Caring for Patients with Acute Neurological Disorders
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
Central Nervous System
Comprises brain and spinal cord; processes impulses.
Brain
Largest and most complex part of CNS.
Skull
Protective structure; smooth superior, rough basilar surfaces.
Meninges
Three protective layers surrounding the CNS.
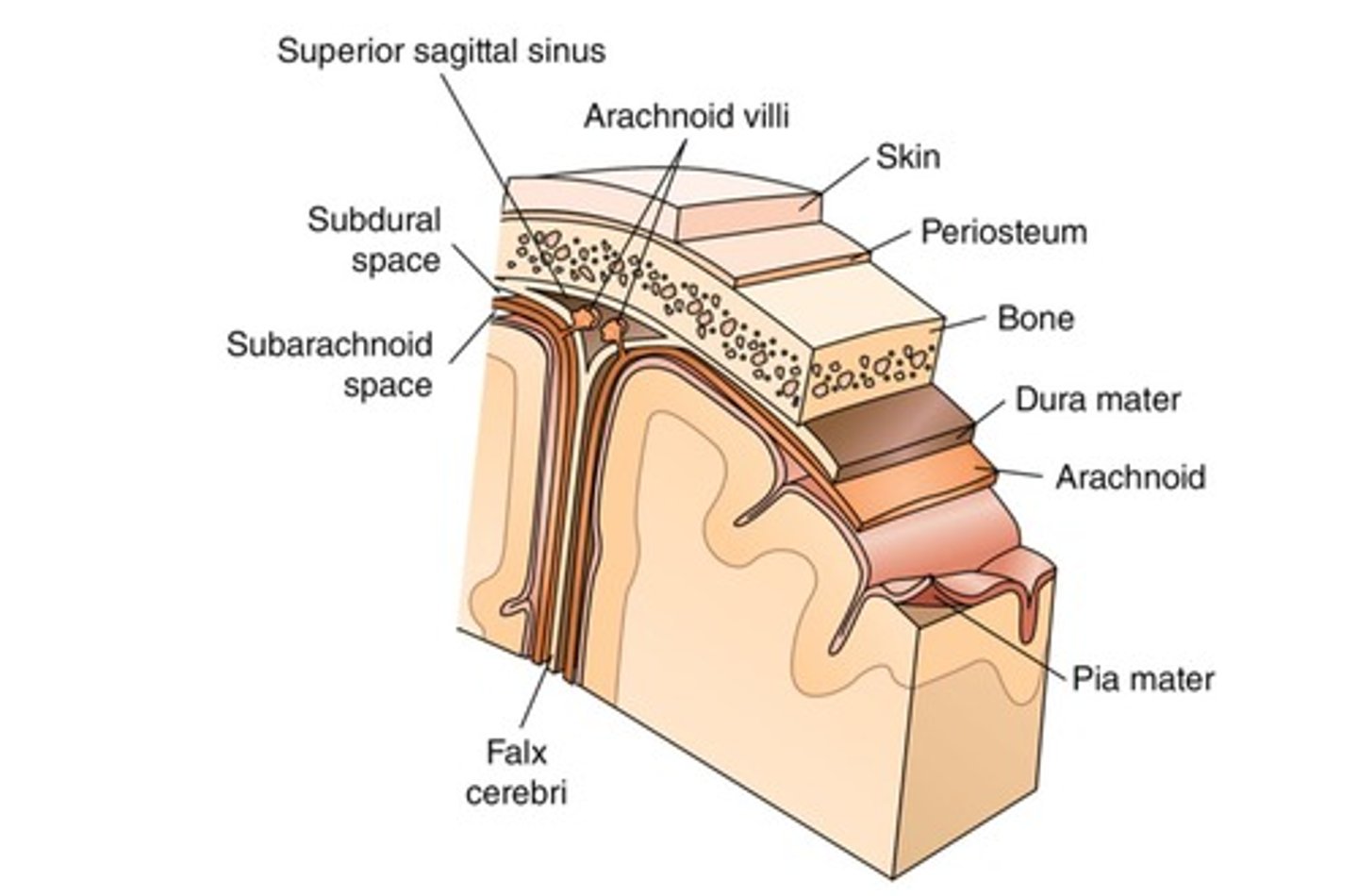
Dura Mater
Outermost layer; supplies blood via middle meningeal artery.
Epidural Space
Space between skull and dura mater.
Subdural Space
Space between dura mater and arachnoid.
Subarachnoid Space
Space between arachnoid and pia mater; contains CSF.
Arachnoid Mater
Second layer; delicate structure with subarachnoid space.
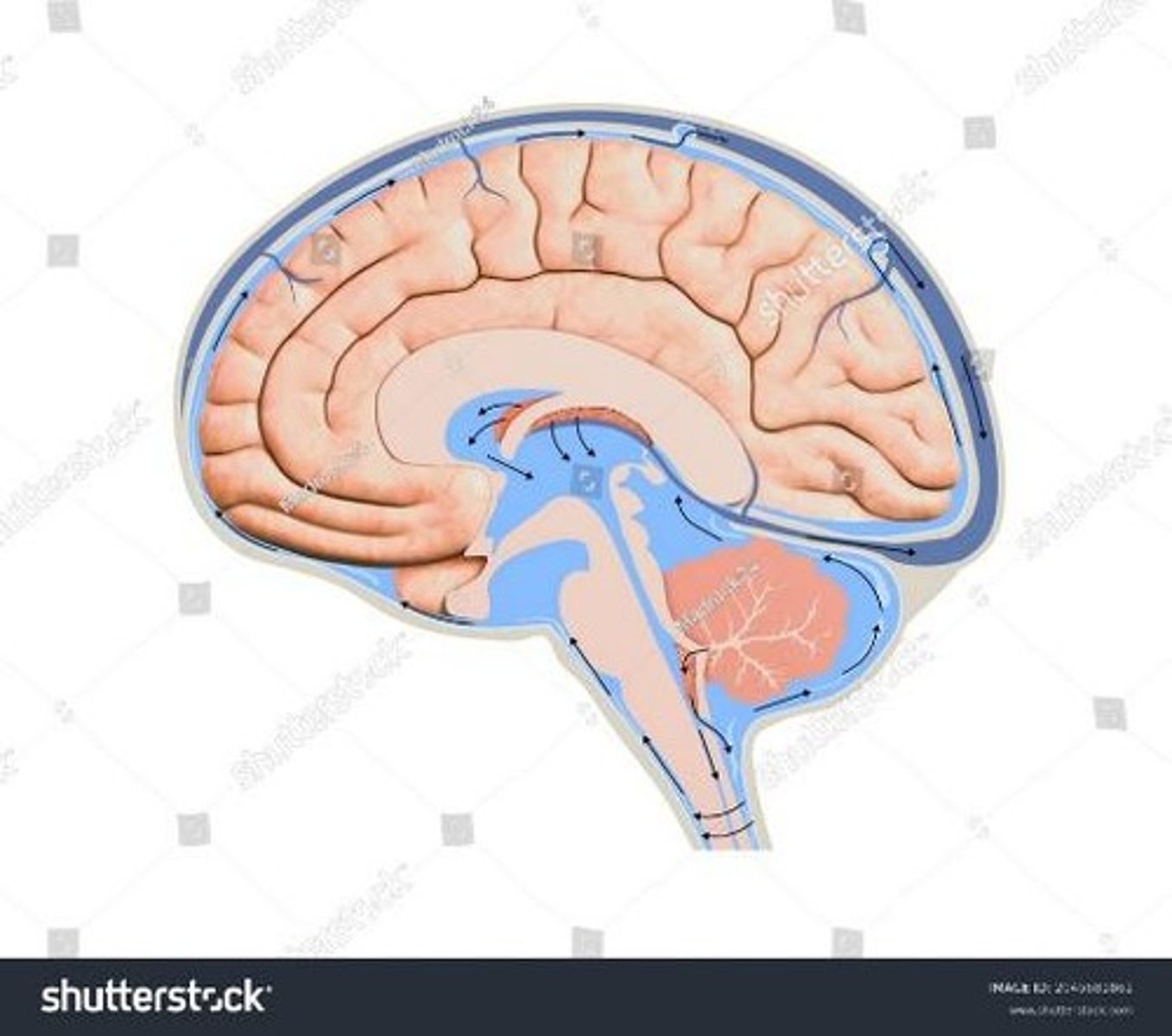
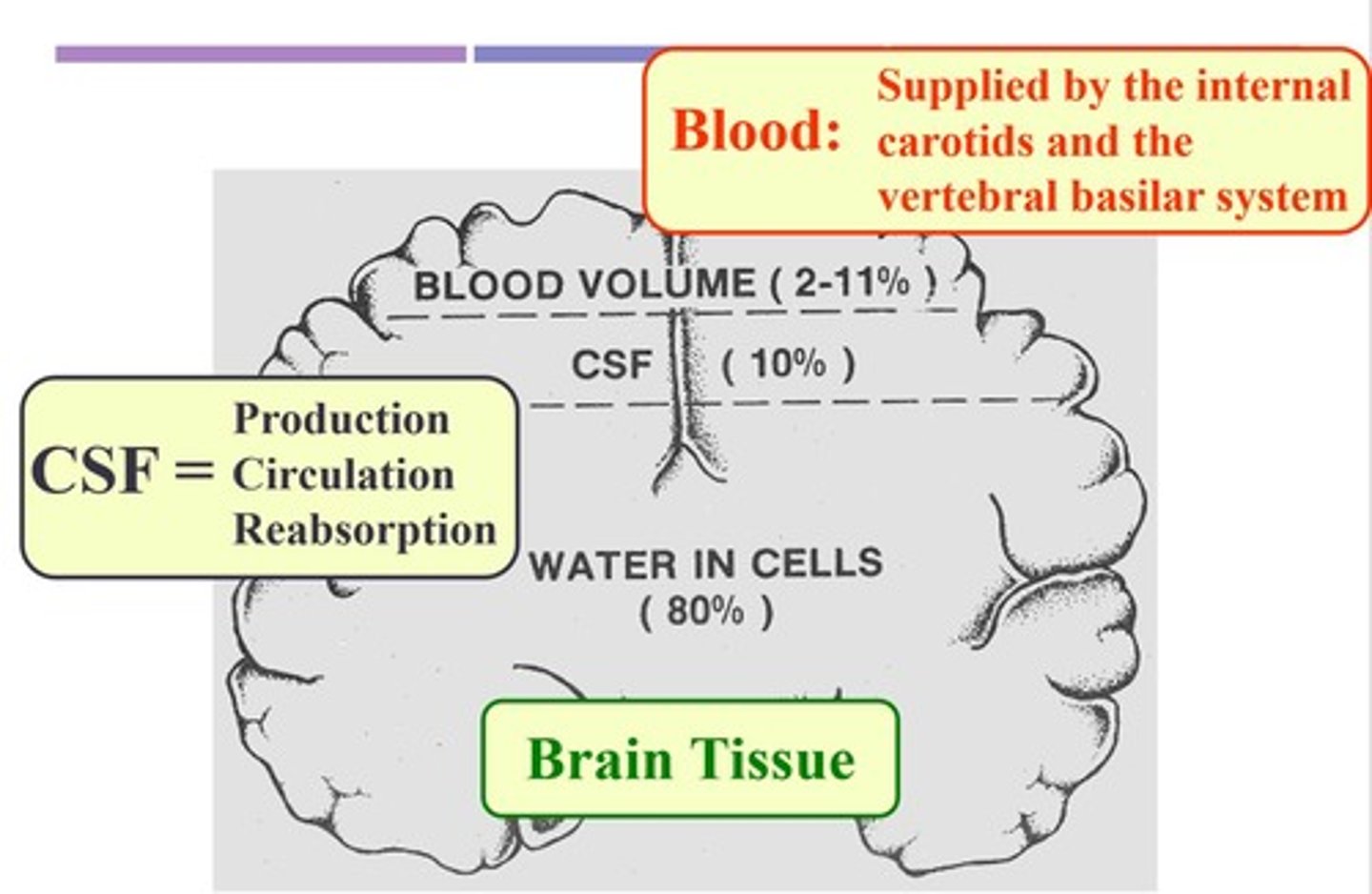
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Clear fluid; protects brain and circulates nutrients.
Choroid Plexus
Produces CSF within the ventricles.
Lateral Ventricles
Two largest ventricles; extend into frontal lobes.
Non-communicating Hydrocephalus
Fluid build-up due to CSF blockage.
Communicating Hydrocephalus
CSF accumulation caused by arachnoid villi blockage.
Arachnoid Villi
Protrusions that absorb CSF for removal.
Pia Mater
Innermost layer; adheres to brain and supplies blood.
Cerebral Vasculature
Receives 20% of cardiac output; supplies brain.
Circle of Willis
Circular network allowing blood flow between hemispheres.
Internal Carotid Arteries
Bifurcate to supply cerebrum and face.
Vertebral Arteries
Form basilar artery; supply cerebellum and brain stem.
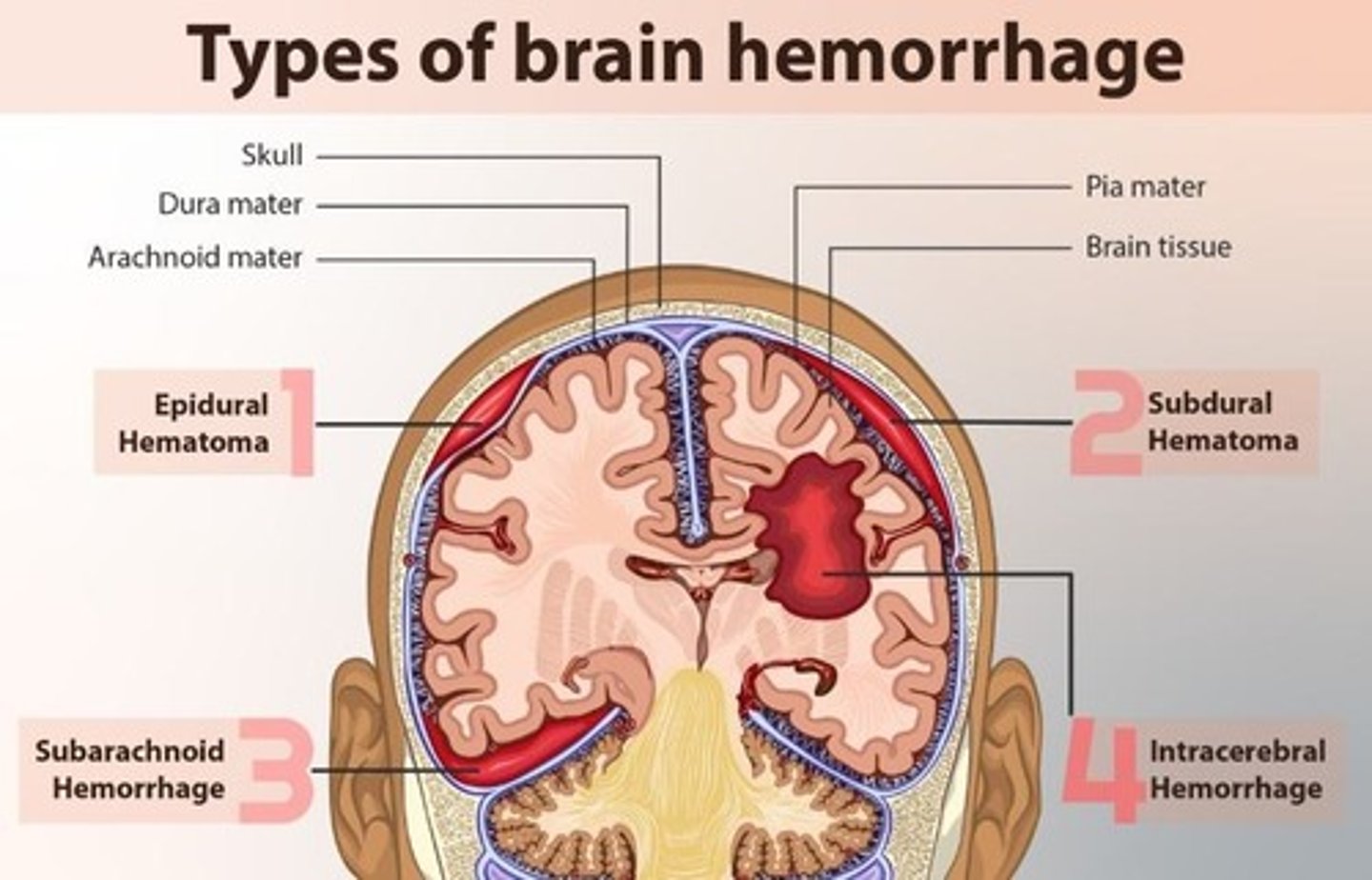
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Arterial rupture causing blood in CSF.
Epidural Hematoma
Arterial rupture leading to rapid blood accumulation.
Intracranial Pressure (ICP)
Pressure within the cranial vault, non-expandable.
Normal ICP
Normal ICP measurements are less than 15 mmHg.
Increased ICP
ICP measurements greater than 15 mmHg.
Monro-Kellie Doctrine
Brain self-regulates volume of intracranial components.
Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF)
Blood flow to the brain, maintained despite changes.
Autoregulation
Ability to maintain CBF despite metabolic changes.
Cerebral Perfusion Pressure (CPP)
Indicates adequacy of oxygen delivery to the brain.
Normal CPP Range
Normal CPP values are 60-100 mmHg.
CPP Calculation Formula
CPP = MAP - ICP.
Compensatory Mechanisms
BP and CO2 significantly affect CBF.
Pressure Autoregulation
MAP 50-150 mmHg critical for brain health.
Metabolic Autoregulation
CO2 levels affect cerebral blood flow.
Cerebral Edema
Swelling in the brain leading to increased ICP.
Causes of Cerebral Edema
Includes trauma, infections, tumors, and strokes.
Vasogenic Edema
Fluid leakage into extracellular space, increased permeability.
Cytotoxic Edema
Swelling of neurons after hypoxic injury.
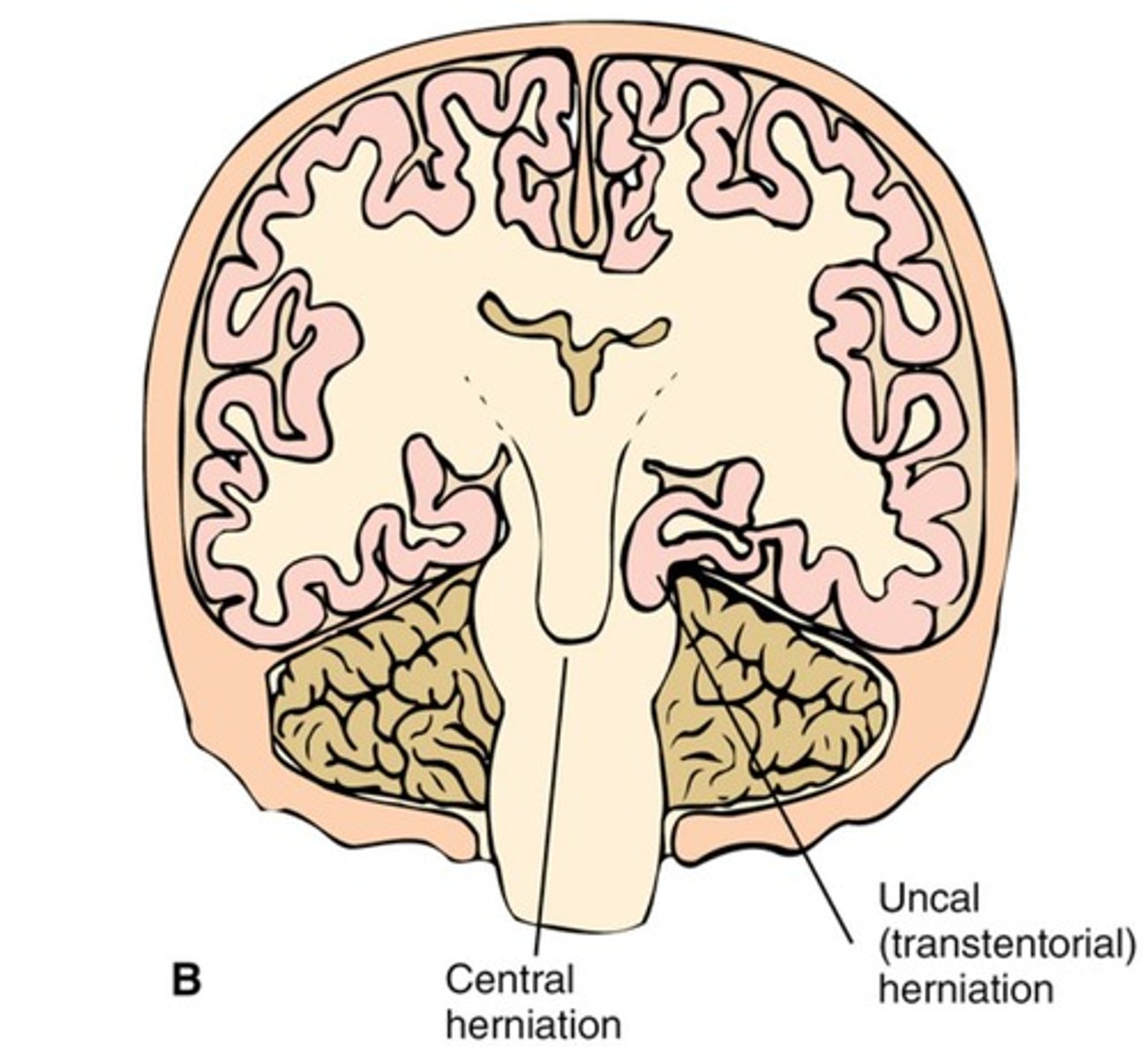
Central Herniation
Displacement of brain tissue due to increased ICP.
Ischemia
Insufficient blood flow to brain tissue.
Anoxic Injury
Damage due to lack of oxygen.
Cerebral Blood Flow Impact
CBF affected by systemic blood pressure changes.
Cerebral Hypoxia
Oxygen deficiency in brain tissue.
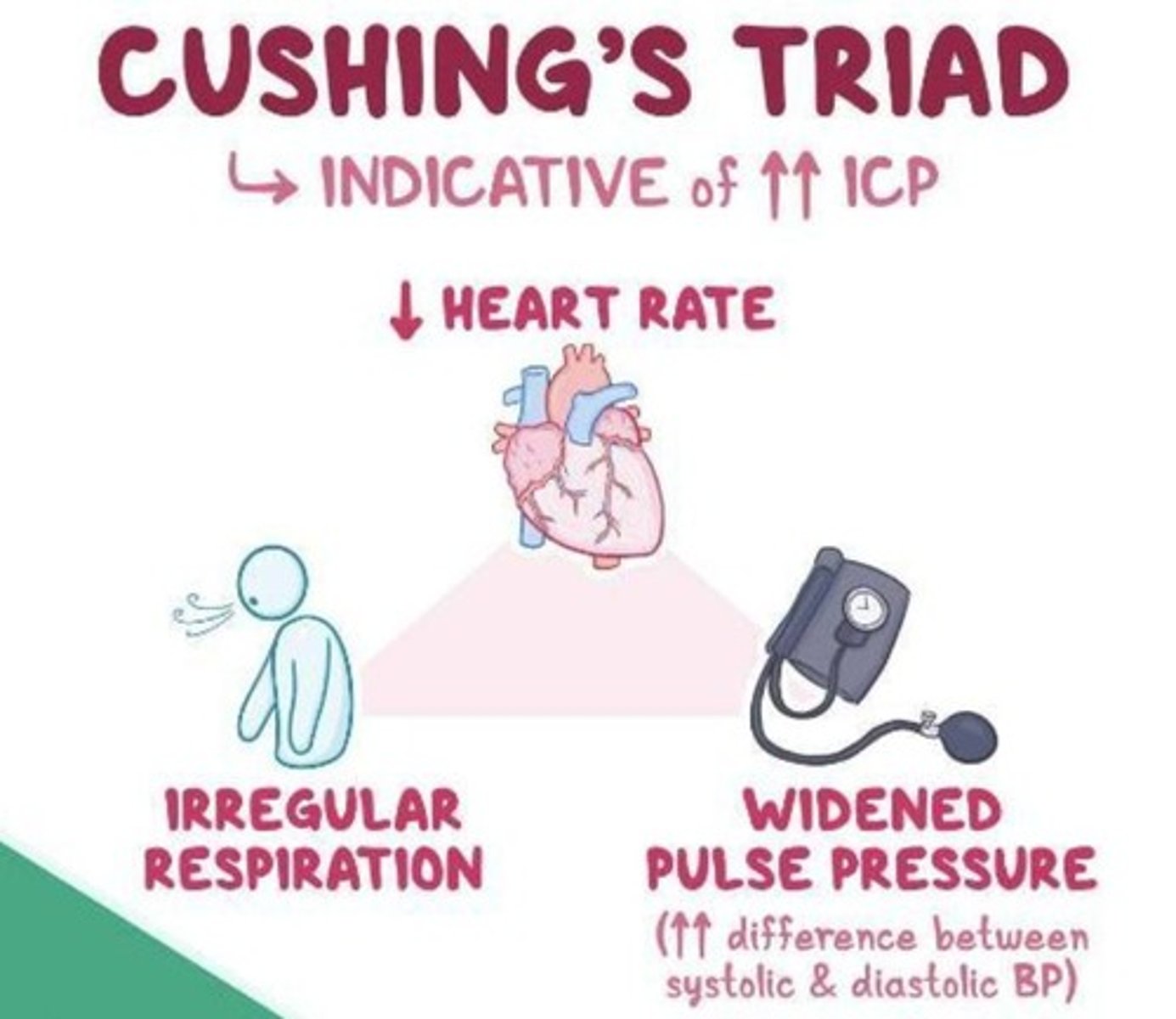
Cushing's Triad
Signs indicating imminent death: widened pulse pressure, bradycardia, irregular respirations.
Widened Pulse Pressure
Increased difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Bradycardia
Heart rate slower than normal, below 60 bpm.
Irregular Respirations
Abnormal breathing patterns indicating brainstem involvement.
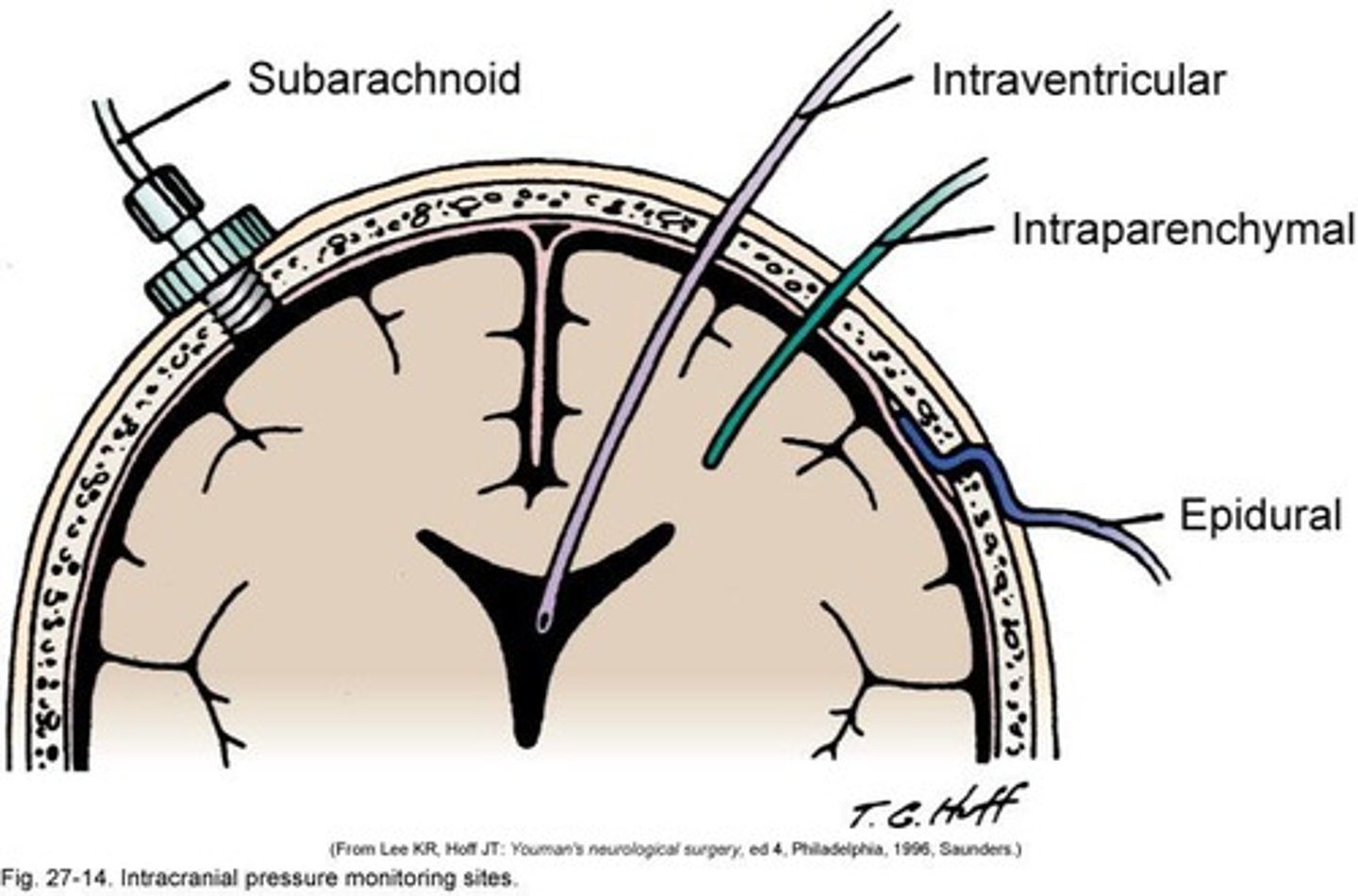
Intracranial Pressure Monitoring
Guides therapy for severe brain injuries.
GCS 3-8
Indicates severe brain injury; ICP monitoring indicated.
Intraventricular Catheter
Device for monitoring ICP; can cause infections.
Intraparenchymal Monitor
Device placed within brain tissue for ICP measurement.
Lumbar/Subarachnoid Monitor
Monitors ICP from lower spinal regions.
Subdural Monitor
Used for ICP monitoring; placed under the dura mater.
Epidural Monitor
Lower risk of infection compared to other devices.
ICP Monitoring Complications
Includes infection, obstruction, hemorrhage, and misplacement.
Space-Occupying Lesions
Tumors, abscesses, and bleeds that increase ICP.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
Bleeding between arachnoid and pia mater layers.
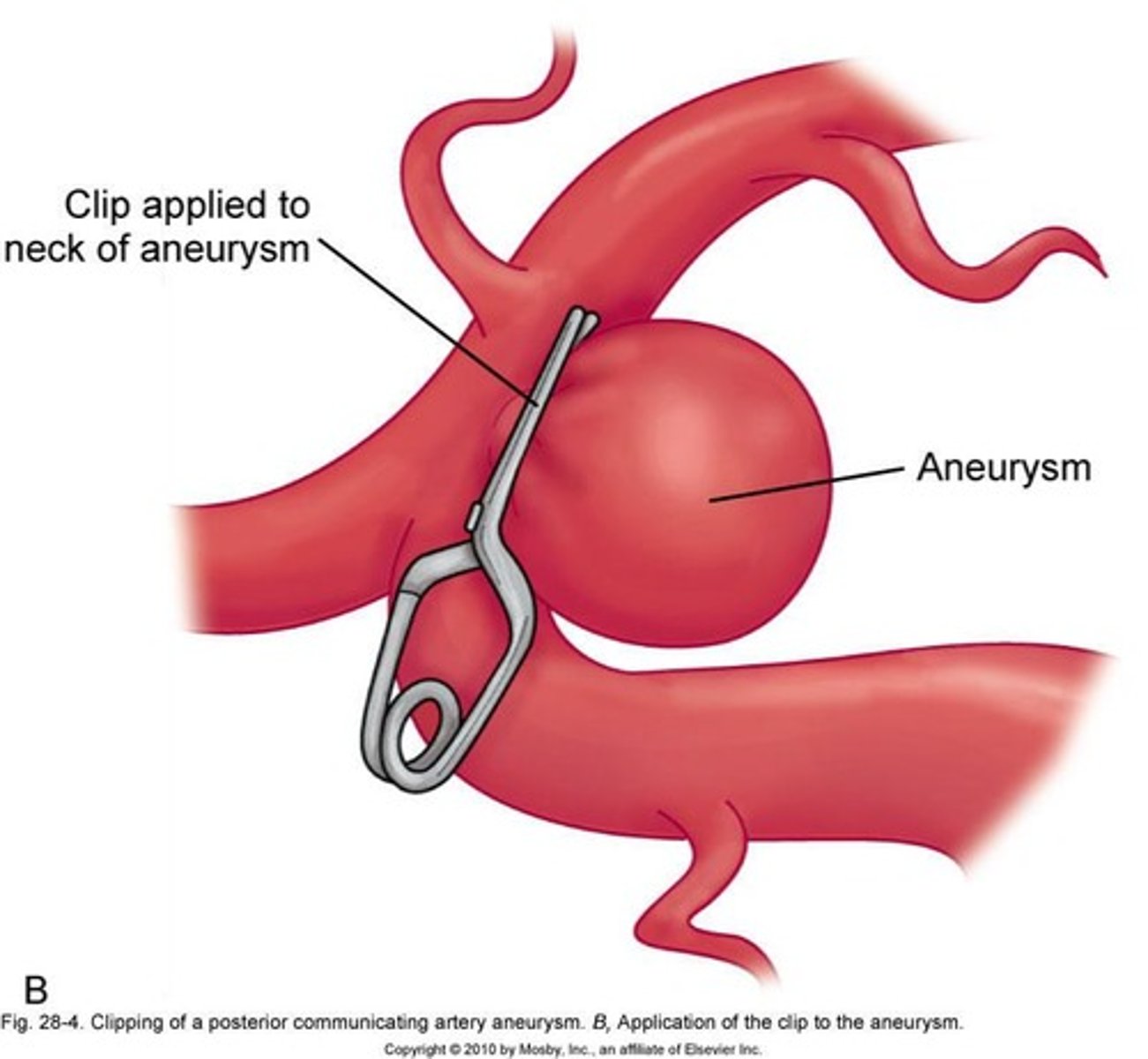
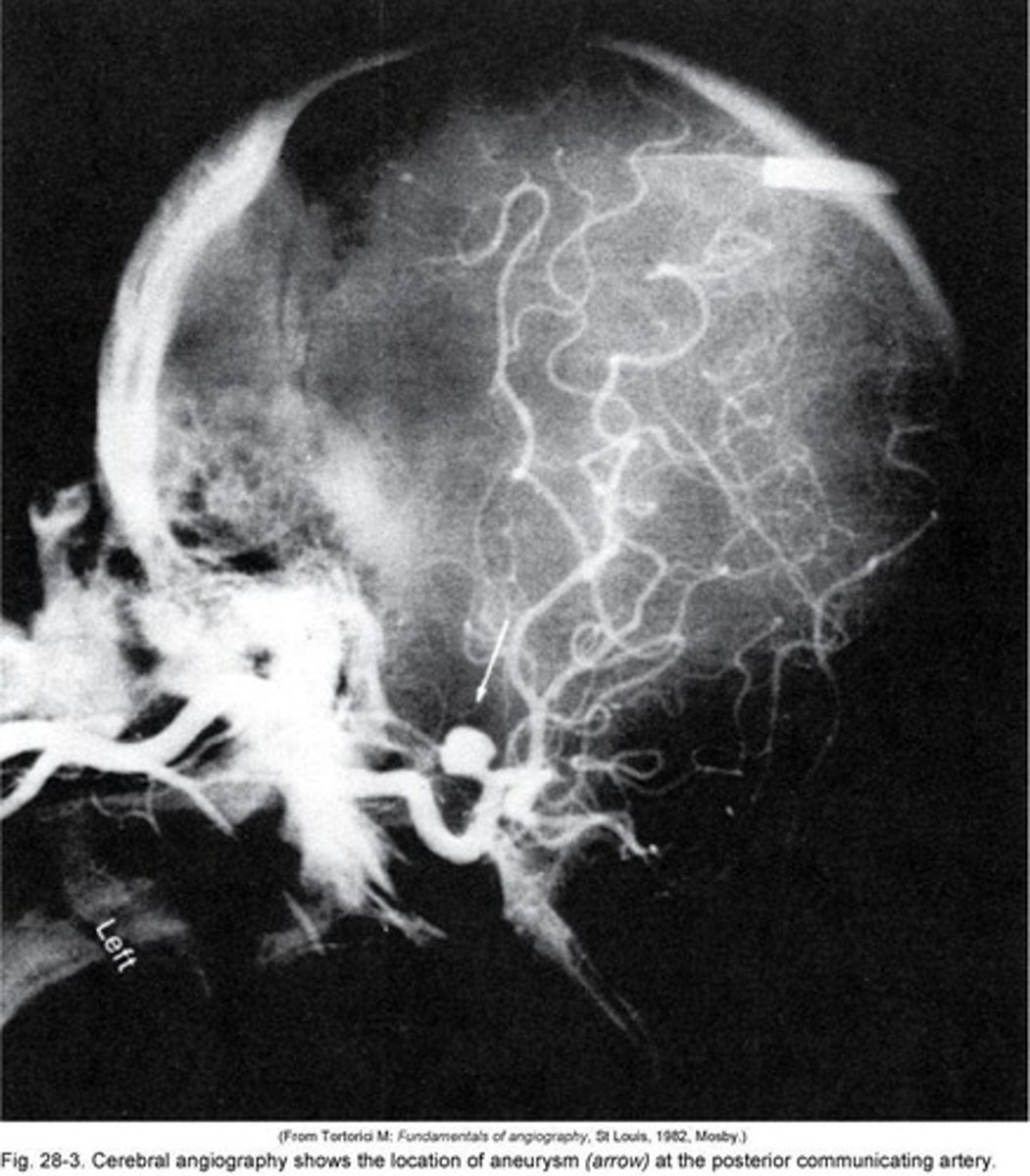
Cerebral Aneurysm
Outpouching of a blood vessel wall.
Subdural Hematoma
Bleeding between the dura mater and brain.
Antibiotic Prophylaxis
Preventive antibiotics to reduce infection risk.
Transducer Leveling
Aligning with the tragus for accurate ICP readings.
Aneurysm
Abnormal blood vessel dilation, 2-7mm diameter.
Rupture
Break in blood vessel, causing bleeding.
CSF
Cerebrospinal fluid, protects brain and spinal cord.
Oculomotor nerve
Controls eye movement and pupil response.

Ipsilateral pupil dilation
Same side pupil enlarges due to pressure.
Clinical manifestations
Signs and symptoms indicating a medical condition.
Worst headache of my life
Common description after aneurysm rupture.
Nuchal rigidity
Stiff neck indicating meningeal irritation.
Photophobia
Sensitivity to light, often with meningitis.
Kernig's sign
Pain on knee extension when hip flexed.
Brudzinski's sign
Knee flexion when neck is flexed.
CT scan
Imaging technique for diagnosing brain conditions.
Lumbar puncture
Procedure to collect CSF for analysis.
Cloudy CSF
Indicates infection, not subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Cerebral angiography
Imaging to visualize cerebral blood vessels.
Surgical clipping
Gold standard procedure to treat aneurysms.
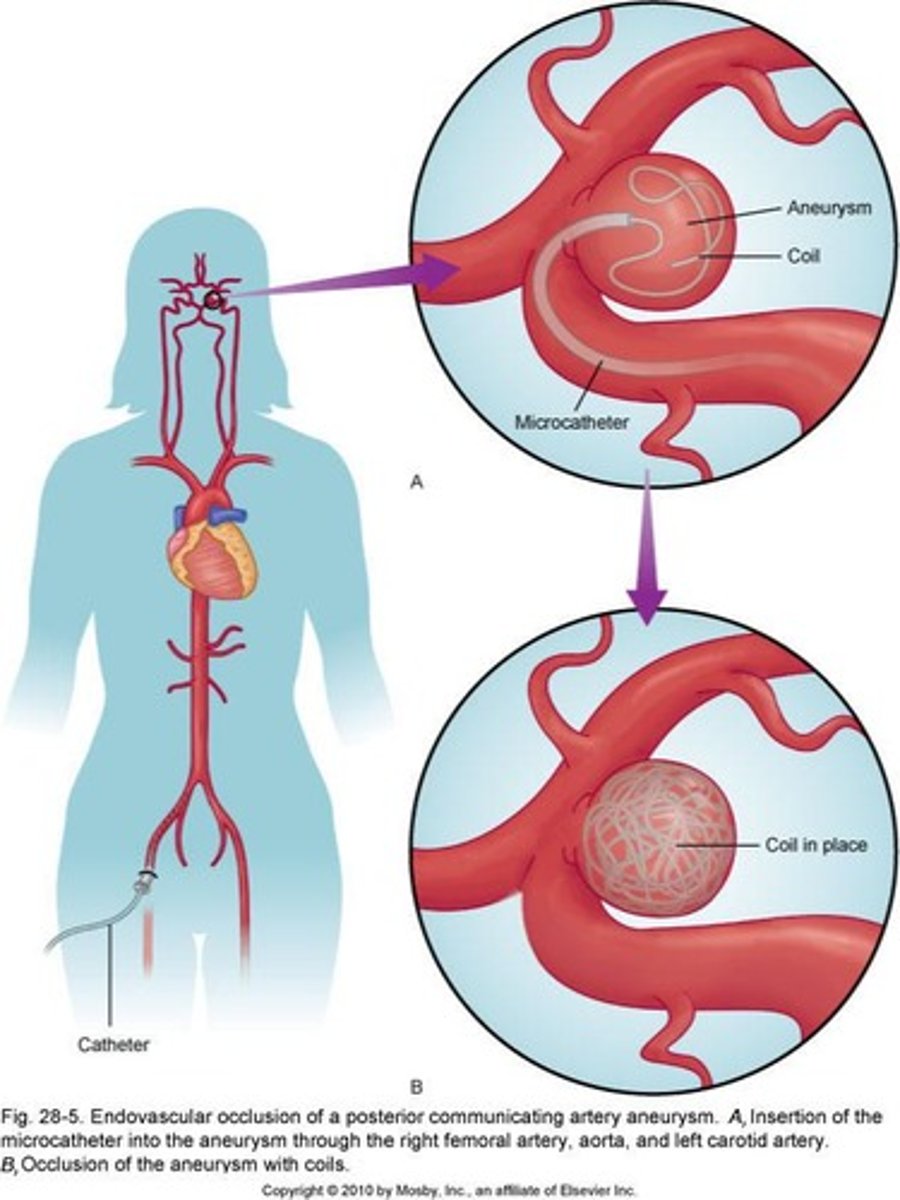
Guglielmi detachable coils
Endovascular treatment to occlude aneurysms.
Vasospasm
Narrowing of blood vessels post-hemorrhage.
Nimodipine
Calcium channel blocker for vasospasm management.
Triple H therapy
Management strategy: Hypervolemia, Hemodilution, Hypertension.
Neuro patients
Avoid giving certain medications to these patients.
Pulmonary edema
Fluid accumulation in lungs, monitor for signs.
Hemodilution
Dilution of blood components with IV fluids.
Hypertension
Blood pressure exceeding normal range, > 120 mm Hg.
Vasopressors
Medications used to increase blood pressure.
Sweet spot BP
Optimal BP range 150-160 mm Hg.
Epinephrine
Used to maintain blood pressure in emergencies.
Hydrocephalus
Fluid buildup in the brain, often CSF.
VP shunt
Catheter from ventricle to peritoneum for drainage.
Seizures
Neurological events due to blood irritants.
Anticonvulsants
Medications to prevent or control seizures.
Rebleeding risk
Increased chance of bleeding within 24 hours.
Minimal stimulation
Reduce environmental stimuli for patient comfort.
Antihypertensives
Medications to lower high blood pressure.
Ventriculostomy
Procedure to control intracranial pressure (ICP).
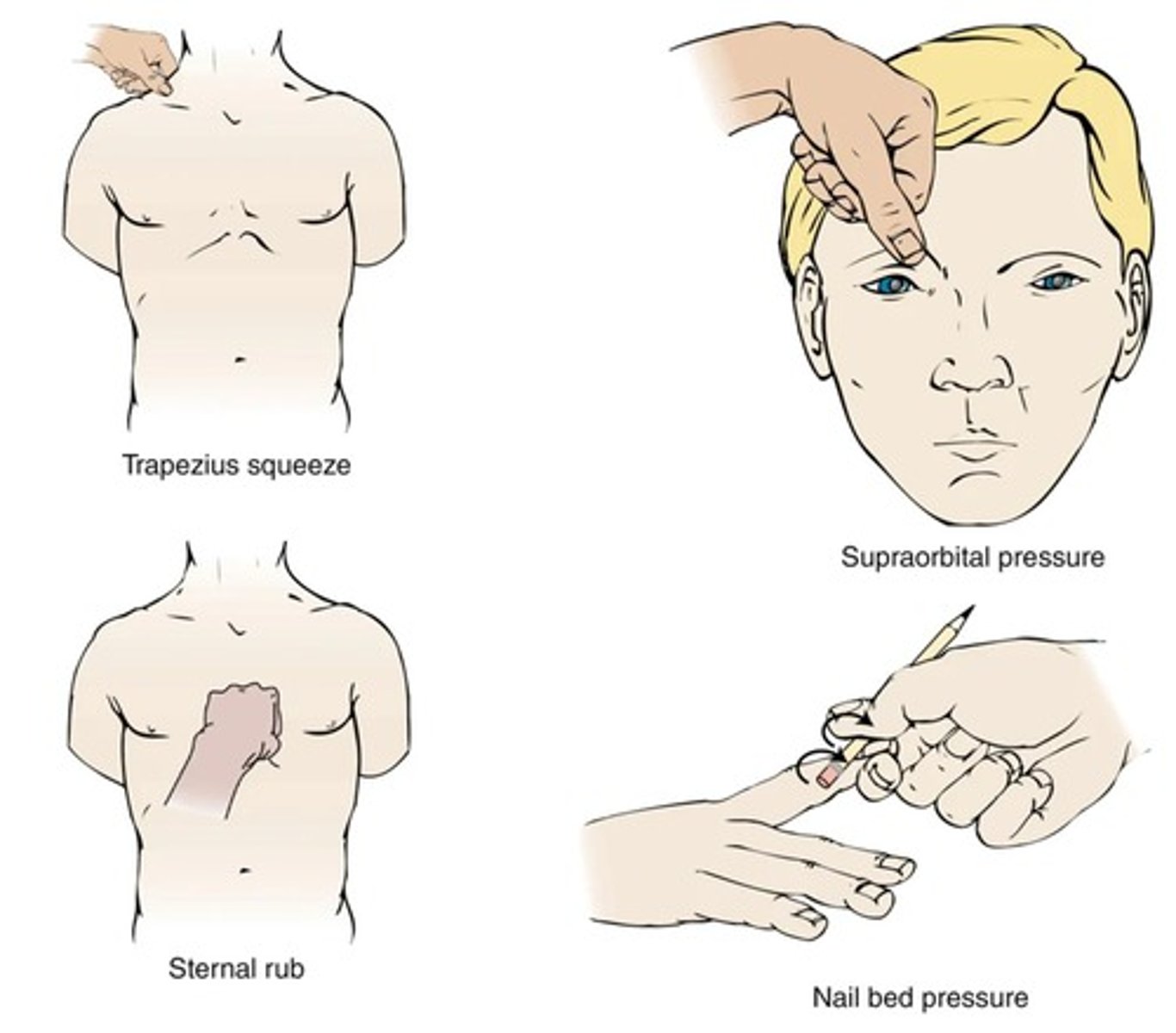
Baseline neurological assessment
Initial evaluation to monitor neurological status.
Primary brain injury
Immediate damage from trauma at injury time.
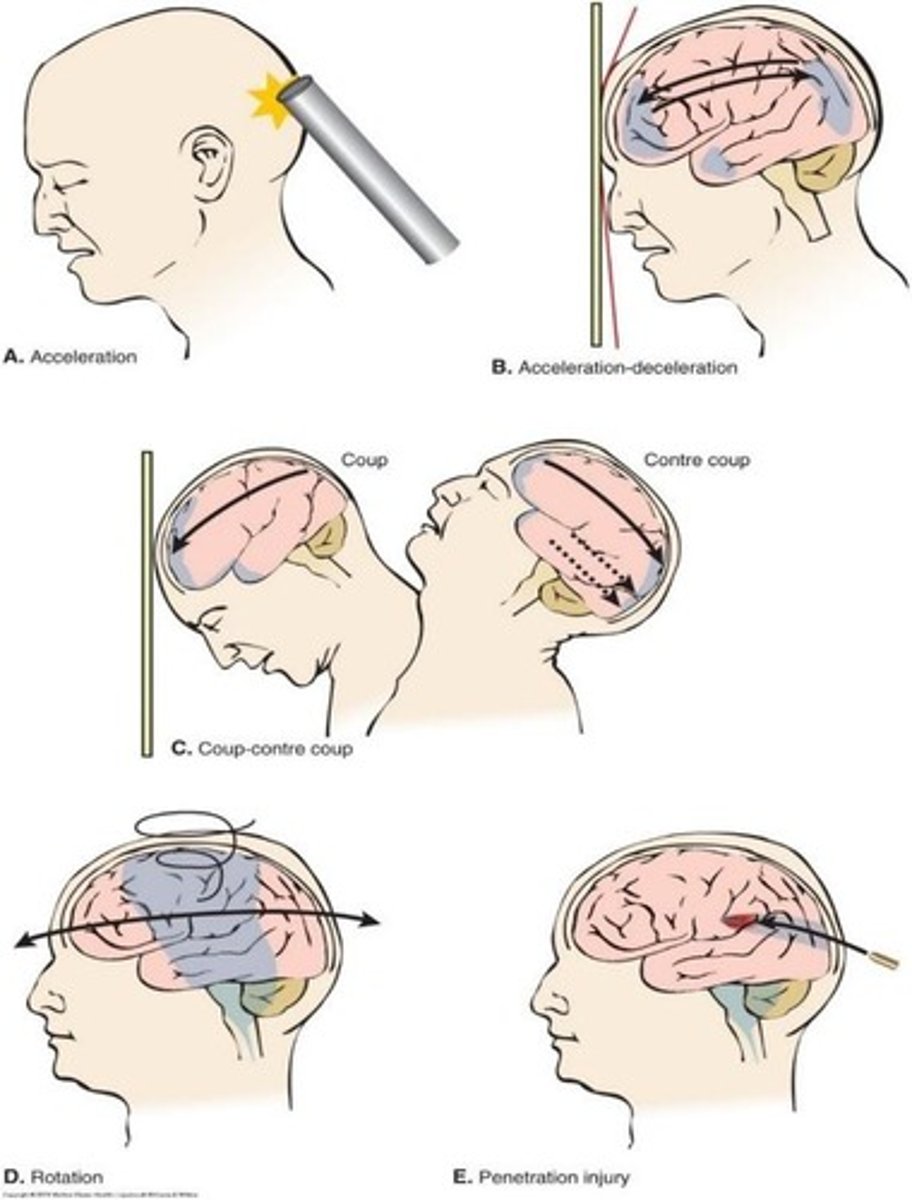
Secondary brain injury
Worsening injury due to body's response mechanisms.
Calm Environment
Quiet setting to reduce stimulation for patients.