Separting solids, liquids and mixtures
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Definition of element
All atoms are the same
Definition of compound
2+ different elements chemically bonded in fixed proportions
Definition of a mixture
2+ elements or compounds that aren’t chemically bonded together
What are the 4 ways of separating mixtures?
Filtration
Distillation
Crystalisation
Chromatography
Filtration
Separating an insoluble solid from a liquid
Crystallisation
Separating a soluble solid from a liquid
How does crystallisation work?
Heat the mixture in an evaporating disc on top of a Bunsen burner.
The liquid will evaporate, leaving behind crystals of the soluble solid.
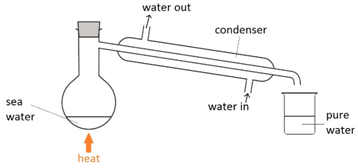
Simple distillation
Separating a dissolved solid from a liquid whilst keeping the liquid.
How does simple distillation work?
The solution is heated and the liquid evaporates. The vapour passes into the condenser which turns it back into a liquid.
Fractional distillation
Separating a mixture of different liquids with different boiling points.
How does fractional distillation work?
The liquid with the lowest boiling point will evaporate first, yet both of them will. They both reach the fractionating column and condense, but drip back down into the flask. This repeats over and over which increases the amount of the vapour of the liquid with the lower boiling point.
When both reach the thermometer the temp rises. The lower boiling point vapour condenses and can be collected in the beaker.
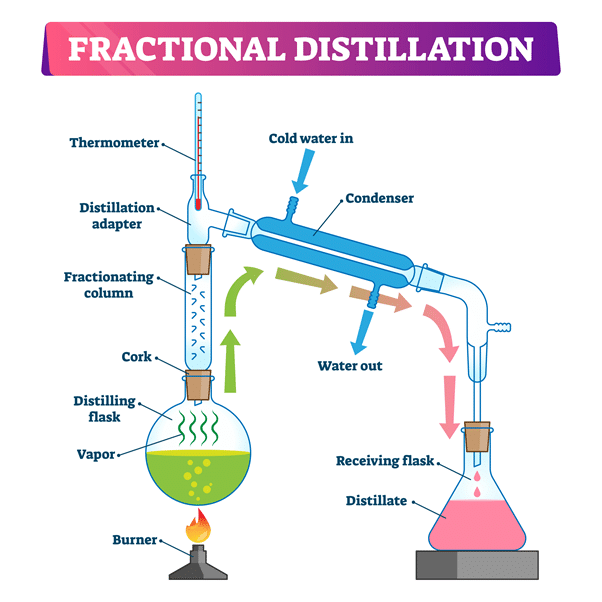
The key difference in equipment between fractional and simple distillation is that…
Fractional distillation uses a fractioning column, which is a glass tube containing lots of glass beads.
How does chromatography work?
Marker ink dots are placed on chromatography paper and then dipped in a solvent. The solvent moves up the paper and carries the ink. If the ink is a single, pure colour, then only that colour will appear, but if it is made up of more than just one, all the colours present will show.

Why does chromatography work?
Different substances have different solubilities. A more soluble substance is more attracted to the solvent than a less soluble substance, so a more soluble stance travels further.