6th Grade - Cells
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Cell
The basic unit of structure and function in living things.
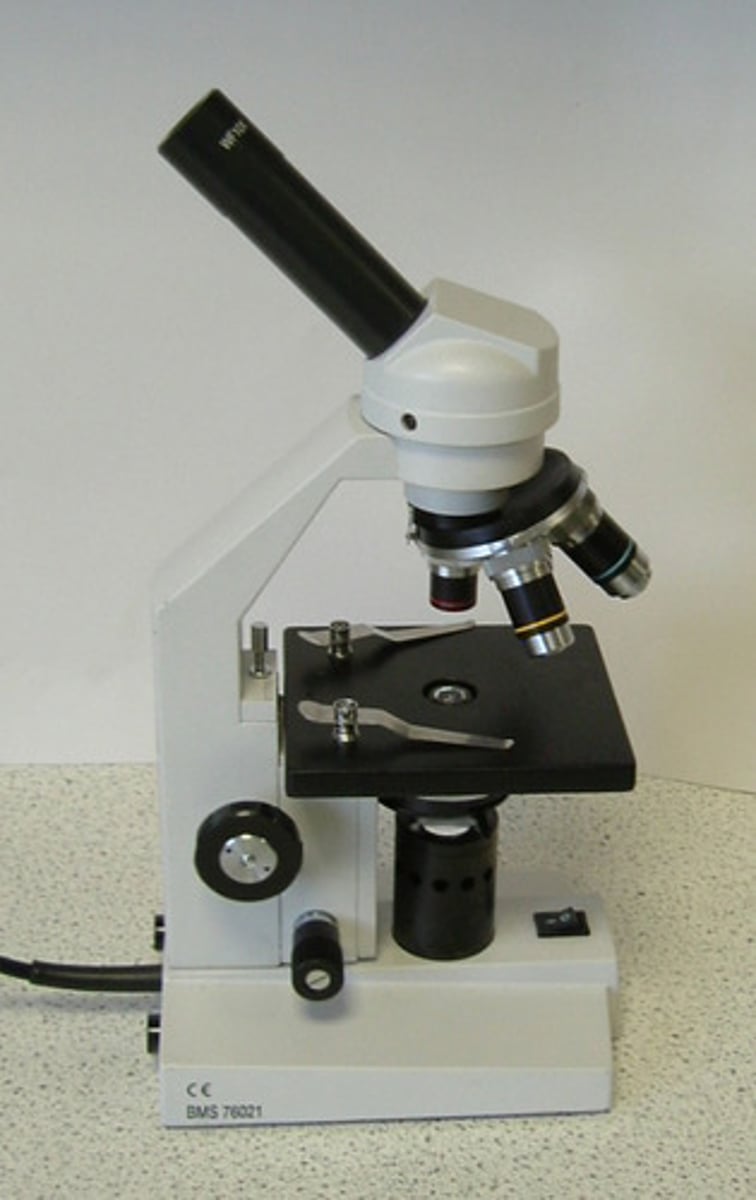
Microscope
An instrument that makes small objects look larger.

Cell theory
A widely accepted explanation of the relationship between cells and living things.
1. All living things are composed of cells.
2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things.
3. All cells are produced from other cells.
Organelles
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell.

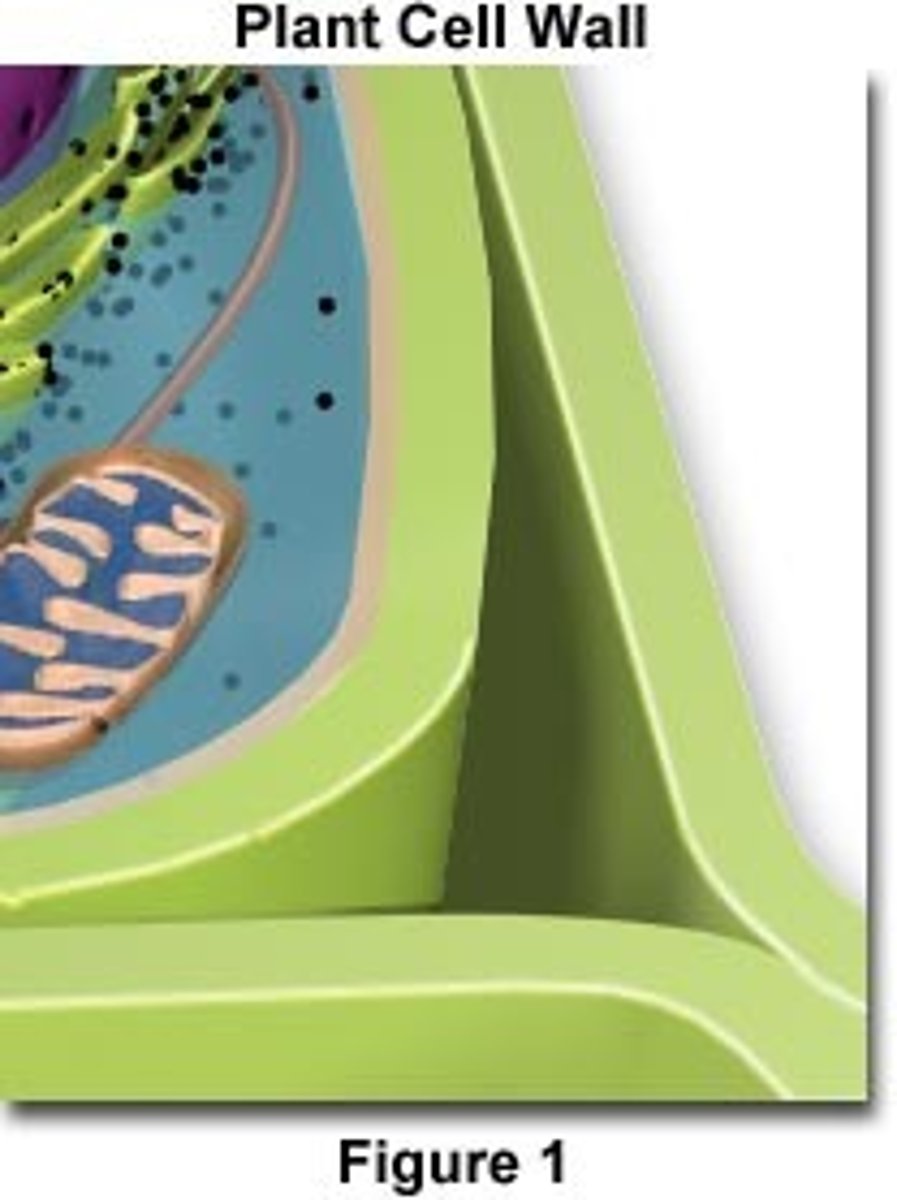
Cell wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. Made of cellulose.
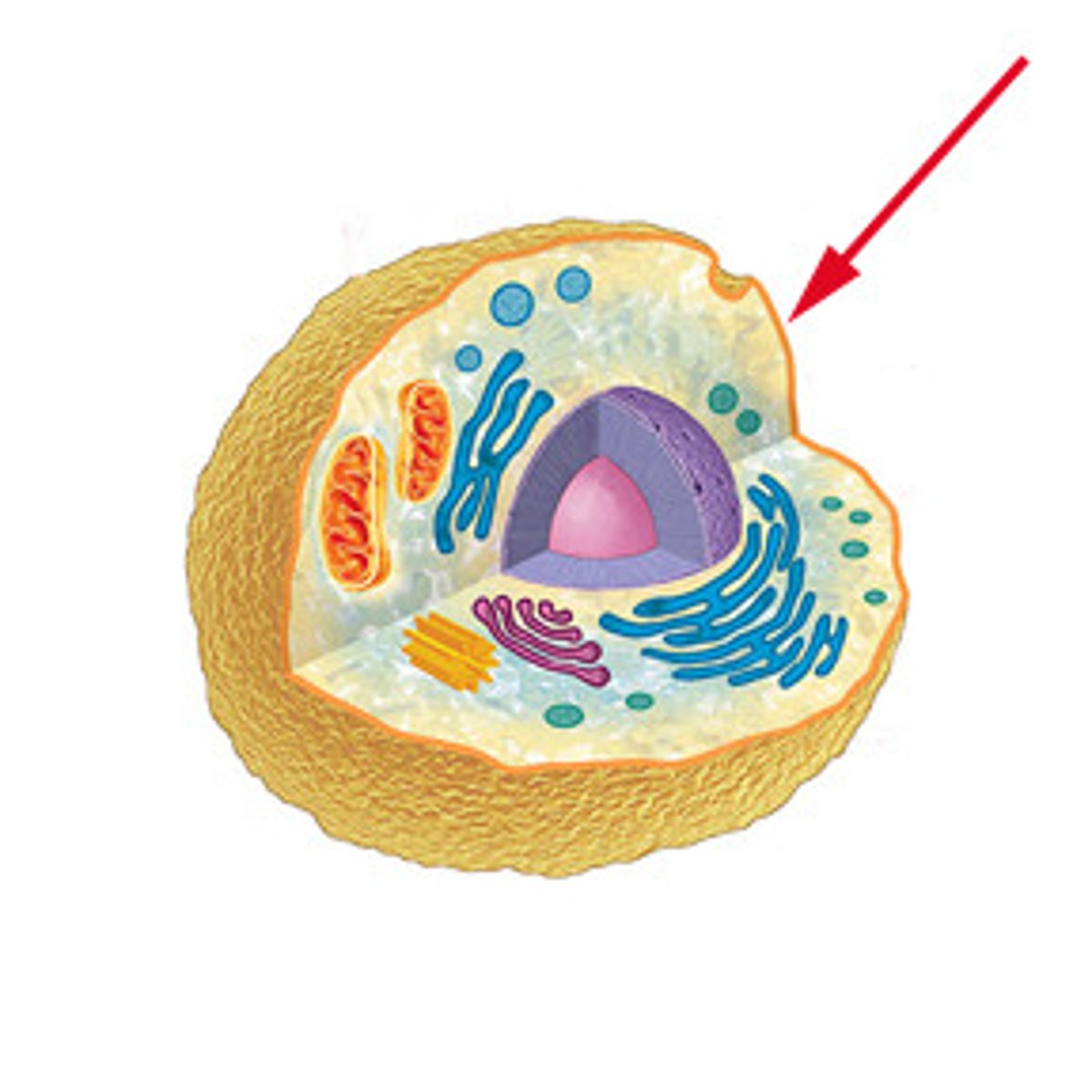
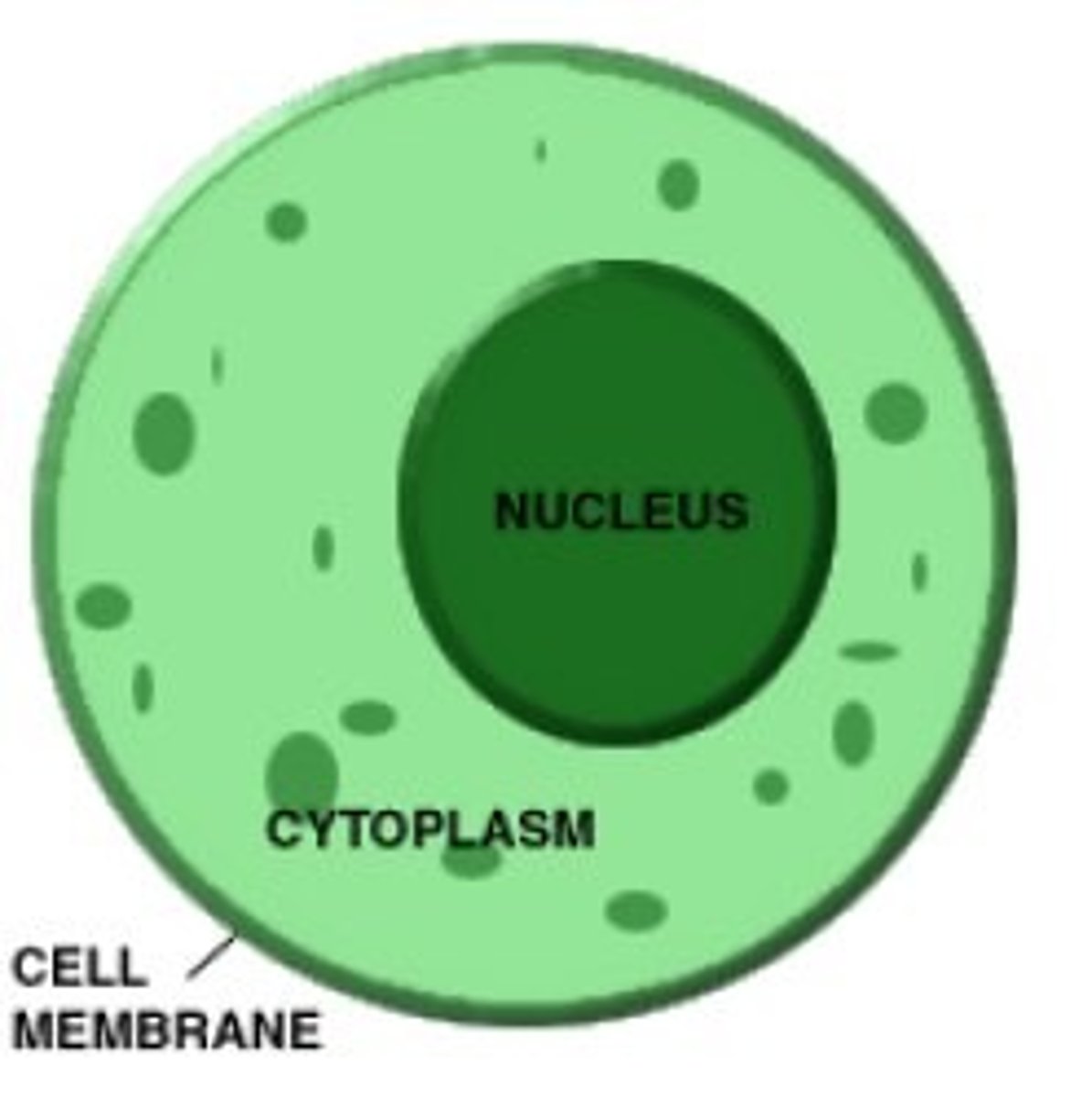
Cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
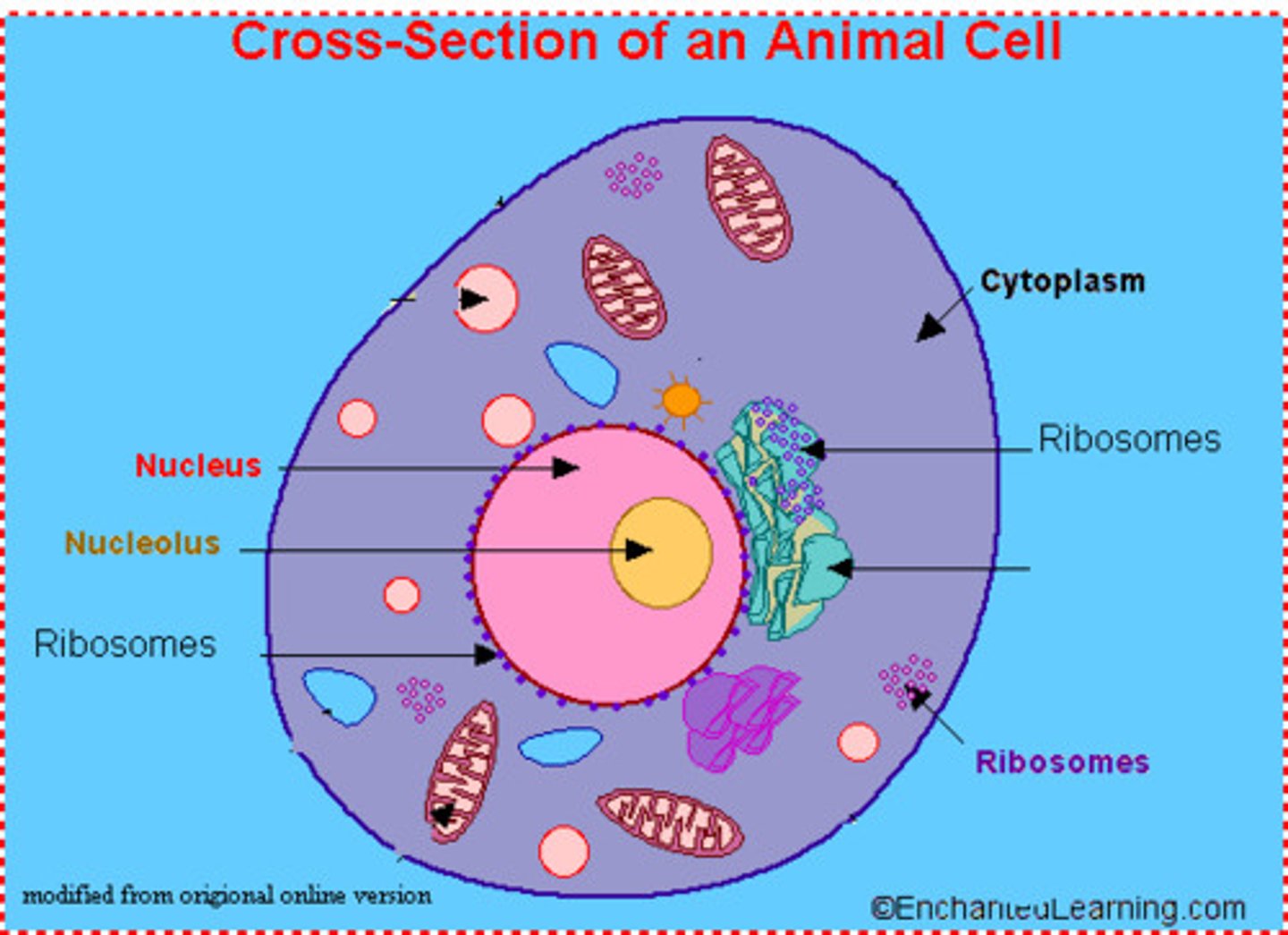
Nucleus
A cell structure that contains nucleic acids, the chemical instruction that direct all of the cell's functions.
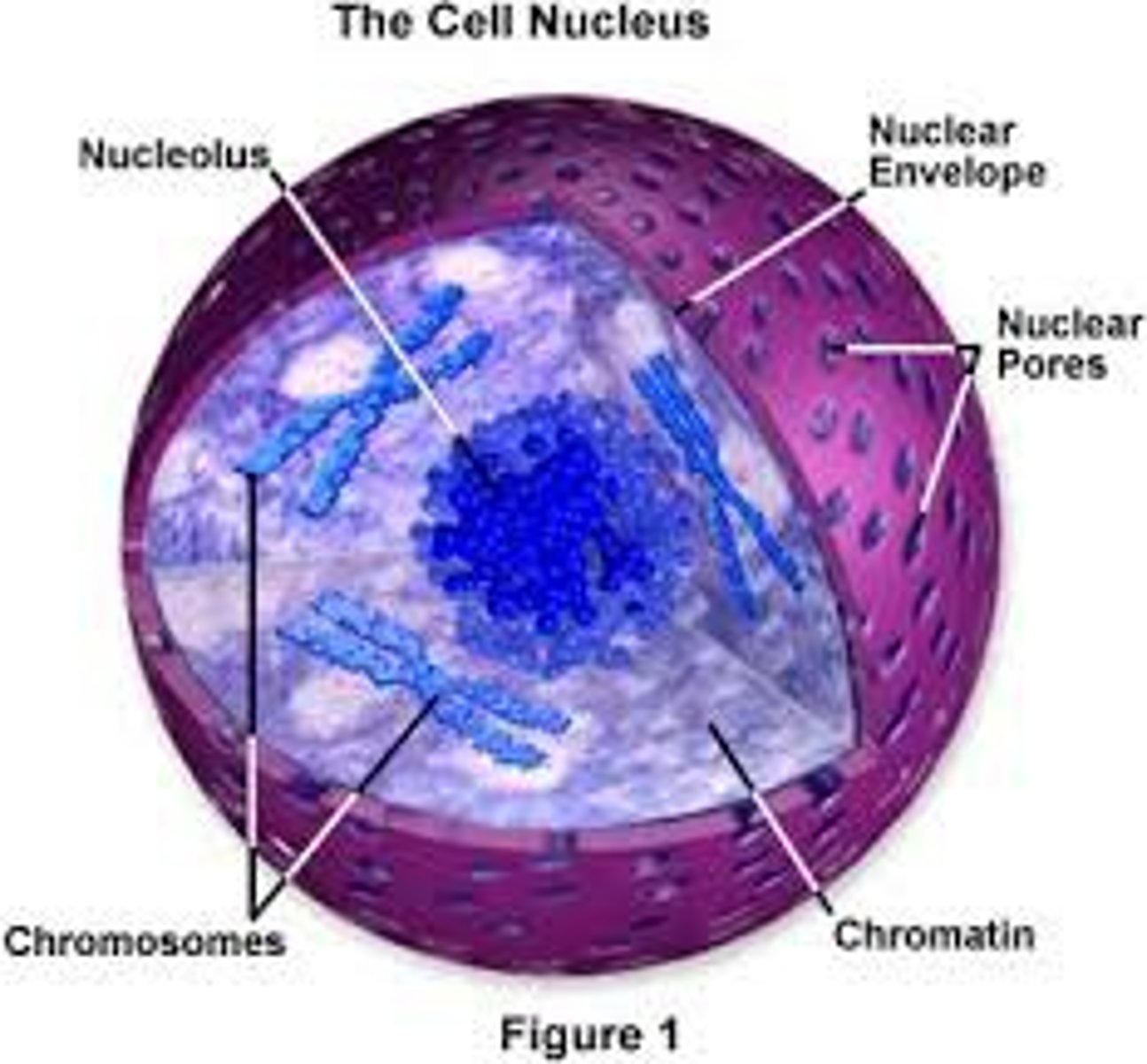
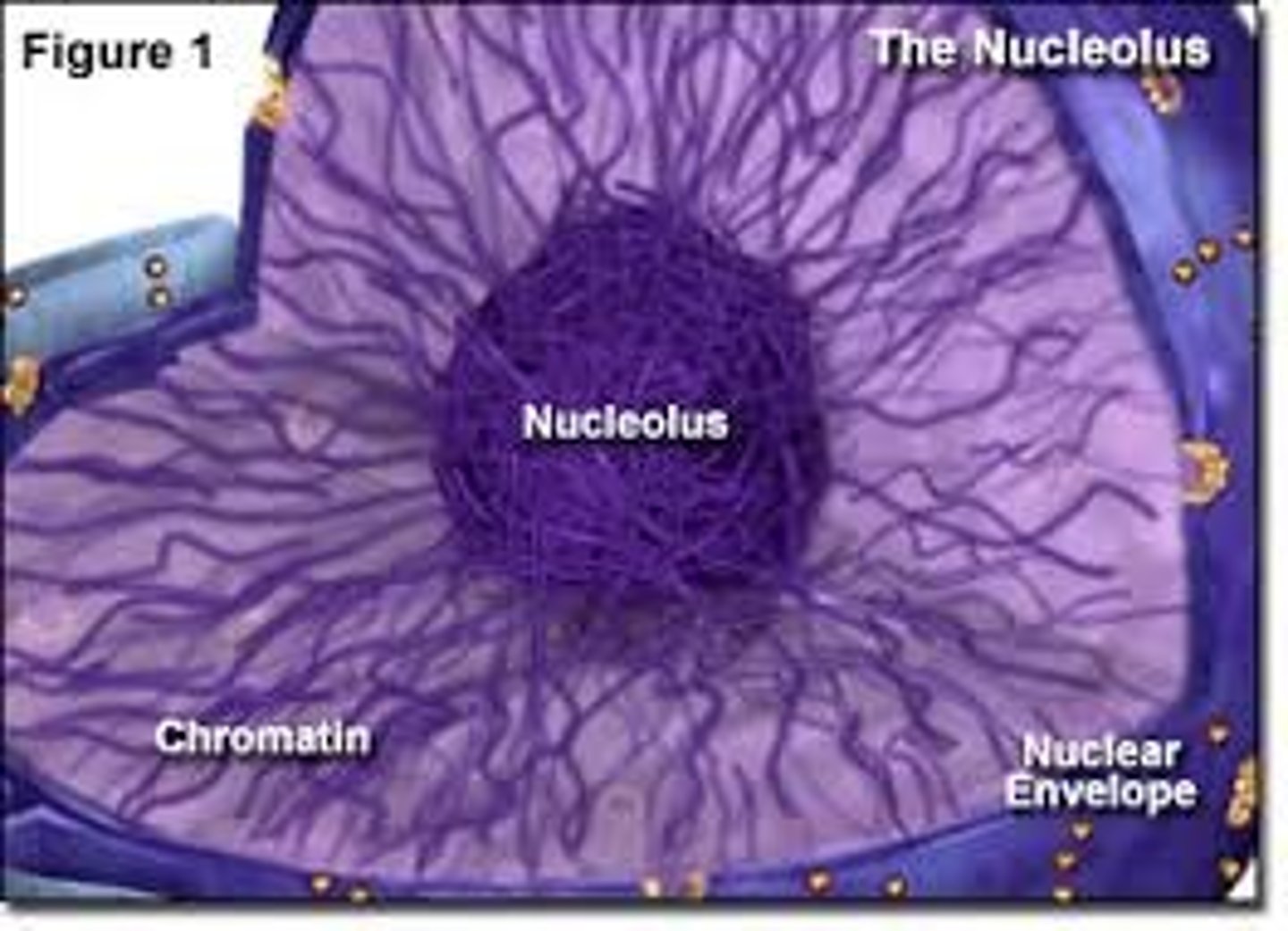
Chromatin
Thin strands in the nucleus that contain genetic material that provides the instructions for the cell function.
Nucleolus
A small object within the nucleus that makes ribosomes.
Cytoplasm
The region between the cell membrane and the nucleus; in organisms without a nucleus, the region located inside the cell membrane.
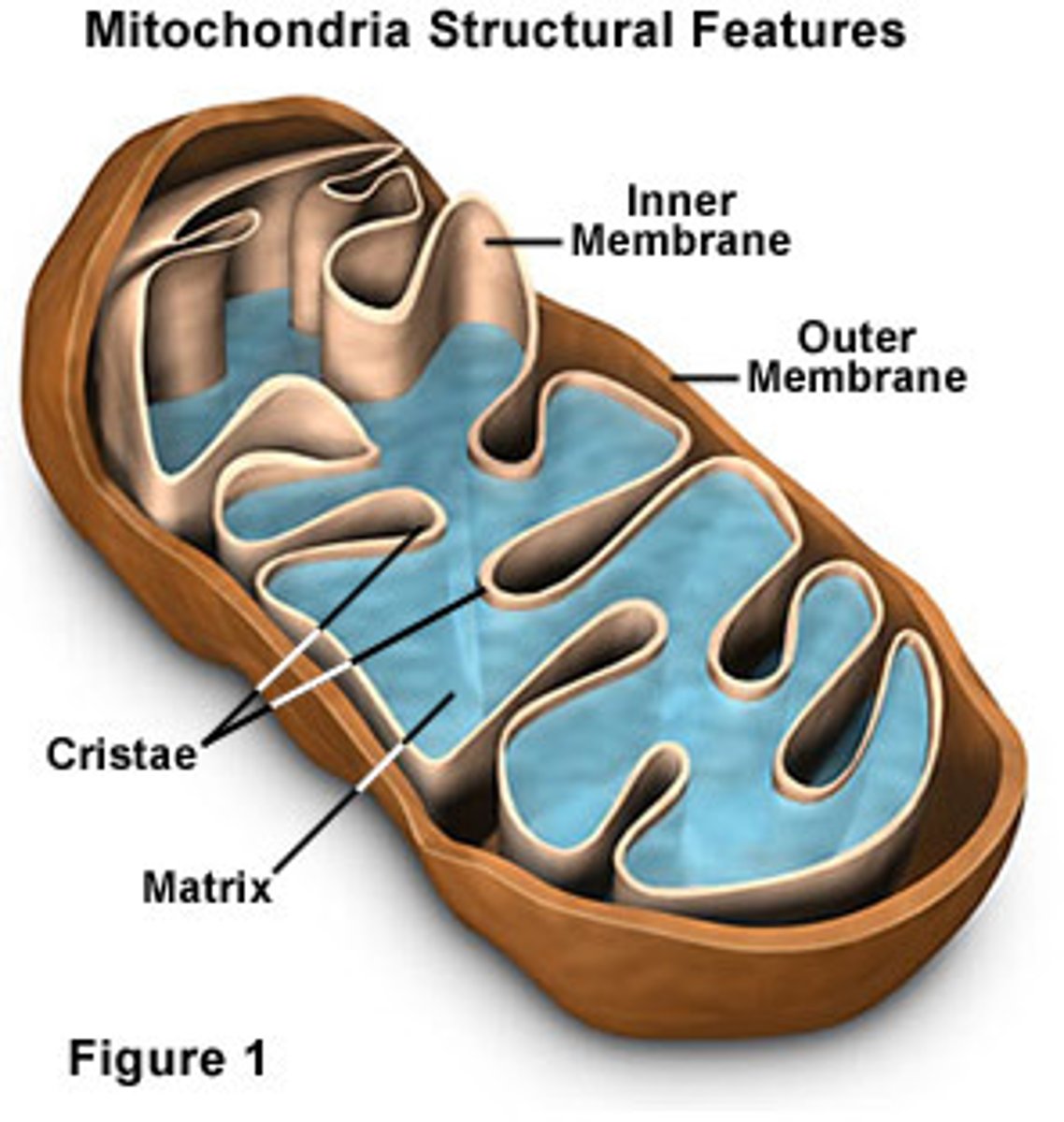
Mitochondria
Rod-shaped cell structures that convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions.
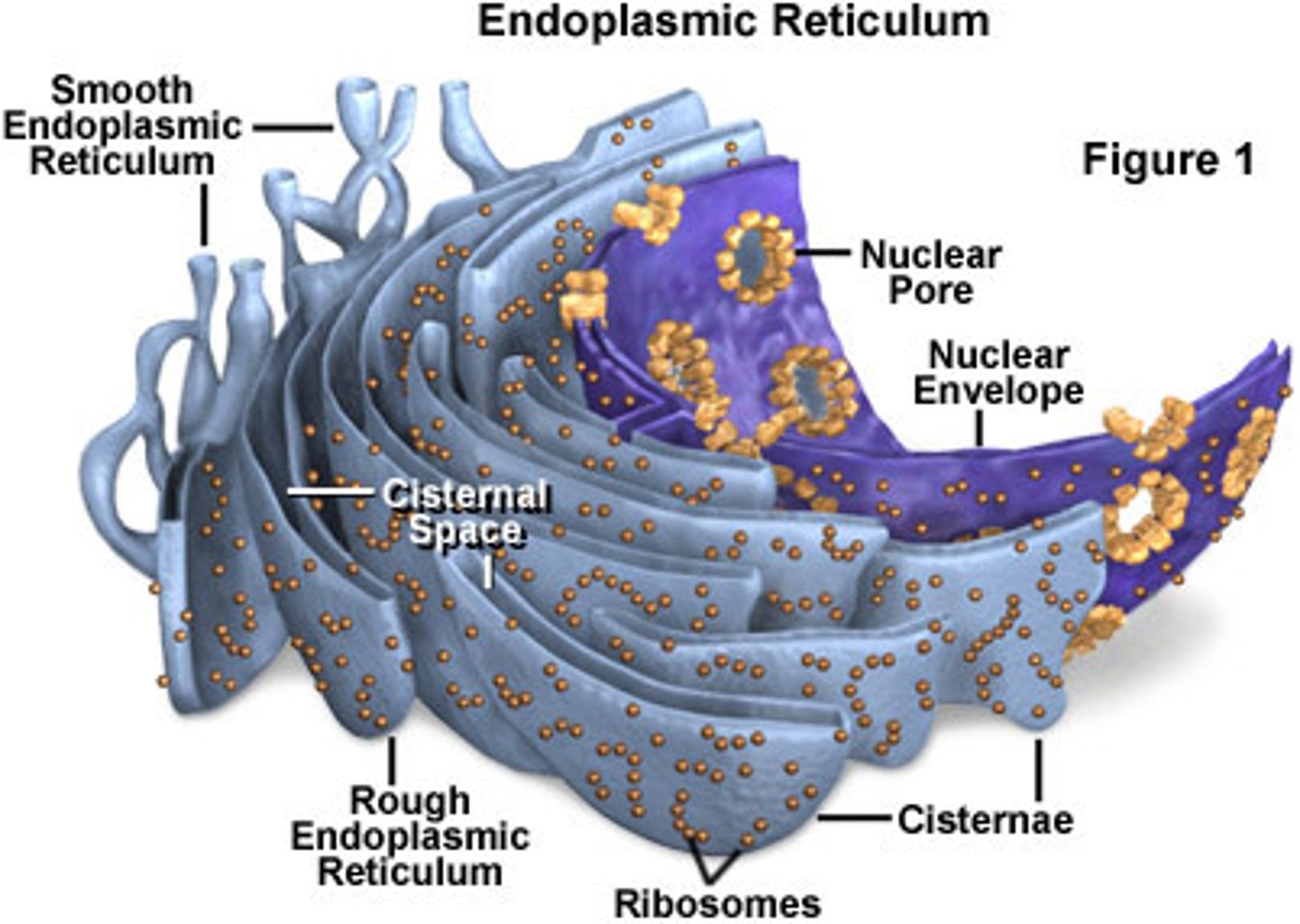
Endoplasmic reticulum
A cell structure that forms a maze of passageways in which proteins and other materials are carried from one part of the cell to another.
Ribosomes
A small grain-like structure in the cytoplasm of a cell where proteins are made.
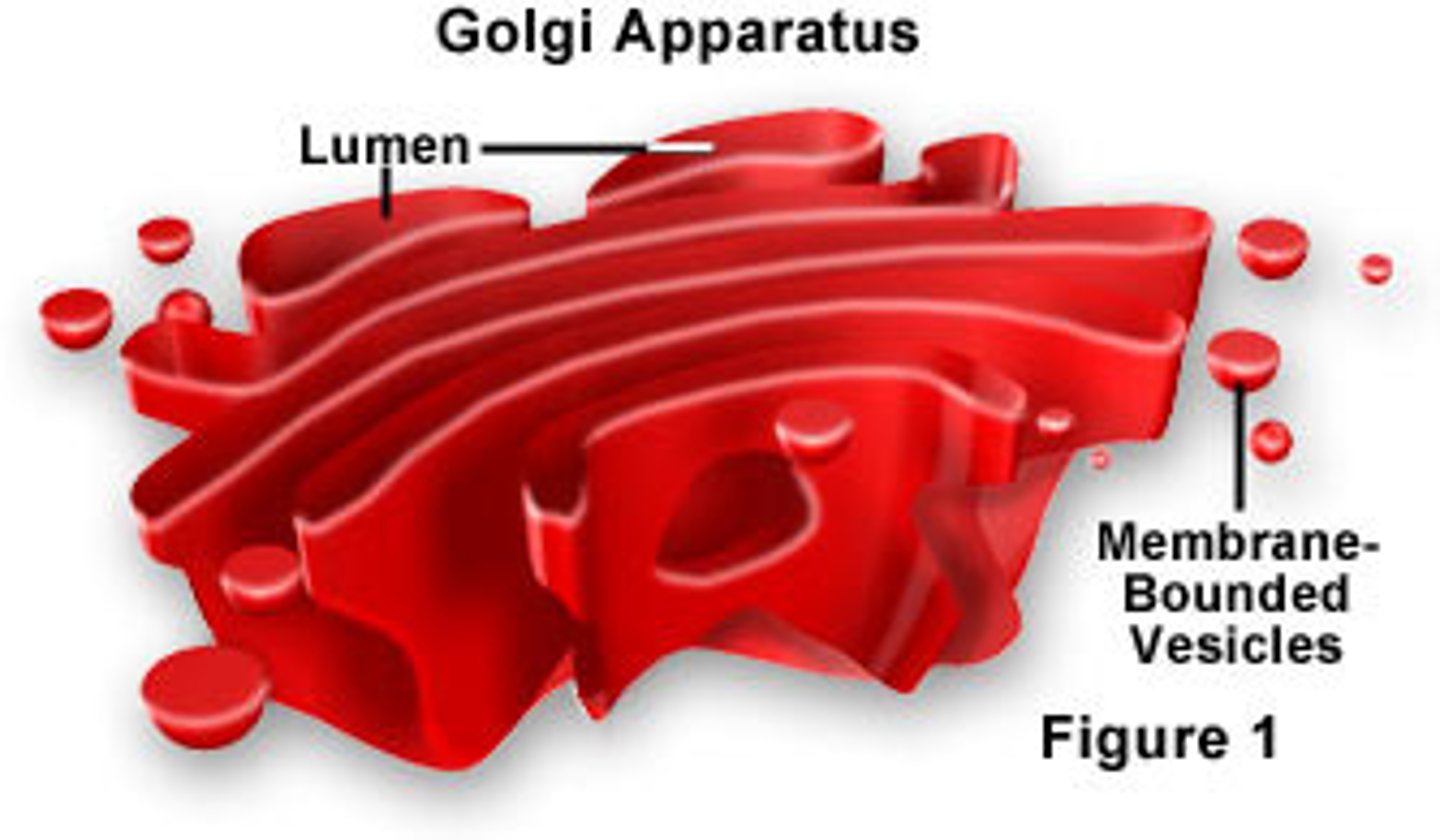
Golgi body
A structure in a cell that receives proteins and other newly formed materials from the endoplasmic reticulum, packages them, and distributes them to other parts of the cell...and other cells
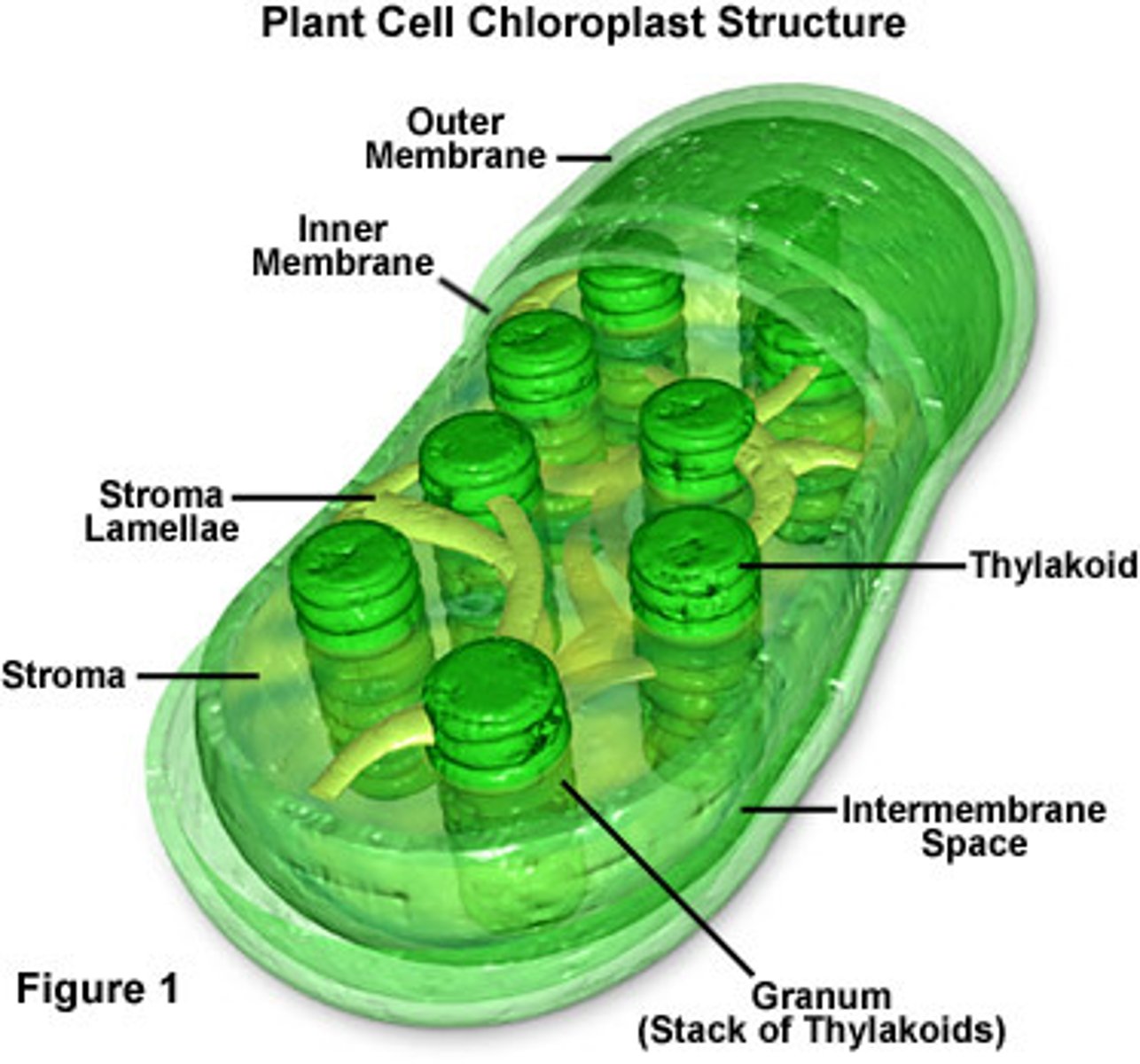
Chloroplasts
A structure in the cells of plants and some other organisms that captures energy from sunlight and uses it to produce food.
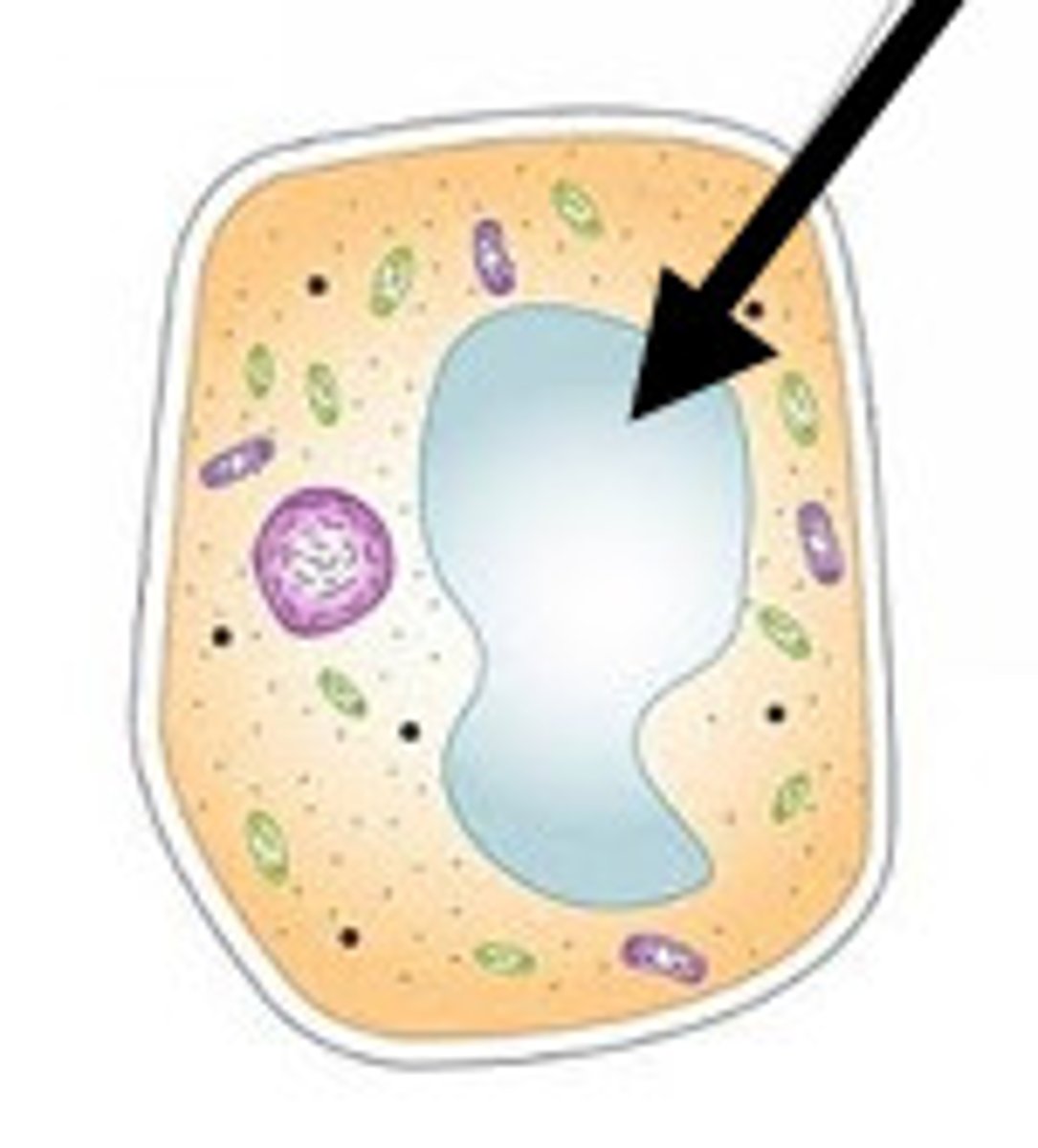
Vacuole
A sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area.
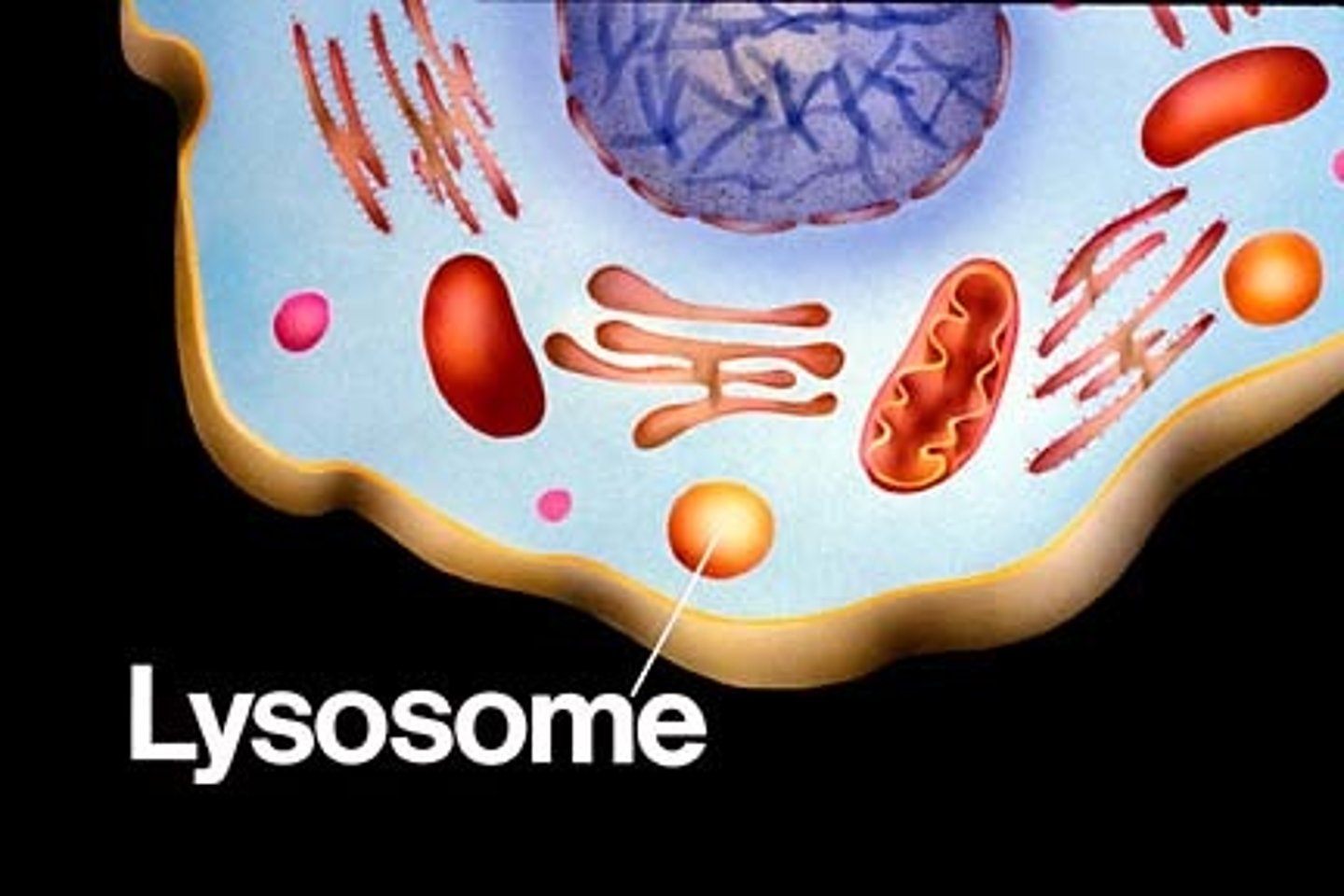
Lysosome
A small, round cell structure containing chemicals that break down large food particles into smaller ones.
Tissue
A group of similar cells that perform the same function.
Organ
A collection of tissues that carry out a specialized function of the body
Organ system
Group of organs that work together to perform a specific function
Organism
A living thing; anything that can carry out life processes independently.
Excretion
The process by which wastes are removed from the body (or cells). Humans excrete feces and urine.
Respiration
The process by which cells break down simple food molecules to release the energy they contain. The oxygen and glucose (sugar) interact to release usable energy. Water and carbon dioxide are also produced as waste products.
Absorption
Cells need to absorb food/nutrients and water. The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of the digestive system into the blood.
Reproduction
The process of producing offspring
cellular reproduction
An original cell divides and produces two identical daughter cells
Mitosis
A part of cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes. Mitosis included prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.