Chemiosmosis + ETC
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is the term for the process where the energy used to transfer the phosphate group to ADP results from the oxidation of reduced coenzymes?
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Name the enzyme that catalyzes the phosphorylation of ADP into ATP.
ATP Synthase
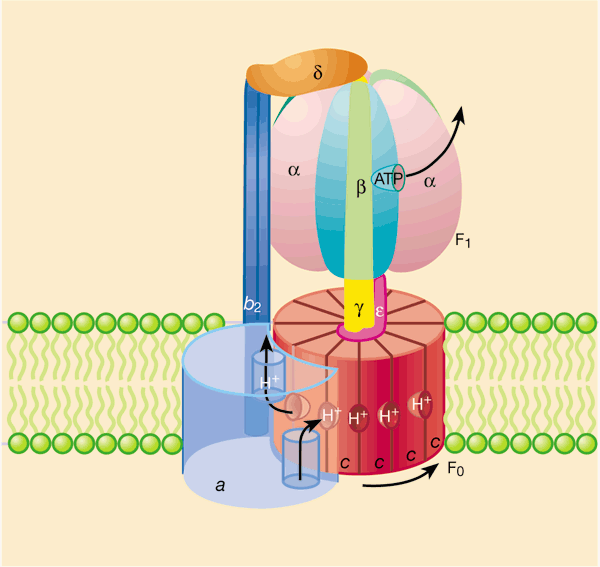
In which specific area of the mitochondrion does the concentration of H+ ions become higher, creating a potential energy gradient?
Intermembrane Space
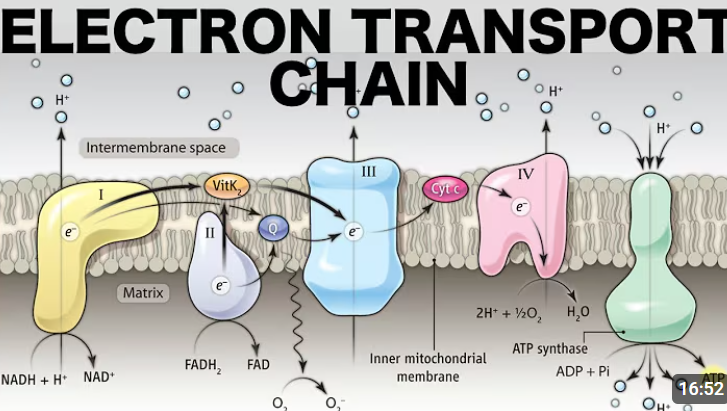
How many enzyme complexes are involved in the electron transport chain along the mitochondrial inner membrane?
4
What molecule acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, reacting with e- and H+ to form water?
Oxygen
According to the text, how many ATPs does each NADH entering the electron transport chain produce enough energy to make?
2.5 ATP
What is the total ATP yield from the NADH, FADH2, and GTP produced during one turn of the citric acid cycle, as calculated in the text?
3 NADH (rxn: 3,4,8 from Krebs) x 2.5 = 7.5 ATP
1 FADH2 (rxn:6) x 1.5 = 1.5
1 GTP (rxn: 5) x 1 = 1 ATP
TOTAL: 10 ATP per cycle
What is the name of the enzyme complex through which protons are propelled back into the mitochondrion, as described by the chemiosmotic theory?
Proton Translocation ATPase
Through which specific unit of ATP synthase do protons flow back into the matrix?
F0 Unit
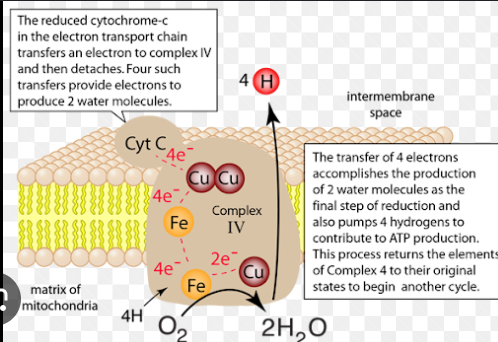
Which specific enzyme of complex IV does the CN- (produced from hydrogen cyanide) bind to?
Cytochrome oxidase
Which compound, found in the seeds and pits of apricots, peaches, and wild cherries, produces HCN by hydrolysis?
Amygdalin
The oxidation of a single FADH2 molecule provides enough energy to generate how many ATP molecules?
1.5
What are the two primary functions of O2 in the overall process of oxidative phosphorylation?
To oxidize NADH to NAD+ and FADH2 to FAD so they can return to the citric acid cycle.
To provide energy for the conversion of ADP to ATP (by accepting electrons and forming water).
At what complex does NADH get processed?
Complex I (NADH Dehydrogenase)
Which Complex in the ETC does not facilitate Hydrogen Movement?
Complex II (Succinate Dehydrogenase)
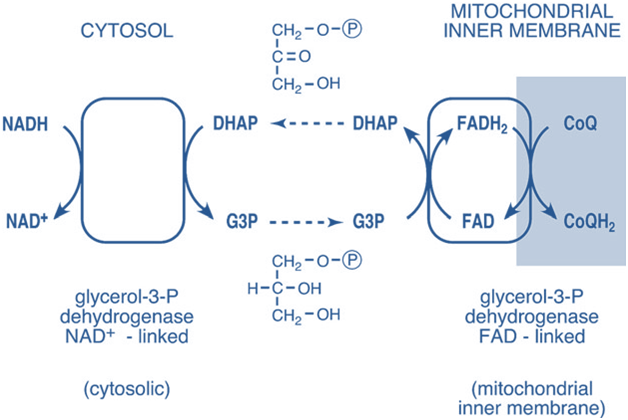
is a metabolic pathway that transports electrons from cytosolic NADH into the mitochondria that works by converting cytosolic NADH and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) into NAD+ and glycerol 3-phosphate, which then moves to the inner mitochondrial membrane
glycerophosphate shuttle
is an indirect process that moves high-energy electrons from NADH in the cytosol into the mitochondrial matrix by using oxaloacetate to form and transport malate across the inner membrane. Once inside, malate is oxidized to regenerate NADH in the matrix, which then proceeds directly to the electron transport chain to generate ATP.
Malate-Aspartate Shuttle
How does electron transfer in Complex I (NADH Dehydrogenase) happen?
Fe-S cluster transfers electrons to FMN (flavin mononucleotide) and then to Ubiquinone (Q10) afterwards to relieve oxidative stress.
H+ is also pumped to the intermembrane space (from the surplus energy of all the RedOx reactions)
is characterized by a negative change in Gibbs Free Energy meaning it releases free energy to the surroundings. These reactions are spontaneous, capable of proceeding without a continuous input of energy, and their products possess lower free energy than the reactants; they often represent catabolic (breakdown) processes
Exergonic/Favorable
has a positive Change in G > 0, signifying that it absorbs free energy from the surroundings. These reactions are non-spontaneous and require a continuous external input of energy to occur, resulting in products that have higher free energy than the reactants, which is typical of anabolic (building-up) processes.
Endergonic/Unfavorable
How does electron transfer in Complex II (Succinate Dehydrogenase) happen?
Uses Fe-S cluster to transfer e- from succinate to FAD, and then to Ubiquinone
No Protons are pumped
At what complex does FADH2 get processed?
Complex II