sexual reproduction in humans 2025 year 2 flash cards
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What is Sexual reproduction?
it is the fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
What are gametes?
Gametes are specialised reproductive cells (male-sperm, female-ovum)
Why are sexually reproduced off spring genetically different from either parent?
The offspring inherit a unique combination of genes from both the mother via the ovum and the father via the sperm. This results in variation between individuals.
What is asexual reproduction?
Reproduction without fusion of gametes.
Why are offspring produced by asexual reproduction genetically identical to the parent?
No genetic variation is introduced as there is only one parent.
Why is sexual reproduction more advantageous in a changing environment?
Genetic variation increases the chances of individuals being better adapted, supporting survival and evolution
Why is asexual reproduction more advantageous in a stable environment?
Off spring are identical to the parents so they are already suited to the environment, and can survive well
Faster reproduction helps the species populate the habitat quickly.
What is the male gonad, gamete and sex hormone respectively?
Testes, Sperm, Testosterone
What are the female gonads, gametes and sex hormones respectively?
Ovary, ova/ovum, Oestrogen AND progesterone
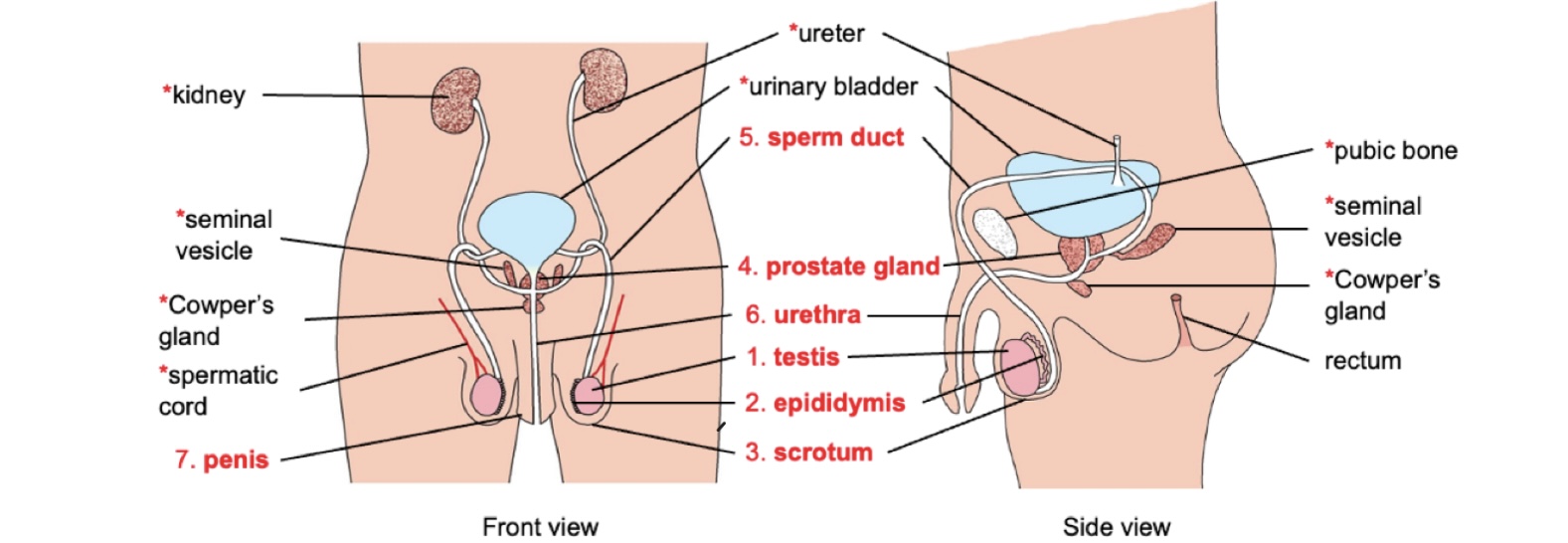
What’s the function of the testis?
To produce sperms and testosterone
What is the function of the epididymis?
To store sperm and allow sperm to mature
What is the function of the scrotums?
To hold testes outside the body at a slightly lower than body temperature for optimum sperm development.
What is the function of the prostate gland, seminal vesicles and Cowper’s gland?
They produce seminal fluid, which is nutrient-rich and slightly alkaline(pH 7.2-8.0). → Seminal fluid mixes with sperm to form semen to support semen survival and provides a medium for super movement
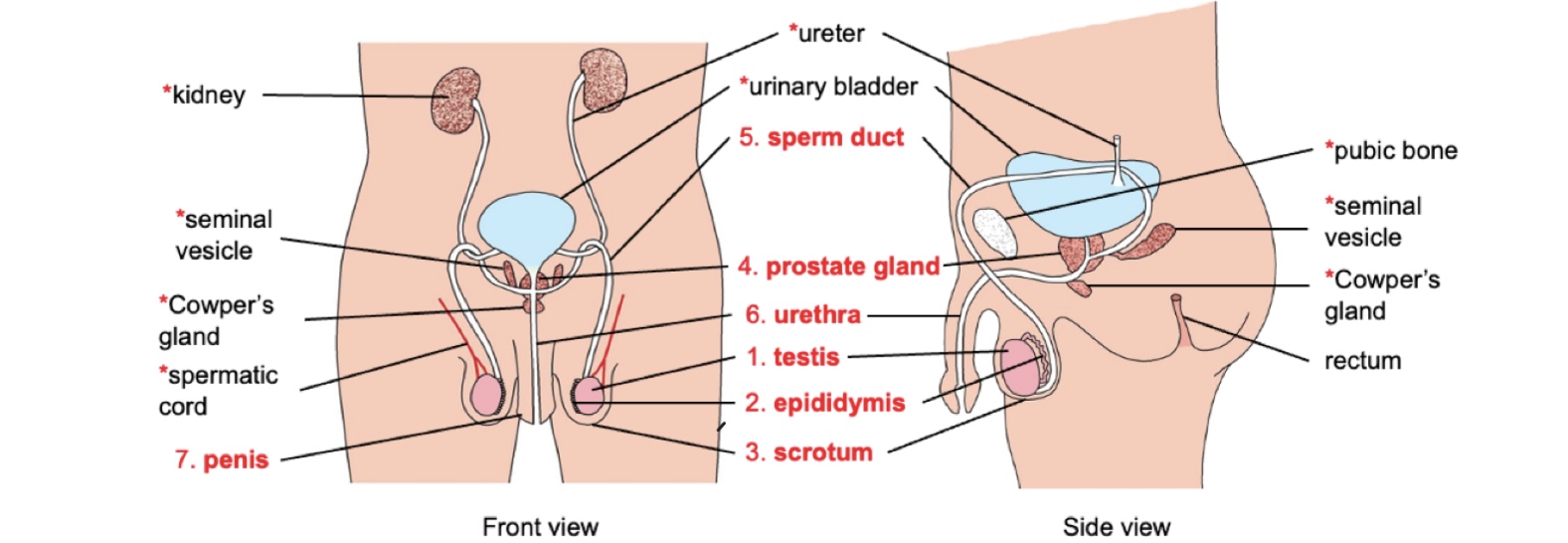
Sperm duct function?
The sperm duct transports sperm from testes to urethra during ejaculation by peristalsis
Urethra function?
Transports sperm or urine out of the body
Penis function?
Penis is an erectile organ that deposits semen into vagina during sexual intercourse.
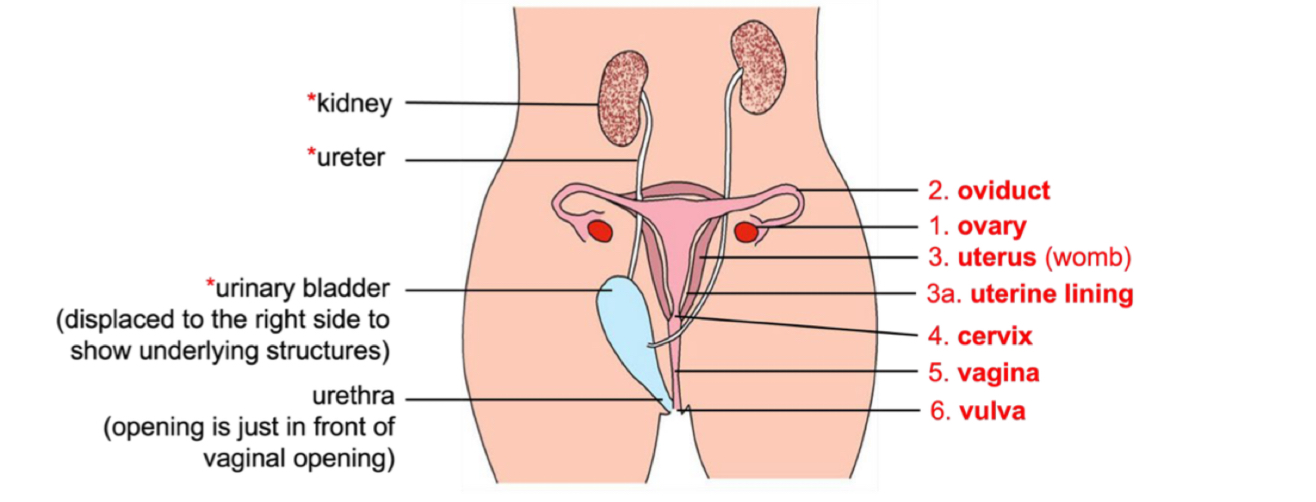
Function of ovary?
Produces ova, oestrogen and progesterone
Releases one mature ovum during each menstrual cycle (per ovary)
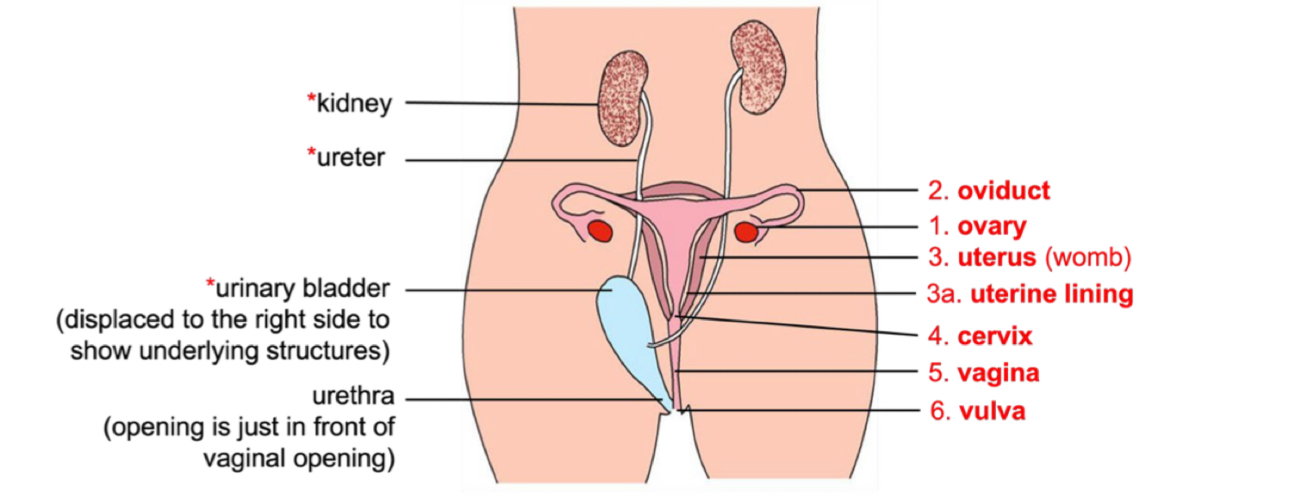
Function of Uterus?
Is a hollow organ where foetus develops.
Embryo implants in the endometrium (uterine lining) at the bottom of the uterus.
The smooth walls of the uterus contracts during child birth
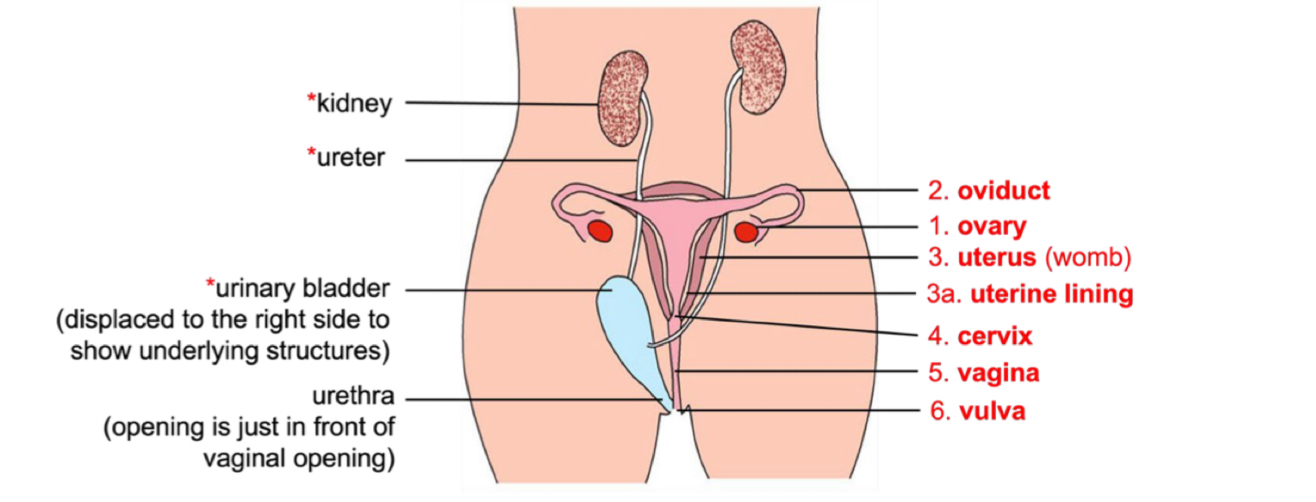
Function of oviduct?
Transports immobile ovum to uterus via cilia sweeping action and peristalsis of oviduct walls
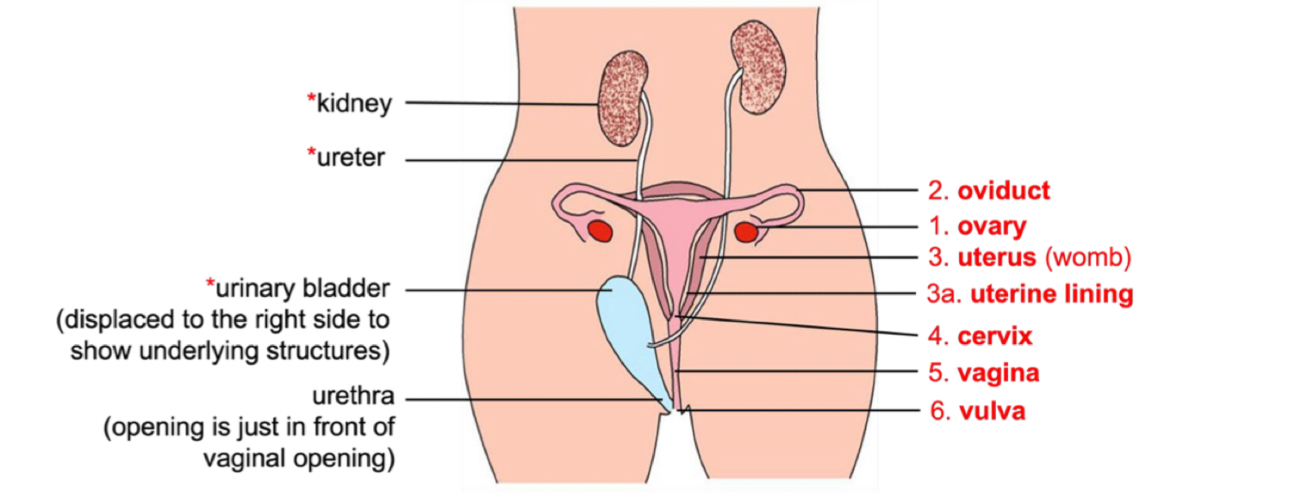
Function of cervix?
Is the narrow neck at the base of the uterus
Dilates during childbirth for baby to pass through
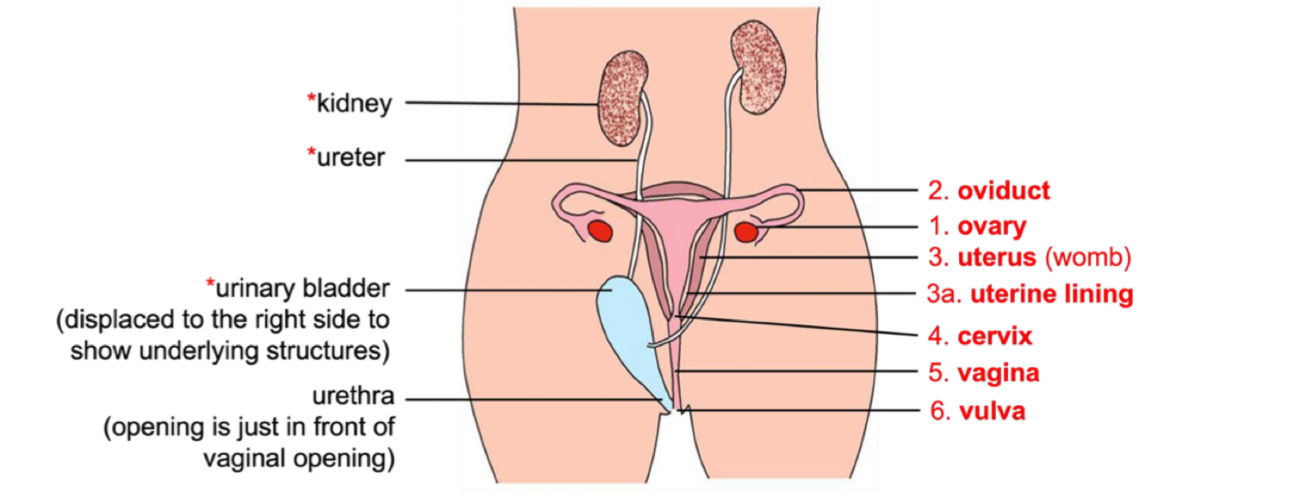
Vagina function?
Receives sperm during sexual intercourse
Passage for blood and uterine tissue to leave during menstruation
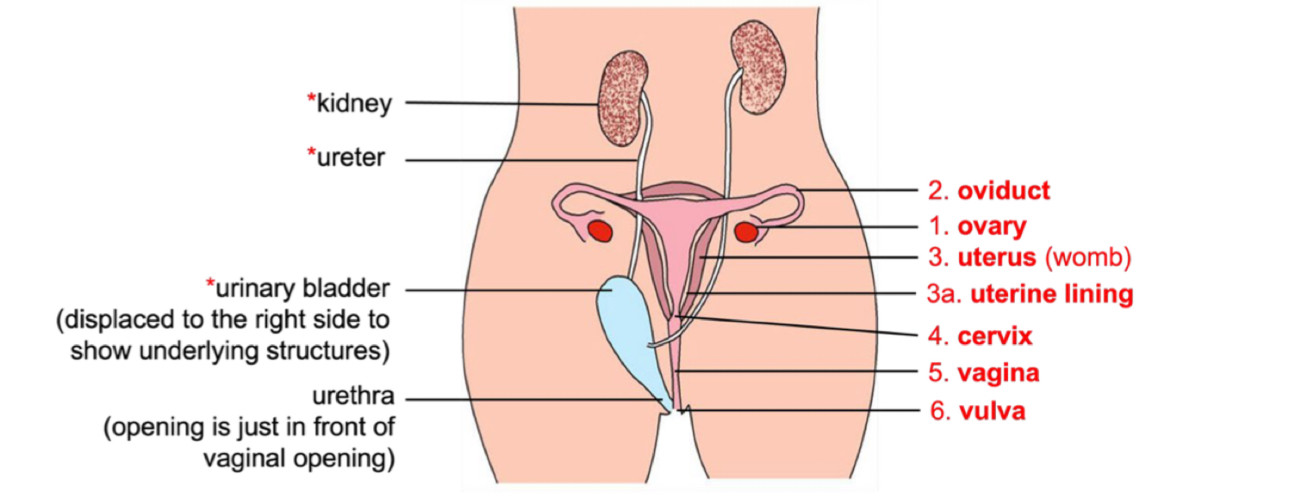
Vulva function?
Vulva is the opening to the vagina
What is the main function of the menstrual cycle?
To prepare the endometrium (uterine lining) for the implantation of an embryo
What hormones are involved in menstrual cycle?
Oestrogen and progesterone and luteinising
What’s the average cycle length of menstrual cycle and what can affect it?
28 days (can vary between 21-35 days)
Is affected by STRESS, ILLNESS, DIET, MALNUTRITION and is PAUSED during PREGNANCY
What happens during first 5 days of menstrual cycle?
Low levels of oestrogen and progesterone causes uterine lining to break down
Menstruation occurs ( blood and uterine lining are discharged through the vagina)
What happens during day 6-14 of the menstrual cycle?
Follicle stimulating hormones stimulates follicles in ovaries to secrete oestrogen, causing thickening of uterine lining
Luteinising hormone triggers OVULATION
When is ovulation day for most women?
Day 14
What happens during day 15-day 28 of the menstrual cycle?(Right after ovulation)
High levels or progesterone maintain the uterine lining.
When is the fertile phase during the menstrual cycle and how to calculate it?
Day 10-15
last day of menstrual cycle-18(day 10) last day of menstrual cycle-13(day 15)
What is the journey to the oviduct of the sperm for fertilisation?
Vagina-cervix-uterus-oviduct
What is the placenta formed from?
Embryonic villi and uterine lining
What is the amniotic sac?
Amniotic sac is a membrane that encloses the embryo and foetus in the amniotic cavity
Function of amniotic cavity? (got 4)
Amniotic cavity contacts amniotic fluid that:
Allows free movement of foetus
Protects foetus from physical shocks
Maintains stable environment for foetus
Lubricates vagina during childbirth
What is the placenta?
A temporary organ formed from both the embryo and the mother’s tissue
Why no direct mixing of maternal and foetal blood? (3 reasons)
Higher bloody pressure of mother may damage foetal capillaries
Possible blood group incompatibility could cause blood clot
Some harmful substances may be blocked from entering foetal blood
How to calculate fertilisation day
Last day-14
How to calculate day of implantation?
Last day-14-5 TO last day-13-7
What is the function of the placenta?(2)
Secrets oestrogen and progesterone to maintain healthy pregnancy
Facilitates exchange of substances between mother and foetus via diffusion and active transport but no direct mixing of maternal and foetal blood
Working principle of abstinence
Penis never enters vagina to deposit sperms to prevent sperm from entering the vagina, preventing fertilisation
Working principle of withdraw method
Penis ejaculates outside vagina to prevent sperm from entering the vagina, preventing fertilisation
Working principle of rhythm method
Prevents fertilisation as sperm will not meet an ovum during the infertile phase
Working principle of condoms/ femidoms
Forms a barrier to prevent sperms from entering the vagina, preventing fertilisation
Working principle of diaphragm
Forms a barrier to prevent sperms from passing through the vagina to prevent fertilisation
working principle of spermicide
Chemical inactivates/kills sperms, preventing them from meeting the ovum, preventing fertilisation
working principle of copper intrauterine device(2)
Copper ions are released to kill/inactivate sperms, preventing fertilisation
Inflames uterine lining to prevent implantation of the embryo
Working principle of the oral contraceptive pills(3)
Prevents ovulation by inhibiting luteinising hormone
Thickens cervical mucus to prevent sperms from swimming to uterine lining, preventing fertilisation
contains synthetic progesterone and synthetic oestrogen to inhibit natural oestrogen and progesterone, thinning uterine lining, preventing implantation of an embryo
Working principle of vasectomy
Prevents fertilisation as the man’s ejaculate will no contain sperms
Working principle of tubal ligation
prevents fertilisation as the sperm is unable to meet the ovum in the oviduct
Syphilis symptoms (stage1,2 and latent)
Stage 1:
Painless sore known as chancre appears where bacteria entered
lymph nodes swell around area of infection
Stage 2:
Non-itchy body rashes develop and can become infectious lesions
Latent stage:
No symptoms
Late stage:
Non-cancerous tumour growth
paralysis,bone deformity, heart failure, blindness and insanity
can syphilis be passed to foetus? What will happen to foetus?
CAN pass. Child is born with skin rashes and poorly developed teeth and nose
symptoms of gonorrhoea
A discharge of pus from penis and vagina
Pain in the lower abdominal area
Painful burning session during urination in men
May spread to other surrounding organs, resulting in sterility if untreated
What two contraceptives method can protect one from STIs
Abstinence, condoms and femidoms
Full-blown AIDS symptoms
Abnormal tissue growth known as cancer of blood vessels
Swelling of lymph nodes
Prolonged fatigue
Persistent fever
Pneumonia and tuberculosis
Chronic diarrhoea
What is given to AIDS patients as treatment?
Antiviral treatment slows down progression from HIV to full-blown AIDS, prolonging lifespan but not curing patient.
What can pass through the placenta?
All digested food molecules, water, mineral salts, urea, vitamins, oxygen, carbon dioxide, antibodies, HIV and syphilis bacteria
What cannot pass through the placenta?
Gonorrhoea bacteria, red and white blood cells, undigested food molecules like proteins and starch