N251 Exam 1 (lectures 1-3)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
What's the professor's name?
Allen W. Davidson
What are microorganisms?
~ range in size (smallest - virus; largest - parasites and fungi)
~ can be prokaryotic or eukaryotic
What is a prokaryote (prokaryotic)?
means "pre-nucleus"; no membrane bound organelles
~ EX: bacteria
What is a eukaryote (eukaryotic)?
means "true-nucleus"; possess membrane bound organelles
~ EX: parasites, amoeba, paramecium, man
structure of a bacterial cell: flagellum
provides motility
structure of a bacterial cell: fimbria
small bristle like fibers on a surface. helps bacteria stick to ea. other and surfaces
structure of a bacterial cell: pillus
elongated, rigid tubular structure; used for sexual reproduction (aka conjugation)
~ conjugation - transfer DNA from 1 cell to another. donor and receiver. donor extends it's pillus into receiver and begins to procreate (pass on DNA) > receiver and donor splits > receiver becomes a donor
structure of a bacterial cell: cell envelope
composed of the glycocalyx, cell wall, and cell membrane. protects the cell
structure of a bacterial cell: gylcocalyx
outermost layer of cell; a coating of macromolecules. protects the cell and helps cell adhere to its environment. can be different among bacteria. can have 2 layers (slime and capsule)
structure of a bacterial cell: gylcocalyx coatings
~ slime: loose, soluble polysaccharide; not bound to the cell; aids bacteria in colonizing surfaces (attaches to surface)
~ capsule: bound to cell; has a thick, gummy consistency; makes bacteria more virulent (protects bacteria from phagocytosis); prevents bacteria from drying out; aids in attachment for colonization
What's the difference between a glycocalyx slime coating and a glycocalyx capsule coating?
slime = loose; not bound to cell; slide across surface
capsule = thick consistency; bound to cell; protect against host's immune system
What kind of glycocalyx coating does Klebsiella pneumoniae have? And what characteristics does it have?
~ capsule coating
~ gives bacterial colonies a sticky, mucoid characteristic
structure of a bacterial cell: cell wall
middle layer - rigidity and structure; gives bacteria shape and protection (differences in cell wall chem. composition determines gram staining properties); helps prevent cell from bursting/collapsing due to changes in environment (stops H2O from going into cell - equilibrium); site of action of some of most effective antibiotics
structure of a bacterial cell: cell wall chemical structure
composed of peptidoglycan. only found in bacteria (similar to chitin on lobster, insects; hard shell)
structure of a bacterial cell: cell membrane
is on actual bacteria (surrounds cell itself) - flexible skin; holds cell together; controls things moving in and out of cell; structure - phospholipids w/ proteins; some areas of membrane fold inward forming mesosomes = folding increases surface area (most chem. needed for biochemical reactions are located on membrane)
structure of a bacterial cell: protoplasm
inside of cell = blood of the bacterial cell (contains 70-80% H2O, sugars, amino acids, salts, enzymes, chromatin body, ribosomes, mesosomes, and granules). site of biochemical and synthetic activity.
structure of a bacterial cell: chromatin body
bacterial chromosome. DNA aggregates in dense area called the nucleoid w/ no membranes surrounding it
structure of a bacterial cell: plasmid
circular piece of DNA (extrachromosomal strand) - outside chromosome. protective f(x) - provides resistance to drugs. advantage to man - uses in genetic engineering techniques. involved in anabolic resistance
structure of a bacterial cell: ribosomes
used in protein synthesis
structure of a bacterial cell: inclusion granules
concentrate nutrients inside the cell, storage, and are not permanent. a storage unit for extra nutrients
What is phagocytosis?
engulfs and destroys microorganisms
What is chemotaxis?
chemical attraction of phagocyte to bacterium. chemical attractants are microbial products, components of damaged tissue, and products of complement system
What is adherence?
attachment of a phagocyte plasma membrane to microorganisms
What are the steps of phagocytosis?
chemotaxsis > adherence > opsonins > ingestion > digestion > excretion.
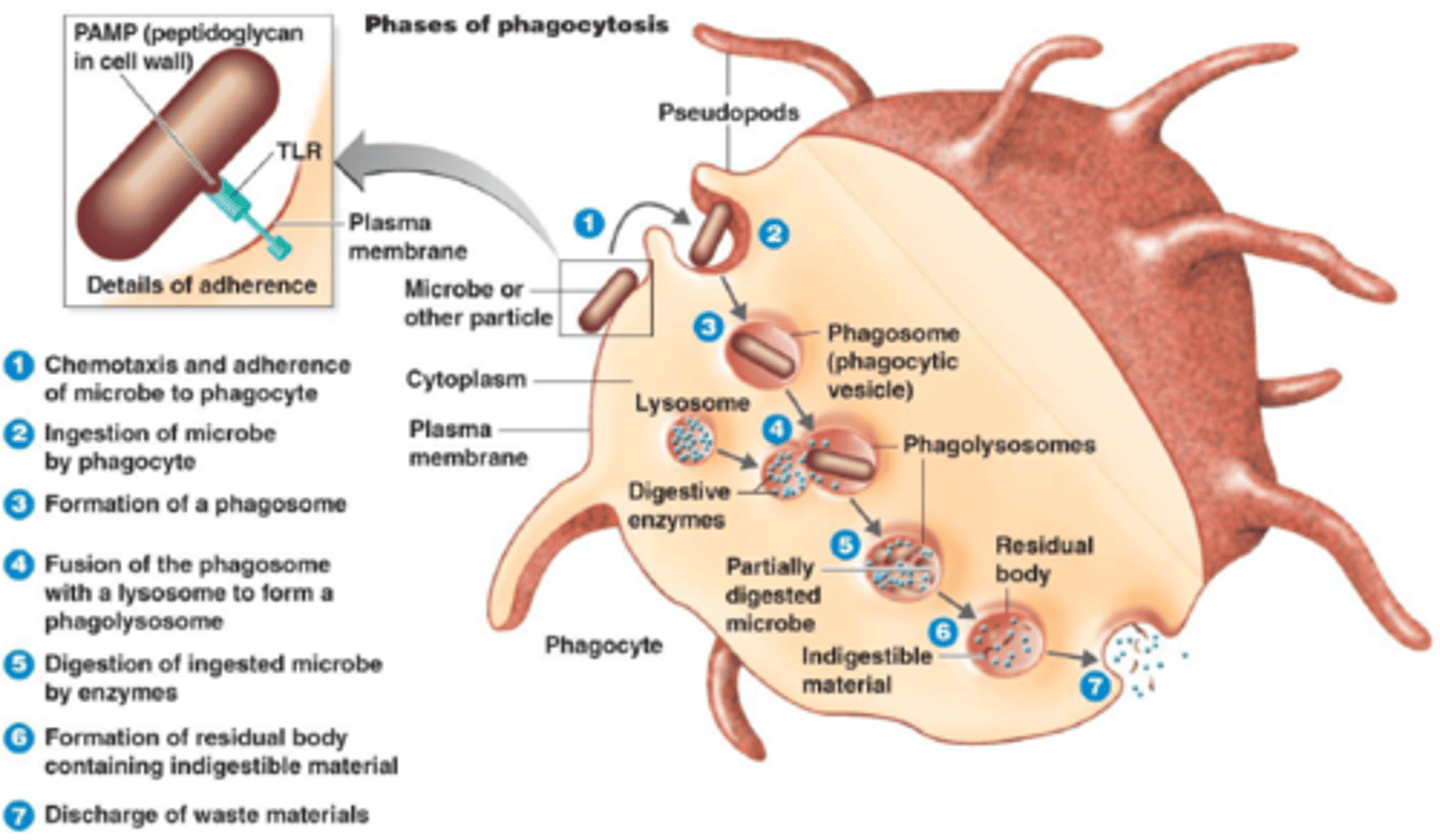
phagocytosis: ingestion
plasma membrane of phagocyte extends out projections called pseudopods that surround microbe. forms sac called phagosome
phagocytosis: digestion
phagosome comes in contact and fuses w/ lysosomes that contain digestive enzymes & bactericidal substances. forms a larger vacuole aka phagolysosome. ingested bacteria are killed. phagolysosome moves to cell membrane
phagocytosis: excretion/exocytosis
elimination of digested contents (waste)
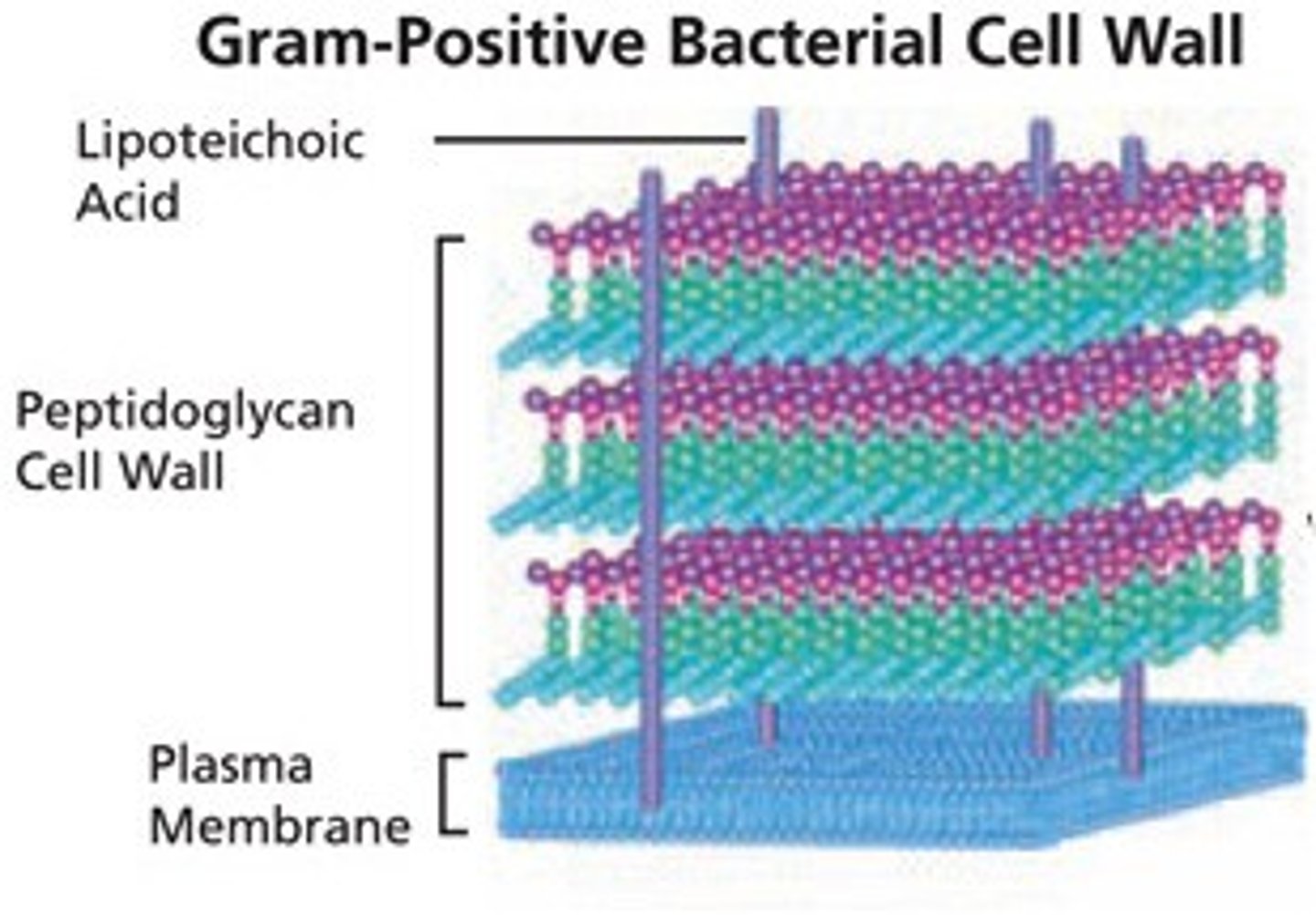
gram positive cell wall
THICK layer of peptidoglycan associated w/ teichoic acid. retain crystal VIOLET stain (purple stain)
Mordent
joins with crystal stain which makes the molecule bigger.
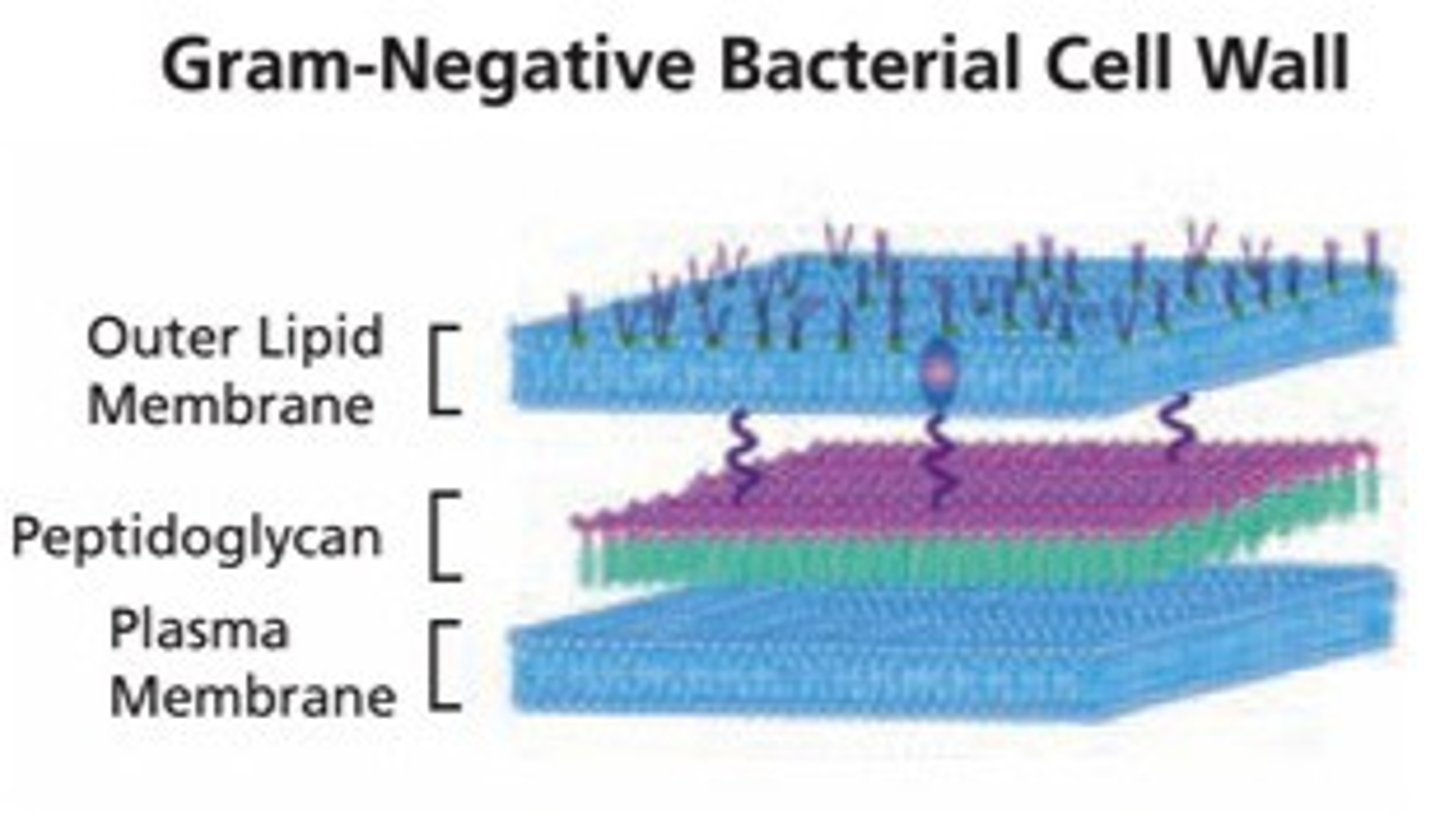
gram negative cell wall
THIN layer of peptidoglycan. outer membrane and periplasmic space. crystal violet-mordant molecule can escape when decolorized (light pink stain). turns pink when safranin is added.
gram staining steps **
1. application of crystal violet (purple dye)
2. application of mordent (iodine)
3. alcohol wash (decolorization)
4. application of safranin (counterstain - pink dye)
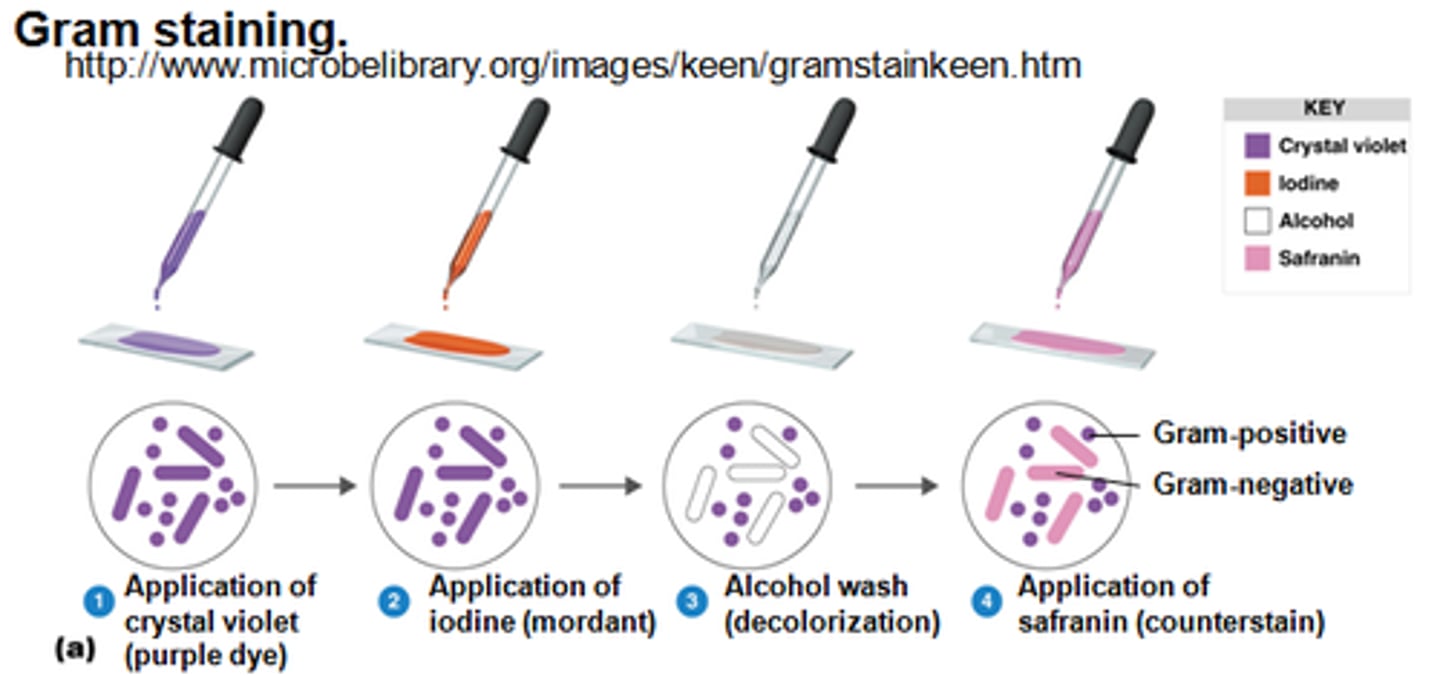
gram staining procedure ***
1. apply primary stain (stains all bacteria) rinse btwn EACH application*
2. apply mordent - binds w/ the stain inside the cell wall making a larger molecule
3. decolorize w/ acetone/alcohol - causes the stain to escape some bacterial cell walls rendering them unstained/colorless
4. add a counterstain - (safranin) this adds color to the cells that were decolorized
crystal violet
primary stain (purple)
gram's iodine
mordent (makes molecules "look" bigger)
acetone alcohol
decolorizer
safranin
counterstain (light pink)
which antibiotics inhibited cell wall synthesis?
beta-lactams, glycopeptides, bacitracin
which antibiotics inhibited protein synthesis (attacked how proteins are made)?
chloramphenicol, macrolides, aminoglycosides
which antibiotics caused membrane integrity lesions?
polymyxin
which antibiotics caused inhibition of replication and transcription? (affects bacterial reproduction)
quinolones, rifampicin
which antibiotics inhibited synthesis of essential metabolites (inhibit how bacteria would metabolize)?
sulfonamide, trimethoprim
characteristics of gram positive
1 layer. thick (20-80nm). no outermembrane. some have a periplasmic space. chem comp = peptidoglycan, teichoic acid, & lipotechoic acid. no porins proteins. has less lipids. has more peptidoglycan. more penetrable. less resistant to molecules
characteristics of gram negative
2 layers. thin (8-10nm). present outermembrane. periplasmic space in present in all. chem comp = lippolysaccharide, lipoporteins, & peptodoglycan. present porins proteins. has more lipids. has less peptidoglycan. less penetrable. more resistant to molecules
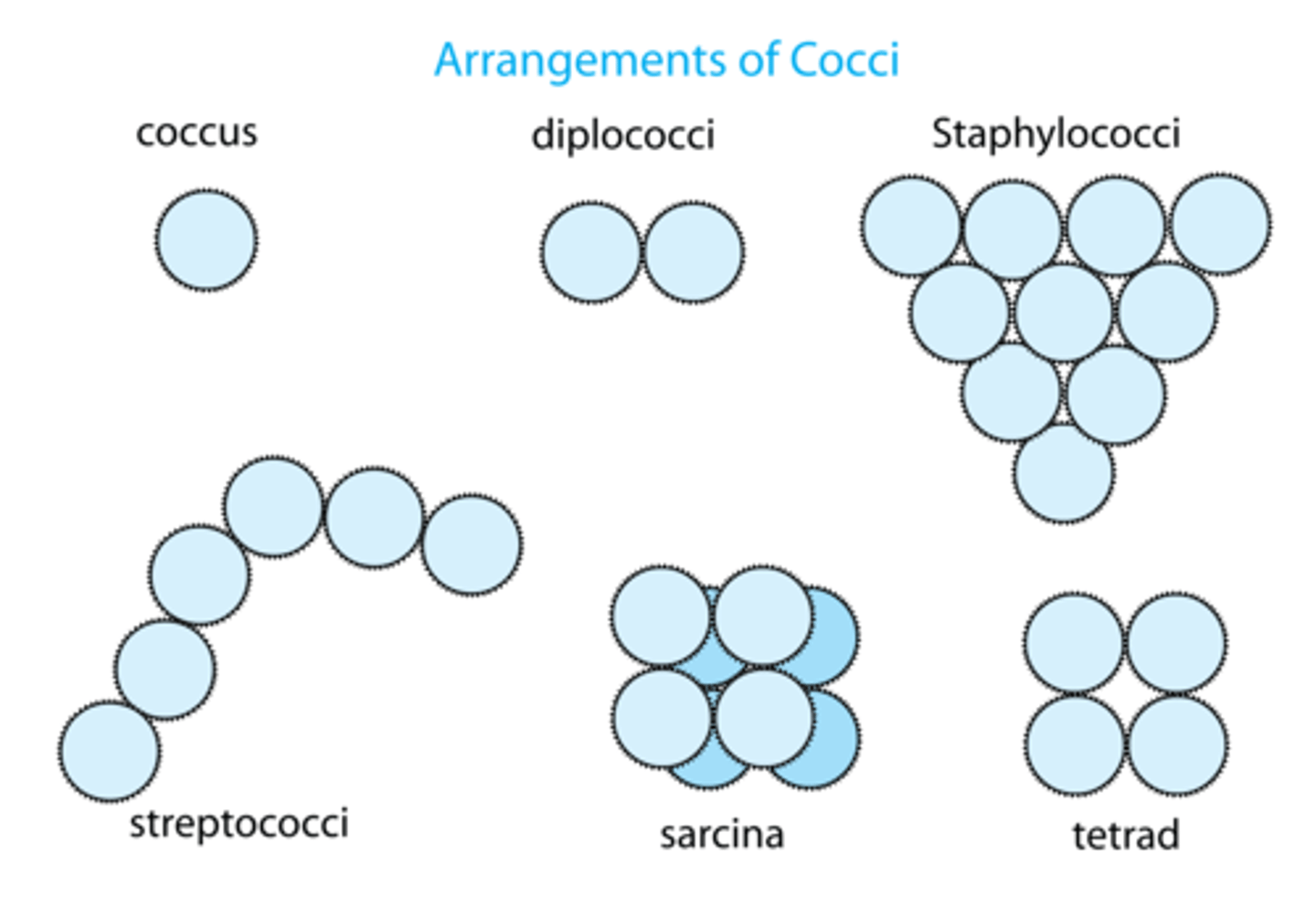
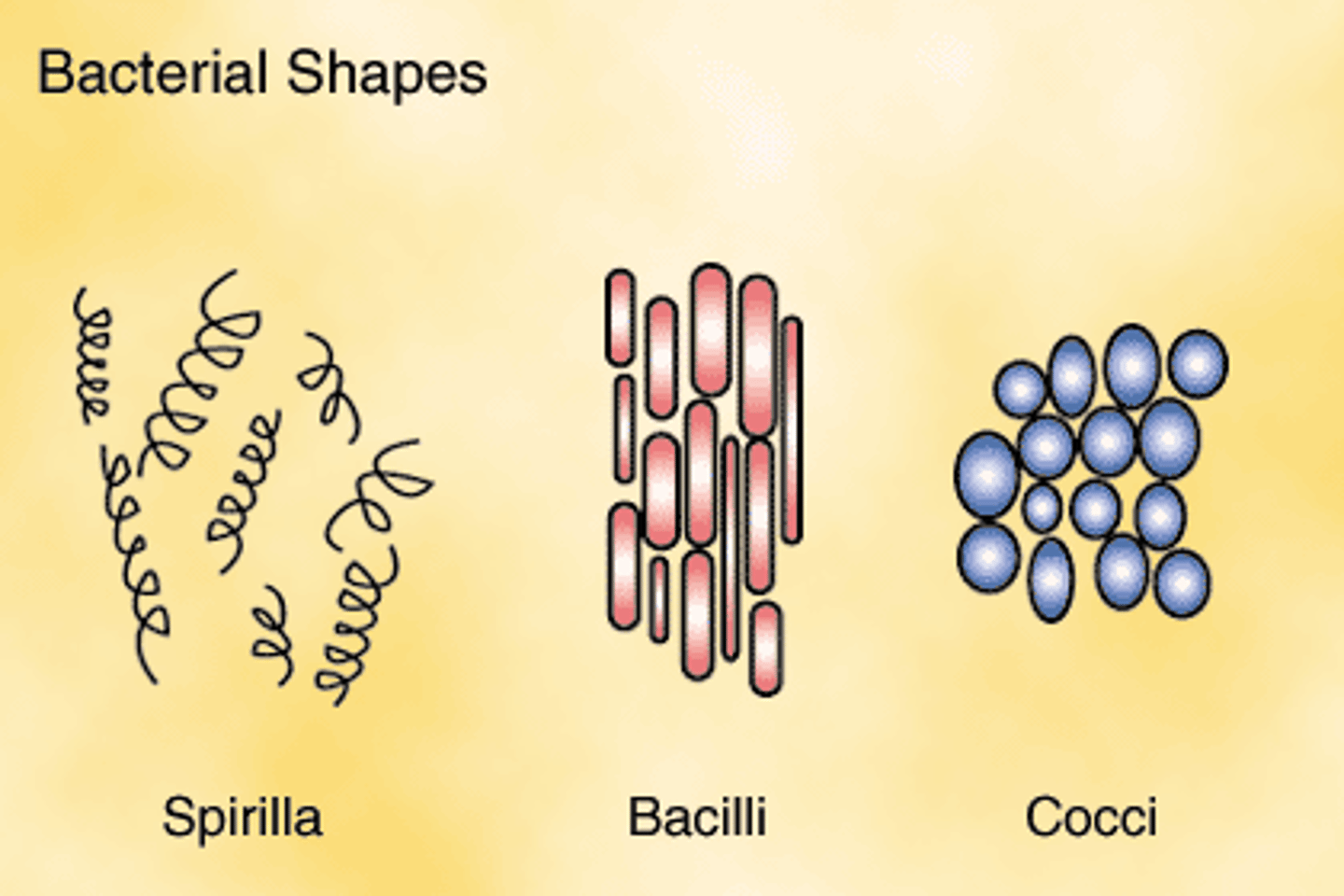
bacterial shapes: coccus
circular shape

bacterial shapes: streptococcus
chain shape
bacterial shapes: staphylococcus
forms masses (looks like a bunch of grapes)
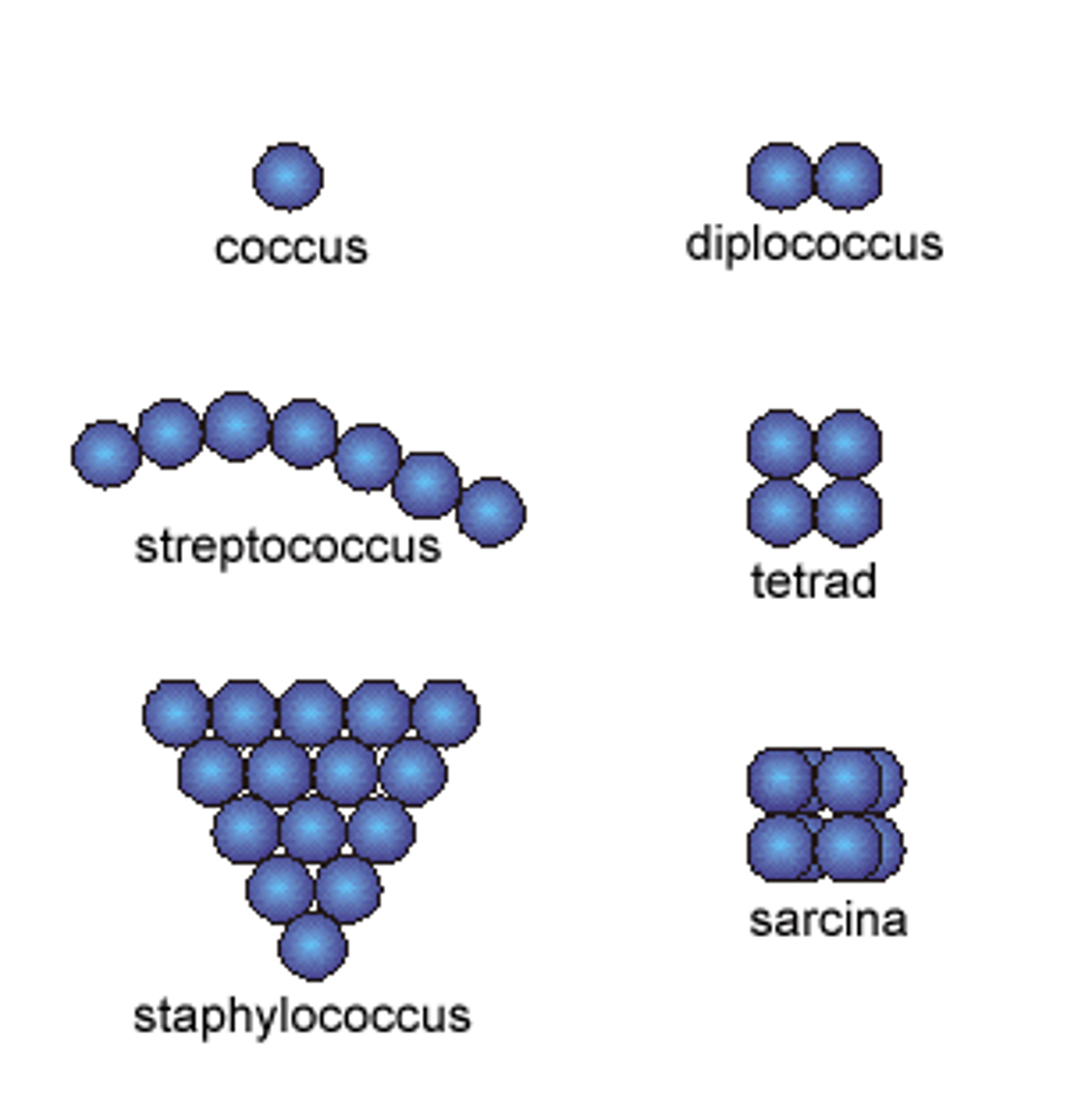
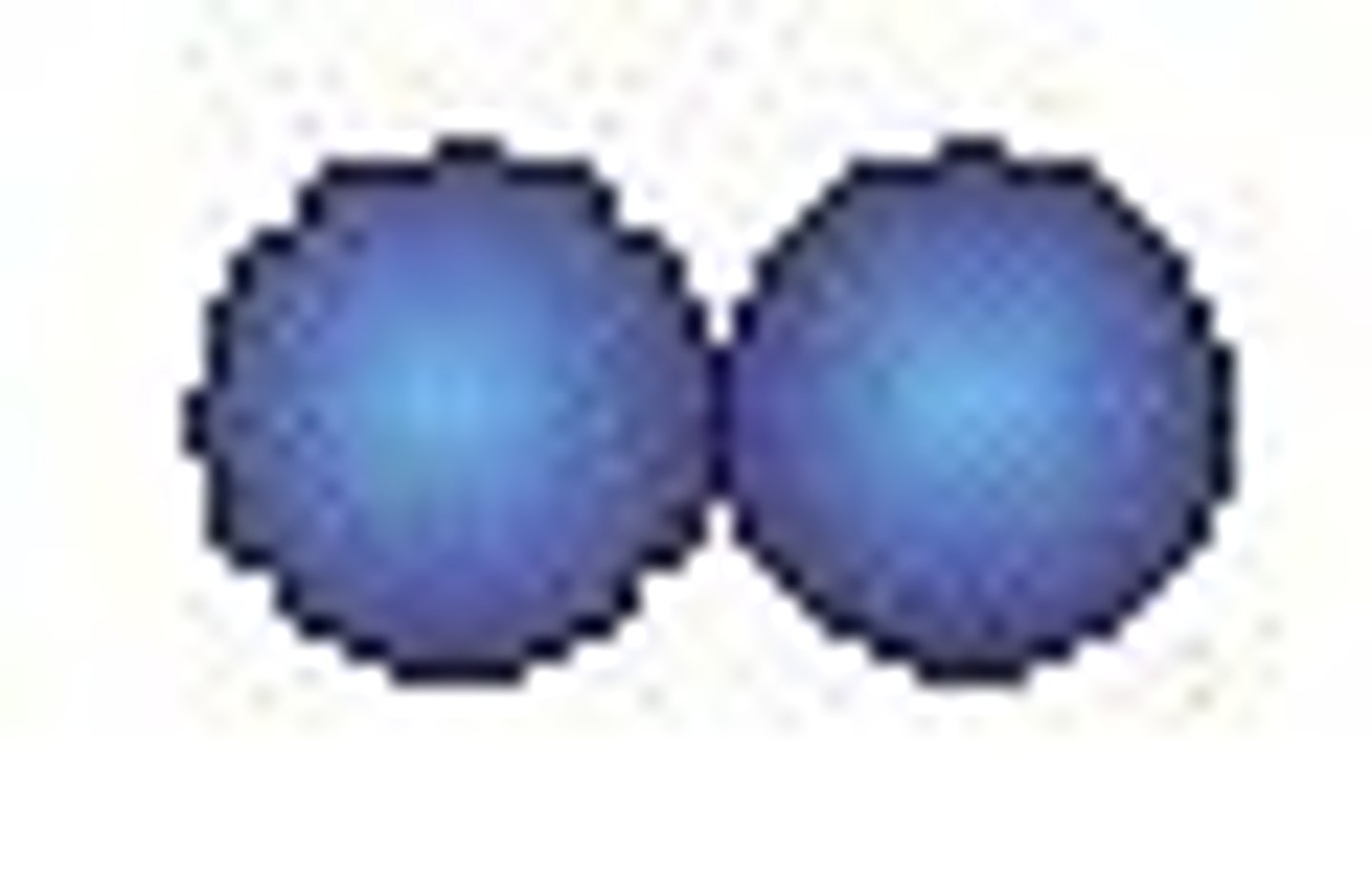
bacterial shapes: diplococcus
usually in pairs of 2 (may look likes 4s bc of binary division)

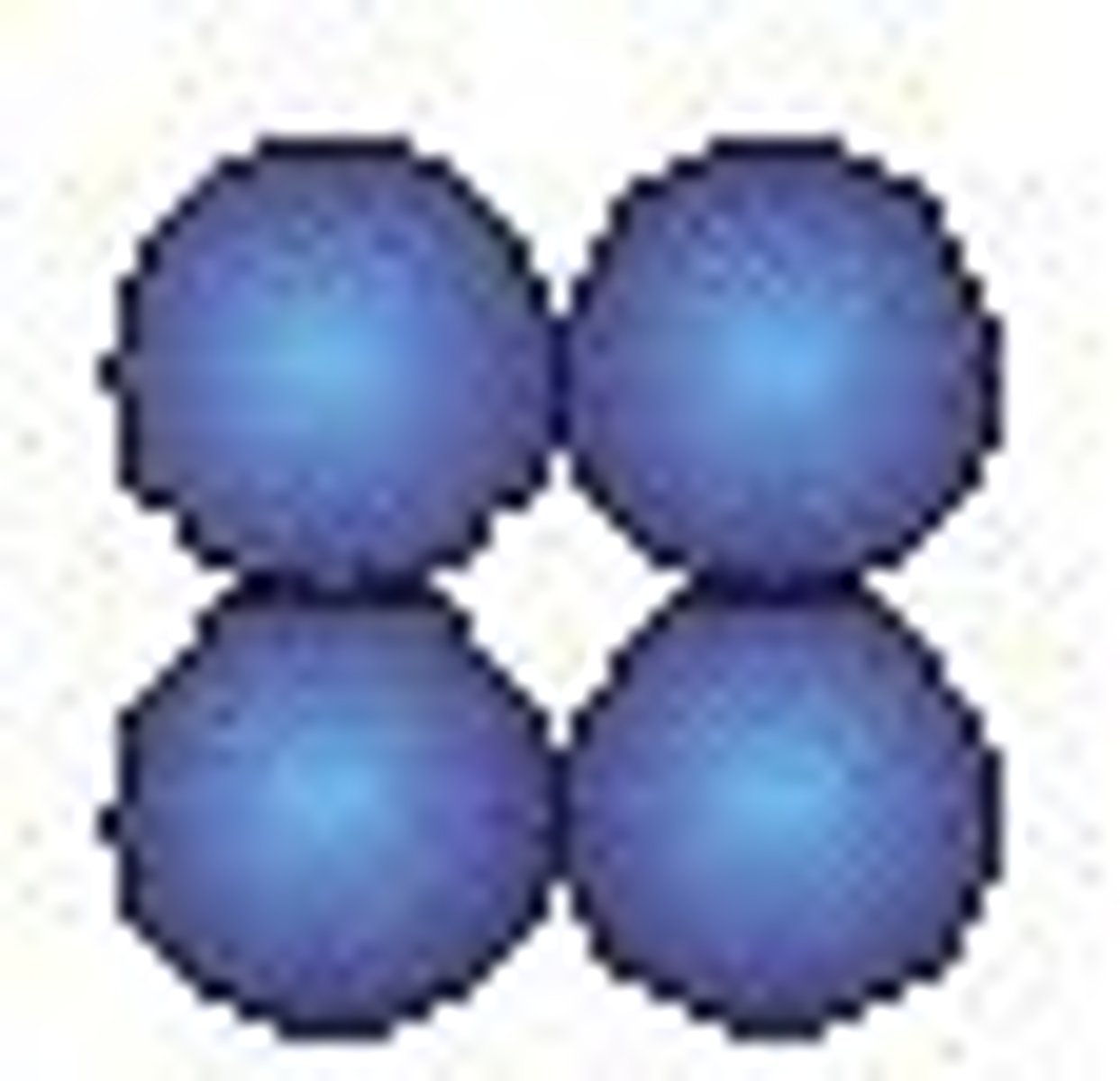
bacterial shapes: tetrad
fours

bacterial shapes: sarcina
cube form
bacterial shapes: bacillus
rod shape
bacterial shapes: diplobacillus
pairs of 2 rods
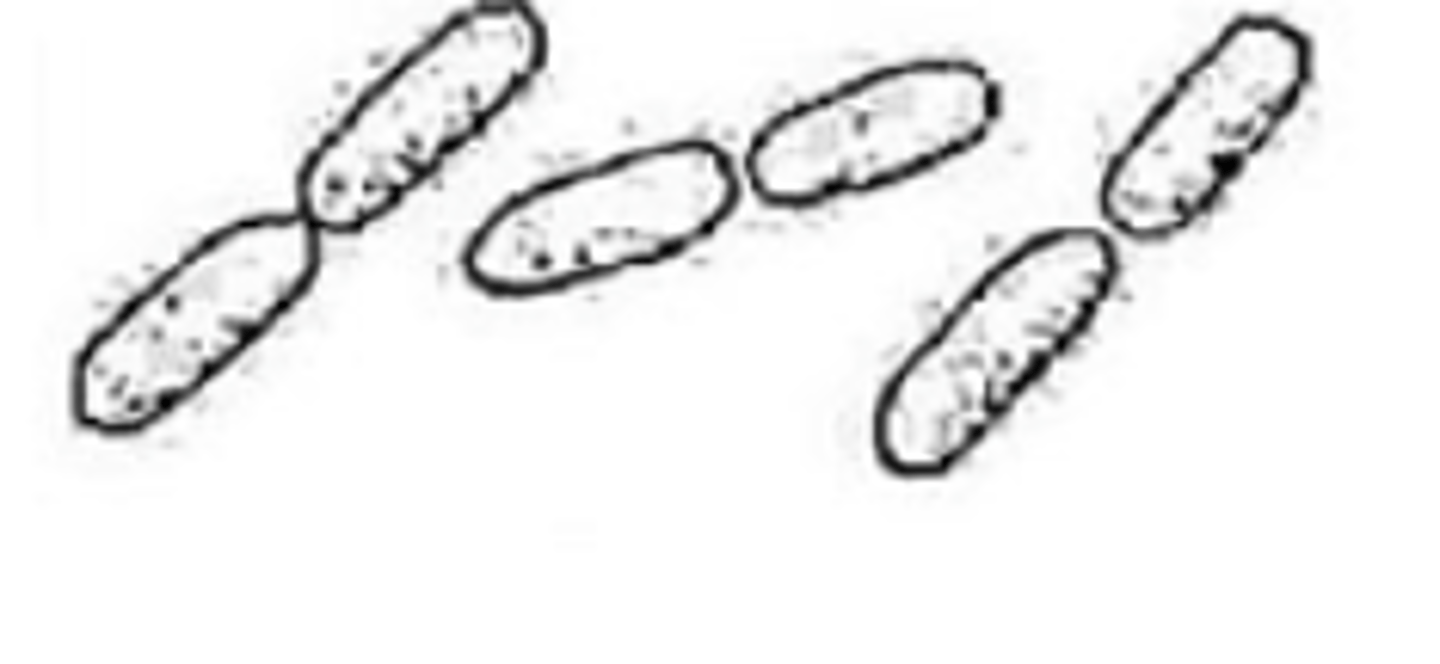

bacterial shapes: streptobacillus
chains of rods
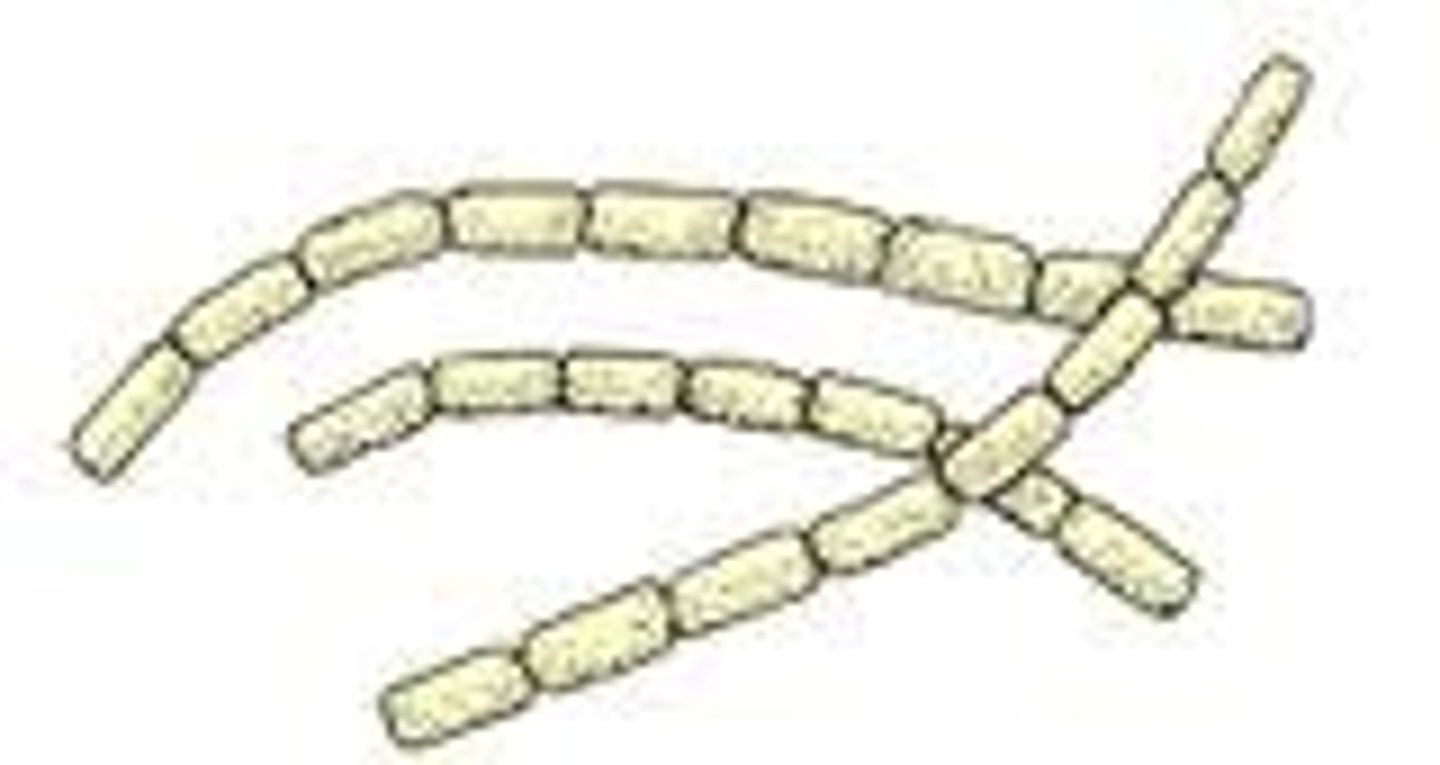
bacterial shapes: coryneform bacillus
look like they have a kink to them
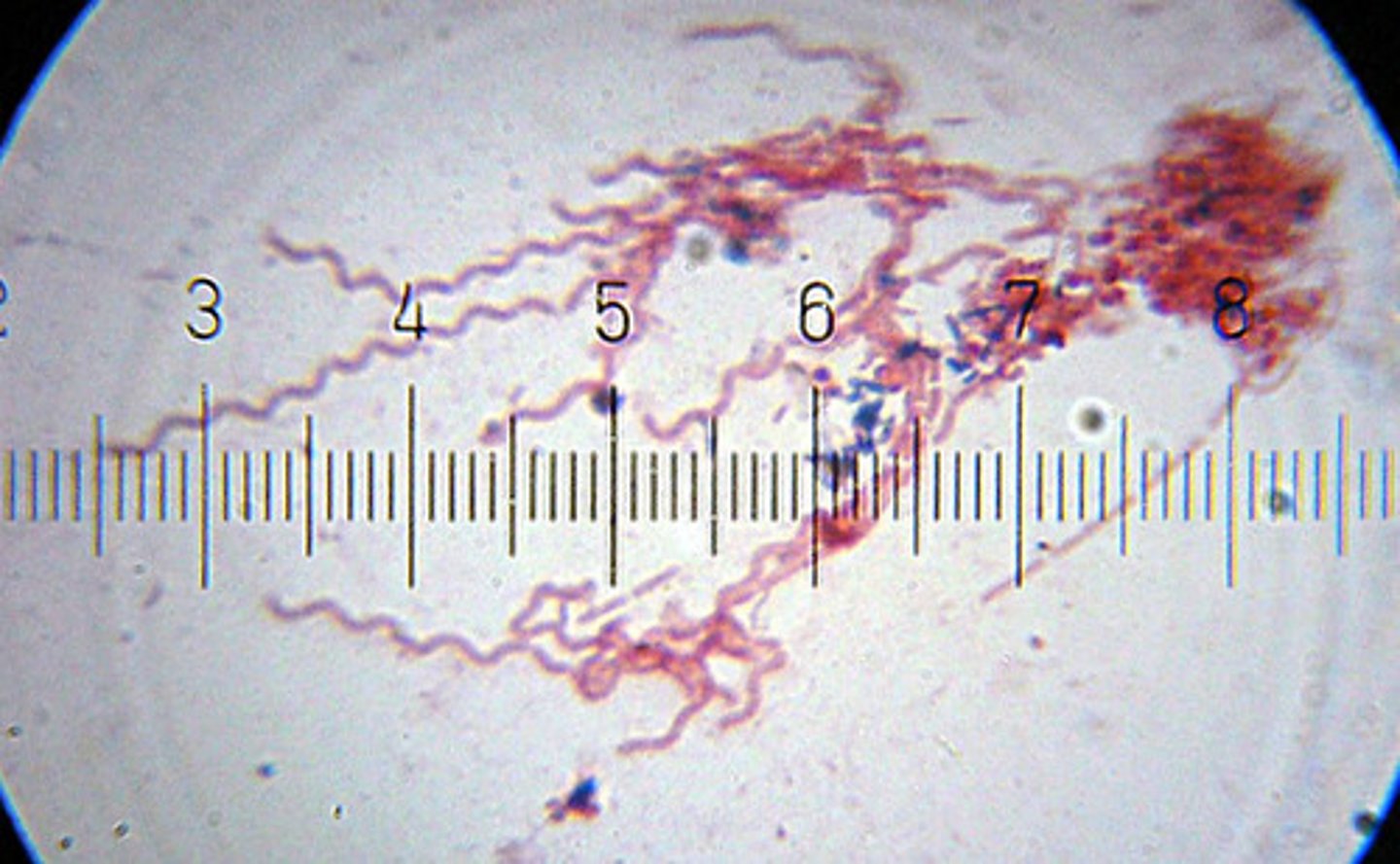
bacterial shapes: spirillum
rob spiral shaped (elongated)
bacterial shapes: vibrio
curved rod
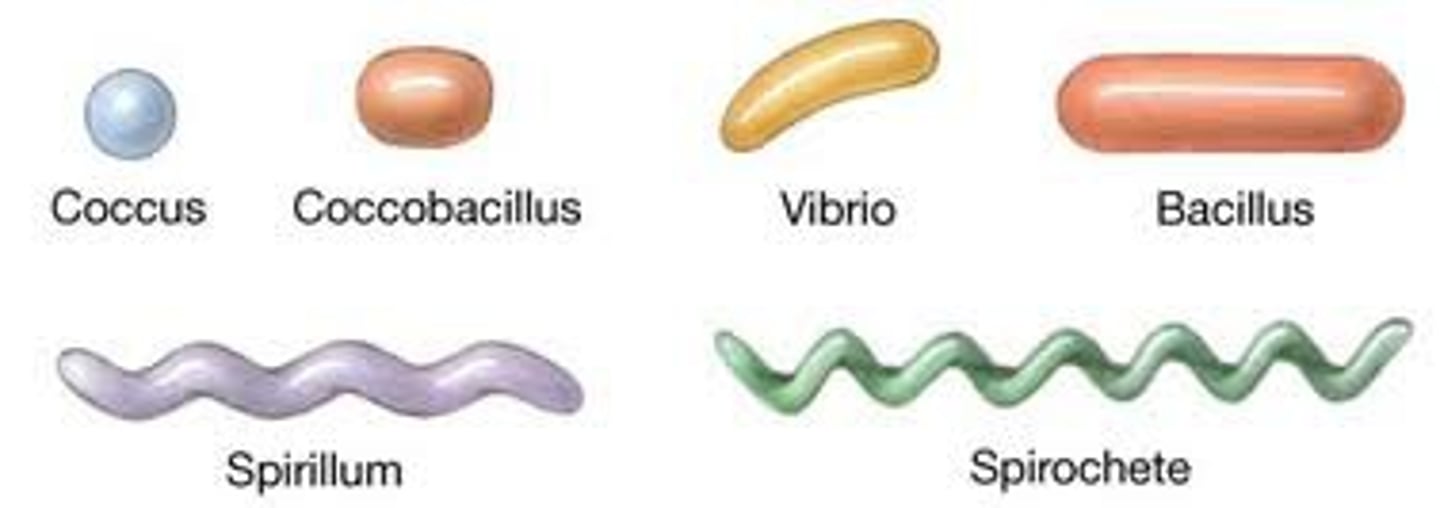
bacterial shapes: spriochete
long ribbon
infection terminology: transmissible
infectious disease agent that's transmitted from either a reservoir or a portal of exit to another host's portal of entry. the disease is transmitted through: contact transmission, vehicle transmission, or vector transmission
infection terminology: contact transmission
~ direct: person-to-person (kissing, touching, sexual, etc)
~ indirect: 1 host to another by fomites (inanimate objects - needles, toothbrushes, drinking glasses, etc)
~ droplet: droplets of mucus that exit mouth/nares during exhaling, coughing, and sneezing (cold/flu)
what are fomites?
objects or materials which are likely to carry infection, such as clothes, utensils, and furniture.
infection terminology: vehicle transmission
the spread of pathogens via air, drinking water, and food. blood and bodily fluids handled outside the body can be considered ______ too. (EX: airborne, waterborne, foodborne, blood & body fluids)
infection terminology: vector transmission
animals that transmit diseases from 1 host to another (biological or mechanical)
infection terminology: biological vectors
affects humans through biting arthropods (mosquitoes, ticks, lice, fleas, mites)
infection terminology: mechanical vectors
animals that passively carry pathogens to new hosts on their feet or other body parts (houseflies, cockroaches)
infection terminology: epidemic
appearance of infectious disease or condition which attacks many people @ THE SAME TIME IN THE SAME GEOGRAPHICAL LOCATION (flu, poison)
infection terminology: pandemic
epidemic that occurs simultaneously on MORE THAN 1 CONTINENT (AIDS, H1-N1, H5-N1 flu); bigger, covers large wide areas
infection terminology: endemic
a disease peculiar and RECURRING CONTINUOUSLY in a PARTICULAR LOCALITY or POPULATION (histoplasmosis- Ohio valley); disease that was already in location
infection terminology: contagious
a communicable disease that's easily transmitted from a reservoir or person (common cold, legionnaires disease)
infection terminology: epidemiology
the study of the occurrence, distribution, and spread of disease in humans (tracking SARS, bird flu (H5-N1), seasonal flu). epidemiologists track outbreaks of diseases through incidence and prevalence.
infection terminology: (epidemiology) incidence
the number of NEW CASES of a disease in a given area or population during a given period of time
infection terminology: (epidemiology) prevalence
the TOTAL NUMBER of cases, new and existing in a given area or population during a given period of time
how are microorganisms our FOE?
~ 750 mil. infectious diseases/yr worldwide
~ >200,000 deaths annually in US
~ tens of billions of $$ in health care
~ leading cause of illness and death (respiratory and diarrheal diseases)
how are microorganisms our FOE?: reasons for rise in infectious diseases
1. due to travel (1 in 5 come from a country where infectious diseases are common)
2. lax in vaccinating children b/c the disease in no long prevalent
3. use of medication to prolong life (w/ aging population; weaker immune sys. tend to get opportunistic infections)
4. development of drug resistance
when and where was the last small pox case? what is small pox?
1977 in Somalia. viral diseases that killed 10 mil and has a worldwide vaccination
what is the bubonic plague?
bacterial infection that happened during 1346-1350; 1/4 of the entire population in Europe died; now < 100 people/yr get infected
what is TODAY'S epidemic?
AIDS
facts about AIDS:
33 mil infected worldwide; >16 mil since beginning of epidemic; leading cause of death among 25-44y/o men; 2nd leading cause of death among 15-44y/o females; highest #'s from Africa, SE Asia, and central America
what are the names of common food borne outbreaks?
salmonella, shigella, E. coli, staph, bacillus cereus, clostridium (botulinum & perfringens), listeria, and noro virus
how are microorganisms our FRIENDS?
1. breakdown food in gut
2. produce foods: yogurt, cheese, wines, breads, sauerkraut
3. used to make: vitamins, insulin, drugs
4. decompose waste
5. recycle nutrients back into the earth
6. used as a food source for other organisms
7. make chem. products: acetone, glycerin, organic acids, enzymes, & alcohols
8. agriculture (helps some vegetables/fruits grow)
laboratory terms: broth
a liquid medium that contains various nutrients & is used to culture bacteria and other microorganisms in culture
laboratory terms: agar
a gelatinous material derived from algae, specifically used as a culture medium of bacteria and other cells for diagnostic or laboratory experiment purposes. agar is a gel @ room temp til 65°C; melts @ approx. 85°C; solidifies @ 32-40°C (property known as hysteresis)
laboratory terms: media w/ agar: deep
used for a culture where you need a DEEP inoculation into a solid medium (gelatin or agar) that's used especially for the growth of anaerobic bacteria
laboratory terms: media w/ agar: slants
a culture made on the slanting surface of a solidified medium in a test tube that has been tilted to provide a greater area for growth
laboratory terms: media w/ agar: plates
a petri dish that contains a solid growth medium, typically agar plus nutrients, used to culture small organisms such as microorganisms
define inoculate
treat (a person or animal) with a vaccine to produce immunity against a disease. introduce (cells or organisms) into a culture medium
laboratory terms: incubation
act of maintaining controlled environment conds. for the purpose of FAVORING growth or development of microbial cultures
laboratory terms: colony
a visible mass of microorganisms all originating from A SINGLE mother cell; therefore a colony constitutes a clone of bacteria all genetically alike
laboratory terms: picking colonies
selecting a colony from a plate and transferring it to another media or slate
laboratory terms: loop
a simple tool used by microbiologists to retrieve an inoculum from a culture of microorganism; it is used in the cultivation of microbes on plates by transferring inoculum for streaking
laboratory terms: needles
used in field of microbiology to transfer and inoculate living microorganisms; 1 of the most commonly implicated biological lab tools and can be disposable/reusable
laboratory terms: bunsen burner
a small adjustable gas burner used in laboratories
what 2 muppets does the professor talk about?
dr. bunsen honeydew and beaker

define metabolism
general term used for all of the reactions occurring in cells
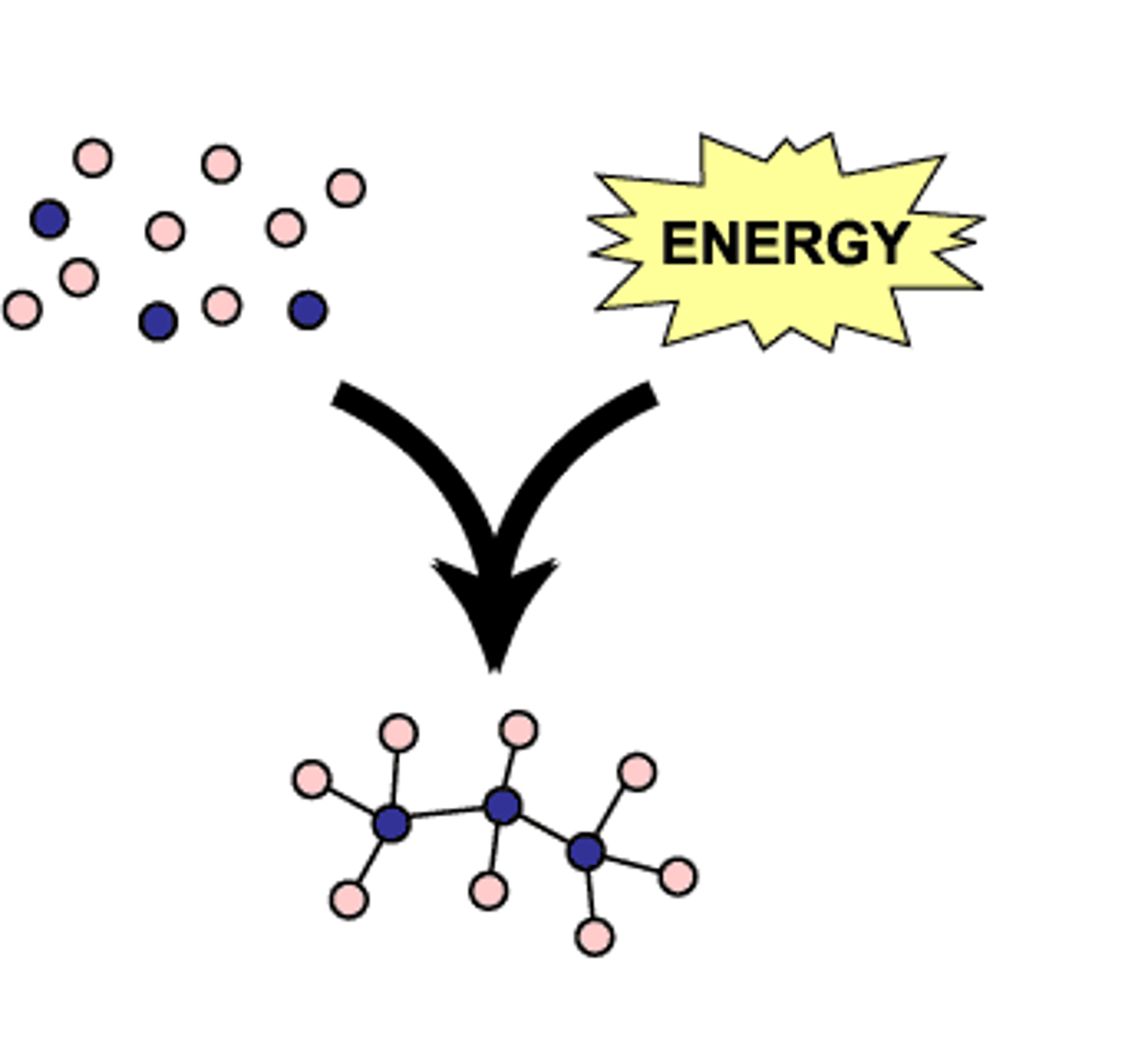
define anabolic reaction (anabolism)
• simple substance is built into a complex substance (A for Adding); creating more complex molecules
• making larger molecules from smaller ones
• molecules are making structures that it'll be able to use
• building requires energy that comes from ATP molecules produced during catabolism (uses ATP)
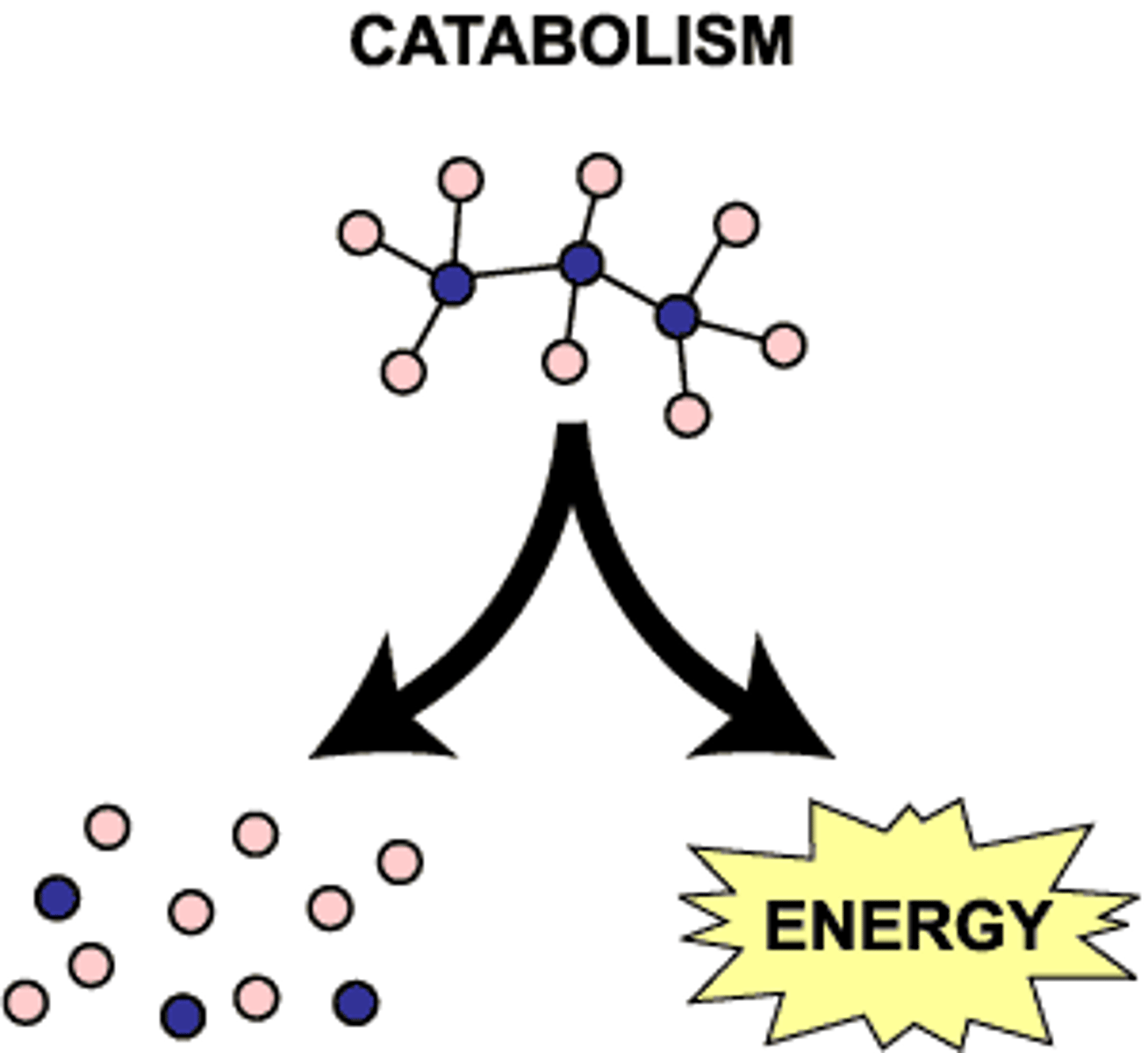
define catabolic reaction (catabolism)
• start w/ a complex molecule and break it down and release energy (C for cutting); cutting the big molecule into small molecules
• degradation of food stuff
• energy is released and stored as ATP
• breakdown of large molecules to produce smaller molecules and release/create energy
what are the characteristics of an enzyme?
• protein molecules that act as catalysts - increases the rate of reaction that would normally occur @ a slow rate; it works w/ a specific substrate; substrate fits into the enzyme active site; lock & key fit = lock is the ________ & key is the substrate
• doesn't permanently change - can be reused again (increases the rate of reaction)
more characteristics about enzymes?
lowers activation energy;
EX: tell student to get up from seat > student slowly gets up > point a flame @ a student > student gets up faster > flame doesn't change > flame is ready to be used on another student
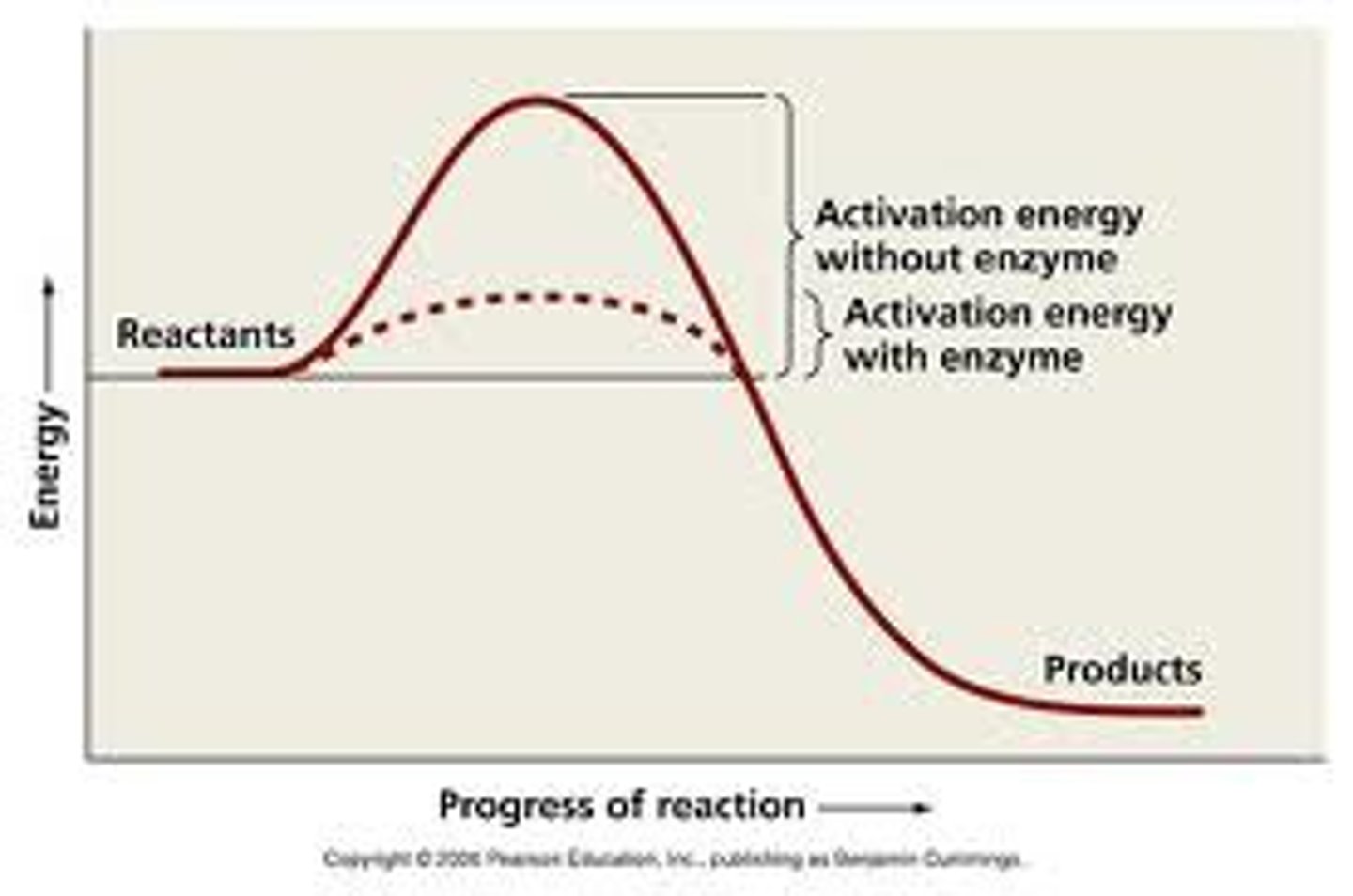
define activation energy
the amount of energy needed to trigger a chemical reaction
• EX: student gets up from chair > it'll be slow but eventually student will
activation energy w/ and w/o enzymes
substrate has higher energy than the products; once activation energy is reach, the reaction proceeds
• a reaction w/ enzymes are happen quicker b/c the enzyme lowers the amount of activation energy that's needed for the reaction
naming enzymes
______ are named after the substrate or the kind of reaction they catalyze;
• usually ends w/ the suffix "-ase"
• some enzymes still go by their old names (EX: trypsin; pepsin)
pathways for producing energy form nutrients (glucose): fermentation (reduction)
the final acceptor in the pathway is an organic molecule - pyruvic acid; doesn't use O2 bc it's made in the pathway itself; produces LESS energy from glucose (less efficient way of producing energy)