Hemostasis Week 3
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
Thrombopoiesis steps
Hematopoietic stem cell
Myeloid progenitor
mega/erythro progenitol
megakaryoblast
promegakaryocyte
megakaryocyte
platelets
Platelets under microscope vs electron microscopy
microscope: purple dots smaller than RBC
electron microscope: resting platelet = flat/circular, activated = spiderlike
GPIIb/IIIa on a resting platelet are activated by what?
Agonist
Fibrinogen can connecting PLTs by which receptor on PLTs' surface?
GP IIbIIIa
PLT morphology:
- peripheral zone refers to ___
PLT surface
PLT morphology:
- Structural zone is _____, it helps maintain ___ shape of the resting PLTs and participate in shape change of activated PLTs
cytoskeleton, discoid
PLT morphology
- membrane system is _____
the tubular system on membrane; canalicular system
PLT morphology
- Organelle zone includes M_____, G______ and G______ (which including three types ___,___, and ____)
mitochondria, glycogen, granules; lysosome, alpha, dense
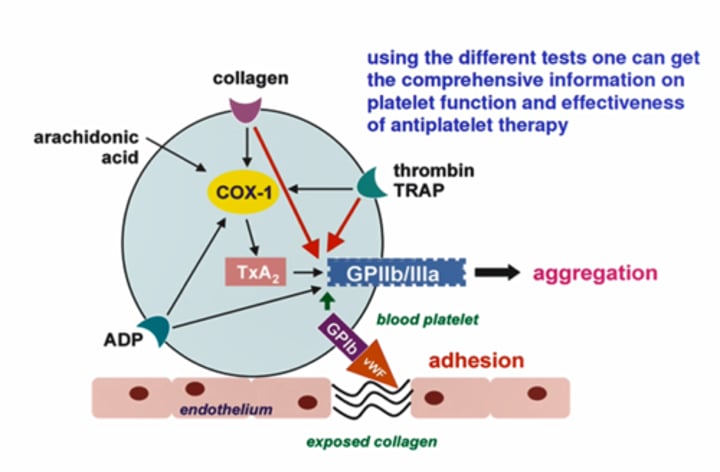
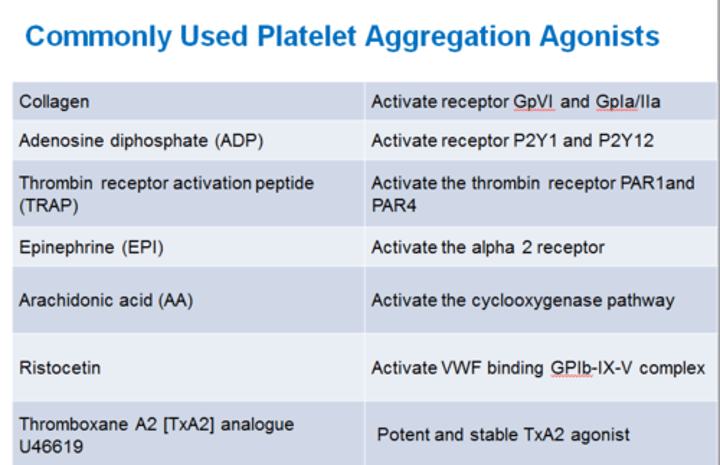
Receptors on PLT surface, which is the primary one?
- Thrombin is the strongest angonist
- Thrombin > ADP, collagen & epinephrine
PLT FXN disorders
-Acquired
Drugs , storage defect, systemic disorders & hematological disorders
PLT FXN disorders
Example of systemic disorders
Uremic, antiplatelet antibodies, cardiopulmonary bypass, liver disease
PLT FXN disorders
Example of hematological disorders
Myeloproliferative disorders, myelodysplasia, leukemia, dysproteinemias, acquired von Willebrand disease
Inherited platelet function disorders based on the fxns are divided into three types:
adhesion, aggregation, activation
Which defect/disorder is associated with adhesion?
GPIb - vWF defect = Von willebrand dz & Bernard-Soulier Syndrome
Which defect/disorder is associated with aggregation?
GPIIb - IIIa defect = Glanzmann thrombasthenia
Which defect/disorder is associated with activation?
AA metabolism defect = [cyclo-oxygenase defect ASA-like] ASA= Aspirin
Granule release defect = [storage pool deficiency & release defect]
cytoskeleton regulation = [Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome]
phosphatidylserine expose = [Scott syndrome]
Factors to consider for platelet disorder eval
clinical picture/history, CBC/DIFF for PLT #/size/morph, Platelet function assay, esoteric testing
global screening tests for PLT fxn are
bleeding time and Platelet function assay PFA-100
Antiplatelet therapy monitoring assay
- PLTMAP
- VerifyNow
Esoteric test for PLT fxn
- electron microscopy
- PLT flow cytometry
- genotyping studies
specimen requirement for PLT fxns (hint TEG specimen)
- centrifuge?
- refrigerated, frozen, room temp
- mixing? using tube system to transport to Lab
- time limited?
- whole blood, no centrifuge
- Room temp only
- NO mixing or tubing system
- within 30 mins is the best, < 4hrs
Bleeding time determines _____
- time to form a PLT plug
bleeding time evaluates
PLT fxn & vascular contribution to hemostasis
Bleeding time test involves making a puncture wound in a superficial area of the skin and monitoring the time needed for bleeding to stop. What are some limitations of this test?
NO standardization for direction of incision/bloting off blood, NO precision, NO sensitivity
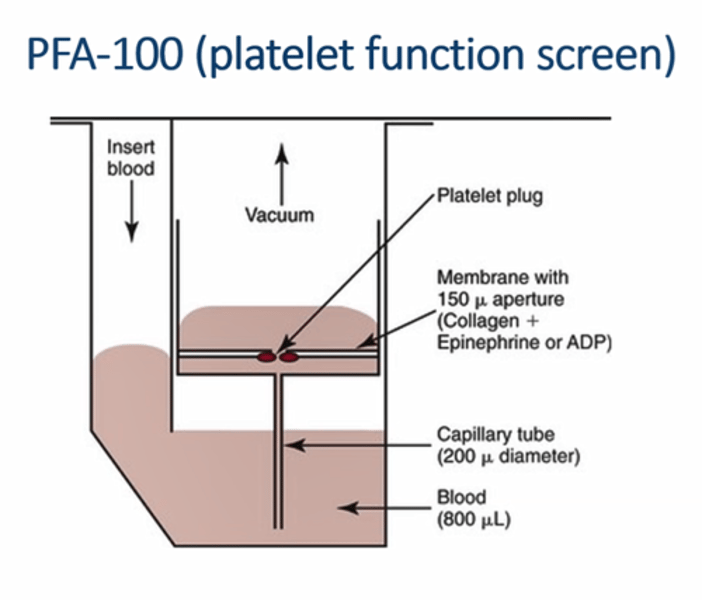
PFA-100
- Principle
- What active the PLTs?
- detect PLT plug forming time
- the membrane contain Collagen + Epinephrine or ADP
- when plug form, covers the aperture, the blood flow stops
- vWB binds to collagen, and bonded vWB binds to PLTs & PLTs are activated by epinephrine or ADP
PFA-100 curve
flow rate rapidly increases then gradually decreases as closure time extends
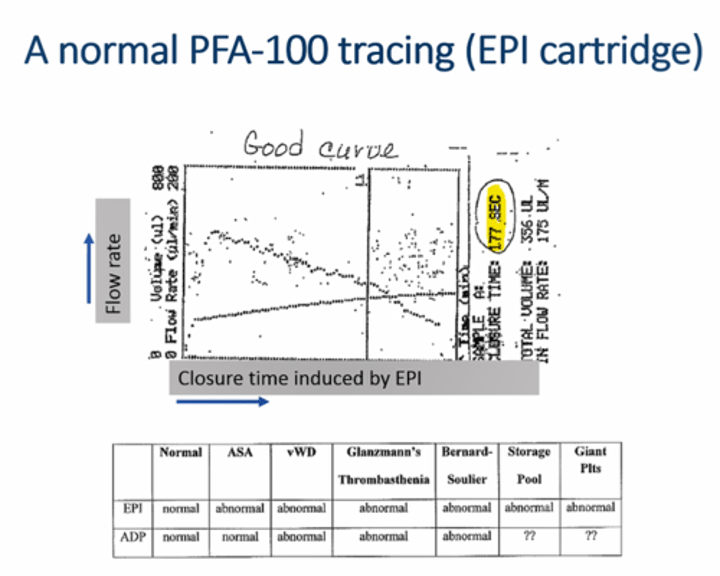
Interpreted PFA-100 result
- EPI & ADP both normal
- normal
Interpreted PFA-100 result
EPI abnormal; ADP normal
pt with Aspirin
Interpreted PFA-100 result
EPI, ADP both abnormal
vWD, Glanzmann's thrombasthenia, Bernard Soulier or PLT defects
PFA-100 tests, the abnormal closure time (CT) is related to which type of vWD
- 2A,2B, 2M & 3
which vWD type has normal PFA-100 result? why?
2N, 2N defect is decreased affinity to Factor VIII; it has normal PLT binding affinity
(T/F)Closure time is related to PLT count only
False,
since RBCs help to form the plug, LOW HCT <30%, the CT is prolonged
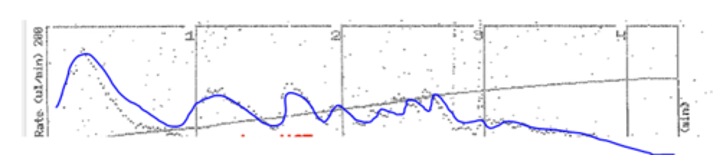
The PFA-100 result looks like the pic with a seesaw tracing and prolonged CT, what might cause it?
HCT is too low <30%
PLT is too low <100K
why should PFA-100 results be interpreted with caution?
test not diagnostic/sensitive for mild platelet disorders
Specific assays of PLT fxn are _____ studies, includes:
Aggregometry studies
- light transmission LTA
- lumi
- whole blood impedance
PRP vs PPP
PPP - PLT poor plasma, 100% of PLT is in aggregation form > settles to bottom of tube
PRP - PLT rich plasma, 0% of PLT is in aggregation form
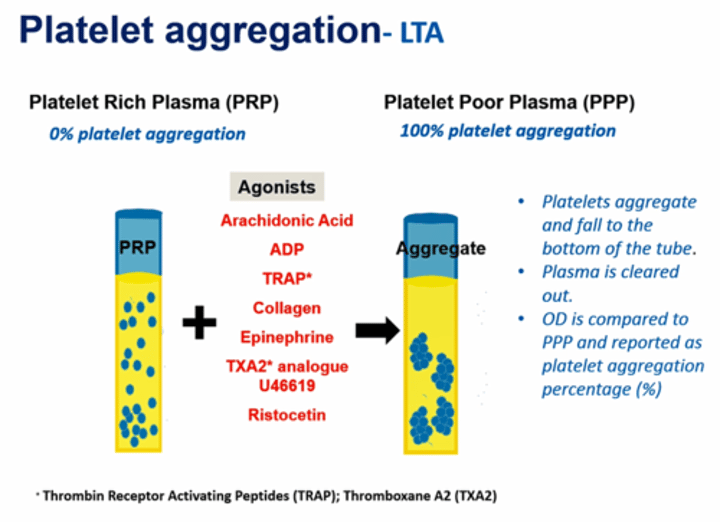
- what is measured in LTA test?
- what is report as result in LTA test?
- LTA test measure the clearance of plasma is compared with PPP by optical density
- reported as PLT aggregation percentage %
- eg. pt's result Agonist + PRP compare to PPP(100%) is 90% then we report the pt's LTA test result is 90% PLT aggregation
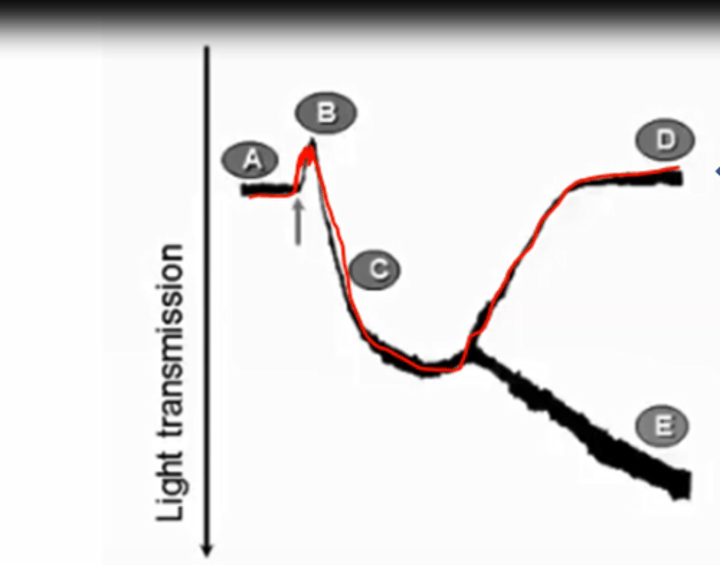
the LTA tracing, B,D went up due to?
- ______ (increase / decrease) turbidity
- what happened to the PLTs in B & D
- increased turbidity
- B: shape change, D: PLT granules secretion
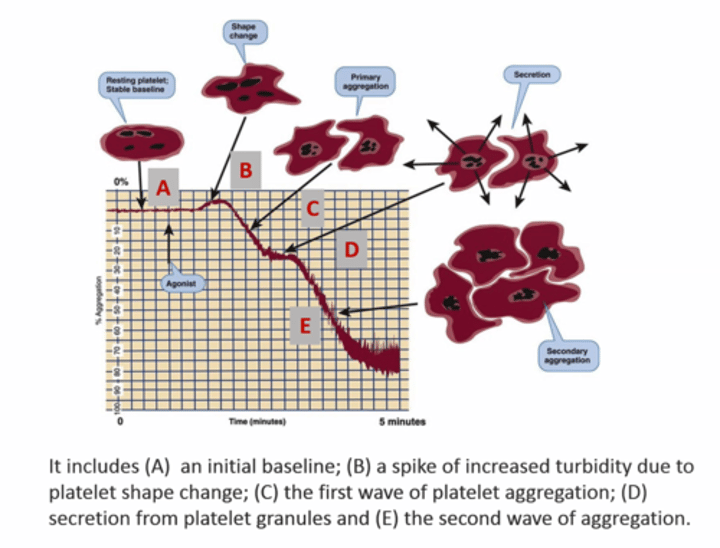
- What is A-B-C-E
- What is A-B-C-D; what causes ABCD situation happen ?
- initial wave of aggregation followed by 2nd wave of aggregation, irreversible
- For weak agonists [ADP & EPI], secondary wave of aggregation not happen and primary wave disagrregate
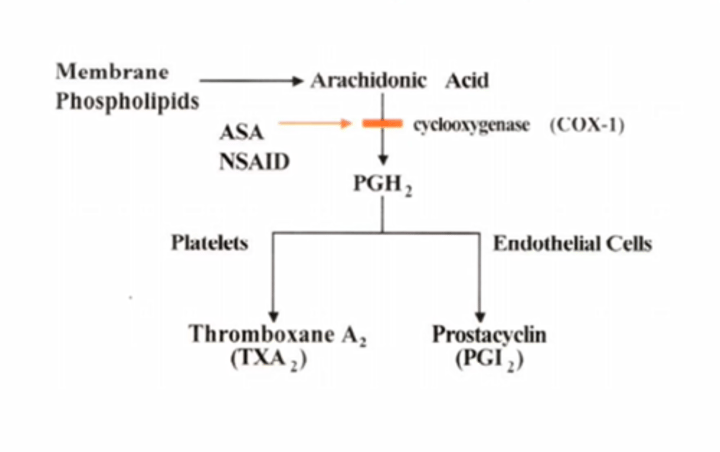
Mechanism of ASA in PLT activation
Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic acid or ASA) inhibits PLT COX1 (cyclo-oxygenase), which is important for TXA2 production (Thromboxane A2).
- it's irreversible inhibition
- TXA2 is needed for PLT activation
- the second wave of aggregation can be inhibited by Aspirin
why low dose of Ristocetin 0.5-0.6 mg/mL is used in the test panel?
diagnostic for type 2B vWD
- _____ (weak/strong) will have biphasic tracing for ADP and epinephrine
Weak agonist
- which wave could dissolve with Aspirin present?
the 2nd wave of aggregation
LTA: lack of agglutination with Ristocetin. Possible diganosis?
Von Willebrand Disease or Bernard Soulier syndrome (plt defect)
LTA: agglutination only with Ristocetin. Possible diagnosis?
Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia (GP2P3a receptor defect) or Afibrinogenemia (no fibrinogen for plt adhesion)
LTA: ADP disaggregation tracing
failure of granule release via platelet storage pool disorder/defect;
platelet agglutination = insensitive to platelet storage pool disorder
LUMI-aggregometry principle
After PLT aggregation, ____ is released from dense-granule.
_____ will react with this molecule and give chemiluminescence.
LUMI-aggregometer used to simultaneously measure ______ & _______
- ATP
- firefly luciferin
- PLT aggregation and ATP secretion of dense-granule ATP
WBIA test principle
when PLT agg, neg charged surface attached to electrical sensors and the impedance between the sensor enhances platelet agglutination = area under curve
WBIA test
- result report as _____
- PLT fxn is _______ to the result
- need duplicate test, so getting a ____ is important
- good for _____ therapy monitoring
- AUC, area under curve
- proportional
- baseline = PLT fxn before therapy
- antiplatelet
Whole blood impedance method limitations
not personalized assay
need to compare with wide normal range
which method correlated well with clinical antiplatelet drug therapy?
whole blood impedance method
When WBIA result is below referance range…
suggests poor platelet function vai antiplatelet drugs, defects, or thrombocytopenia
Three main tests in platelet transmision electron microscopy (PTEM)
- whole mount : quantitate dense granule #
- thin : visualize ultra-structures such as alpha granules and inclusions
- buffy coat/Particle TEM: for WBC aberrant inclusions
which test is gold standard for assessing platelet structures especially dense & alpha granules
platelet transmission electron microscopy
Gray platelet is due to?
alpha granule deficiency
which granules contains protein molecules + more visible with Wright-Geimsa stain?
alpha
which granules contains nonprotein molecules + high content of calcium?
dense
FC gamma II receptor
- which molecule can activate PLT via this receptor?
- associate with _____ dz
- Heparin & PF4 complex
- HIT, heparin induced thrombocytopenia
What is essential for platelet function?
platelet surface receptors
____ is the test of choice for diagnosing platelet surface receptor deficiencies
platelet flow cytometry
what receptor it is & what dz associate with its deficiency
- GPIIb/IIIa
- fibrinogen; Glanzmann's thrombasthenia
what receptor it is & what dz associate with its deficiency
- GP Ib/IX
- von Willebrand; Bernard - Soulie syndrome
what receptor it is & what dz associate with its deficiency
- GP Ia/IIa/VI
- collagen; abnormal PLT aggregation response to collagen
what receptor it is & what dz associate with its deficiency
platelet CD62P
P-selectin; platelet activation def
____ & ___are used for monitoring PLT fxn & antiPLT drug therapy
TEG & ROTEM
Thromboelastography & Rotational Elastometry
What test/tests used to
- provide global information on the dynamics of clot development, stabilization and dissolution that reflect in vivo hemostasis
TEG/ROTEM
TEG/ROTEM is used to assess the contribution of
fibrinogen-platelet interaction
TEG/ROTEM is a Modified method for _____________ _____________
antiplatelet monitoring
What test/tests used to
- converting mechanical strength b/t fibrinogen-PLT into electrical signal
TEG/ROTEM
TEG/ROTEM is a whole blood based assay where whole blood is added to a heated cuvette at 37C. using the TEG/ROTEM device, movement is initiated and as the blood clots, fibrin strands form btw TEG and ROTEM. In other words,
this assay can convert mechanical strength interactions of fibrin to electrical signals
TEG Parameters
- Reaction Time
- Angle & Kinetics
- Maximum Amplitude
- Lysis 30
- RT: time from test start to initial fibrin formation = clotting time
TEG Parameters
- Reaction Time
- Angle & Kinetics
- Maximum Amplitude
- Lysis 30
- Angle& K: Fibrinogen activity; how fast to form and how strong the fibrin is
TEG Parameters
- Reaction Time
- Angle & Kinetics
- Maximum Amplitude
- Lysis 30
- MA the interaction b/t PLT & fibrin @ a maximum strength, 80% of MA contribute from activated PLTs, 20% from fibrin = MA is mostly reflect the PLTs fxn
TEG Parameters
- Reaction Time
- Angle & Kinetics
- Maximum Amplitude
- Lysis 30
- lysis 30: percent lysis 30mins after MA; not a reliable parameter, instrument cannot differentiate real clot lysis vs artifitial effect ; not sensitive to fibrinolysis
In TEG result, high RT means?
RT is proportional to clotting time of PTT reflect low Factor activity = hypocoagulable
in TEG result, high MA and normal Angle means?
MA: hyperplatelet function = hypercoagulability
Angle: normal fibrinogen
in TEG result, low MA and normal angle means?
MA: low platelet function = hypocoagulable
Angle: normal fibrinogen
in TEG result, low angle means?
low fibrinogen level
in TEG result, low RT and high MA and angle means?
RT: fast clotting time
MA: increased platelet/fibrinogen
Angle: increased fibrinogen level
= platelet and enzymatic hypercoagulability
in TEG, high LY30, normal MA means?
increased clot formation and fibrinolysis > primary fibrinolysis
secondary fibrinolysis based on
increased clot formation and relatively increase fibrinolysis = increased MA + increased fibrinomatic parameters (Angle, kinetics)
T/F: TEG is NOT sensitive to Von Willebrand Disease and antiplatelet therapy. Normal results could be observed.
True
TEG result
- Angel 8.8 NR 53-72
- MA 11.5 NR 50-70
what to expect?
low FIB & PLT (PLT
PLT Mapping assay
- used to monitor?
- agonist used?
- unit of result
- antiplatelet therapy; modified test based on TEG
- Arachidonic Acid (AA) & adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
- % inhibition
VerifyNow
- measure PLT response to ___,___,&____ antiplatelet agents
- method, clotting, antibody, optical
P2Y12 inhibitiors, aspirin, GP IIb/IIIa
- optical measure
What proteins/factors does warfarin decrease the synthesis of?
Factor II, VII, IX, X, Protein C and S
warfarin inhibits ______, which leads to Vitamin K depletion, and further decreasing Vitamin K dependent clotting factor, preventing clot forming
Vitamin K epoxide reductase
What are the functional vitamin K-dependent clotting factors
II, VII, IX, X
Wafarin-induced skin necrosis occurs due to ________
acquired protein C deficiency
Warfarin treatment affects Protein______ & Factor _____ most because they have the shortest half-life time among Vitamin K dependent factor/protein
- Protein C & Factor VII
Wafarin-induced skin necrosis occurs after _____ (how long) after drug therapy or with ______ initial dose
3-5 days after drug therapy OR with High initial dose
CON of using Warfarin
- ______ (Narrow/wide) Therapeutic range
- _____ (slow/fast) onset , offset action
-_____ (few/multiple) interactions
- _____ & ______ are the major interactions as drugs
- ______ may increase warfarin activity
-______ may decrease warfarin activity
- does it need monitor?
- Narrow
- Slow
- 727 drugs; multiple
- Aspirin, Ibuprofen
- cooked onions
- broccoli, kale, spinach (rich in VitK)
- required monitoring
What are the ideal attributes for anticoagulants
Oral administration, rapid onset, wide therapeutic range, predictable therapeutic effect, no food/drug interactions, no monitoring required, defined pharmacokinetics in renal/hepatic disease, reversible, cost effective
WHat is DOACs and the example of it? (D-, R-, A-)
and they inhibits IIa or Xa?
Direct Oral AntiCoagulants
- Dabigatran (IIa) - Pradaxa
- Rivaroxaban (Xa) - Xarelto
- Apixaban(Xa) - ELIQUIS
- Edoxaban (Xa) - Savaysa
mechanism of DOACs vs Warfarin
- directly inhibit either Factor IIa (Thrombin) or Factor Xa
- warfarin lowers the functional lvl of all the VitK dependent clotting factors (2,7,9,10,CS)
For Factor Xa & IIa inhibitors, there are two catogories:
Direct & Indirect
- traditional / new anticoagulants
- reversible / inreversible
- inhibits free factor/ bound factor
- catalytic/ stoichiometric
- ATIII dependent/ independent
Which ones apply to direct factor Xa and IIa inhibitors?
new anticoagulants
specific and reversible inhibition of a single factor
inhibits bounded and free
stoichiometric
For Factor Xa & IIa inhibitors, there are two catogories:
Direct & Indirect
- traditional / new anticoagulants
- reversible / inreversible
- inhibits free factor/ bound factor
- catalytic/ stoichiometric
- ATIII dependent/ independent
Which ones apply to indirect factor Xa and IIa inhibitors?
traditional anticoagulants except Warfarin
irreversible ATIII-mediated inhibition of factor IIa or Xa
inhibits only free factor
Catalytics = accelerate the binding of anti-thrombin with Factor IIa or Xa
Examples of Indirect ATIII-dependent factor Xa inhibitors
Unfractionated Heparin (usually we call Heparin)
LMWHs including: Enoxa-, Dalte-, Tinza- + -parin
Pentasaccharides: Fondaparinux
Examples of direct factor Xa inhibitors
Apixaban(Eliquis)
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
DU176b Edoxaban (Savaysa)
Examples of Vitamin K antagonists for factor Xa
Warfarin depletes factor Xa, no inhibit