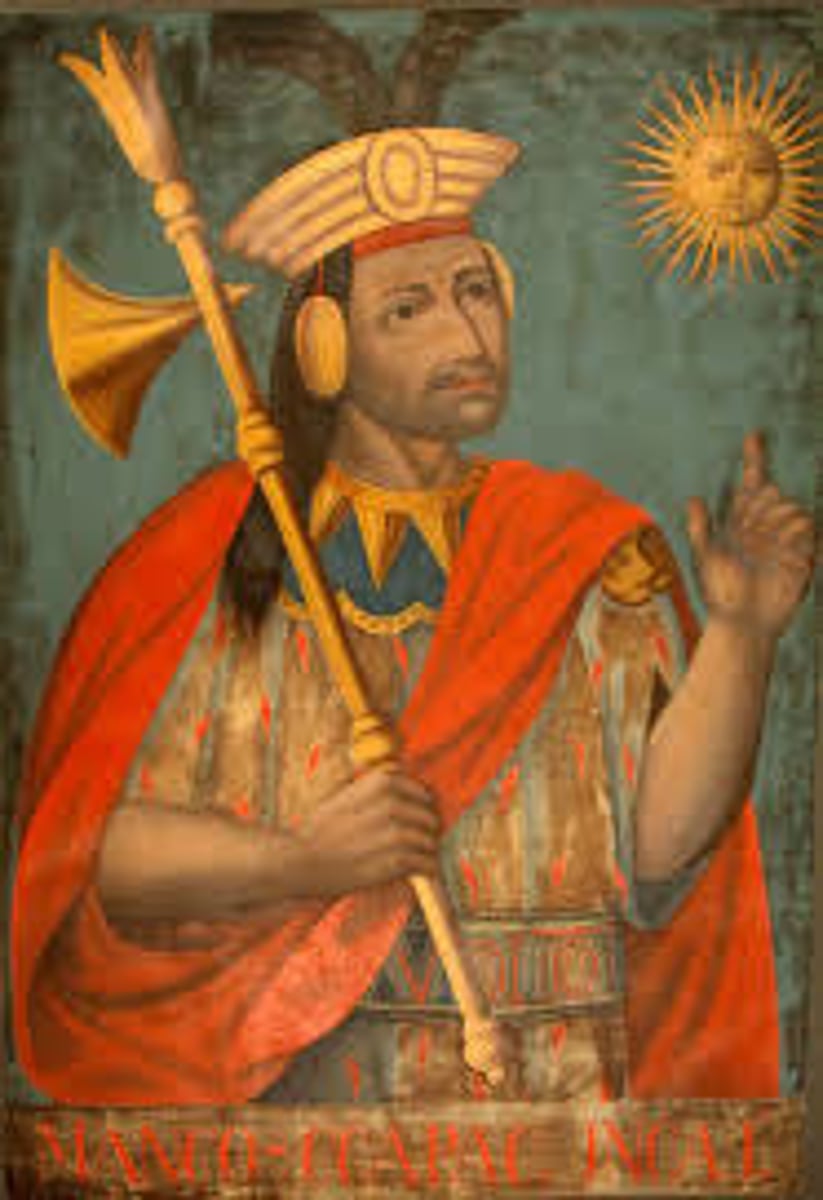

Motezuma II
was a renowned warrior and emperor of the Aztecs who was killed amid Spanish conquest

Cahokia
Mississippian settlement near present-day East St. Louis, home to as many as 25,000 Native Americans
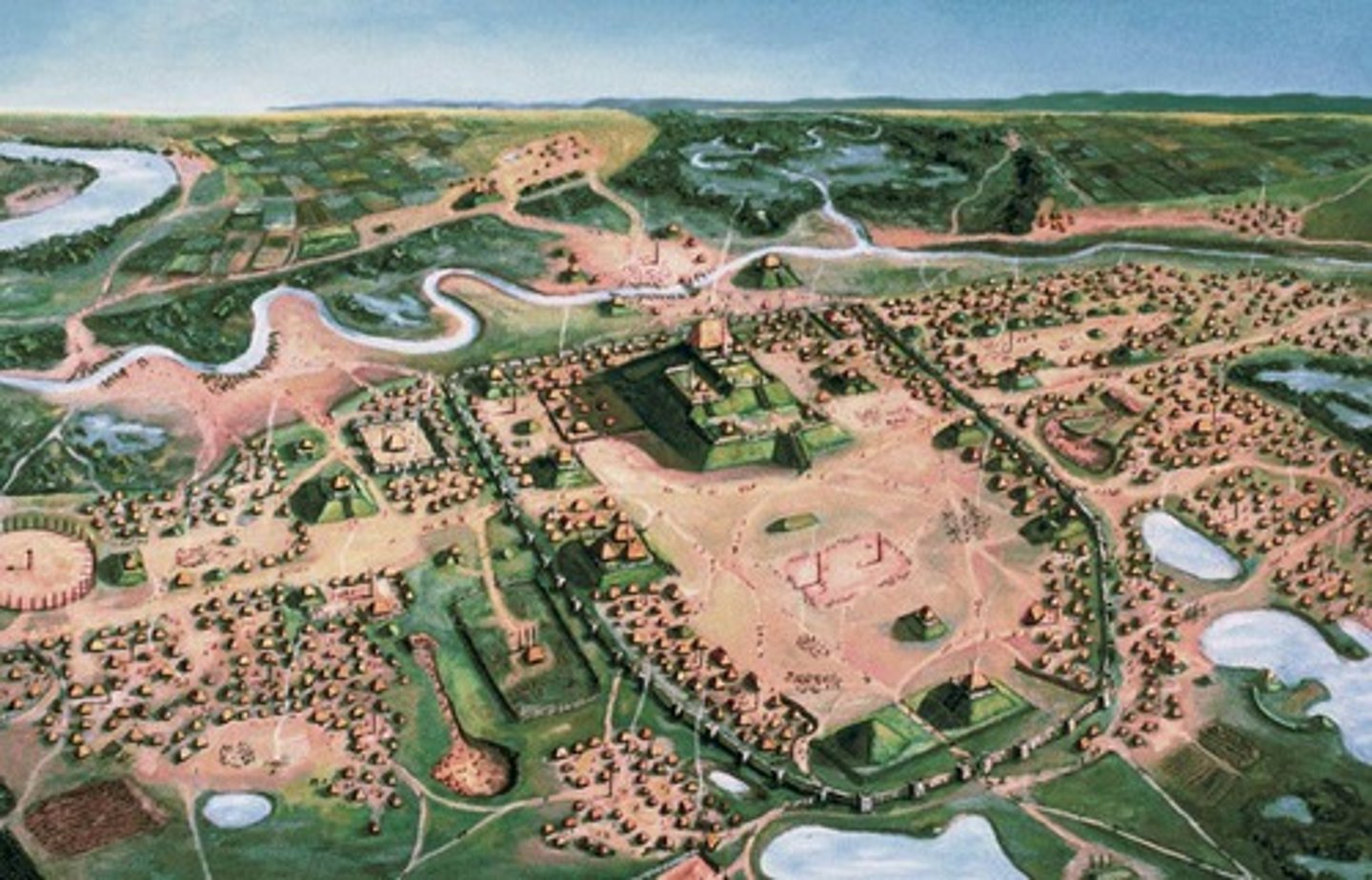
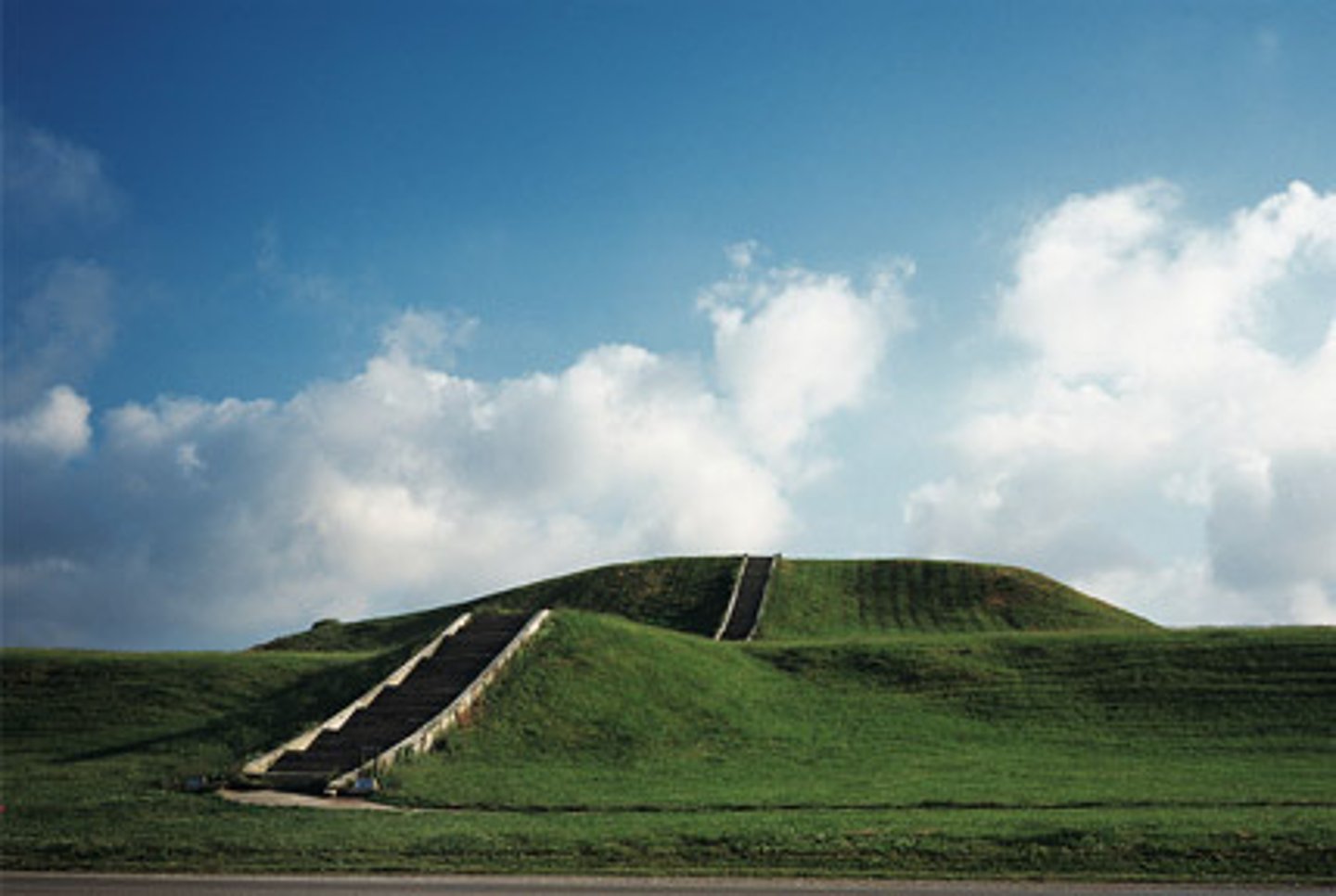
Monk's Mound, Cahokia
-Late Woodland, Mississippian (950-400 bp)
-American Bottom
-100 feet tall, 16 acres (50,000 people)
-22 million cubic feet of soil
-part of larger plaza and enclosed by wooden palisade wall
-each side of plaza lined by smaller mounds
-four cardinal directions "diamond" pattern
-State of Chiefdom? both?

Mound 72 (Cahokia)
an Early Mississippian period burial mound at Cahokia, Illinois, IT contains evidence for elaborate burials rituals for elite male individuals, as well probable sacrifice burials (usually of numerous females) and offerings of exotic goods such as mica, copper, and shell beads.
Huitzilopochtli
Aztec tribal patron god; central figure of cult of human sacrifice and warfare; identified with old sun god

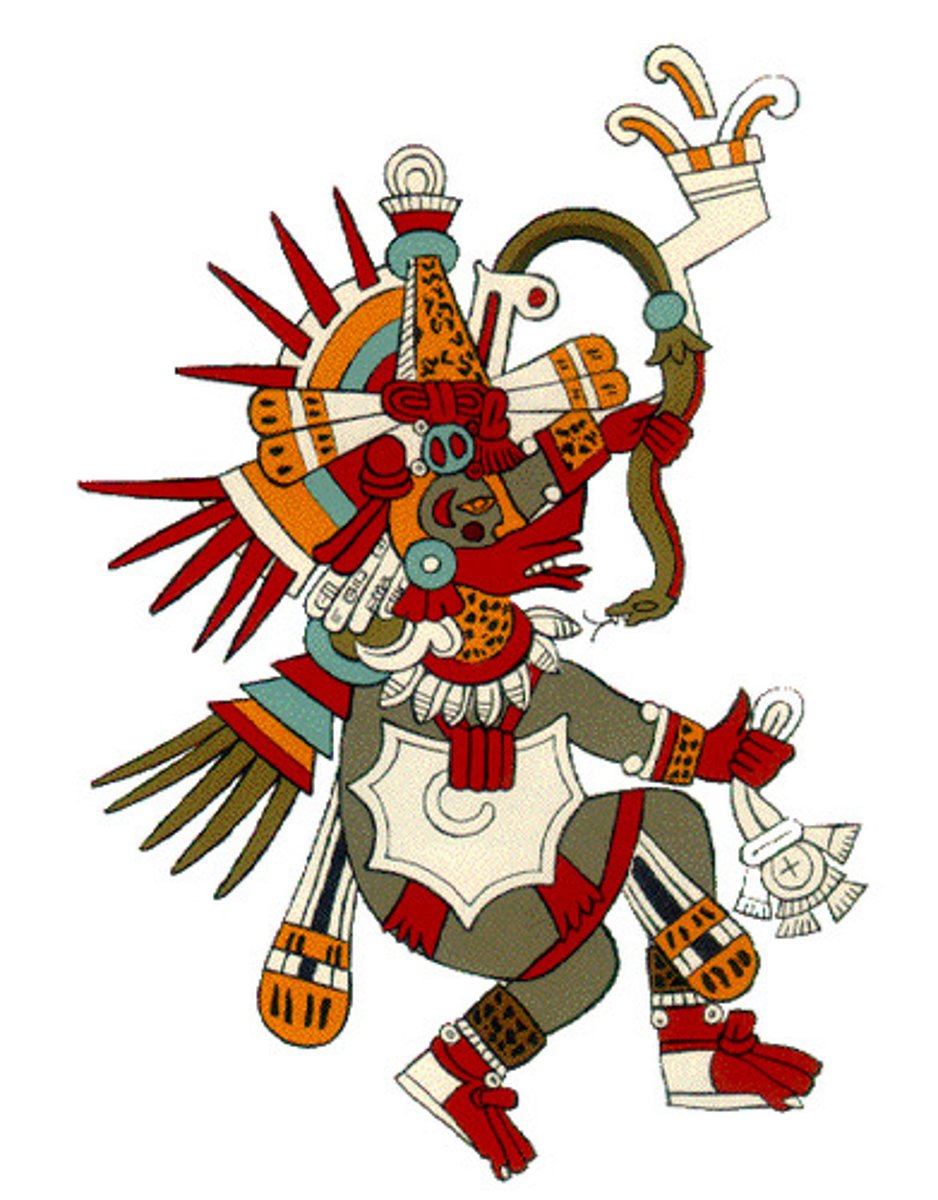
Quezalcoatl
A god, known as the Feathered Serpent, worshipped by the Toletcs (aka an Aztec group).

Chichen Itza, Mexico
900-1100
Toltec people
City plan merges axial planning of Teotihuacan and additive urban compositions of Maya (irregular and clustered)
Cenotes: water source, sacred, natural well to underground

Palenque
Name of Mayan city ruins that had an aqueduct

Tikal
the largest ancient Mayan city in the northern part of Guatemala

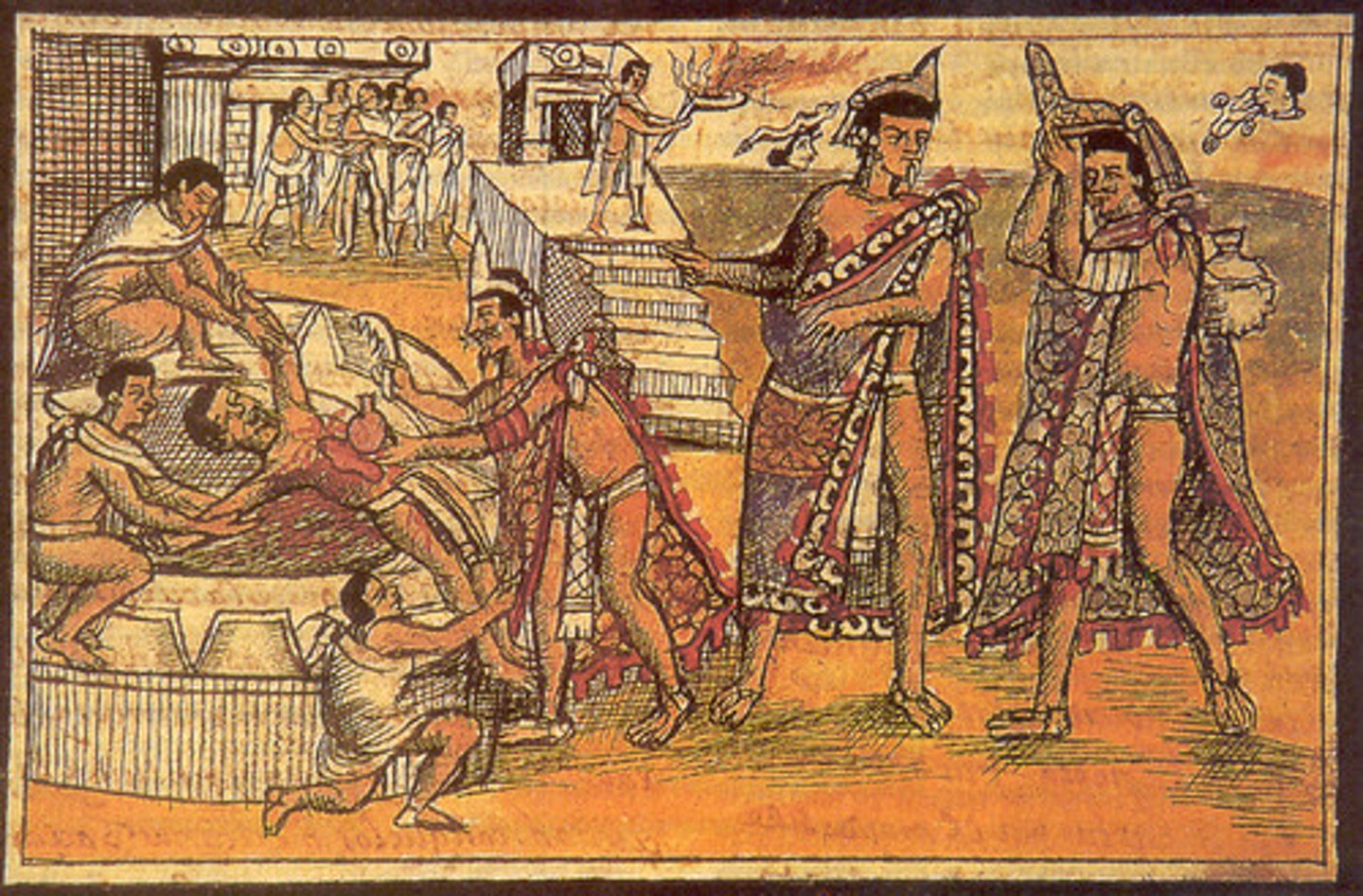
Aztec Human Sacrifice
of captured enemies or citizens was often intended to please the gods. They were often killed in elaborate ceremonies with specially made and adorned knives.

Valladolid Debate (1550-1551)
the first moral debate in European history to discuss the rights and treatment of a colonized people by colonizers.
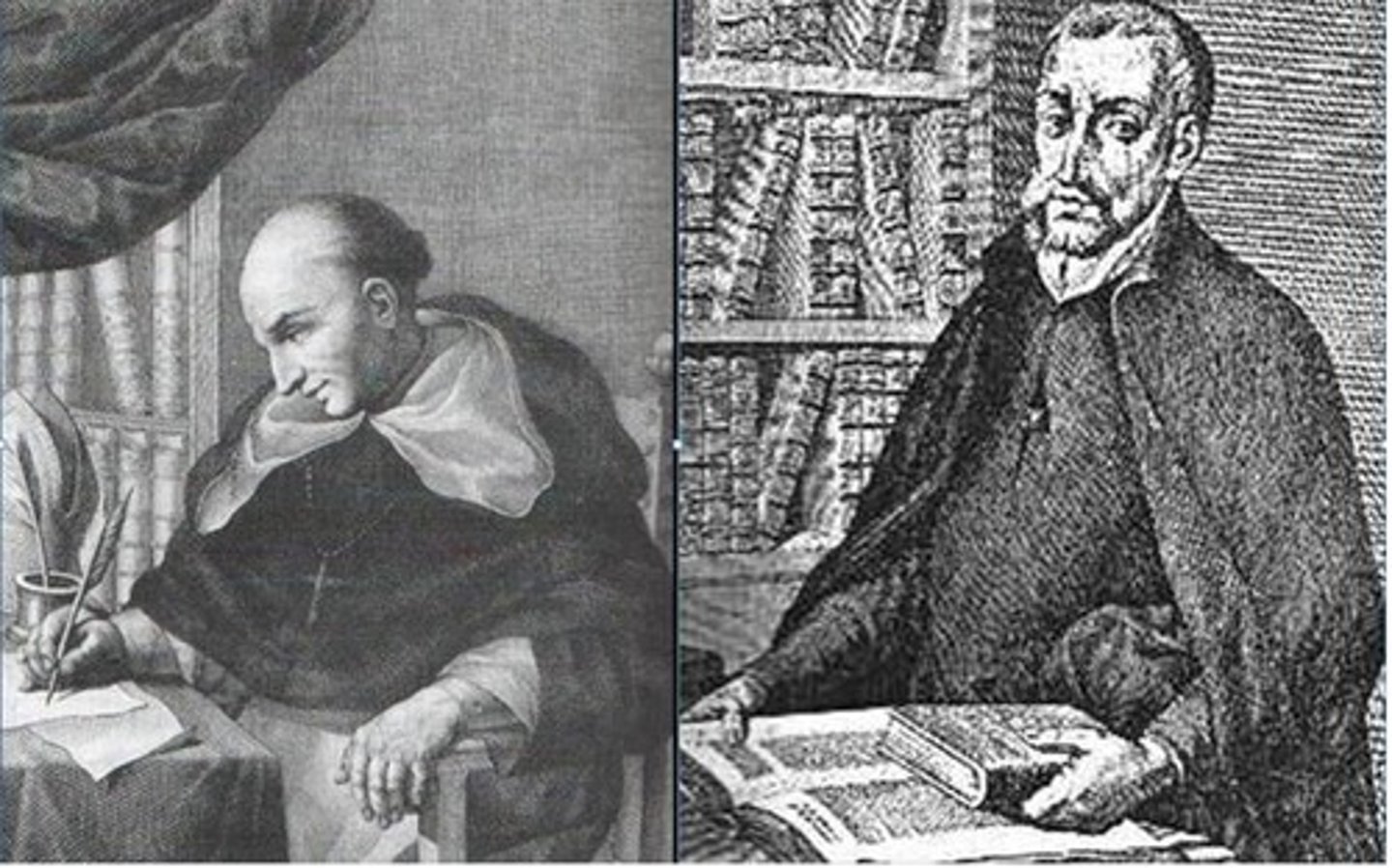

Bernal Diaz del Castillo
Soldier in Cortez's army, wrote the True History of the Conquest of New Spain, a populist history, exalting courage of common soldier. Along with Cortes he greatly admired the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan.

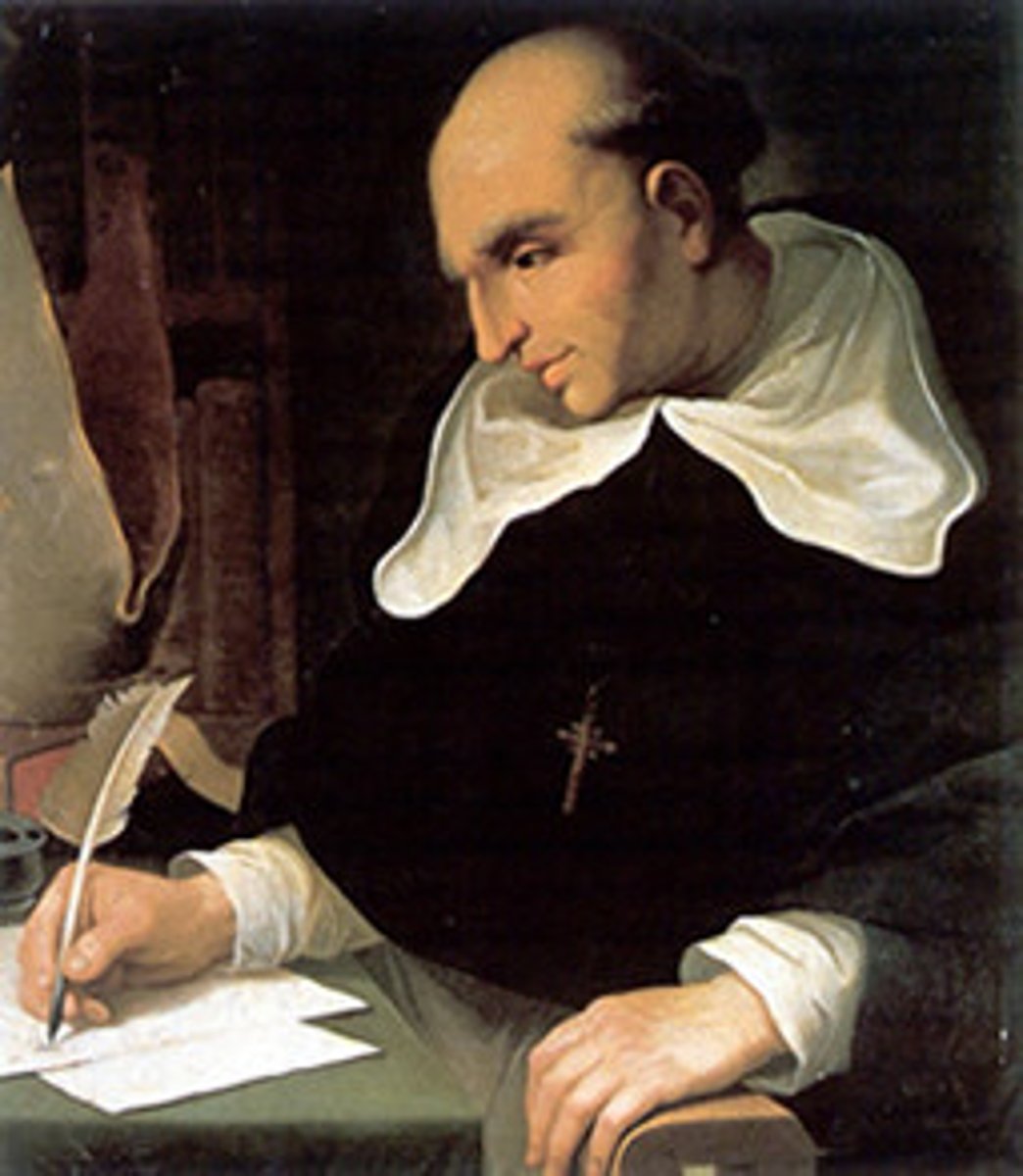
De Las Casas, Bartolome
A Spanish soldier involved in the conquest of Cuba, became a priest. He concluded that many of the activities of the Spanish in the New World were morally wrong. As a missionary, he dedicated his life to the protection of Native Americans.

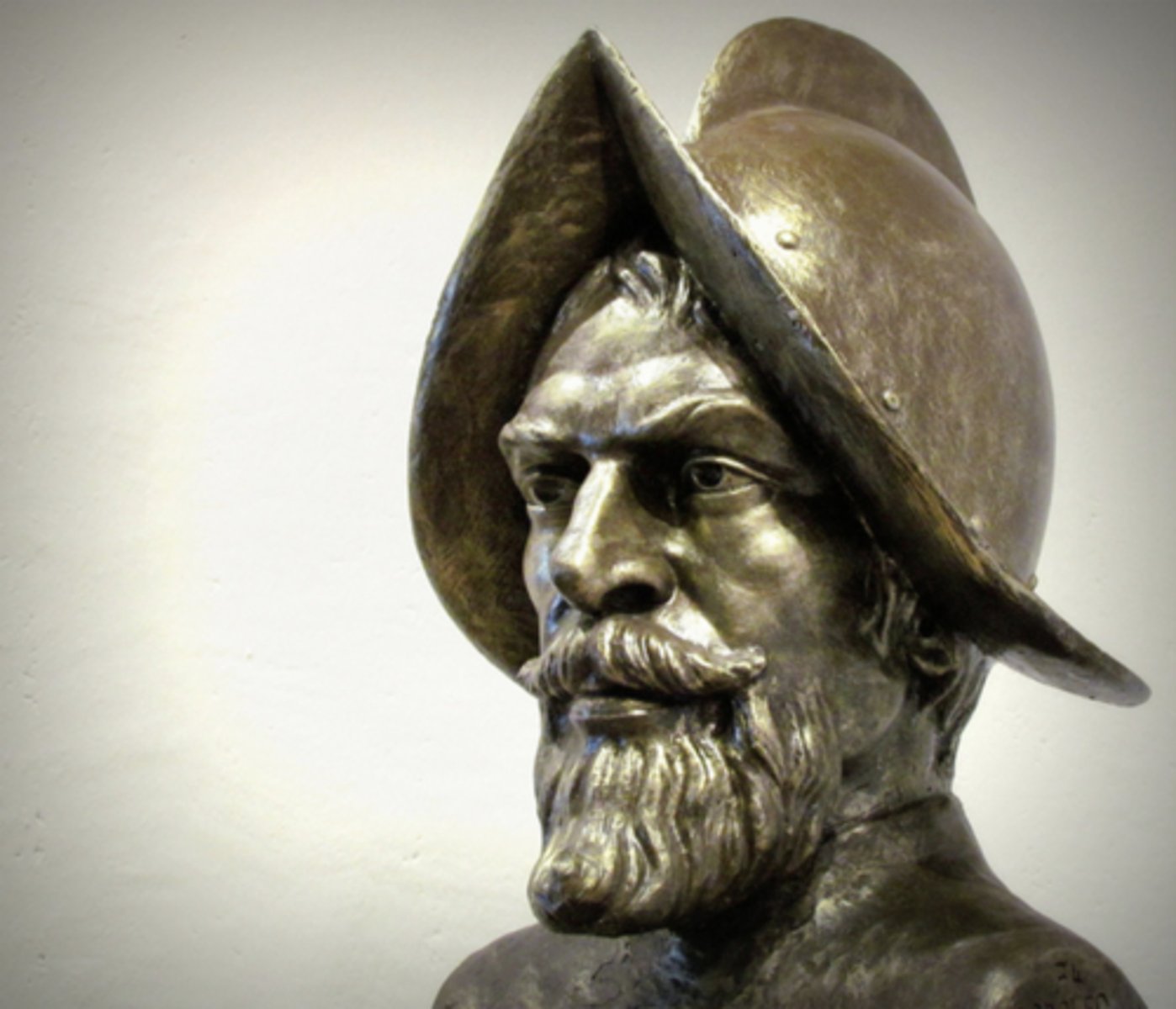
Sepulveda
argued that Biblical text stated that natives were inferior and destined to slavery
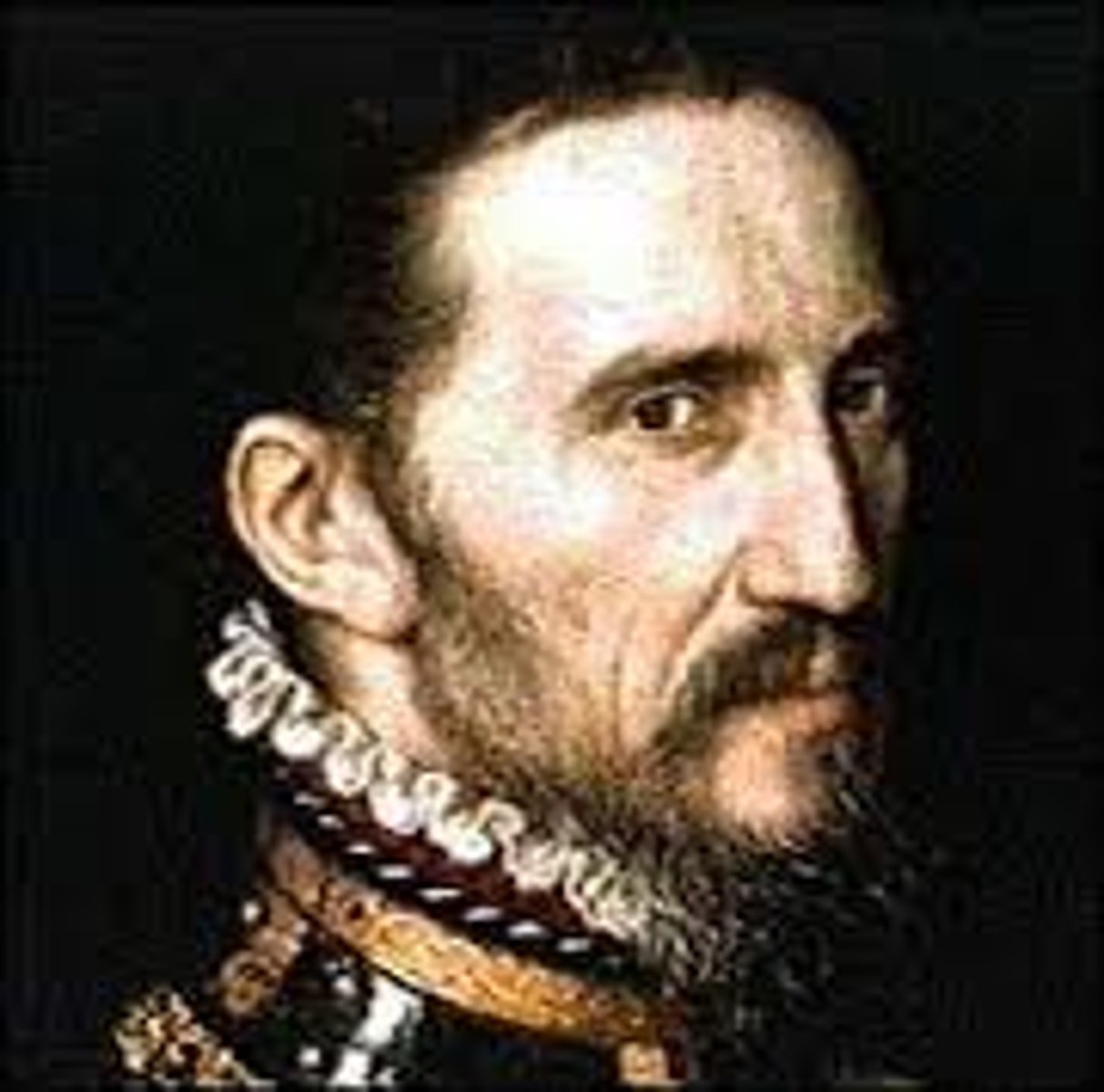

Christopher Columbus (1451-1506)
Genoese explorer who stumbled upon the West Indies in 1492 while in search of a new water route to Asia. Columbus made three subsequent voyages across the Atlantic and briefly served as a colonial administrator on the island of Hispaniola, present day Haiti.

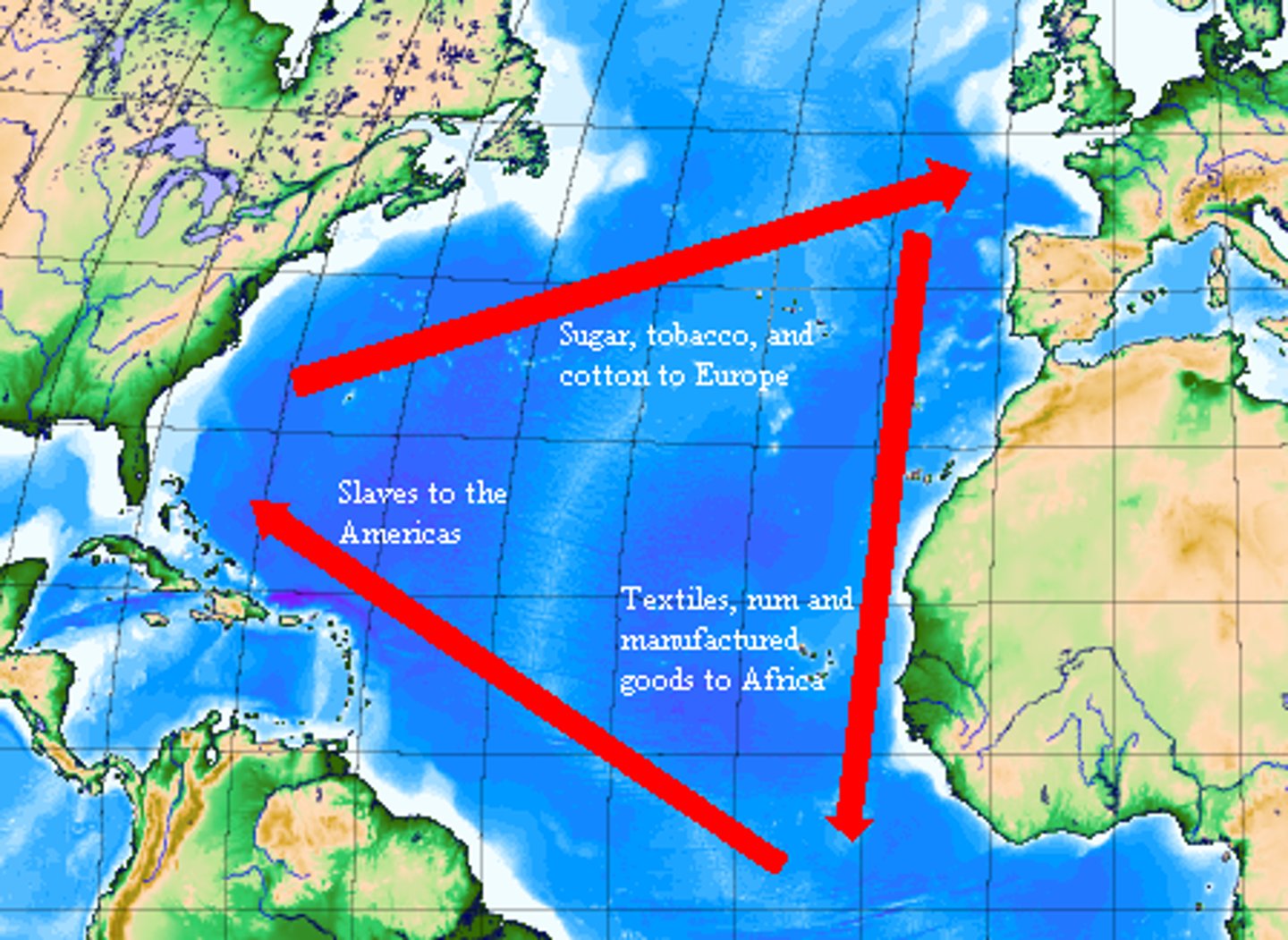
Triangle Trade
a trade route that exchanged goods between the West Indies, the American colonies, and West Africa