BOTANY LAB POST LAB 2 (microscope, animal and plant cell)
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
Nucleus
The control center of the cell that contains DNA and regulates cell functions.
Chromatin
Material that makes up chromosomes and contains DNA.
Nucleolus
Structure inside the nucleus that helps make ribosomes.
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane that surrounds and protects the nucleus.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Network of membranes involved in protein synthesis.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Network of membranes involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
Ribosomes
Structures that help make proteins.
Central Vacuole
Large sac filled with fluid in plant cells for storage and support.
Tonoplast
Membrane surrounding the central vacuole in plant cells.
Cytoskeleton
Network of protein filaments that gives shape and assists in cell division, movement, and transport.
Microfilaments
Thin protein filaments involved in cell movement and support.
Intermediate filaments
Filaments that provide support to the cell.
Microtubules
Hollow protein tubes involved in cell shape, movement, and division.
Chloroplast
Organelle in plant cells that helps with photosynthesis.
Plasmodesmata
Channels connecting plant cells for communication and material sharing.
Cell wall
Strong outer layer providing support and protection in plant cells.
Plasma membrane
Outer boundary of the cell controlling what enters and exits.
Peroxisome
Organelle involved in various chemical processes in the cell.
Mitochondrion
Organelle producing energy for the cell.
Golgi apparatus
Organelle modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins.
Centrosome
Region near the nucleus organizing microtubules during cell division.
Lysosomes
Organelles containing digestive enzymes.
Centrioles
Organelles involved in cell division, organizing microtubules for chromosome separation.
Flagella
Tail-like structures involved in cell movement (not present in all plant cells).
Lysosomes, Centrioles, Flagella: are not found in plant cell.
They are not found in plant cell.
Eukaryotic 1
Animal, plant, fungi, and protist cells is an example of? 1
Prokaryotic 2
Bacteria and archaea is an example of 2
Eukaryotic 3
Any cell that contains a clearly defined nucleus and membrane bound organelles 3
Prokaryotic Cell 4
Any unicellular organism that does not contain a membrane bound nucleus or organelles 4
Prokaryotic 5
its a broad categorizes of cell where Nucleus is Absent. 5
Eukaryotic 6
its a broad categorizes of cell where Nucleus is present. 6
Prokaryotic😃
its a broad categorizes of cell where Cell size is Small.😃
Eukaryotic: 7
its a broad categorizes of cell where Cell size is Large. 7
Prokaryotic 8
its a broad categorizes of cell where Cell size is Small. 8
Eukaryotic 9
its a broad categorizes of cell where DNA replication is Highly regulated with selective origins and sequences 9
Prokaryotic 10
its a broad categorizes of cell where DNA replication Replicates entire genome at once 10
Eukaryotic: 11
its a broad categorizes of cell where Organism type is Usually multicellular 11
Prokaryotic: 12
its abroad categorizes of cell where Organism type is Unicellular 12
Eukaryotic: 13
its a broad categorizes of cell where Chromosomes is More than one 13
Prokaryotic: 14
its abroad categorizes of cell where chromosomes is One long single loop of DNA and plasmids. 14
Eukaryotic😁
its a broad categorizes of cell where ribosome is large😁
Prokaryotic: ^
its abroad categorizes of cell where Small ^
Eukaryotic
its a broad categorizes of cell where Growth rate/generation time is Slower
Prokaryotic:
its abroad categorizes of cell where Growth rate/generation time is faster
Eukaryotic:
its a broad categorizes of cell where Organelles is Present
Prokaryotic:
its abroad categorizes of cell where Organelles is absent
Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes:
its abroad categorizes of cell where it has Ability to store hereditary information
Eukaryotic😃
its a broad categorizes of cell where Cell wall is Simple, present in plants and fungi.😃
Prokaryotic:
its abroad categorizes of cell where Cell wall is Complex.
Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes:
its abroad categorizes of cell where Plasma membrane is found
Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes:
its abroad categorizes of cell where Cytoplasm is found
Biological stains
Used to enhance visibility of cell structures during microscopy.
Differences between plant and animal cells
Centrosome, Central vacuole, Tonoplast, Flagellum, Cell wall, Chloroplasts , plasmodesmata, wall of adjacent cell, Lysosomes, Centrioles, Ribosomes and Flagella
are some parts of animal and plant cell, Are they the similarities or difference between plant and animal cell?
Similarities in plants and animals
Plasma membrane, Cytoskeleton (Intermediate filament , Microfilament and microtubule), Mitochondrion, Nucleus, smooth and rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), Golgi Apparatus, Ribosomes, and Peroxisome
are some parts of animal and plant cell, Are they the similarities or difference between plant and animal cell?
slide first, put specimen and Biological stains then cover slips:
What is first to do when using slide, cover slip or specimen ?
Cytoplasmic streaming:
also called protoplasmic streaming or cyclosis.
Cytoplasmic streaming:
is the movement of the fluid substance (cytoplasm) within a plant or animal cell.
Cytoplasmic streaming
Movement of cytoplasm within a cell, transporting nutrients, proteins, and organelles.
Cytoplasmic streaming
It is important because it transports nutrients, proteins, and organelles within cells.
Microscopes are important for observing cells because they allow for the visualization of structures that are too small to be seen with the naked eye.
What is the purpose and importance of microscopes in observing cells?
It is important to obtain a thin section of the specimen when preparing it for viewing under the microscope to ensure clear and focused images
Why is it important to just obtain a thin section of the specimen when preparing a specimen for viewing under the microscope
Micrographia
A book published by English scientist Robert Hooke in 1665, illustrating the smallest complete parts of an organism, which he called cells.
Cells
The smallest complete parts of an organism, according to Robert Hooke's cell theory.
Microscope
An instrument used to magnify and observe small objects or organisms.
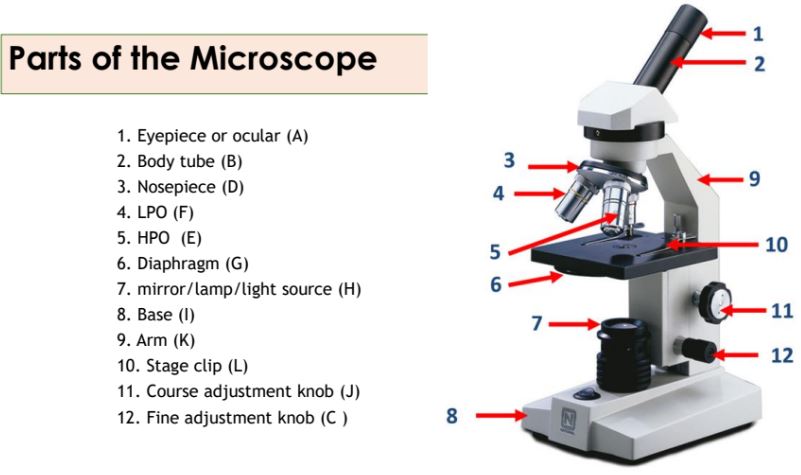
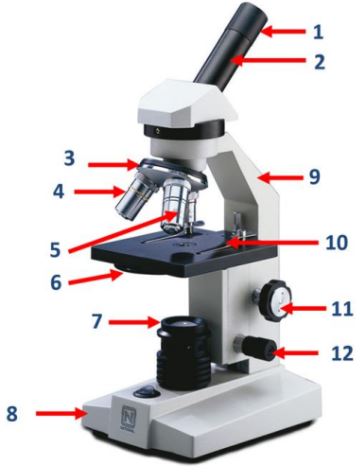
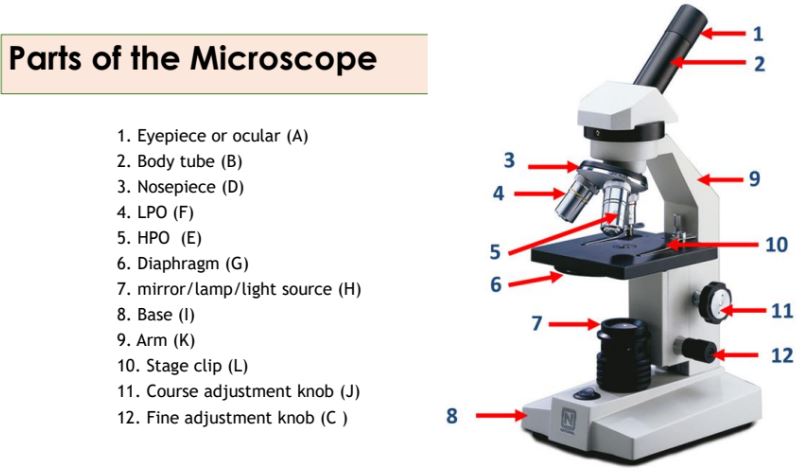
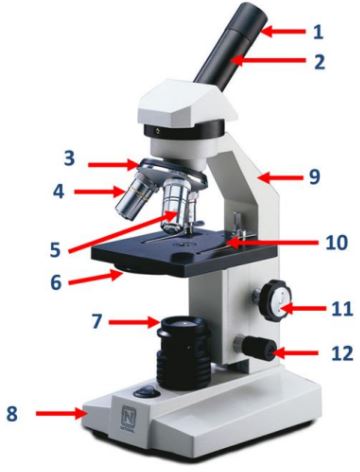
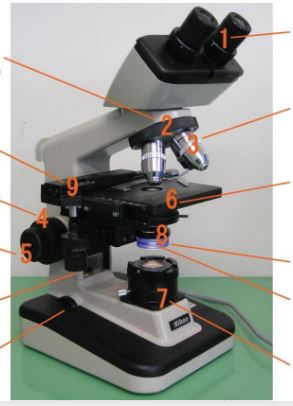
Eyepiece
The part of the microscope that contains the ocular lens.
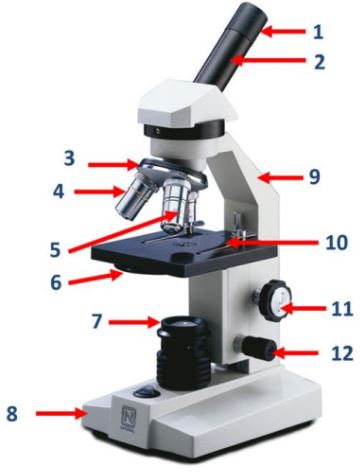
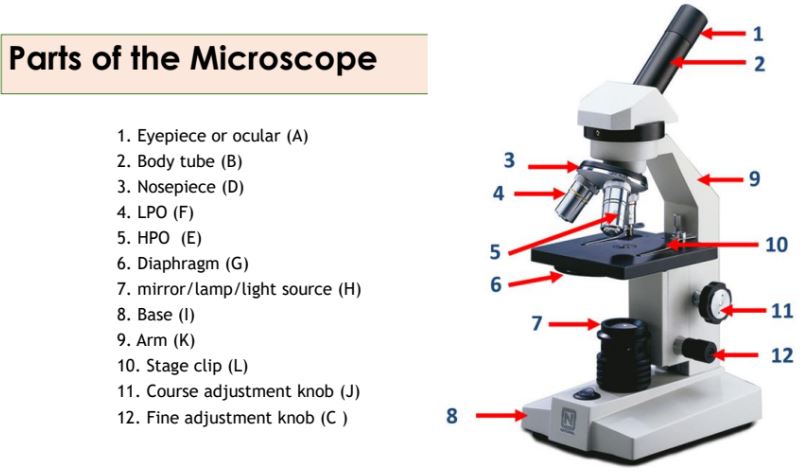
Body tube
The part of the microscope that connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses.
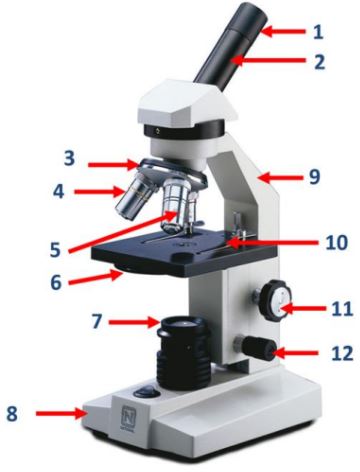
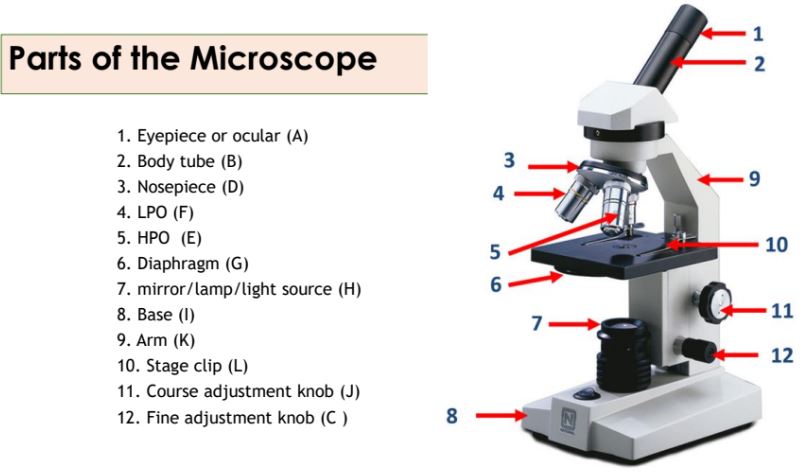
Nosepiece
The part of the microscope that holds the objective lenses and can be rotated to change magnification.
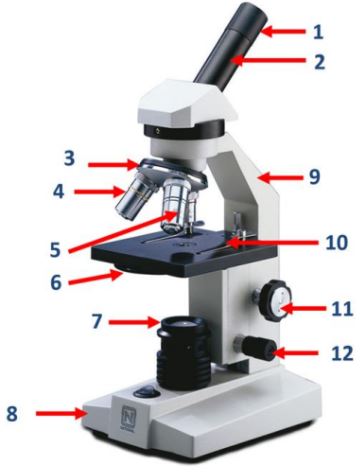
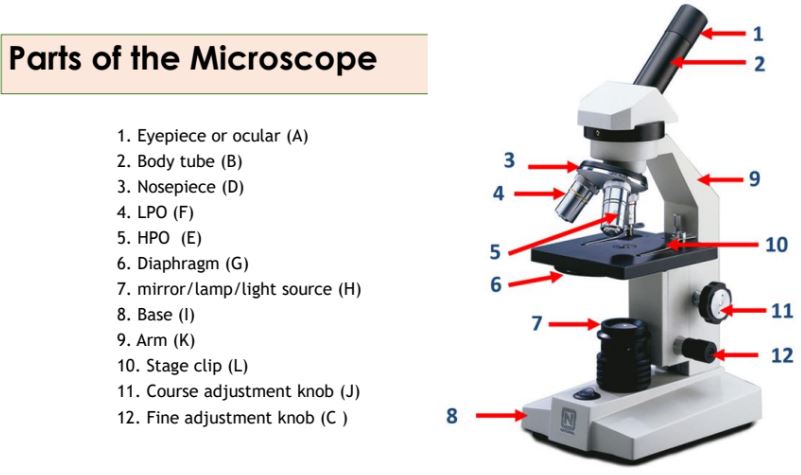
Objective lenses
Lenses on the microscope that provide different levels of magnification.
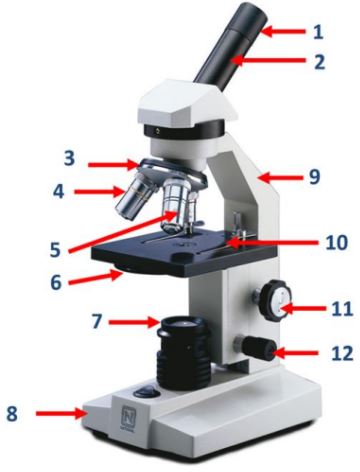
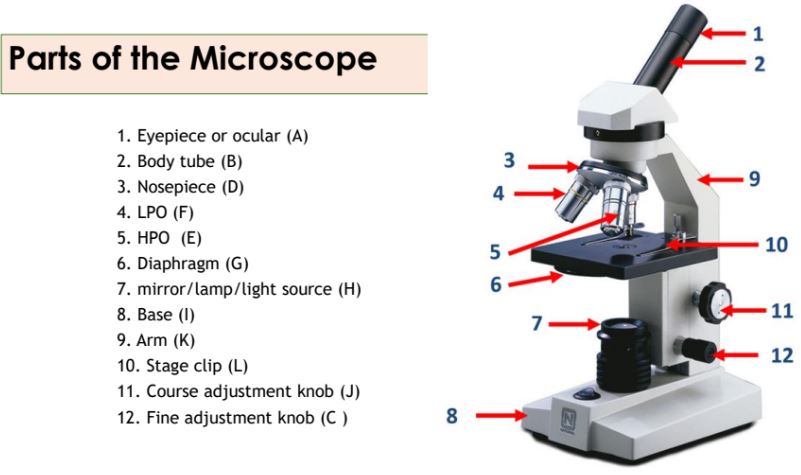
Diaphragm
A part of the microscope that controls the amount of light passing through the specimen.
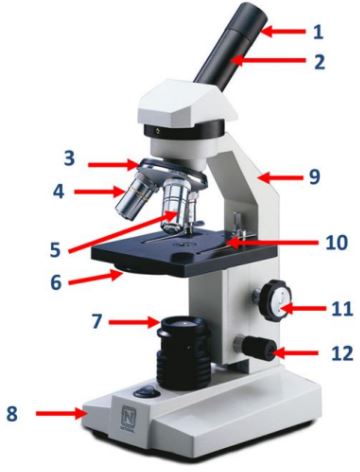
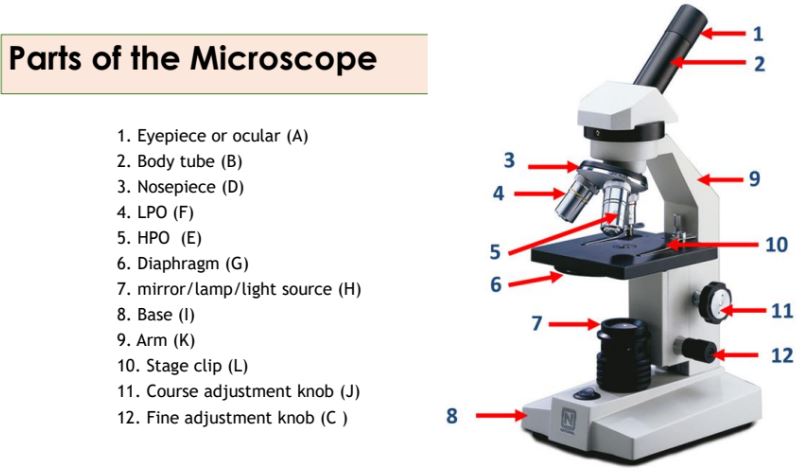
Mirror/lamp/light source
The part of the microscope that provides illumination for the specimen.
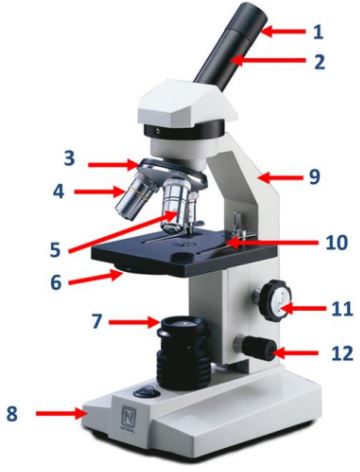
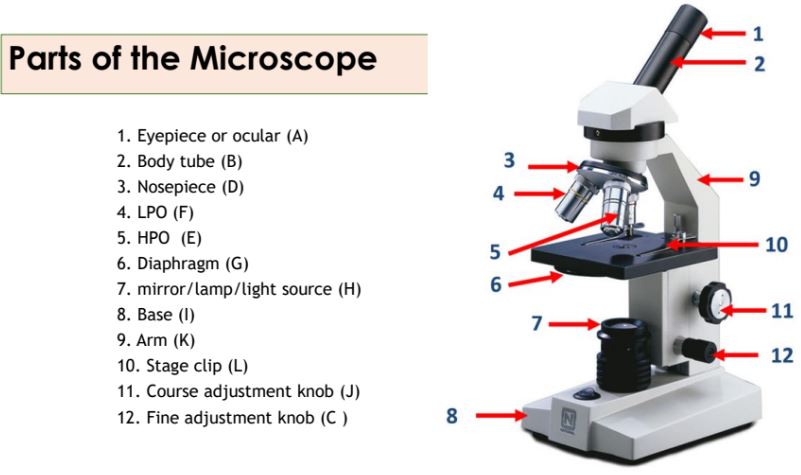
Base
The bottom part of the microscope that supports the entire instrument.
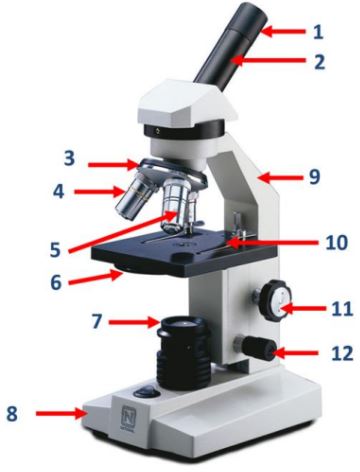
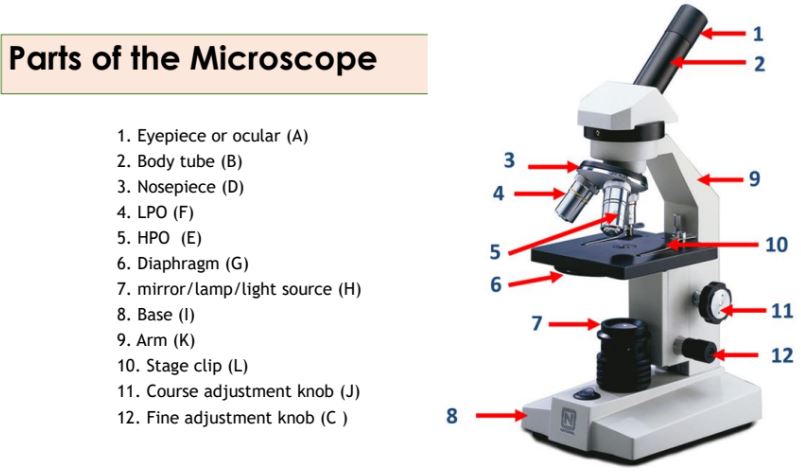
Arm
The part of the microscope that is used to carry and support it.
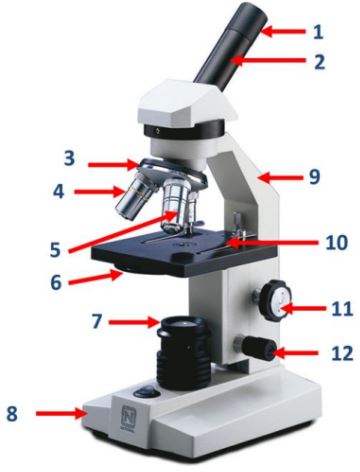
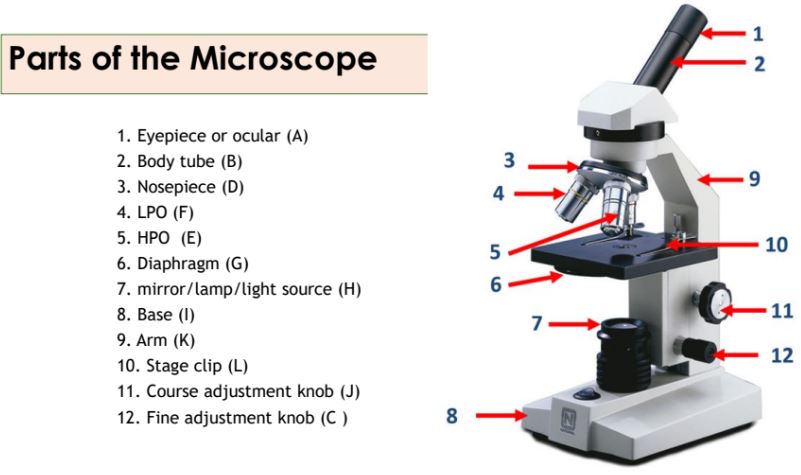
Stage clip
Clips on the stage of the microscope that hold the slide in place.
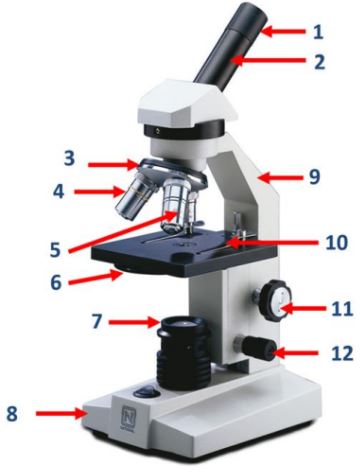
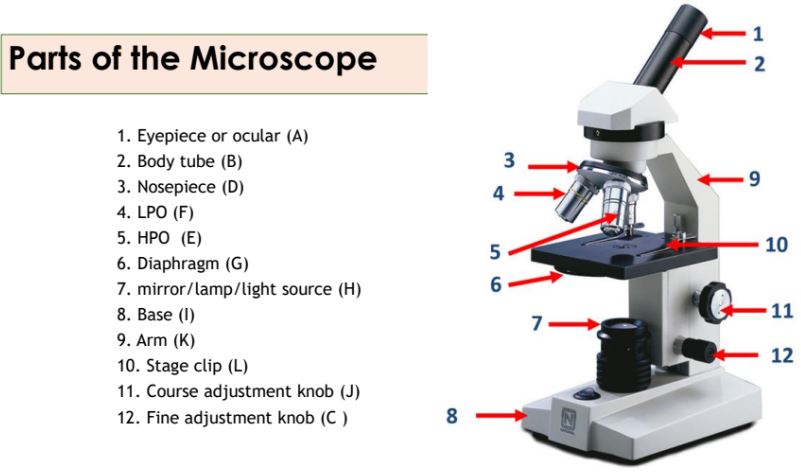
Course adjustment knob
A knob on the microscope used for rough focusing.
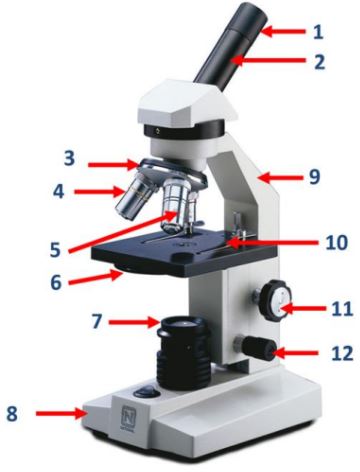
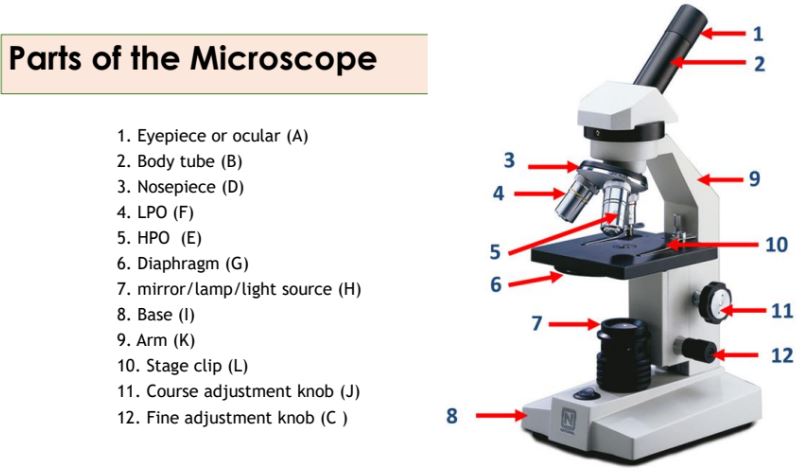
Fine adjustment knob
A knob on the microscope used for precise focusing.
Total Magnification
The overall magnification achieved by multiplying the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece.
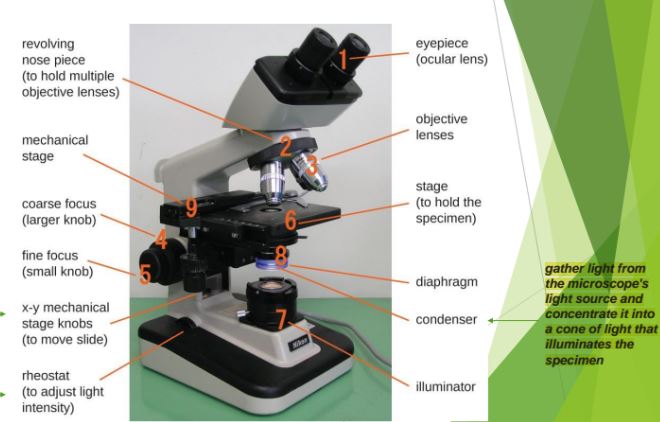

Condenser
Gathers the light from the microscope's light source and concentrate it into a cone of light that illuminates the specimen
The numerical aperture of the condenser and objective are nearly equal
What kind of Resolution error in photomicrography is this ?
Condenser aperture size that produces a numerical aperture approximately 70 percent that of the objective
What kind of Resolution error in photomicrography is this ?
Diaphragm is closed to the smallest setting at about 25 percent of the objective numerical aperture
what kind of Resolution error in photomicrography is this ?
Magnification
Refers to the increase in apparent size of an object.
Resolution
Refers to the ability to distinguish between two closely spaced objects. It is commonly used in the context of imaging systems, such as cameras or microscopes, to describe the level of detail that can be captured or observed. In general, higher __________ means that smaller details can be resolved and distinguished more clearly.
CELL THEORY POSTULATES by (Schleiden & Schwann)
All living organisms are composed of cells.
CELL THEORY POSTULATES by (Schleiden & Schwann)
The cell is the basic unit of all living organisms.
CELL THEORY POSTULATES by (Virchow)
All cells are produced by the division of pre -existing cells.
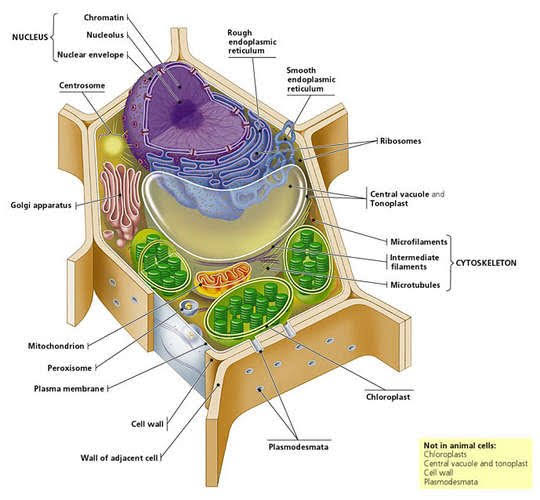
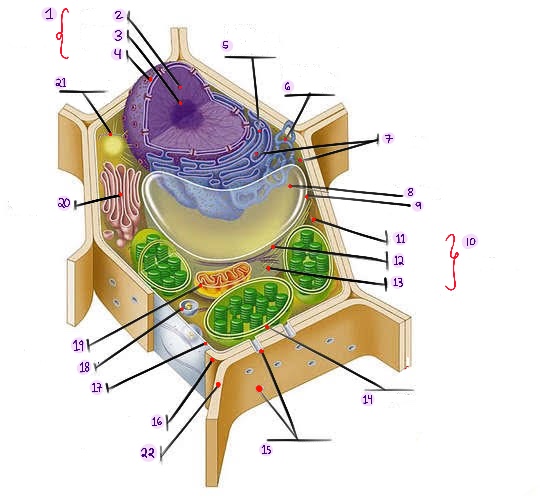
Nucleus: The central organelle in a cell that contains the genetic material (DNA) and Control center of the cell.
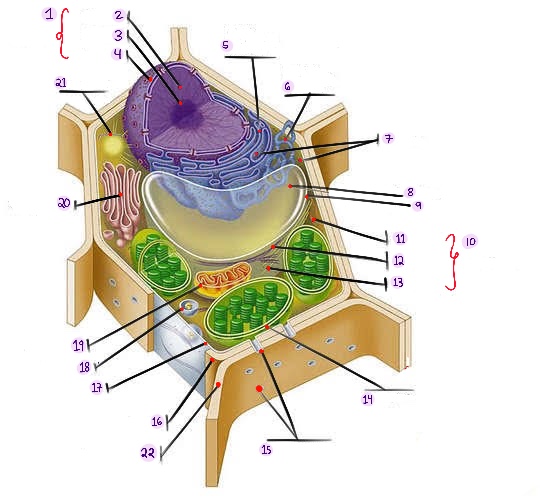
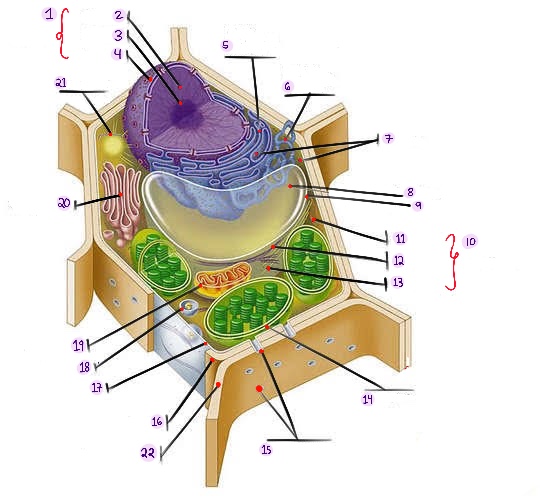
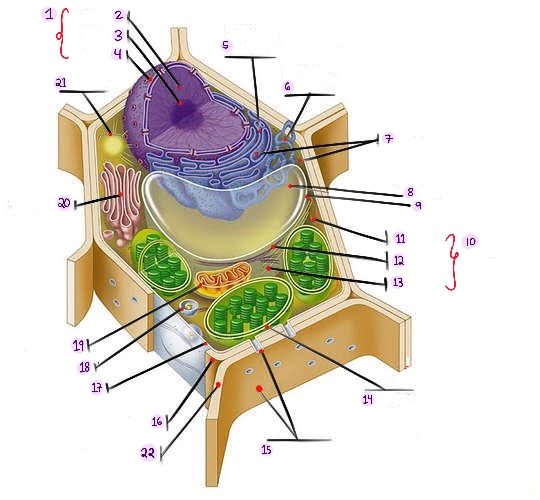
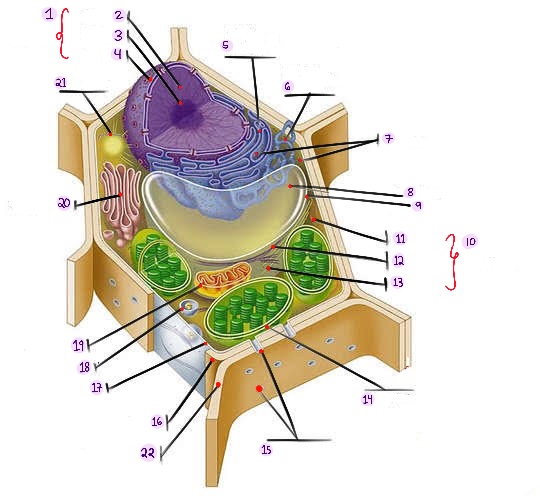
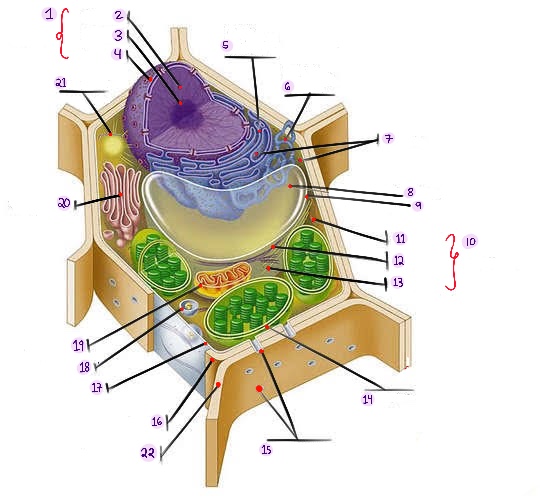
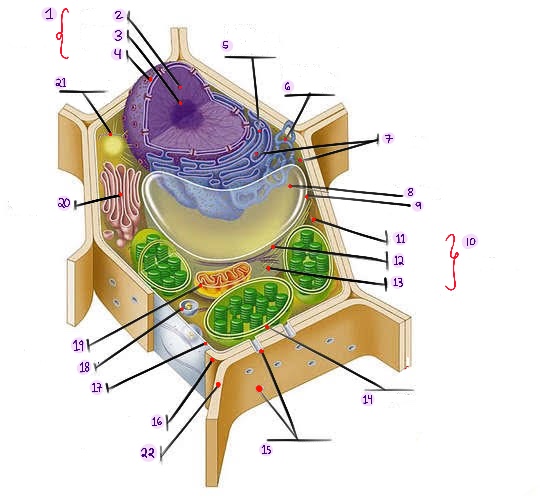
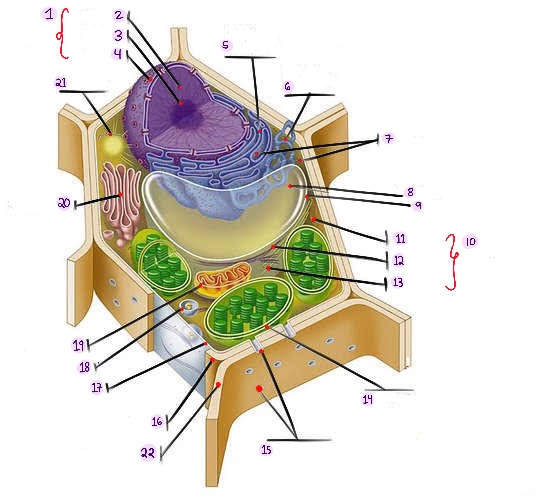
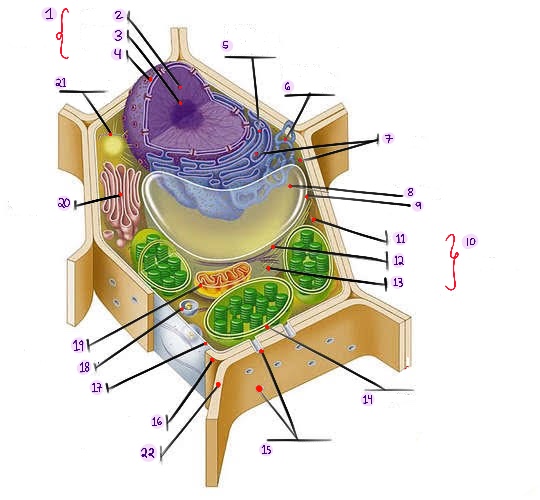
what part of plant cell is no.1? (in the image)
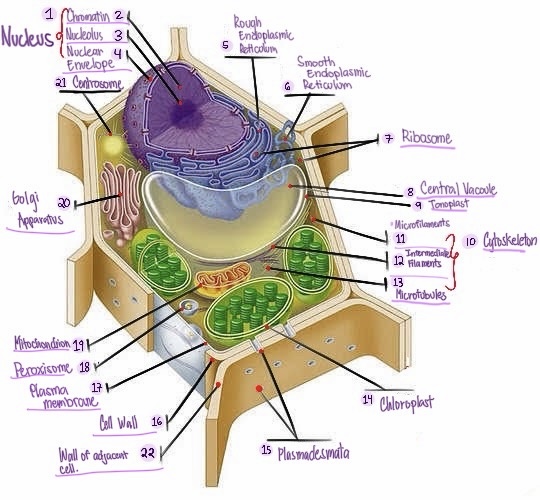
Chromatin: The material that makes up the chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell , consisting of DNA and proteins.
what part of plant cell is no. 2? (in the image)
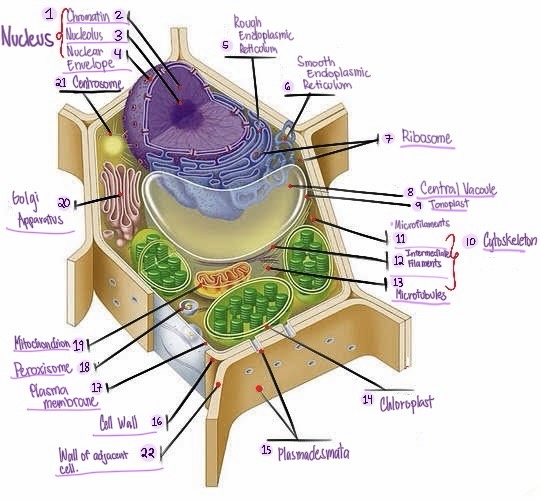
Nucleolus: Structure within the nucleus involved in ribosome production.
what part of plant cell is no. 3? (in the image)
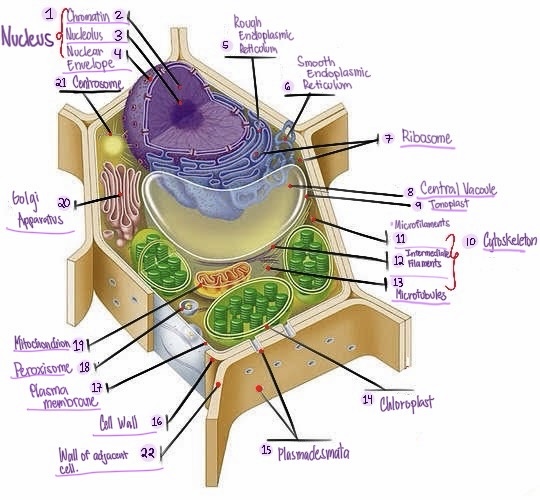
Nuclear envelope: Double membrane surrounding the nucleus.
what part of plant cell is no. 4? (in the image)
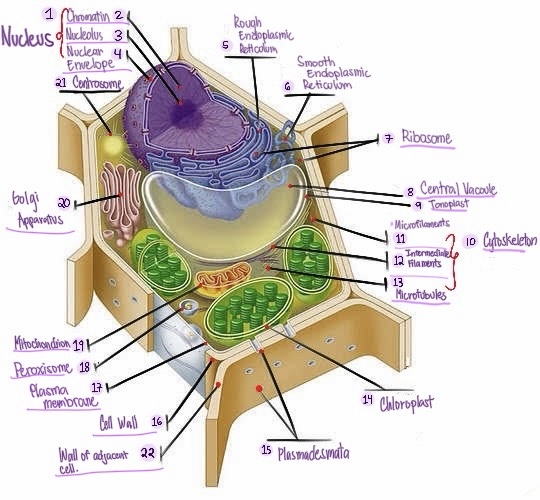
Rough Smooth endoplasmic reticulum: Ribosomes, protein synthesis & modification.
what part of plant cell is no. 5? (in the image)
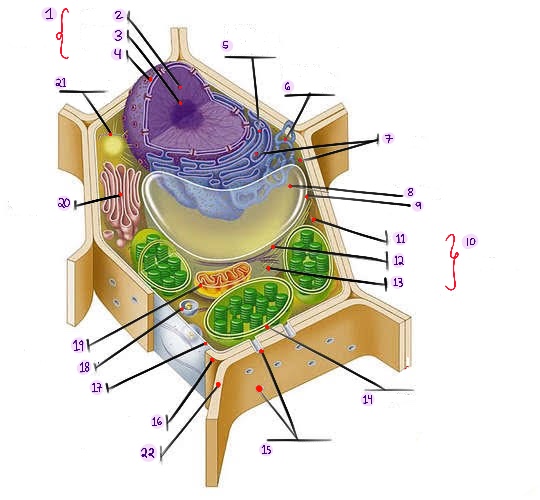
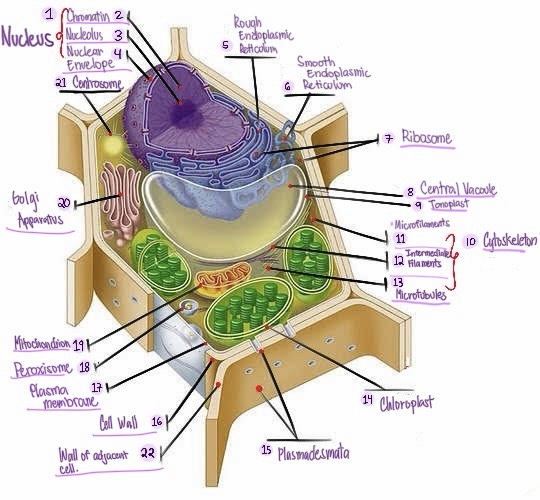
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum: Network of membranes involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. No ribosomes, lipid synthesis, detoxification, calcium storage.
what part of plant cell is no. 6? (in the image)
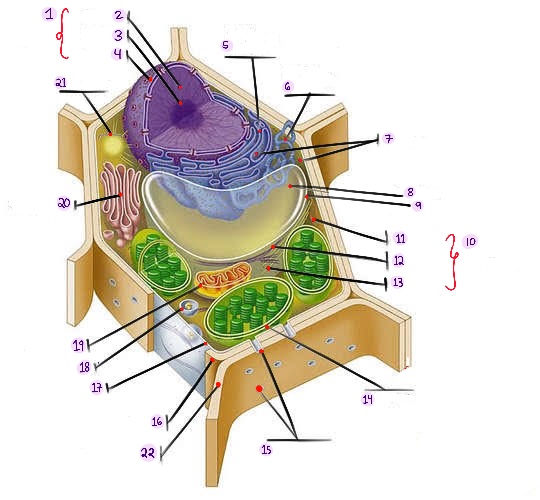
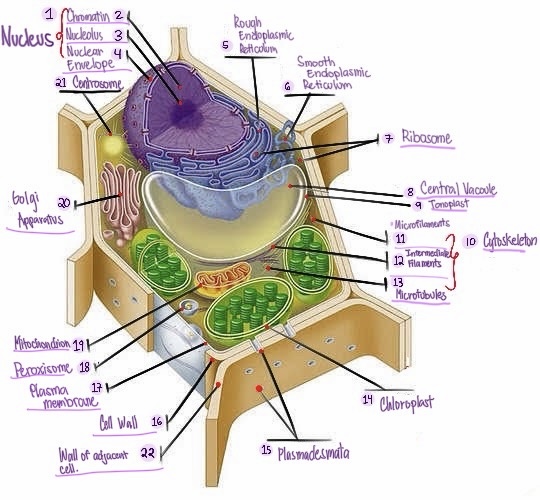
Ribosomes: Cellular structures involved in protein synthesis.
what part of plant cell is no. 7? (in the image)
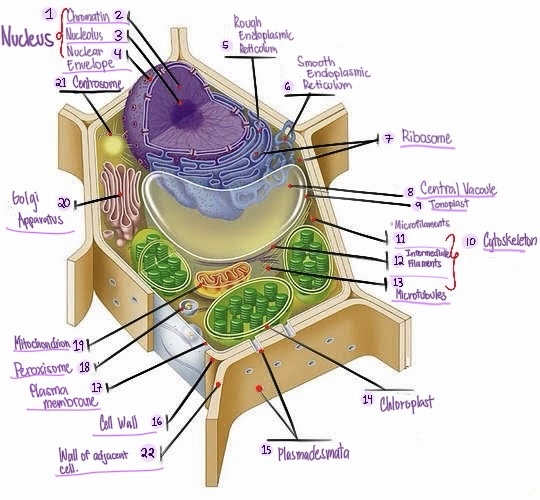
Central vacuole: Large fluid-filled sac found in plant cells, involved in storage and support.
what part of plant cell is no. 8? (in the image)
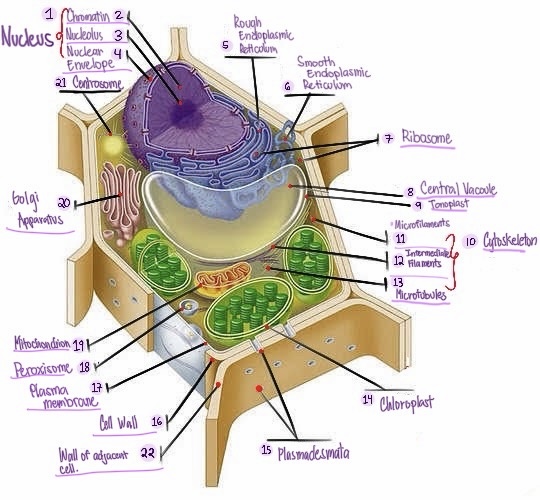
Tonoplast: Membrane surrounding the central vacuole in plant cells.
what part of plant cell is no. 9? (in the image)
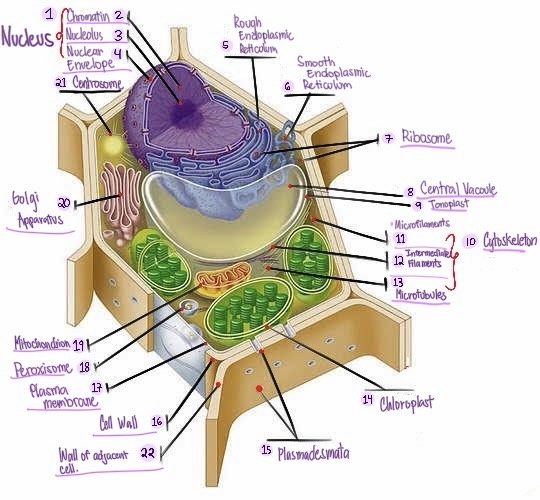
Cytoskeleton: a network of protein filaments that provides structural support and maintains the shape of the cell. It is involved in various cellular processes, including cell division, cell movement, and intracellular transport.
what part of plant cell is no. 10? (in the image)
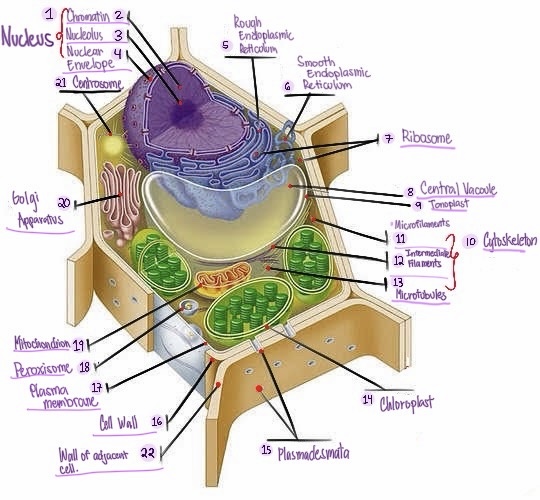
Microfilaments: Thin protein filaments involved in cell movement and support.
what part of plant cell is no. 11? (in the image)
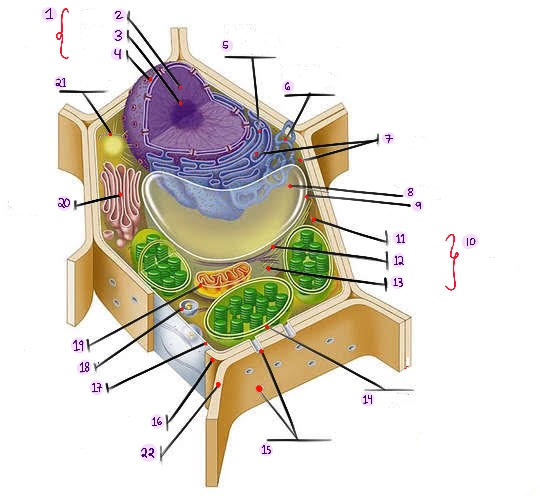
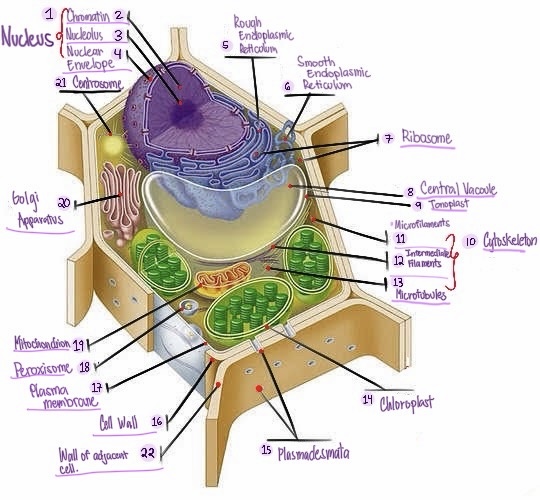
Intermediate filaments: Structural filaments providing mechanical support to the cells.
what part of plant cell is no. 12? (in the image)