Psych 275 PART 1 (Weeks 1-6)
1/226
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
227 Terms
Mechanism (Causation)
How does the behaviour occur
Ontegeny
How does the behaviour develop in the individual
Adaptive Value
What function does the behaviour serve
Phylogeny
How did the behaviour evolve in the species
Niko Tinbergen’s 4 Q’s
Mechanism, Ontogeny, Adaptive Value, Phylogeny
Reductionist techniques
This is needed to study the brain, in order to try and control variation and simplify the incredible complexity present in the brain
Human subject pros
Communication, low maintenance, cost effective, have the brain we are trying to study
Human subject cons
Need ethics, uncontrolled lifestyle
Animal subject pros
Can be invasive, direct measurement/manipulation, comparative approach, controlled lifestyle, simple NS
Animal subject cons
No communication, high maintenance, ethics cost
3 R’s
Reduce, refine, replace (trying to use less and less animal subjects)
Descriptive Research
Observing - creates a snapshot of the current conditions. Able to show the full picture but unable to assess relationships between the various variables present
Correlational Research
Assesses the relationships between variables present. Can assess them in everyday life scenarios but unable to definitively prove causation
Experimental Research
Assesses the causal relationship between manipulated variables on a dependent variable. Difficult to simulate real world scenarios, as so many of the conditions need to be controlled
Between subjects
2 different groups participate in different stages of the experiment
Within subjects
The same group goes through all the stages of the experiment
Analogous traits
Similar traits which evolved separately due to convergent evolution. Not related.
Homologous traits
Traits which arose from the same origin (related)
Cerebrum - Brain Stem size
Best indicator of intelligence. Bigger the number = smarter the animal.
Epigenetics
The turning “off and on” of genes, through various factors or tagging done at the molecular level. In other words, just because something is present in our genotype does not mean it will be expressed
1%
Only __ of our DNA actually codes for genes
99%
__ of our DNA are introns, mRNA and serve to regulate coding
Histones (beads on a string)
We need relaxed DNA, in the form of ______ in order to begin transcription.
Chromosomes or Chromatin
When DNA is in the form ______ it is too big to undergo transcription
Heterochromatin
DNA is unable to undergo transcription
Euchromatin
Transcription is possible, genes can be expressed
Structuralism
A now unpopular theory that aimed to understand the human mind by breaking it down into its simplest components to understand the “structure”
Functionalism
A more popular theory that treats the whole mind as a computer, and tries to understand the purpose/development of mental process.
CNS
Brain and spinal cord
PNS
Motor and sensory nerves outside of brain and spinal cord
Somatic Nervous System
Voluntary reactions/movements.
Autonomic Nervous System
Involuntary actions and changes to homeostasis. 2 types
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The efferent nerves in the autonomic division which aid in digestion, relaxation, energy storage etc. Winding down. Nerves from Cranial/Sacral
Sympathetic Nervous System
The efferent nerves in the autonomic division which stop digestion, increase heart rate, increase breathing, constrict pupils etc. Winding up. Nerves from Thoracic and lumbar
Afferent Nerves
Approach the CNS, bring info (Sensory)
Efferent Nerves
Exit the CNS, do actions (motor)
Cranial nerves
12 pairs of nerves in periphery that originate on ventral surface of brain instead of spinal cord. 2 purely sensory (eyes and nose), rest are autonomic
Meninges
3 layers, providing protection to the brain underneath the skull
Dura Mater
First layer of brain protection after skull. Hard, contains sinus’ to clean waste.
Arachnoid Mater
Second layer of brain protection, weblike, contains subarachnoid space with blood vessels and CSF
Pia Mater
Covers entire area of brain (even in between folds), third layer of protection
CSF
Perfect cocktail of nutrients, ions etc for the brain, also provides some shock absorption
Ventricles
4 fluid filled cavities/gaps within the brain, produce and circulate CSF
Blood brain barrier
Tightly packed cells surrounding the blood vessels and glial cells. Electrochemically isolates the PNS from the CNS, keeps “bad” molecules from the entering the brain, semipermeable.
High lipid solubility
Molecules (drugs for ex) which possess this quality are more easily able to pass through the blood brain barrier
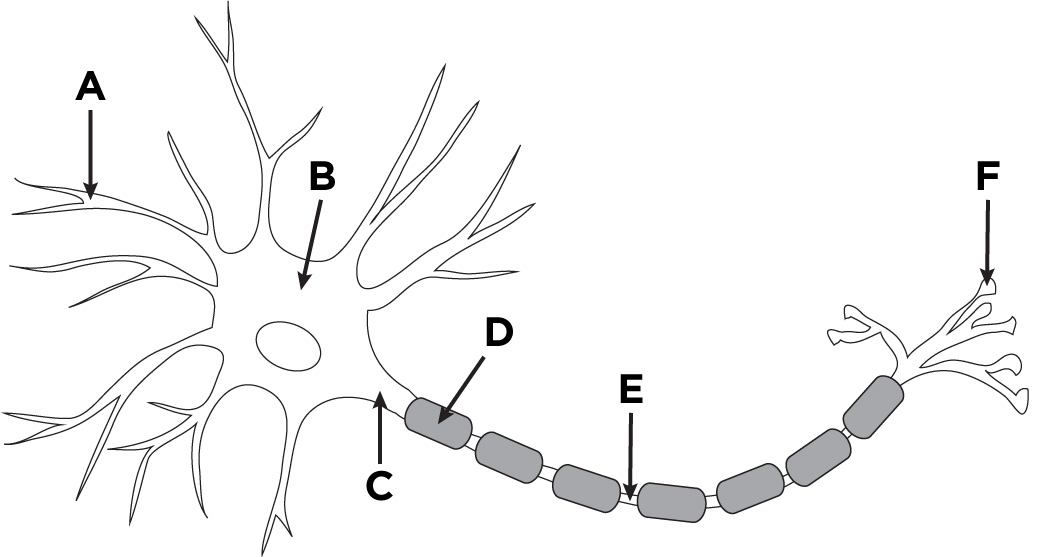
Dendrite
A
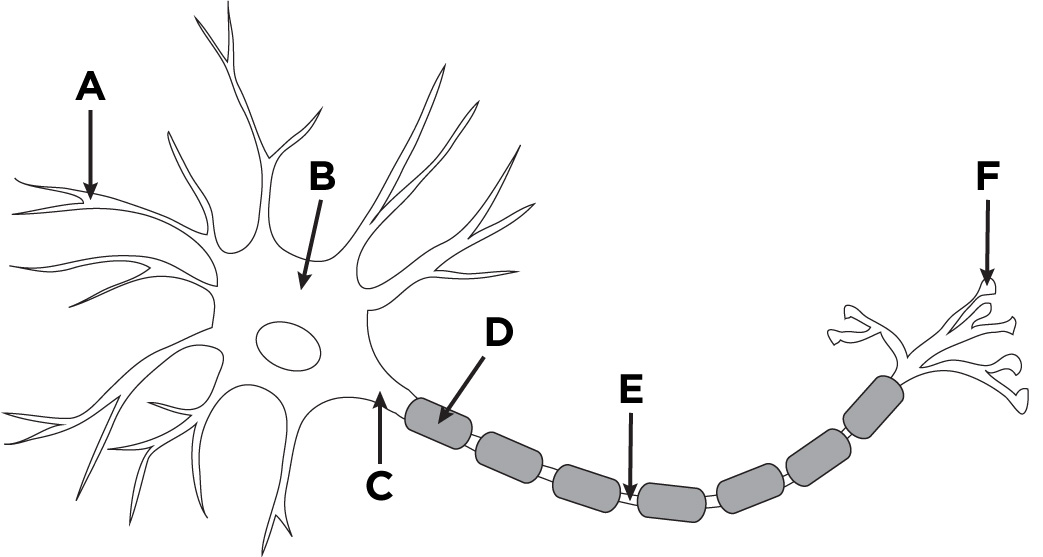
Axon
D + E
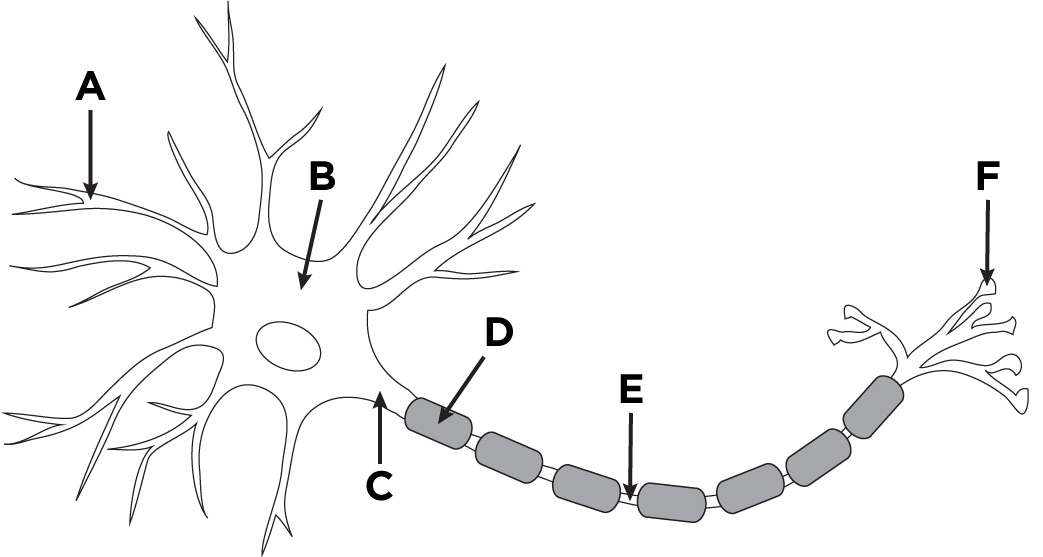
Nodes of Ranvier
E
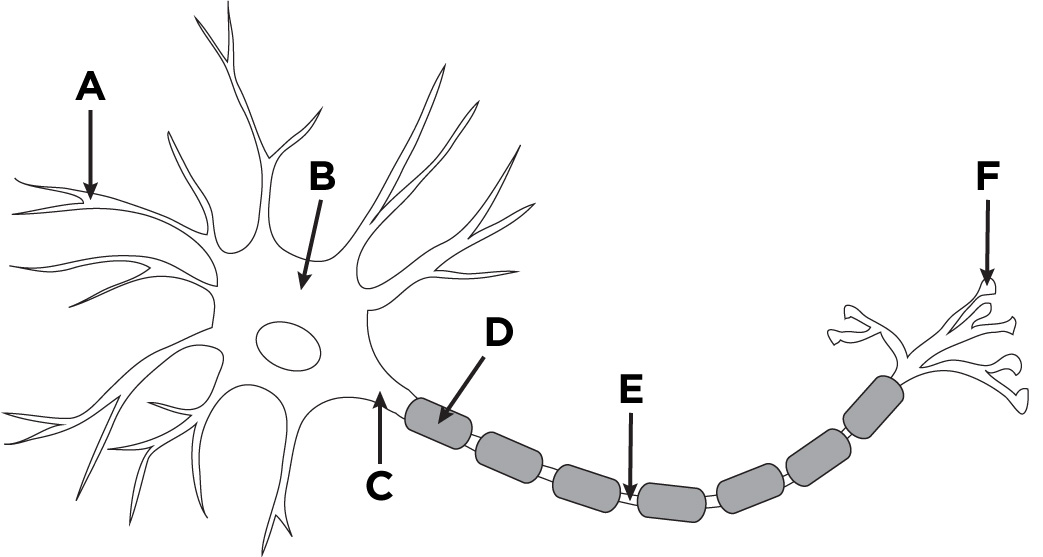
Soma (Cell body)
B
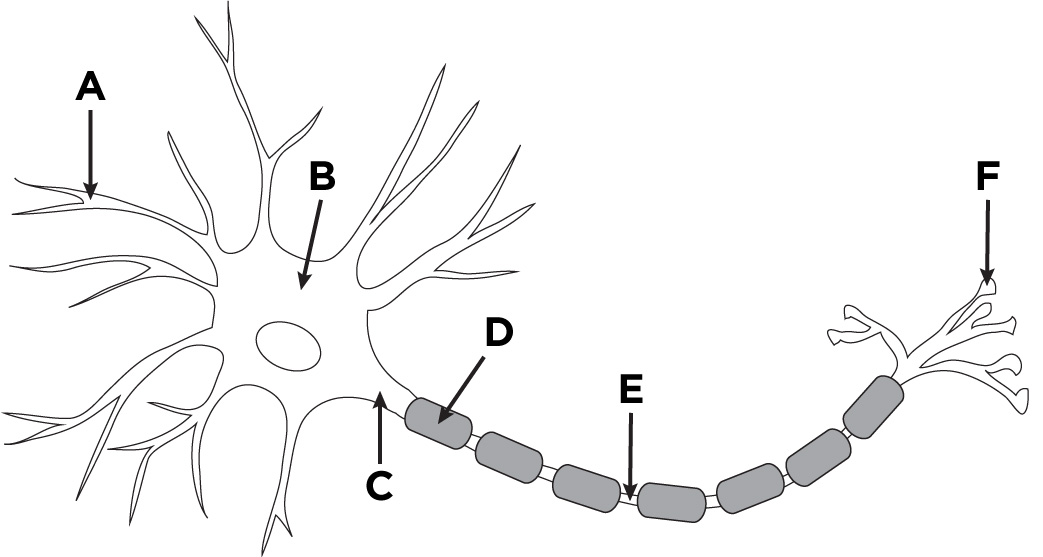
Buttons
F
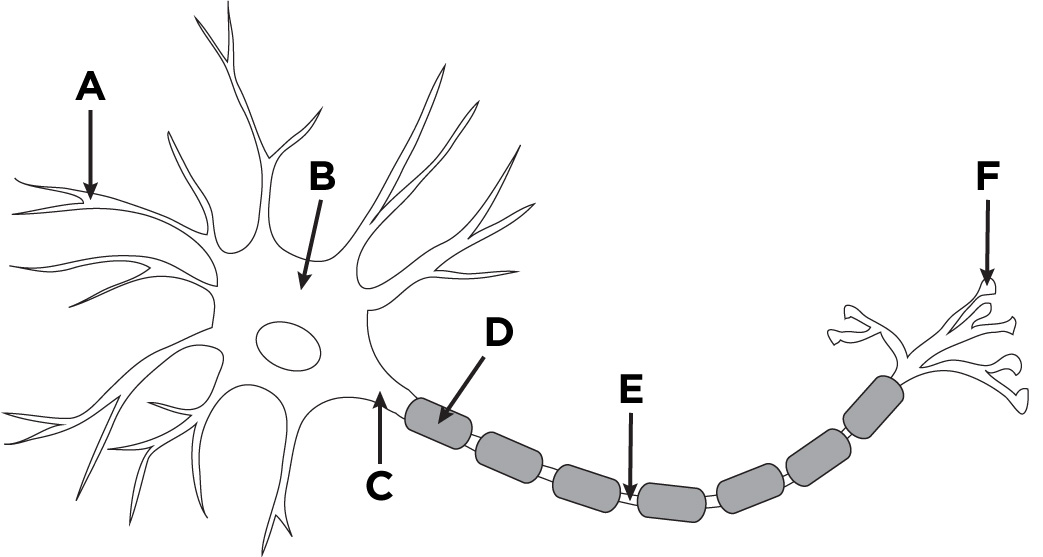
Axon Hillock
C
Glia
Nervous system cell that is able to regenerate/divide, makes up 90% of brain and do not form synapses
Astrocytes
Largest type of glia cell, thought to be correlated with cognition, clean up neurotransmitters, able to rearrange synapses, all connected and star shaped. Very important in GABA cleanup
Microglia
Very small glia cell, macrophage, mediates cell death and has roles in immunity
Oligodendrocytes
Glia cell found only in the CNS, wraps around axons and forms the myelin sheath and white matter in the brain
Schwann Cells
Glia cell found only in the PNS, guides axon regeneration and forms myelin sheath
First axis
Anterior and Posterior (from front to back) - flips when changing from brain to spinal cord
Second axis
Dorsal and ventral (top to bottom) - flips when changing from brain to spinal cord
Third axis
Medial (inner side) vs Lateral (outer side)
Axial Plane
Top - down view
Coronal Plane
Front on view
Sagittal Plane
Side view
Cervical cord
Top region of spinal cord, rich in white matter
Thoracic cord
Second region of spinal cord
Lumbar cord
Third region of spinal cord
Sacral cord
Lowest region of spinal cord, highest grey : white matter ratio
3
Early brain development starts as ___ swellings
5
Once the brain further develops it forms ___ swellings/areas
Mylencephalon
Most posterior, makes up the lower part of the hindbrain. Contains medulla, reticular formation
Reticular formation
The central core network of brain stem made of 100 nuclei located in the myelencephalon. Involved in sleep, attention, movements, muscle tone, circulatory and respiratory reflexes.
Metencephalon
Posterior, located in the front part of hindbrain. Contains the cerebellum (tiny brain) and the pons, as well as ascending and descending tracts
Mesencephalon
The midbrain, where the reticular formation ends. Contains the tectum roof (inferior and superior colliculi), and tegementum (red nucleus, substantia nigra, periaqueductal grey)
Diencephalon
Back part of frontal lobe. Contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary, mammillary bodies and optic chiasm
Telencephalon
Biggest portion of brain. Contains the corpus callosum, Limbic system (hippocampus, amygdala, fornix and septum), basal ganglia and the 4 lobes.
Outside cell
Where is Na+ concentration higher?
Inside cell
Where is K+ concentration higher?
Sodium/K pumps
Moving 3 Na out and 2 K in via 1 ATP
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potentials
Cause the neuron to depolarize and get closer to an action potential. Able to be built upon (graded response). Causes Na to flow in
Inhibitory Postsynaptic potentials
Causes the neuron to hyperpolarize. Graded response, Cl ion flow inwards.
Bigger IPSP or EPSP
Stronger stimuli will produce
decay over time
Unlike AP, EPSP and IPSP gradually _______
Spatial summation
Occurs at axon hillock, where multiple different IPSP or EPSP are combined together at a given time to determine what action the cell should take. Oftentimes EPSP and IPSP cancel each other out
Temporal Summation
Where a single input is monitored and if it is sending rapid/multiple signals, a EPSP or IPSP is much more likely to occur.
Action Potentials
After the cell EPSP goes past -65 mV, an AP is generated where the cell is depolarized in a domino effect to pass along a message - does not degrade along the axon due to gated voltage channels. Has an equal strength (all or none)
Na+ Voltage gated ion channels
Initially open due to AP to allow sodium in, but close soon after depolarization to allow the domino effect to continue along and make it all the way through the axon
K+ Voltage gated ion channels
Open after the sodium channels, allow for K+ to rush out of the cell. Remain open for a while after sodium channels close to allow the cell to re-polarize appropriately
Absolute Refractory period
1 msec post AP, blocks the Na channels and prevents the signal from travelling backwards back towards the soma
1000x per second
Max neuron firing rate
Relative refractory period
AKA hyperpolarization - cell still able to fire, it just needs a stronger AP during this time
Increase speed of transmission
Increase myelination and diameter of axon
Saltatory conduction
Ion exchange in myelinated cells, happens at the nodes of ranvier (this is why they are faster, since it concentrates this process to only specific places along the axon - “jumping”)
Orthodromic conduction
Normal spreading of the signal (hillock to buttons)
Antidromic conduction
Reverse spreading of the signal (buttons to hillock/soma)
Neurotransmitter steps
AP reaches axon terminal, Ca floods cell, NT release and binding, receptors cause PSP, NT reuptake/recycling
MS (multiple sclerosis)
Scarring of the myelin, attacks both schwann and oligocytes
Axosomatic
Common for inhibitory signals, as this overrides PSP from generating an AP
Directed synapse
Pre and post synaptic neuron are close together and form a tiny cleft where NT are released into. Most common
Undirected synapse
NT released as “beads on a string” along the length of the axon (Varicosities). NT have a long way to travel, common in monoamines
Muscles NT
Only acetylcholine (Ach).
Monoamines
CLASSICAL NT group all derived from either phenylalanine/tyrosine (Dopaminem = DA, norepinephrine = NE, epinephrine = E) or from tryptophan (5HT = serotonin)