Introduction to Engineering Design Process
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
Engineering Design Process
Method for creating solutions to complex problems.
Concept Development
Generating and refining ideas for solutions.
Design Thinking
Human-centered approach focusing on user empathy.
Ideation
Generating creative solutions through brainstorming.
Problem Definition
Identifying the need or challenge to address.
Research
Gathering information and understanding constraints.
Prototyping
Creating models to test design concepts.
Testing and Evaluation
Assessing prototypes against requirements and criteria.
Refinement
Making improvements based on testing results.
Empathy
Understanding users' needs and experiences.
Collaboration
Working together in multidisciplinary teams.
Critical Thinking
Analyzing and evaluating information for problem-solving.
Creativity
Generating innovative ideas and solutions.
Life-long Learning
Continuous self-improvement and knowledge acquisition.
Professional Responsibility
Ethical obligations in engineering practice.
Communication Skills
Effectively conveying information to diverse audiences.
Safety Standards
Guidelines ensuring safety in engineering practices.
ISO 9001:2015
International standard for quality management systems.
Accreditation
Recognition of educational institution's quality standards.
Synchronous Learning
Real-time online learning activities.
Asynchronous Learning
Self-paced online learning activities.
Evaluation Criteria
Standards to assess the effectiveness of solutions.
Real-world Challenges
Practical problems requiring engineering solutions.
Problem Identification
Defining issues accurately for effective design solutions.
User Interviews
Gathering insights through direct conversations with users.
Observations
Studying user behavior to identify design needs.
Detailed Problem Statements
Clear descriptions of issues to guide design focus.
Creativity in Engineering
Fostering innovative thinking in design processes.
Brainstorming
Generating diverse ideas without immediate judgment.
Mind Mapping
Visual representation of relationships between concepts.
Lateral Thinking
Solving problems through unconventional methods.
Case Studies
Analyzing successful designs for practical insights.
TRIZ
Systematic techniques for inventive problem-solving.
QFD
Translating customer needs into engineering specifications.
FMEA
Analyzing potential failure points and impacts.
CAD
Software for creating detailed digital design models.
Prototyping
Creating preliminary models for testing design concepts.
Low-Fidelity Prototypes
Inexpensive, quick models like sketches or mock-ups.
High-Fidelity Prototypes
Accurate models, often 3D-printed, for detailed testing.
Testing and Evaluation
Assessing prototypes against design requirements.
Functional Tests
Evaluating how well a prototype performs its intended function.
Usability Tests
Assessing user interaction and satisfaction with a design.
Stress Tests
Testing prototypes under extreme conditions for durability.
Teamwork in Design
Collaborative efforts requiring clear communication and roles.
Project Management Skills
Essential skills for guiding design projects to completion.
Sustainability in Design
Using resources efficiently and minimizing environmental impact.
Lifecycle Analysis
Evaluating environmental impact from production to disposal.
Critical Thinking
Analyzing problems systematically for effective solutions.
Evidence-Based Decision-Making
Using evidence and reasoning for decisions.
Risk Assessment
Evaluating risks and benefits of options.
Identifying Flaws
Finding weaknesses in designs early.
Refinement and Optimization
Improving designs based on performance and cost.
Clear Argumentation
Constructing well-reasoned arguments in communication.
Constructive Feedback
Providing and receiving feedback for improvement.
Continuous Improvement
Fostering ongoing learning and reflection.
Adaptability
Adjusting to new challenges using analytical skills.
Ethical Decision-Making
Evaluating ethical implications of engineering choices.
Problem Resolution
Resolving dilemmas considering broader impacts.
Team Dynamics
Promoting collaboration through open dialogue.
Conflict Resolution
Addressing issues to reach consensus.
Bloom's Taxonomy
Hierarchical classification of cognitive learning levels.
Remembering
Recalling basic facts and concepts.
Understanding
Explaining ideas or concepts clearly.
Applying
Using information in new contexts.
Analyzing
Connecting ideas and drawing conclusions.
Evaluating
Justifying decisions or opinions effectively.
Creating
Producing new or original work.
Kolb's Experiential Learning Model
Learning through experience in four stages.
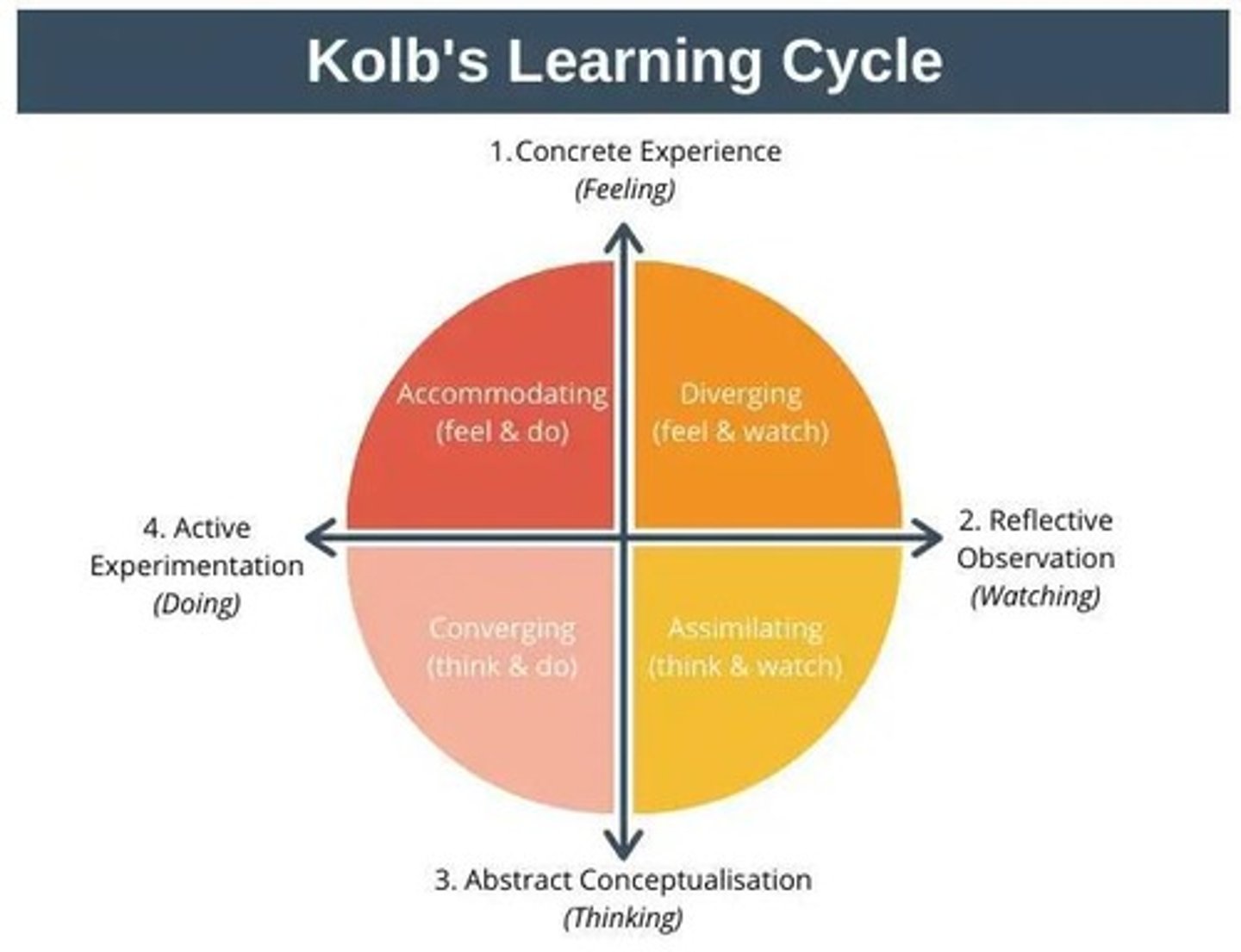
Concrete Experience
Engaging in new experiences or situations.
Reflective Observation
Reflecting on experiences to gain insights.
Abstract Conceptualization
Developing theories from observations.
Active Experimentation
Testing theories in new situations.
CDIO Framework
Conceive, Design, Implement, Operate model for engineering.
Conceive
Define the problem and develop ideas.
Design
Create detailed plans and specifications.
Implement
Build and test prototypes or solutions.
Operate
Use and maintain the solution.
Problem-Based Learning (PBL)
Student-centered approach using real-world problems.
Student-Centered
Focuses on student-driven learning and problem-solving.
Real-World Problems
Engages students with complex, real-world issues.
Collaborative Learning
Promotes teamwork and communication among students.
Learner-Centered Model
Focuses on students' needs and interests.
Active Learning
Encourages engagement with the material.
Personalized Instruction
Tailors learning to individual needs and interests.
Student Engagement
Promotes motivation and participation in learning.
Scientific Method
Systematic approach to explore and explain phenomena.
Ask a Question
Identify a problem based on observations.
Do Background Research
Gather information to understand the context.
Form a Hypothesis
Make a testable prediction.
Conduct an Experiment
Design and perform tests to validate the hypothesis.
Analyze Data
Examine results to support or refute the hypothesis.
Draw a Conclusion
Summarize findings and suggest further research.
Communicate Results
Share findings with the scientific community.
Engineering Design Process
Focuses on creating practical solutions to problems.
Identify the Problem
Understand the need or challenge requiring a solution.
Research and Gather Information
Investigate existing solutions and constraints.
Define Requirements
Set criteria for the solution's achievements.
Brainstorm and Generate Ideas
Develop multiple approaches to solve the problem.
Choose the Best Solution
Evaluate ideas and select the most feasible one.
Develop and Prototype the Solution
Create a model to test the concept.