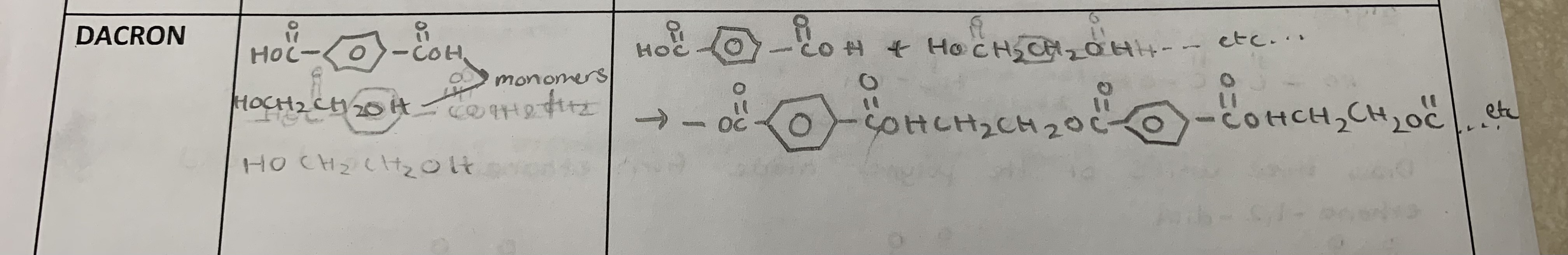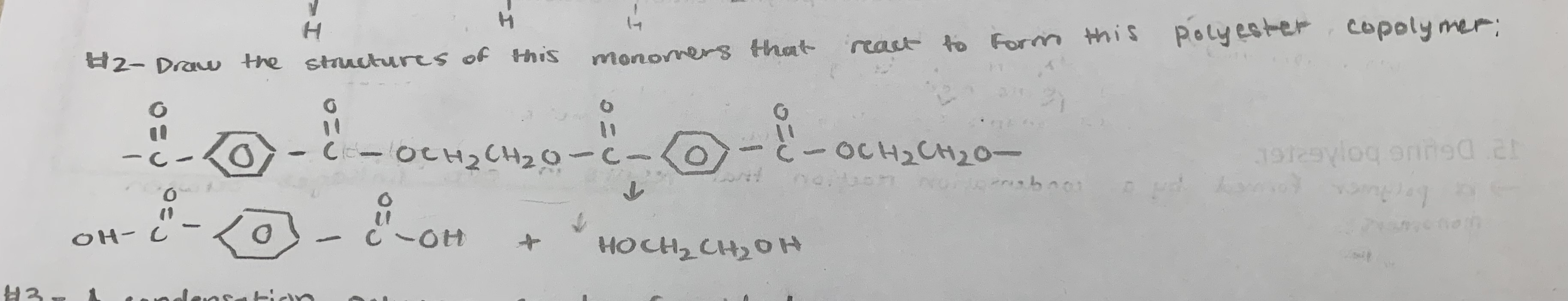Chapter 2 polymers
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Why are plastics ubiquitous (found everywhere)?
because they are lightweight, durable, inexpensive, and can be shaped into almost any form
Their versatility (ability to adapt) and wide range of useful properties make them suitable for countless products, do they are found everywhere in modern life
Make a T-chart to summarize the advantages and disadvantages of plastics
advantages
lightweight and easy to shape into many forms
strong, durable, and resistant to corrosion and chemicals
inexpensive to produce from petroleum feedstocks
Disadvantages
non-biodegradable (doesn’t decompose easily in env) therefore making it bad for the env
contributes to pollution
breaks down into microplastics that harm wildlife and enter foodchains
burning plastics releases toxic gases and greenhouse emissions
Make a T-chart to compare some natural polymers to synthetic polymers
natural polymers
made by all living things
examples include: DNA, RNA, starch, cellulose
biodegradable
used in biological structures and processes
synthetic polymers
man-made, produced in laboratories or factories
made from plants or petrochemicals
examples include: polyester and polyamide fabrics, containers made of polyethene or polypropene
non-biodegradable
used in everyday products like plastic bags, containers, fabrics, etc…
can be easily modified
Define:
a) polymer
b) monomer
c) addition polymer
d) homopolymer
e) copolymer
a) large, usually chain-like molecule that are built from small molecules/monomers
b) small molecules that make up polymers
c) the result of the reaction between monomers with unsaturated carbon-carbon bonds
in other words, very long organic molecule formed as the result of addition reactions between monomers with unsaturated carbon-carbon bonds
d) a polymer formed by reactions involving a single type of monomer
in other words, polymer of a single type of monomer
e) polymer made of two or more different types of monomers combined
Draw the monomer and polymer of the following (5 monomers in length):
polyethene
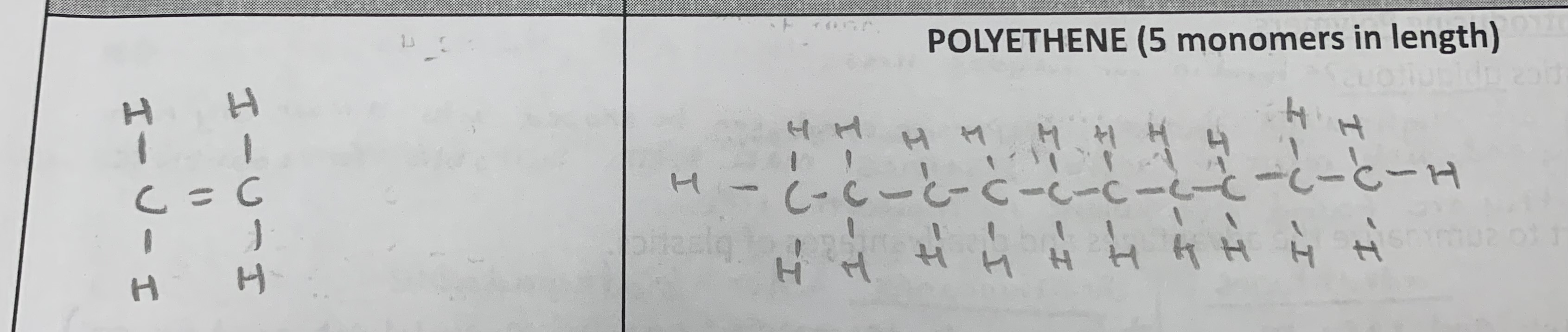
Draw the monomer and polymer of the following (5 monomers in length):
polypropene
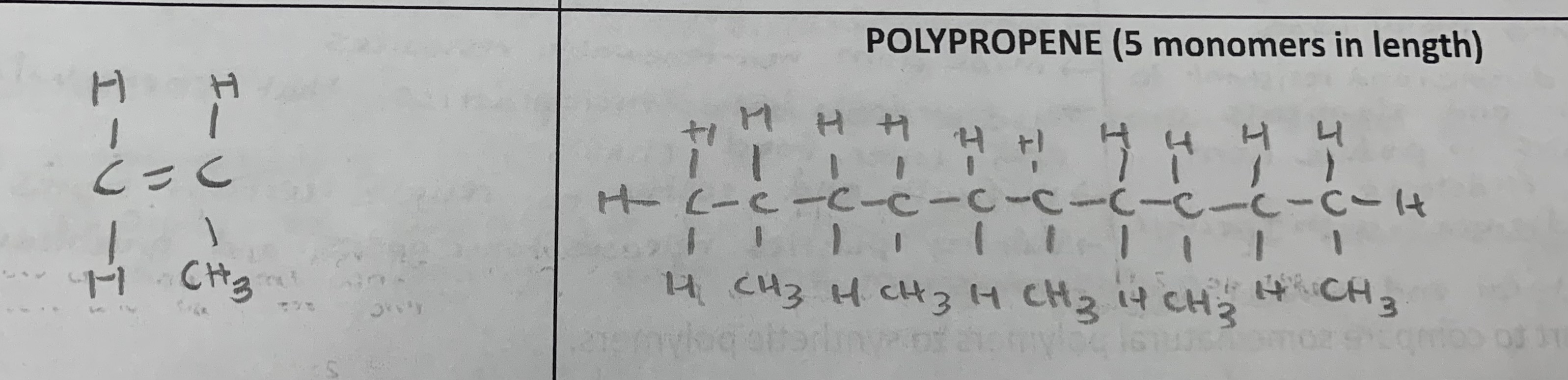
Draw the monomer and polymer of the following (5 monomers in length):
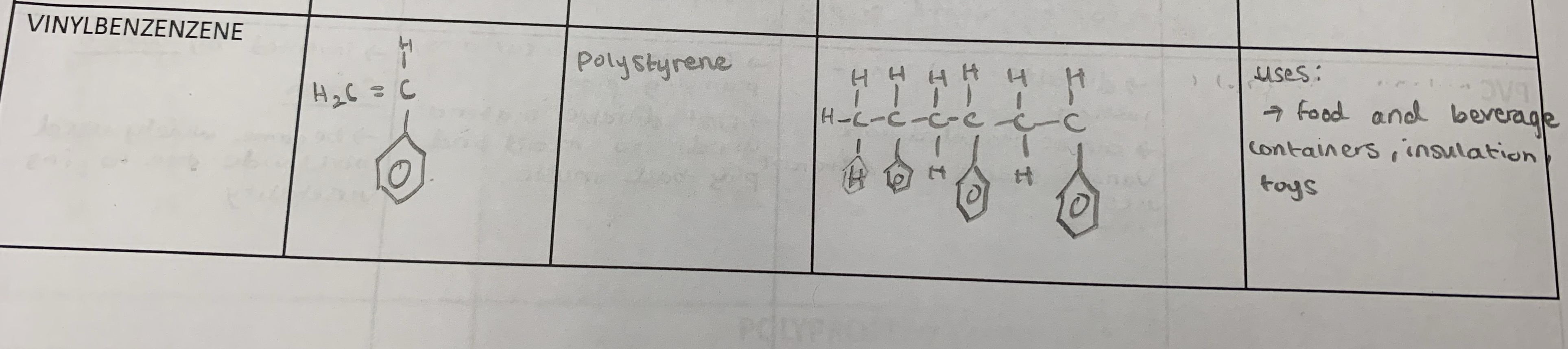
polystyrene
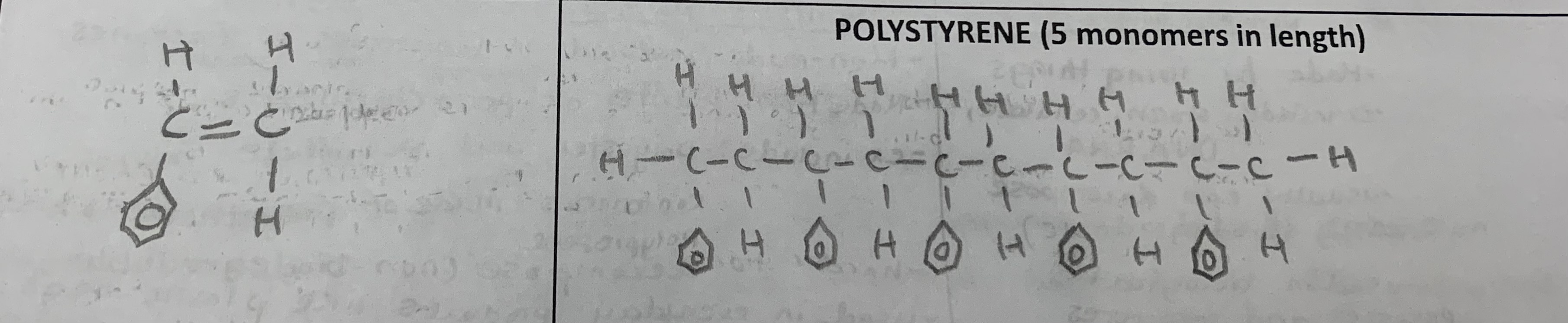
Name the 2 types of reactions involved in making copolymers
addition reactions
condensation reaction (where a molecule of water is eliminated as each new bond forms)
make a chart listing the advantages, applications, and others for the following polymer:
Vulcanized rubber
advantages:
stronger and more durable than natural rubber
less brittle in cold temps and less soft in heat
higher melting point
better resistance to wear
applications
used in battery boxes, pumps, dental plates, and fountain pens
most importantly used in automobile tires
Other
developed by Charles Goodyear (American inventor)
Made by heating natural rubber with sulfur (process called vulcanization)
improves the physical properties of natural rubber by forming cross-links between polymer chains
make a chart listing the advantages, applications, and other for the following polymer:
bakelite
advantages:
fully synthetic polymers (first of its kind)
lightweight
heat and moisture resistant
non-conductive and chemically stable
can be colored easily
helped reduce pressure on endangered species by replacing natural materials
applications
replaced wood, ivory, and ebony in many products
used for jewelry, dishes, telephones, toys, and other consumer/industrial products
others:
invented by Leo Hendrick
many bakelite items are now considered collectables
make a chart listing the advantages, applications, and other for the following polymer:
PVC
advantages
durable and long-lasting
can be modeled into various shapes for different uses
applications
flooring, shower curtains, plumbing pipes
first durable material used to record and play back music
others:
invented by Waldo Semon
became widely used worldwide due to its versatility
make a chart listing the advantages, applications, and other for the following polymer:
Celluloid
advantages:
could replace ivory in products like billiard balls
flexible and moldable
applications
billiard balls
celluloid film played a central role in the development of the movie industry
others:
one of the early synthetic polymers
helped reduce the use of natural ivory
make a chart listing the advantages, applications, and other for the following polymer:
Kevlar
advantages
extremely strong and lightweight
resistant to heat and corrosion
does not conduct electricity
applications
used in bulletproof vests and other protective gear
found in tires, ropes, cables, and sports equipment
others:
developed by Stephanie Kwolek at DuPoint in 1965
first used commercially in early 1970s
Kevlar is a type of para-aramid synthetic fiber
What is an addition polymer? Give an example of a very common addition polymer
a very long organic molecule formed as the result of addition reactions between monomers with unsaturated carbon-carbon bonds
a very common example is what plastic is made of, being polyethene
Draqw the formula of the monomer, the name of the polymer, formula of polymer (3 monomers in length), and applications for the following monomer:
chloroethene
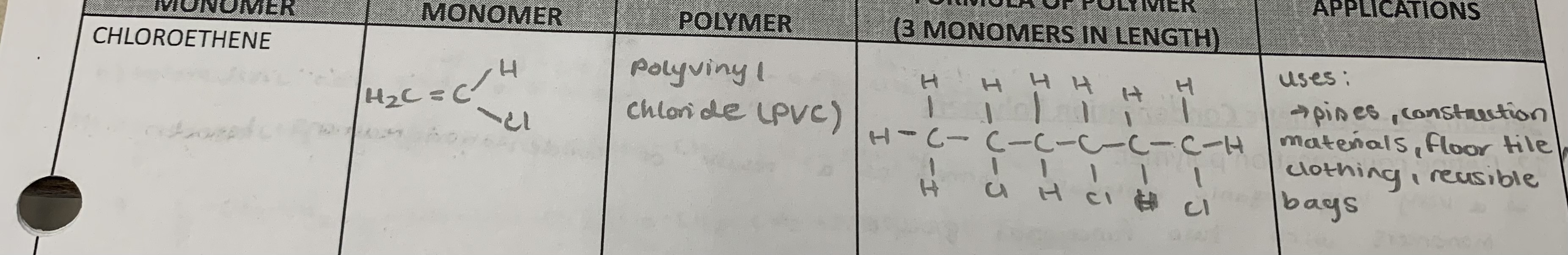
Draw the formula of the monomer, the name of the polymer, formula of polymer (3 monomers in length), and applications for the following monomer:
tetrafluoroethene
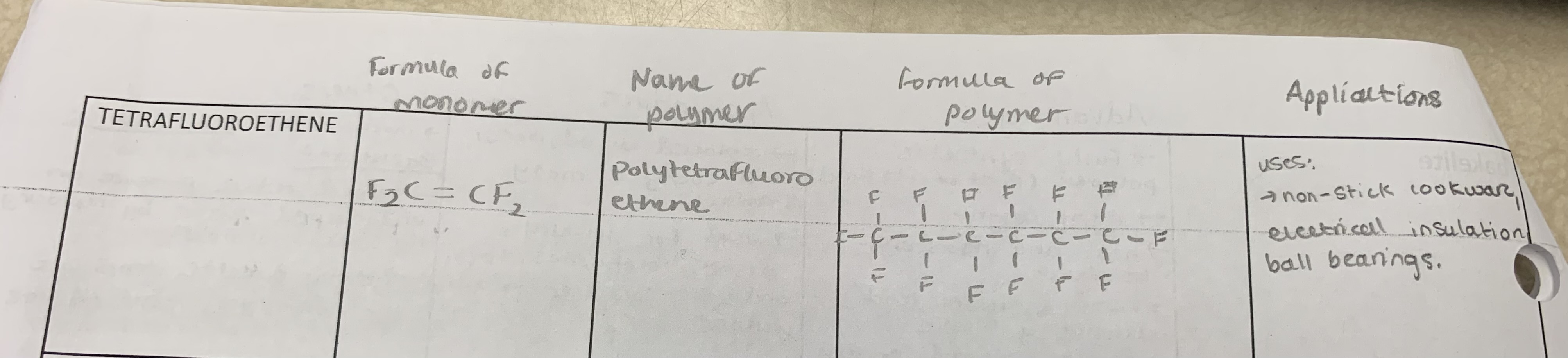
Draw the formula of the monomer, the name of the polymer, formula of polymer (3 monomers in length), and applications for the following monomer:
vinzylbenzene


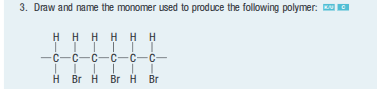
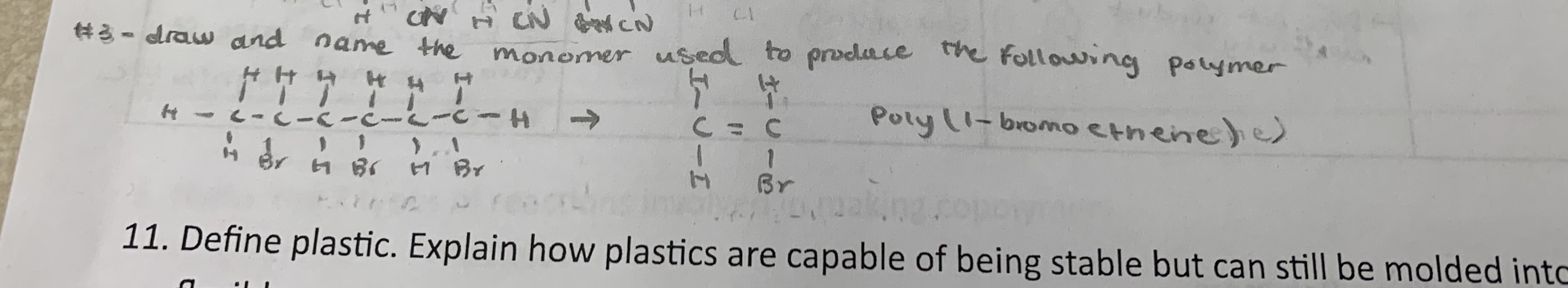
Define plastics. Explain how plastics are capable of being stable but can still be molded into shapes and be flexible.
plastic →a synthetic substance that can be moulded (often under heat and pressure) and that can retain its shape
plastics are stable because their long polymer chains are chemically strong and resistant to breaking down, but they are also flexible and moldable because when heated, their molecular motion increases, allowing their chains to glide past each other
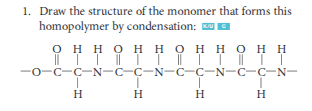
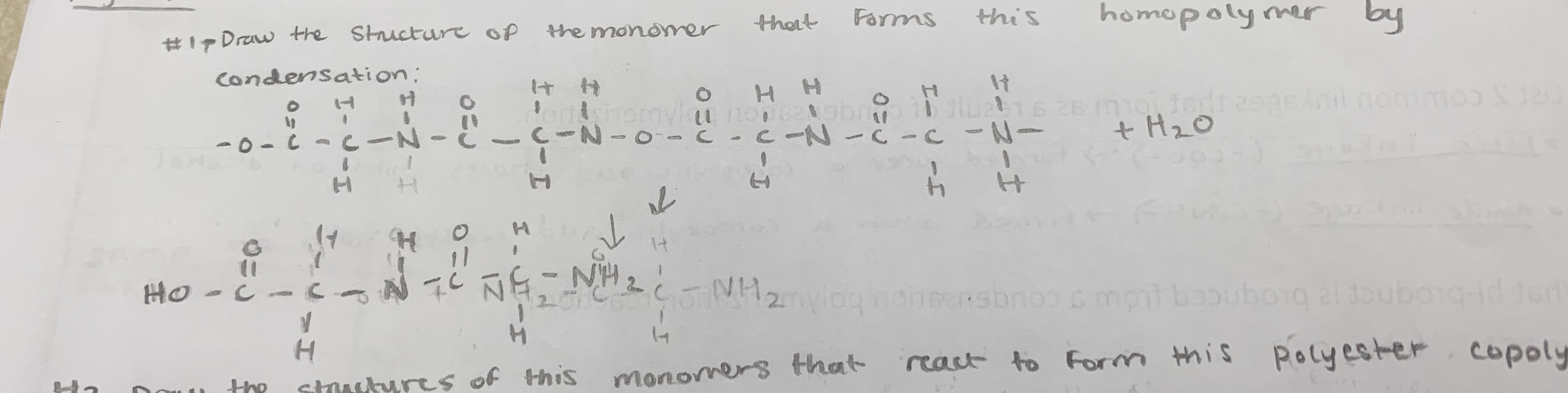
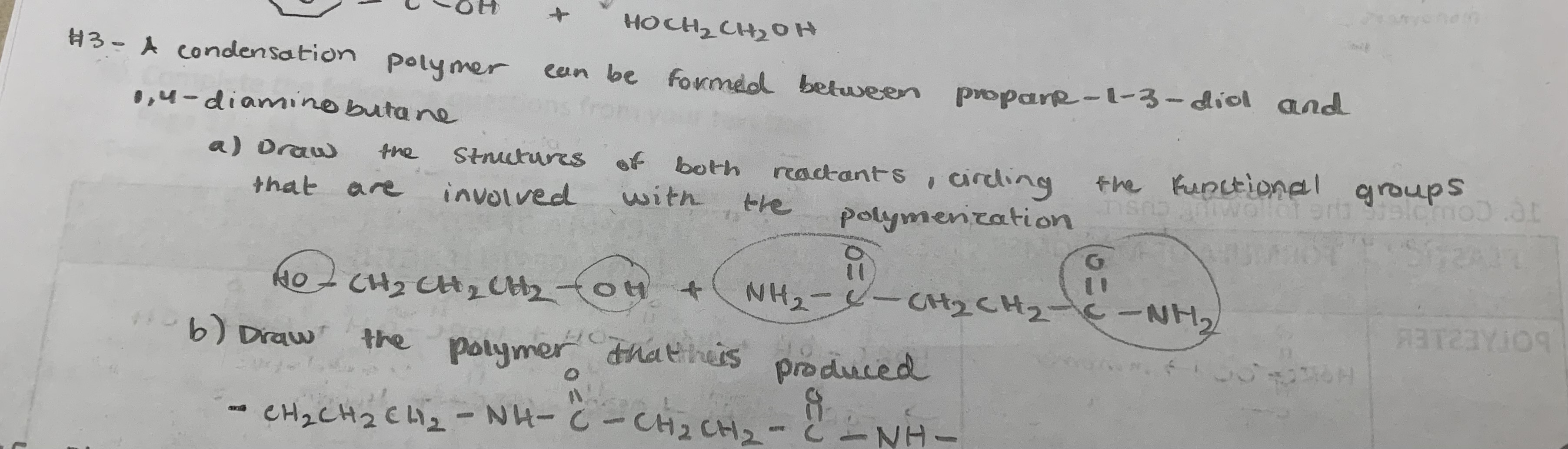
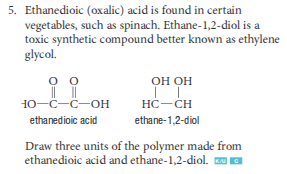
Define condensation polymer
a very long organic molecule formed as a result of condensation reactions between monomers with two functional groups
List 2 common linkages that form as a result of condensation polymerization
ester linkage (-COO-) →formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol
amide linkage (-CONH-) →formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an amine
What bi-product is produced from a condensation polymerization reaction?
water (H2O)
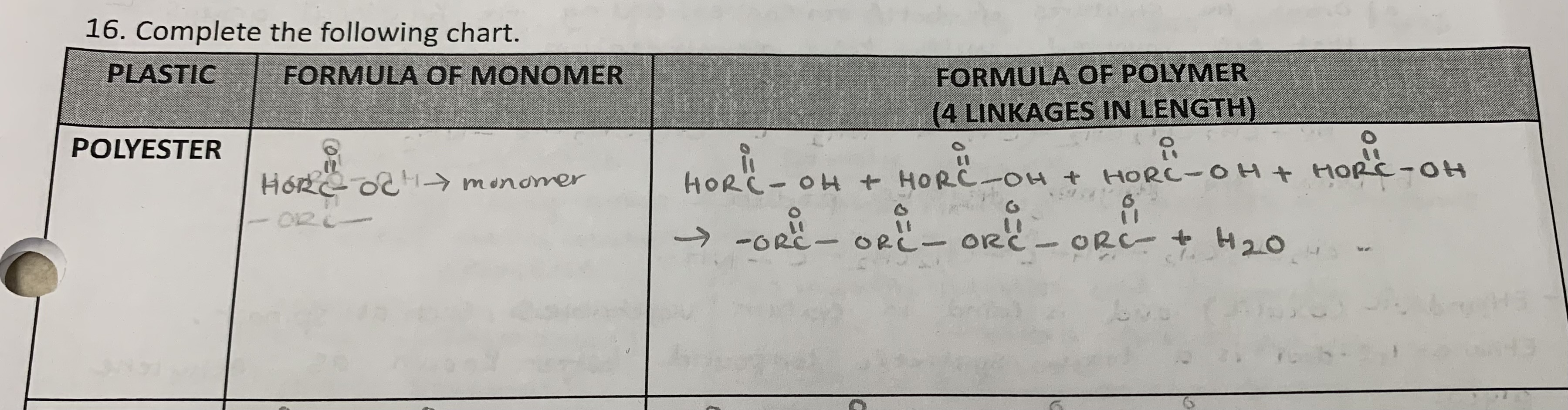
Define polyester
a polymer formed by a condensation reaction that results in ester linkages between monomers
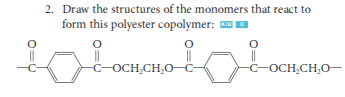
Draw the formula of the monomer and the polymer ( 4 linkages in length) for the following plastic:
polyester
Draw the formula of the monomer and the polymer ( 4 linkages in length) for the following plastic:
dacron