Metamorphic rocks
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
When does metamorphism happen?
When a rock is subjected to an increase in temperature and pressure following progressive burial…
Another cause of metamorphism?
Contact with a magmatic intrusion
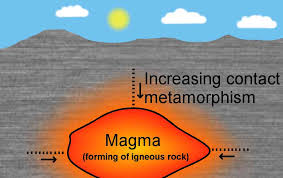
What appears during metamorphism?
Schistosity and foliation” + “new mineral associations at the expense of pre-existing minerals

Define a metamorphic rock.
Formed by the recrystallization… under the action of temperature and/or pressure.

Does metamorphism melt the rock
No, metamorphism occurs entirely in the solid state. without melting the rock
Two main metamorphism factors?
“Pressure” and “Temperature.”
What is hydrostatic pressure?
Exerted in an identical manner in all directions.
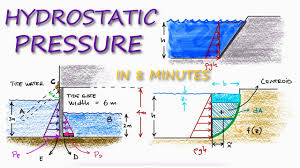
What are oriented pressures linked to
Rock cracking” and “circulation of fluids
Average geothermal gradient?
30°C/Km
What causes pressure to increase at depth?
“Generally the weight of the overlying rocks causes an increase in pressure at depth.
How can temperature affect minerals?
Temperature alters the crystal lattice of minerals.
Main modifications due to metamorphism?
Textural changes, chemical modifications, mineralogical changes.
Schistosity (definition).
“Preferential orientation of minerals whose flattening and elongation develop on the same plane.
Schistosity: how is the texture characterized?
A family of subparallel and regularly spaced sheets, resulting from recrystallization and stretching (flattening)
Examples of rocks with schistosity (given).
slate, schist.

Schistosity is specific to which grain sizes?
Specific to rocks with more or less fine or clayey grain sizes
Define foliation
Mineral segregations… newly formed mineral species concentrate along certain preferred planes


Foliation: what is the texture characterized by?
Alternation of beds of different mineralogy visible to the naked eye, most often micas.

Define granoblastic texture.
Mosaic of crystals of approximately equal size… without particular orientation.”

Examples for granoblastic texture
Cipolin, Quartzite, Corneal

Define lepidoblastic texture
Juxtaposition of crystals in sheets typically oriented micas
Examples for lepidoblastic texture
Schist, Micaschist

Define granolepidoblastic texture
Alternation of beds with a granoblastic texture and beds with a lepidoblastic texture
Example for granolepidoblastic texture
Gneiss

Chemical modifications are often due to what?
Additions or departures from fluids
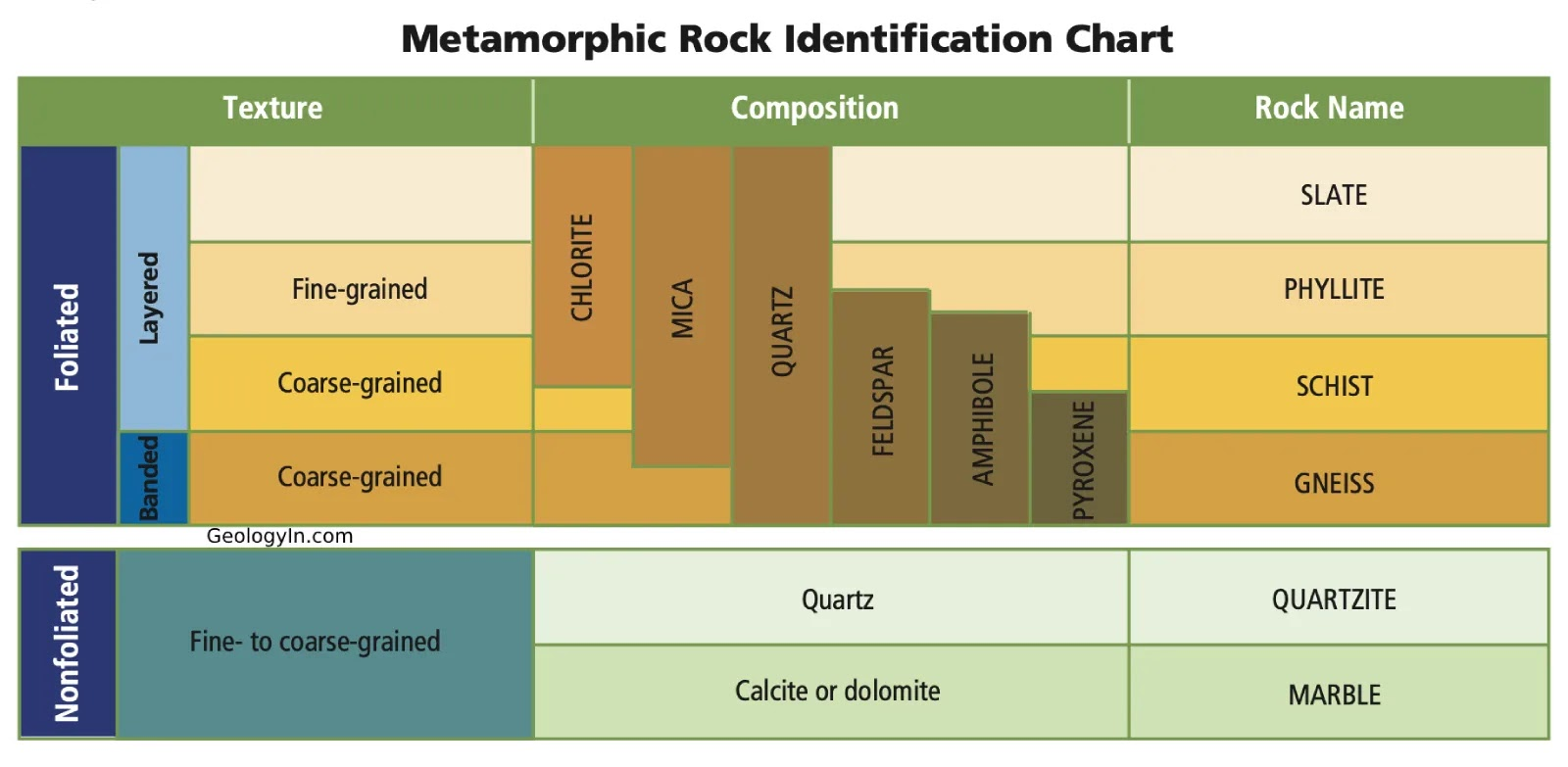
What are polymorphic transformations?
Modifications of the structure of a mineral without changing its mineralogical composition
Give the Al₂SiO₅ polymorphs listed.
Andalusite, kyanite, sillimanite (general formula Al2SiO5)
What is paragenesis
New associations of minerals, called paragenesis.

Example reaction: muscovite + quartz → ?
Potassium feldspar + andalusite + H2O.
Example sequence: kaolinite + quartz →
Pyrophyllite → andalusite, kyanite
Which types are responsible for the majority of metamorphic rocks
Contact metamorphism and regional metamorphism and dynamo-metamorphism
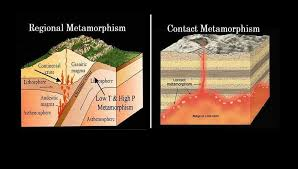
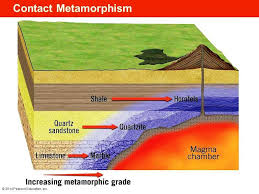
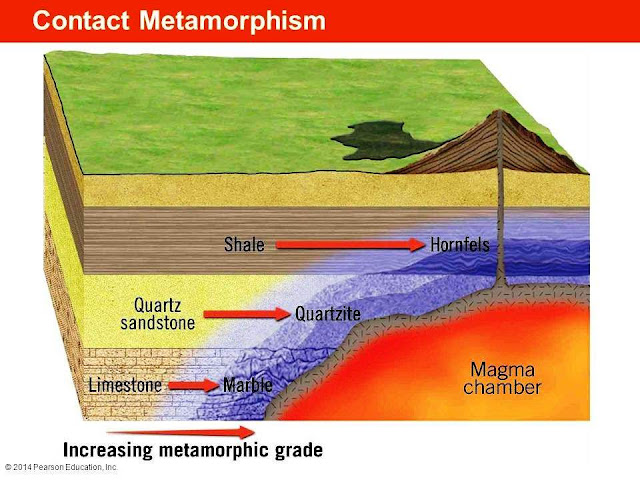
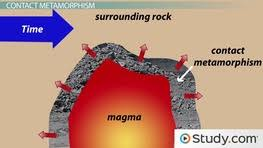
Define contact metamorphism
Occurs in the surrounding rock in contact with intrusives
What happens when hot magma meets cold rocks?
Heat transfer and cooking of the surrounding rock at the edges
Structure of contact metamorphism rocks
Have a granoblastic structure

Flamanville halo: what do corneals contain?
Quartz, feldspar, mica, andalusite, cordierite
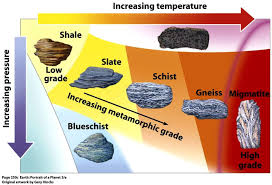
What does regional metamorphism form?
Large metamorphic regions, characteristic of many mountain range roots
Regional metamorphism is due to what
An increase in temperature and pressure… burial producing high temperatures controlled by the depth reached.
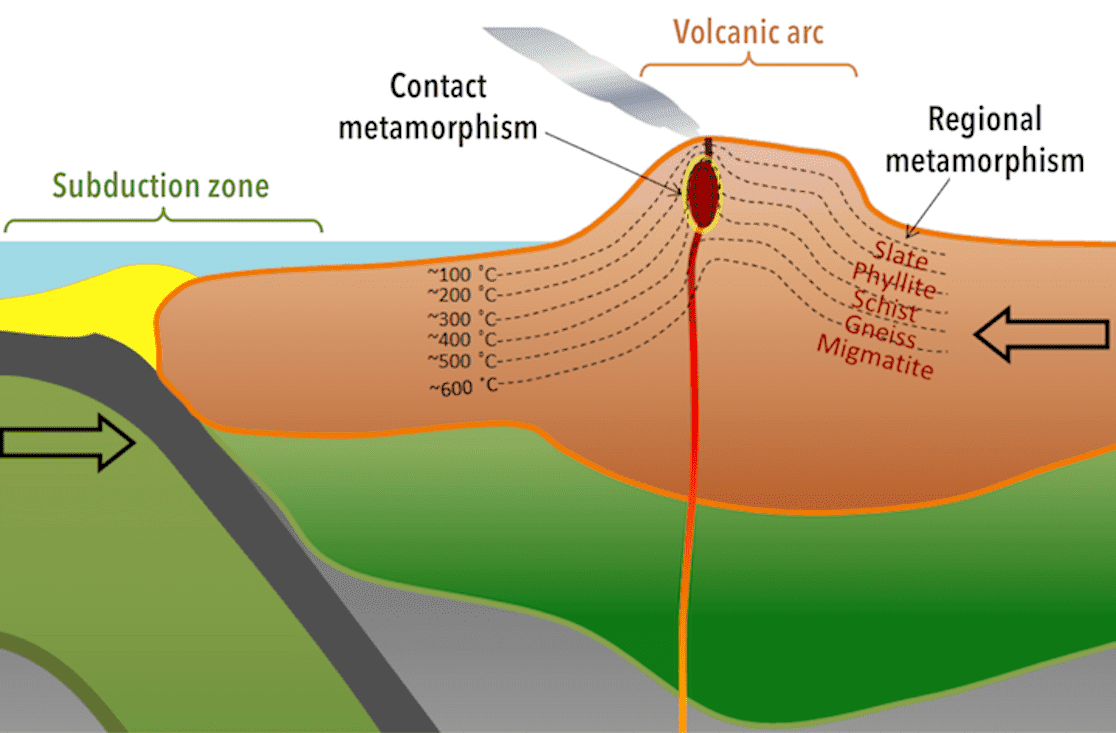
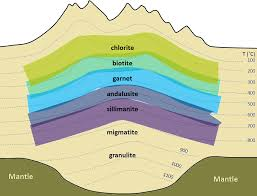
Texture of regional metamorphism rocks
schistose and foliation texture due to the influence of oriented pressures
With increasing temperature and pressure, what sequence is obtained?
Slate, schist, mica schist and gneiss.

Dynamo-metamorphism is due to what?
Due to the effect of pressure (intensely deformed rocks with relatively little new formation of minerals
What are these rocks called
Cataclasite rocks
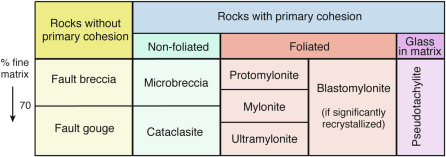
Where does dynamo-metamorphism take place?
At the border between two rock blocks… in a fault zone or base of a thrust sheet

When does mylonite form?
In case the rock is stuck between the two blocks and ductile, it transforms into mylonite.
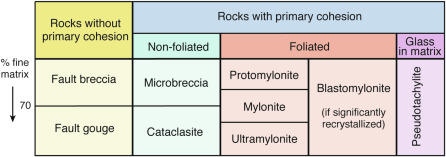
What is special about deformation into mylonite?
The rock never breaks, but its minerals rearrange themselves and allow it to deform
Mylonite: one property compared to gneiss
A hard rock that has foliation, like gneiss.

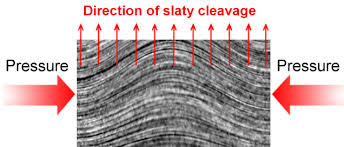
Slates: definition line (grain + origin)
Fine-grained, homogeneous clay shales… ancient clays having undergone very low intensity metamorphism.

Slates: possible coloring.
Gray, black, bluish or wine-colored.

Slates: role of schistosity
The schistosity allows them to be cleaved into thin plates

Slates: common recrystallizations
Small cubes of pyrite (iron sulphide)


Marbles: origin.
Resulting from the transformation of limestone or dolomites.

what happens to calcite elements?
Calcite elements are entirely recrystallized

Marble: effect of recrystallization
Gives greater hardness to the rock and promotes its polishing
Marble: why can color vary
Impurities, oxides, etc.


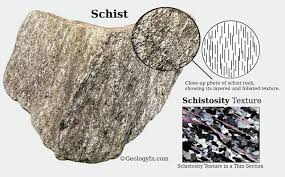
Schists: key property.
Capable of being cut into sheets (schistosity).
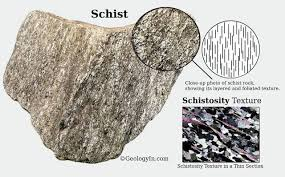
Many schists come from what?
Metamorphism of ancient clays.

Mica schists: what makes them shiny?
Rich in micas which give them a shiny appearance on their cleavage surface.
Schists: mineralogical composition
Mica, a little feldspar, sometimes quartz… staurolite, tourmaline and andalusite.


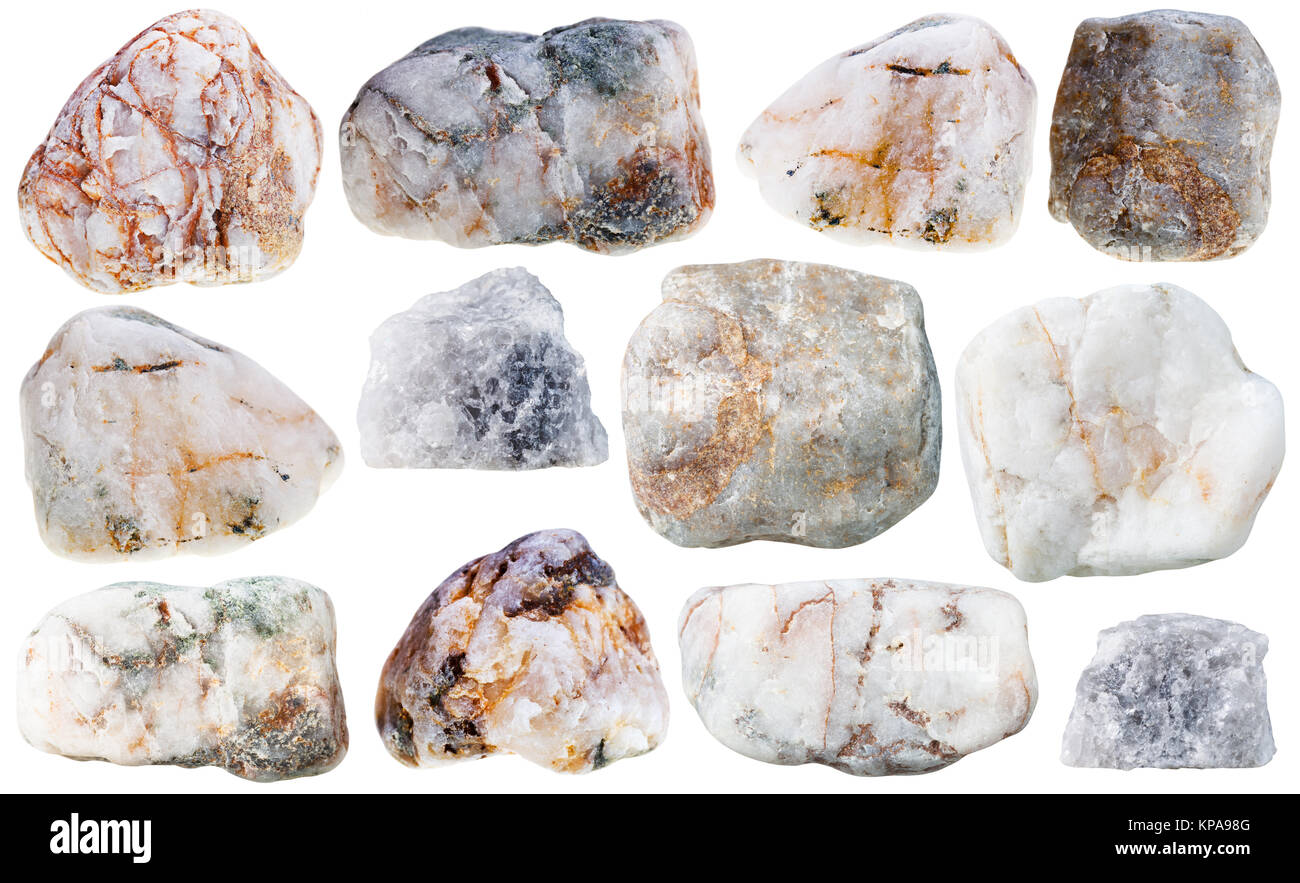
Quartzite: definition.
completely recrystallized sandstone… inseparable quartz grains are intertwined with each other


Quartzites: under what effect do they recrystallize?
Under the effect of pressure and temperature.

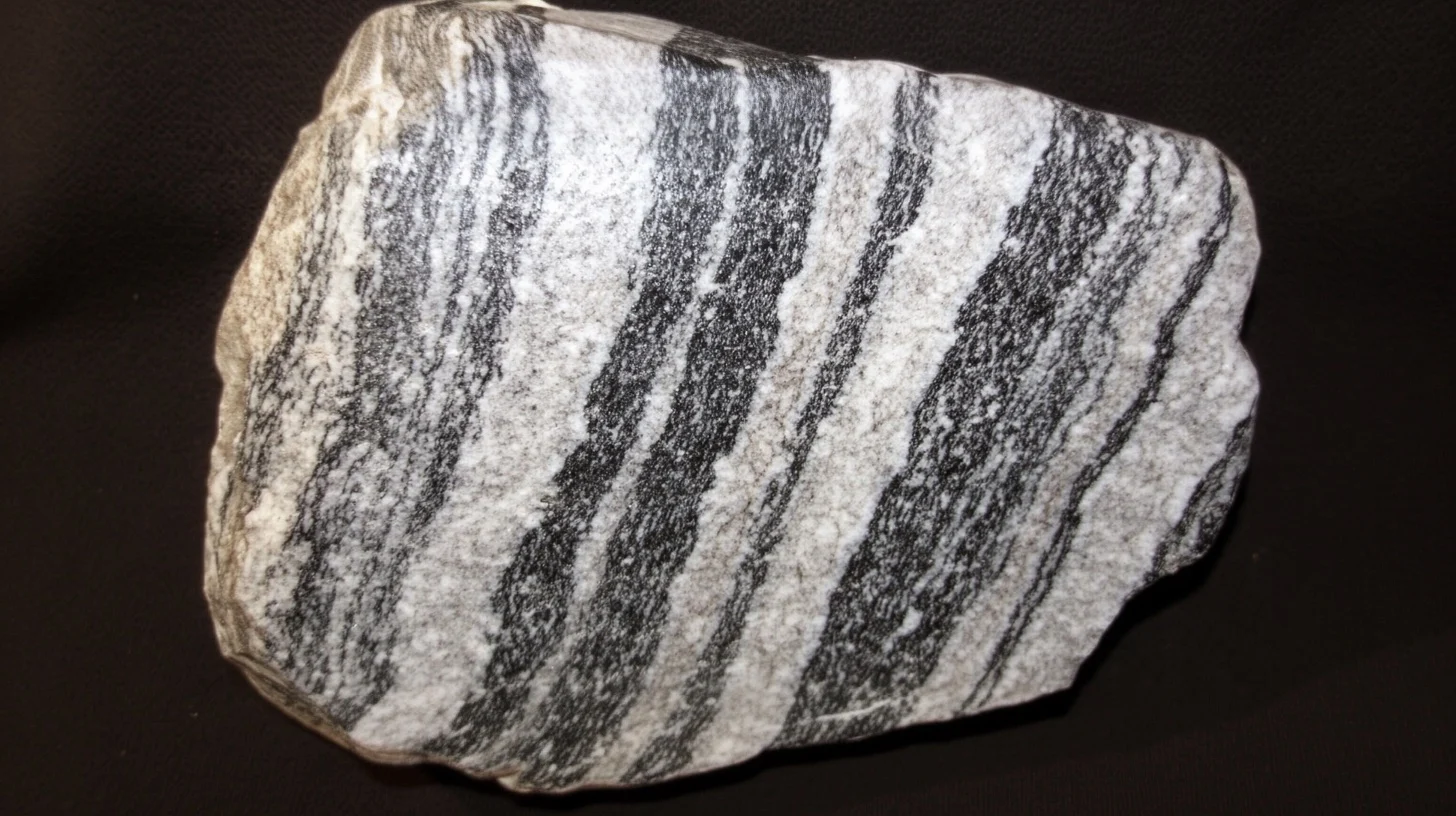
Gneiss: relation to granite.
Having the same mineralogical composition as the granites.


Gneiss: what distinguishes it?
Succession of parallel beds… alternation of light beds… and darker beds of micas
Most gneisses come from what?
Metamorphism of ancient granite

Gneisses can also come from which sedimentary rocks?
Ancient sedimentary rocks such as sandstones rich in feldspars.


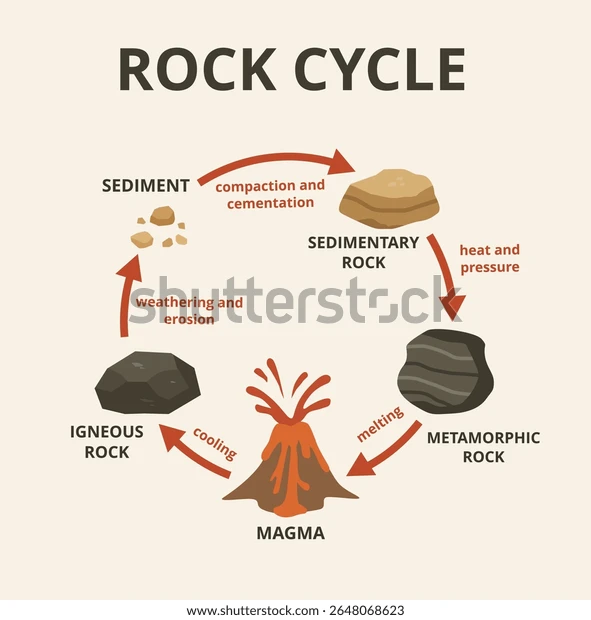
What is the rock cycle?
A continuous process where igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks transform into each other through melting & crystallization, weathering/erosion & deposition + lithification, and heat/pressure (metamorphism)—driven by Earth’s internal heat and surface processes.