topic 4 : the water cycle
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
topic 4: the uk's evolving physical landscape
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
evaporation
the transfer and change of water from the ground into water vapour in the air
evapo-transpiration
the transfer and change of water from plants into water vapour in the air
condensation
water vapour in the air changing back into a liquid
how are clouds formed through condensation?
it forms small droplets which are visible as cloud
precipitation
the transfer of water from the air to the land. water can fall as snow, rain, or sleet
overland flow (surface run-off)
the transfer of water back to the sea over the ground surface
groundwater flow
the transfer of water through the ground back to the sea
perlocation
water seeping deeper below the surface into the ground layer
interception
water being prevented from reaching the surface by trees or grass
the water cycle diagram
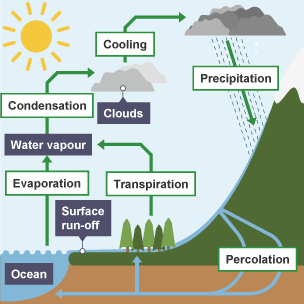
explain how surface run off could be impacted by human actions (4 marks)
key points:
-human actions can speed up surface run-off
-buildings roads because roads can be large, flat and impermeable
-human actions slows down surface run-off
-planting more trees because trees can intercept rainfall preventing it from reaching the ground
drainage basin
an area of land drained by a river and its tributaries
what is the source in a drainage basin?
the starting point of the river
tributaries
the streams and smaller rivers that feed into a main river
most rivers flow down towards sea level even if they don't reach the sea. true or false?
false. the correction should be "all rivers flow down towards sea level
confluence
the point where two rivers join
watershed
an imaginary line that seperates one drainage basin from the next
flood plain
the area of low-lying ground that gets flooded when the river overflows
the river gets ________ as you go from the source to the mouth.
wider
surface storage
where water is held on the ground surface e.g. lakes, puddles
infiltration
where water sinks into the soil or rock from the ground surface
water table
the current upper level of saturated rock/soil where no more water can be absorbed
throughflow
water flowing through the soil layer parallel to the surface
groundwater
water stored in rock