Exploring Health, Wellness, and Consumerism
1/249
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
250 Terms
Physical Self
Embodiment central to personal identity and health.
7 Dimensions of Wellness
Includes physical, emotional, social, spiritual, environmental, intellectual, occupational.
Embodiment
Physical existence as a foundation for personal being.
World Health Organization (1948)
Defined health as complete well-being, not just absence of disease.
Dr. Halbert Dunn
Pioneered concept of wellness and upper health limits.
Wellness
Dynamic process of achieving optimal well-being.
Health
State of complete physical, mental, and social well-being.
Physical Dimension
Embodied aspect of self related to health.
Physical Fitness
Body's ability to function at optimal efficiency.
Skill-related Components
Factors important for athletic success, not health.
Health-related Components
Essential for daily functional activities and health.
Cardiorespiratory Endurance
Ability to deliver oxygen efficiently during activity.
Muscular Strength
Maximal force exerted by a muscle against resistance.
Muscular Endurance
Sustaining repeated force against resistance over time.
Flexibility
Range of motion in joints for efficient movement.
Body Composition
Ratio of body fat to fat-free weight.
Self-Worth
How a person feels about themselves.
Body Image
Perception and feelings about one's physical appearance.
Healthy Body Image
Acceptance and respect for one's body.
Body Dissatisfaction
Negative feelings and thoughts about one's body.
Self-Acceptance
Comfort and happiness with one's appearance.
Healthy Outlook
Balanced lifestyle with positive attitudes towards health.
Negative Body Image Factors
Age, media influence, societal pressures contribute.
Medical Self-Care
Regular health checkups and self-monitoring practices.
Balance in Wellness
Essential for pursuing overall health and well-being.
Lifelong Growth Mindset
Attitude of continuous improvement in all life dimensions.
Preventive Health Behaviors
Actions taken to maintain health and prevent illness.
Agility
Ability to move quickly and easily.
Coordination
Ability to use different body parts together smoothly.
Reaction Time
Time taken to respond to a stimulus.
Power
Ability to exert maximum force in a short time.
Body Image Problems
Common issues affecting self-worth across all ages.
Body Dissatisfaction
Prevalent in midlife and youth, affecting self-esteem.
Gender Differences
Adolescent girls show more body dissatisfaction than boys.
Sexual Self
Influenced by societal standards and personal perceptions.
Low Self-Worth
Often linked to body dissatisfaction and depression.
Medial Pre-optic Area (mPOA)
Brain region crucial for sexual behavior and mate selection.
Sexually Dimorphic
Functionally different in males and females.
Perfectionist Tendencies
Associated with higher risk of body dissatisfaction.
Teasing Effects
Negative feedback can exacerbate body image issues.
Role Models
Influence body image concerns through expressed dissatisfaction.
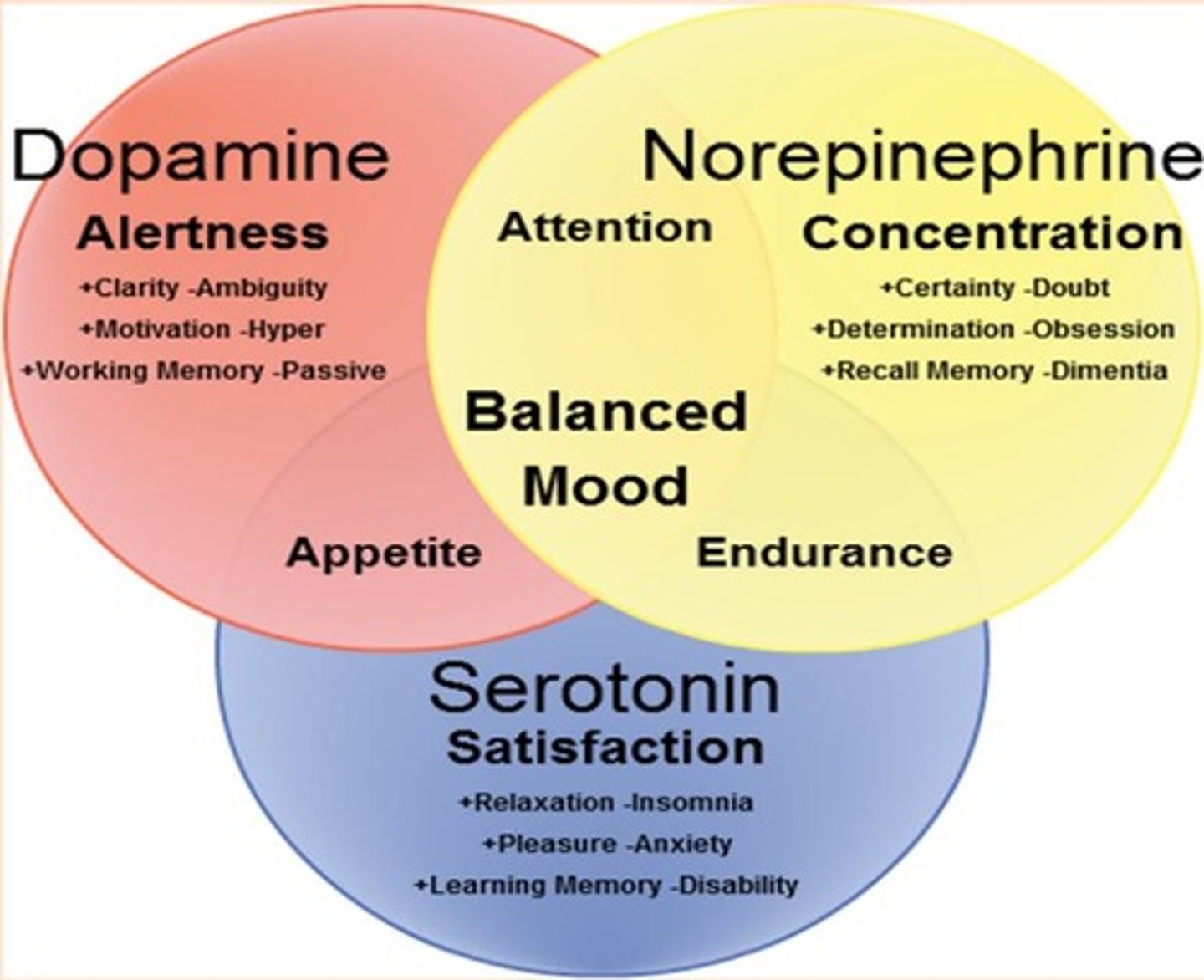
Dopamine (DA)
Important for appetitive behaviors in the mPOA.
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Enhances DA activity, promoting appetitive behaviors.
3 Stages of Love
Lust, Attraction, and Attachment define romantic feelings.
Lust
Driven by estrogen and testosterone levels.
Attraction
Characterized by adrenaline, dopamine, and serotonin.
Attachment
Involves oxytocin and vasopressin hormones.
GnRH
Regulates sex hormone release from the pituitary gland.
Hypothalamus Role
Controls endocrine system and hormone secretion.
Electrical Stimulation of mPOA
Increases mating speed in male rats.
Lesions in mPOA
Prevent mating behaviors in male rats.
Testosterone Implants
Restore mating behavior in castrated males.
Aromatase Enzyme
Converts testosterone to estrogen, influencing behavior.
Seasonal Birth Patterns
Humans exhibit fertility changes based on daylight.
Melatonin's Role
Regulates GnRH secretion and sleep patterns.
Appetitive Behaviors
Actions to attract mates, influenced by mPOA.
Mating Behaviors
Consummatory phase controlled by the mPOA.
Body Image Concerns
Can develop from societal pressures and comparisons.
Comparison to Others
Heightens risk of body dissatisfaction.
Lordosis
A mating posture influenced by the mPOA.
Gonadotropins
Hormones released by the anterior pituitary.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Stimulates testosterone production in males.
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Essential for sperm maturation in males.
Onset of Puberty
Initial release of LH and FSH occurs.
Mountain and Prairie Voles Experiment
Study on monogamous behavior in voles.
Dopamine
Brain chemical linked to pleasure and reward.
Oxytocin
Hormone involved in bonding and childbirth.
Vasopressin
Hormone related to social behavior and bonding.
Testosterone
Male hormone influencing sexual behavior and mood.
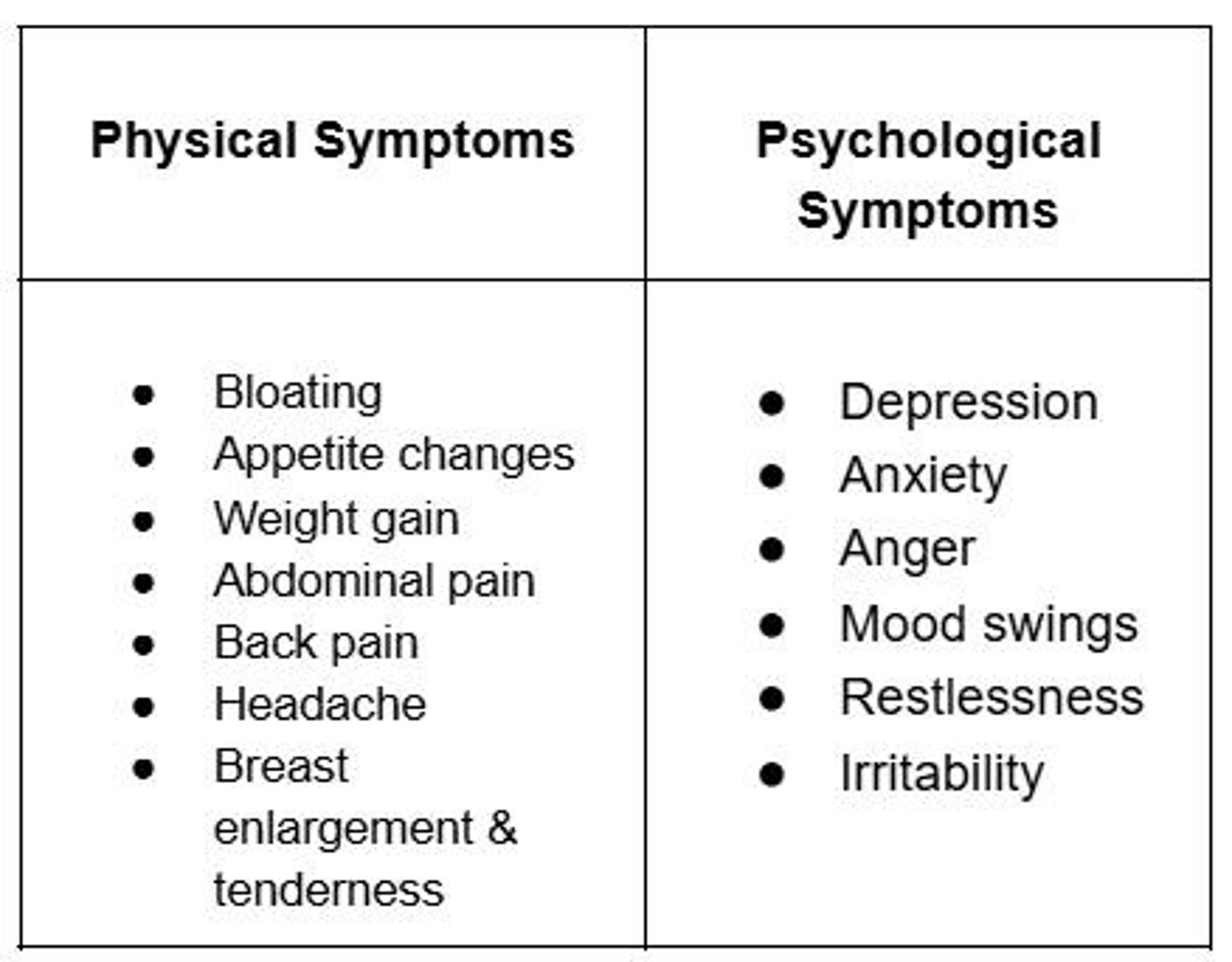
Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
Symptoms affecting 48% of reproductive-age women.
Estrus
Period when females are receptive to mating.
Nonestrus Period
Females reject mating advances aggressively.
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)
Severe mood changes before menstruation.
Oxidative Stress
Possible cause of PMS and PMDD symptoms.
Peripartum Depression
Depression occurring within one year of childbirth.
Romantic Love
Establishment of long-term emotional relationships.
Sexual Desire
Motivates mating and reproduction behaviors.
Oxytocin Functions
Stimulates contractions, milk release, and bonding.
Dopaminergic Reward System
Reinforces pleasure and bond formation.
Menstrual Cycle Control
LH and FSH regulate female reproductive cycles.
High Testosterone Effects
Increases interest in uncommitted sexual encounters.
Cultural Factors
Influence sexual behavior alongside hormones.
Evolutionary Perspective
Sexual receptivity may conceal female fertility.
Symptoms of PMS
Include mood swings and physical discomfort.
Bonding during Orgasm
Oxytocin release enhances partner connection.
Sexual Activity and Dopamine
Triggers pleasure and reinforces partner satisfaction.
Childbirth and Oxytocin
Facilitates labor and enhances maternal bonding.
Insula
Brain region dividing temporal, frontal, parietal lobes.
Sexual Desire
Correlated with caudal insula activity; sensory experiences.
Reproductive Success
Primary goal of sexual behavior.
Male Reproductive Strategies
Promiscuous due to potential for many offspring.
Romantic Love
Associated with rostral insula; future-oriented thinking.
Oxytocin
Hormone important for pair bonding and attachment.
Vasopressin
Hormone linked to social behaviors and bonding.
Prairie Voles
Monogamous species; strong pair bonds.
Montane Voles
Non-monogamous; abandon young early.
Female Reproductive Strategies
Selective mate choice due to reproductive costs.
Oxytocin Receptor Distribution
Influences monogamous behavior in voles.
Paternal Involvement
Improves offspring survival; promotes monogamy.
Cultural Norms
Rules dictating expected behaviors for specific sexes.