Chapter 7: Microscopic Anatomy of Bone Connective Tissue
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are the cells found in bone?
osteoprogenitor, osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts
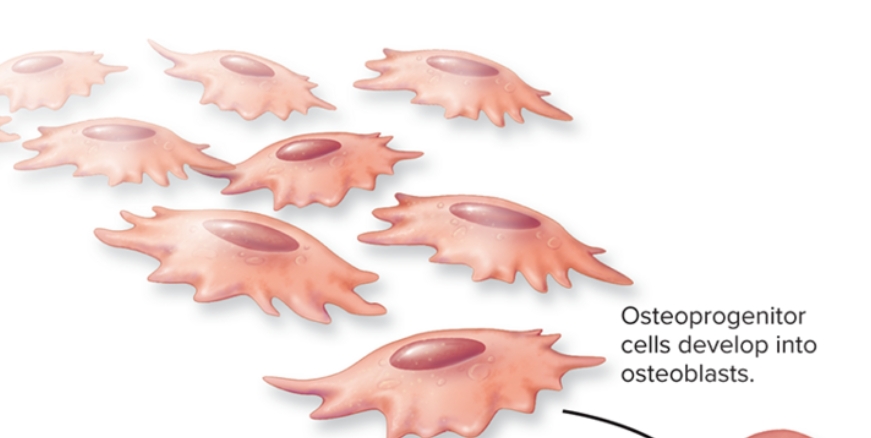
What are osteoprogenitor cells in bone?
S: Stem cells derived from mesenchyme
F: Cellular division yields another stem cell and a “committed cell”. Matures to become an osteoblast
L: periosteum and endosteum
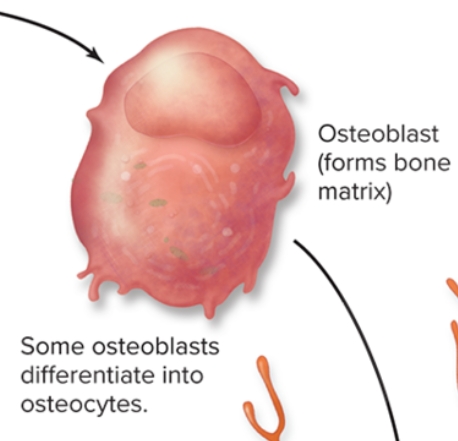
What are osteoblasts in bone?
S: Form from osteoprogenitor stem cells
F: synthesize and secrete osteoid (Initial semisolid organic form of bone matrix), Osteoid later calcifies, · become entrapped within the matrix and differentiate into osteocytes.
L: bone matrix
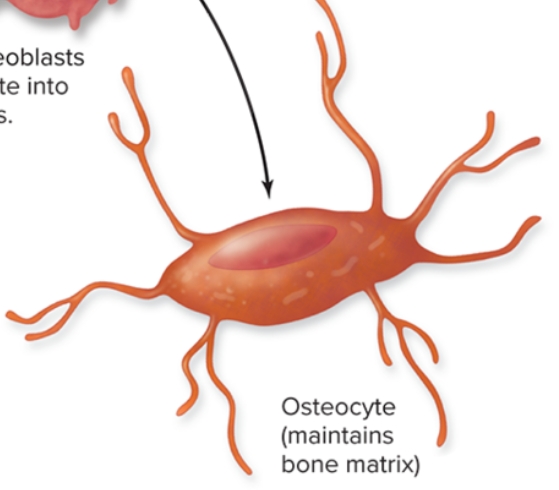
What are osteocytes in bone?
S: Mature bone cells derived from osteoblasts
F: Detect stress on bone; trigger new bone formation
L: bone matrix
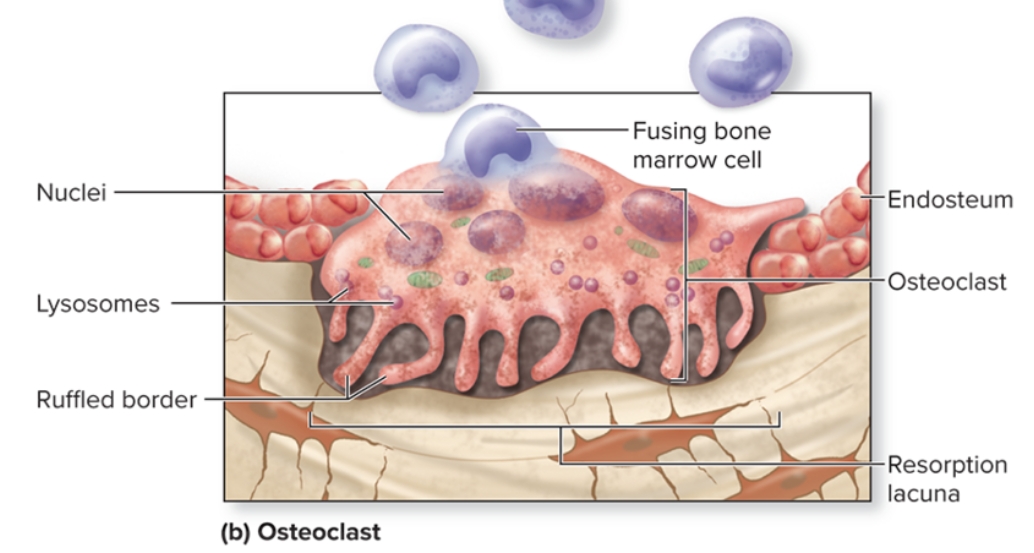
What are osteoclasts in bone?
S: Large, multinuclear, derived from fused bone marrow cells, Ruffled border increases surface area exposed to bone
F: phagocytic cells
L: Located within/adjacent to a depression/pit on bone surface
What makes up the bone matrix?
organic compounds, inorganic compounds, bone formation, bone resorption
What are the organic compounds of the bone matrix?
Osteoid produced by osteoblasts
contains collagen protein and semisolid ground substance of proteoglycans and glycoproteins
Gives bone tensile strength by resisting stretching and contributes to bone flexibility
What are the inorganic compounds of the bone matrix?
Salt crystals, calcium phosphate, Ca3(PO4)2. Interacts with calcium hydroxide and forms crystals, hydroxyapatite, Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2.
Other substances incorporated into crystals, for example, calcium carbonate, sodium, magnesium, sulfate, fluoride
Crystals deposit around collagen fibers and harden matrix to make bones rigid
What is bone formation in the bone matrix?
starts w/ secretion of osteoid
Calcification (mineralization) occurs, deposition of hydroxyapatite crystals
Calcium and phosphate ions precipitate out, form crystals
process requires Vitamin D—enhances calcium absorption from GI tract,
Vitamin C—required for collagen formation
calcium and phosphate for calcification.
What is bone resorption in the bone matrix?
Bone matrix is destroyed by substances released from osteoclasts.
Proteolytic enzymes released from lysosomes within osteoclasts that chemically digest organic matrix components.
Calcium and phosphate are dissolved by hydrochloric acid.
Freed calcium and phosphate ions enter the blood and occurs when blood calcium levels are low.
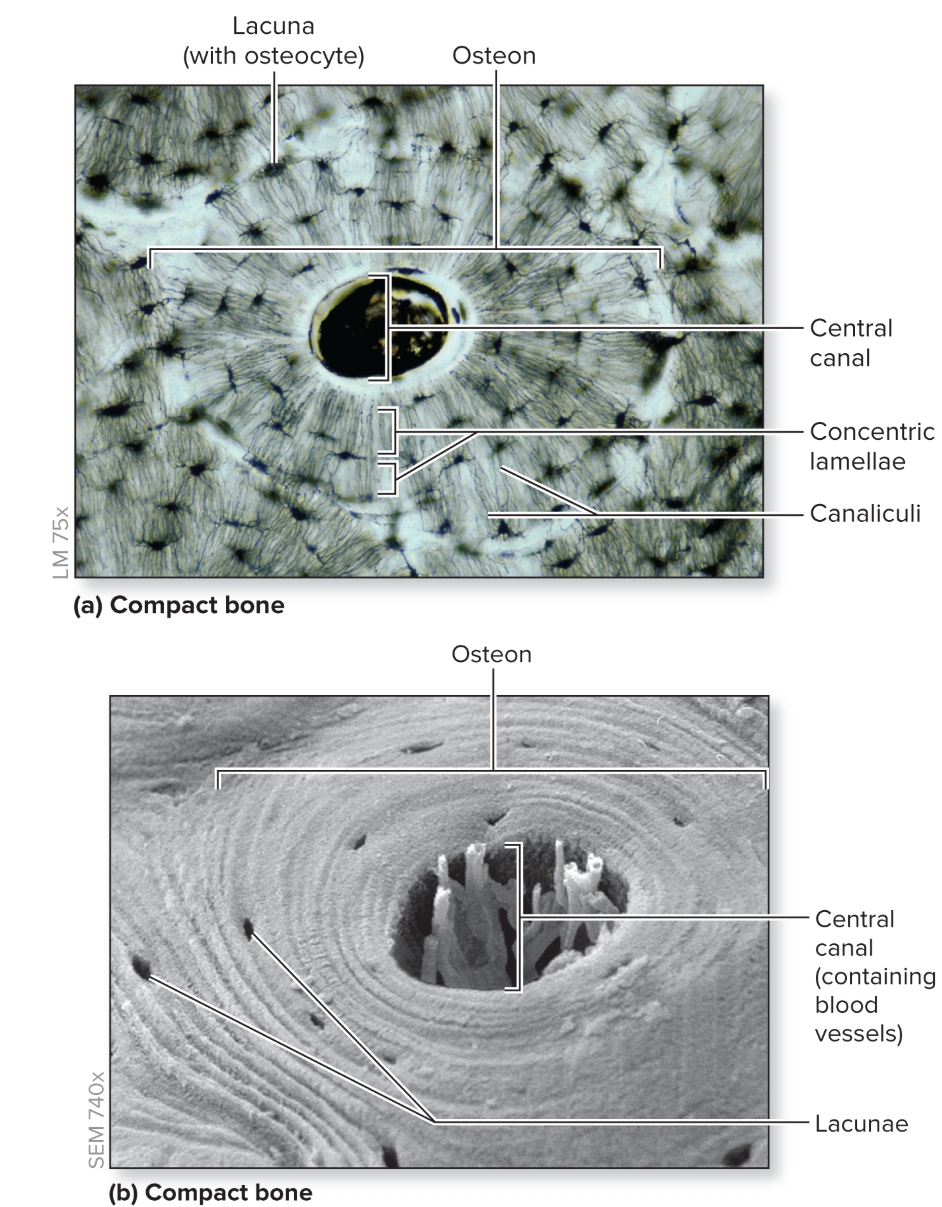
What is compact bone?
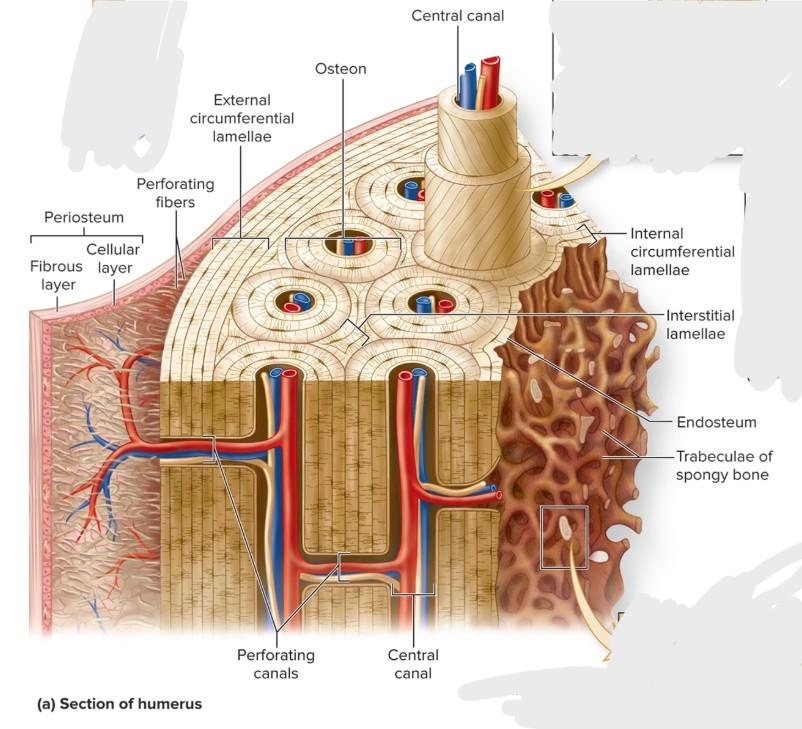
Composed of small cylindrical structures—osteons (Haversian systems) that are the basic functional and structural unit of mature compact bone.
oriented parallel to bone diaphysis and appear as bull’s-eye targets (or tree rings)
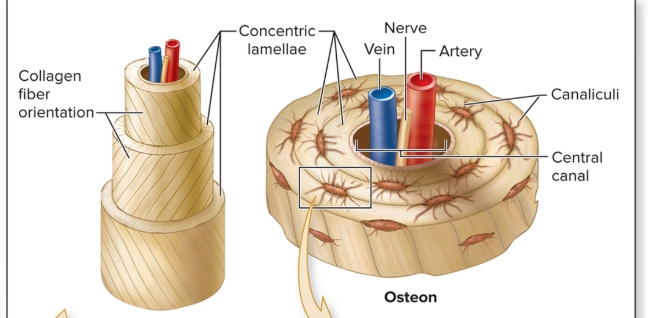
What are the components of an osteon?
central canal, concentric lamellae, osteocytes, canaliculi, perforating canals, circumferential lamellae (internal and external), interstitial lamellae
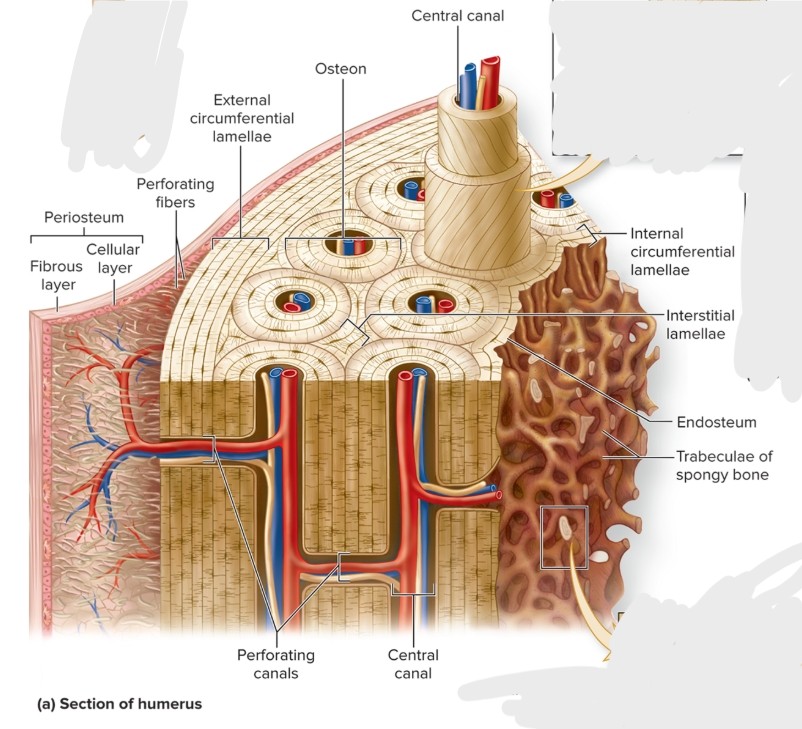
What is the central (haversian) canal of an osteon?
S: Cylindrical channel
F: Blood vessels and nerves extend through channel
L: center of osteon and parallel to it
What is the concentric lamellae of an osteon?
S: Rings of bone CT, collagen fibers 90 degrees from previous and next lamellae
F: collagen gives bone strength and resilience
L: surround central canal
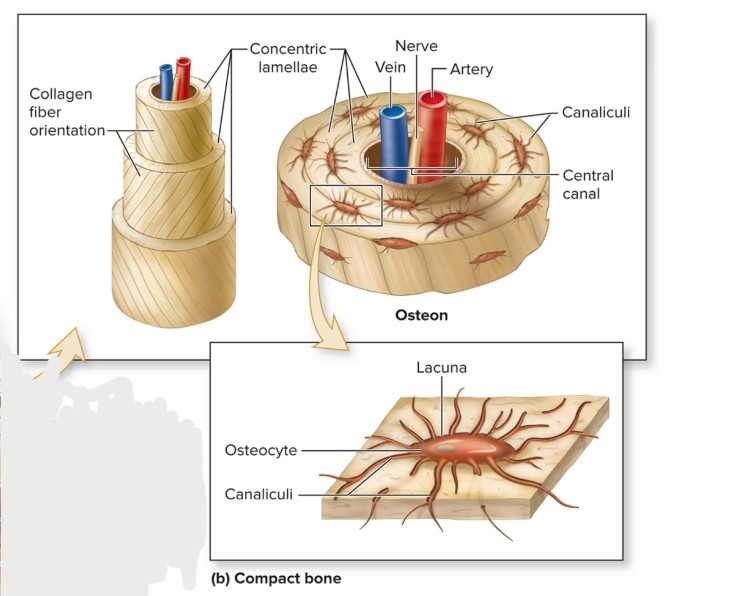
What are the osteocytes of an osteon?
S: Mature bone cells
F: maintain bone matrix
L: small spaces between concentric lamellae (lacunae)
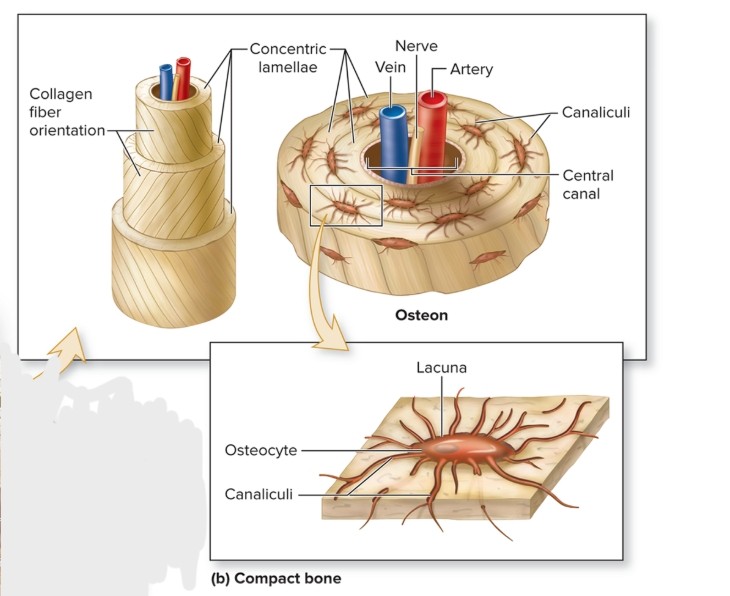
What are the canaliculi of an osteon?
S: Tiny, interconnecting channels within bone CT
F: House osteocyte projections that allow intercellular contact for the exchange of nutrients, minerals, gases, and wastes between blood vessels and osteocytes
L: extend from each lacuna, travel through lamellae; connect to lacunae and central canal
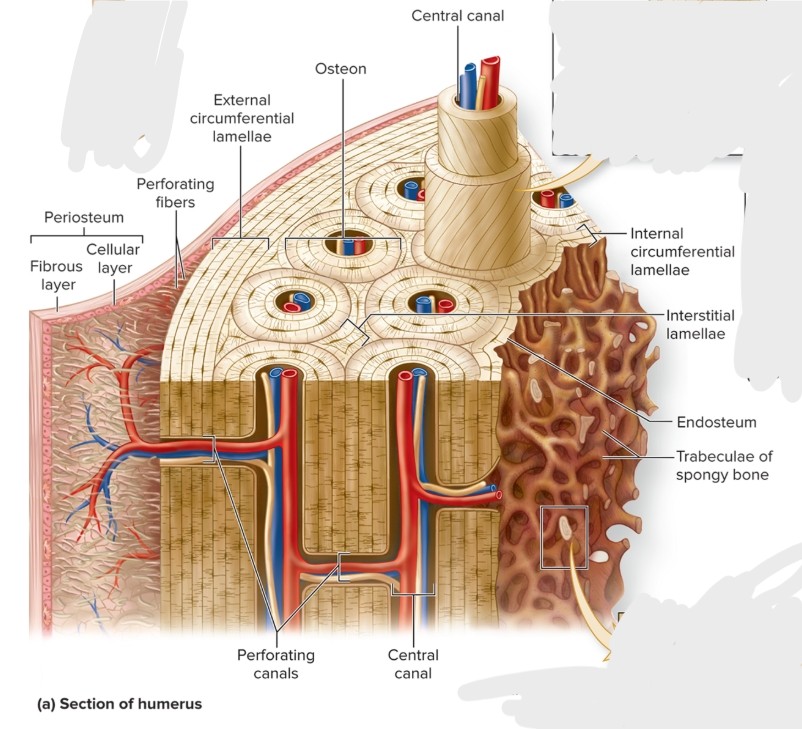
What are the perforating (Volkman) canals of an osteon?
S: Perpendicular to central canals
F:connect central canals within different osteons
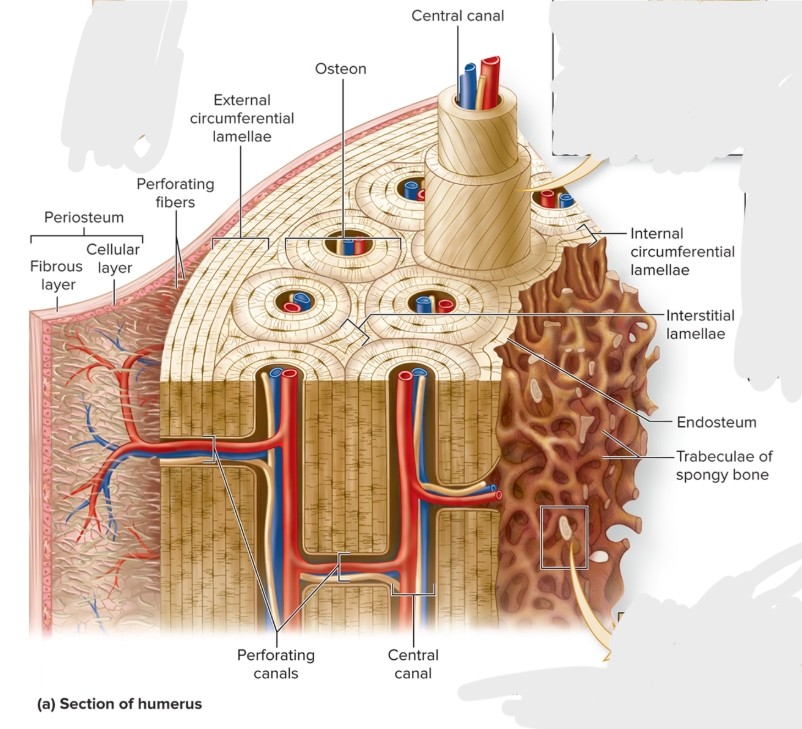
What are the circumferential lamellae of an osteon?
External—rings of bone run immediately internal to periosteum; Internal—rings of bone run internal to the endosteum
Both run the entire circumference of the bone
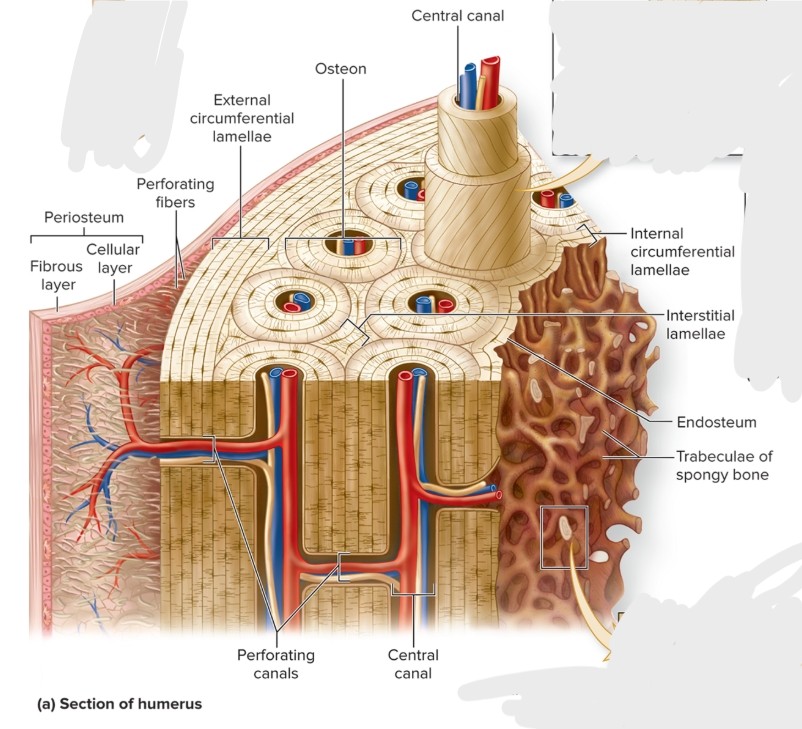
What is the interstitial lamellae of an osteon?
Components of compact bone between osteons or partially resorbed osteons
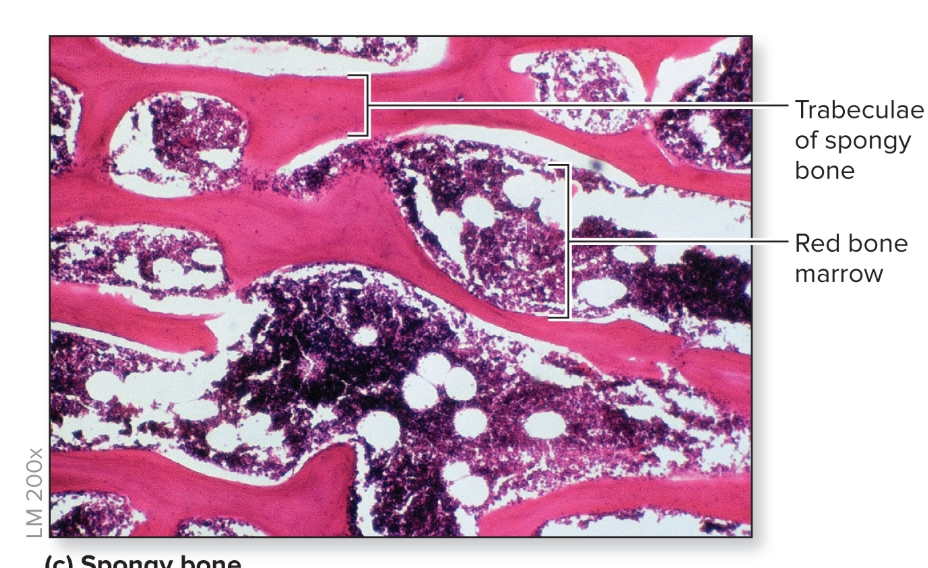
What is spongy bone?
Trabeculae are an open lattice of narrow rods and plates of bone where bone marrow fills spaces
meshwork of crisscrossing bars gives resistance to stresses
parallel lamellae in the bone matrix with osteocytes between lamellae and canaliculi radiate from lacunae