Human Anatomy Lab 4
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
temporomandibular joint syndrome
a group of conditions, typically caused by painful spasms of the chewing muscles, that result in the ear and face pain, jaw muscle tenderness, popping or clicking sounds during mouth movement, and joint stiffness; these disorders often stem from factors such as stress-induced teeth grinding, physical injury to the joint, or poor alignment (occlusion) of the teeth.
Sinusitis
inflammation of the paranasal sinuses typically caused by viral, bacterial, or fungal infections; occurs when the passages connecting the sinuses to the nasal cavity become blocked by swollen nasal mucosa, leading to a partial vacuum or painful pressure from accumulated fluid, which often results in localized sinus headaches
Osteosarcoma
an aggressive form of bone cancer arising from connective tissue cells that primarily affects individuals aged 10 to 25; it typically originates in the long bones of the limbs–frequently near the knee–where cancerous, mesenchymal-derived osteoblast-like cells rapidly secrete disorganized osteoid; this growth destroys the bone by eroding the internal medullary cavity and the external compact bone, often metastasizing to the lungs, which is the leading cause of death associated with the disease
Mastoiditis
infection in the mastoid air cells that can spread form the throat to the middle ear to the mastoid cells and to the brain
Deviated Nasal Septum
a septum that is markedly off center; result of trauma to the nose and can cause difficulty in breathing through the nose, as well as nasal congestion, frequent nosebleeds, and frequent sinus infections
Craniotomy
surgery to remove part of the cranium, usually done to gain access to the brain (e.g., remove a brain tumor, a blood clot, or a sample of brain tissue for a biopsy); the piece of skull is removed by drilling a series of round holes through the bone at regular intervals to outline a square and then cutting between these holes with a string-like saw; at the end of the operation, the square piece of bone is replaced, and it heals normally
Cleft palate/lip
occurs when right and left halves of the palate fail to join medially. This deviation leaves an opening between the mouth and nasal cavities that interferes with sucking and thus the baby’s ability to nurse. It can also lead to inhalation of food into the nasal cavity and lungs, possibly resulting in pneumonia. This condition can be repaired surgically
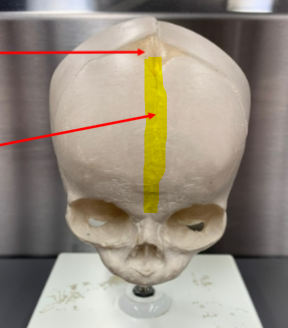
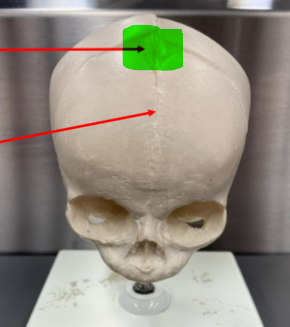
metopic/frontal suture
runs continuous with the sagittal suture, between the two halves of the frontal bone; this suture only persists if the frontal bones do not fuse; suture is found in the neonatal skull
metopic/frontal suture
mastoid/posterolateral fontanelle (paired)
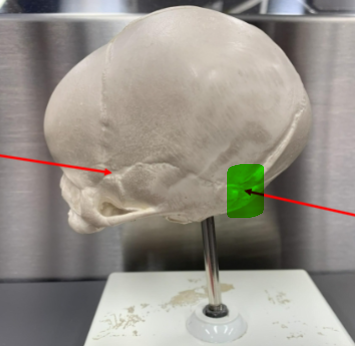
mastoid/posterolateral fontanelle (paired)
at the junction of the parietal, occipital, and the temporal bones
sphenoid/anterolateral fontanelle (paired)
at the junction of the frontal, parietal, temporal, and sphenoid bones
sphenoid/anterolateral fontanelle (paired)
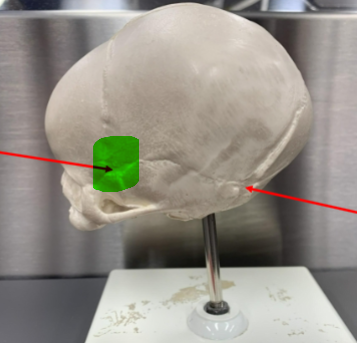
occipital/posterior fontanelle (unpaired)
at the junction of the occipital and parietal bones, along the midsagittal plane
occipital/posterior fontanelle (unpaired)
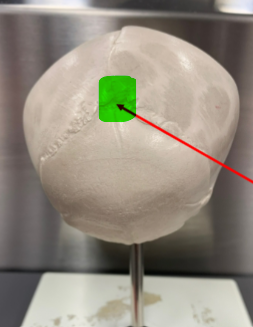
frontal/anterior fontanelle (unpaired)
at the junction of the frontal and the parietal bones
frontal/anterior fontanelle (unpaired)
stylomastoid foramen
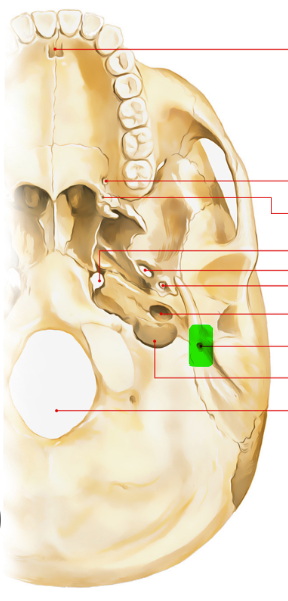
facial nerve (CN VII)
what exits the skull through the stylomastoid foramen
inferior alveolar nerve (CN V)
what passes through the mandibular foramen
mandibular foramen of the mandible bone
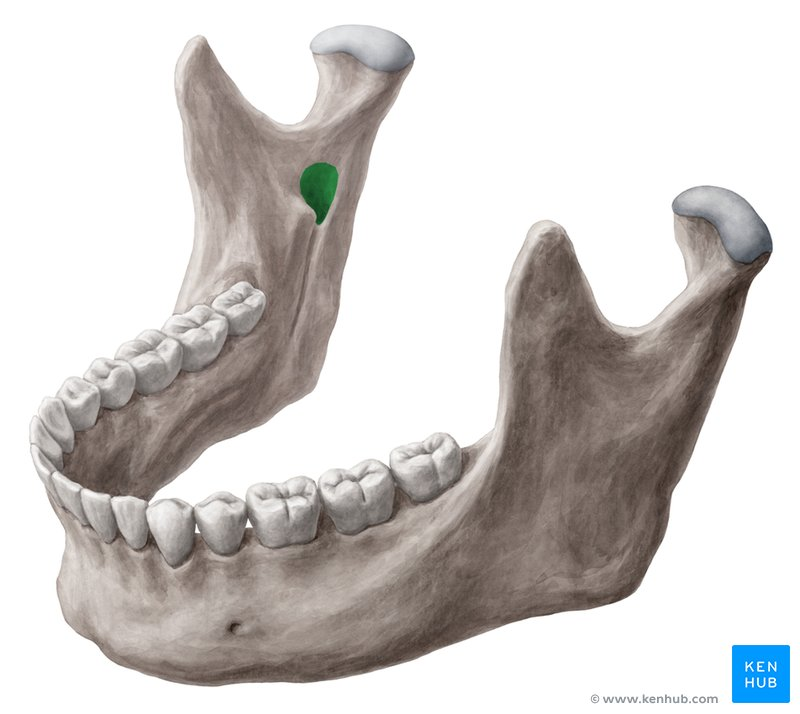
nasopalatine nerve
what passes through the incisive foramen
incisive foramen of the maxillary bone
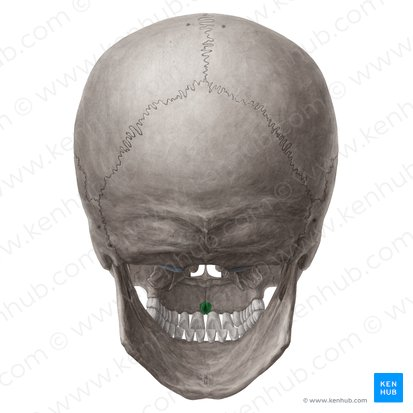
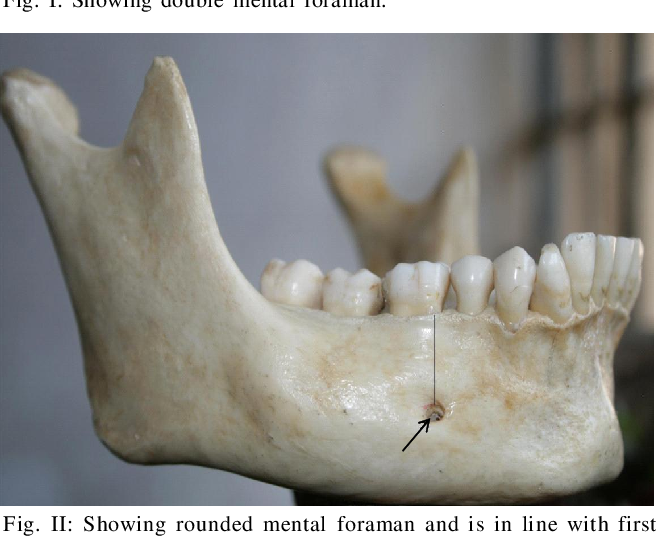
mental nerve (CN V)
what passes through the mental foramen
mental foramen of the mandible bone
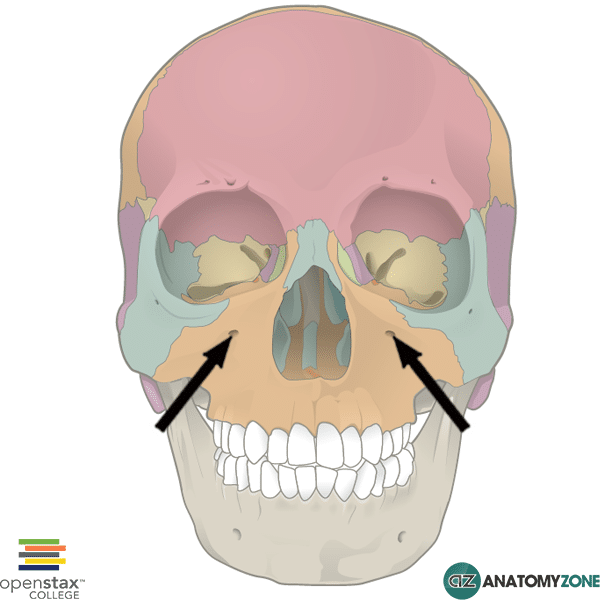
trigeminal nerve (CN V)
what passes through the infra-orbital foramen
infra-orbital foramen of the maxillary bone
hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
what passes through the hypoglossal canal
hypoglossal canal
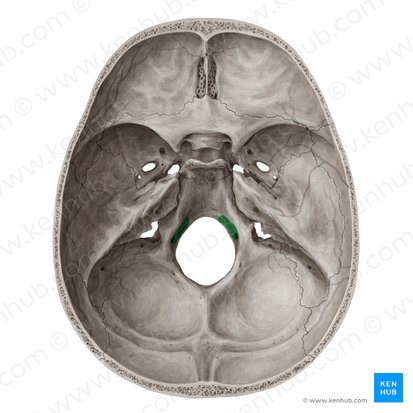
accessory nerve (CN XI), vertebral arteries Rt & Lt
what passes through the foramen magnum
foramen magnum
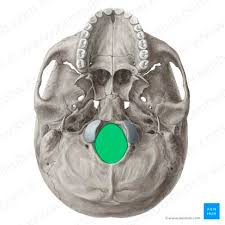
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), vagus nerve (CN X), accessory nerve (CN XI), spinal motor and cranial motor component of internal jugular vein
what passes through the jugular foramen
jugular foramen
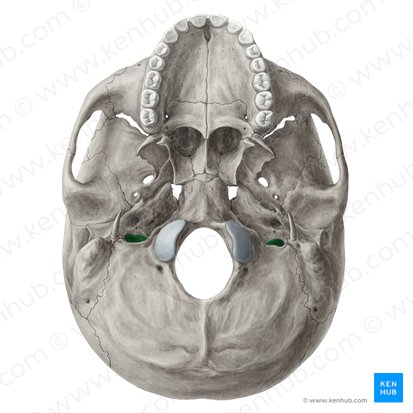
internal carotid artery
what passes through the carotid canal
carotid canal
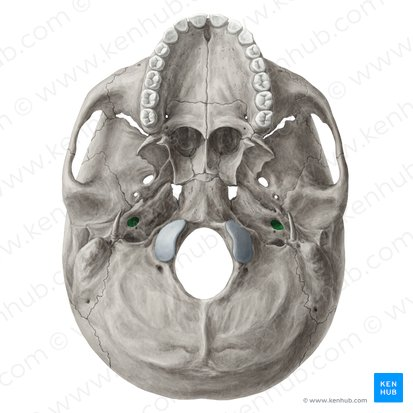
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII), facial nerve (CN VII)
what nerves enter the skull through the internal acoustic/auditory canal
internal acoustic/auditory canal
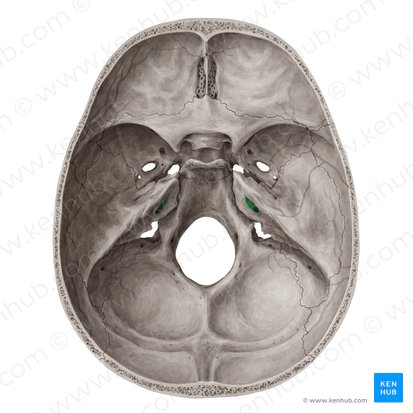
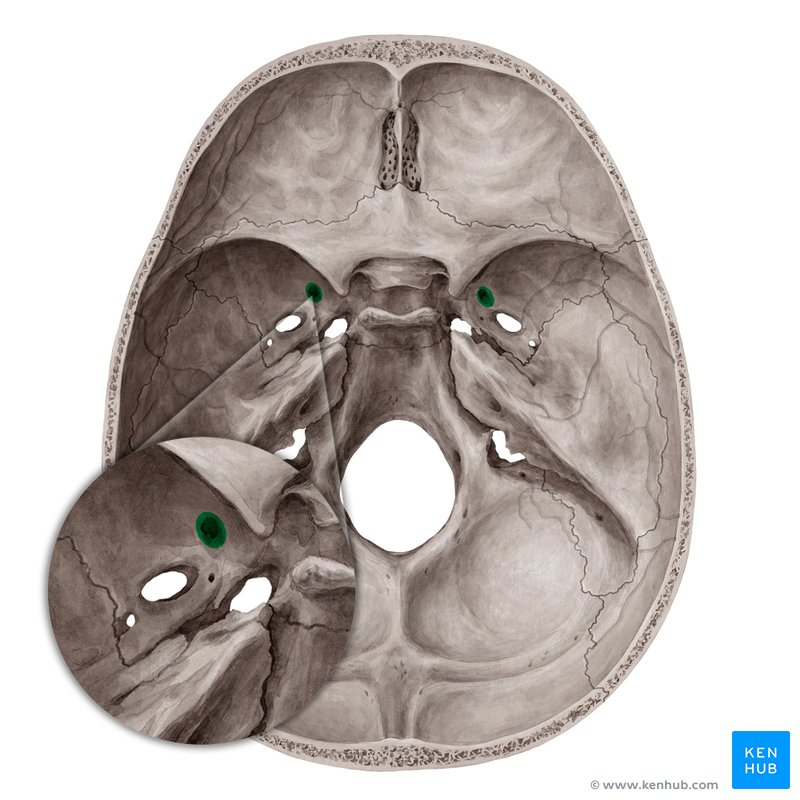
foramen lacerum
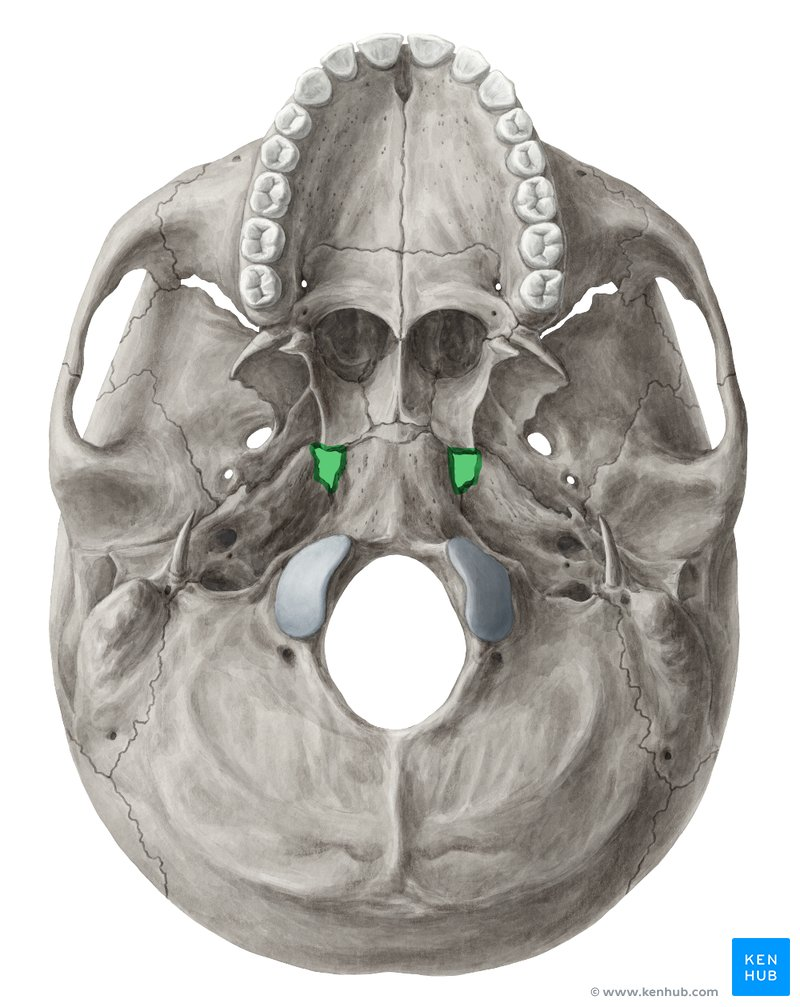
middle meningeal artery
what passes through the foramen spinosum
foramen spinosum
mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)
what passes through the foramen ovale
foramen ovale
maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)
what passes through the foramen rotundum
foramen rotundum
oculomotor nerve (CN III), trochlear nerve (CN IV), ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), abducens nerve (CN VI)
what passes through the superior orbital fissure
superior orbital fissure

optic nerve (CN II), ophthalmic artery
what passes through the optic canal
optic canal
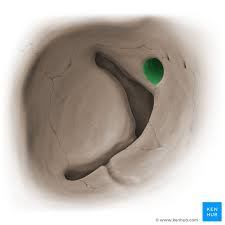
olfactory nerve (CN I)
what passes through the cribriform plate
cribriform plate
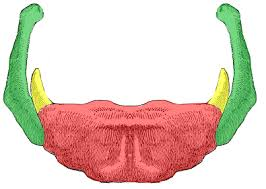
lesser cornua of the hyoid bone
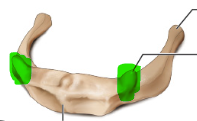
greater cornua of the hyoid bone
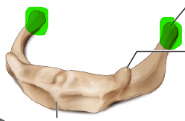
hyoid bone
alveolar processes of the mandible bone
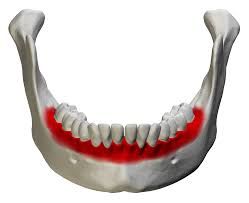
alveoli of the mandible bone
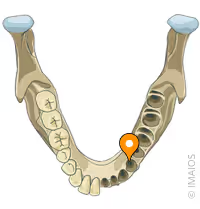
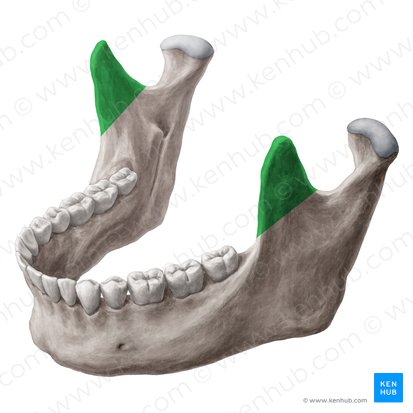
coronoid processes of the mandible bone
condylar processes of the mandible bone
ramus of the mandible bone
mandible bone
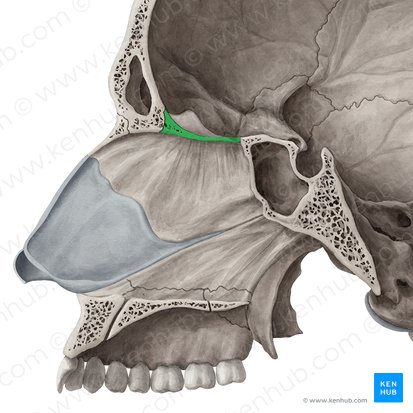
vomer bone
inferior nasal concha bone
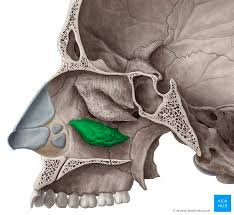
nasal bones
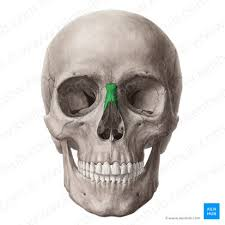
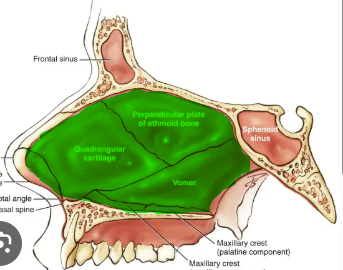
nasal septum
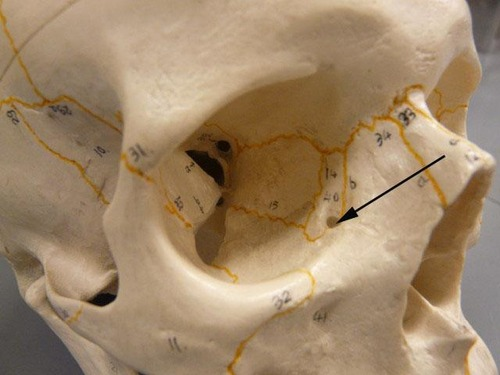
nasolacrimal canal of the lacrimal bone
lacrimal bones
temporal process of the zygomatic arch of the zygomatic bone
zygomatic arch of the zygomatic bone
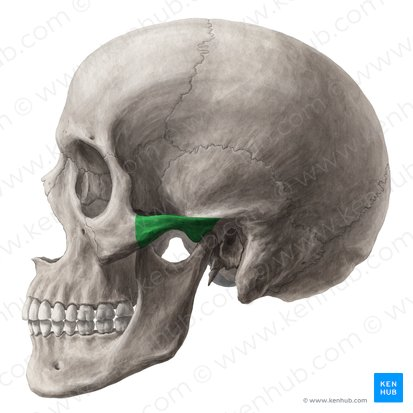
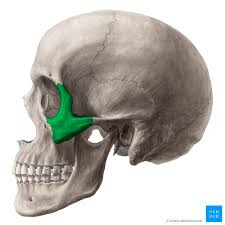
zygomatic bone
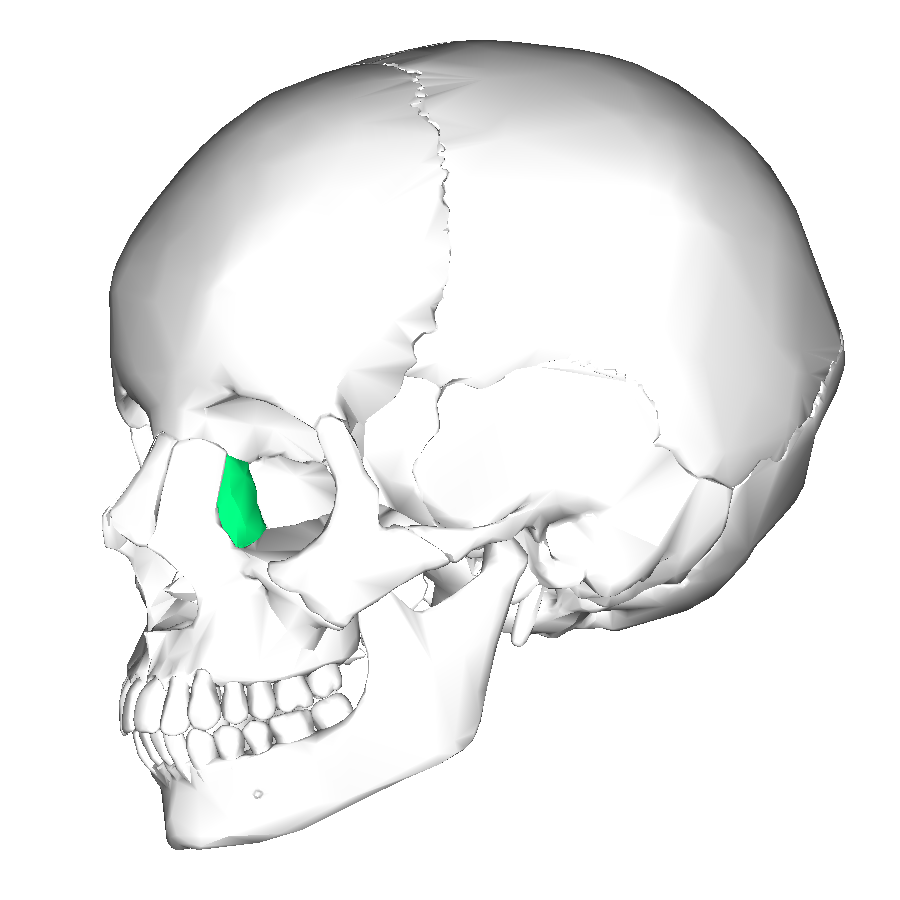
perpendicular plate of palatine bone
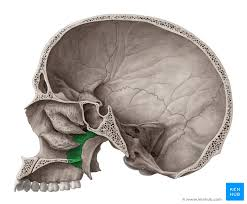
horizontal plate of palatine bone
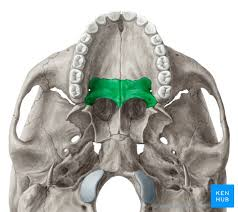
greater palatine foramen of palatine bone
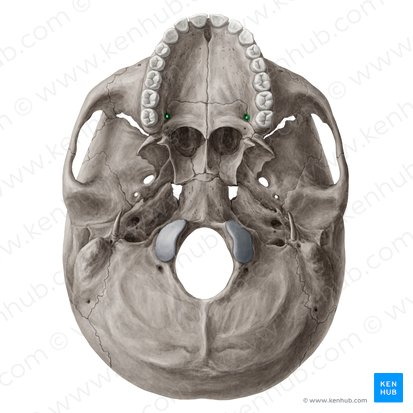
palatine bones
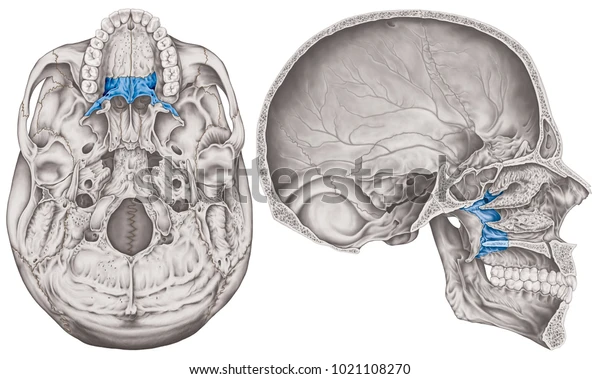
inferior orbital fissure
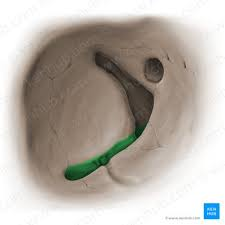
alveolar processes of the maxillary bone
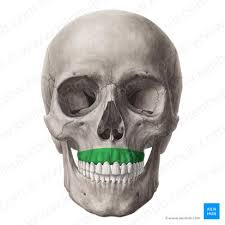
alveoli of the maxillary bone
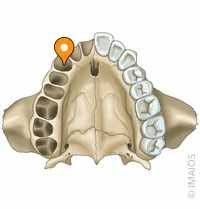
palatine/palatal processes of maxillary bone
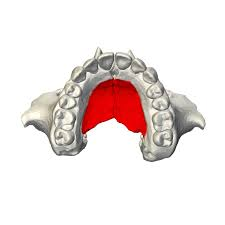
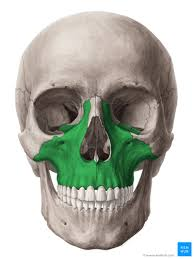
maxillary sinus of maxillary bone
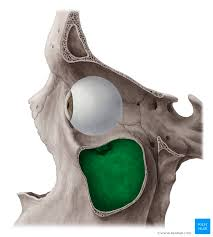
maxillary bones