Graph Traversal - Dijkstra's Algorithm
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
1
New cards
what is the shortest path problem?
the problem of finding a path between 2 nodes in a graph such that the weight of its edges is minimised
* eg. shortest path between 2 intersections on a map
* eg. routing a packet through a network
* eg. shortest path between 2 intersections on a map
* eg. routing a packet through a network
2
New cards
what are the possible variations of the shortest path problem?
* single source shortest path problem
* single destination shortest path problem
* all pair shortest path problem
* single destination shortest path problem
* all pair shortest path problem
3
New cards
what is the single source shortest path problem?
shortest path from source node to all other nodes in the graph, the most common version of this problem
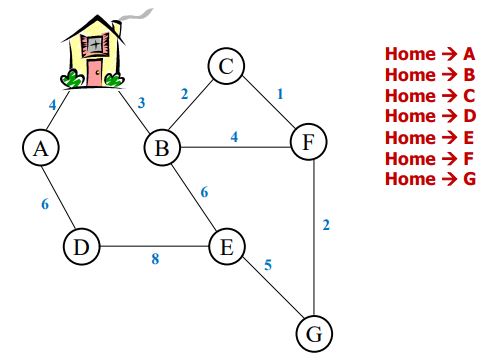
4
New cards
what is the single destination shortest path problem?
shortest path from all nodes in directed graph to single destination node
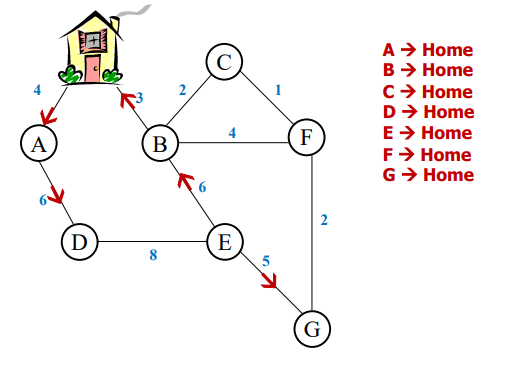
5
New cards
what is the all pairs shortest path problem?
shortest path between each pair of nodes, for n nodes there are n \* (n-1) pairs??
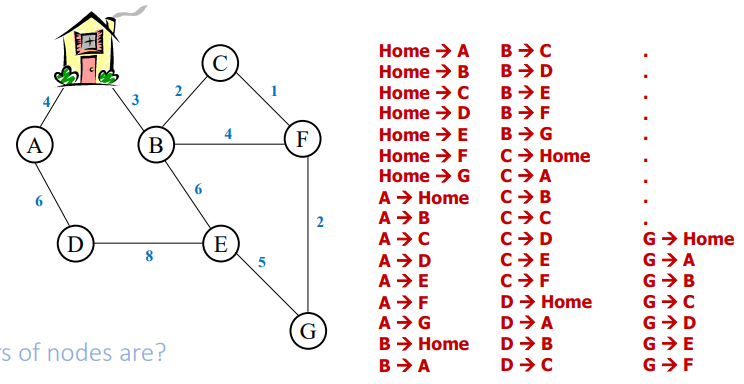
6
New cards
what are the different algorithms we can use to solve the shortest path problem?
* Dijkstra's algorithms
* Floyd-warshall algorithm
\
* Bellman-ford algorithm
* A\* search algorithm
* Floyd-warshall algorithm
\
* Bellman-ford algorithm
* A\* search algorithm
7
New cards
what is Dijkstra’s algorithm?
* given a start point, the algorithm finds the shortest paths between the start node and all other nodes in a graph
* given an end destination we can keep track of visited nodes and find a path
* greedy approach
* given an end destination we can keep track of visited nodes and find a path
* greedy approach
8
New cards
what is a greedy approach?
makes an optimal choice at each stage hoping end result is the best solution
9
New cards
what variation of shortest path problem does Dijkstra’s algorithm solve?
solved single source shortest path
10
New cards
what type of graph does Dijkstra’s algorithm work with?
* works for both directed and undirected
* edges must be ≥ 0
* graph must be connected
* edges must be ≥ 0
* graph must be connected
11
New cards
what is the code for Dijkstra’s algorithms?
implemented with 3 stacks
* unvisited
* distances
* parent
* unvisited
* distances
* parent

12
New cards
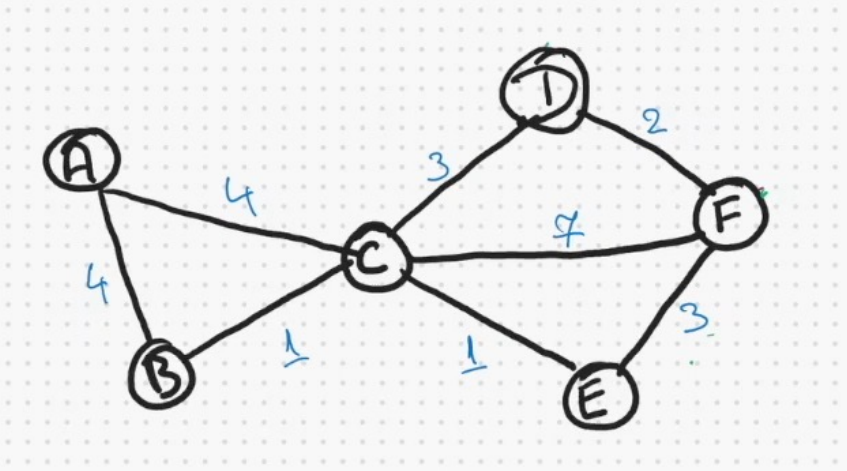
carry out Dijkstra’s algorithm on this graph
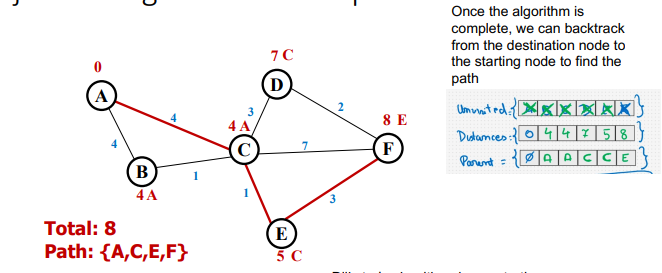
13
New cards
what is the time complexity of Dijkstra’s algorithm?
dependant on the implementation where n = the number of nodes in the graph
* classic implementation = O(n²)
\[while unvisited is not empty\], unvisited contains each node n so for 1 while loop, time complexity = n. nested for loop has n squared total
* other implementation like heaps = O(E + n log n), E is the number of edges and n is the number of nodes, time complexity is lowered
* classic implementation = O(n²)
\[while unvisited is not empty\], unvisited contains each node n so for 1 while loop, time complexity = n. nested for loop has n squared total
* other implementation like heaps = O(E + n log n), E is the number of edges and n is the number of nodes, time complexity is lowered
14
New cards
what are the applications of Dijkstra’s algorithm?
* Finding Shortest Path
* GPS System
* A geographical map as a graph
* Locations in the map are nodes/ vertices
* Road between locations are edges
* Weights of edges are distance between two locations
* Network routing
* Commercial Shipping
* GPS System
* A geographical map as a graph
* Locations in the map are nodes/ vertices
* Road between locations are edges
* Weights of edges are distance between two locations
* Network routing
* Commercial Shipping
15
New cards
what are the disadvantages of Dijkstra’s algorithm?
* since it is a greedy algorithm it has no sense of direction (can’t guarantee the lowest edges we’re following is the right direction to goal node
* does not work with negative weights
* does not work with negative weights
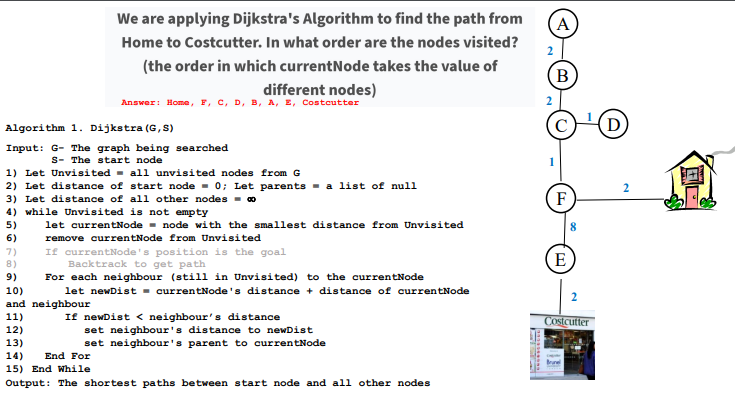
16
New cards
what is the Floyd-Warshall algorithm?
computes how far each node is from every other node in the input graph
* computes 1-step paths, 2-step paths etc. since intermediate paths between nodes may be more optimal than going directly through 2 nodes
* works with negative edges but not negative cycles
* does not return all the paths but can if needed
* uses dynamic programming
* computes 1-step paths, 2-step paths etc. since intermediate paths between nodes may be more optimal than going directly through 2 nodes
* works with negative edges but not negative cycles
* does not return all the paths but can if needed
* uses dynamic programming
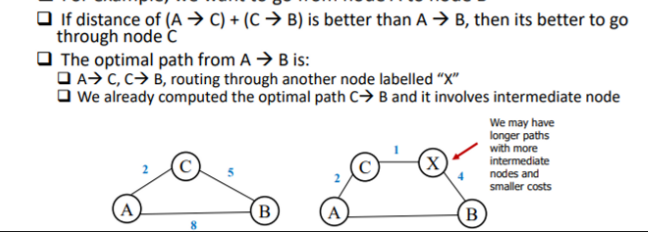
17
New cards
what variation of the shortest path problem does the Floyd-Warshall algorithm solve?
all pairs shortest path problem
(unlike dijstra’s algorithms only computes from 1 start node to every other node)
(unlike dijstra’s algorithms only computes from 1 start node to every other node)
18
New cards
what is dynamic programming?
* a problem solving approach
* systematically pre-computes and store answers to sub problems to build a solution to the complex problem ⇒ reuses these results instead of recomputing them
* systematically pre-computes and store answers to sub problems to build a solution to the complex problem ⇒ reuses these results instead of recomputing them
19
New cards
what data structures does the Floyd-Warshall algorithm use?
* distance matrix (a 2D adjacency matrix)
* path matrix
* path matrix
20
New cards
what is the distance matrix in the Floyd-Warshall algorithm?
* the real edges between nodes - directly represents the graph and is not changed
* if there is no edge between 2 nodes then set edge `weight = infinity` (not connected directly)
* if there is no edge between 2 nodes then set edge `weight = infinity` (not connected directly)
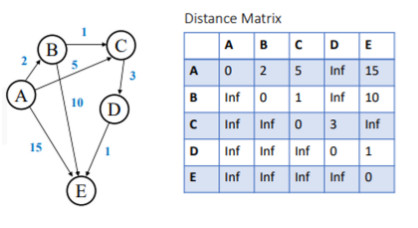
21
New cards
what is the path matrix?
* the shortest path between the 2 nodes, does not have to be a single-step path and can include intermediate nodes that overall have a smaller edge weight
* -1 represents that there is no connection to the nodes, similar to the infinity in the distance matrix
* -1 represents that there is no connection to the nodes, similar to the infinity in the distance matrix
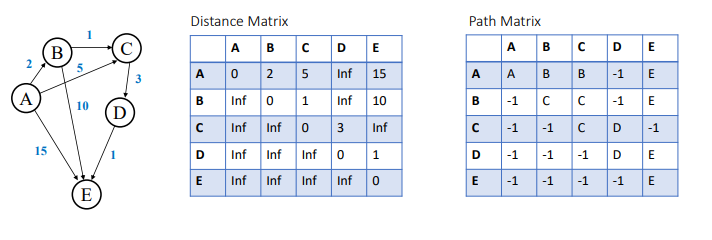
22
New cards
how do the values in the path matrix change as the Floyd-Warshall algorithm runs?
* in the beginning assume shortest path is the direct pair path (mirrors the distance matrix)
* afterwards see if there is a shorter path by going through other nodes
* afterwards see if there is a shorter path by going through other nodes
23
New cards
how does the Floyd-Warshall algorithm work?
1. variable k shows the number of nodes we will route through during the path eg. k = 0 means no routing nodes and just the direct path A → B . k = 1 equals 1 route node A → C → B
2. we need to find the shortest paths between each pair for each value of k up to k = n (meaning every node in the graph is used as an intermediate node)
3. 3 nested for loops.
1. for each value of k
2. for each node i
3. compare each node i to each node j
i and j iterations are needed when searching through a 2D matrix and k is specific to the FW algorithm to find new paths
4. ==**using the number of intermediate nodes k and the 2 nodes i and j, calculate the cost of the path using the Distance Matrix**==
5. ==**if the cost of the new path is less than the cost of the existing path i → j saved to Path Matrix, save the new cost to the Path Matrix**==
6. carry out the pink park for all the 3 loops stated above to parse every value of k, j, and i
7. return the final Path Matrix
24
New cards
what is the code for the Floyd-Warshall algorithm?

25
New cards
what is the time complexity of the Floyd-Warshall algorithm?
O(n³) because there are 3 nested for loops
26
New cards
what is the disadvantage of the Floyd-Warshall algorithm?
ideal for smaller graphs but not good for graphs larger than a few hundred nodes due to its time complexity