Spinal Cord Anatomy
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
What does the grey matter contain?
neuron cell bodies
unmyelinated axons
What are nuclei?
aggregations of neuron cell bodies in the brain
What are ganglia
aggregations of neurone cell bodies in the PNS
What is in white matter?
myelinated axons
fasciculi/tracts
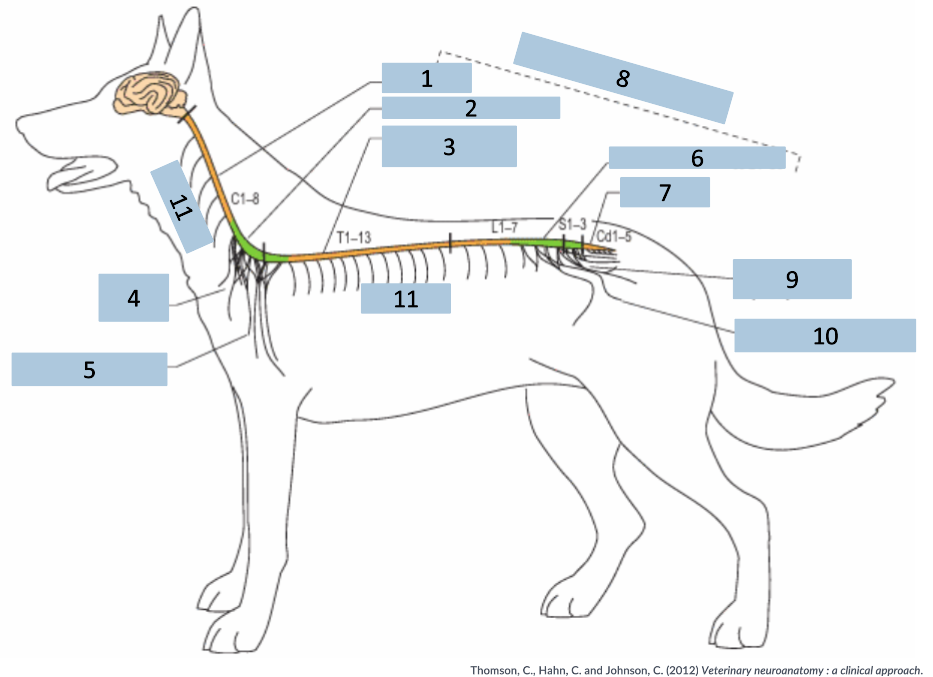
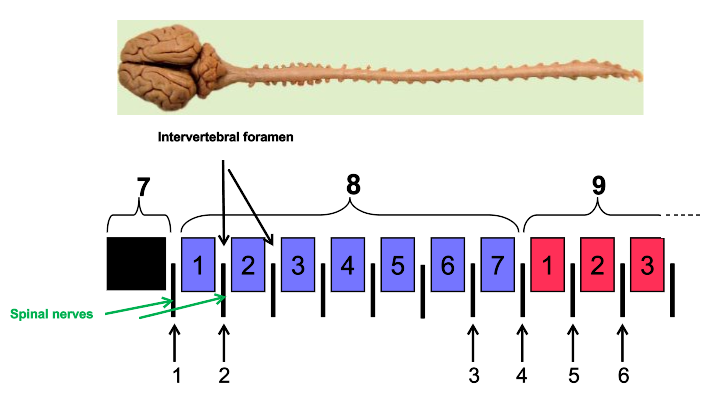
1
cervical C1-5
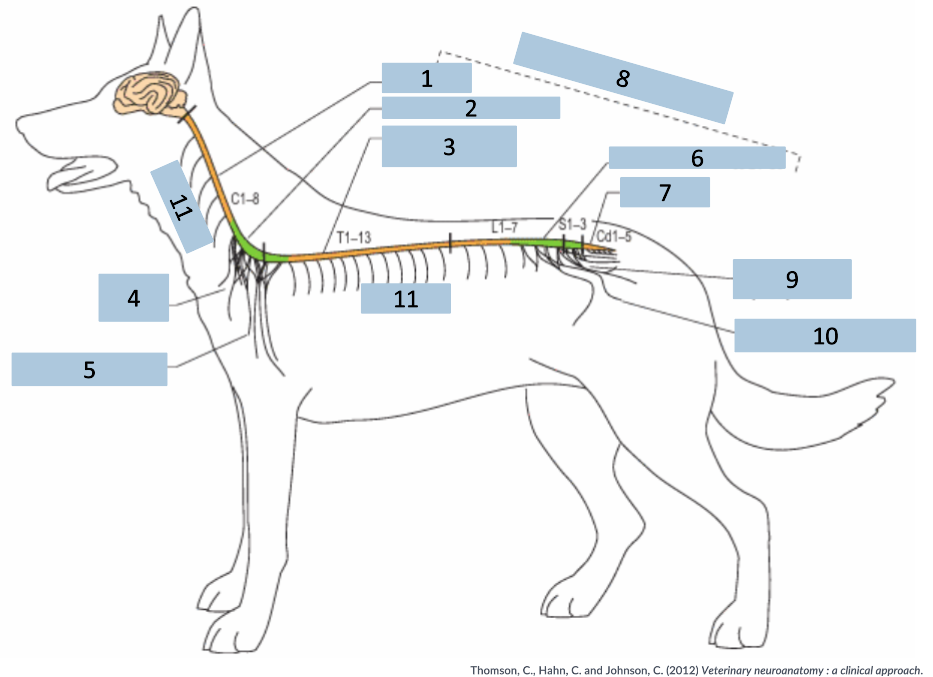
2
cervical intumescence C6-T2
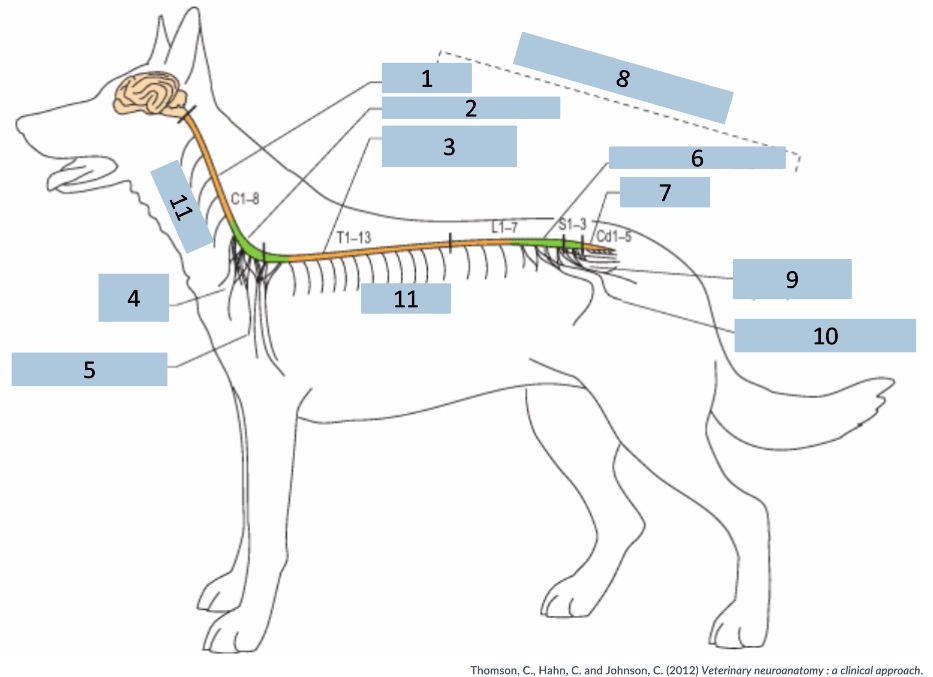
3
Thoracolumbar T3-L3
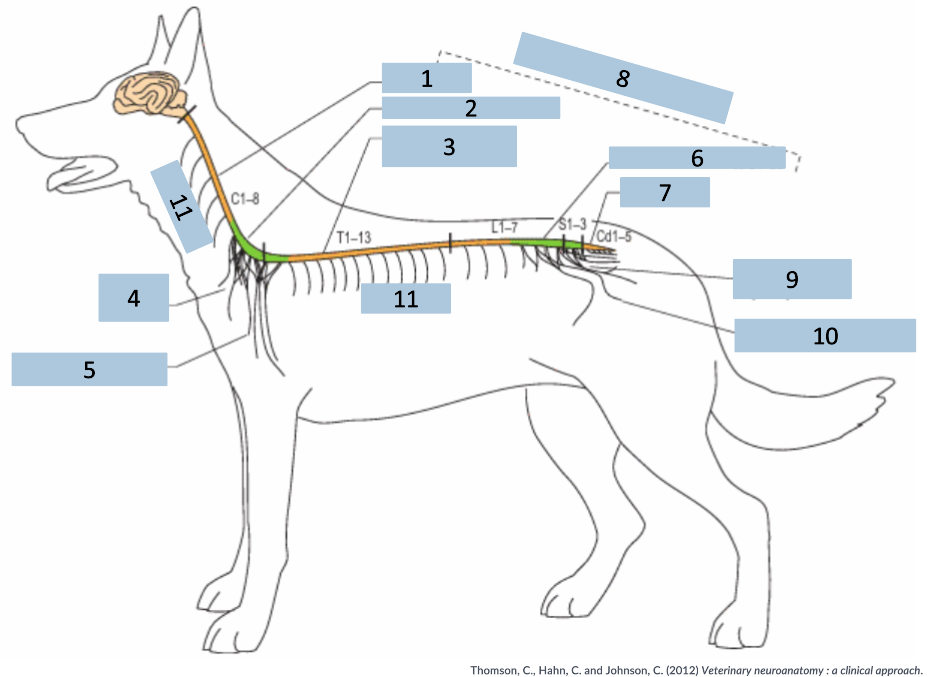
4
brachial plexus
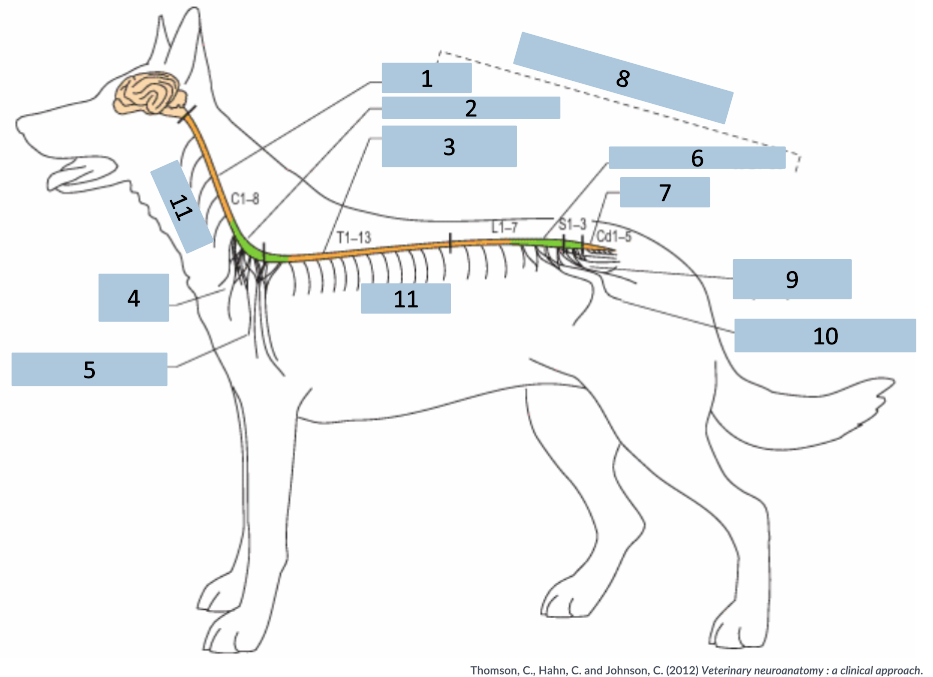
5
named nerves of the limb
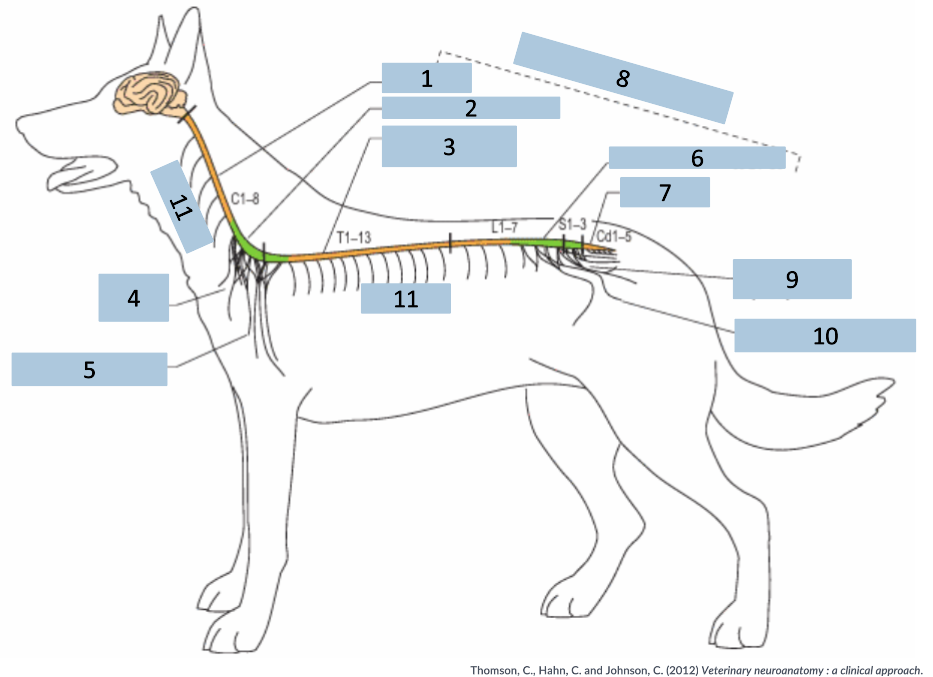
6
lumbar intumescence L4-S3
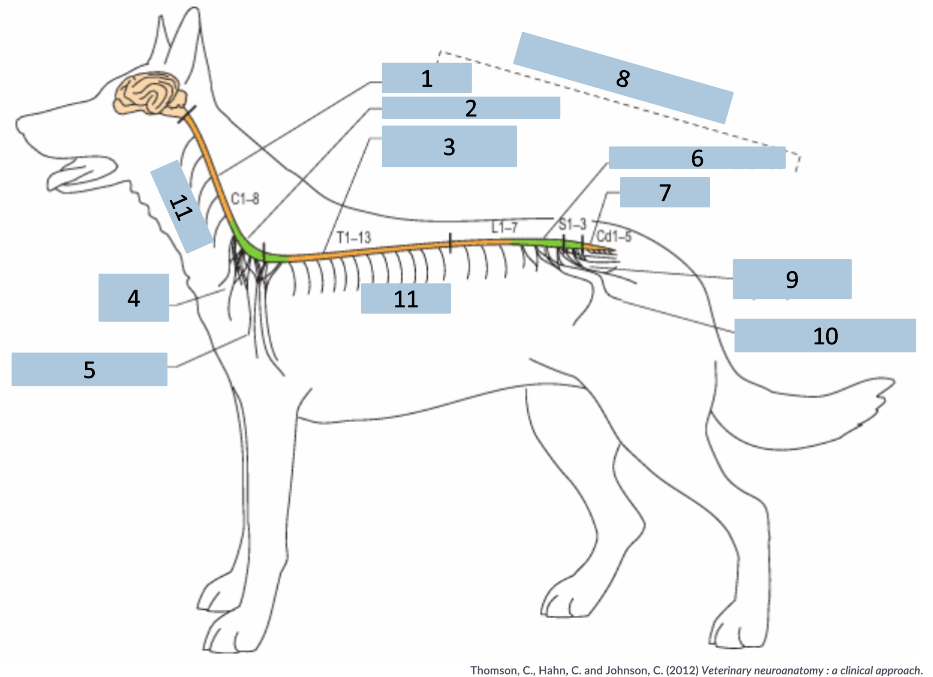
7
caudal Cd1-5
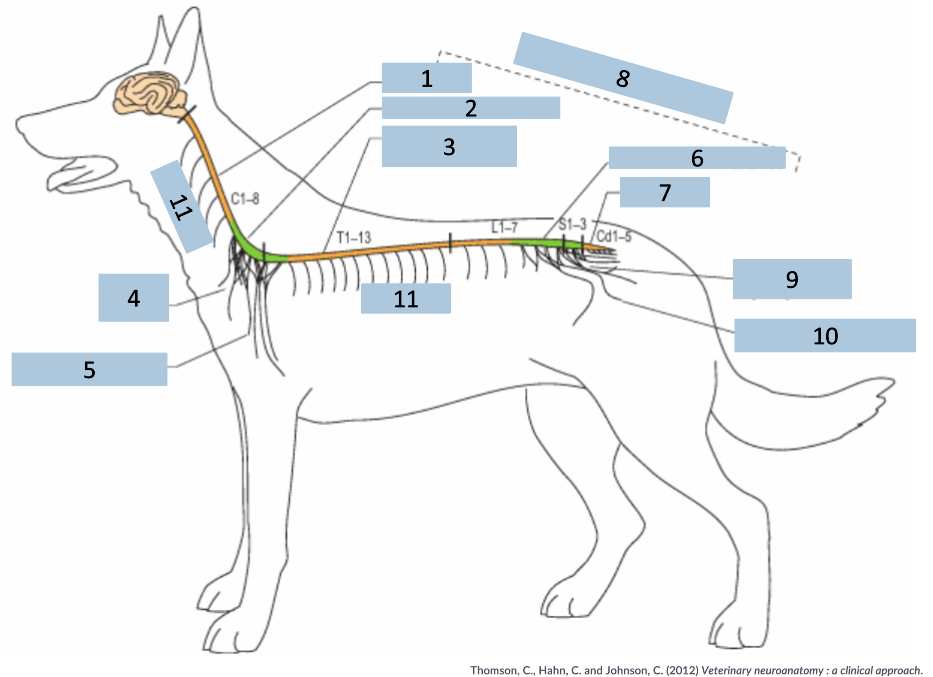
8
functional divisions of the spinal cord
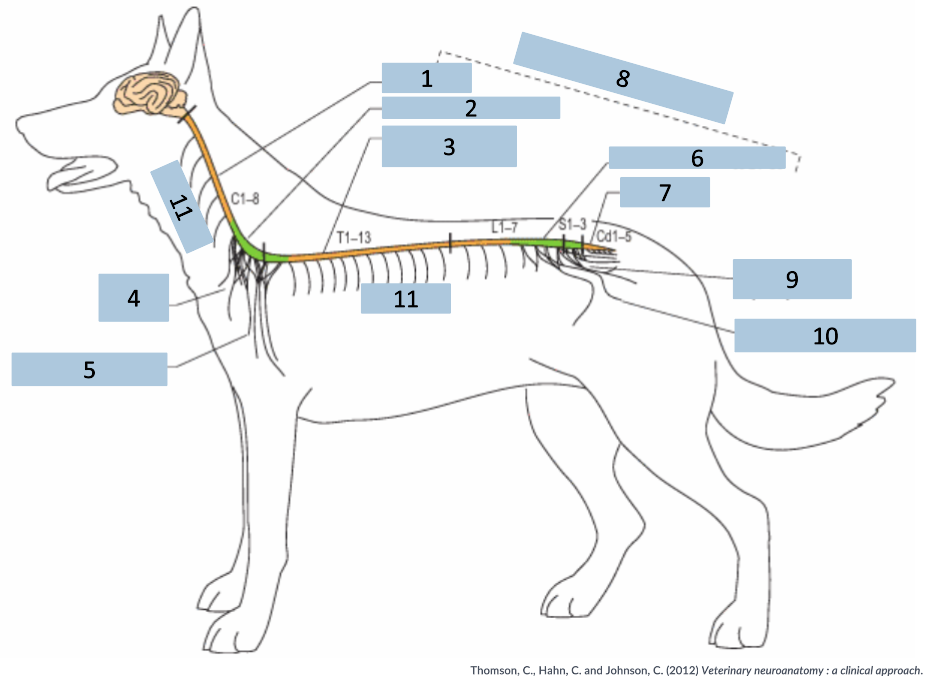
9
lumbosacral and pelvic plexi
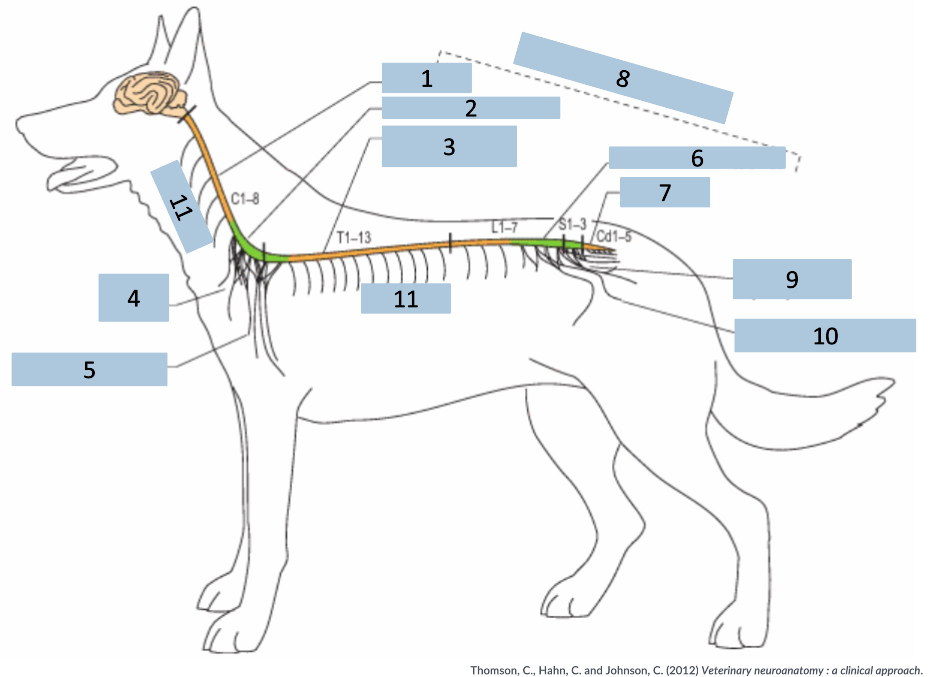
10
named nerves of the limb
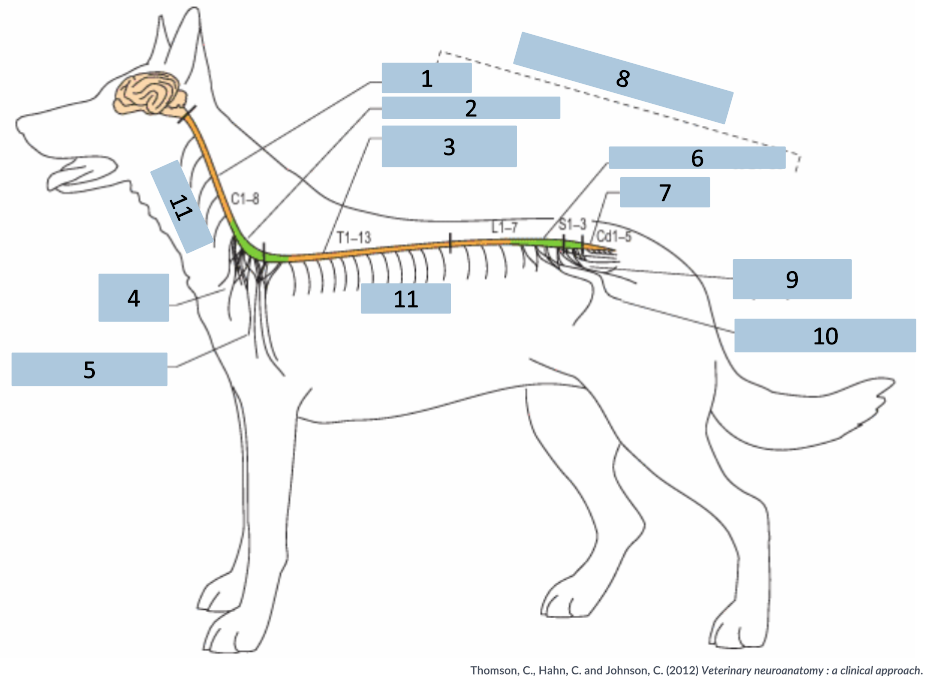
11
spinal nerves
What does the name of the spinal nerve follow?
vertebrae that part of the spinal cord is related to
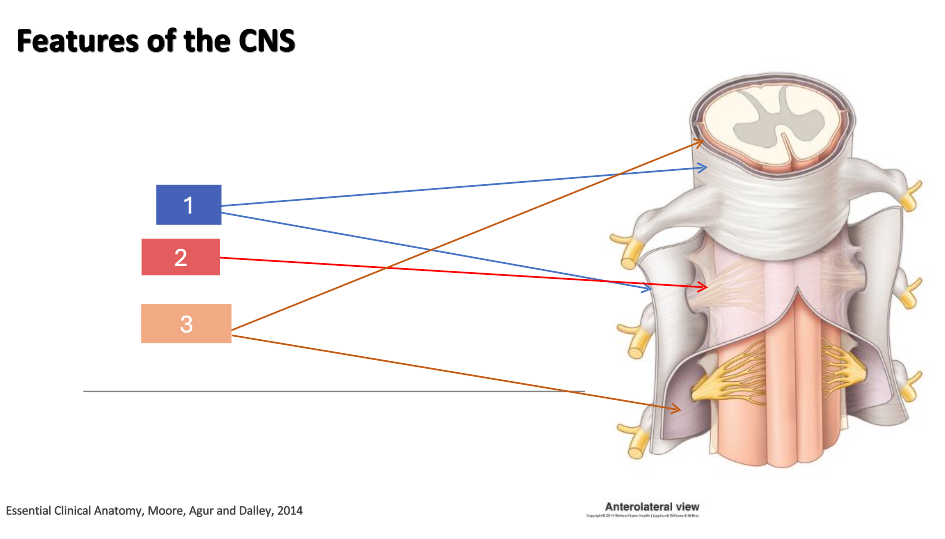
1
dura mater
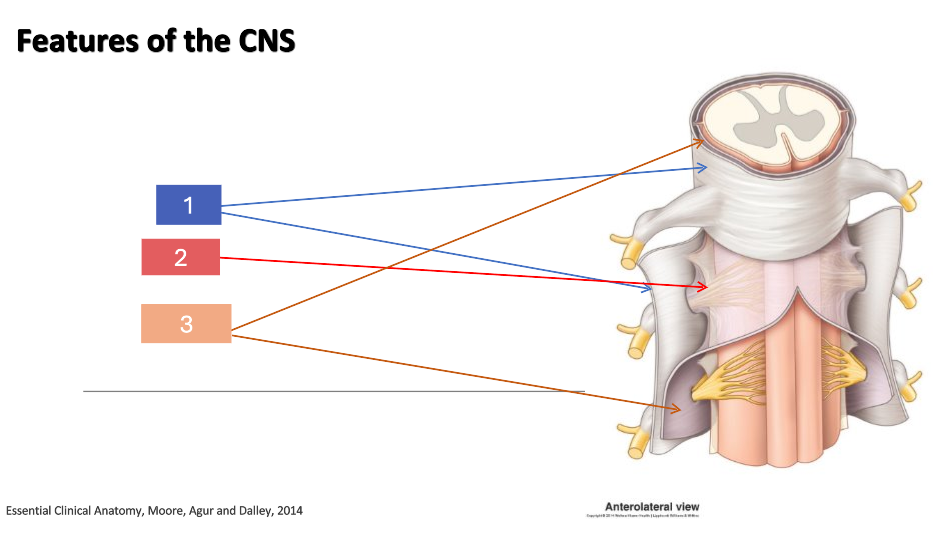
2
arachnoid
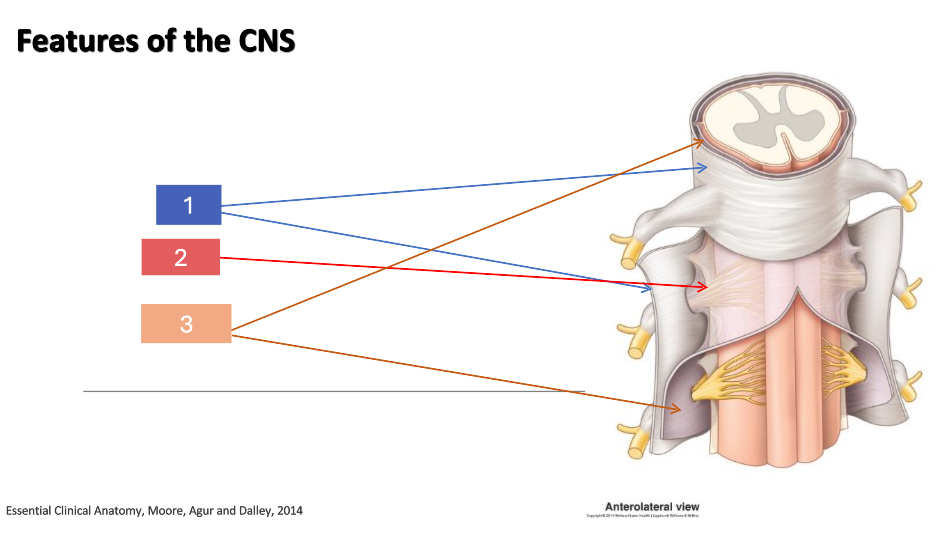
3
pia mater
What is the CNS housed in?
bone
What is the CNS covered in?
meninges
Is the dura mater, arachnoid or pia mater the outermost layer?
dura mater
Is the dura mater, arachnoid or pia mater the innermost layer?
pia mater
What is the epidural space?
space between dura mater and bone
Where do peripheral nerve axons converge to form a single spinal nerve?
intervertebral foramina
What do peripheral nerve axons do at each of the intervertebral foramina?
converge to form a single spinal nerve
Is the dorsal root of a spinal nerve sensory or motor?
sensory
Is the ventral root of a spinal nerve sensory or motor?
motor
What are the 2 roots of spinal nerves called?
dorsal root
ventral root
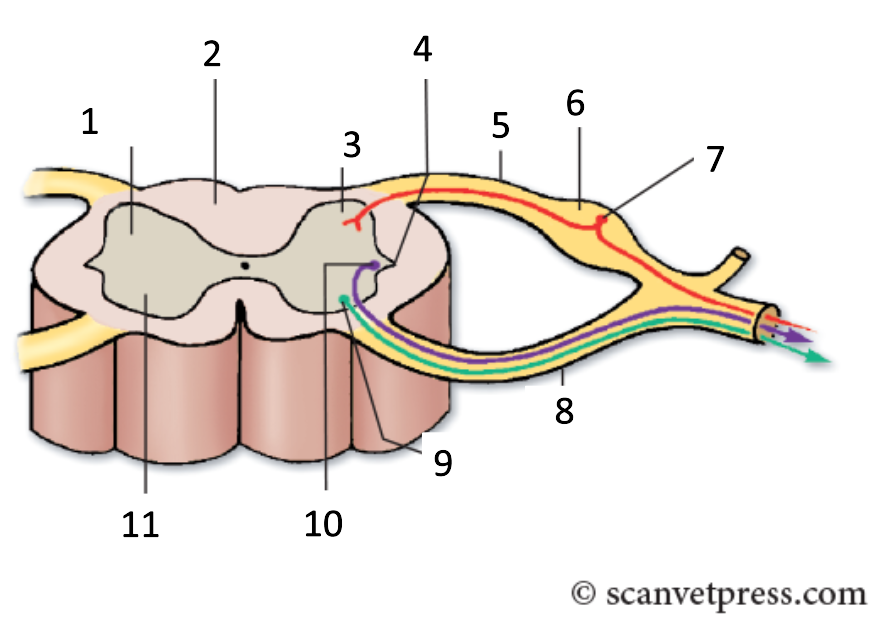
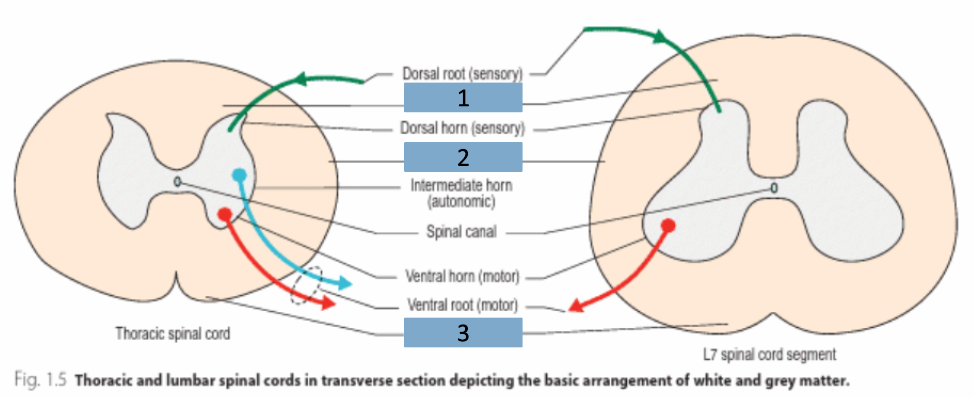
1
grey matter
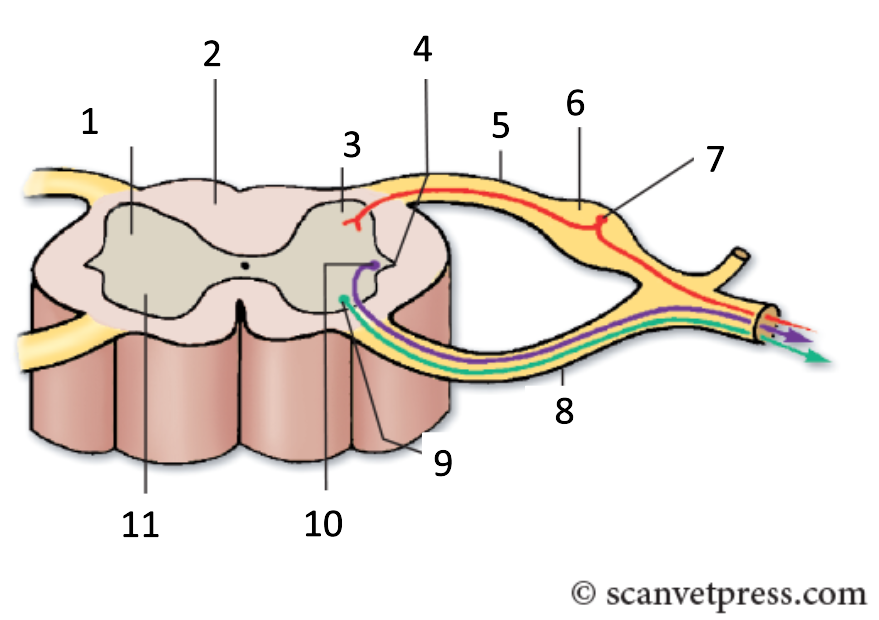
2
white matter
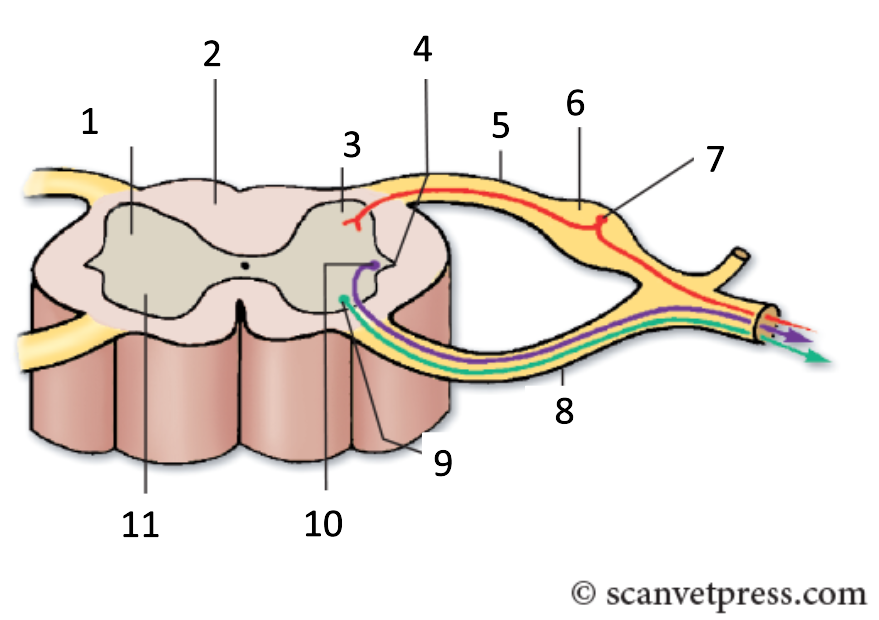
3
dorsal horn
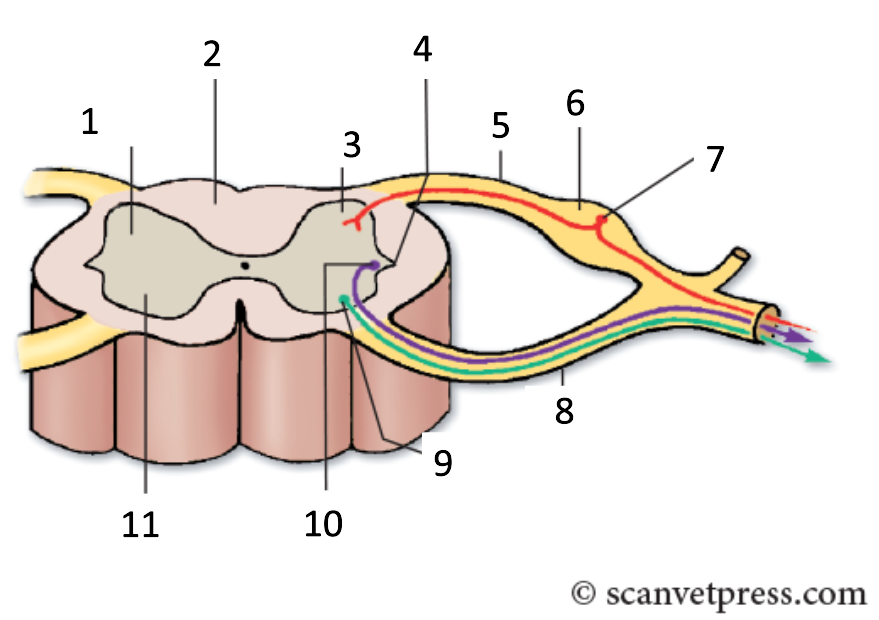
4
lateral horn
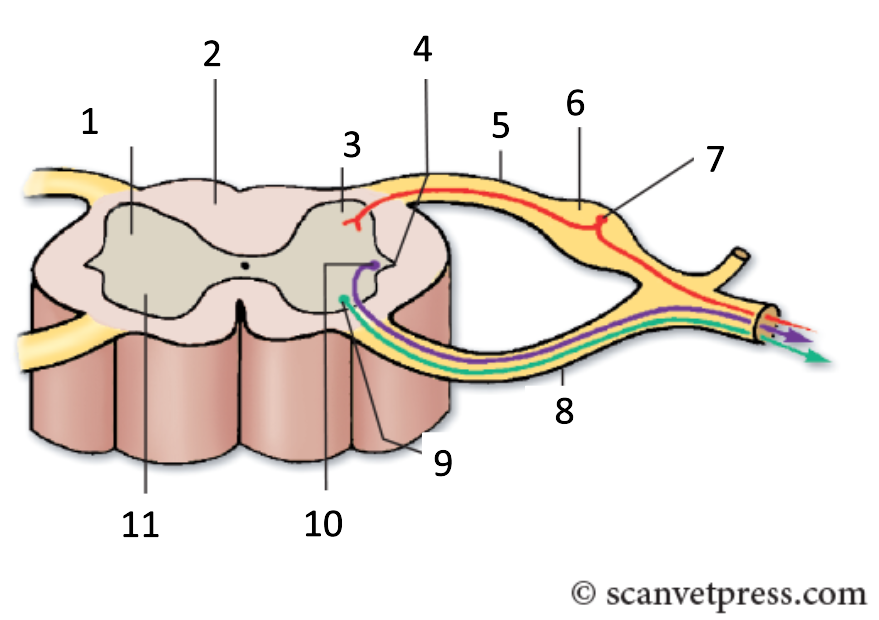
5
dorsal root
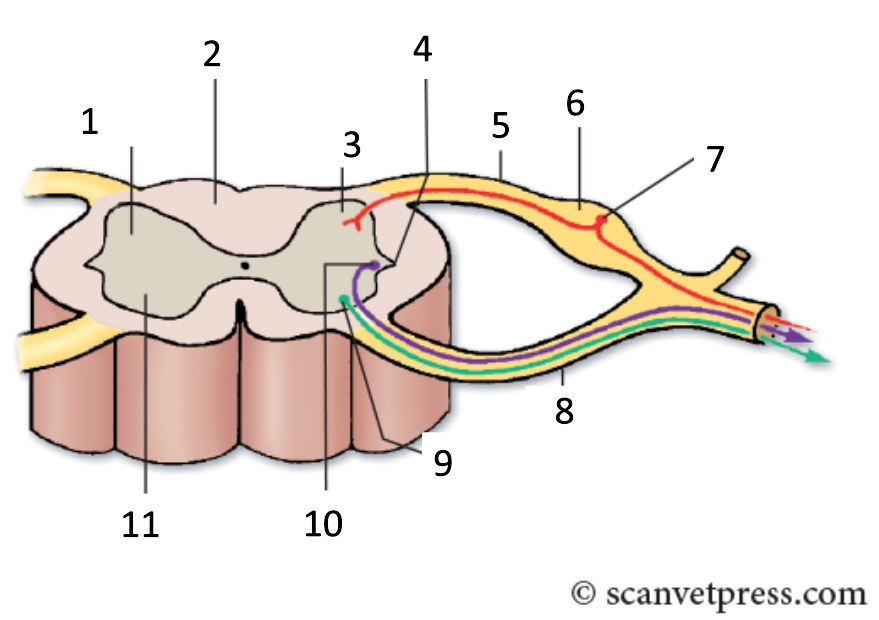
6
spinal ganglion
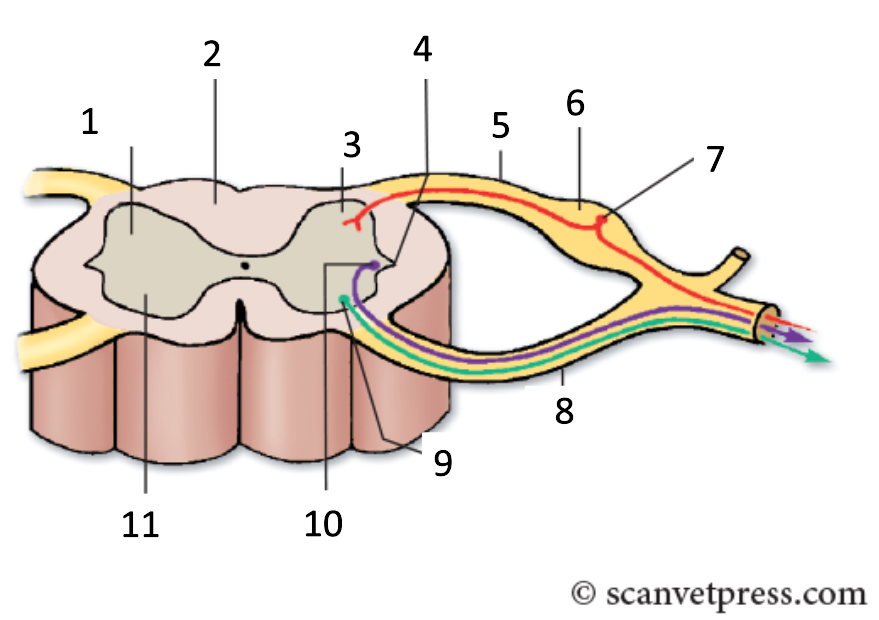
7
sensory neurone
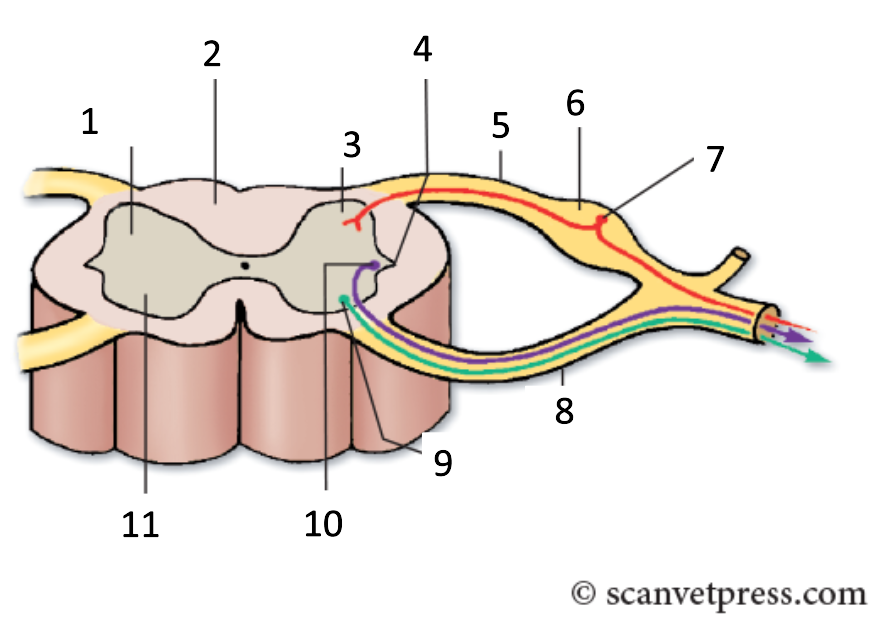
8
ventral root
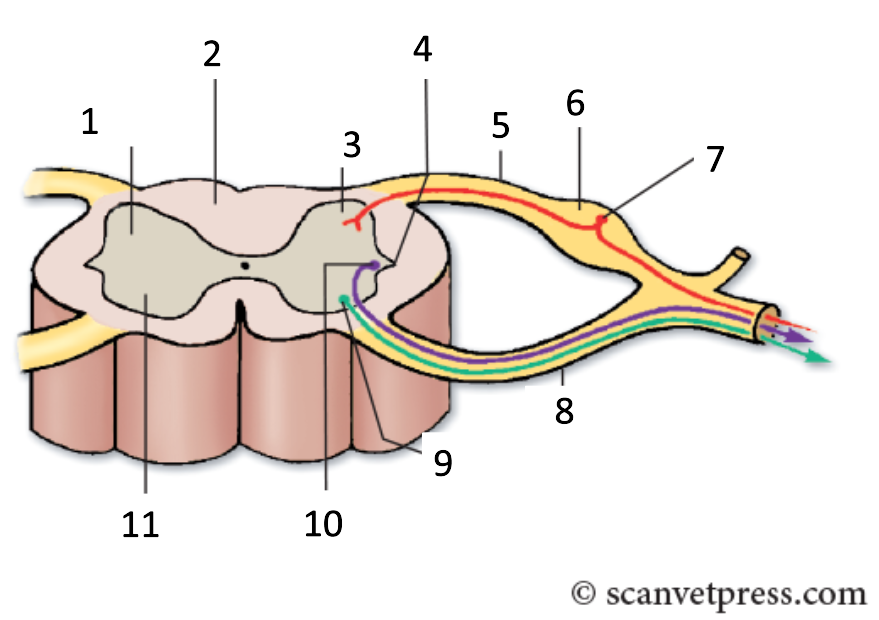
9
somatic motor neuron
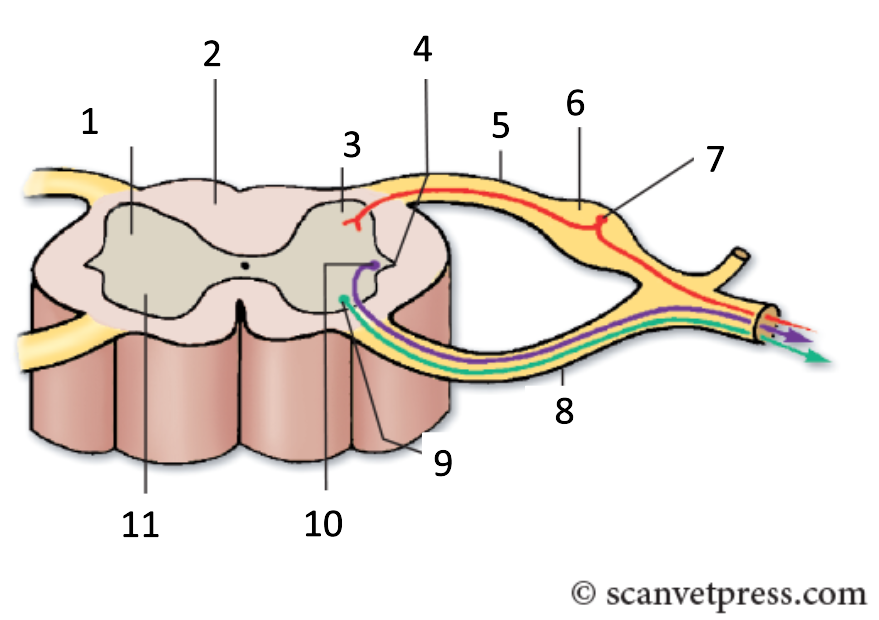
10
preganglionic autonomic neurone
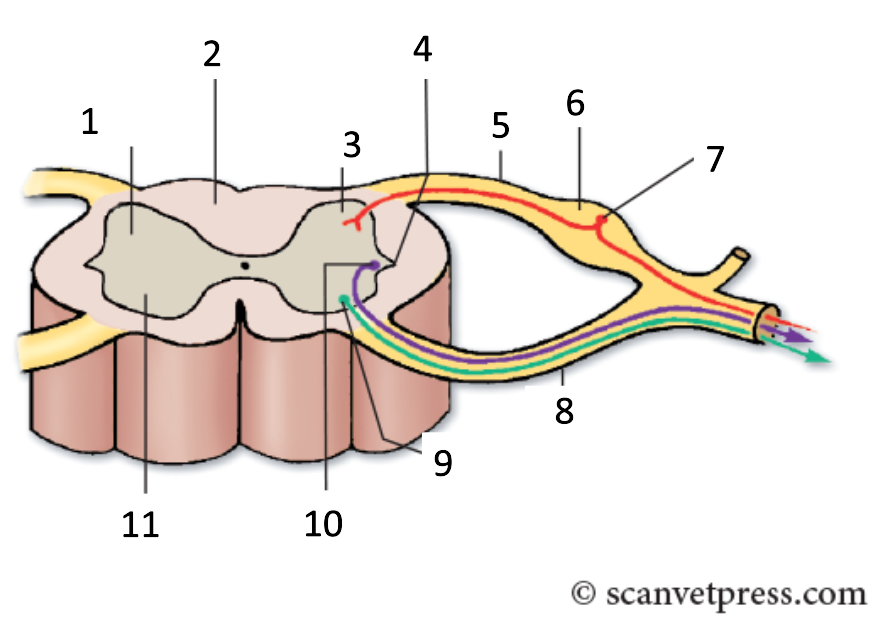
11
ventral horn
Where are there lateral horns?
between T1&L2, S2,S3 & S4 (species dependent)
Where does the dorsal ramus go?
dorsal to transverse processes of spine
Where does the ventral ramus go?
muscles ventral or below transverse processes of spine (hypaxial)
What does DRG stand for?
dorsal root ganglion
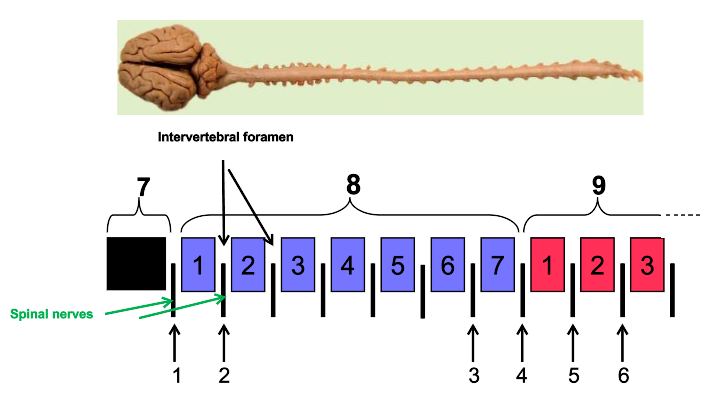
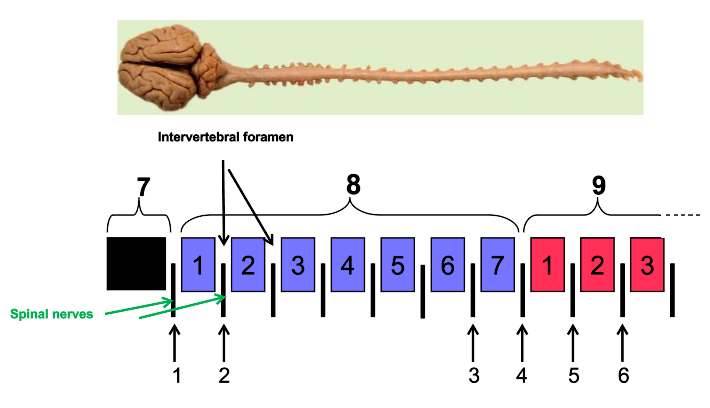
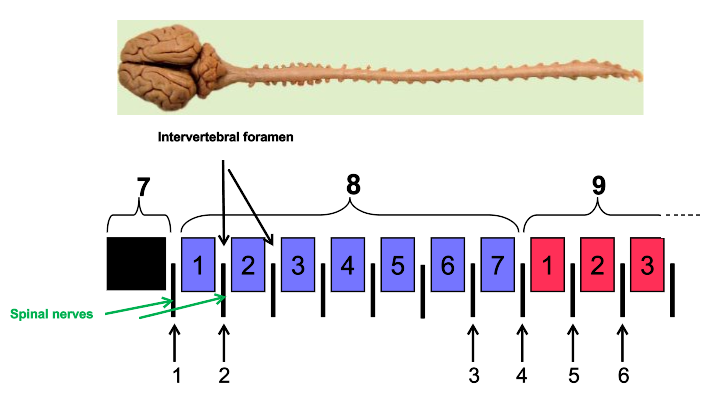
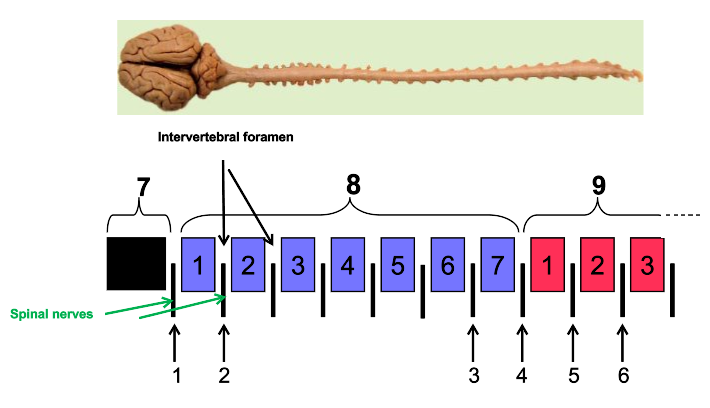
What are intervertebral foramen?
holes
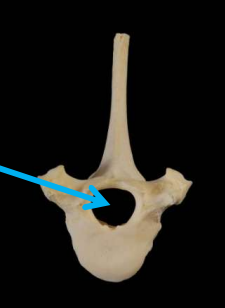
What is the arrow pointing to?
vertebral foramen
Where do spinal nerves originate?
spinal cord
Where do spinal nerves emerge?
from vertebral column
What are the arrows pointing to?
intervertebral foramen
How many cervical nerves are there?
8
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
7
What is C1 between?
occipital bone (back of skull) and first cervical vertebrae (atlas)
1
C1
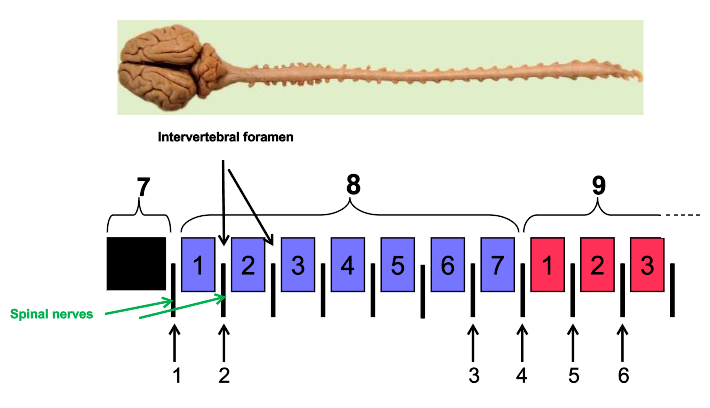
2
C2
3
C7
4
C8
5
T1
6
T2
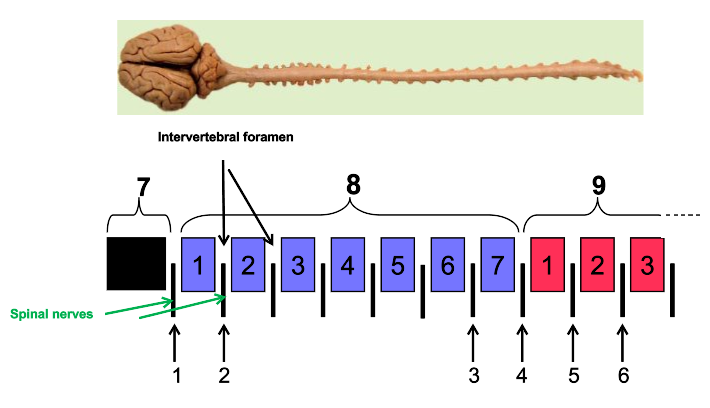
7
skull
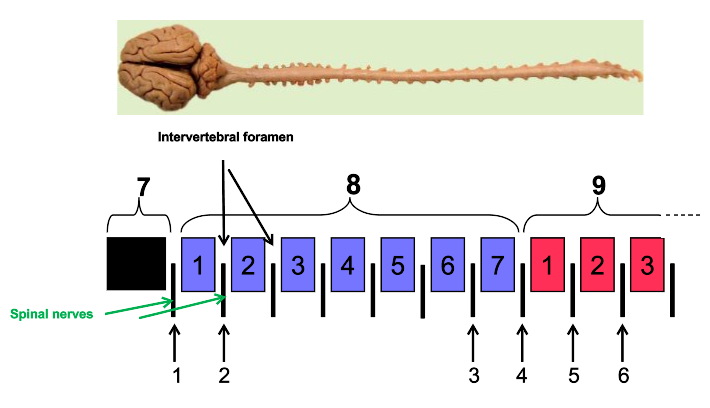
8
cervical vertebrae
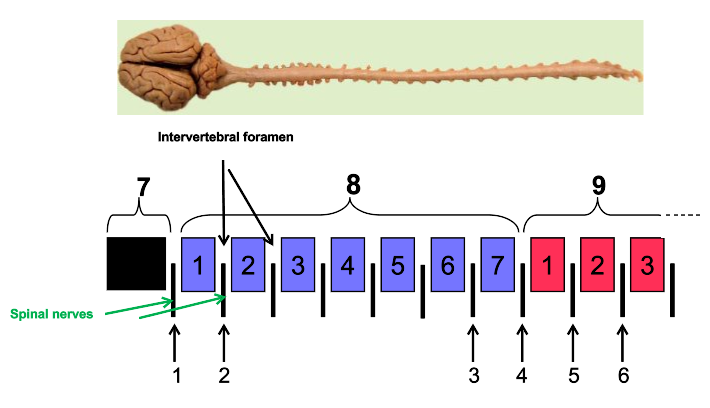
9
thoracic vertebrae
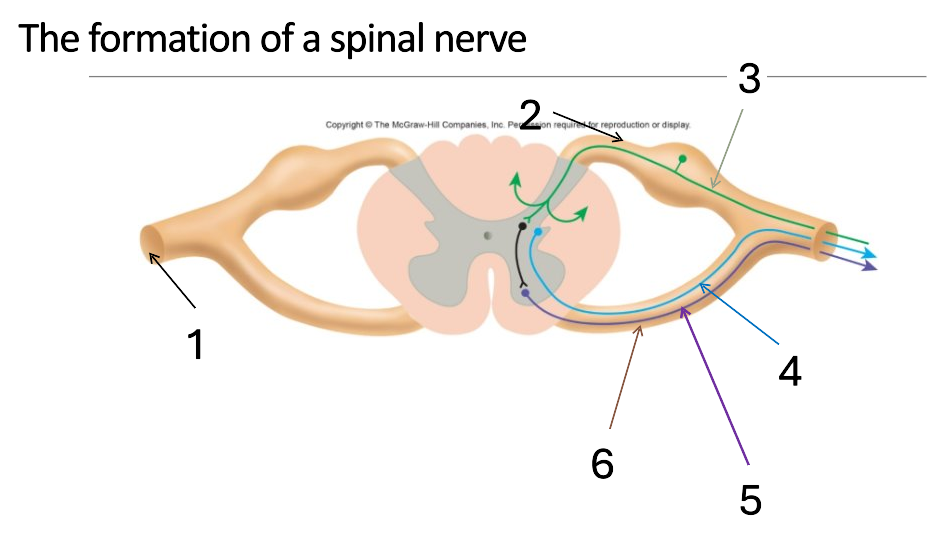
1
mixed spinal nerve
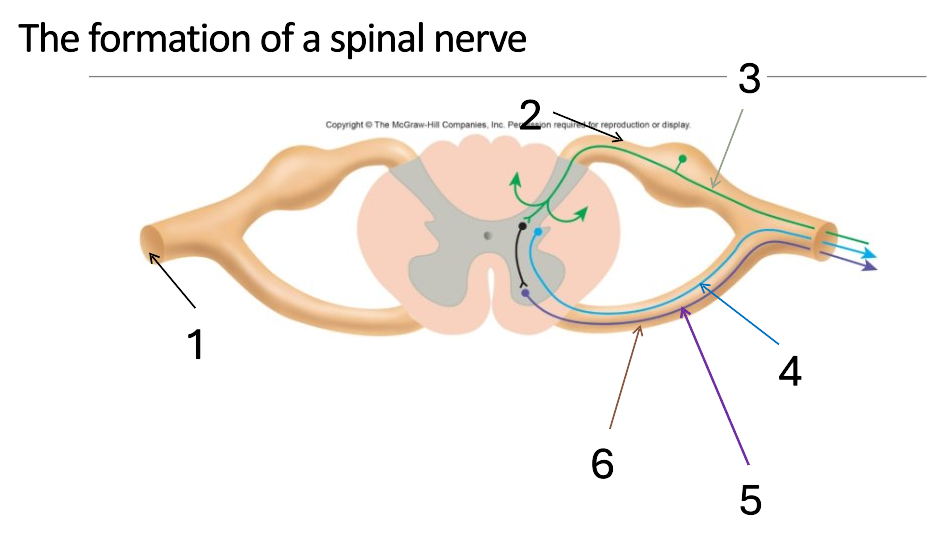
2
dorsal root
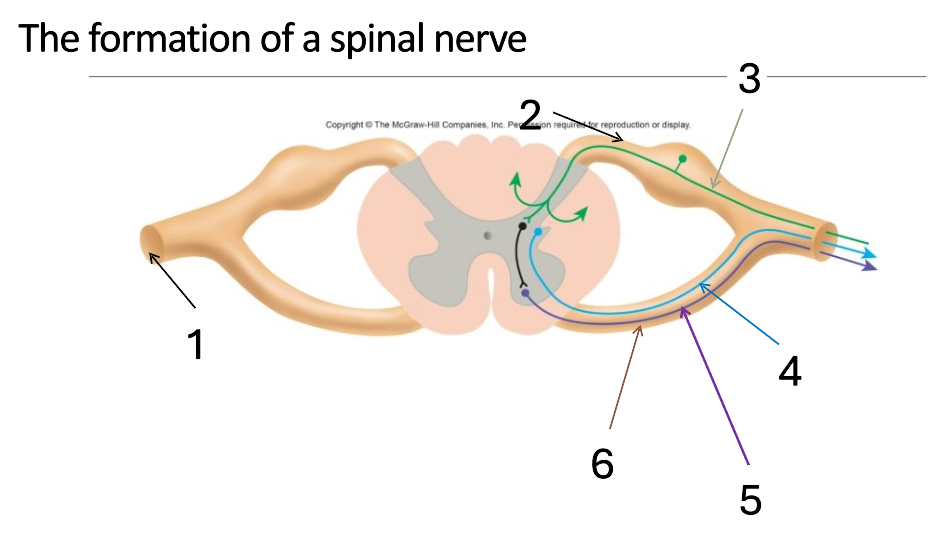
3
sensory neurone
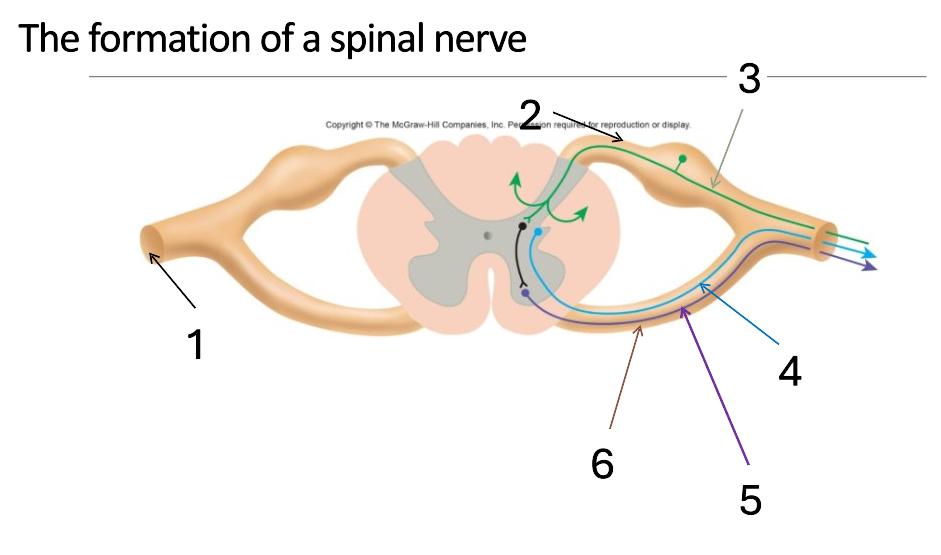
4
autonomic neurone
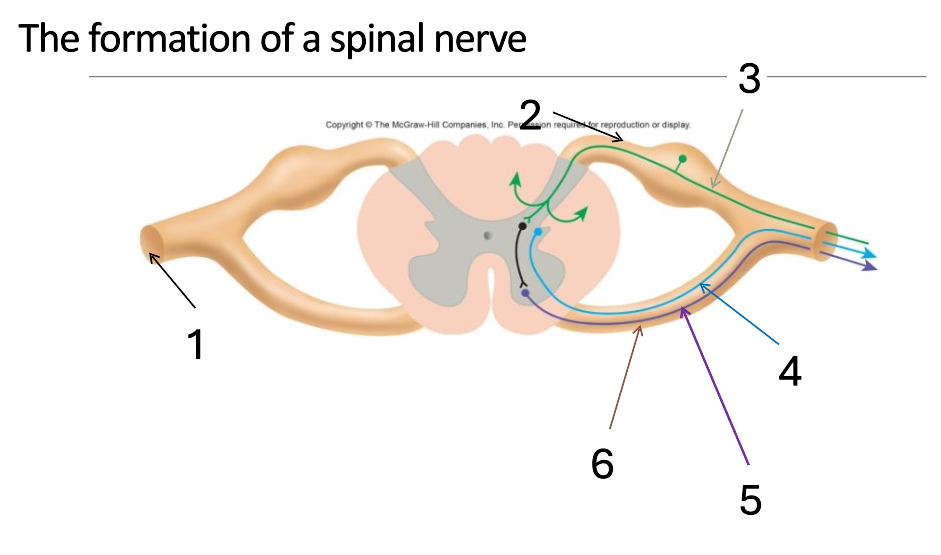
5
somatic motor neurone
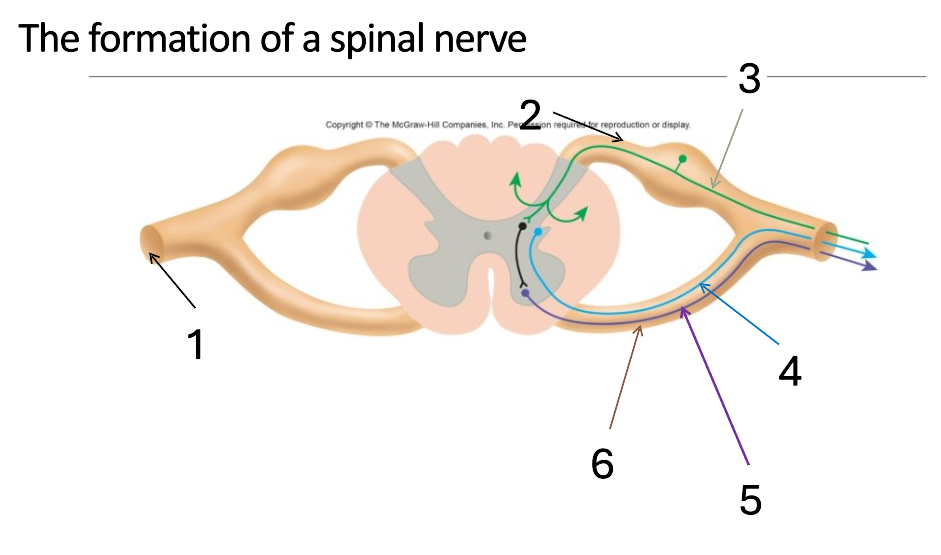
6
ventral root
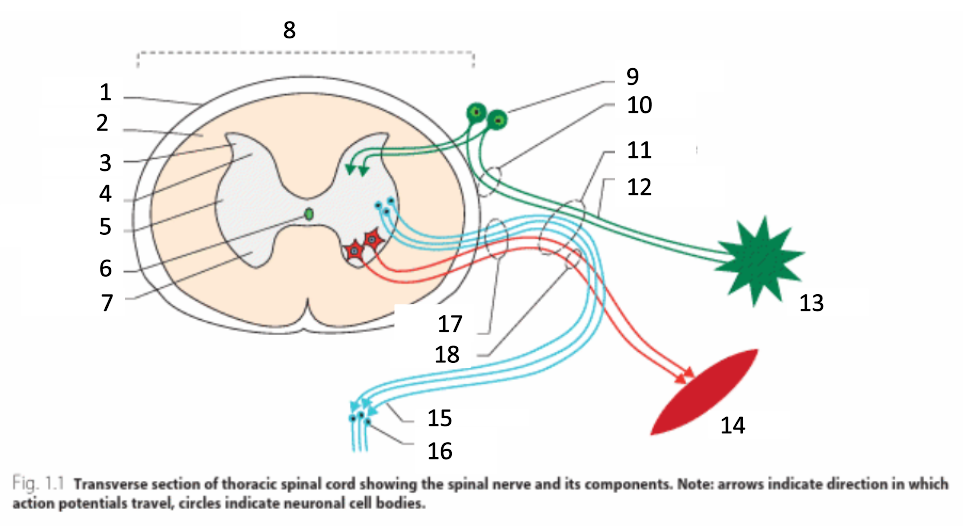
1
dura mater
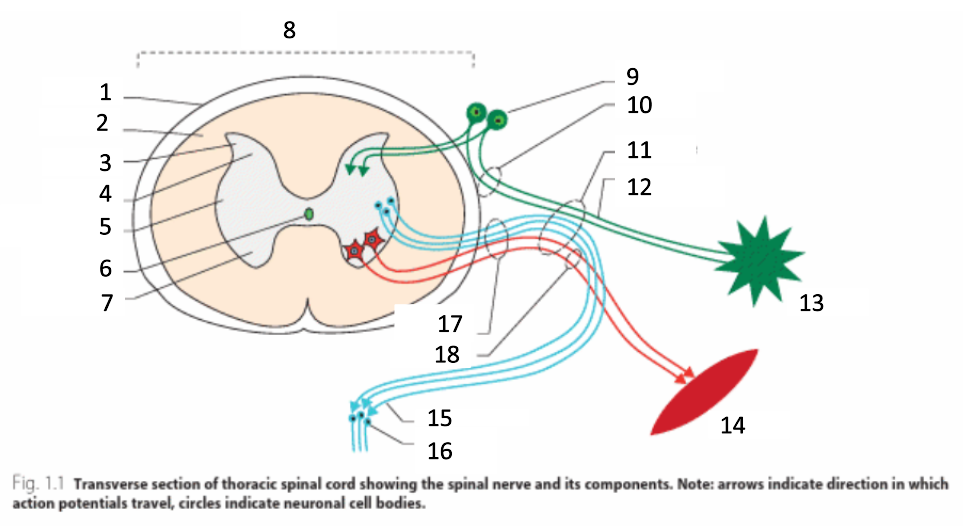
2
white matter
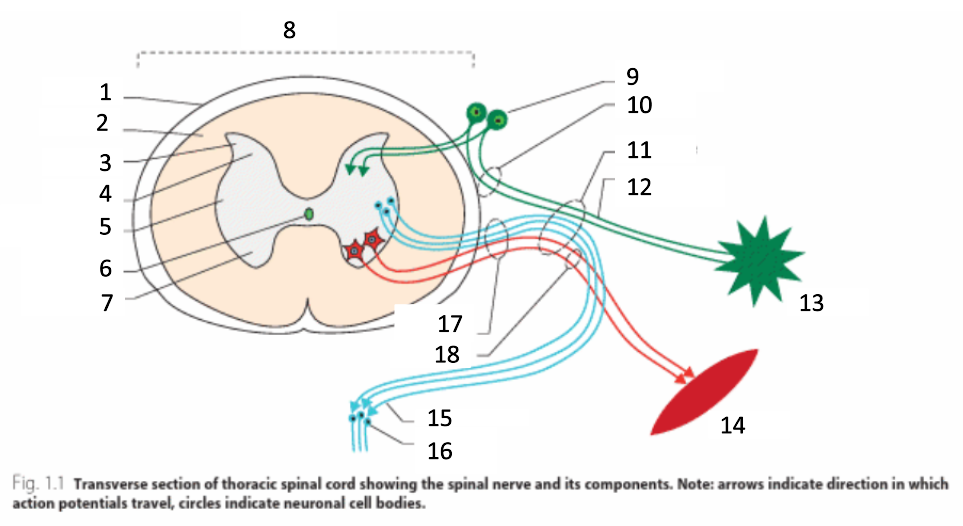
3
grey matter
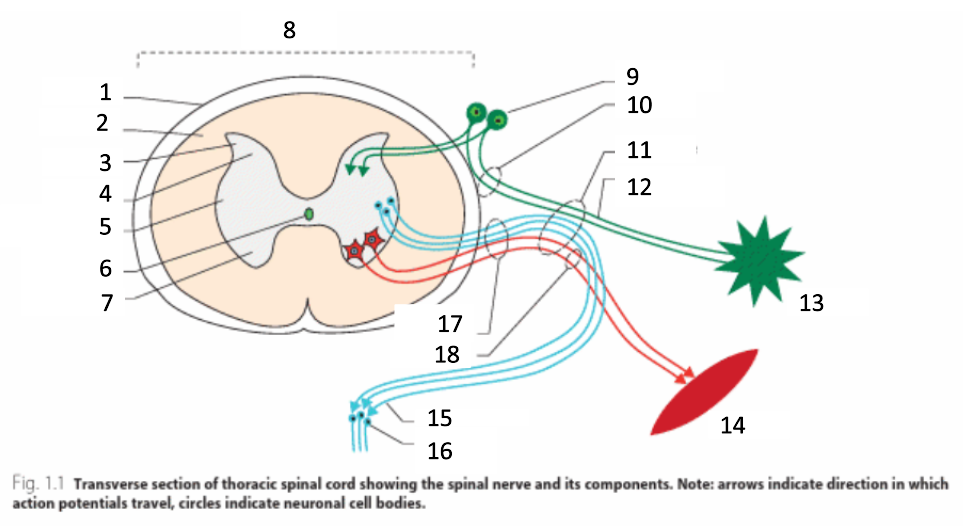
4
dorsal horn
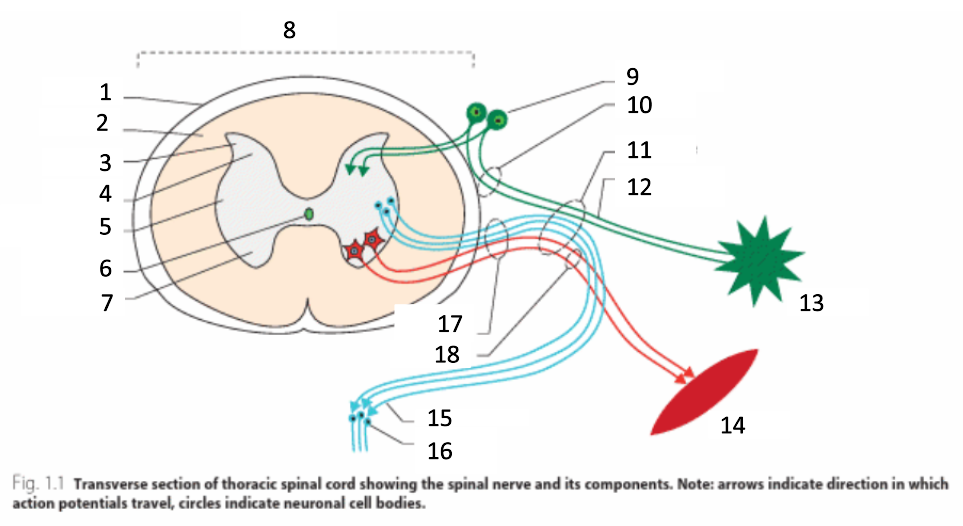
5
intermediate horn
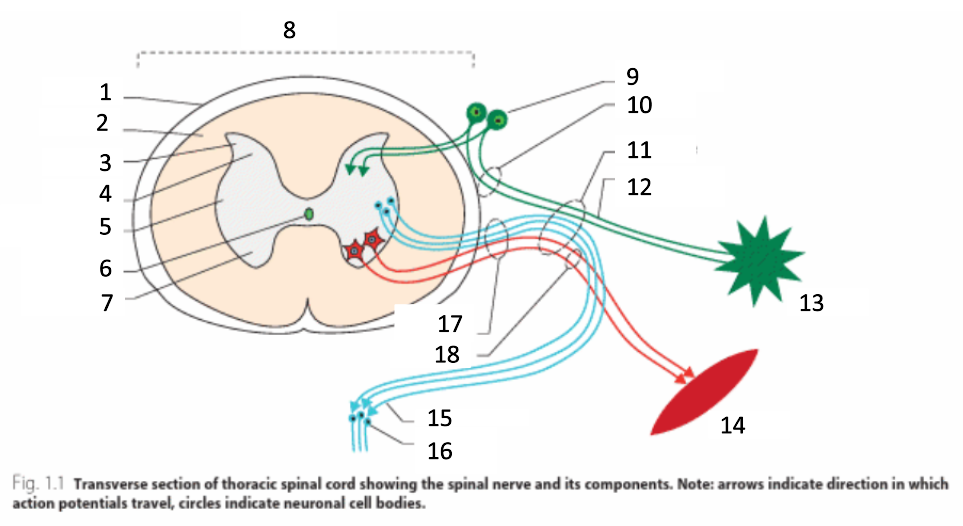
6
central canal with CSF
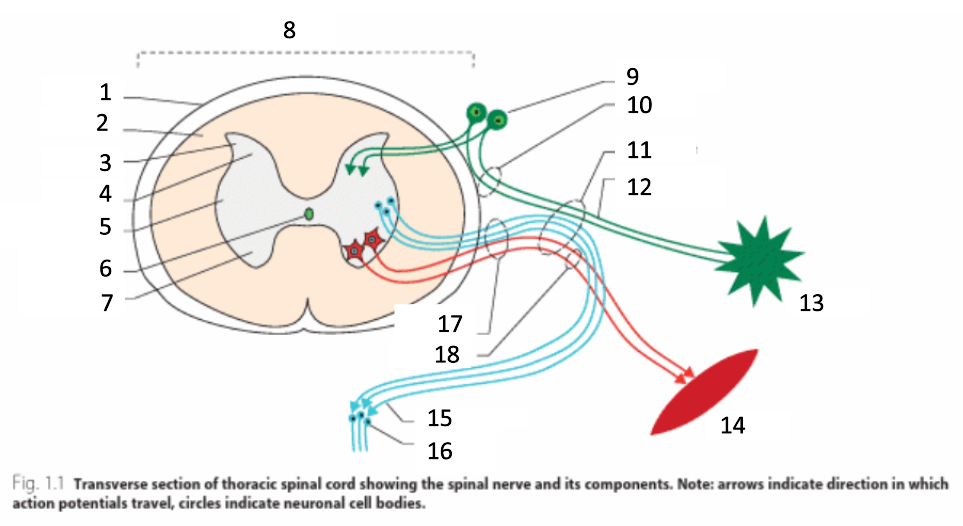
7
ventral horn
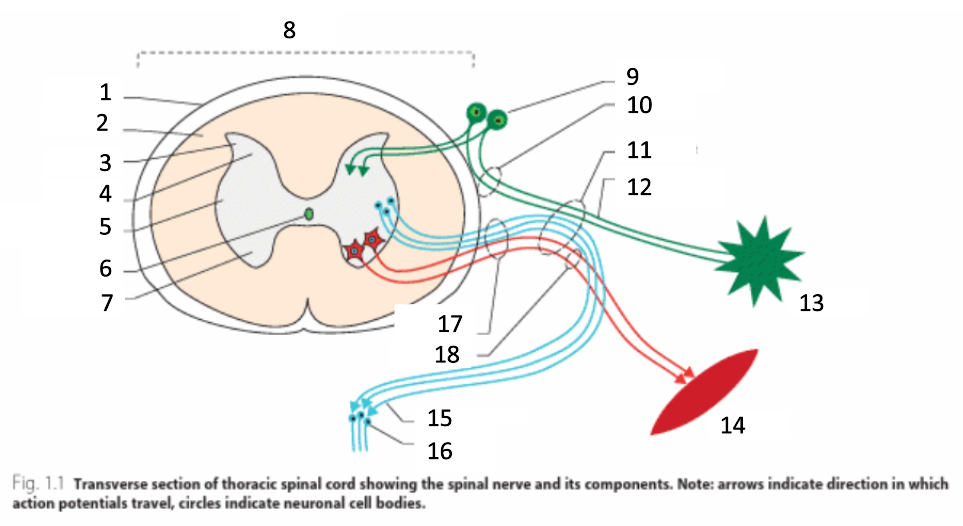
8
spinal cord
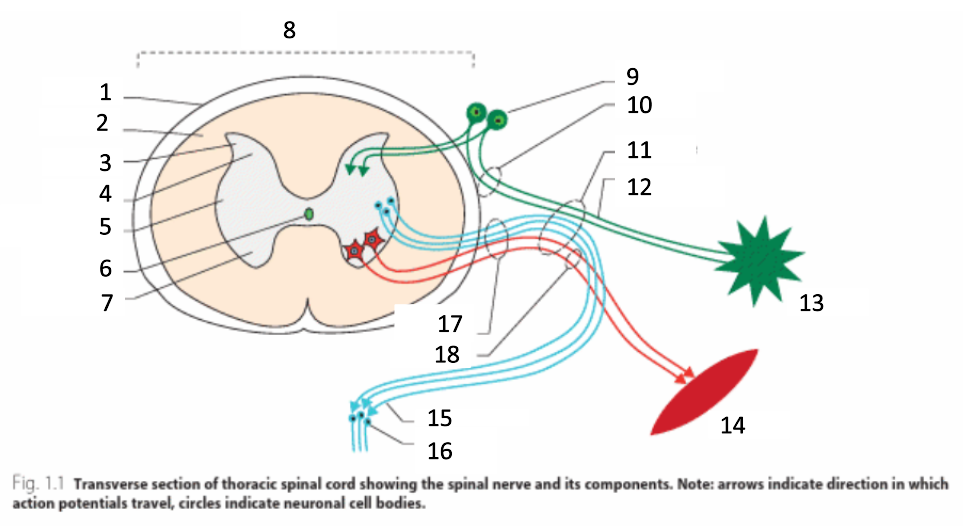
9
spinal ganglion
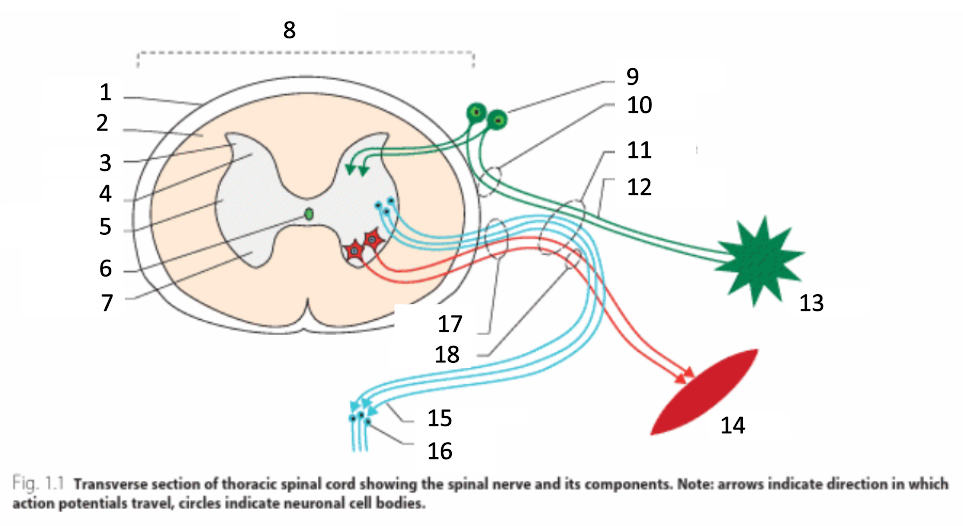
10
dorsal root
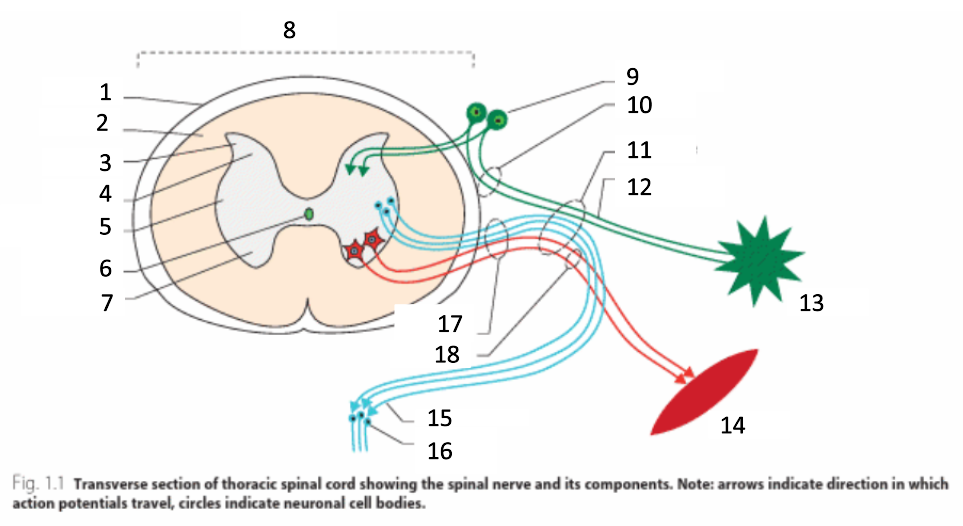
11
spinal nerve
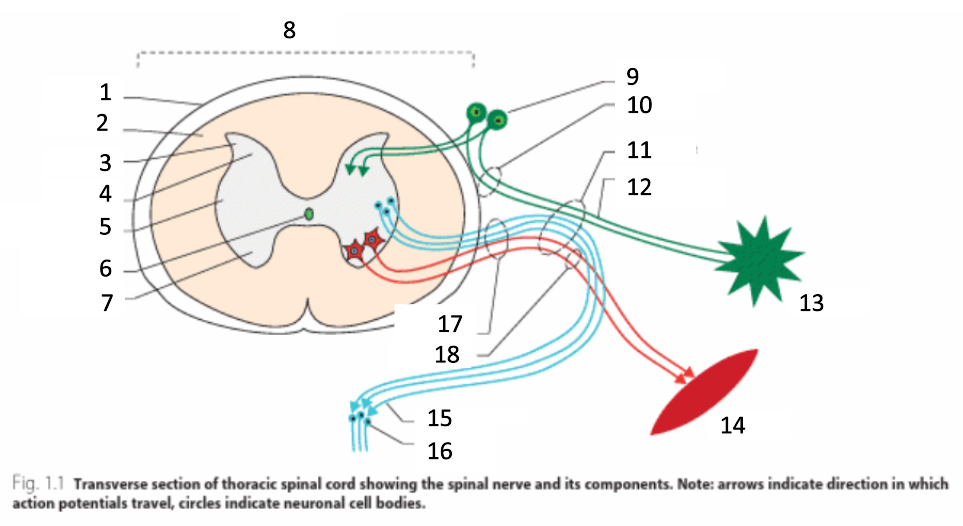
12
sensory nerves
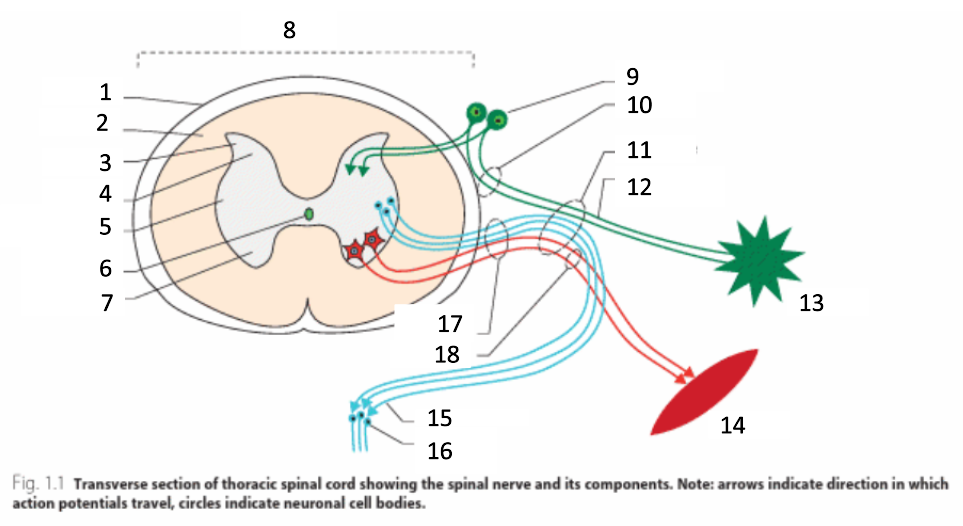
13
receptor
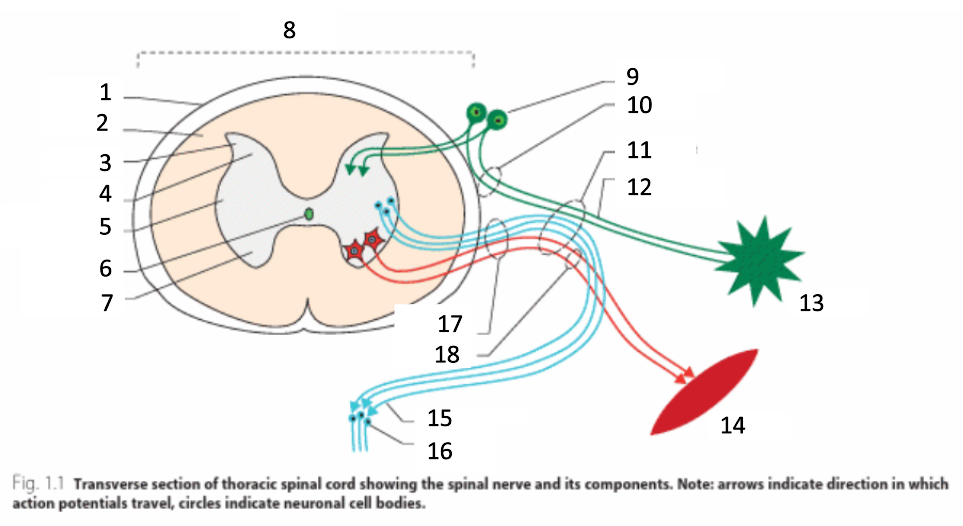
14
muscle
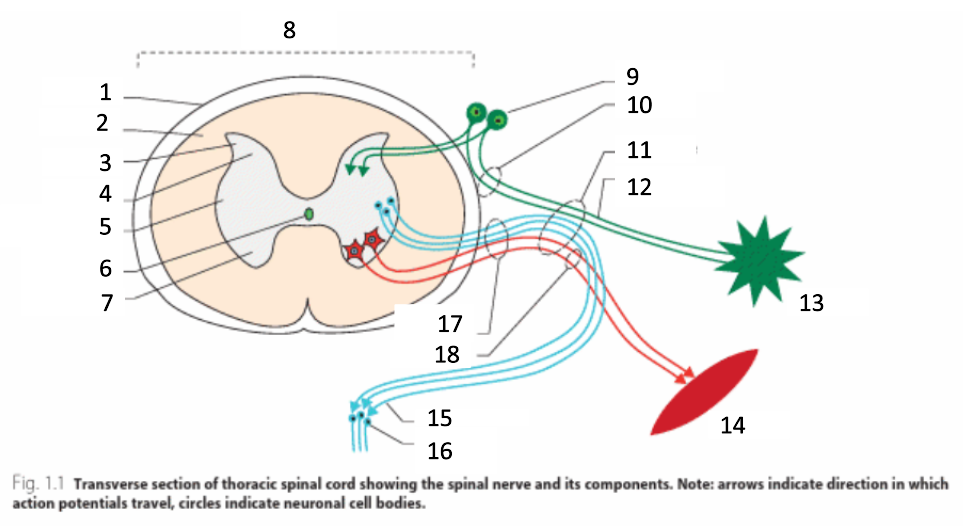
15
autonomic nerves
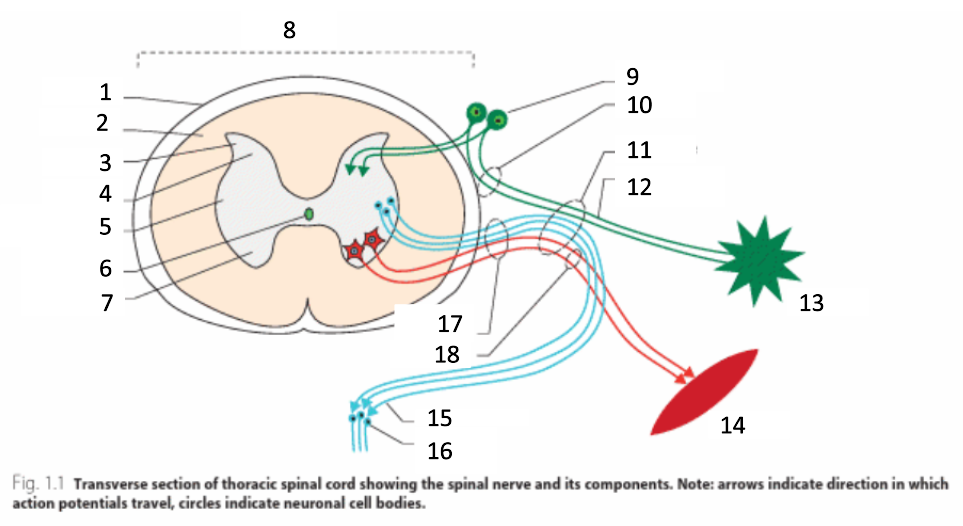
16
autonomic ganglion
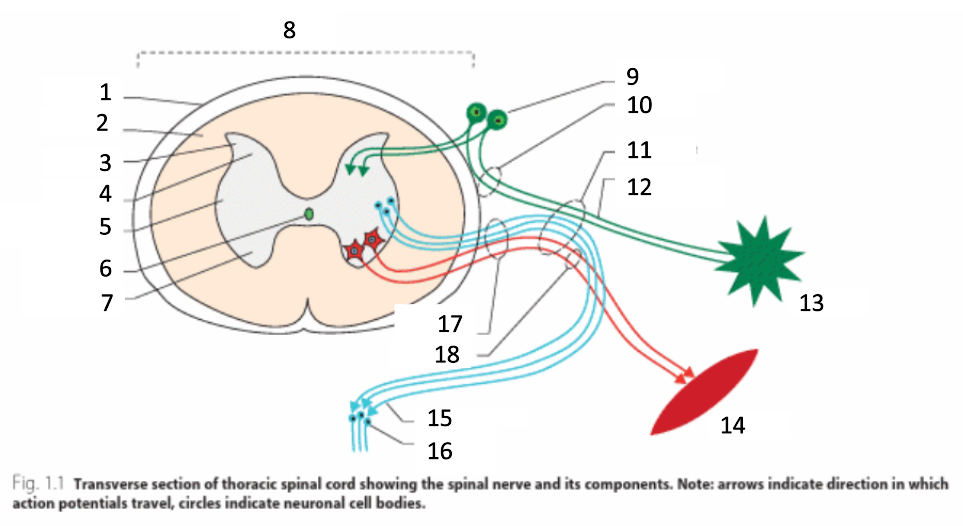
17
ventral root
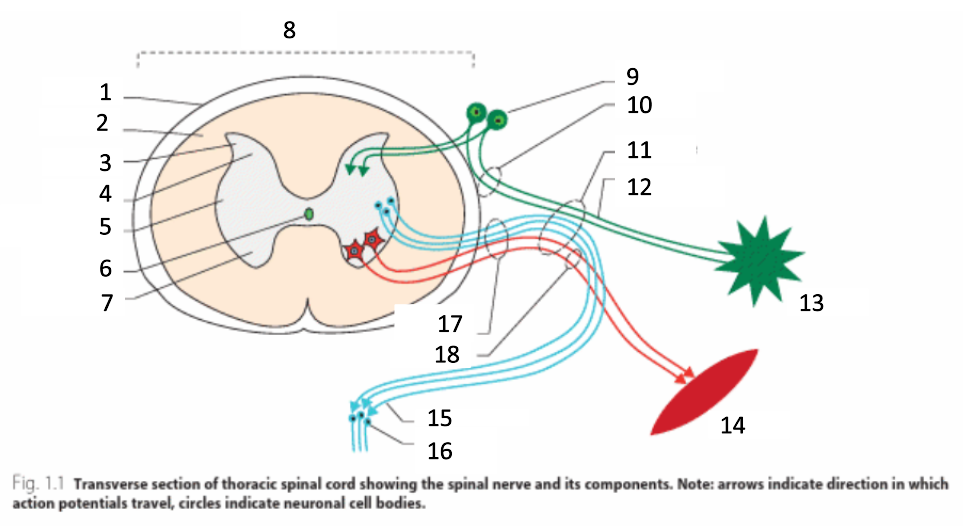
18
motor nerves
Does the dorsal funiculus contain sensory or motor fibres?
sensory
Does the lateral funiculus contain sensory or motor fibres?
mix
Does the ventral funiculus contain sensory or motor fibres?
mix (mostly motor)
What does the lateral funiculus go to supply?
flexor muscles
What does the ventral funiculus go to supply?
extensor muscles
1
dorsal funiculus
2
lateral funiculus
3
ventral funiculus
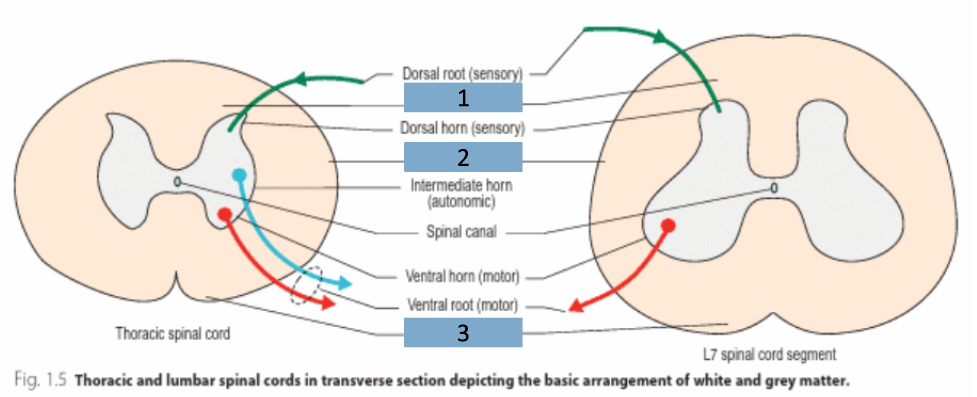
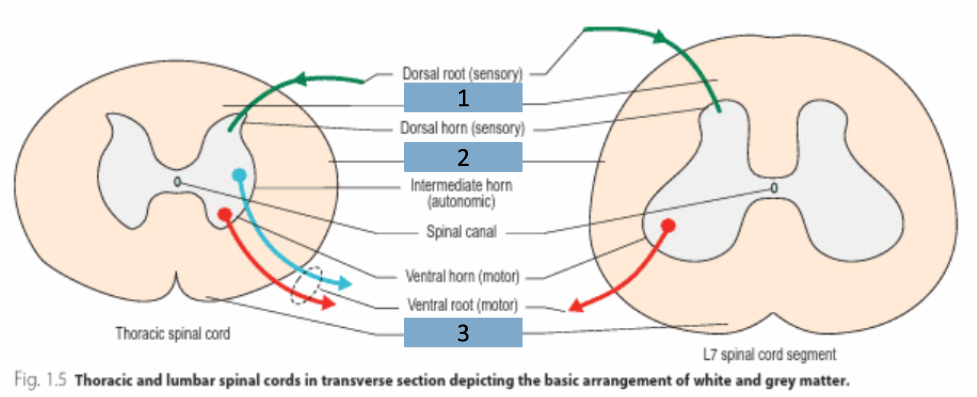
What are the 3 horns that are in grey matter?
dorsal
intermediate
ventral
Is the dorsal horn sensory, autonomic or motor?
sensory
Is the intermediate horn sensory, autonomic or motor?
autonomic
Is the ventral horn sensory, autonomic or motor?
motor
What are the 3 different funiculi in white matter?
dorsal
lateral
ventral
Are the funiculi in grey or white matter?
white
What are the functions of the spinal cord?
receiving and distributing information to the PNS
local integration of sensory and motor functions for reflex activity
relaying afferent/sensory info to brain centres
relaying efferent/motor information from UMN & motor cortex
forming connections between caudally directed tracts from the brain and cranially directed tracts, so they can regulate transmission of impulses in sensory systems