Chapter 09: Ventilator Graphics & Mechanical Vent chapter 10 Assessment of Respiratory Function
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
A pulse oximeter differentiates oxyhemoglobin from deoxygenated hemoglobin by which of the following methods?
Shining and comparing two wavelengths of light through the sampling site
What is the minimum pulse oximetry finding that indicates an arterial blood gas should be done to confirm O2 saturations?
80%.
A pulse oximeter reading will be most accurate when used with a patient in which of the following situations?
An intensive care unit patient with hyperbilirubinemia
A patient arrives in the emergency department via ambulance following rescue from a house fire. The instrument that would be most appropriate to assist the respiratory therapist in assessing this patient's oxygenation status is which of the following?
CO-oximeter
While trying to use a finger probe to assess a patient's oxygenation status, the respiratory therapist finds that the pulse rate and the ECG monitor heart rate are not consistent and the oxygen saturation measured by pulse oximeter (SpO2) reading is blank. The patient is awake, alert, and in no obvious respiratory distress. The respiratory therapist should first take which of the following actions?
1. Change the probe site.
2. Draw an arterial blood gas.
3. Adjust the probe position on the finger.
4. Remove the probe, and perform a capillary refill test
3,4
Pulse oximetry is most useful in which of the following situations?
Monitoring patients undergoing chest physical therapy
During which phase of a capnograph does alveolar gas containing carbon dioxide (CO2) mix with gas from the anatomical airways and the CO2 concentration rises?
Phase 2
During which phase of a capnogram does inhalation occur?
Phase 4
The respiratory therapist has just stopped postural drainage for a 24-year-old patient with cystic fibrosis because of shortness of breath and slight cyanosis in the "head-down" position. The respiratory therapist should recommend which of the following adjustments to therapy?
Administer oxygen via nasal cannula and monitor with pulse oximetry
A patient receiving mechanical ventilation is being continuously monitored for oxygen saturation measured by pulse oximeter (SpO2) for the past 48 hours. When initially applied, the SpO2 and the arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2), as well as the pulse on the pulse oximeter, ECG, and manual pulse, were consistent. During clinical rounds, the respiratory therapist notices that although the probe is appropriately placed and capillary refill is normal, the SpO2 reading is down to 90% from 95%. The most appropriate immediate action is to do which of the following?
Draw an arterial blood gas
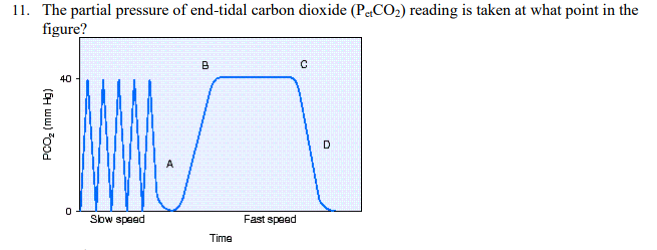
The partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide (PetCO2) reading is taken at what point in the figure?
Point C
A patient in the intensive care unit is receiving mechanical ventilation, has a pulmonary artery catheter in place, and is being monitored continuously with a capnometer. The patient's arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) is 41 mm Hg and the partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide (PetCO2) is 36 mm Hg. There is a sudden decrease in the PetCO2 to 18 mm Hg causing an alarm to sound. The most likely cause of this development is which of the following?
Pulmonary embolism
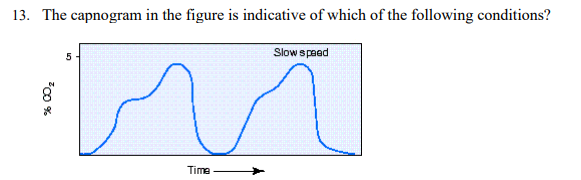
The capnogram in the figure is indicative of which of the following conditions?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
For a given minute ventilation, partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide (PetCO2) is a function of which of the following?
1. Metabolic rate
2. Cardiac output
3. Alveolar dead space
4. Physiologic shunt
1,2,3
The normal range for arterial-to-end-tidal partial pressure of carbon dioxide [P(a-et)CO2] is which of the following?
4-6 mm Hg
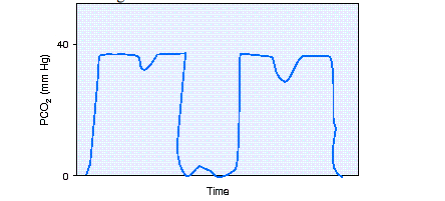
During shift report, the day shift respiratory therapist informs the night shift respiratory therapist about a freshly postoperative patient who is receiving full support via mechanical ventilation. At the time of the last patient-ventilator system check the patient had not awaken from anesthesia. During first round on the day shift the respiratory therapist notes the capnography shown in the figure. The most appropriate action to take would be to do which of the following?
Begin the weaning process
The area under the curve of a single-breath carbon dioxide (SBCO2) curve represents which of the following?
Effective alveolar ventilation
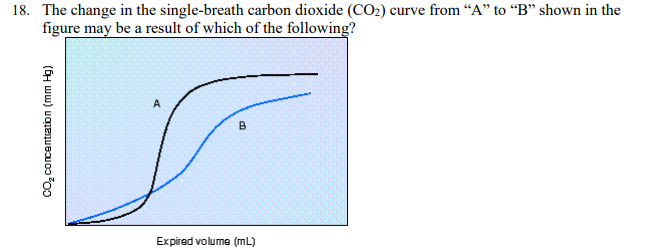
The change in the single-breath carbon dioxide (CO2) curve from "A" to "B" shown in the figure may be a result of which of the following?
Increased mean airway pressure
Which of the following situations will cause an increase in the single-breath carbon dioxide (SBCO2) curve?
Increased metabolic rate and decreased ventilation

The area represented by the letter "Y" in the figure is which of the following?
Alveolar dead space
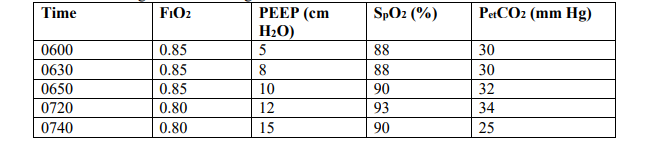
A patient is receiving mechanical ventilation with a fractional inspired oxygen (FIO2) of 0.85 and a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of 5 cm H2O. His arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) is 68 mm Hg, arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) is 88%, and partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide (PetCO2) is 32 mm Hg. Over the next few minutes his PEEP is titrated resulting in the following data:
Reduce the PEEP to 12 cm H2O.
Exhaled nitric oxide is used to monitor the effectiveness of which drug used in the treatment of asthma?
Inhaled corticosteroids
The condition that is associated with a reduction in exhaled nitric oxide is which of the following?
Cystic fibrosis
What type of electrode is used by a transcutaneous partial pressure of oxygen (PtcO2) device
Polarographic
To properly operate, the transcutaneous partial pressure of oxygen electrode needs to be at what temperature range?
42-45° C
A transcutaneous partial pressure of oxygen (PtcO2) reading is reliable in which of the following situations?
Infant respiratory distress syndrome
What type of electrode is used by a transcutaneous partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PtcCO2) device?
Stow-Severinghaus
During calibration of a transcutaneous monitor the respiratory therapist notices a signal drift. The respiratory therapist should do which of the following?
Change the electrolyte and sensor's membrane.
How often should the respiratory therapist reposition the sensor of a transcutaneous monitor?
4-6 hours
The clinical data that should be recorded when making transcutaneous measurements include which of the following?
1. Electrode temperature
2. Skin temperature
3. Probe placement
4. Fractional inspired oxygen (FIO2)
1,2,3,4
Components of an indirect calorimeter may include which of the following?
1. Pressure manometer
2. Pneumotachometer
3. Pressure-sensitive transducer
4. Oxygen and carbon dioxide analyzers
2,4
An energy expenditure (EE) of 60 kcal/hr/m2 for an adult is indicative of which of the following conditions?
Burns
An energy expenditure (EE) of 20 kcal/hr/m2 for an adult is indicative of which of the following conditions?
Starvation
The respiratory quotient (RQ) value associated with substrate utilization patterns in normal, healthy individuals is which of the following?
0.8
A patient whose carbon dioxide (CO2) production is 390 mL/min and oxygen (O2) consumption is 375 mL/min is most likely experiencing which of the following?
Hyperventilation
A mechanically ventilated patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is in the process of being weaned from mechanical ventilation. A diet containing which of the following will be most beneficial to this process?
Low carbohydrate with increased fats and proteins
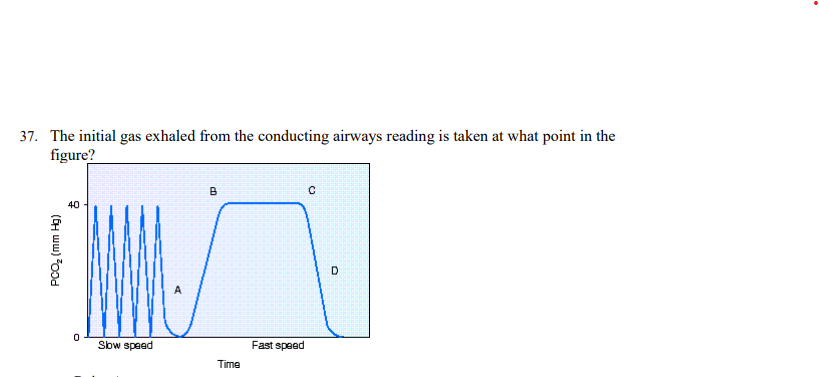
The initial gas exhaled from the conducting airways reading is taken at what point in the figure?
Point A
Which of the following actions is indicated when a disparity exists between SpO2, SaO2, and the clinical presentation of a patient?
Measure arterial oxygen saturation by CO-oximetry
To measure plateau pressure, inspiration should be held for how many seconds
1-2
Select the ventilator flowmeter that will read accurately when used with heliox
Vortex ultrasonic
Bidirectional flow can be measured by which of the following devices?
Variable orifice pneumotachometer
During the application of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), the monitoring of which pressure will alert the respiratory therapist specifically to alveolar overdistention?
Plateau pressure (Pplat)
A patient-ventilator system check reveals the following information: peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) 27 cm H2O, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) 5 cm H2O, plateau pressure (Pplat) 14 cm H2O, inspiratory time (TI) 0.75 second, and set frequency 20/minute. Calculate the mean airway pressure
7.75 cm H2O
A patient-ventilator system check reveals the following information: peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) 32 cm H2O, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) 12 cm H2O, plateau pressure (Pplat) 20 cm H2O, inspiratory time (TI) 1 second, and set frequency 12/min. Calculate the mean airway pressure.
14 cm H2O
Calculate the dynamic compliance given the following clinical data: tidal volume 500 mL, peak inspiratory time (PIP) 35 cm H2O, plateau pressure (Pplat) 20 cm H2O, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) 5 cm H2O, and tubing compliance (CT) 2.5 mL/cm H2O.
14.2 mL/cm H2O
Calculate dynamic compliance given the following clinical data: tidal volume 600 mL, peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) 28 cm H2O, plateau pressure (Pplateau) 15 cm H2O, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) 10 cm H2O, and CT 2 mL/cm H2O.
31.3 mL/cm H2O
Calculate the static compliance given the following clinical data: tidal volume 500 mL, peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) 35 cm H2O, plateau pressure (Pplat) 25 cm H2O, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) 12 cm H2O, measured unintended positive end-expiratory pressure (auto-PEEP) 3 cm H2O, and tubing compliance (CT) 2.5 mL/cm H2O.
47.5 mL/cm H2O
Calculate the static compliance given the following clinical data: tidal volume 600 mL, peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) 40 cm H2O, plateau pressure (Pplat) 30 cm H2O, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) 15 cm H2O, and tubing compliance (CT) 2 mL/cm H2O.
38 mL/cm H2O
Calculate the airway resistance given the following clinical data: flow rate 60 L/min, peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) 42 cm H2O, plateau pressure (Pplat) 15 cm H2O, and positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) 5 cm H2O.
30 cm H2O/L/sec
Calculate the airway resistance given the following clinical data: flow rate 60 L/min, PIP 28 cm H2O, Pplat 21 cm H2O, and PEEP 8 cm H2O
7 cm H2O/L/sec
The energy required to move gas through the airways and expand the thorax is known as which of the following?
Intrinsic work of breathing
An increase in intrinsic work of breathing due to a decrease in static compliance is caused by which of the following?
Pulmonary fibrosis
The best assessment of the function of the diaphragm during inspiration is obtained by measuring which of the following?
Pressure-time product
At which point in the pressure-time curve of a spontaneous breath should the transdiaphragmatic pressure be greatest?
Mid-inspiration
Which of these parameters may be used as a predictor of weaning success?
1. O2Hb
2. Hb
3. COHb
4. MetHb
1,2
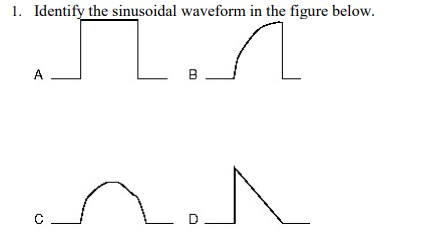
Identify the sinusoidal waveform in the figure below.
Figure C
The two waveforms that are common for pressure scalars are which of the following?
Rectangular and exponential rise
The most important factor to affect the degree of resistance in the airways is which of the following?
Diameter of the airways
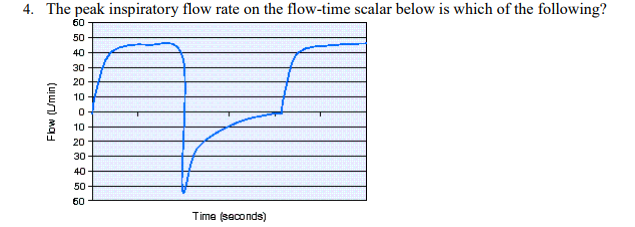
The peak inspiratory flow rate on the flow-time scalar below is which of the following?
46 L/min
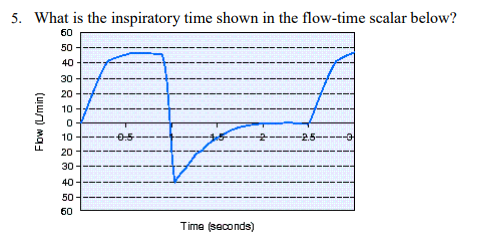
What is the inspiratory time shown in the flow-time scalar below?
1 second
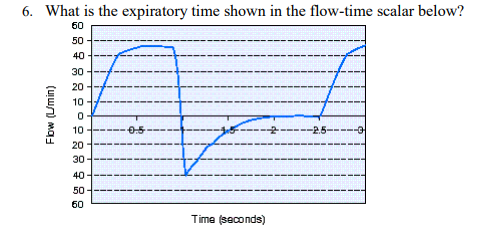
What is the expiratory time shown in the flow-time scalar below?
1.5 second
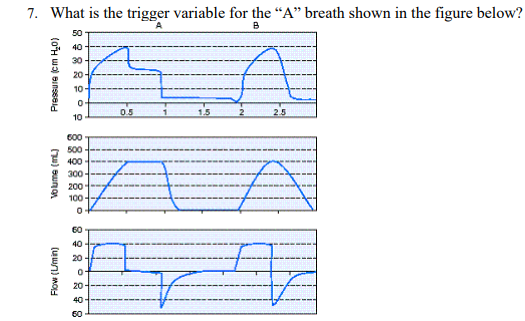
What is the trigger variable for the "A" breath shown in the figure below?
Time
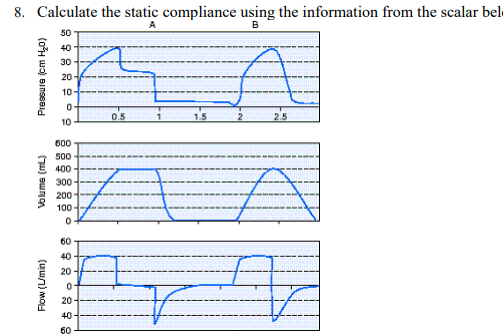
Calculate the static compliance using the information from the scalar below.
20 mL/cm H2O
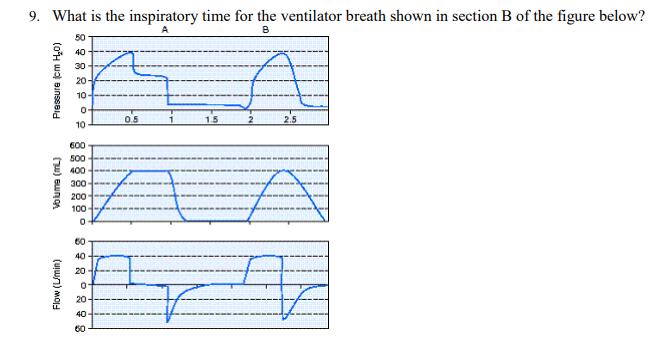
What is the inspiratory time for the ventilator breath shown in section B of the figure below?
0.5 second
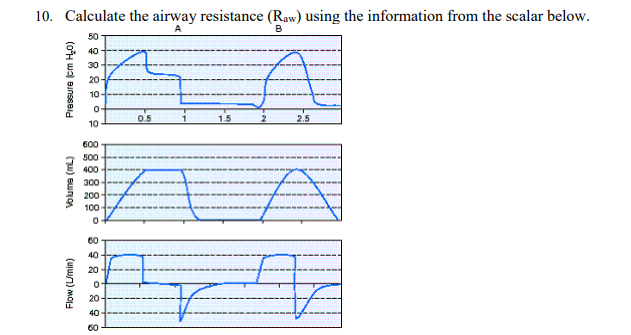
Calculate the airway resistance (Raw) using the information from the scalar below.
22.4 cm H2O/L/sec
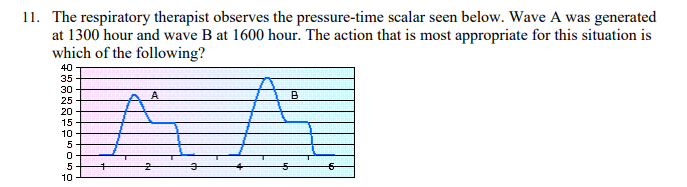
The respiratory therapist observes the pressure-time scalar seen below. Wave A was generated at 1300 hour and wave B at 1600 hour. The action that is most appropriate for this situation is which of the following?
Administer a bronchodilator.
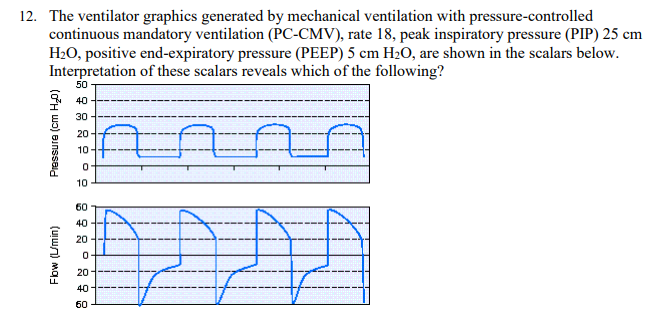
The ventilator graphics generated by mechanical ventilation with pressure-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation (PC-CMV), rate 18, peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) 25 cm H2O, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) 5 cm H2O, are shown in the scalars below. Interpretation of these scalars reveals which of the following?
There is air trapping that could be due to a high respiratory rate.
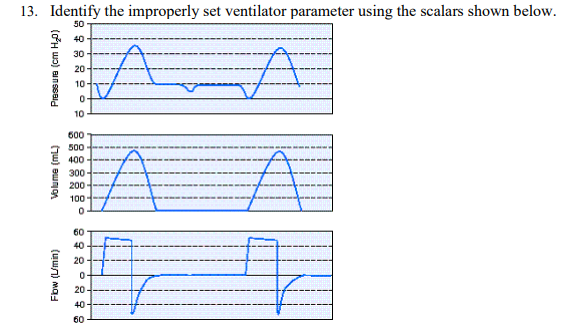
Identify the improperly set ventilator parameter using the scalars shown below
Sensitivity
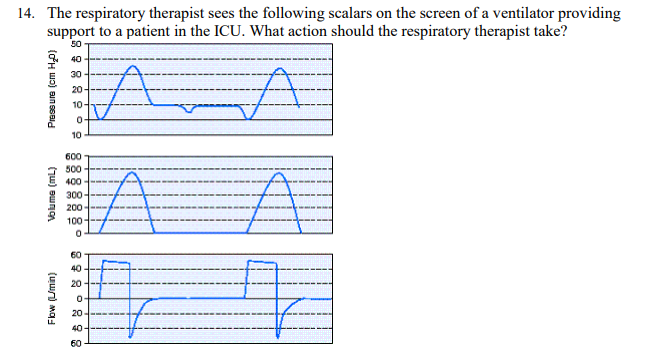
The respiratory therapist sees the following scalars on the screen of a ventilator providing support to a patient in the ICU. What action should the respiratory therapist take?
Decrease the sensitivity to 2 cm H2O
The volume curve on a volume-time scalar is consistently dropping below the baseline during exhalation. The first action to take is which of the following?
Assess the patient for active exhalation.
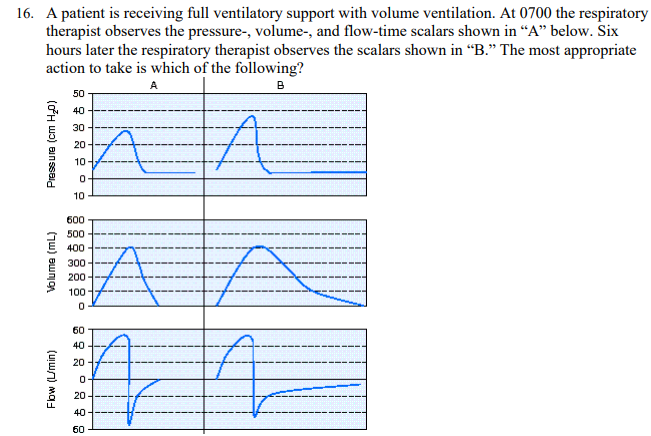
A patient is receiving full ventilatory support with volume ventilation. At 0700 the respiratory therapist observes the pressure-, volume-, and flow-time scalars shown in "A" below. Six hours later the respiratory therapist observes the scalars shown in "B." The most appropriate action to take is which of the following?
Administer a bronchodilator.
An inadequate flow setting during volume ventilation will cause which of the following to occur?
The pressure-time curve will appear concave during inspiration.
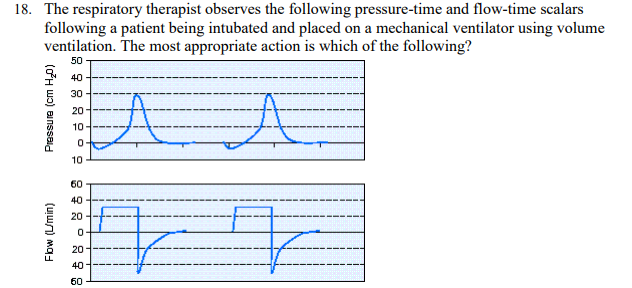
The respiratory therapist observes the following pressure-time and flow-time scalars following a patient being intubated and placed on a mechanical ventilator using volume ventilation. The most appropriate action is which of the following?
Increase the set flow rate.
The type of flow curve produced by volume ventilation with constant flow is which of the following?
Rectangular
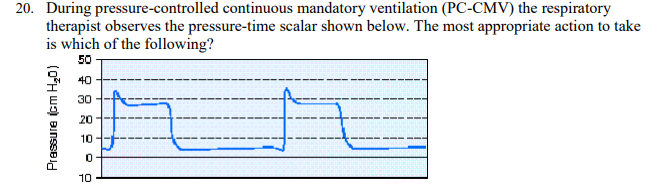
During pressure-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation (PC-CMV) the respiratory therapist observes the pressure-time scalar shown below. The most appropriate action to take is which of the following?
Adjust the inspiratory rise time control
An increase in airway resistance during pressure ventilation will result in which of the following?
Inspiration will end prior to flow tapering to zero.
A reduction in compliance during pressure ventilation will cause which of the following?
Delivered tidal volume will decrease.
Delayed termination during pressure support ventilation (PSV) can be avoided with patients who have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) by doing which of the following?
Increase flow-cycle percent
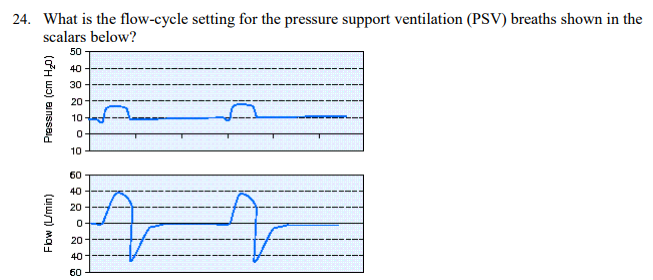
What is the flow-cycle setting for the pressure support ventilation (PSV) breaths shown in the scalars below?
50%
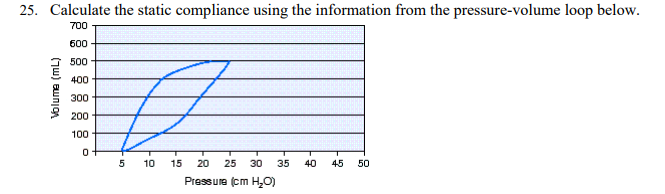
Calculate the static compliance using the information from the pressure-volume loop below.
30 mL/cm H2O
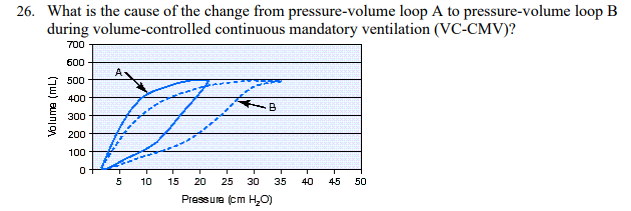
What is the cause of the change from pressure-volume loop A to pressure-volume loop B during volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation (VC-CMV)?
Decreased compliance
. During a patient-ventilator system check the respiratory therapist notices that the pressure-volume loop begins at zero on the x-axis but does not return to zero during expiration. The cause of this is which of the following?
Ventilator circuit leak
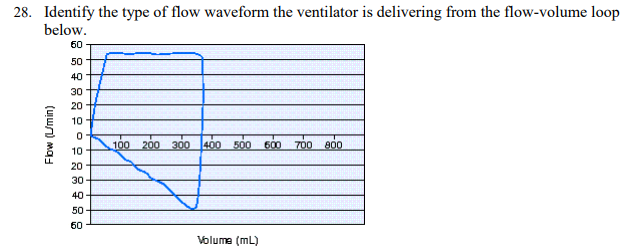
Identify the type of flow waveform the ventilator is delivering from the flow-volume loop below
Rectangular
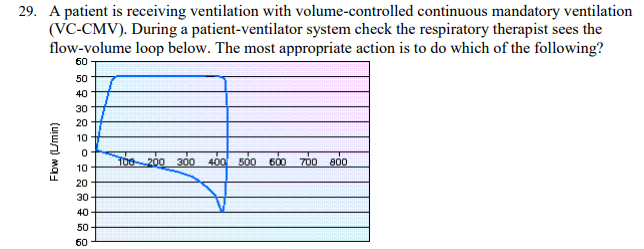
A patient is receiving ventilation with volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation (VC-CMV). During a patient-ventilator system check the respiratory therapist sees the flow-volume loop below. The most appropriate action is to do which of the following?
Administer a bronchodilator.
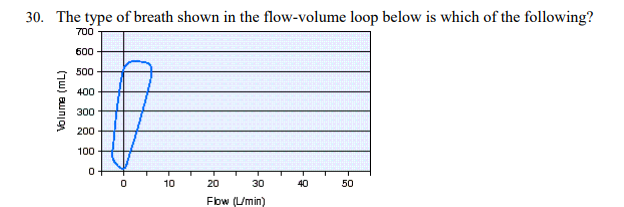
The type of breath shown in the flow-volume loop below is which of the following?
Spontaneous without support
Which of the following conditions causes a pressure-volume loop during volume-controlled continuous mandatory ventilation (VC-CMV) to extend farther to the right and flatten out
Pneumonia
The term used to specify the flow, pressure, and volume waveforms that are graphed relative to time is called:
Scalar
A difficult to wean patient with COPD has an RQ of 0.98. The most likely cause of this patient's inability to be weaned is which of the following?
Excessive carbohydrates are overloading the patient's ventilatory reserve
The partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide is read at what point on a capnogram?
During Phase 3
Which of the following most directly affects the response time of a pulse oximeter?
The location of the sensor or probe
A pulse oximeter is generally considered accurate for oxygen saturation's greater than which of the following?
80%
A respiratory therapist is called to the bedside of a patient who is being transcutaneously monitored for P02 and PC02. The signal is drifting and will not stabilize during calibration. The most appropriate action includes which of the following?
1. Recalibrate the monitor with 15 and 20% C02.
2. Clean the electrode and change the sensor membrane.
3. Remove excess electrolyte solution from the electrode surface.
4. Add a drop of electrolyte solution to the electrode surface.
2,4
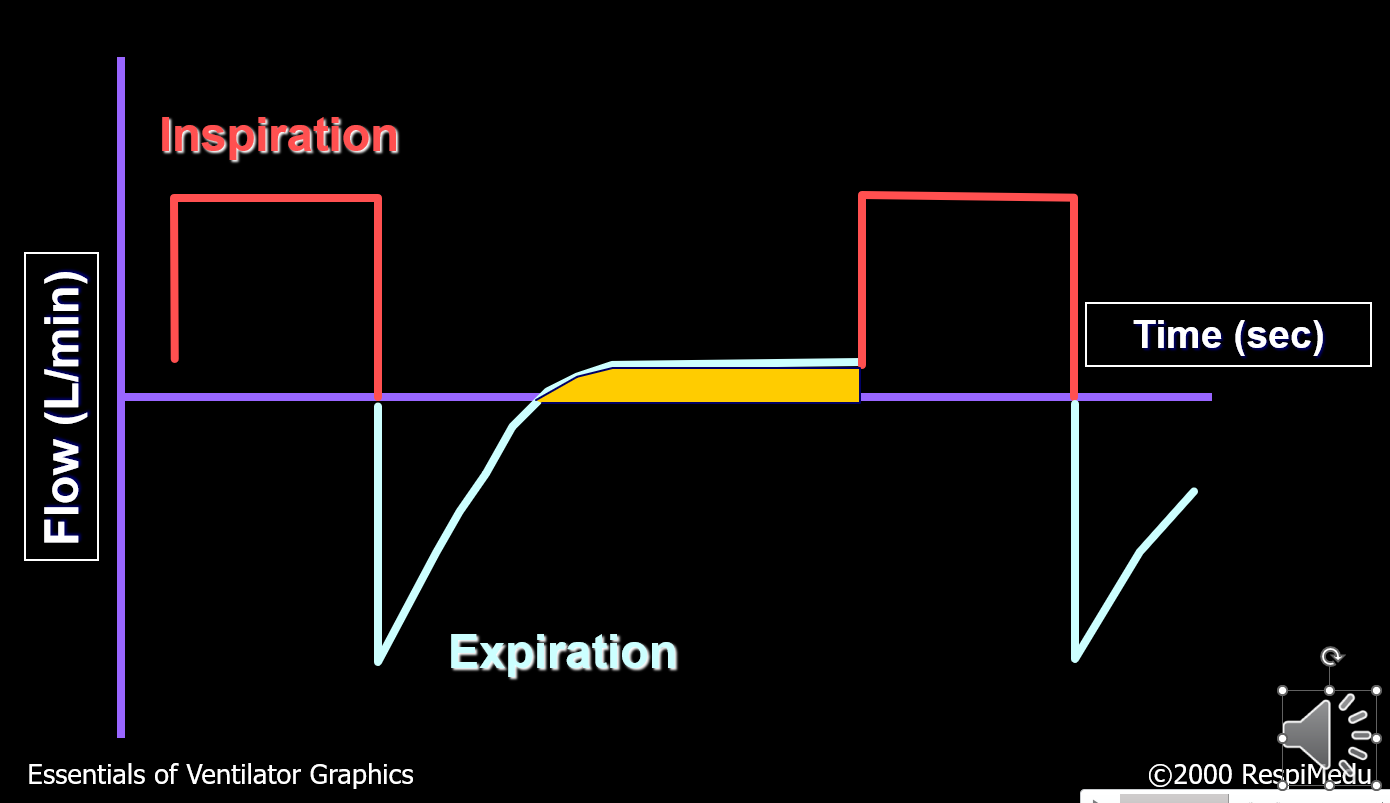
What abnormality is shown in the picture?
Air Leak
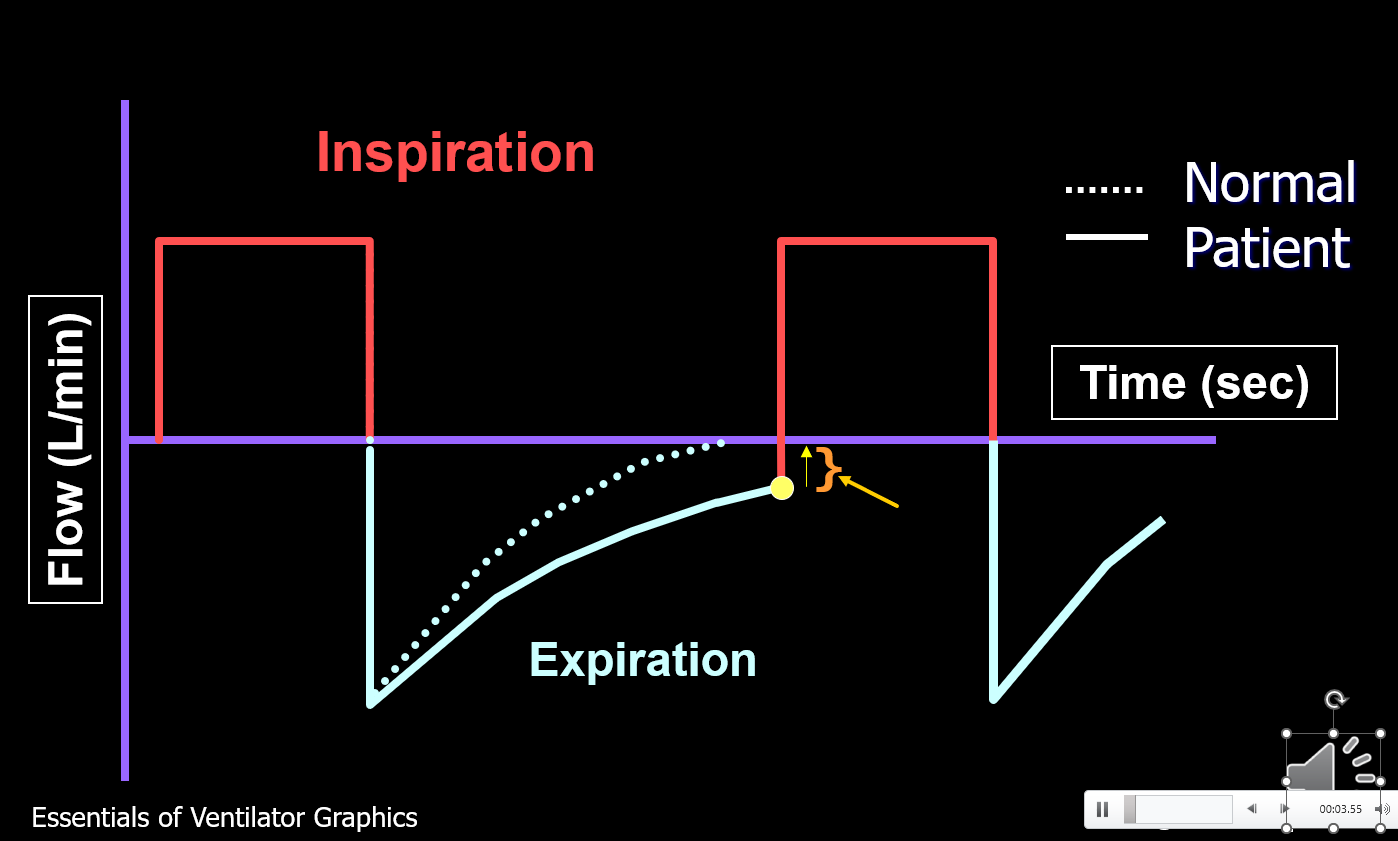
What is shown in the picture?
Air Trapping aka Auto PEEP
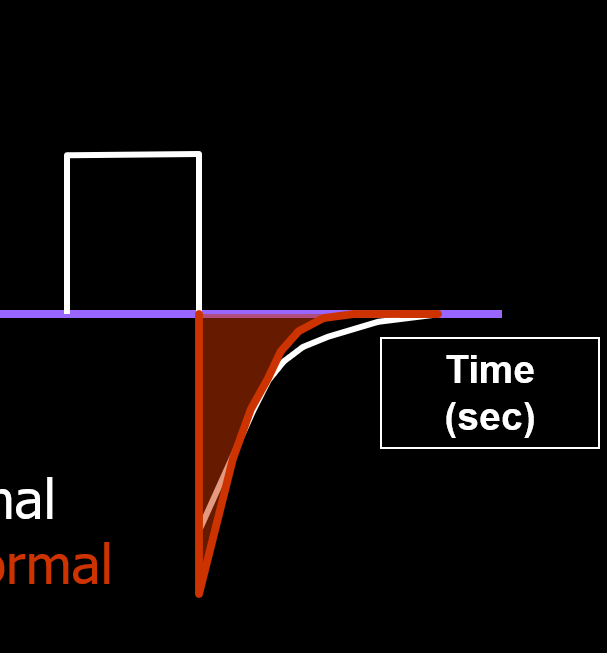
What is show in the picture?
Active Expiration
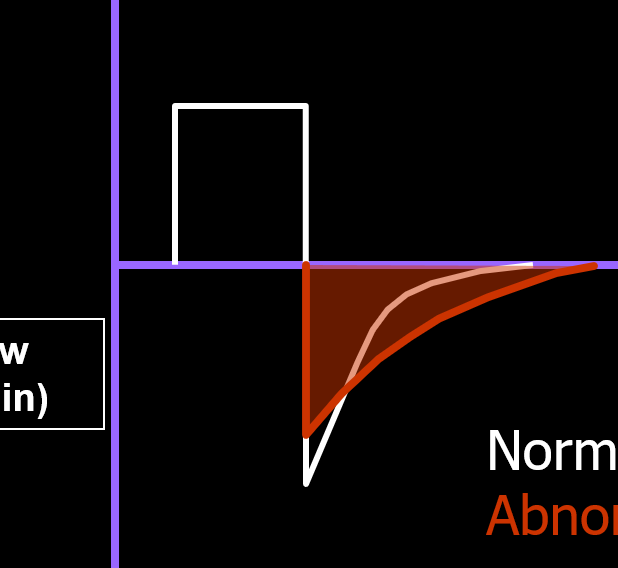
What is shown in the picture?
Obstruction
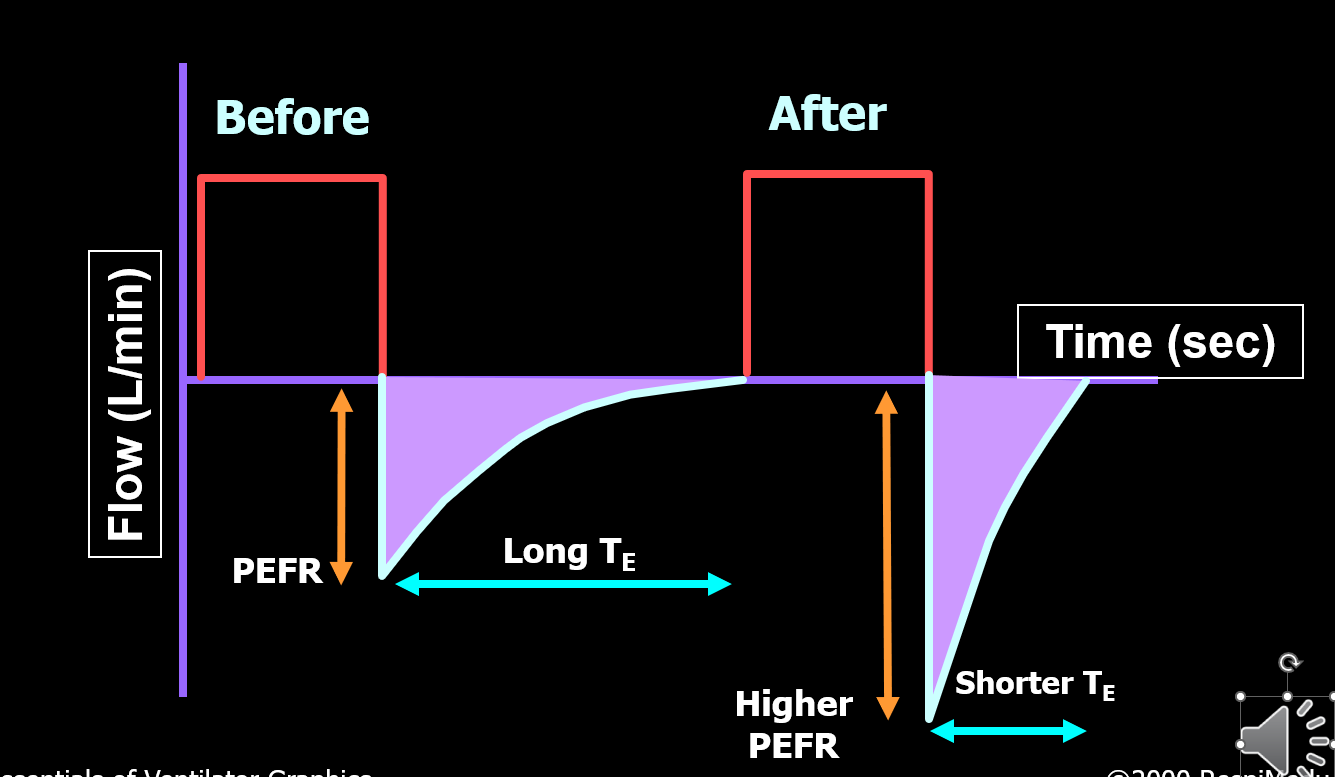
What is going on in the flow time waveform?
Flow response after bronchodilator treatment
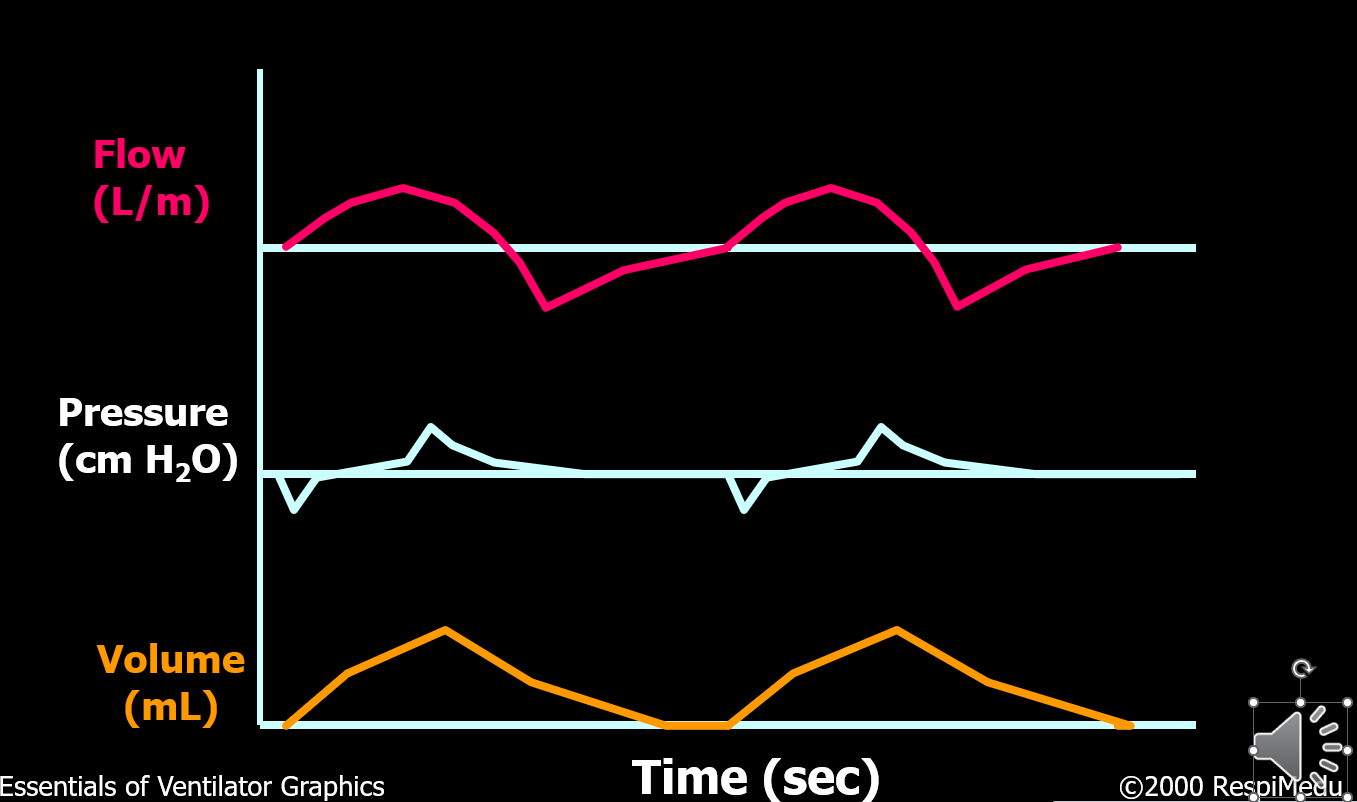
What type of breath is this?
Spontaneous
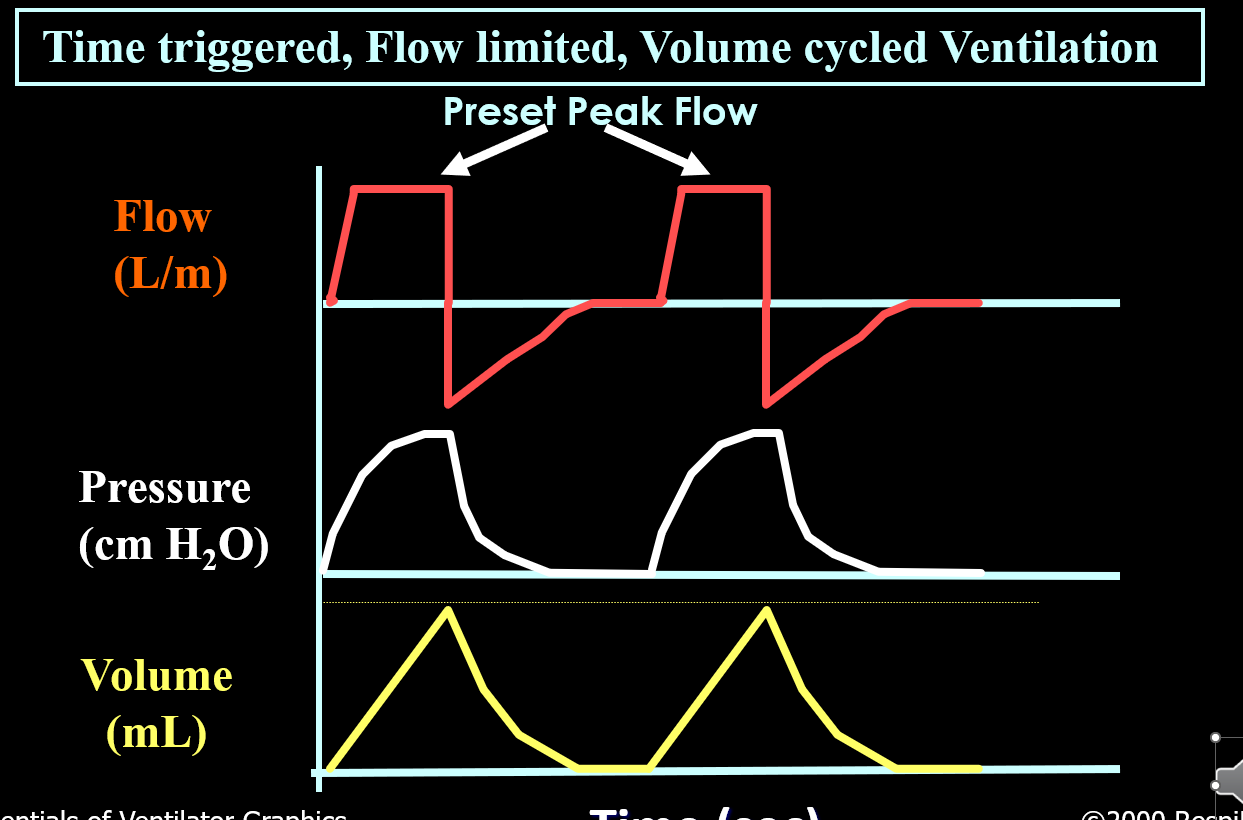
What mode is this?
Assist Control / Volume control
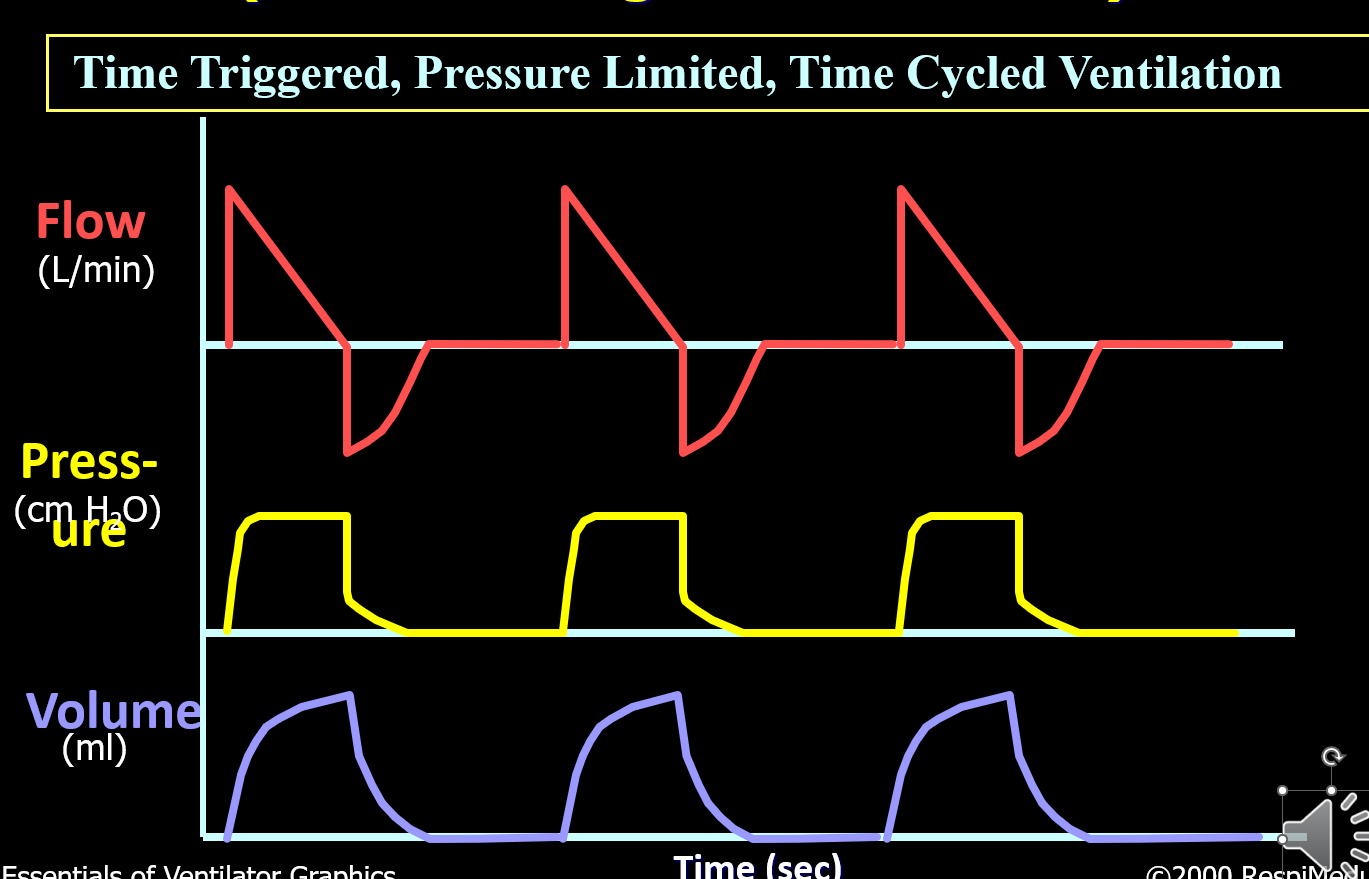
What mode is this?
Assist control / Pressure control