`Introduction to Vector Calculus
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What is a scalar quantity?
A scalar has only magnitude and sign, represented by a single number.
What is a vector quantity?
A vector has both magnitude and direction.
How is a vector represented in 2D Cartesian coordinates?
\mathbf{v} = \begin{pmatrix} \mathbf{v}_x \\ \mathbf{v}_y \end{pmatrix}
How is a vector represented in 3D Cartesian coordinates?
\mathbf{v} = \begin{pmatrix} \mathbf{v}_x \\ \mathbf{v}_y \\ \mathbf{v}_z \end{pmatrix}
What is the magnitude of a 3D vector \mathbf{v}?
|\mathbf{v}| = \sqrt{\mathbf{v}_x^2 + \mathbf{v}_y^2 + \mathbf{v}_z^2}
What is a unit vector?
A vector of magnitude 1: \hat{v} = \dfrac{\mathbf{v}}{|\mathbf{v}|}.
What does the unit vector represent?
The direction of the vector with a magnitude of 1
What is the zero vector?
A vector with zero magnitude and no defined direction, denoted \mathbf{0}.
What are the standard unit basis vectors in 3D?
\mathbf{i} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 0 \\ 0 \end{pmatrix},\;\mathbf{j} = \begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 1 \\ 0 \end{pmatrix},\;\mathbf{k} = \begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \\ 1 \end{pmatrix}
How is vector addition defined for \mathbf{v}_1 = \begin{pmatrix} \alpha \\ \beta \\ \gamma \end{pmatrix}
and \mathbf{v}_2 = \begin{pmatrix} a \\ b \\ c \end{pmatrix}
?
\mathbf{v}_1 + \mathbf{v}_2 = (\alpha + a,\; \beta + b,\; \gamma + c)
How is scalar multiplication defined for a\in\mathbb{R} and \mathbf{v}=(\alpha,\beta,\gamma) ?
a\mathbf{v} = (a\alpha,\; a\beta,\; a\gamma)
List key vector algebra properties.
Commutative and associative addition, distributive laws, additive identity, additive inverse.
What is a 2\times2 matrix?
An array of 4 scalars
M = \begin{bmatrix} a & b \\ c & d \end{bmatrix}
Define a 2\times2 matrix–vector product.
\begin{bmatrix} a & b \\ c & d \end{bmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} \alpha \\ \beta \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} a\alpha + b\beta \\ c\alpha + d\beta \end{pmatrix}
What is the 2D rotation matrix for angle \phi?
\begin{bmatrix} \cos\phi & -\sin\phi \\ \sin\phi & \cos\phi \end{bmatrix}
What is the determinant of a 2\times2 matrix?
\det(M) = ad - bc
Geometric meaning of \det(M) for 2\times2 ?
Area scaling factor; if \det(M)=0 the map is non-invertible.
Give a 3\times3 determinant formula (cofactor along first row).
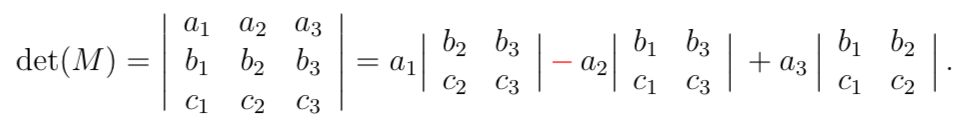
Geometric meaning of a 3\times3 determinant?
Volume scaling factor; non-zero means invertible.
Define the scalar (dot) product.
\mathbf{v}_1 \cdot \mathbf{v}_2 = |\mathbf{v}_1|\,|\mathbf{v}_2|\cos\theta
Where \theta is the angle between the two vectors.
Also equivalent is v1=(a,b) v2=(x,y) then the cross product is (ax,by) and the same applies in 3d vectors
Dot product in components (3D).
\mathbf{v}_1 \cdot \mathbf{v}_2 = \alpha \mathbf{a} + \beta \mathbf{b} + \gamma \mathbf{c}
What does a zero dot product imply?
Vectors are orthogonal (perpendicular) and \theta=\frac{\pi}{2}
What are some other things to note about dot products?
If v1=v2 then the it product = \left\vert v_1\right\vert^2
Algebraic properties follow from the definition, such as
V1 . V2 = V2 . V1
V1 .(cV2)= (cV1).V2 for any scalar c
V1 . (V2+V3) = V1.V2 + V1.V3
Component of \mathbf{v}_1 in direction of \mathbf{v}_2
The component of a vector v1 in the direction of another vector v2 is the scalar quantity
|\mathbf{v}_1|\cos\theta = \frac{\mathbf{v}_1 \cdot \mathbf{v}_2}{|\mathbf{v}_2|}
Where \theta is the angle between the vectors.
Define the vector (cross) product.
\mathbf{v}_1 \times \mathbf{v}_2 = |\mathbf{v}_1|\,|\mathbf{v}_2|\sin\theta\,\hat{n}
Where \hat{n} is a unit vector perpendicular to both v1 and v2 such that {v1,v2,v3} form a right handed set, and \theta is the angle between the vectors.
Cross product in components for \vec{v}_1\times\vec{v}_2=|\vec{v}_1|\,|\vec{v}_2|\cos\theta
and the determinant form
\mathbf{v}_1\times\mathbf{v}_2=(\beta c-\gamma b,\;\gamma a-\alpha c,\;\alpha b-\beta a)
Think of it as the same way of calculating a determinant.
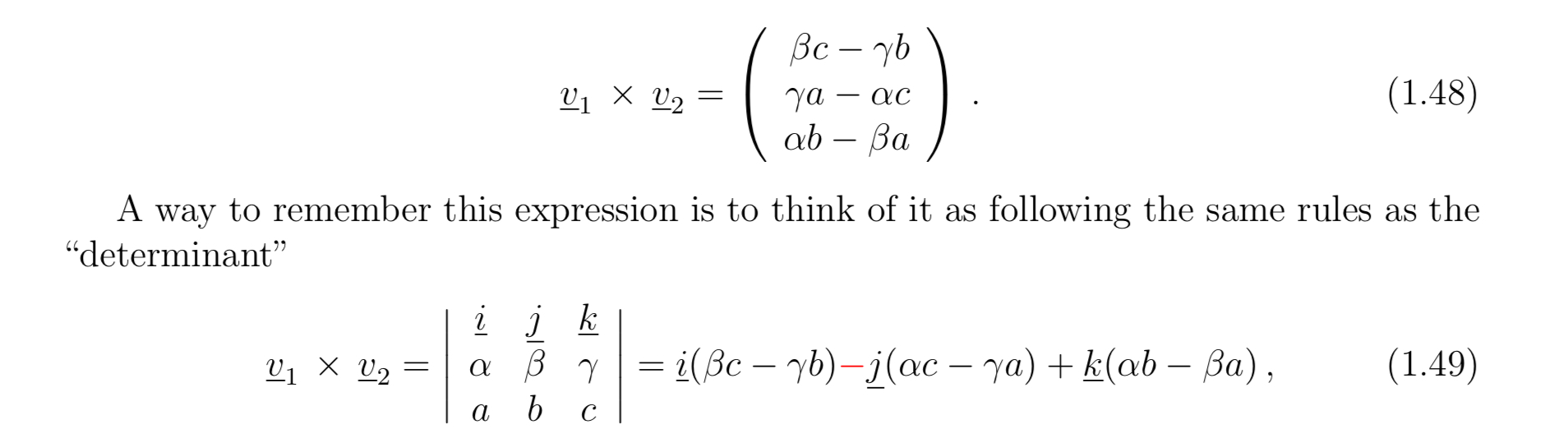
What is the cross product always perpendicular to?
The two ‘input vectors’
Does the cross product commute?
No
\vec{v}_1 \times \vec{v}_2 = -\,(\vec{v}_2 \times \vec{v}_1)
Is the cross product associative?
Not in general
(V1xV2)xV3 isn’t generally the same as V1x(V2xV3)
What are the algebraic properties of the vector cross product?
Basis-vector cross products.
\mathbf{i}\times\mathbf{j}=\mathbf{k},\; \mathbf{j}\times\mathbf{k}=\mathbf{i},\; \mathbf{k}\times\mathbf{i}=\mathbf{j}
Cross product when vectors are parallel.
\vec{v}_1 \times \vec{v}_2 = \vec{0}
Dot vs cross product roles.
Dot:
The dot product of two vectors represents their similarity or how much they point in the same direction.
Outputs a scalar
Cross:
a new vector that is perpendicular to both original vectors. The magnitude of this new vector represents the area of the parallelogram formed by the two original vectors.
vector output