Physical Science Exam Unit 2
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GET A
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Propagation
The wave moves in both ways
Wavelength measurement
Space between two Crests or 2 Troughs
Amplitude
Distance between the equillibrium position and the highest point (amount of disturbance)
Types of waves
Sheer waves, compression waves, & Surface waves
Sheer Waves
Moves in right angle (hitting a cymbal) (perpendicular to wave travel)
Surface Waves
Can only travel across the surface of a medium, but like a sheer wave
Compression Waves
Moves left to right
Push and pull molecules in the way of propagation (speaker moving in and out)
Waves
Energy moving from one place to another
What waves do
Reflect
Diffract
Refract
Interference
Diffraction
When a wave bends around a corner (goes through a hole, lights goes through a whole to light up a rooms)
Refraction
Bent light
Constructive interference
Crest
Top of wave
Trough
Bottom of the wave
Wave Speed Equation
Wave speed = Wavelength x Frequency
Standing waves
When waves reflect and interfere with the new waves
Nodes vs. Anti Nodes
Nodes are the points with no movement, anti nodes are troughs and crests
Ambulance Thing
When ambulance is coming towards you → lower wavelength, higher frequency (sounds higher)
When ambulance passes you → Higher wavelength, lower frequency (sounds lower)
A wave where the medium is displaced parallel to the direction the wave travels.
Longitudinal wave
What makes it so light transfers more electrons energy?
Changing the frequency (photons)
Amplitude Determines the total energy of a light wave, and
Frequency determines the individual energy of each photon
Double slit - unobserved
The interference makes vertical lines
Single slit- unobserved
Scatters everywhere but most concentration in the middle
Single slit- observed
Light dots appear where the slit is (light doesn’t refract)
Double slit- observed
Light dots appear where the slits are (light doesn’t refract)
Photoelectric Effect
The ejection of electrons from metals when light is shined on the metal's surface
Pictures teach us about
particles
Carrier wave modulated by changing the frequency
FM
A particle of light. It possesses energy, frequency, and wavelength but neither mass nor charge.
Photon
A series of bright lines separated by dark areas.
Interference Pattern
Carrier wave modulated by changing the amplitude.
AM
Light is an electromagnetic disturbance spread throughout space according to electromagnetic laws.
True
Longest wavelength (lower energy) → Shortest wavelength (highest energy)
ROYGBIV
Sheer Forces
Force that pushes the edges of an object in different directions.
(tearing)
Compression Forces
When something is compressed
Tension Forces
pulling away (opposite directions)
Tension force in a liquid
Sucking liquid up a straw
Electromagnetic Spectrum (highest to lowest)
Gamma
Xray
UV
Visibile Light
Infared
Micro
Radio
(Grandma examines ultra vaccums in my room)
Discrete spectrum
When something only emits a few colors
Conductors
Something that carries a charge, like metalsI
Ionic conductors
Can conduct when it is melted or dissolved (like salt)
A physical state of matter characterized by fluid properties but in which positive and negative charges move independently.
Plasma
Continuous model of matter
You could cut something in half for infinity
Molecular model of matter
Everything is made of molecules
Always in motion (solids vibrate, gases move around more)
Obey fundamental laws
What does the molecular model explain?
Temperature (depends on mass and velocity (KE equation))
Heat flow
Pressure
Density (Solids are moving slower in a smaller space, gases are moving faster in a larger space, so you can fit less)
Rutherford’s Model (solar system)
All the positively charged particles are condensed in the nucleus, so dense it can take a blow. Electrons then orbit around the nucleus
Alpha particles
Positively charged particles
Issue with the solar system model
When viewed, atoms show discrete spectrum, not a continuous one.
Modified Solar System Model
Nucleus surrounded by energy levels (lowest to highest)
Electron orbits around on the lowest level, has to gain energy to move levels
Wavelength Equation
Lambda = Planks Constant/Momentum
Heisenburgs uncertainty principle
If we know the momentum of a particle, we can’t know much about the position and vise versa
Quantum Atomic Model
Map the probability of where electrons are
Issue with the modified solar system model
Electrons aren’t supposed to be accelerating

Different types of orbitals
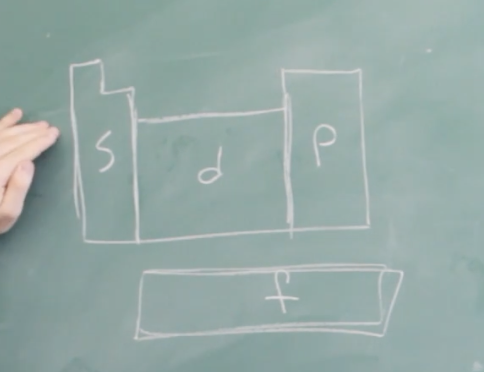
Periodic table based on orbitals
Period Table Directions
Ionization energy increases slightly from the bottom to top of a group and much more from the bottom left to the top right.
Atomic size increases from top right to bottom left (NOT MASS)
Ionization energy
Energy required to strip an atom of its valence electrons
Valence electron
Electrons that are in the outermost shell
Elements that occur in the same row of the Periodic Table.
Period
A kind of matter that contains atoms that all have the same number of protons in their nuclei.
Element
Elements in the periodic table which are placed in the same column and have similar chemical properties.
Family
How do I know the number of valence electrons that an element has?
Based on the last digit of the group number
Elements with atomic numbers heavier than 92 (uranium) are all man-made elements.
True
Within a given period, metals have higher ionization energies than non-metals do.
False
How to tell the density of things from a periodic table
Density = M/V
If they all have similar volumes, the atomic mass that’s biggest will be the most dense
Mass gets bigger going from top-right to bottom-left
On which side of the periodic table are non-metals found?
Right
Why do elements in the same column of the periodic table react in similar ways?
Each element in the column has the same number of valence electrons.
What determines if an element is likely to give away an electron
How high the ionization is