IB Biology HL - B2.3: Cell Specialization
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
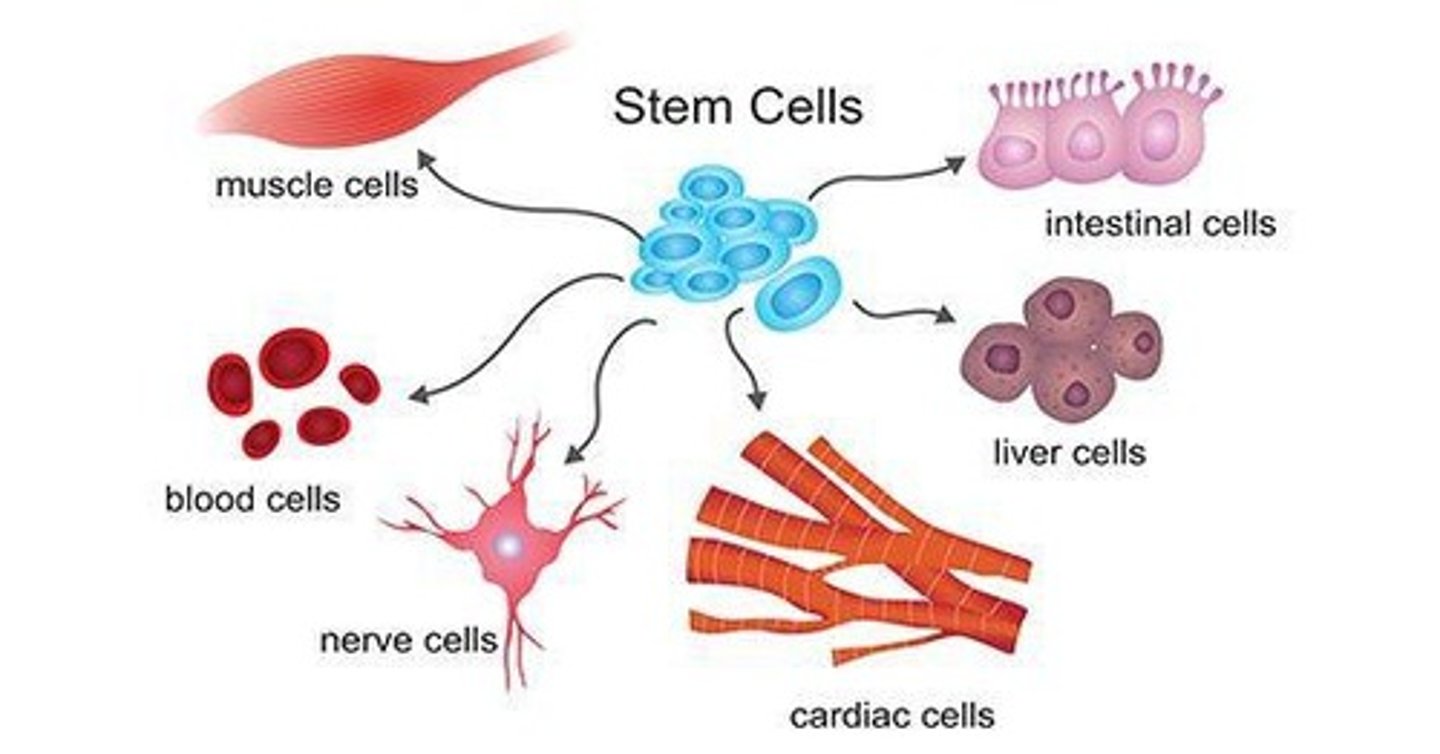
Stem Cells
Undifferentiated cells that can divide indefinitely.
Zygote
Single, unspecialized cell formed after fertilization.
Differentiation
Process of unspecialized cells becoming specialized.
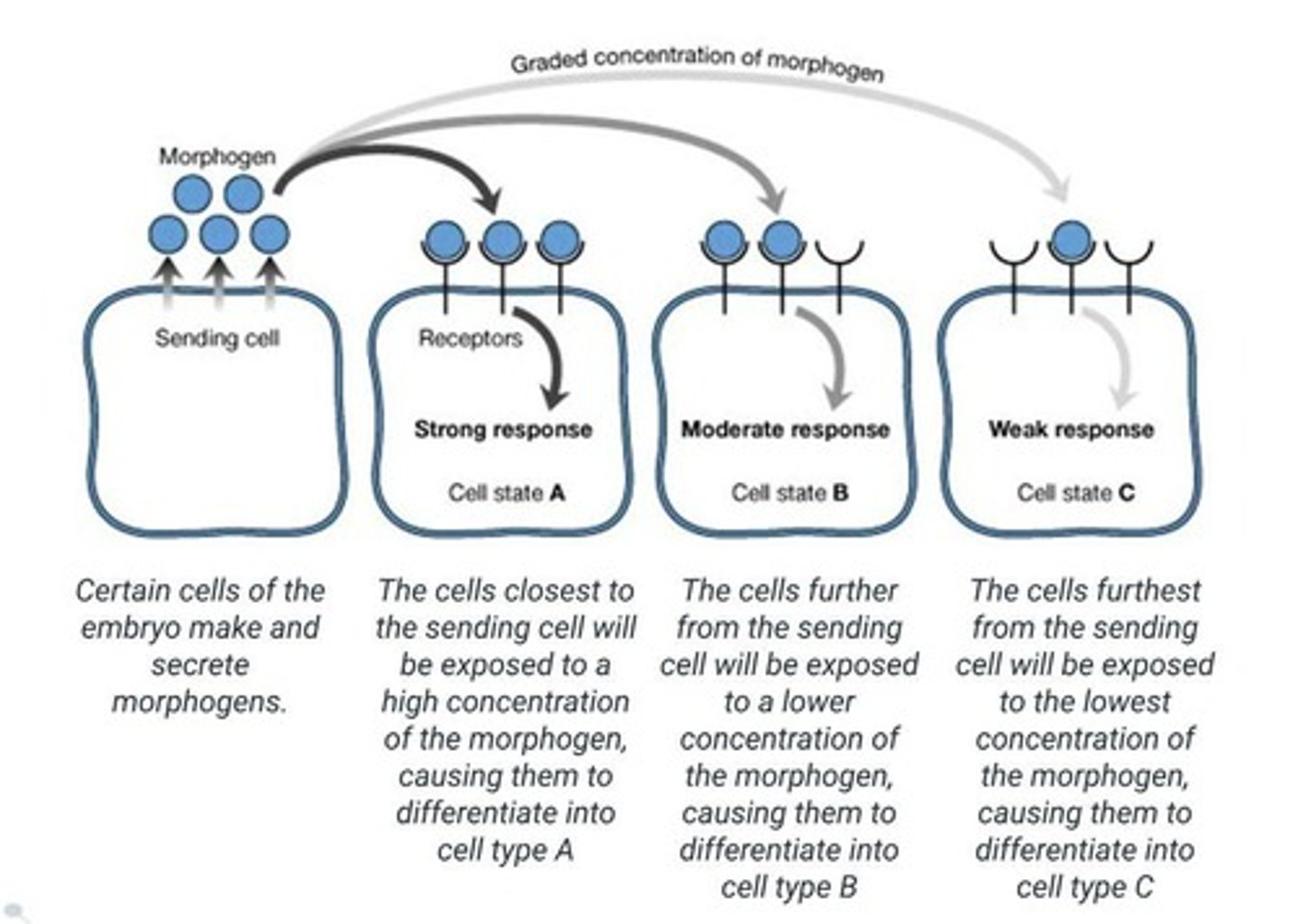
Morphogens
Signaling molecules influencing gene expression and cell fate.
Cell Specialization
Cells perform specific functions with increased efficiency.
Self-Renewal
Stem cells can divide without limit.
Potency
Ability of stem cells to differentiate into specialized cells.
Stem Cell Niche
Microenvironment regulating stem cell behavior.
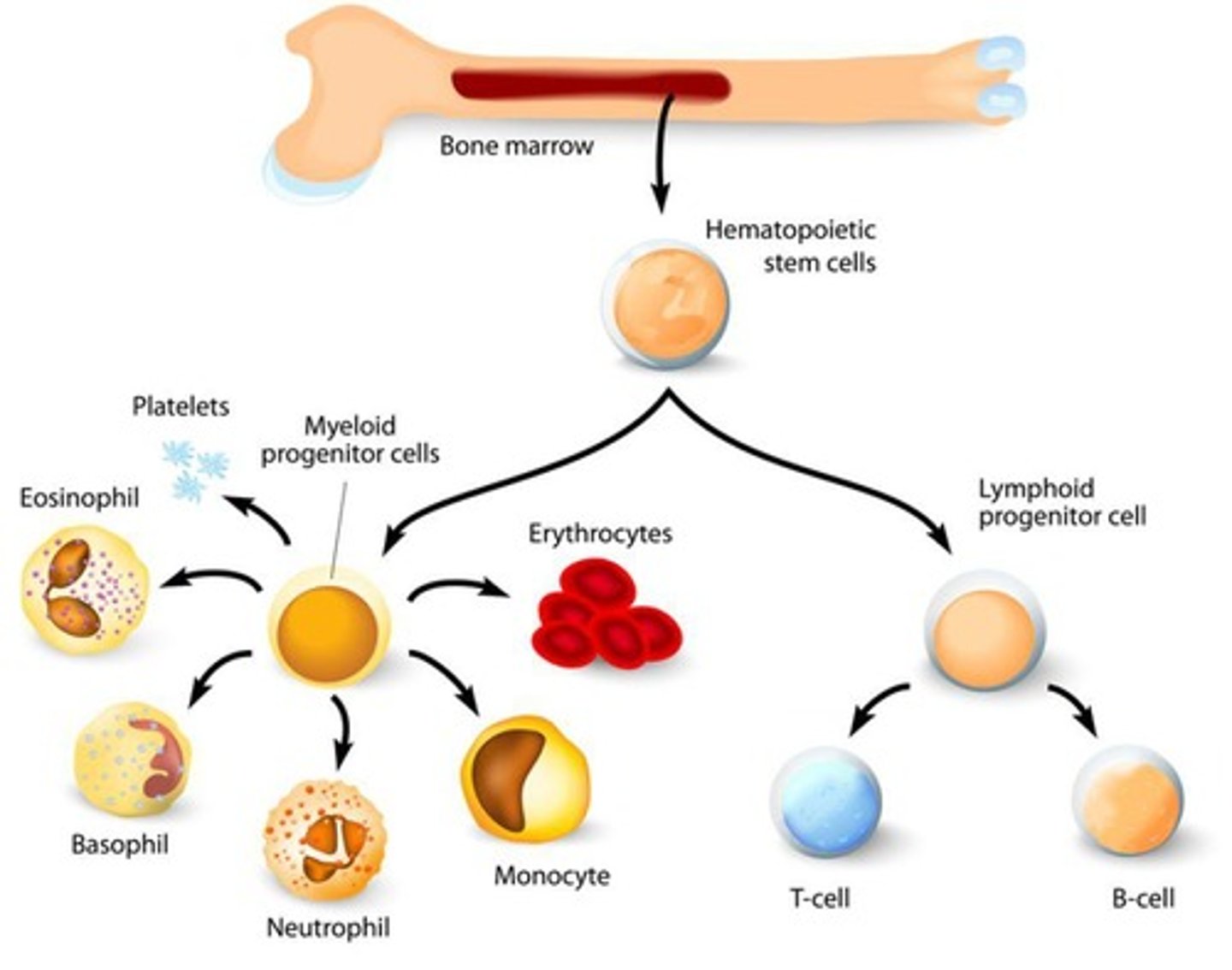
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Produce blood cells in bone marrow.
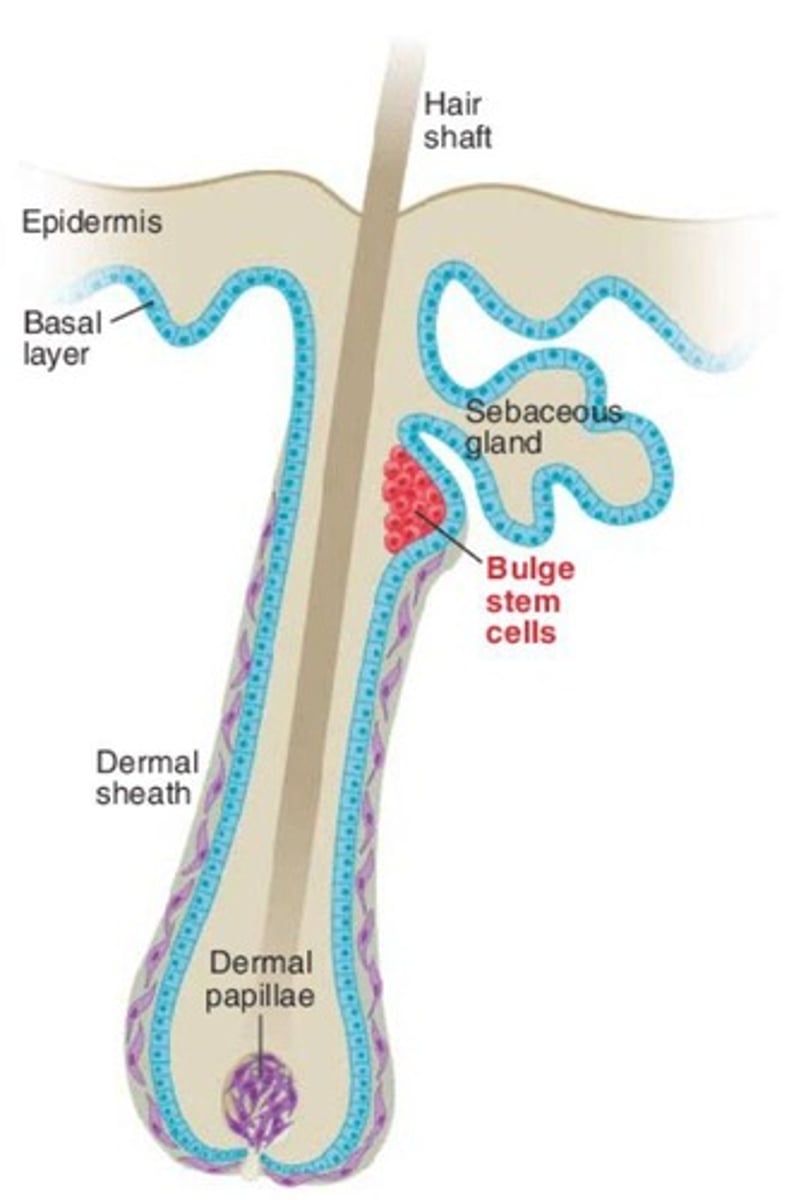
Epithelial Stem Cells
Regenerate from hair follicle bulge.
Totipotent Stem Cells
Can become any cell type, e.g., zygote.
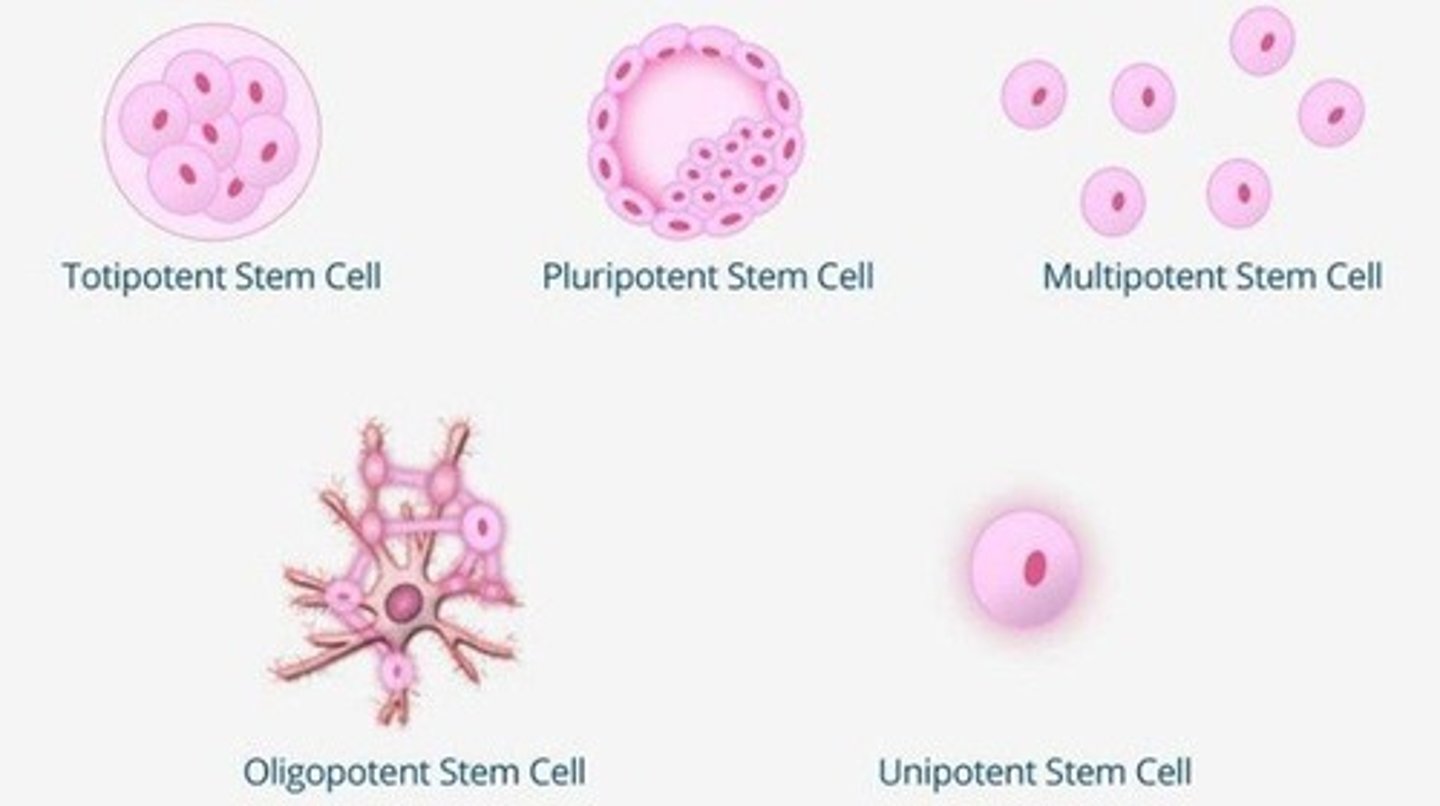
Pluripotent Stem Cells
Can become any body cell except placenta.
Multipotent Stem Cells
Can become a limited range of cell types.
Blastocyst
Early embryo stage with pluripotent stem cells.
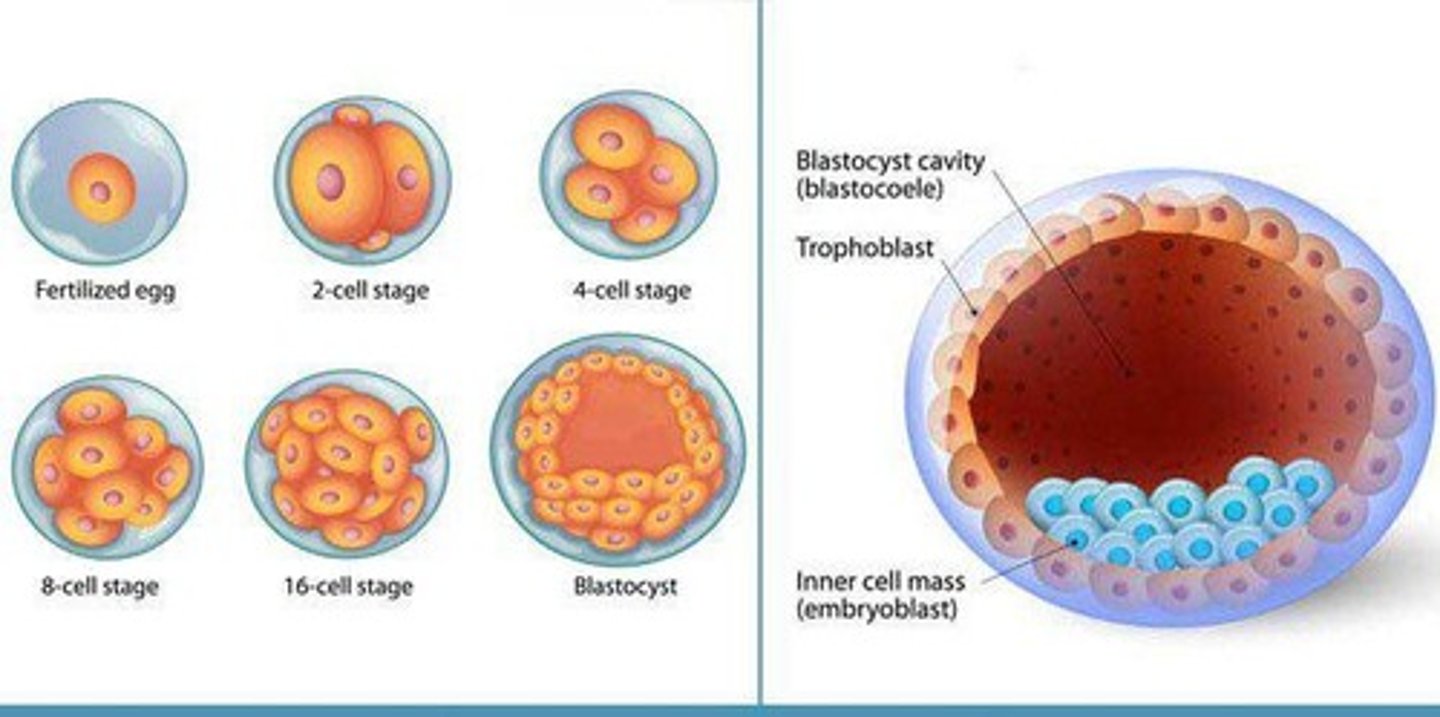
Ectoderm
Germ layer forming skin and nervous system.
Mesoderm
Germ layer forming muscles and internal organs.
Endoderm
Germ layer forming digestive and respiratory systems.
Surface Area-to-Volume Ratio
Measurement affecting cell size and efficiency.
Cell Size Constraints
Limits on cell size due to surface area.
Adaptations for Surface Area
Changes to increase surface area-to-volume ratios.
Embryonic Development
Process where cells specialize as the fetus forms.
Specialized Functions
Unique roles cells perform based on their structure.
Gene Expression
Process by which information from genes is used.
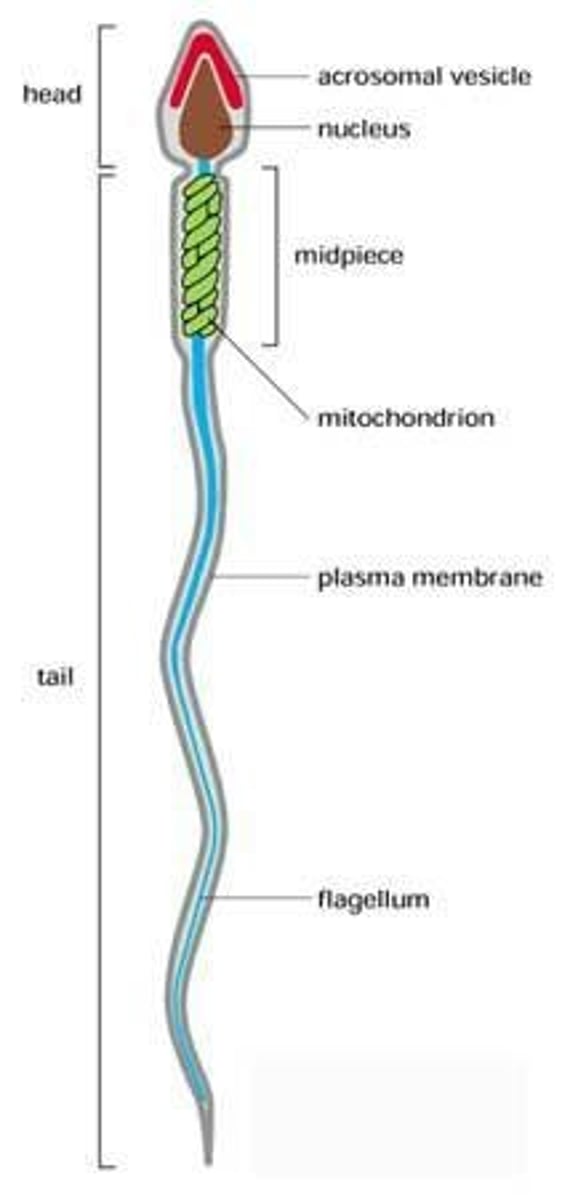
Human Sperm Cell
Smallest human cell, specialized for fertilization.
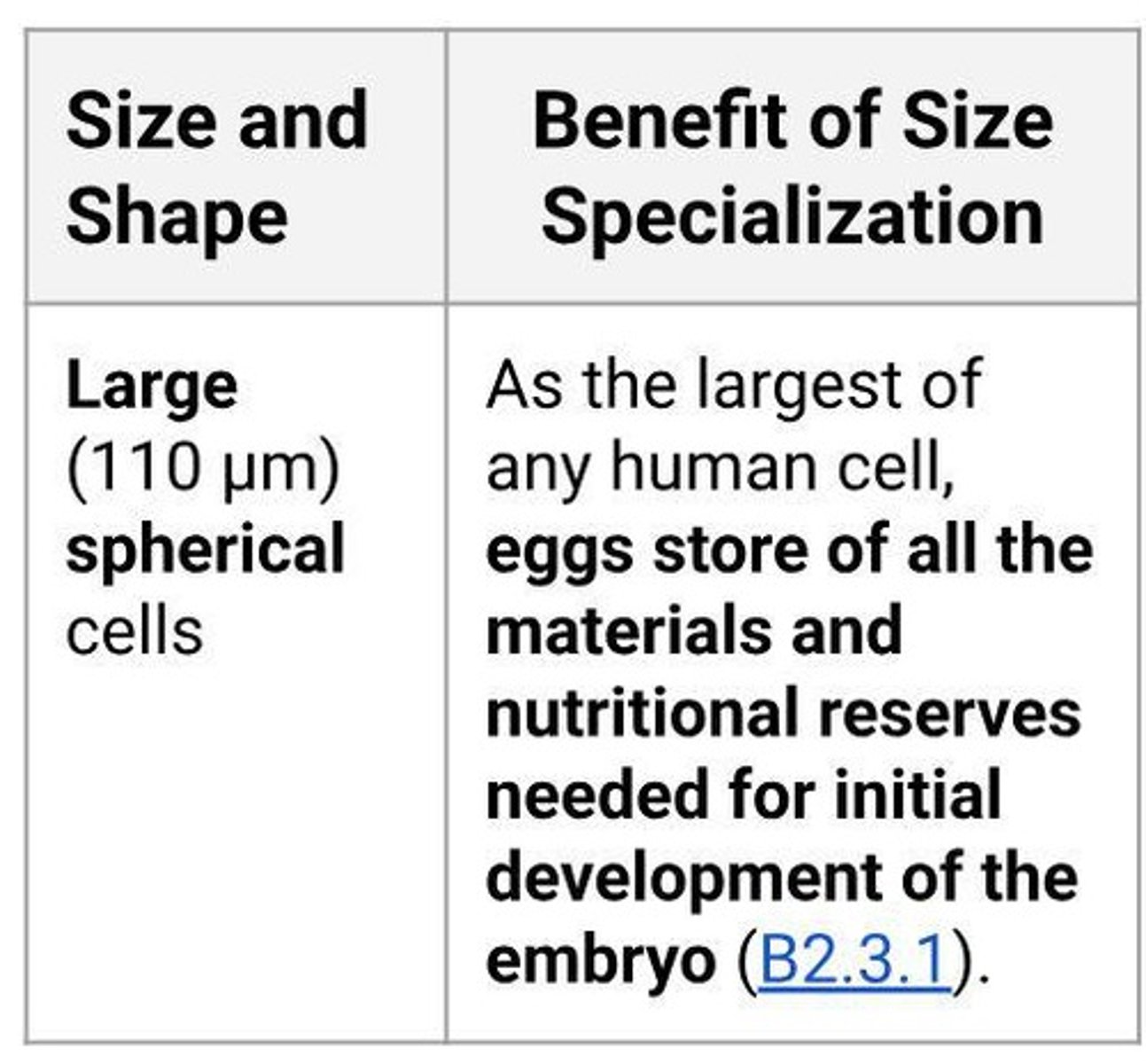
Human Egg Cell
Largest human cell, provides nutrients for embryo.
Red Blood Cell
Biconcave shape increases oxygen transport efficiency.
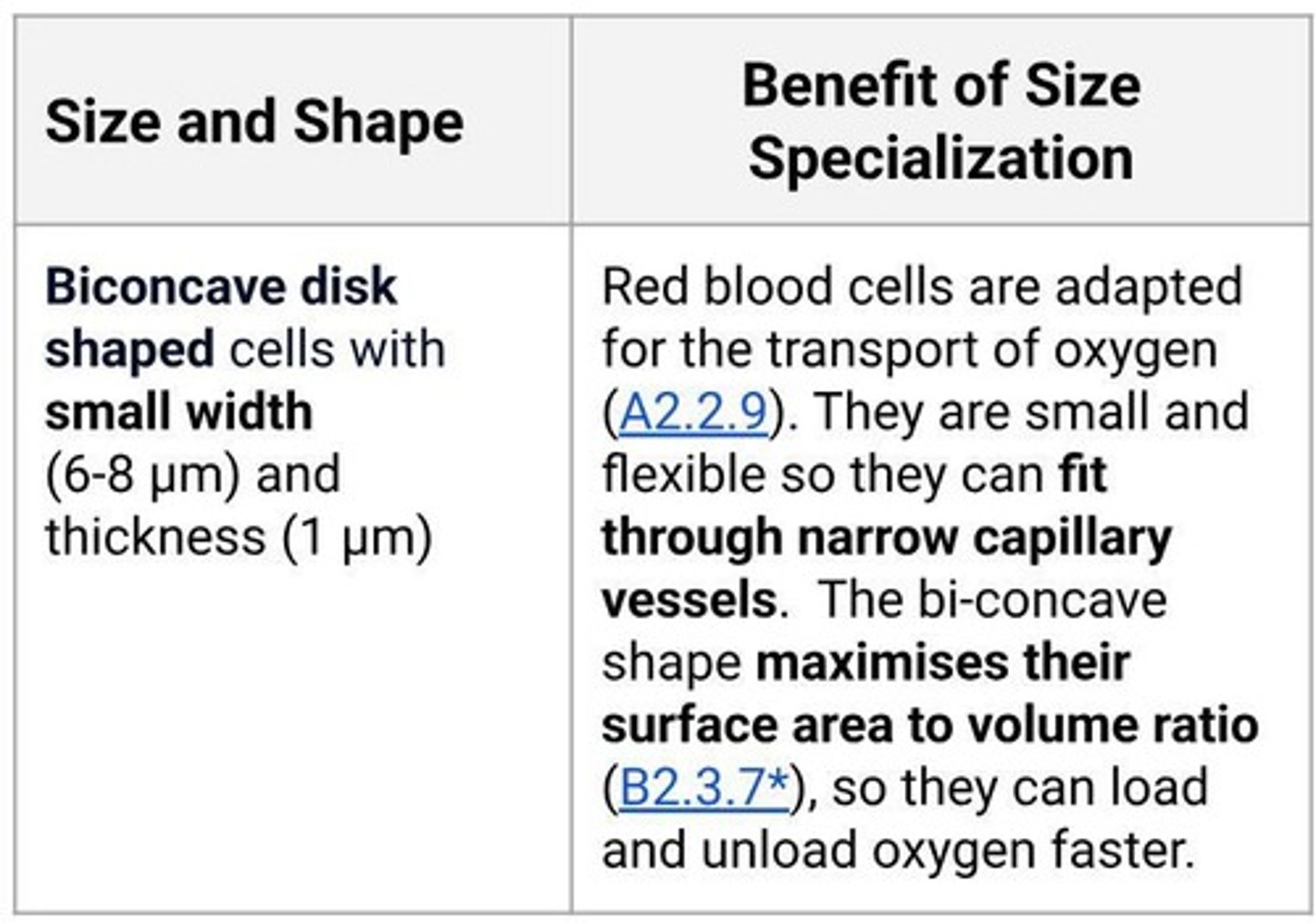
White Blood Cell
Variety of types involved in immune response.
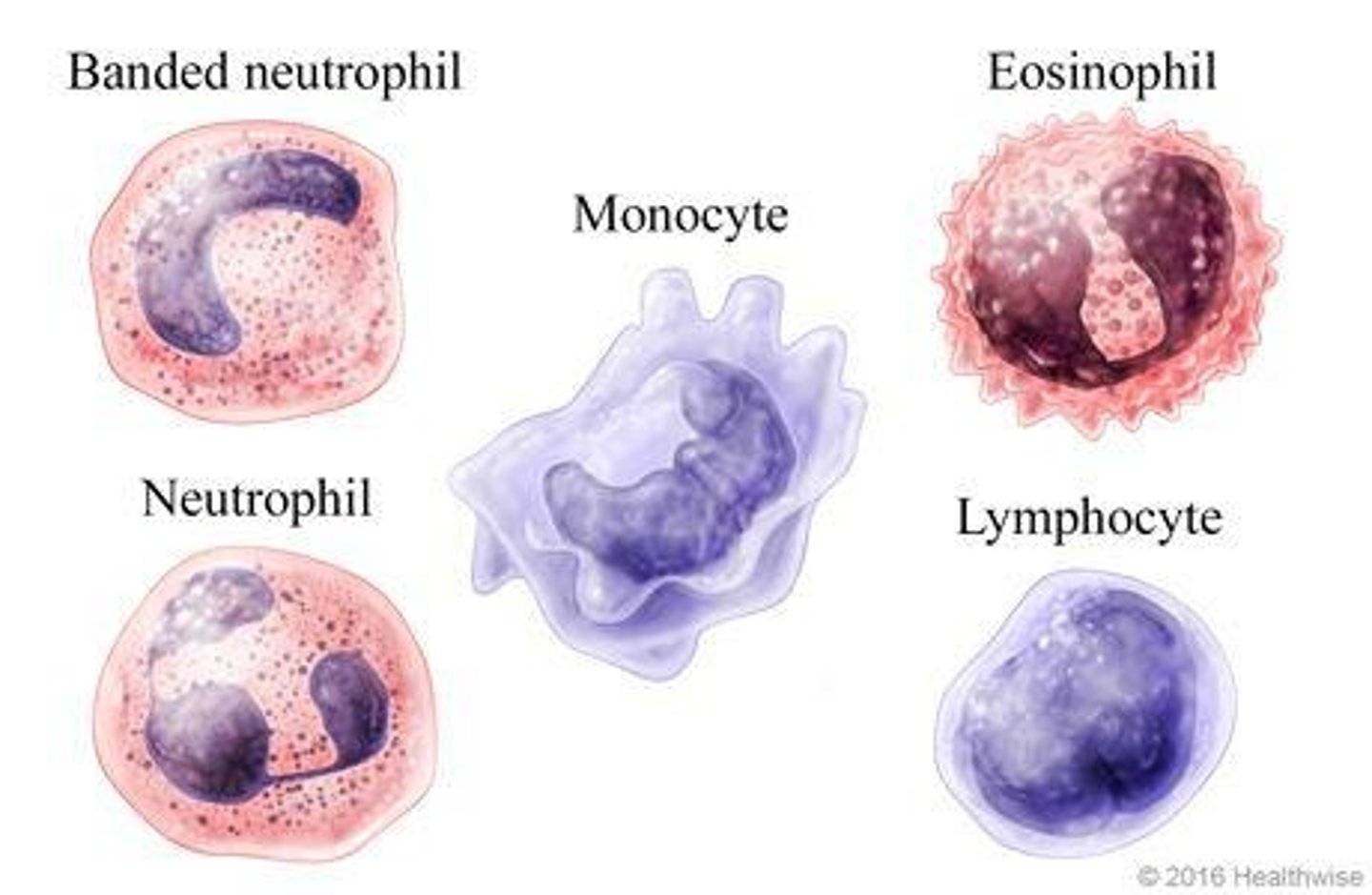
Neuron
Specialized cell for transmitting nerve impulses.
Striated Muscle Fiber
Long, multinucleated cells for muscle contraction.
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Key factor influencing cell size and function.
Adaptations to Increase SA:V
Structural changes enhancing efficiency of material exchange.
Axons of Neurons
Long extensions increasing surface area for signal transmission.
Root Hairs of Plants
Thin extensions increasing surface area for water absorption.
Pneumocytes
Cells lining alveoli, involved in gas exchange.
Type 1 Pneumocytes
Thin cells facilitating gas diffusion in alveoli.
Type 2 Pneumocytes
Rounded cells secreting surfactant to reduce surface tension.
Surfactant
Lipid-protein mixture preventing alveolar collapse.
Basement Membrane
Extracellular matrix separating alveolar and capillary epithelium.
Cristae of Mitochondria
Folded membranes increasing internal surface area.
Thylakoids of Chloroplasts
Membrane structures maximizing surface area for photosynthesis.
Brush Border
Microvilli-covered surface enhancing absorption in epithelial cells.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Kidney structure lined with microvilli for solute reabsorption.
Intestinal Epithelium
Cells with brush border for nutrient absorption.
Epithelial Cells
Flattened cells optimizing gas and nutrient diffusion.
Alveoli
Air sacs in lungs for gas exchange.
Capillary Endothelium
Thin layer facilitating gas exchange with alveoli.
Basement Membrane
Layer anchoring cells with adhesion proteins.
Pneumocytes
Cells in lungs facilitating gas exchange.
Capillary Endothelium
Single layer of flat cells in capillaries.
Efficient Diffusion
Optimal gas exchange across thin capillary walls.
Striated Muscle Fibers
Muscle cells with a striped appearance.
Contractile Tissue
Tissue capable of shortening for movement.
Types of Muscle Tissue
Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle types.
Smooth Muscle
Involuntary muscle, non-striated in appearance.
Skeletal Muscle
Voluntary, striated muscle attached to bones.
Cardiac Muscle
Striated muscle forming the heart walls.
Myofibrils
Cylindrical structures in muscle fibers for contraction.
Sarcomeres
Repeating units in myofibrils containing actin and myosin.
Titin
Protein allowing muscle fiber relaxation after contraction.
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (SR)
Specialized ER for calcium storage in muscle cells.
Myofibers
Multinucleated muscle fibers with peripheral nuclei.
Fascicles
Bundles of muscle fibers running lengthwise.
Intercalated Discs
Junctions between cardiac cells for electrical impulse transmission.
Cardiac Cell Characteristics
Short, branched, single nucleus muscle cells.
Electrical Impulse Transmission
Rapid signal propagation in cardiac muscle.
Gametes
Haploid cells for sexual reproduction.
Sperm Cells
Male gametes delivering DNA to egg cells.
Egg Cells
Female gametes surrounded by protective structures.
Acrosome
Enzyme sac in sperm for egg fertilization.
Receptor Proteins
Bind sperm to egg cell's zona pellucida.