AP World History Review (Units 1-9)
1/685
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
686 Terms
United Nations
An international organization formed after WWII to promote international peace, security, and cooperation.
Portuguese explorer. In 1497-1498 he led the first naval expedition from Europe to sail to India, opening an important commercial sea route.
Vasco Da Gama
(1394-1460) Portuguese prince who promoted the study of navigation and directed voyages of exploration down the western coast of Africa.
Henry the Navigator
The effort by Christian leaders to drive the Muslims out of Spain, lasting from the 1100s until 1492.
Reconquista
A small, highly maneuverable three-masted ship used by the Portuguese and Spanish in the exploration of the Atlantic.
Caravel
the making of maps and charts
Cartography
A triangle sail used to sail through the crosswinds
Lateen Sails
an instrument used by sailors to determine their location by observing the position of the stars and planets
Astrolabe

"Returning through the sea," a fifteenth-century Portuguese sea route that took advantage of the prevailing winds and currents.
Volta do mar
Spanish Catholic monarchs who unified Spain, sponsored Columbus, Spanish Inquisition, and Reconquista.
Ferdinand and Isabel of Spain
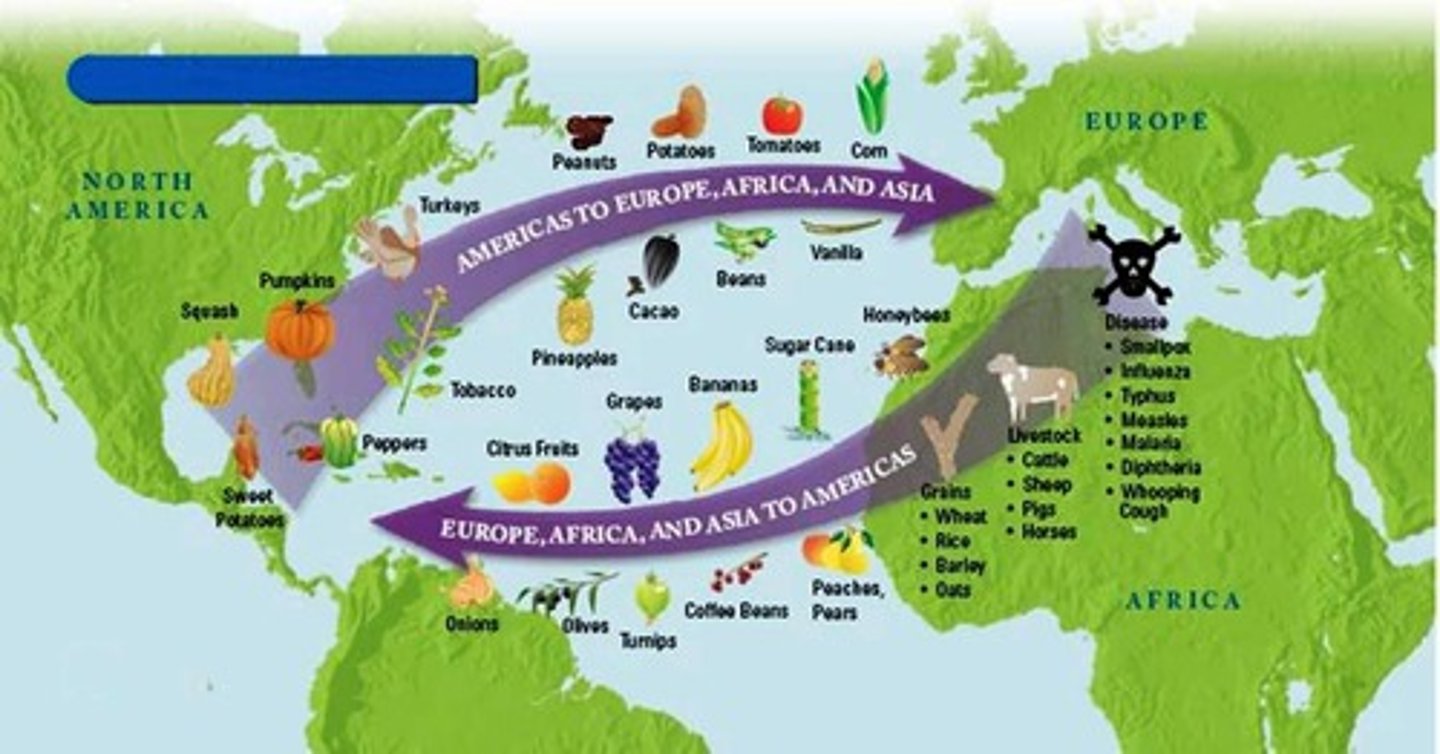
The transfer of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus's voyages.
Columbian Exchange
sailing completely around something, such as the world
Circumnavigation
Heavily armed, fast ships that brought luxury goods from China to Mexico and carried silver from Mexico to China.
Manila Galleons

relating to the Eastern Christian Church
Orthodox
Two of the main diseases brought over by the Europeans in the Columbian Exchange
Smallpox/Influenza
A German monk who became one of the most famous critics of the Roman Catholic Chruch. In 1517, he wrote 95 theses, or statements of belief attacking the church practices.
Martin Luther

Religious movement within the Latin Christian Church that clarified Catholic theology and reformed clerical training and discipline.
Catholic Reformation
Also known as the Society of Jesus; founded by Ignatius Loyola (1491-1556) as a teaching and missionary order to resist the spread of Protestantism.
Jesuits
a Catholic-Protestant religious conflict. It was primarily a battle between France and the Hapsburg's, rulers of the Holy Roman Empire.
Thirty Years' War

A body of representatives that makes laws for a nation
Parliament
separation or balance of powers/3 branches of gov't
Montesquieu

a palace built for Louis XIV outside of Paris
Versailles

king of France from 1643 to 1715; his long reign marked the expansion of French influence in Europe and by the magnificence of his court and the Palace of Versailles
Louis XIV

The Russian term for ruler or king; taken from the Roman word caesar.
Tsar (Czar)
czar of Russia who introduced ideas from western Europe to reform the government
Peter the Great

empress of Russia who continued to Westernize Russia, created a new law code, and greatly expanded Russia
Catherine the Great
Treaty that ended the Thirty Years' War (1648) and readjusted the religious and political affairs of Europe.
Peace of Westphalia
distribution of military and economic power that prevents any one nation from becoming too strong
Balance of Power
An association of individuals in a business enterprise with transferable shares of stock, much like a corporation except that stockholders are liable for the debts of the business
Joint Stock Companies

economic concept that states the price of a good rises and falls depending on how many people want it and its availability
Supply and Demand
merchants/artisans who cooperated to protect their economic interests
Guilds
Scottish economist who advocated private enterprise and free trade (1723-1790)
Adam Smith

English mathematician and physicist who devised the laws of motion and gravity
Isaac Newton

believed in a heliocentric conception of the universe.
Nicholas Copernicus
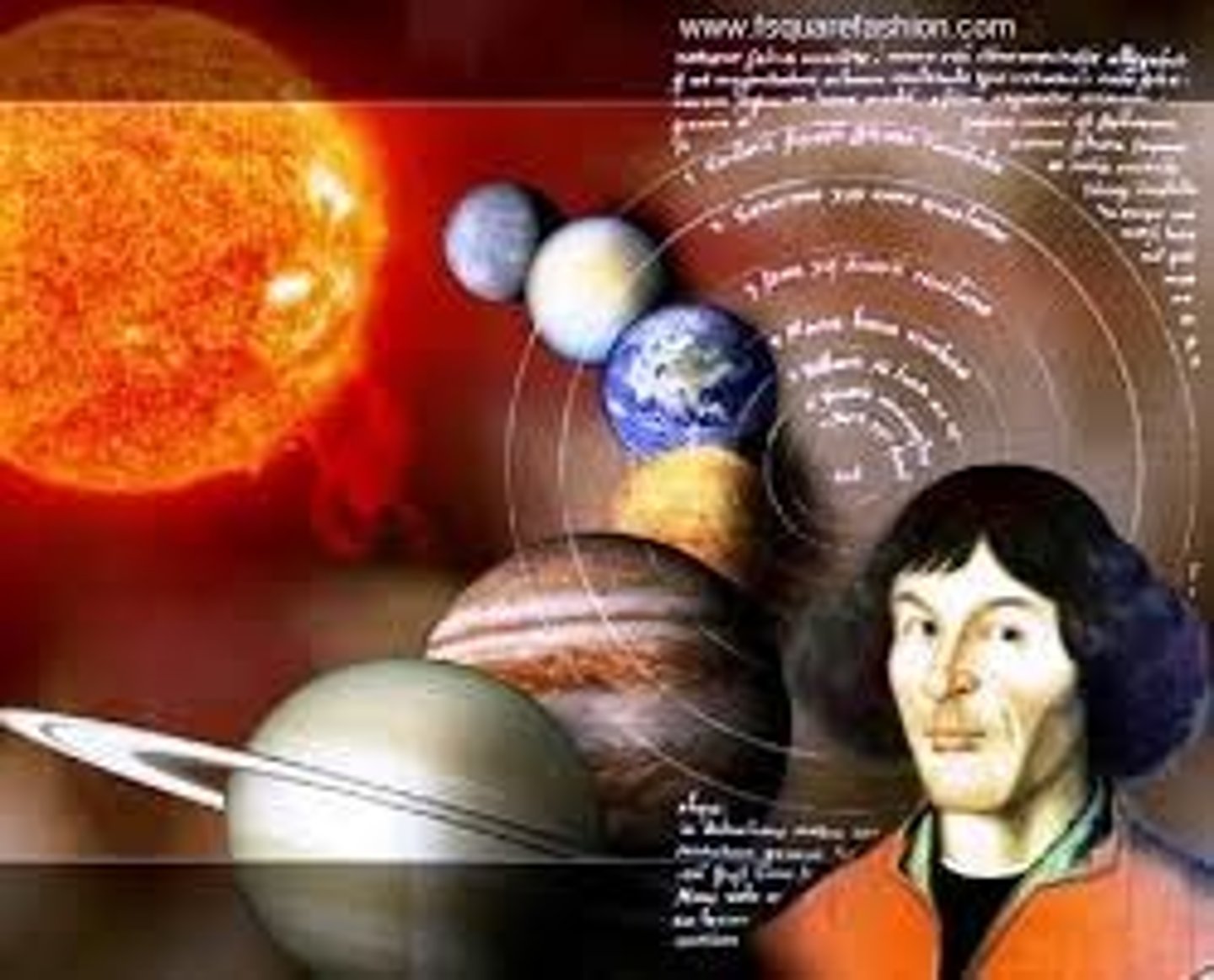
Italian astronomer and mathematician who was the first to use a telescope to study the stars
Galileo Galilei

a movement in the 18th century that used reason in the reappraisal of accepted ideas and social institutions
Enlightenment
English philosopher; believed all knowledge is from sensory experience
John Locke

French writer who was the embodiment of 18th century Enlightenment(freedom of speech/religion)
Voltaire

Informal social gatherings at which writers, artists, philosophes, and others exchanged ideas
Salons
A mechanical device for transferring text or graphics from a woodblock or type to paper using ink.
Printing Press
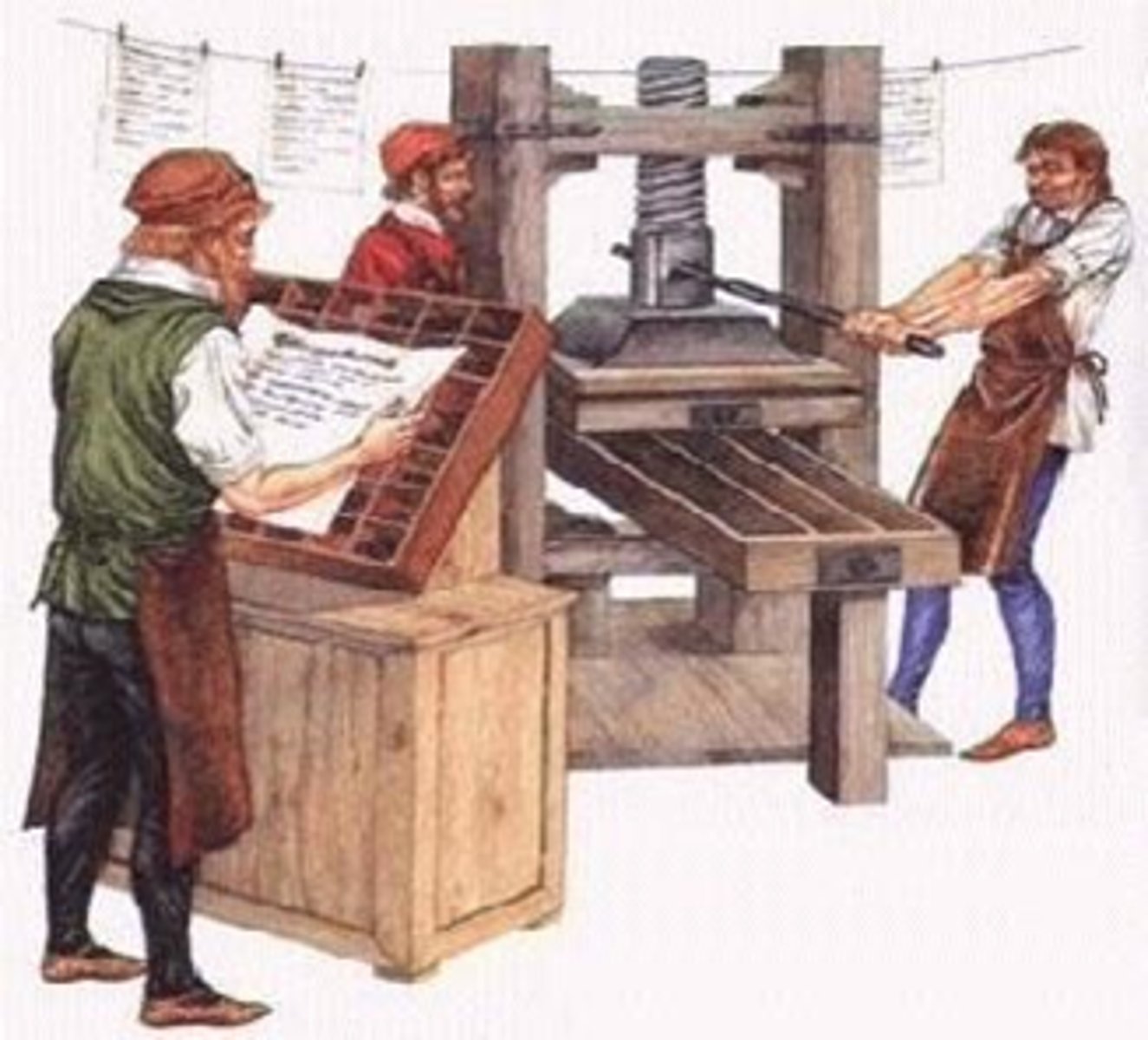
the first full-sized book printed with movable type and a printing press
Gutenberg Bible
The great period of rebirth in art, literature, and learning which marked the transition modern European history
Renaissance

Spanish conquistador who defeated the Aztecs
Hernan Cortes

settled the valley of Mexico. Believed the sun god needed human blood to continue his journeys across the sky
Aztecs

Capital of the Aztec Empire, population was about 150,000
Tenochtitlan
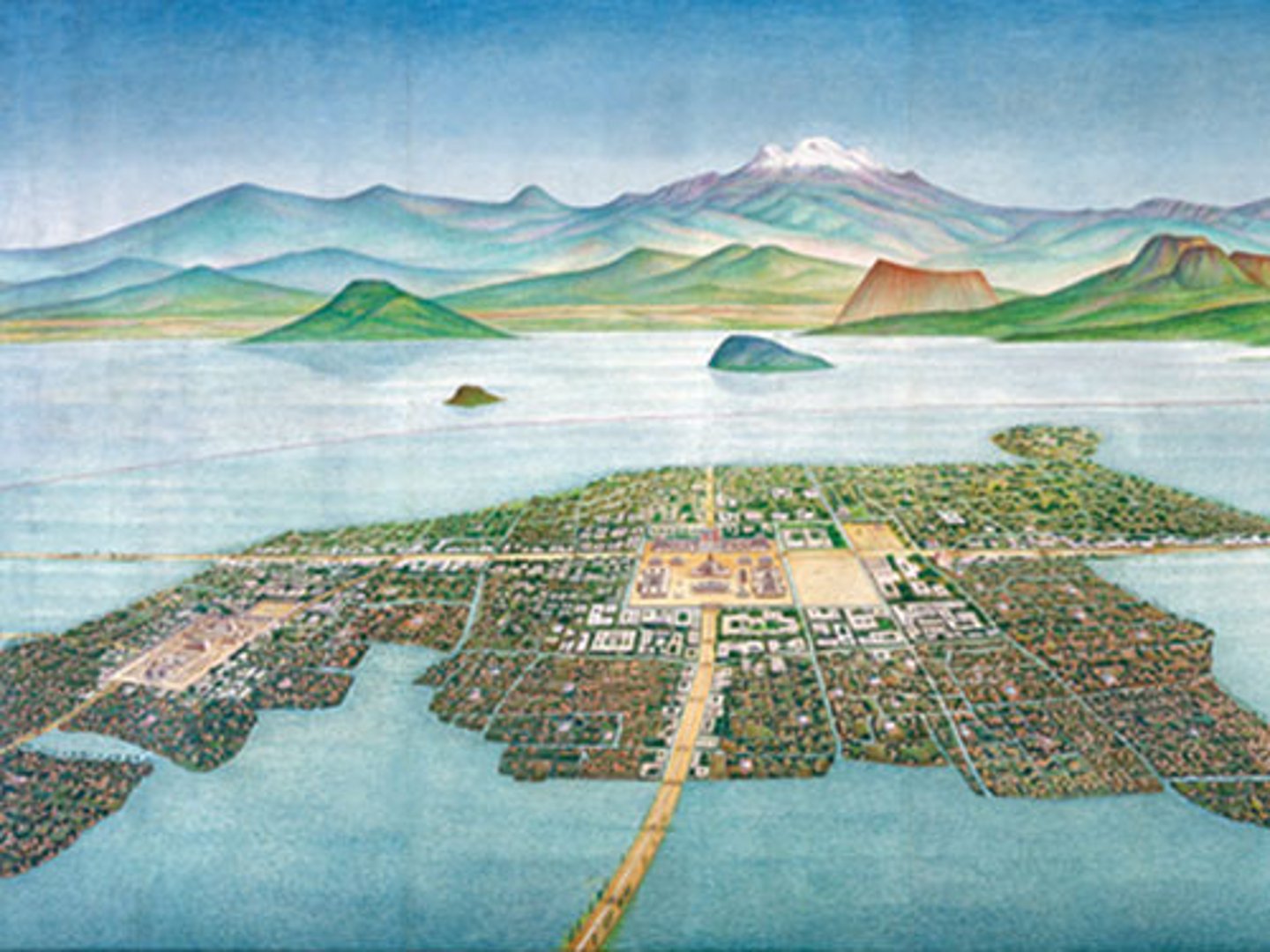
last Aztec emperor of the Aztecs
Montezuma

the first island that was found by Christopher Columbus
Hispanola
A grant of land made by Spain to a settler in the Americas, including the right to use Native Americans as laborers on it
Encomienda

Spanish explorer who conquered the Incas
Francisco Pizarro

Highly advanced South American civilization that occupied present-day Peru until it was conquered by Spanish forces under Francisco Pizarro in 1532. The Incas developed sophisticated agricultural techniques, such as terrace farming, in order to sustain large, complex societies in the unforgiving Andes Mountains.
Incas
Spanish soldier in the New World. searching for the 3-G's: gold, God, and glory.
Conquistadores

the main house on a ranch or large estate
Hacienda

governor of a province who rules as the representative of his or her king
Viceroy
religious settlements run by Catholic Priests and friars.
Missions

Set the Line of Demarcation, a boundary in 1493 to define Spanish and Portuguese possessions in the Americas.
Treaty of Tordesillas
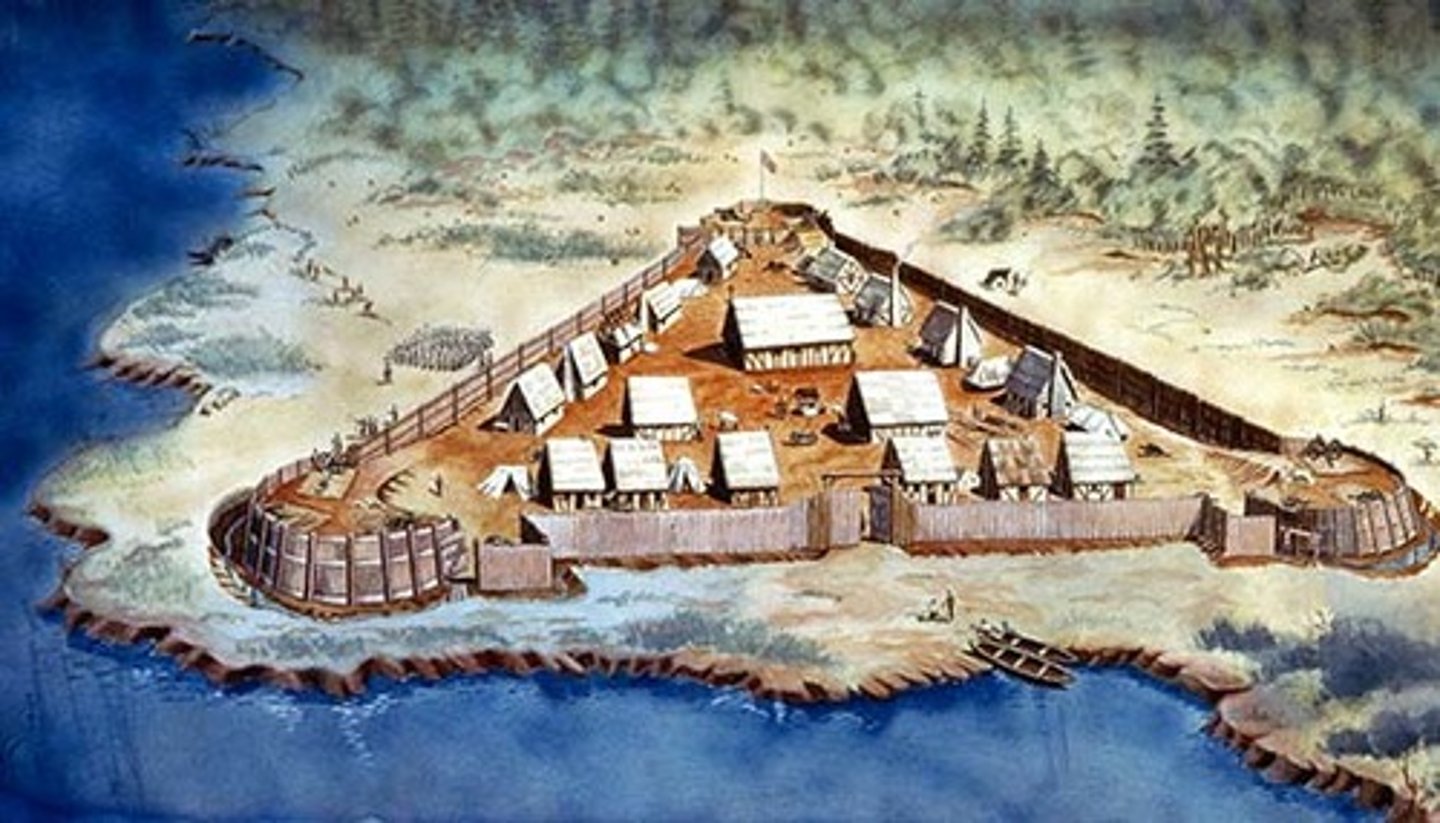
first successful settlement in Virginia
Jamestown
descendents of Spanish-born BUT born in Latin America; resented inferior social, political, economic status
Creoles
a person of mixed african and european ancestry
Mulatto
Labor extracted for lands assigned to the state and the religion; all communities were expected to contribute; an essential aspect of Inca imperial control.
Mita
Located in Bolivia, one of the richest silver mining centers and most populous cities in colonial Spanish America
Potosi

a crop that is grown and gathered for the market
Cash Crop
colonists who received free passage to North America in exchange for working without pay for a number of years
Indentured Servants
all parts of the world participated in a global trade network in which European's played dominant roles except here
Australia
A document whose purchase was said to grant the bearer the forgiveness of sins
Indulgence
A European economic policy that held that there was a limited amount of wealth available, and that each country must adopt policies to obtain as much wealth as possible for itself; key was the acquisition of colonies
Mercantilism
A government with a king or queen whose power is limited by the power of a parliament
Parliamentary Monarchy
A route through North American that was sought by explorers as a route to trade with Asia
Northwest Passage
A practice of the Ottoman empire to take Christian boys from their home communities to serve as Janissaries
Devshirme
A religious movement that attempted to restore the beliefs and practices of the Roman Catholic Church; it resulted in the formation of new Christian denominations
Protestant Reformation
A sovereign area whose people share a common culture and national identity
Nation-state
A way of gaining knowledge by means of direct observation or experience
Empirical Research
A white marble mausoleum built at Agra, India, by the Mogul emperor Shah Jahan for his favorite wife
Taj Mahal
A concept that holds that the government should not interfere with or regulate business and industries
Laissez-Faire Economics
An economic system based on private ownership and opportunity for profit-making
Capitalism
French Enlightenment social thinkers
Philosophes
Persons of mixed European and native descent in the Spanish colonies
Mestizos
Those born in Europe living in the Spanish colonies
Peninsulares
Manchurian rule of China in 1644 and lasting until 1914
Qing Dynasty
Members of the Ottoman army, often slaves, who were taken from Christian land
Janissaries
Peoples from northeastern Asia who founded China's Qing dynasty
Manchus
Principles that govern the universe
Natural Laws
Rule by a king or queen whose power is not limited by the constitution
Absolute Monarchy
Rulers who controlled most of India in the 16th and 17th centuries
Mughal Dynasty
Russian nobility
Boyars
Russian-Slavic military that settled Siberia
Cossacks
Self-rule
Sovereignty
came up with concept of the Social Contract
Jean-Jacques Rousseau
The belief of absolute rulers that their right to govern is granted by God
Divine Right
The belief of Protestant reformer John Calvin that God had chosen some people for heaven and others for hell
Predestination
The bloodless overthrow of English King James I and the placement of William and Mary on the English throne
Glorious Revolution
The church in Constantinople that was converted to a mosque after the Ottoman conquest
Hagia Sophia
The concept of God common to the scientific revolution; the god was believed to have set the world in motion and then allowed it to operate by natural laws
Deism
The concept that the sun is the center of the solar system
Heliocentric Revolution
The 18th century network between Europe, Africa, and the Americas
Triangular Trade
The feudal rulers of Japan who moved the capital to Edo and ruled from 1603 to 1868
Tokugawa Shogunate

The Hindu custom of secluding women
Purdah
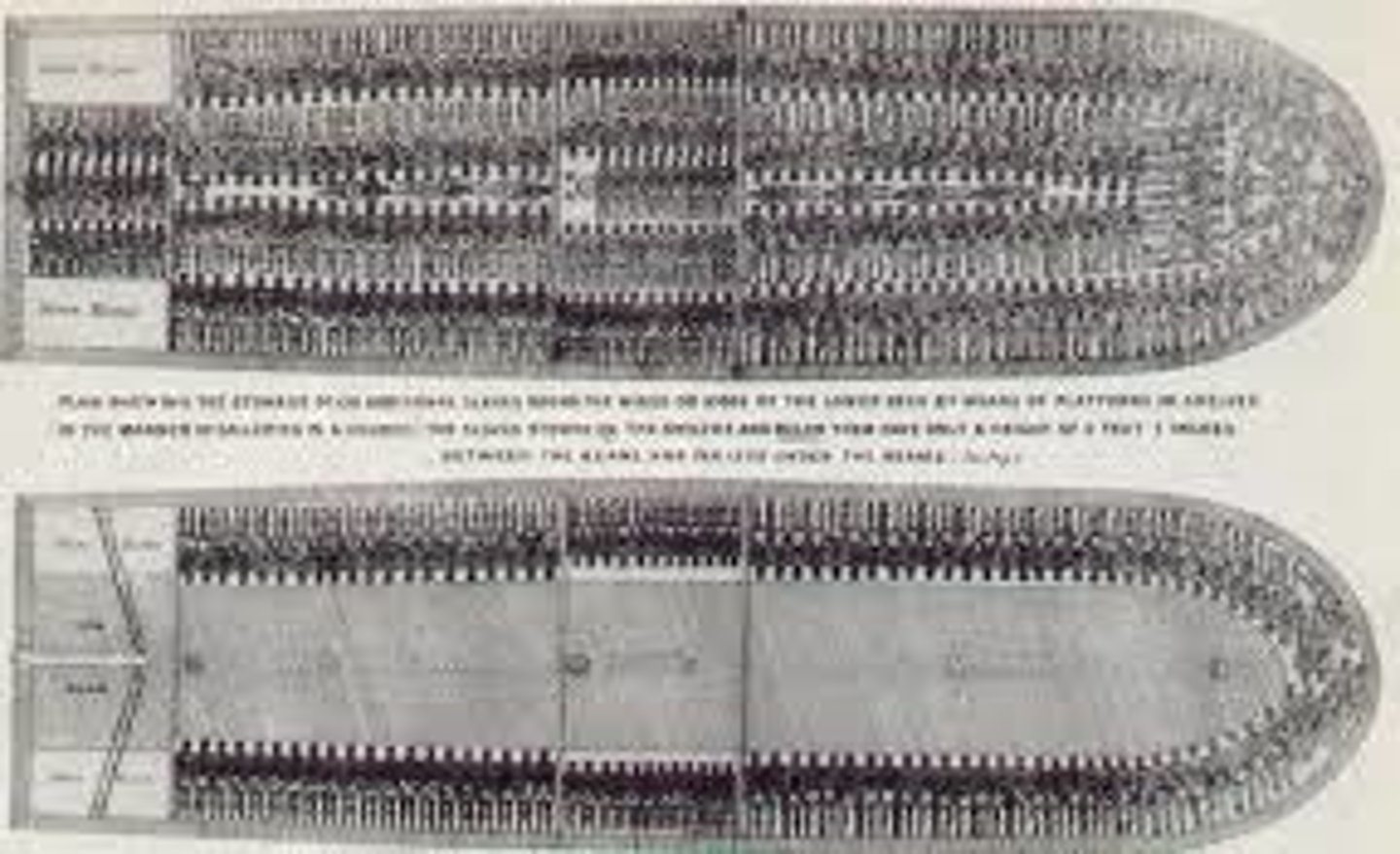
The portion of the trans-Atlantic trade that involved the transporting of Africans to the Americas
Middle Passage
The practice of the Roman Catholic and other Christian churches of prohibiting the sacraments to those who do not comply with church teachings or practices
Excommunication

The traditional legislative body of France
Estates-General
Work by Martin Luther where he laid out his arguments against the Roman Catholic Church
95 Theses
