Chemistry Definitions
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
Atom
An atom is the smallest particle of matter and is made up of protons, neutrons and electrons
Element
Element is only made up of one sort of atom. They are all listed in the periodic table
Molecule
Molecule is two or more atoms covalently bonded together. The bonding can be either ionic or covalent
Compound
Compound has two or more different types of atom bonded together. The bonding can be either ionic or covalent
Mixture
Mixture has two or more different elements and/or compounds in the same space and can be separated into the individual components.
Acid
An acid is a substance that donates H+ ions
Base
A base is a substance that accepts H+ ions
Alkali
An alkali is a base that releases hydroxide ions in aqueous solution
Salt
A salt is formed when the hydrogen ions from an acid are replaced by a metal or ammonium ion
Atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Mass number
The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons
Why do Isotopes have the same chemical properties?
They have the same electron configuration
Isotopic mass
The mass of an isotope relative to 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon 12
Relative atomic mass
The weighted average mass of all the isotopes relative to 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon 12
Isotopic peaks
Some molecules will contain 13C or 2H
Outlier Elements
Cr and Cu are more stable with half full and full 3d sub shells respectively
Ionisation energy
The energy needed to remove one mole of electrons from one mol of atoms in the gaseous state
Relative atomic mass
The weighted average mass of all the isotopes relative to 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon 12
Relative formula mass
The mass of one formula unit of an ionic compound relative to 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon 12
The mole
The amount of substance that contains as many particles as there are in exactly 12 grams of carbon 12
Empirical formula
The simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element present in a molecule
Molecular formula
The actual number of atoms of each element present in a molecule
Ionic Bond
The electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
Metallic Bond
The attraction between positive ions and delocalised electrons
What is the charge on CN
negative one
what is the charge on HPO4
negative 2
what is the charge on SO3 and SO4
negative 2
Coordinate/dative covalent
A covalent bond which both electrons of the shared pair come from the same atom
How is a coordinate bond formed?
The atom with the lone pair donates a pair of electrons to the electron deficient atom that does not have a full outer shell of electrons
Bond Areas
In a double or triple bond
2 Bond pairs and 0 Lone pairs.
Linear shape
180 degrees
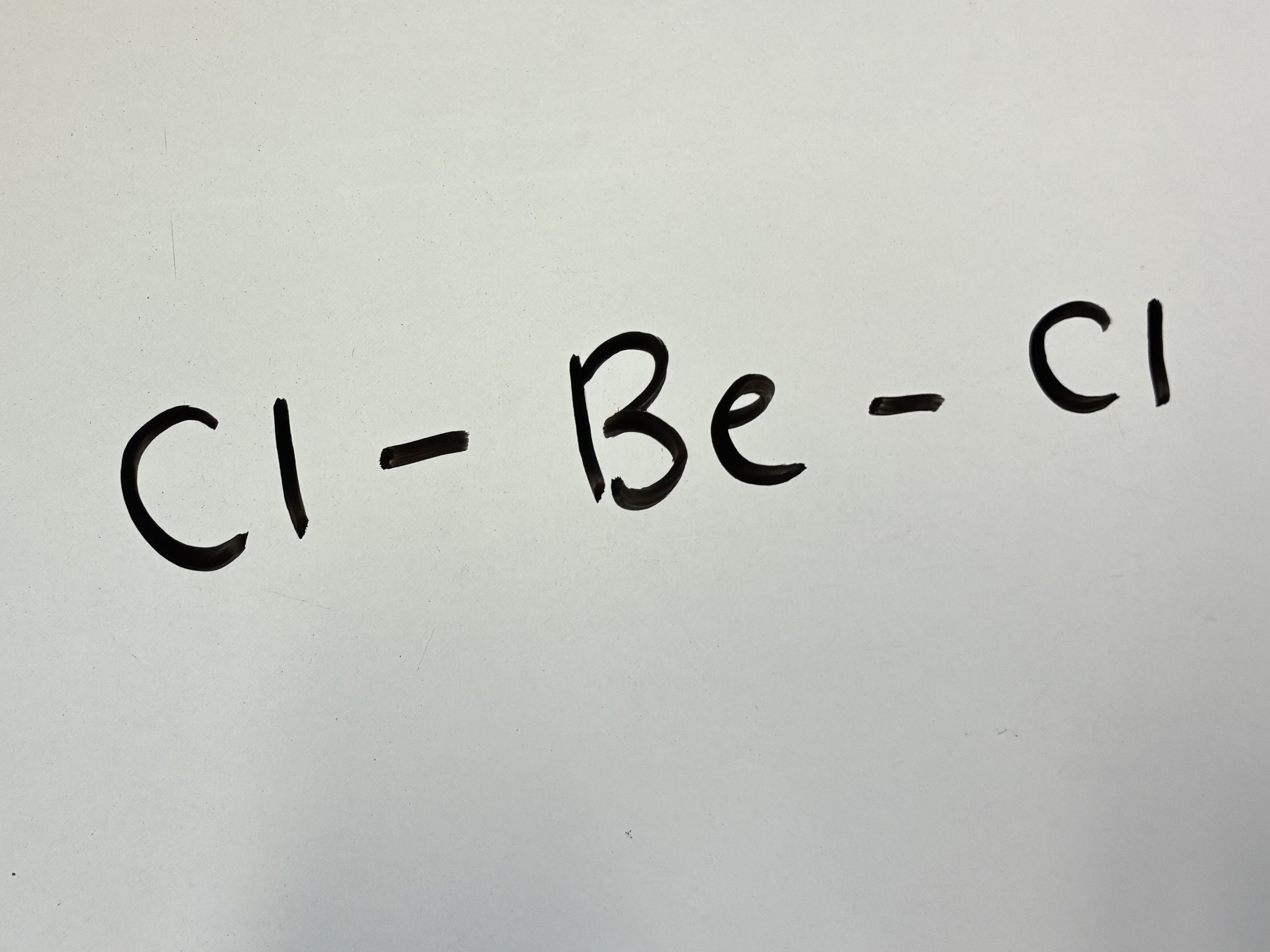
3 Bond pairs 0 lone pairs
Trigonal planar shape
120 degrees

4 Bond pairs 0 lone pairs
Tetrahedral shape
109.5 degrees
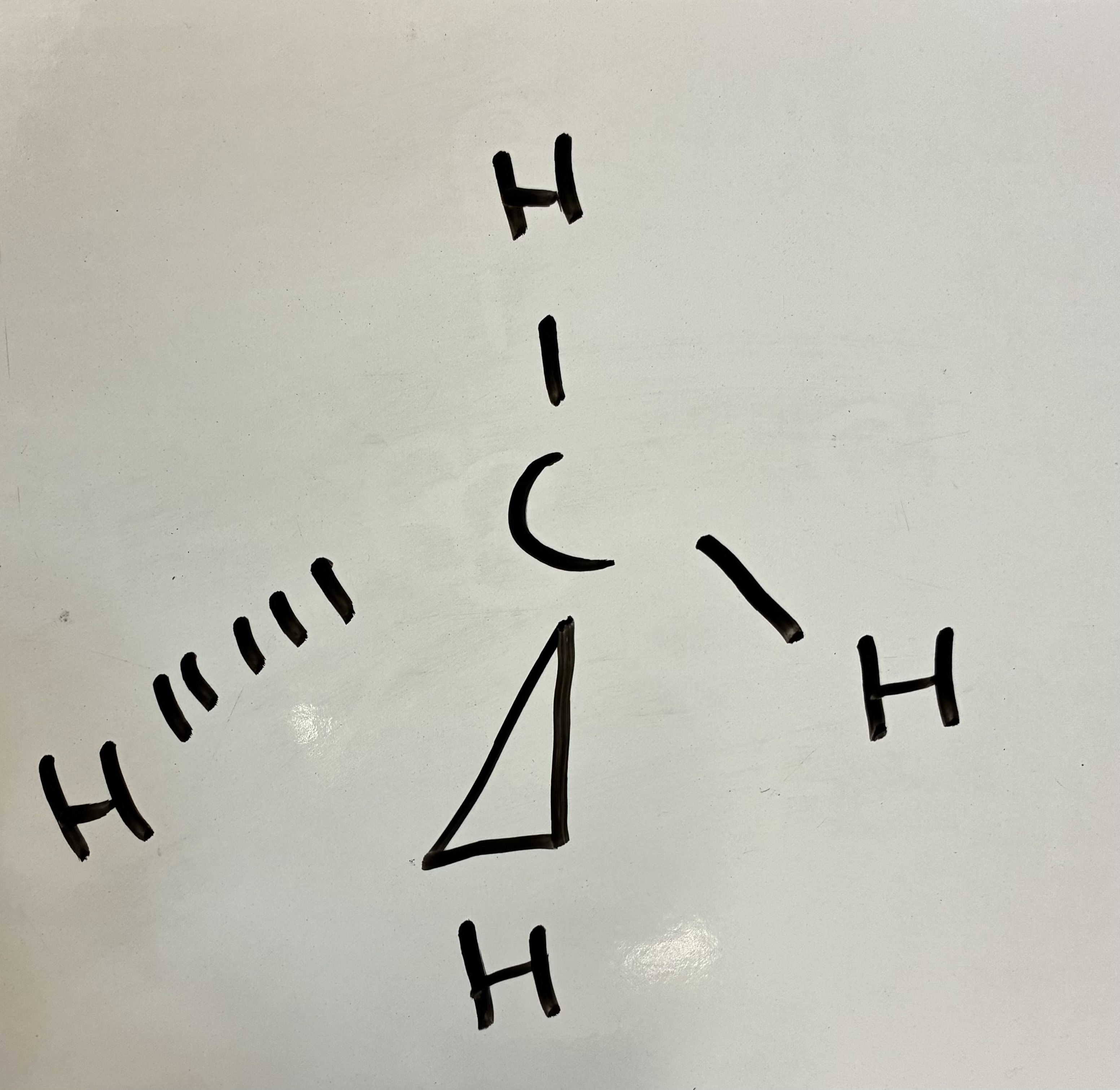
5 Bond pairs 0 lone pairs
Trigonal Bipyramidal shape
90 degrees and 120 degrees
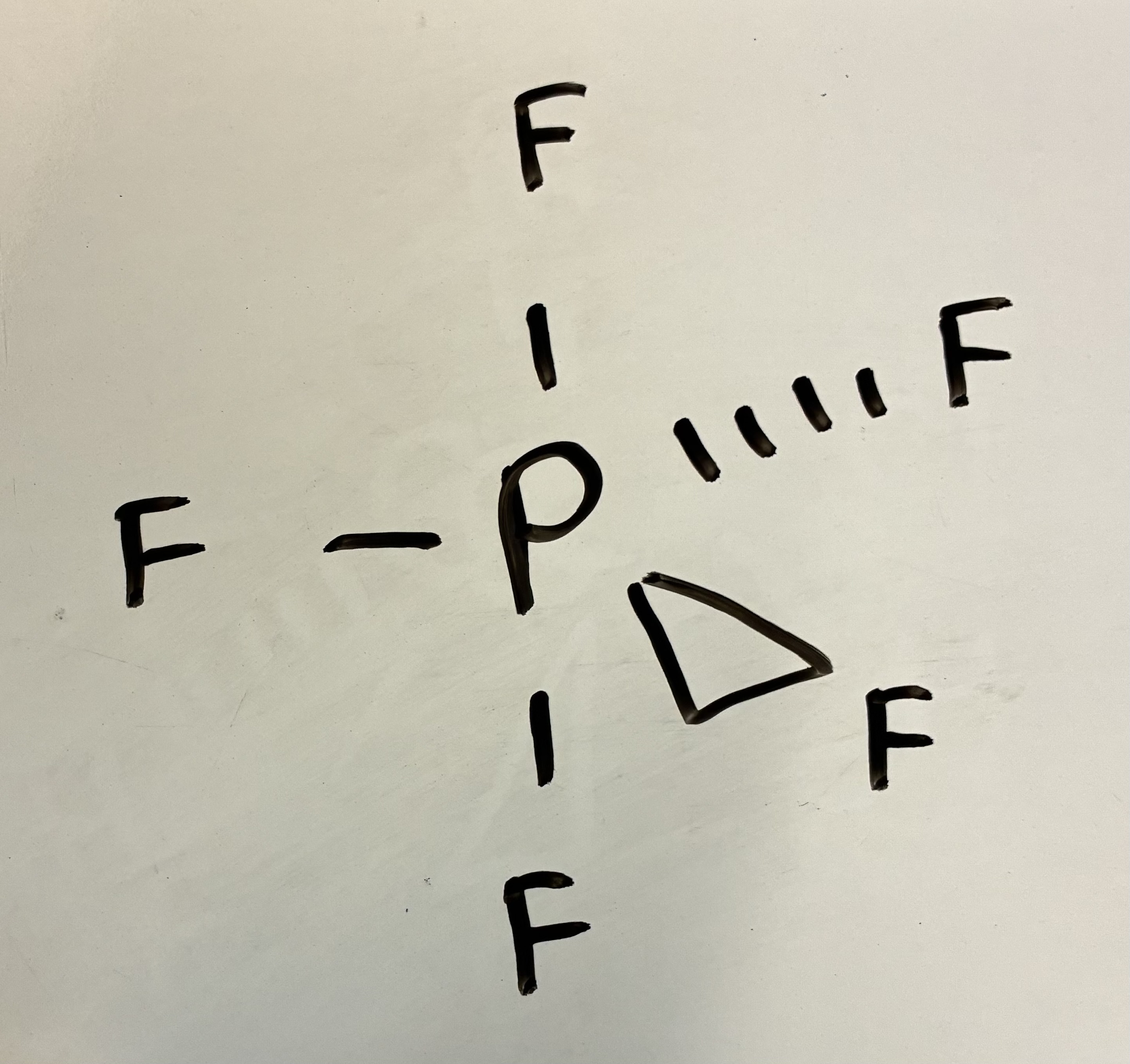
6 Bond pairs 0 lone pairs
Octahedral shape
90 degrees

2 Bonding areas 0 lone pairs
Linear shape
180 degrees
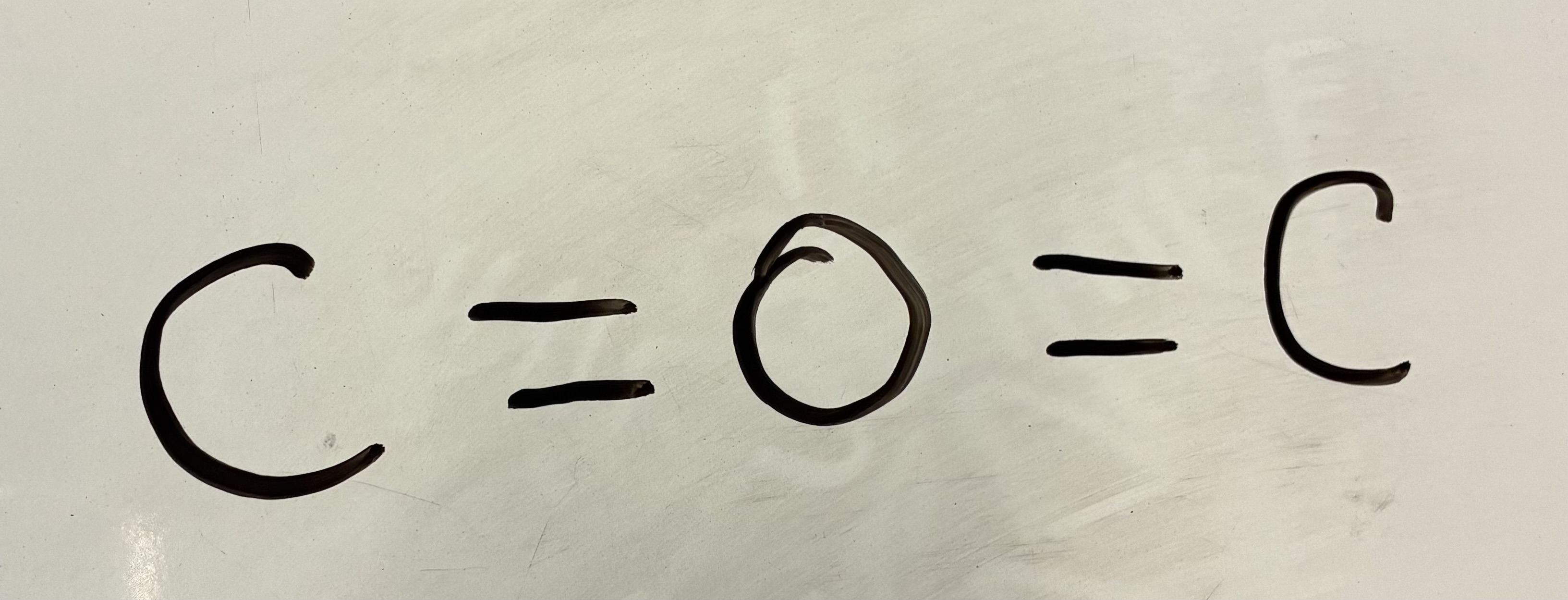
3 Bonding areas 0 lone pairs
Trigonal planar shape
120 degrees

2 Bond pairs 1 lone pair
V-shaped/Non Linear shape
117.5 degrees
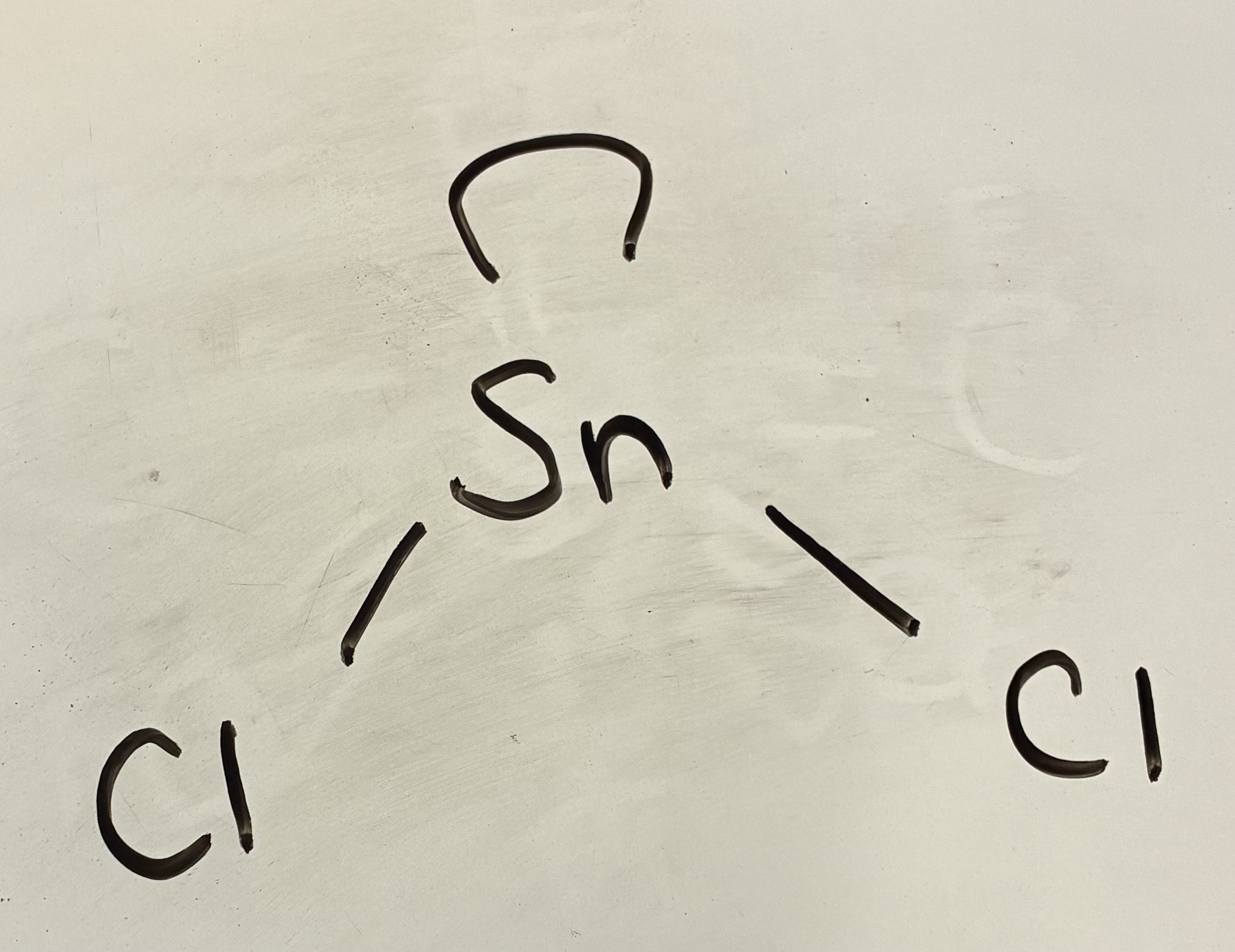
3 Bond pairs 1 lone pair
Trigonal Pyramidal shape
107 degrees
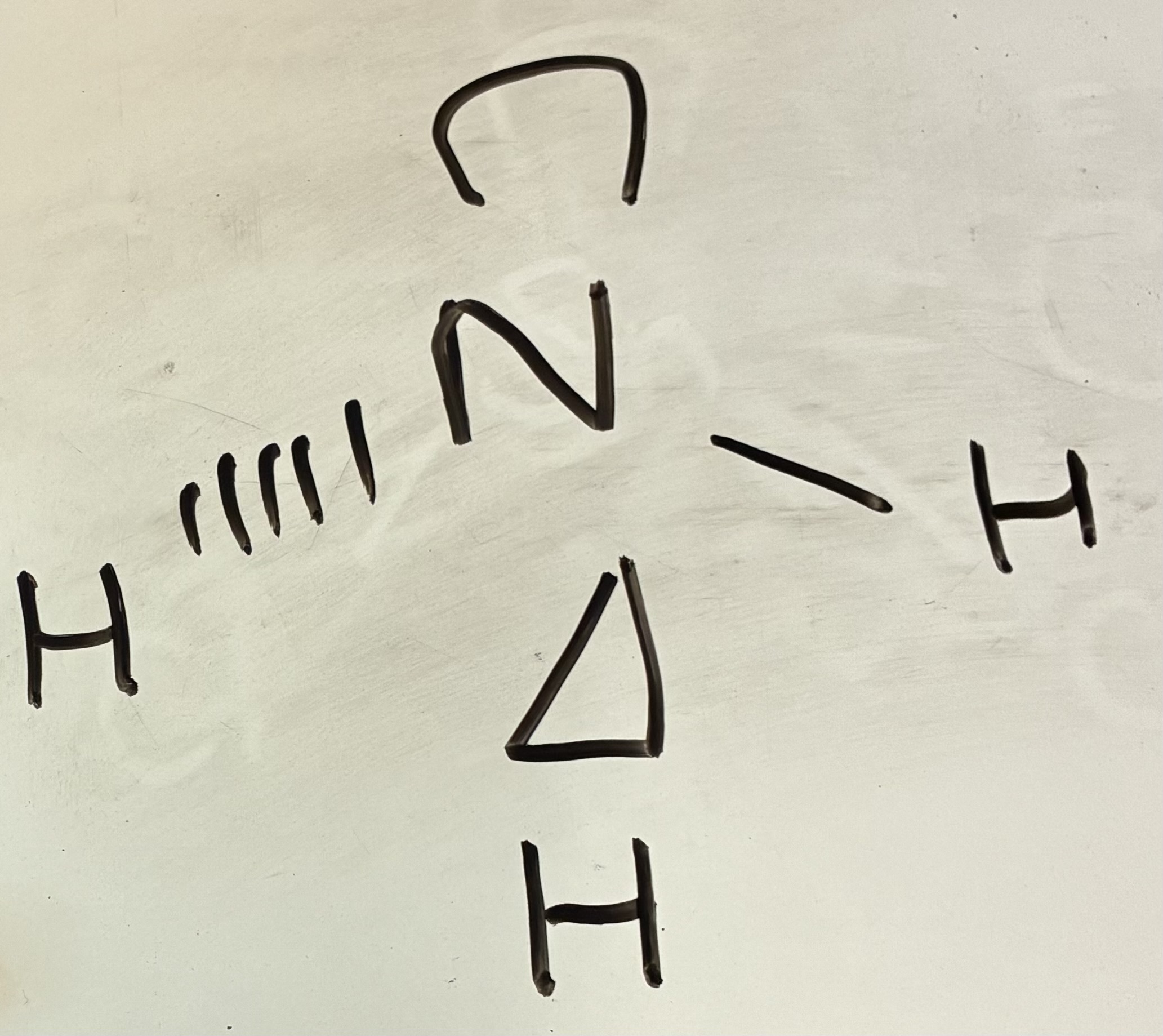
2 bond pairs 2 lone pairs
V-shaped shape
104.5 degrees
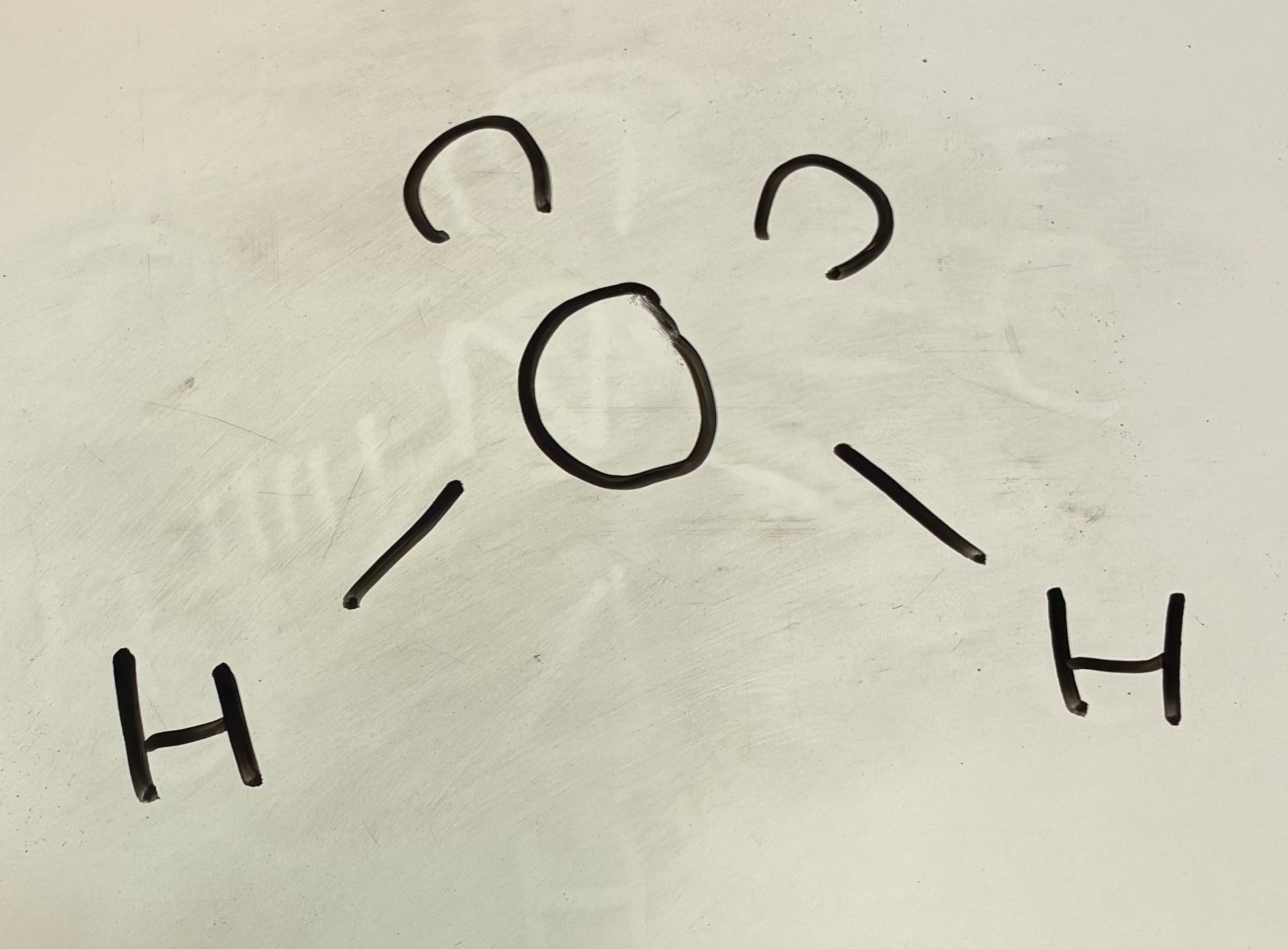
4 bond pairs 2 lone pairs
Square planar shape
90 degrees
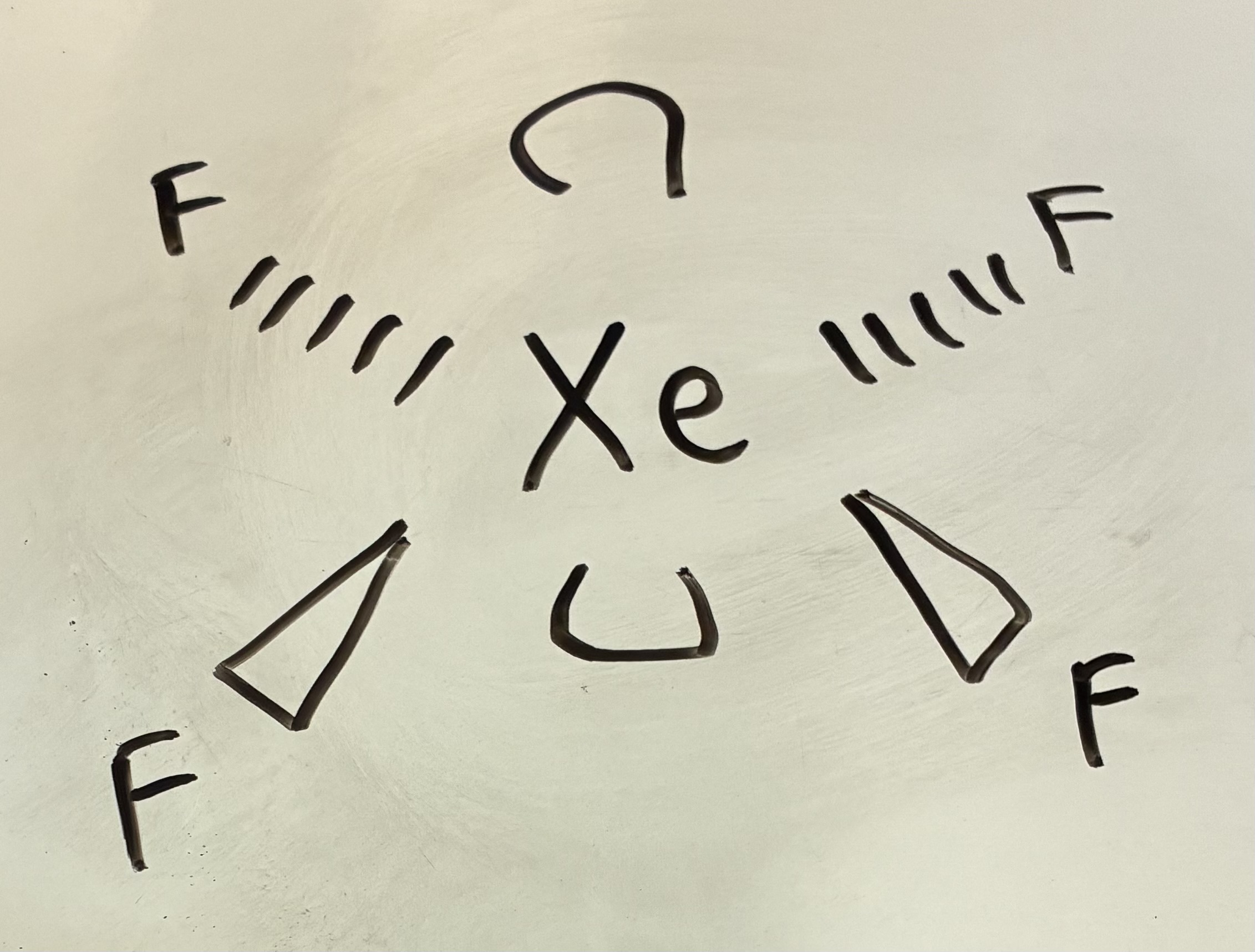
Electronegativity
The power of an atom to attract the pair of electrons in a covalent bond
Across a period electronegativity…
Increases as there are more protons and similar shielding so stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electron pair in the covalent bond
The most electronegative atom is
Flourine
Down a group electronegativity…
Decreases as there is greater shielding and a larger atomic radius so there is a weaker attraction between the nucleus and the pair of electrons in covalent bond
Polar covalent bond
When there is an uneven distribution of electrons. The atom with the greater electronegativity attracts the bonding pair more and has a slightly negative charge. Must include O, N, F, Cl, I, or Br.
Non-polar covalent bond
No or very small difference in electronegativity. Atoms have the same electronegativity so the bonding pair is shared equally. Carbon and hydrogen have similar electronegativity so hydrocarbons are non-polar.
A molecule is non-polar if it is…
Symmetrical as the bond dipoles cancel
A molecule is polar if it is…
Asymmetric as the bond dipoles do not cancel
What are the types of intermolecular forces
Van der Waals forces, permanent dipole-dipole forces, hydrogen bonds
Van der Waals forces are caused…
By the movement of electrons which unbalances the charge distribution within the molecule. This creates an instantaneous dipole across the molecule that is constantly forming and disappearing. Inducing a dipole in neighbouring molecules, resulting in weak forces of attraction between molecules.
Van der Waals forces are present in…
All molecules but they are the only forces present between non-polar molecules
Bigger molecules have stronger van der waals forces because…
They have greater Mr so have more electrons so the induced dipoles are larger.
Permanent Dipole-Dipole Forces
Occur between polar molecules which have a permenant dipole, in addition to but stronger than Van der Waals forces. The positive dipole end of one molecule is attracted to the negative dipole end of a neighbouring molecule.
Hydrogen Bonding
Occurs between molecules which contain a hydrogen atom bonded to either F, O, N. A hydrogen bond is formed between a positive dipole H atom in one molecule and a lone pair of electrons on an N, O or F in a neighbouring molecule. The strongest intermolecular force.
Drawing hydrogen bonds…
Show two molecules, all lone pairs, partial charges, and partial alignment (H bond has to be a straight line with at least 3 atoms in line)
To change states…
Energy is needed to overcome the forces holding the particles together. The stronger the forces, the more energy is needed, the higher the melting or boiling point
An electric current can only flow…
If there are charged partices which are free to move. Current can be carried by delocalised electrons or free ions.
Substances can dissolve if…
Solute and solvent molecules attract one another.
Ionic and polar substances dissolve in
polar solvents
Non-polar substances dissolve in
Non polar solvents
Ionic compound
Giant ionic lattice, ionic bonding, strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Ionic solids conductivity?
Don’t conduct as the ions are fixed in position in the lattice so cannot move and therefore don’t carry charge
Dissolved or molten ionic conductivity?
Can conduct as ions become free to move and carry current so molten or dissolved ionic substances conduct
When enough force is applied to ionic substances…
The layers slide over one another. Ionic substances are brittle, so like charges move next to each other causing repulsion as the lattice structure breaks down
Ionic substances are generally…
Soluble in water, so positive ions attract the negative dipole in O, the negative ions attract the positive dipoles in H2
Metallic structure
Giant metallic lattice, bonding is metallic, strong forces of attraction between delocalised electrons and positive ions.
Why do metals have high melting points?
It takes a lot of energy to overcome the strong forces of attraction between positive ions and delocalised electrons
Why do metals conduct?
Because the delocalised electrons can move through the structure and carry the current
Why are metals strong?
Metals have strong forces of attraction between positive ions and delocalised electrons
Why are metals malleable and ductile?
The layers of ions in the giant metallic lattice can slide over each other into new positions without disrupting the metallic bond and the attraction between positive ions and delocalised electrons remains.
what are the types of covalent substances
Macromolecular and simple molecular
Melting point of covalent substances…
is low because intemermolecular forces are weak, so less energy is required to break the forces
Solubility of covalent substances
Non polar molecules dissolve in non polar solvents, they form van der Waals forces with solvent molecules. Polar molecules dissolve in polar solvents (eg H2O if they can form hydrogen bonds with water)
Conductivity of covalent substances
Don’’t conduct as the lattice doesn’t contain mobile electrons/ions (charged carriers) that are free to move
Substances with hydrogen bonding have…
Higher boiling points than expected due to the strength of the hydrogen bond between molecules. Tends to dissolve in water because they form hydrogen bonds with water
What are the anamalous properties of water?
Ice is less dense than water as hydrogen bonds hold neighbouring molecules far apart in an open lattice in ice. Water has a higher boiling point than expected. Forms more hydrogen bonds than eg NH3, as N has one lone pair, O has two lone pairs.
What is different about H2O, HF, NH3?
They have hydrogen bonds that are stronger than Van der Waals forces, so more energy is needed to overcome the hydrogen bonds between molecules
Boiling point trend down a group…
Increasing, as there are more electrons and higher Mr, there are stronger Van der Waals forces, so more energy is required to overcome them
What sort of bonds does carbon form and how many?
Four covalent bonds
Structural formula
Shows how the atoms in a molecule are arranged
Displayed formula
Shows all the atoms and bonds in a molecule
Skeletal formula
Shows the shape of the carbon skeleton
Homologous series
A family of compounds containing the same functional group and having the same general formula but having a different carbon chain length, each successive member has an extra CH2
Functional group
AN atom or group of atoms which gives an organic compound its chemical properties
List all 10 homologous series in order of increasing priority when naming
Halogenoalkanes, alkenes, amines, alcohols, ketone, aldehyde, nitrile, acyl chloride, ester, carboxylic acid, alkane
Suffix and functional group of amines?
-amine and -NH2
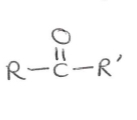
Suffix and functional group of ketones
-one
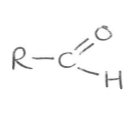
Suffix and functional group of aldehydes
-al
Suffix and functional group of nitriles
-nitrile

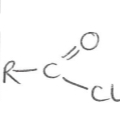
Suffix and functional group of acyl chlorides
-oyl chloride
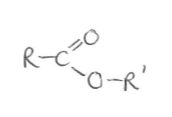
Suffix and functional group of esters
-oate
Suffix and functional group of carboxylic acid
-oic acid
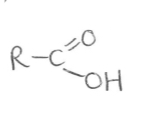
Hydrocarbons
Compounds containing carbon and hydrogen atoms only
Saturated hydrocarbons
Contain single carbon-carbon bonds only
Unsaturated hydrocarbons
Contains one or more carbon-carbon double bonds
Aliphatic hydrocarbons contains…
Chains
Alicylic hydrocarbons contains…
Rings
Aromatic hydrocarbons contains…
benzene rings