APUSH Chapter 22
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/189
Earn XP
Last updated 3:00 PM on 11/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
190 Terms
1
New cards
Allied Powers
Great Britain, Russia, Serbia, France

2
New cards
Machine guns
shoot in rapid succession, changing how wars are fought

3
New cards
Poison gas
Form of warfare introduced by Germans which used chemical or biological means

4
New cards
Tanks
new technology allowing soldiers to advance across No Man's Land

5
New cards
Airplanes
New technology allowing aerial support

6
New cards
War of Attrition
warfare where one side tried to wear down the other
7
New cards
Neutrality
original U.S. position toward WWI

8
New cards
Zimmerman Telegram
decoded message from German diplomat to Mexico offering U.S. territory (Texas) if Mexico fought the U.S. in WWI.

9
New cards
Henry Cabot Lodge
Rejected President Wilson's 14 points and was the main driving force behind the U.S. not approving the Treaty of Versailles

10
New cards
Espionage and Sedition Act
Congress made it illegal to speak out against the government's war efforts, incite disloyalty or persuade men from avoiding the draft, and outlawed disloyal or profane language directed against the constitution, military uniforms & flag
11
New cards
Wilson's 14 Points
plan for organizing post-war Europe in order to avoid future wars
12
New cards
League of Nations
an international organization formed in 1920 to promote cooperation and peace among nations. Senate did not allow the US to join.
Made in hopes to prevent future wars
Made in hopes to prevent future wars
13
New cards
Reparations
War payments made by a losing country after war
14
New cards
Treaty of Versailles
Treaty that ended WWI and was one of the main driving forces for WWII
Blamed Germany for WW I and handed down harsh punishment.
Blamed Germany for WW I and handed down harsh punishment.
15
New cards
General John Pershing
leader of the U.S. AEF forces in Europe

16
New cards
American Expeditionary Force
the U.S. armed forces sent over to fight in Europe during WWI. Not a legitimate army
17
New cards
War to End All Wars
the idea that WWI would, with all its destruction & devastation, end warfare
18
New cards
no man's land
A strip of land between the trenches of opposing armies along the Western Front during WW1

19
New cards
total war
A conflict in which the participating countries devote all their resources to the war effort

20
New cards
propaganda
Ideas spread to influence public opinion

21
New cards
armistice
A temporary peace agreement to end fighting.

22
New cards
Eastern Front
In WWI, the region along the German-Russian Border where Russians and Serbs battled Germans, Austrians, and Turks.
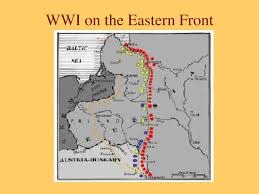
23
New cards
Western Front
in WWI, the region of northern France where the forces of the Allies and the Central Powers battled each other
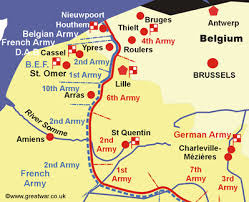
24
New cards
U-Boat warfare
A policy that the Germans announced on January 1917 which stated that their submarines would sink any ship in the British waters

25
New cards
Fourteen Points
A series of proposals in which U.S. president Woodrow Wilson outlined a plan for achieving a lasting peace after World War I.

26
New cards
reparations
As part of the Treaty of Versailles, Germany was ordered to pay fines to the Allies to repay the costs of the war. Opposed by the U.S., it quickly lead to a severe depression in Germany.

27
New cards
main causes of the war
militarism, alliances, nationalism, imperialism
28
New cards
Allies of World War I (Triple Entente)
Composed of France, Britain, Serbia, and Russia, and later Japan and Italy, the Allies fought the Central Powers in World War I. The United States joined the Allies in 1917.
29
New cards
Central Powers
A military alliance between Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, Turkey, and the Ottoman Empire.

30
New cards
Lusitania
British passenger boat sunk by a German submarine that claimed 1,000 lives. 128 Americans died, turning public opinion into war.
One of the main reasons the US decided to join the war.
One of the main reasons the US decided to join the war.

31
New cards
stalemate
A deadlock in which neither side is able to defeat the other.

32
New cards
Versailles Peace Treaty
Treaty that ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand.
33
New cards
U-boat
German submarine - u boat is short of the German word, Unterseeboot (Under Sea Boat)
34
New cards
barbed wire
was laid out between the trenches to slow down advancing enemy forces
35
New cards
WWI
Expanded the role/control of the federal government.
36
New cards
Unrestricted Submarine Warfare
Germany's Policy of sinking ships with their U-boats, enemy or neutral, that carry war material
37
New cards
Sussex Pledge
A promise Germany made to America, after Wilson threatened to sever ties, to stop sinking their ships without warning.
38
New cards
Freedom of the Seas
declared by Wilson, the right of merchant ships to travel freely in international waters
39
New cards
War Guilt Clause
A provision in the Treaty of Versailles by which Germany acknowledged that it alone was responsible for WWI
40
New cards
Foreign entanglements
Reason that's given for the US being dragged financially into WWI
41
New cards
Schenck v. United States
A 1919 decision upholding the conviction of a socialist who had urged young men to resist the draft during World War I. Justice Holmes declared that government can limit speech if the speech provokes a "clear and present danger" of substantive evils.
42
New cards
November 11, 1918
day that Germany signed Armistice ending WWI. 11th month, 11th day, 11th hour
43
New cards
War Industries Board
Agency established during WWI to increase efficiency & coordinate war production.
44
New cards
Rationing
Used during WWI and WWII. A limited portion or allowance of food or goods; limitation of use
45
New cards
Conscription
A military draft
46
New cards
Selective Service Act
Law passed by Congress in 1917 that required all men from ages 21 to 30 to register for the military draft
47
New cards
National War Labor Board
A board that negotiated labor disputes and gave workers what they wanted to prevent strikes that would disrupt the war.
48
New cards
Liberty Bonds
Bonds citizens bought so the government could get that money now for war. The bonds increased in interest over time.
49
New cards
Franz Ferdinand
Archduke of Austria-Hungary assassinated by a Serbian nationalist. A major catalyst for WWI.
50
New cards
Russian Revolution
The revolution against the Tsarist government which led to the abdication of Nicholas II and the creation of a communist government in March 1917.
51
New cards
Vladmir Lenin and the Bolsheviks
The communists in Russia who overthrew the government in 1917 and made peace with Germany.
52
New cards
Committee on Public Information
The purpose of this committee was to mobilize people's minds for war, both in America and abroad.
53
New cards
Palmer Raids
A 1920 operation coordinated by Attorney General Mitchel Palmer in which federal marshals raided the homes of suspected radicals and the headquarters of radical organization in 32 cities. A part of the Red Scare
54
New cards
Panama Canal
(TR) The United States built the _________ _________ to have a quicker passage to the Pacific from the Atlantic and vice versa. (wanted more ability to protect both coasts)
Colombians would not let Americans build, but then with the assistance of the United States, a Panamanian Revolution occurred. The new ruling people allowed the United States to build.
Colombians would not let Americans build, but then with the assistance of the United States, a Panamanian Revolution occurred. The new ruling people allowed the United States to build.
55
New cards
Commodore Perry
After arriving with a fleet of warships, he gets Japan to sign the Treaty of Kanagawa (1854) opening some ports to America. Helps to end Japanese isolation
56
New cards
Treaty of Kanagawa
An 1854 agreement between the United States and Japan, which opened two Japanese ports to U.S. ships and allowed the United States to set up an embassy in Japan.
57
New cards
Open Door Policy in China (1899)
A policy proposed by the US in 1899, under which all nations would have equal opportunities to trade in China.
Sent 2 sets of letters which both weren't replied to so he just assumed it was a yes
Later revised again in 1900
Sent 2 sets of letters which both weren't replied to so he just assumed it was a yes
Later revised again in 1900
58
New cards
Spheres of Influence
Areas in which countries have some political and economic control but do not govern directly (ex. Europe and U.S. in China)
59
New cards
Informal Empires
Term commonly used to describe areas that were dominated by Western powers in the nineteenth century but that retained their own governments and a measure of independence, e.g., Latin America and China.
60
New cards
Boxers (Harmonious Righteous Fists)
An anti-foreign secret society
Killed thousands of foreigners and Chinese Christians and in 1900 they occupied Beijing, the Chinese Capital, and besieged the foreign legations
Revolution ended when an international army (aided by the US) marched on Beijing and recaptured the city
- violated the US nonentanglement protocol
Killed thousands of foreigners and Chinese Christians and in 1900 they occupied Beijing, the Chinese Capital, and besieged the foreign legations
Revolution ended when an international army (aided by the US) marched on Beijing and recaptured the city
- violated the US nonentanglement protocol
61
New cards
Open Door Policy (1900) Revision
Hay feared that China's regime collapse would allow European powers to carve up China and issued a second series of Open Door Notes
- Reaffirmed the principle of open trade in China for all nations and announced America's determination to preserve China's territorial and administrative integrity
- Reaffirmed the principle of open trade in China for all nations and announced America's determination to preserve China's territorial and administrative integrity
62
New cards
Control Corporations
Consumer Protection
Conservation of Resources
Consumer Protection
Conservation of Resources
Teddy Roosevelt's 3 C's
63
New cards
Nicaragua/Panama Canal
__________________
- closer to the U.S.
- both oceans were on the same level on both sides of the country
- had many water ways that could be used to extend the canal more easily
________________
- the distance across the land was much shorter
- 1/3 of a canal was already completed by the New Panama Canal Company
- rights to the Panama canal were restricted until 1903
- closer to the U.S.
- both oceans were on the same level on both sides of the country
- had many water ways that could be used to extend the canal more easily
________________
- the distance across the land was much shorter
- 1/3 of a canal was already completed by the New Panama Canal Company
- rights to the Panama canal were restricted until 1903
64
New cards
John Hay
Secretary of State under McKinley and Roosevelt who pioneered the open-door policy and Panama canal
65
New cards
Clayton-Bulwer Treaty (1850)
Great Britain and US said that neither nation would or could attempt to take exclusive control of any future istmainian waterway
66
New cards
Theodore Roosevelt
Who called Colombians "Greedy little anthropoids"
67
New cards
Hay-Pauncefote Treaty (1901)
Great Britain recognized U.S. Sphere of Influence over the Panama canal zone and allowed the US to take full control over construction and management of the canal, as well as it's fortification
68
New cards
French Canal Company
French company that was eager to salvage something from their costly failure to make canal alone at Panama. (Wanted Panama and not Nicaragua)
69
New cards
Phillippe Bunau-Varilla
French engineer who helped organize a revolt against Columbia, while serving as Chief Engineer of the Canal Company, and became Panama's new ambassador to the US
70
New cards
$40 million
Price the French Canal Company wanted for the canal before Panama rebelled against Columbia
71
New cards
10 miles
How long was the strip of land granted to the US for the Panama Canal?
72
New cards
Hay-Herran Treaty
Treaty that opened the door for the building of the Panama Canal; in return for a Canal Zone six miles wide, the United States agreed to pay Colombia $10 million in cash and $250,000 a year; the United States Senate ratified the Treaty in 1903 but the Colombian Senate struck it down (Had become hugely unpopular in Bogotá)
73
New cards
$10 million + $250,000/year
What was the US's initial offer to Columbia for a 6-mile strip of land for the Panama Canal? (Before the Panama revolution)
74
New cards
Hay-Bunau-Varilla Treaty (1903)
In 1903, the Panama government signed this treaty with the United States. It granted the U.S. all rights to the 51 mile long and 10 mile wide Canal Zone, in exchange for U.S. protection
75
New cards
Lock System
a section of a waterway with closed gates where water levels are raised or lowered, through which ships pass
(Solved the elevation issues in the Panama Canal Project)
(Solved the elevation issues in the Panama Canal Project)
76
New cards
Theodore Roosevelt
Who was the 1st president to leave American soil
("Operated" a steam shovel during the Panama Canal's Construction)
("Operated" a steam shovel during the Panama Canal's Construction)
77
New cards
$25 million
Amount US paid to Colombia for having used illegal means to acquire the Canal Zone
78
New cards
Disney Magic Cruise Liner
What ship paid the highest toll when going through the Panama Canal?
79
New cards
Walter Reed
United States physician who proved that yellow fever is transmitted by mosquitoes (1851-1902)
80
New cards
Richard Halliburton
Who paid 36 cents to swim through the Panama Canal?
81
New cards
Theodore Roosevelt
First President to get a Nobel Peace Prize
82
New cards
Roosevelt Corollary (1904)
Roosevelt's extension of the Monroe Doctrine, stating that the United States has the right to protect its economic interests in South And Central America by using military force. we were the "police of the western hemisphere" Example of US imperialism in Latin America. Used to justify hundreds of interventions, mostly to protect US business interests, sometimes to the detriment of democratic movements in Latin America
83
New cards
Venezuela and Dominican Republic
Couldn't pay their debts to Germany and Britain so the US interfered using the Roosevelt Corollary. Guaranteed Germany and Britain payment but wanted to make sure they didn't use debts as a means to send their military and get past the Monroe Doctrine
84
New cards
Dollar Diplomacy (Taft)
A policy for "substituting dollars for bullets" by William Howard Taft. It would link American business interests to diplomatic interests abroad without force, but with investments.
85
New cards
Russo-Japanese War (1904-1905)
War over Manchuria, ended in a Japanese victory, establishing Japan as a formidable military competitor in East Asia. (First time an Asian power beat a European power)
Foreshadowing the Russian Revolution
Foreshadowing the Russian Revolution
86
New cards
Portsmouth Peace Conference (1905)
Where President Theodore Roosevelt helped negotiate an end to the Russo-Japanese War.
Roosevelt won the Nobel Peace Prize for his efforts, but neither side was happy with the resulting treaty which harmed American relations with both nations.
Roosevelt won the Nobel Peace Prize for his efforts, but neither side was happy with the resulting treaty which harmed American relations with both nations.
87
New cards
Great White Fleet (1907-1909)
Roosevelt sent the ______ ______ ______ on a world tour to show the world the U.S. naval power. Also to pressure Japan into the "Gentlemen's Agreement."
16 ships
16 ships
88
New cards
Gentlemen's Agreement (1907)
Tokyo voluntarily halted Japanese emigration ot America, however California continued to poison US-Japanese Relations
89
New cards
Bull Moose Party
nickname for the new Progressive Party, which was formed to support Roosevelt in the election of 1912
90
New cards
John Flammang Schrank
Man who shot Roosevelt claiming he didn't intend to kill "citizen Roosevelt" but "Roosevelt, the third termer"
Said the Ghost of McKinley told him to do it
Said the Ghost of McKinley told him to do it
91
New cards
Woodrow Wilson
28th president of the United States, known for World War I leadership, created the Federal Reserve, Federal Trade Commission, Clayton Antitrust Act, progressive income tax, lower tariffs, women's suffrage (reluctantly), Treaty of Versailles, sought 14 points post-war plan, League of Nations (but failed to win U.S. ratification)
- First president to throw out the first ball at a World Series
- Face was on the $100,000 bill
- First president to throw out the first ball at a World Series
- Face was on the $100,000 bill
92
New cards
Wilson vs Triple Wall of Privilege
- Tariff reforms
- Banking Regulations
- Monopoly/Trust regulations
- Banking Regulations
- Monopoly/Trust regulations
93
New cards
Clayton Antitrust Act (1914)
Strengthened the Sherman Antitrust Act by spelling out specific activities businesses could not do
- exempted labor and agricultural organizations
- legalized strikes
- exempted labor and agricultural organizations
- legalized strikes
94
New cards
Federal Farm Loan Act (1916)
made credit available to farmers at low rates of interest
95
New cards
Warehouse Act (1916)
authorized loans on the security of staple crops
96
New cards
La Follette Seamen's Act (1915)
required decent treatment and wages on American merchant ships
97
New cards
Working Compensation Act (1916)
Granted assistance of federal civil service employees if the got injured on the job
98
New cards
Adamson Act (1916)
established an 8-hour work day for all employees on trains in interstate commerce.
99
New cards
Louis Brandeis
First Jew on the Supreme Court
100
New cards
Blacks
Wilson did not improve conditions for _______?