PSYC 1001 Exam 1
1/176
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
Psychology
the scientific study of behavior and mental processes
Behavior
all of our outward/overt actions and reactions (i.e. facial expressions, movement, speech)
Mental Processes
all the internal/covert activity of our minds (i.e. thinking, feelings, and remembering)
Psychologist
a professional with an academic degree and specialized training in one or more areas of psychology
Basic Research
research for the sake of gaining scientific knowledge
Applied Research
research aimed at answering real-world, practical questions
Psyciatrist
a physician who specializes in the diagnoses and treatment of psychological disorders (has an MD).
Psychologist
a professional with an academic degree and specialized training in one or more areas of psychology (does not have MD).
Four goals of psychology
Description (what’s happening?)
Explanation (why is it happening?)
Prediction (when will it happen again?)
Control (How can it be changed?)
Theory
a general explanation of a set of observations and facts
William Wundt
the first to attempt the application of objectivity in psychology
attempted to apply scientific principles to the study of the human mind
believed that consciousness could be broken down into thoughts, experiences, emotions, etc., which created objective introspection
Objective introspection
the process of examining and measuring one’s own thoughts and mental activities
Edward Titchner
expanded on Wundt’s ideas and created structuralism
believed that objective introspection could be used on thoughts as well as physical sensations
Structuralism
the focus of study is the structure or basic elements of the mind
William James
interested in the importance of consciousness to everyday life than just its analysis
influenced by Darwin’s ideas of natural selection
objected to structuralism; created functionalism
Functionalism
the focus of study is how the mind allows people to adapt, live, work, and play
Max Wertheimer
created the concept of Gestalt psychology
objected to the idea that the mind/perceiving/sensing can be broken down into smaller elements and still be understood
Gestalt Psychology
“organized whole”/“configuration”; focused on perception and sensation, particularly the perception of patterns and whole figures
Sigmund Freud
a neurologist trying to figure out what was wrong with his patients
the “unconscious” or “unaware” mind; personality forms within the first 6 years of life
created the concept of psychoanalysis
Psychoanalysis
an insight therapy based on the theory of Freud, emphasizing the revealing of unconscious conflicts; Freud’s term for both the theory of personality and the therapy based on it
Ivan Pavlov
Was a physiologist who figured out the process of conditioning
Conditioning
a reflexive response generated even though the usual cause is not present.
Watson
father of behaviorism
focused on observable behavior
created the “Little Albert” experiment
Behaviorism
the science of behavior
Skinner
Post-Watson; developed the theory of operant conditioning
Operant Conditioning
voluntary behavior is learned through positive reinforcement to certain actions – behavioral responses are reinforced
Maslow
Developed the humanistic perspective
Humanistic Perspective
the ability of the individual to direct and control his/her life, free will, self-actualization
Psychodynamic Perspective
modern version of psychoanalysis that is more focused on the development of a sense of self and the discovery of motivations behind a person’s behavior other than sexual motivations
Humanistic Perspective
the “third force” in psychology that focuses on those aspects of personality that make people uniquely human, such as subjective feelings and freedom of choice.
Cognitive Perspective
modern perspective in psychology that focuses on memory, intelligence, perception, problem solving, and learning
Cognitive Neuroscience
the study of the physical changes in the brain and nervous system during thinking.
Sociocultural Perspective
perspective that focuses on the influence of social interactions, society, and culture on an individual’s thinking and behavior
Biopsychological Perspective
perspective that attributes human and animal behavior to biological events occurring in the body, such as genetic influences, hormones, and the activity of the nervous system
Evolutionary Perspective
perspective that focuses on the biological bases of universal mental characteristics that all humans share
Critical Thinking
making reasoned judgements about claims
Four basic criteria for critical thinking
There are very few “truths” that do not need to be subjected to testing.
All evidence is not equal in quality.
Just because someone is considered to be an authority/has expertise does not make everything they claim automatically true.
Critical thinking requires an open mind.
Scientific Approach Steps
Perceiving the question
Description
Forming a hypothesis (testable educated guess).
Testing hypothesis
Drawing conclusions
Report results
If failed? Replicate/go back to hypothesis and rework it
Naturalistic Observation
watching the subject in their normal environment
advantage —> realistic picture of how behavior occurs
disadvantage —> observer bias, observer effect
Laboratory Observation
watching the subject in a controlled and regulated environment
advantage —> is a loophole for naturalistic settings that aren’t practical
disadvantage —> artificial situation may lead to artificial behvaior
Case Studies
study of one individual in great detail
advantage —> the tremendous amount of detail it provides, and it may be the only way to get certain kinds of information
disadvantage —> lack of generalizability; detailed observation is vulnerable to bias
Surveys
a way to ask about private behavior via a series of questions
advantage —> ability to get private information; a tremendous amount of data from a large group of people.
disadvantage —> must select representative sample; people won’t always be truthful; courtesy bias.
Experimenter effect
tendency of the experimenter’s expectations for a study to unintentionally influence the results of the study
Single-blind
study in which the participants do not know if they are in the experimental or control group
Double-blind
study in which neither the experimenter nor the participants know if the participants are in the experimental or the control group.
Ethical Guidelines in Psychology
Rights and well-being of participants must be weighed against the study’s value to science. (People first, research second).
Participants must be allowed to make an informed decision about participation. (Researchers must explain the study to potential participants).
Deception must be justified.
Participants may withdraw from the study at any time.
Participants must be protected from risks or told explicitly of risks.
Investigators must debrief participants, telling the true nature of the study and expectations of results.
Data must remain confidential.
Nervous System
an extensive network of specialized cells that carries information to and from all parts of the body.
Central Nervous System
includes spinal chord and the brain
Peripheral Nervous System
autonomic (parasympathetic, sympathetic), somatic
Neurons
the basic cell that makes up the nervous system and that receives and sends messages with that system.
Dendrites
branchlike structures of a neuron that receive messages from other neurons
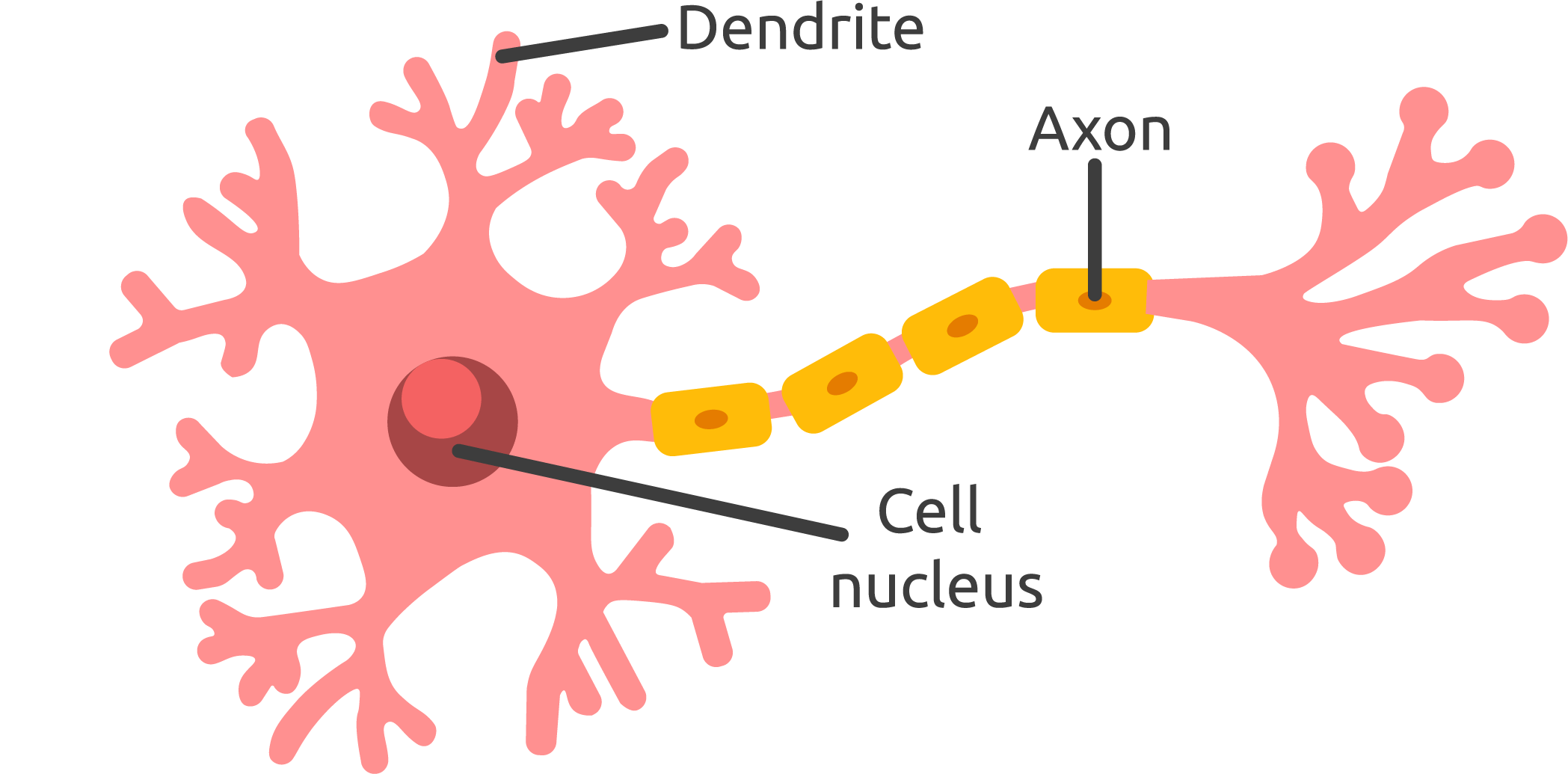
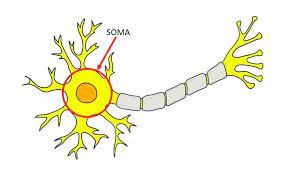
Soma
the cell body of the neuron that receives messages from other neurons.
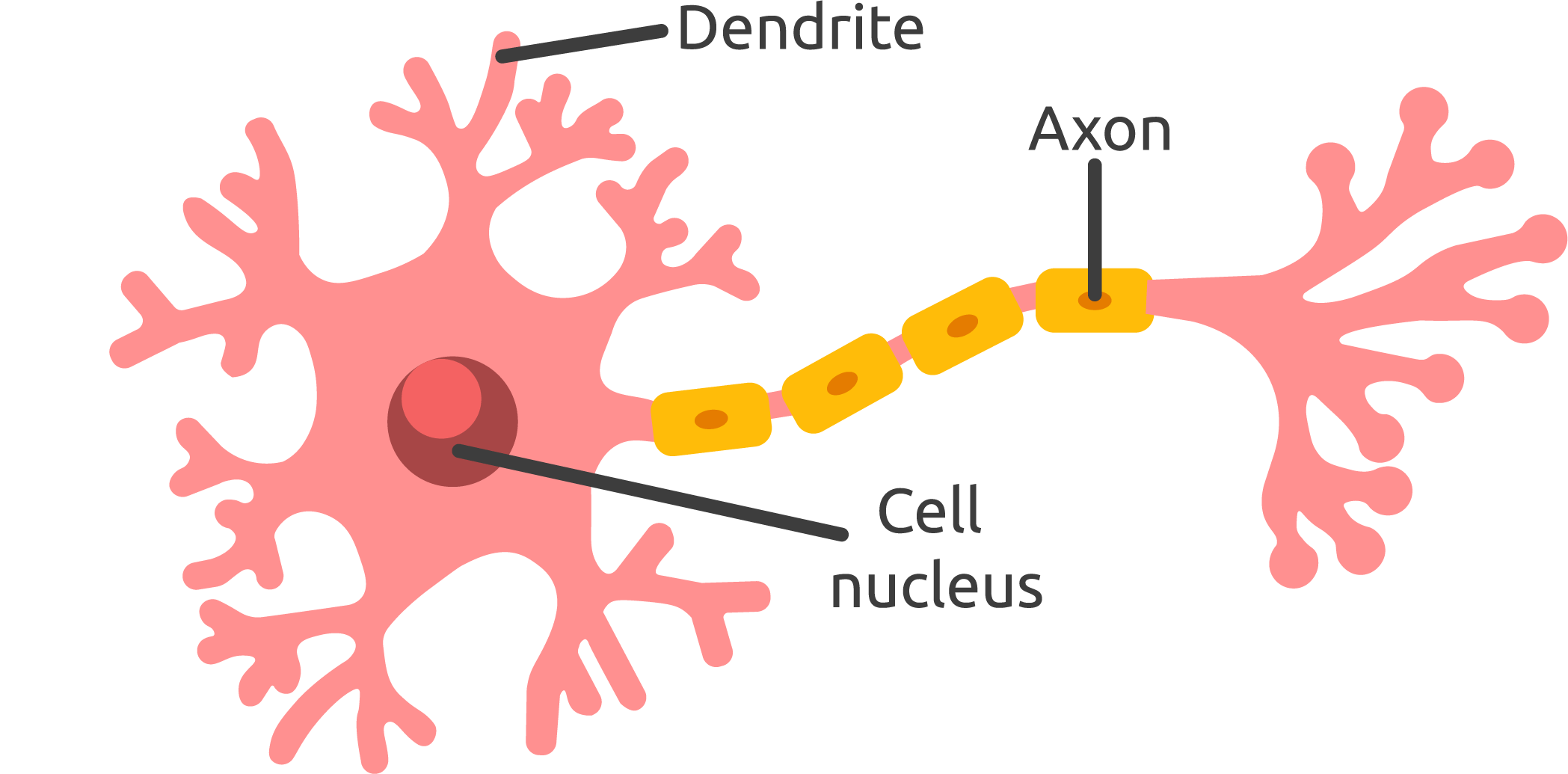
Axon
tubelike structure of a neurons that carries the neural message from the cell body to the axon terminals, for communication with other cells
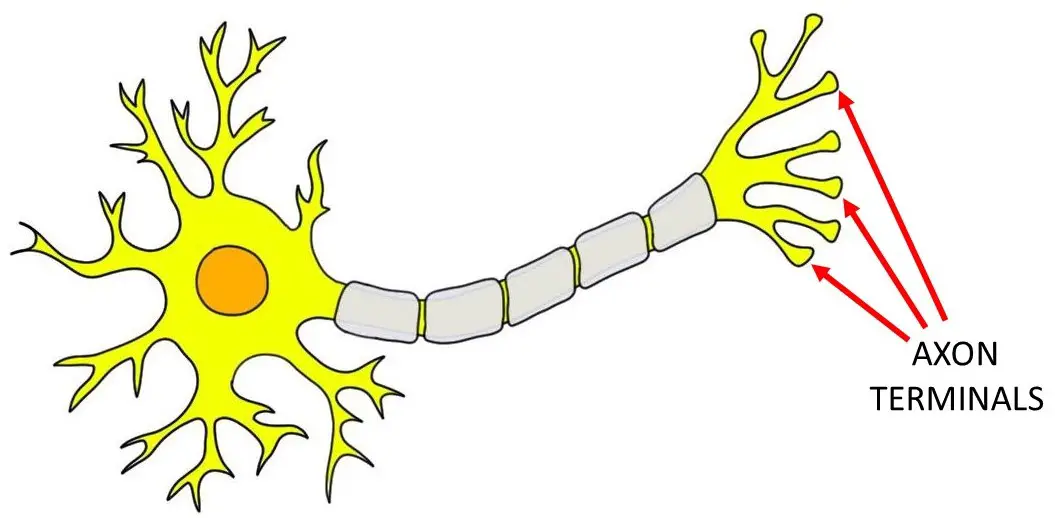
Axon terminals (aka presynaptic terminals, terminal buttons, synaptic knobs)
enlarged ends of axonal branches of the neuron, specialized for communication between cells.
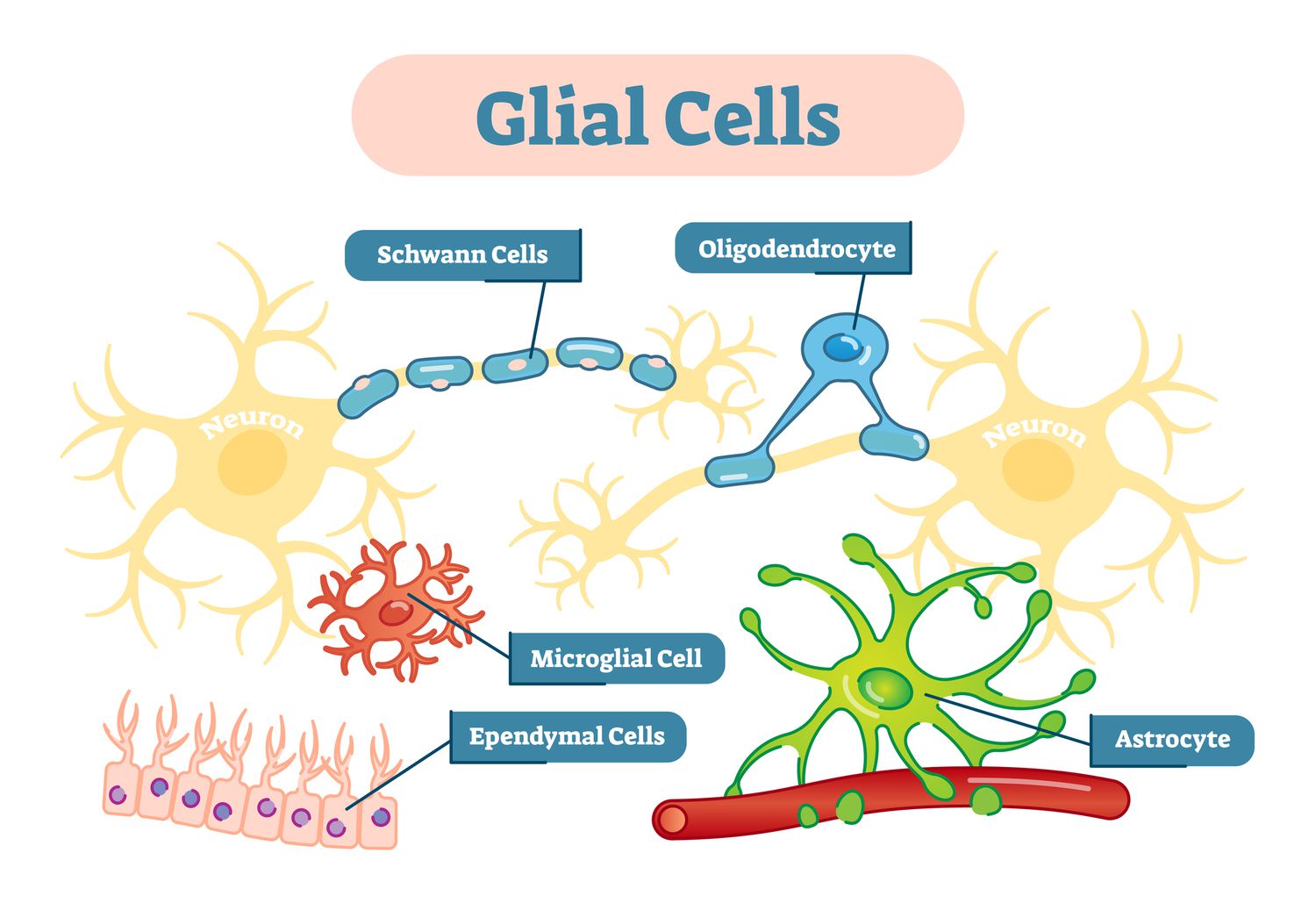
Glial cells/glia
cells that provide support for the neurons to grow on and around, deliver nutrients to neurons, produce myelin to coat axons, clean up waste products and dead neurons, influence information processing, and, during prenatal development, influence the generation of new neurons.
Myelin
fatty substances produced by certain glial cells that coat the axons of neurons to insulate, protect, and speed up the neural impulse
Nerves
bundles of axons coated in myelin that travel together through the body.
What two types of communication are in the neurons?
electrical communication (within the neuron)
chemical communication (between neurons)
Resting potential
the state of the neuron when note firing a neural impulse
Action potential
the release of the neural impulse, consisting of a reversal of the electrical charge within the axon
Excitatory synapse
synapse at which a neurotransmitter causes the receiving cell to fire
Inhibitory synapse
synapse at which a neurotransmitter causes the receiving cell to stop firing.
Antagonists
chemical substances that block or reduce a cell’s response to the action of other chemicals or neurotransmitters.
direct effects:
inhibiting/blocking neurotransmitters
indirect effects:
decrease synthesis of neurotransmitters
decrease release of neurotransmitters
increase degredation/reuptake of neurotransmitters
Agonist
chemcial substances that mimic or enhance the effects of a neurotransmitter on the receptor sites of the next cell, increasing or decreasing the activity of that cell
direct effects:
facilitating/mimicking the binding of neurotransmitters
indirect effects:
increase synthesis of neurotransmitters
increase release of neurotransmitters
decrease degradation/reuptake of neurotransmitters
Saltatory conduction
action potentials only occur at unmyelinated spaces on the axon; the signal jumps from node to node.
speeds up transmission
conserves energy
Afferent Neuron (sensory)
a neuron that carries information to the central nervous system
Efferent neuron (motor)
a neuron that carries messages from the central nervous system to the muscles of the body
Interneuron
a “connector” neuron found within the central nervous system.
Multiple Sclerosis
myelin sheath is destroyed.
movement of action potentials along the axon may be slowed or stopped altogether
Symptoms can include fatigue, numbness or tingling, muscle weakness, spasticity, lakc of motor coordination, vision problems, and bladder/bowl, sexual, and cognitive dysfunction.
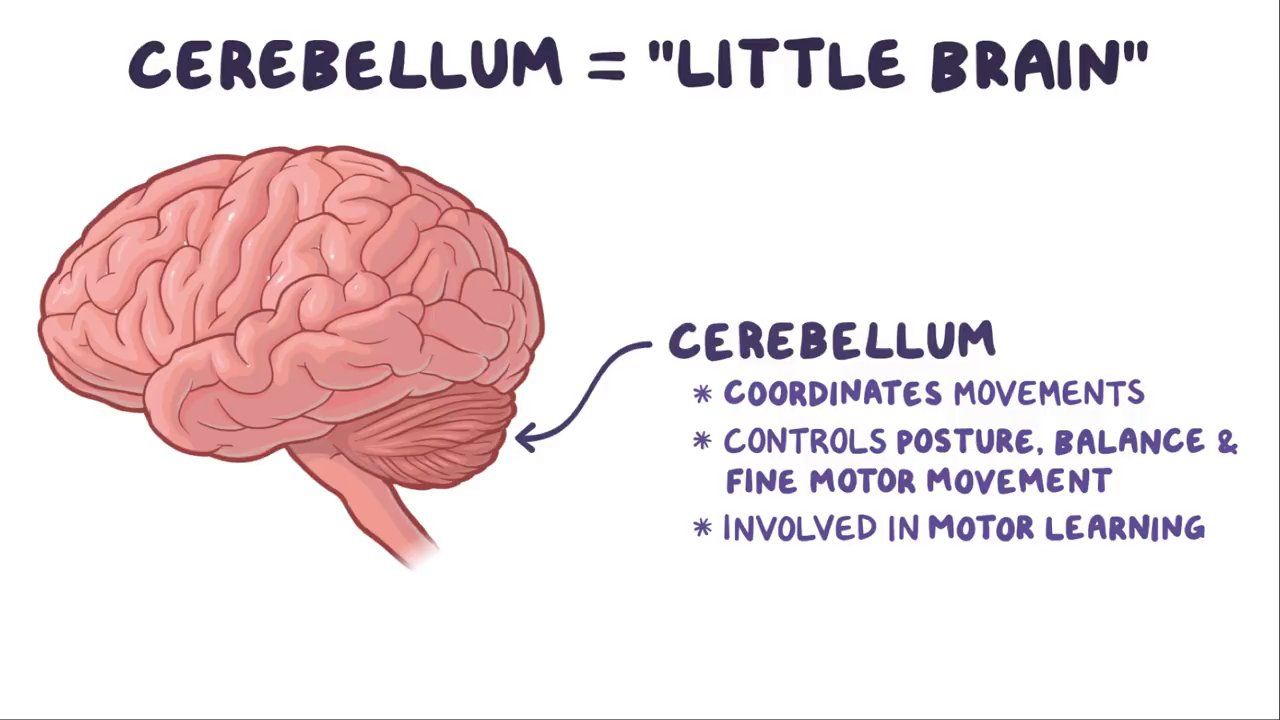
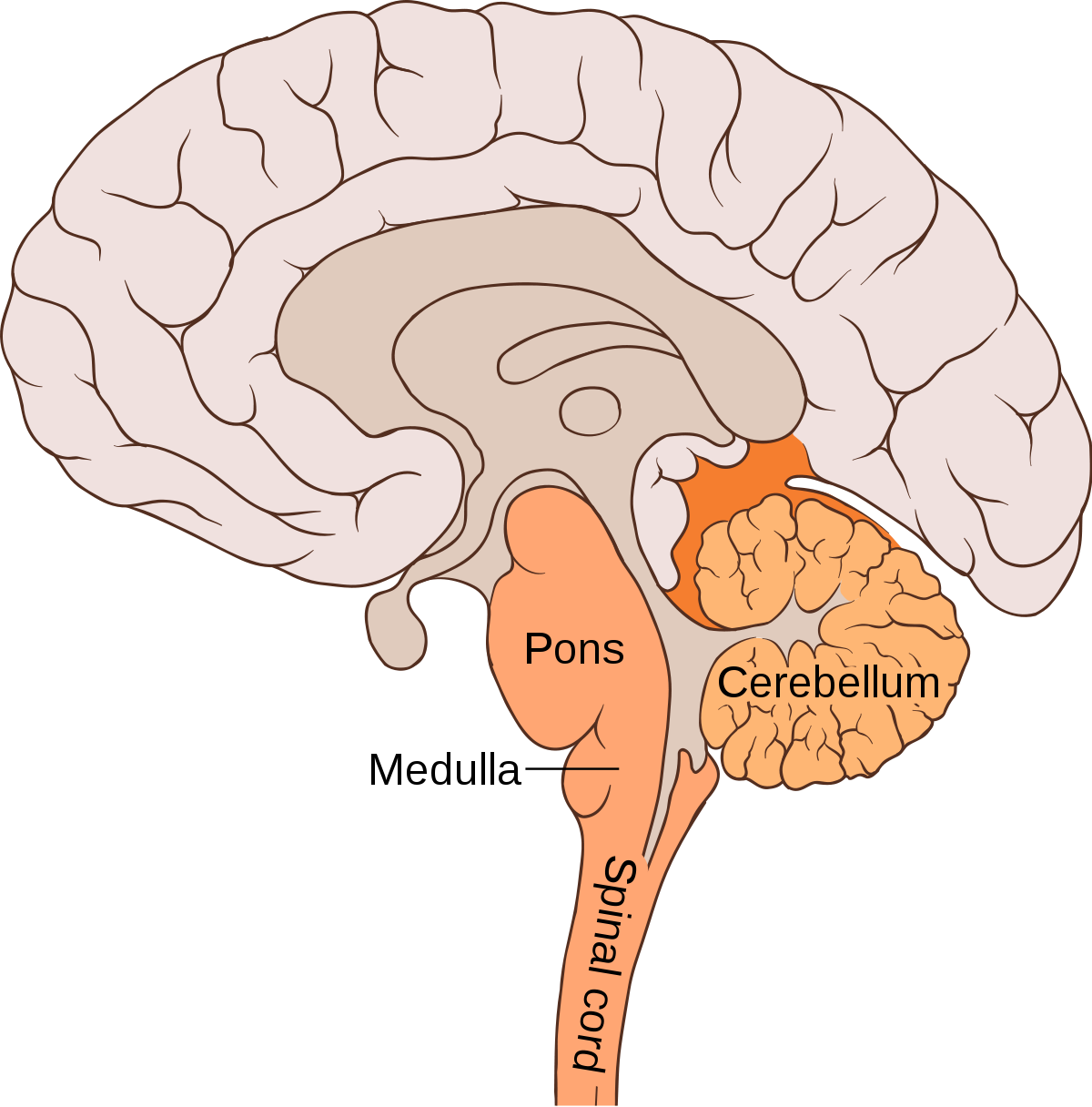
Cerebellum
part of the lower brain located behind the pons that controls and coordinates involuntary, rapid, and fine motor movement and may have some cognitive functions.
if damaged, you will be very uncoordinated.
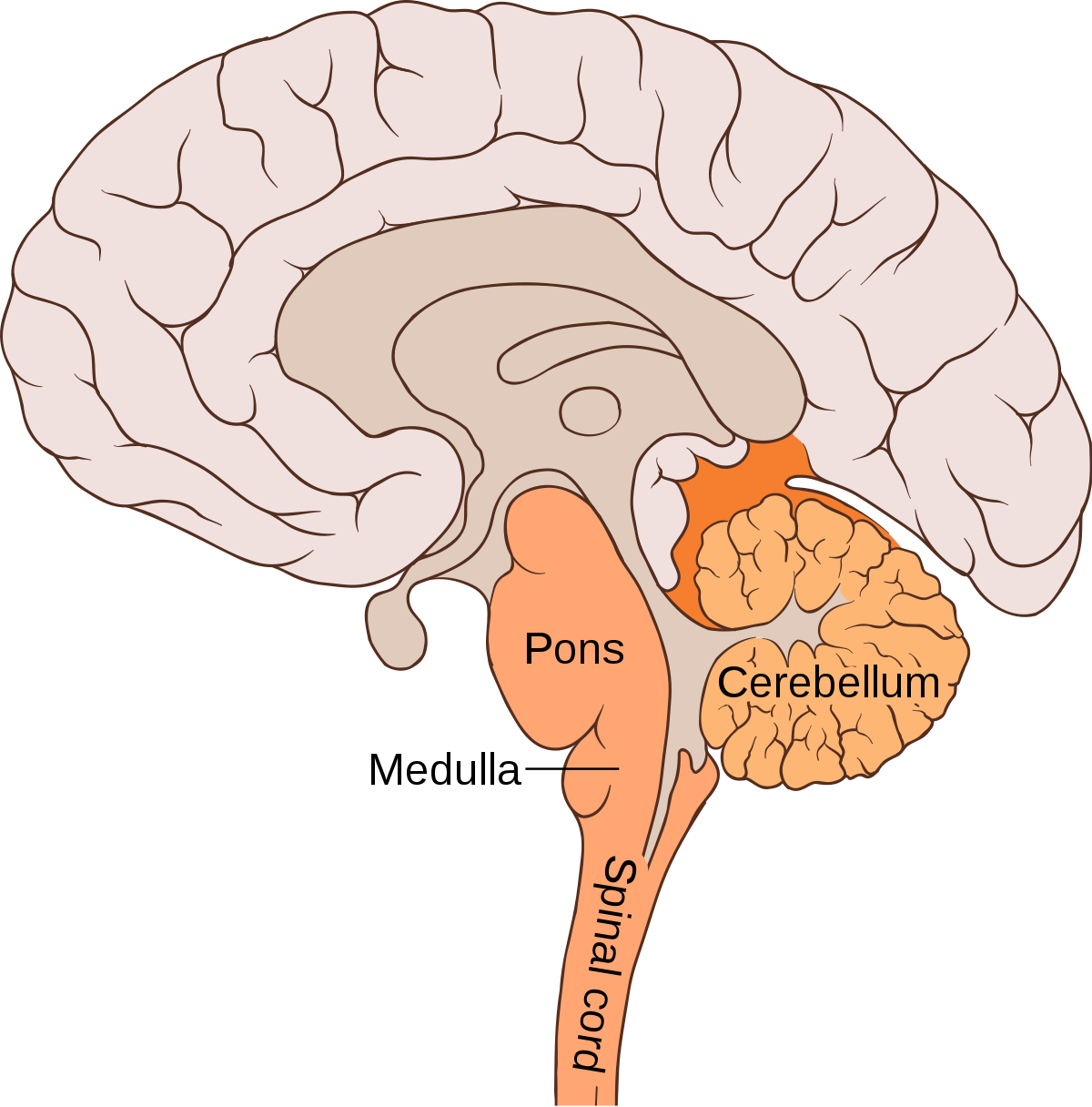
Pons
the larger swelling above the medulla that connects the top of the brain to the bottom and that plays a part in sleep, dreaming, left-right body coordination, and arousal.
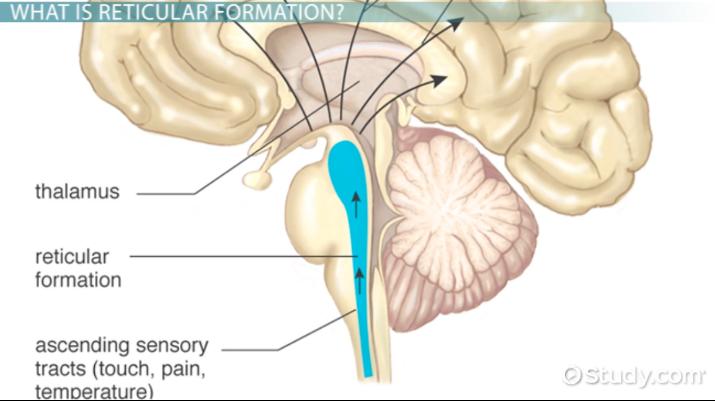
Reticular Formation (RF)
an area of neurons running through the middle of the medulla and the pons and slightly beyond that is responsible for general attention, alertness, and arousal.
Medulla
the first large swelling at the top of the spinal cord, forming the lowest part of the brain, which is responsible for life-sustaining functions such as breathing, swallowing, and heart rate.
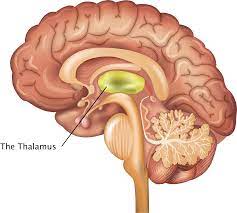
Thalamus
part of the limbic system located in the center of the brain, this structure relays sensory information from the lowest part of the brain to the proper areas of the cortex and processes some sensory information before sending it to its proper area.
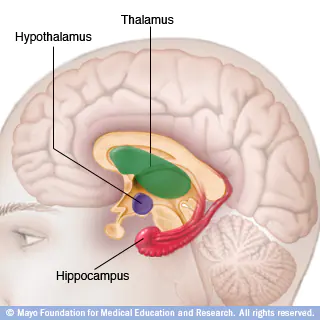
Hypothalamus
small structure in the brain located below the thalamus and directly above the pituitary gland, responsible for motivational behavior such as sleep, hunger, thirst, and sex.
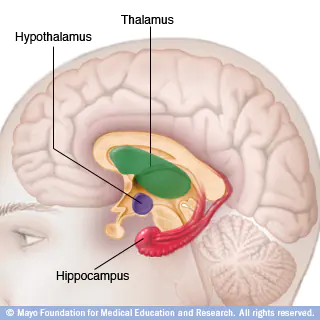
Hippocampus
curved structure located within each temporal lobe, responsible for the formation of long-term declarative memories.
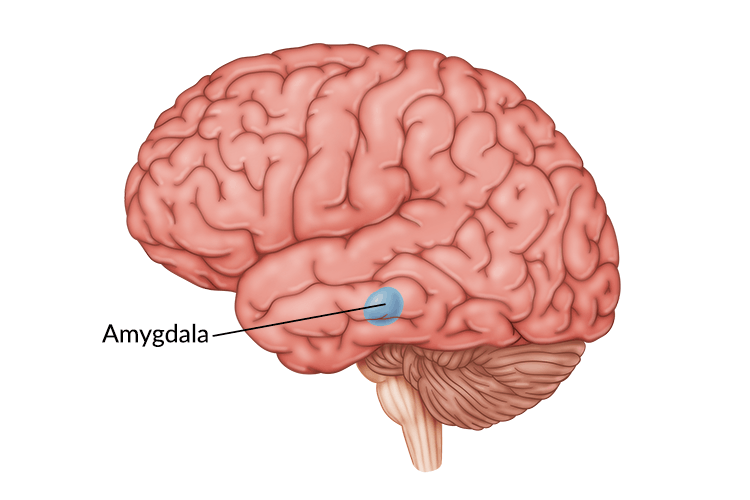
Amygdala
brain structure located near the hippocampus, responsible for fear responses and memory of fear
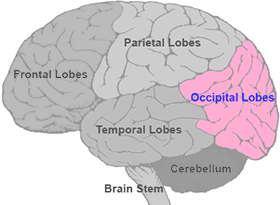
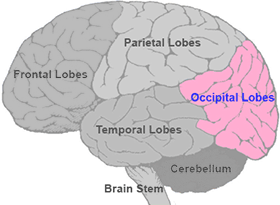
Occipital Lobe
section of the brain located at the rear and bottom of each cerebral hemisphere containing the primary visual centers of the brain.
Parietal Lobe
Processes information from the skin and internal body receptors for touch, temperature, and body position.
Temporal Lobe
Contains the neurons responsible for the sense of hearing and meaningful speech.
Frontal Lobe
Responsible for higher mental processes and decision-making, the production of fluent speech, and emotional control.
Consciousness
A person’s awareness of anything going on around them or inside their mind at any given time.
Waking consciousness
the state in which thoughts, feelings, and sensations are clear and organized and the person feels alert.
Altered state of consciousness
the state in which there is a shift in the quality or pattern of mental activity as compared to waking consciousness.
Sleep-wake cycle
also known as circadian rhythm, which is the cycle of bodily rhythm that occurs over a 24-hour period.
Role of hypothalamus in sleep-wake cycle:
it signals to the pineal gland to secrete melatonin, and it controls body temperature.
Adaptive theory
theory of sleep proposing that animals and humans evolved sleep patterns to avoid predators by sleeping when predators are most active (explains when we sleep).
Restorative theory
theory of sleep proposing that sleep is necessary to the body’s physical health and serves to replenish chemicals and repair cellular damage. (Brain plasticity is enhanced and sleep is critical for memory formation; explains why we sleep).
Most adults requires ________ hours of sleep a night. Sleep duration _______ with age.
7-9; decreases
Microsleeps
brief sidesteps into sleep that only lasts a few seconds.
Sleep deprivation
any significant loss of sleep.
Symptoms of sleep deprivation
trembling hands, droopy eyes, inattention, staring off into space, difficulty completing simple tasks, irritability, depression.
long term effects: increased risk for: insulin increase (precursor to diabetes), obesity, Alzheimer’s disease, psychological issues, depressed immune system, delayed onset of puberty, reduced longevity.
Rapid eye movement (R or REM)
stage of sleep in which the eyes move rapidly under the eyelids and the person is typically experiencing a dream.
muscles are inhibited
paradoxical sleep because the brain is sleep psychologically active
more emotionally taxing day —> longer time spent in REM
REM rebound —> increased amounts of REM sleep after being deprived of REM sleep on earlier nights.
Non-rapid eye movement (NREM)
any stages of sleep that do not include REM.
spans from lighter to deeper, more restful sleep.
body is free to move around.
N1: light sleep (may experience hallucinations, will not know they were asleep, hypnic jerks (falling senation)
N2: sleep spindles (bursts of brainwave activity that lasts 1-2 seconds), body temp drops and heart rate slows
N3: Deepest stage of sleep, aka slow-wave sleep. Growth hormones released, body is at it’s lowest level of functioning
Sleep pattern across lifespan:
Infants spend an (about) equal amount of time in REM and NREM sleep, as you get older, the time spent in REM sleep significantly decreases.
Infants sleep significantly longer than full grown adults.
Sleep problems
REM:
Nightmares (bad dreams)
REM behavior disorder (muscles are not inhibited; people thrash around and act out their dreams.
NREM:
Sleepwalking (somnambulism)
Night terrors (person experiences extreme fear and screams/runs around during sleep without waking up.
Other:
Insomnia
Sleep apnea (you stop breathing for 10+ seconds)
Narcolepsy (person falls into REM sleep randomly throughout the day)
Freuds take on dreams:
dreams are a form of wish fufillment
Manifest content
what is literally occurring in the dream.
Latent content
the true, hidden meaning of a dream.
Activation-synthesis hypothesis
dreams are created by the higher centers of the cortex to explain brain activity during REM sleep periods.