diagnostic imaging module 1 and 2
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
which term is used for
"prevention, diagnosis and treatment of pathology"
-radiology
-MSK
-radiography
radiology
which term is used for
"Subspecialty of radiology that is focused on diagnostic evaluation of the musculoskeletal system"
-radiology
-MSK
-radiography
MSK
which term is used for
The primary tool and the first ordered diagnostic study
-radiology
-MSK
-radiography
radiography
what do PTs use radiographic images for
assess bony alignment
identify bony blocks
visualize fx location to plan interventions
id exact position of fixation devices
assess bone healing to make decisions about movement or weight bearing
when are clinical decision making rules (CDR) used?
used for clinicians when imaging is necessary for trauma
is this the right order
radiograph -> PT -> medication -> MRI
no
radiograph>medication>PT>MRI
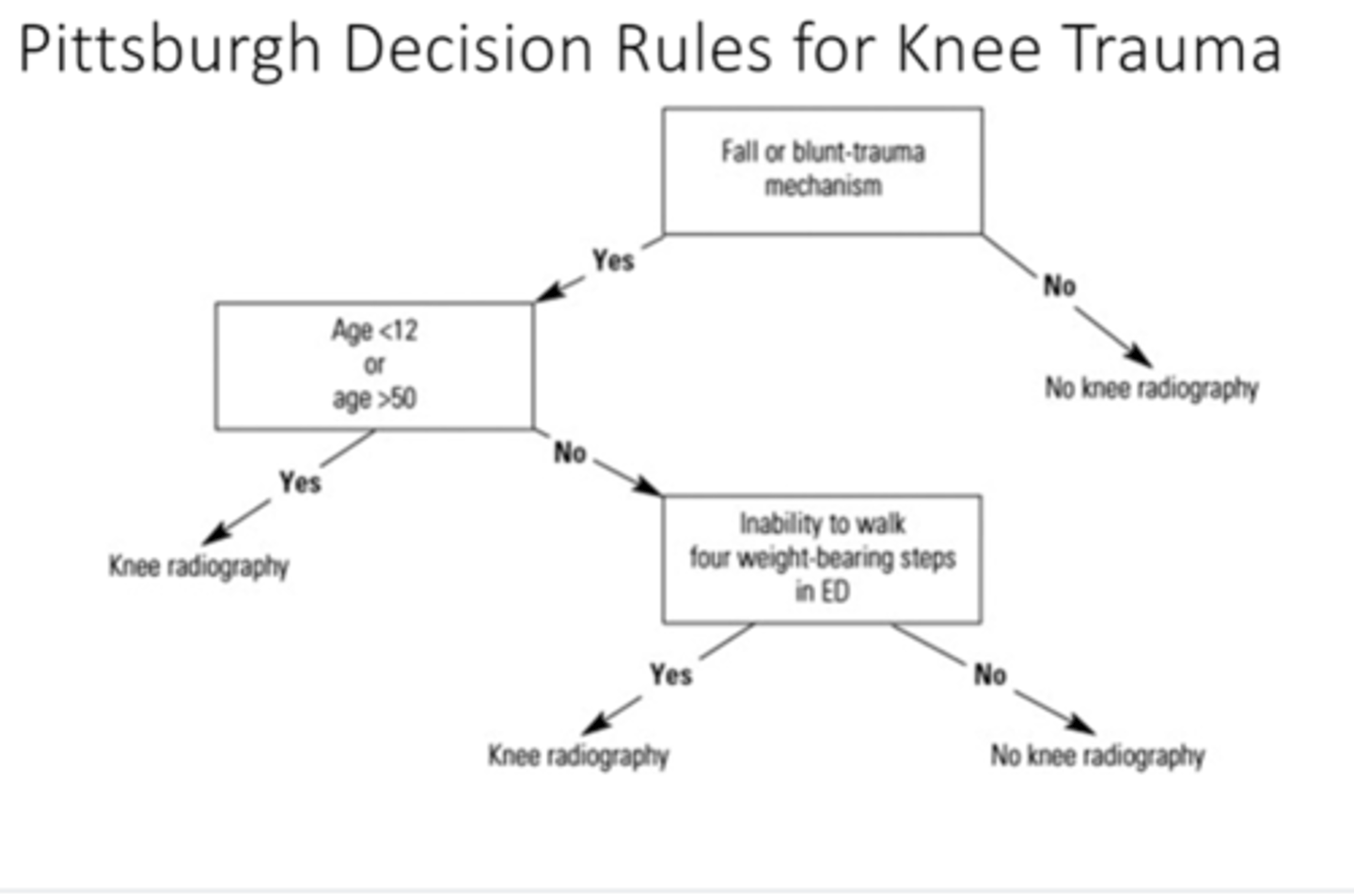
what is the pittsburgh decision for knee trauma
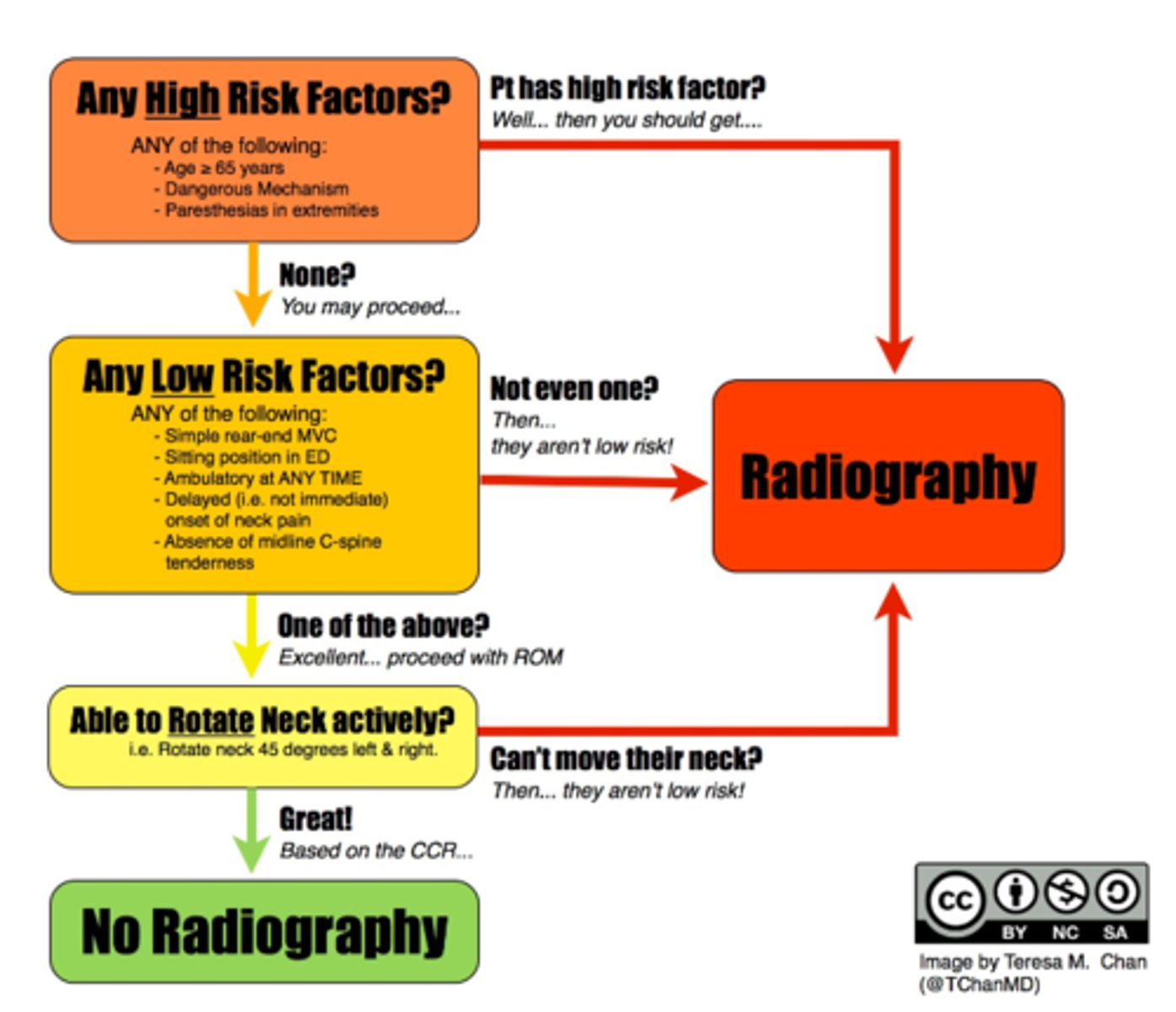
what is the Canadian c/s rules
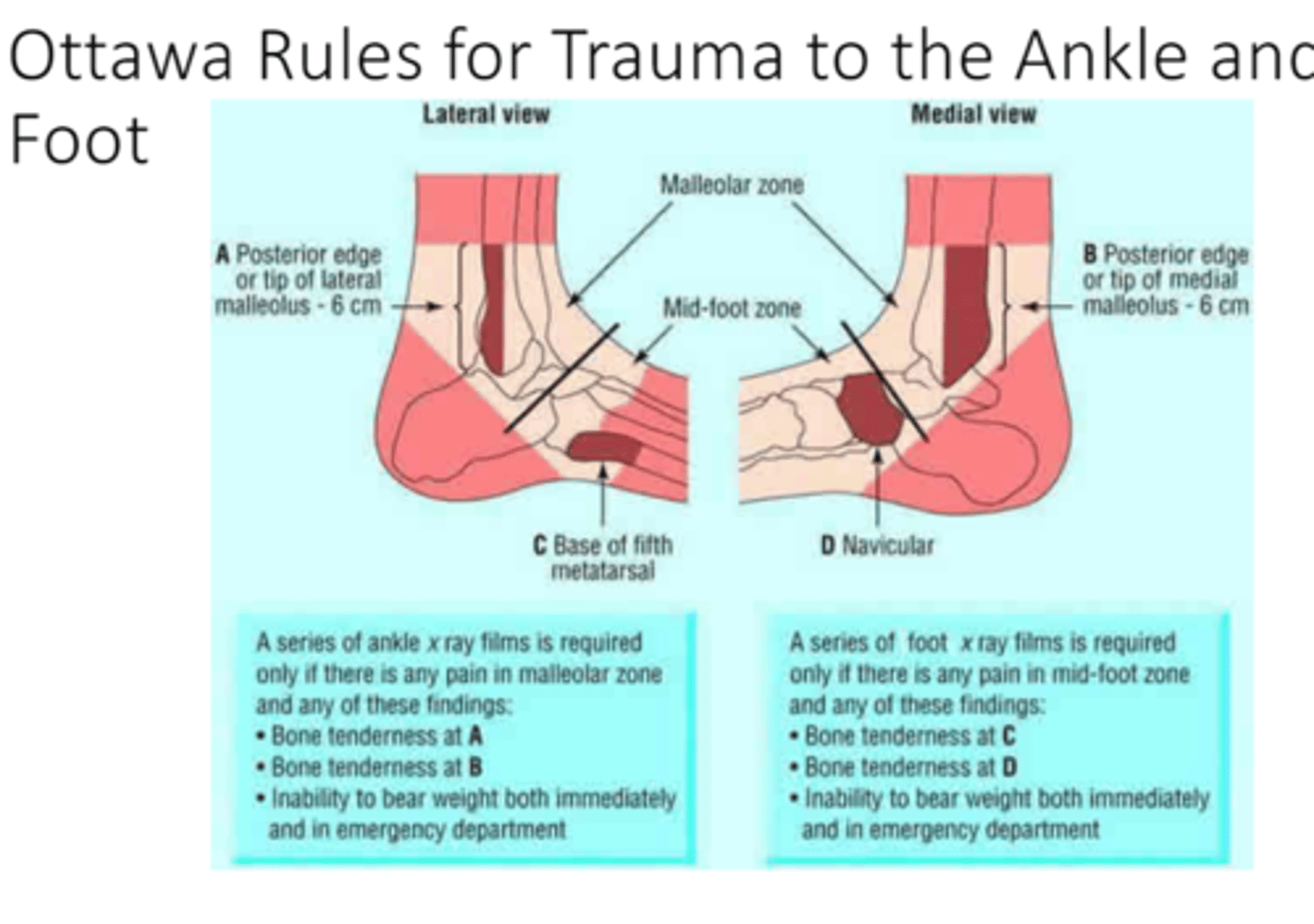
What are the Ottawa ankle rules?
what are the ottawa knee rules

Why are radiographic films usually the first imaging technique ordered?
A. It is the quickest
B. It is the cheapest
C. It is easy to read the films
D. They are the most accurate
B. It is the cheapest
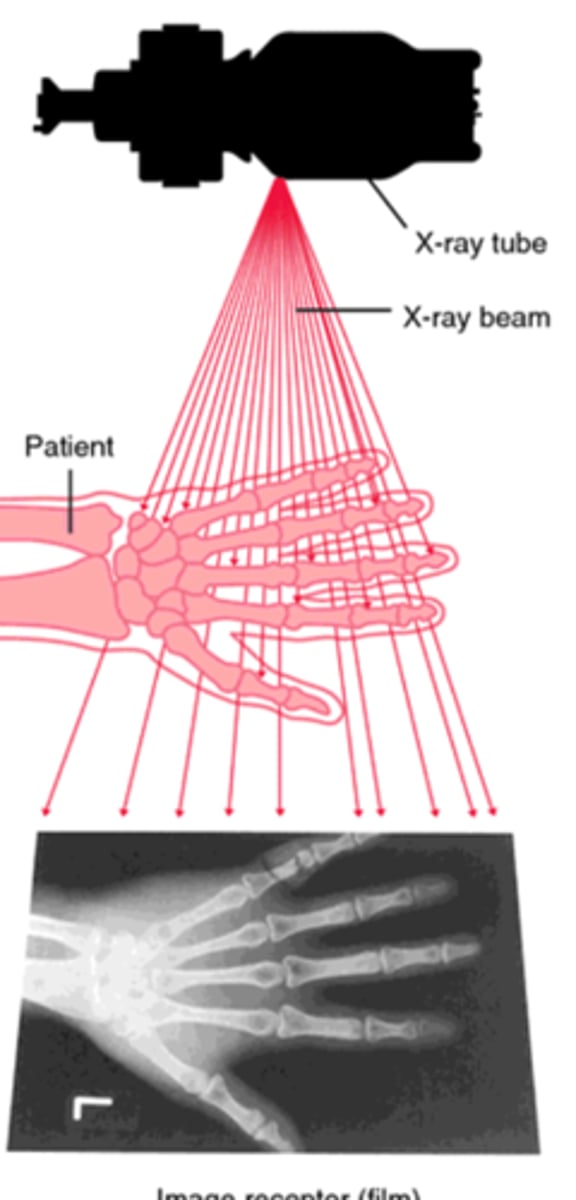
what are the three necessary things for radiograph
•X-‐ray beam
•The patient
•Image receptor
what is an X-ray
Form of ionizing electromagnetic radiation
•Ionizing-The ability of an atom or molecule to gain or lose and electron
Electromagnetic - Interaction of electronically charged particles
Radiation - Energy that is transferred through space or matter
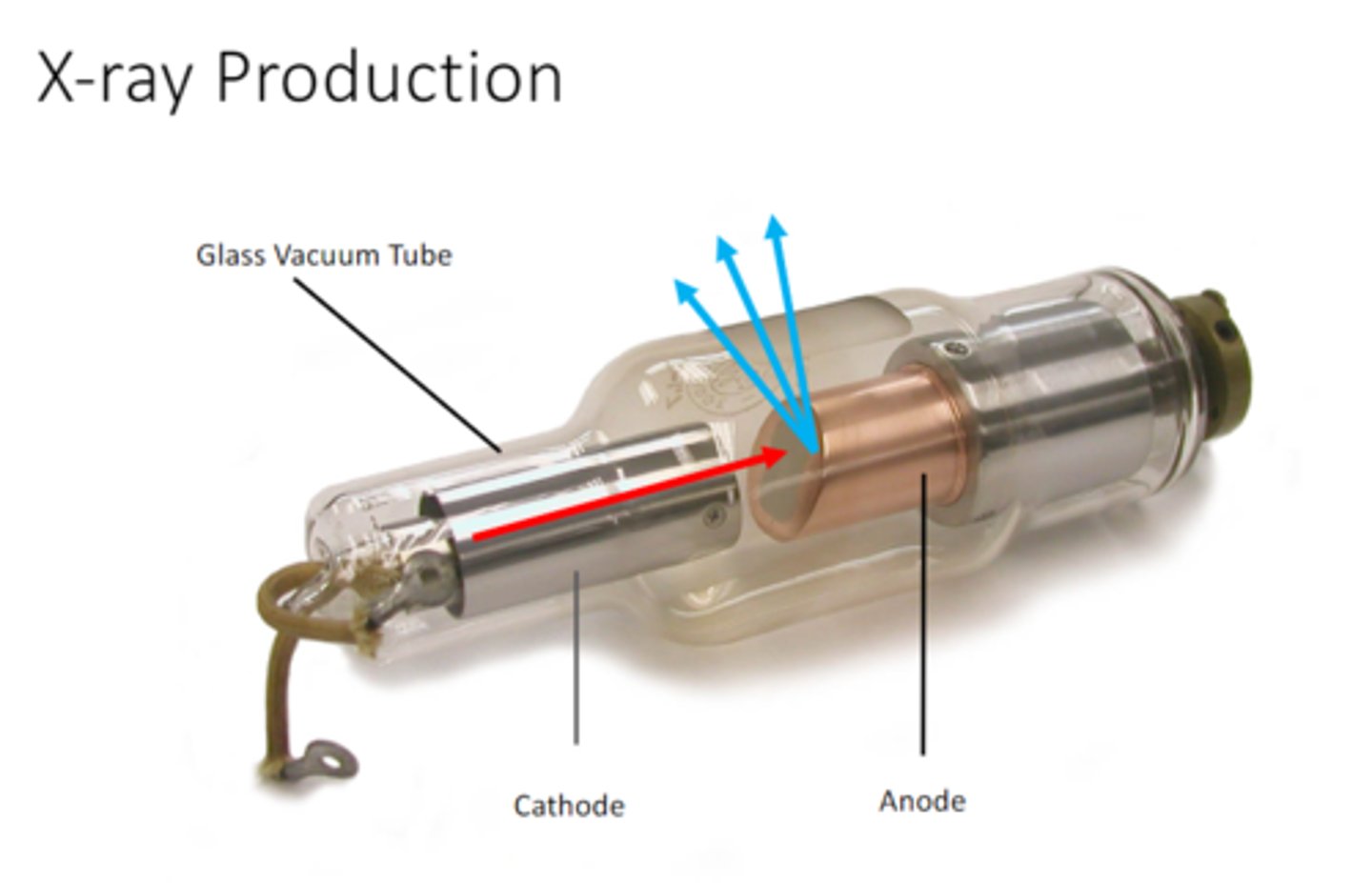
what is required in step one of X-ray production
-electrons
-something to move e quickly
-something to stop them
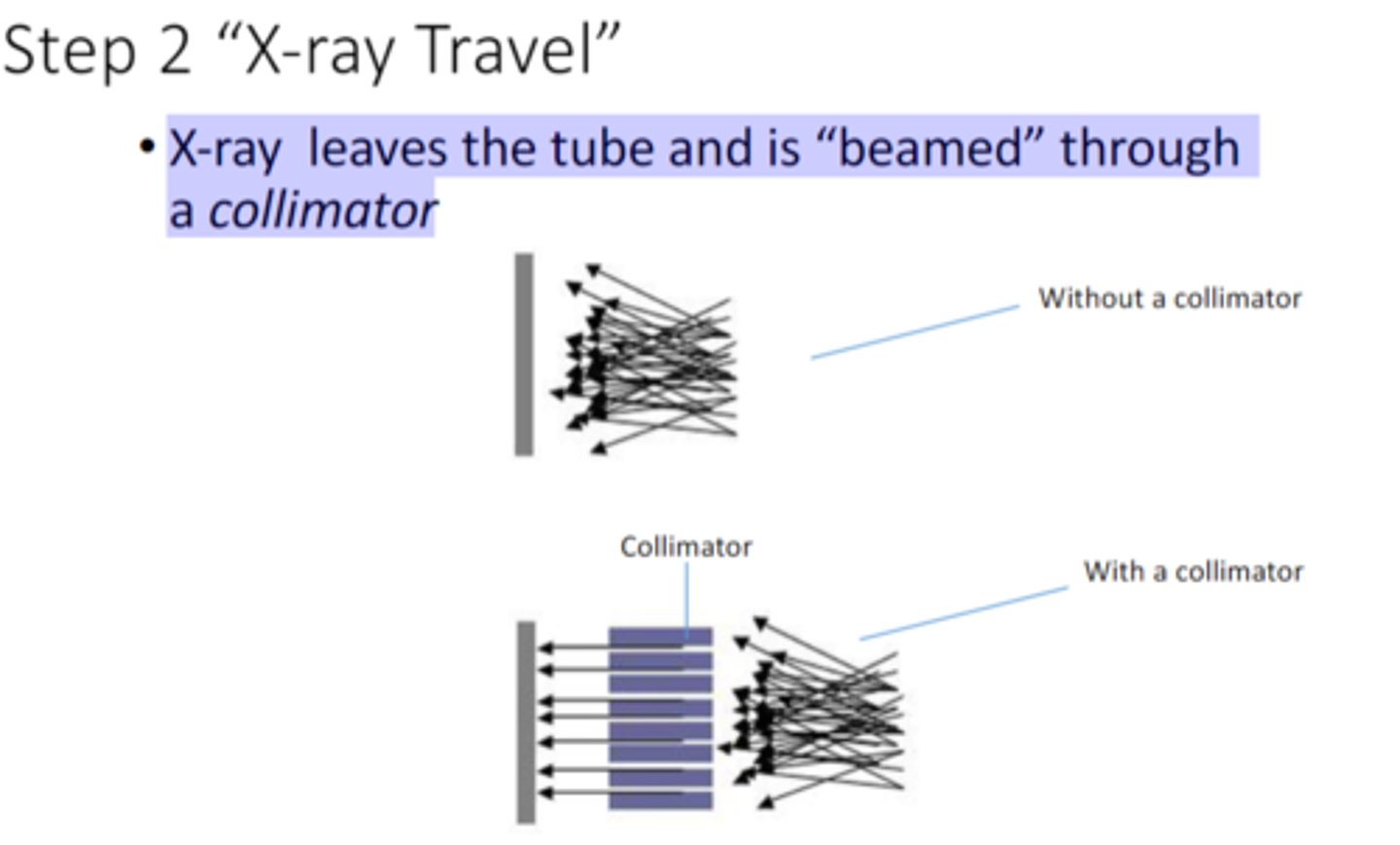
what is step 2 of X-ray travel
X-‐ray leaves the tube and is "beamed" through a collimator
what does this mean
"The beam passes through the patient and is attenuated"
Attenuation is the reduction in the number of photons in the beam due do energy loss
(depends on radiodensity)
less density = less attenuation (directly proportional)
what is remnant radiation
Radiation coming out of patient, aka 'exit radiation'
what effects the radiodensity of the tissue
1. What is the tissue made of
•atomic number (number of electrons in the tissue)
•volume density
2. How thick is the tissue
would a thicker object have a higher or lower radiodensity
higher
what color would a high radiodense object appear
what about low?
high: white
low: black
what would air look like on an x ray?
black
what would metal look like on an x ray
white
what does it mean if something is radiodense?
very little x-‐ray reaches the film, more white. Usually seen in heavy metals not human tissue.
what does it mean if something is radiolucent
most of the x-‐ray reaches the film, mostly black, air in the lungs
what is contract media and what can it be used for ?
Contrast studies of viscera
Barium Sulfate
What are the 4 image quality factors?
radiographic density, radiographic contrast, recorded detail, distortion
what are the 3 factors you can adjust to affect the radiographic density
if you want the image to appear as dark as possible what are the parameters for radiographic density
what about as white as possible?
current, exposure time, and distance from the beam
darkest: high current &exposure time and close to the beam
white: low current & exposure time and far from the beam

would this image be white or dark
low current with low exposure and close to the beam
white but not as white if the beam was far away
if the an area of an x-ray is black
is it over or under exposed
overexposed

if the an area of an x-ray is white
is it over or under exposed
underexposed

true or false
radiographic density is the amount of black on the film
true

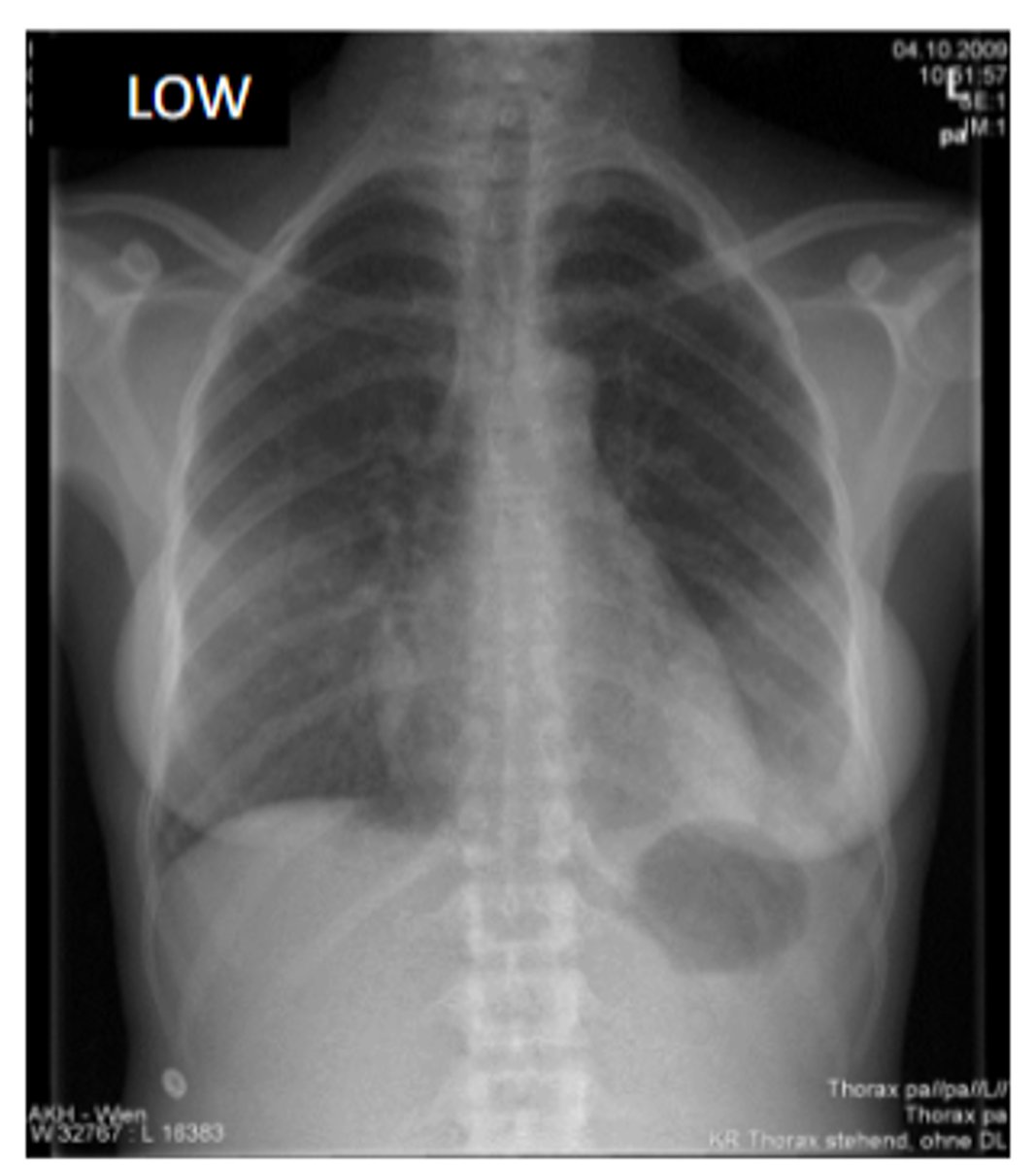
in regards to radiographic contrast:
what kind of contrast would you use to view lungs?
low contrast
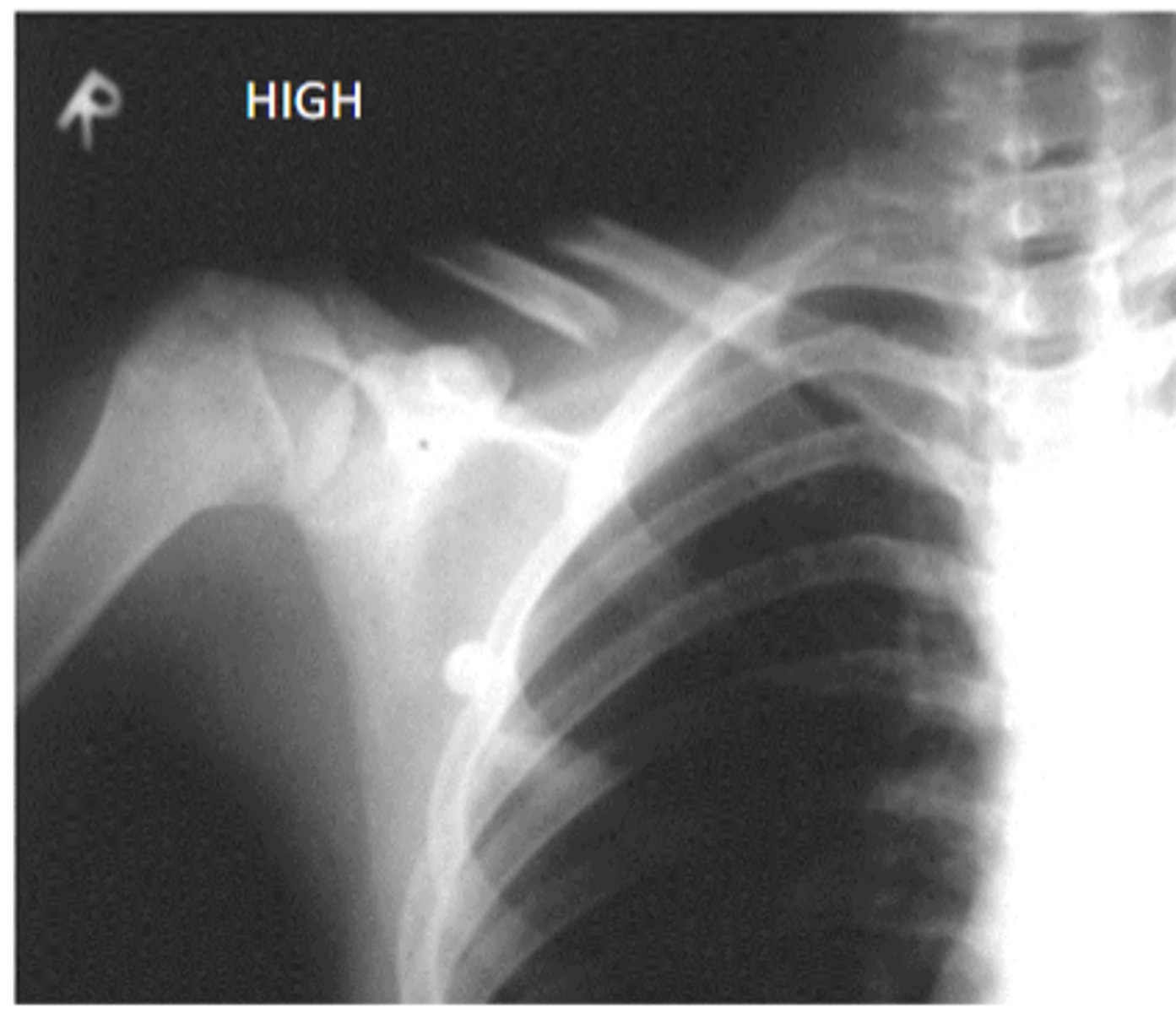
in regards to radiographic contrast:
what kind of contrast would you use to view bone
high contrast
what two factors effect the recorded detail of the x ray image
(sharpness of the image)
-movement
-distance from the beam
what is the most common view for lumbar spine
Lumbar spine AP view most common
(because the spine is closest to the image receptor)
radiographic distortion: if an object is closer to the X-ray tube
what is the result
more distortion and magnification
(flashlight example)
(the image can look bigger if its closer to the beam and the farther away it is to the image receptor, the image will be closer to the actual size)
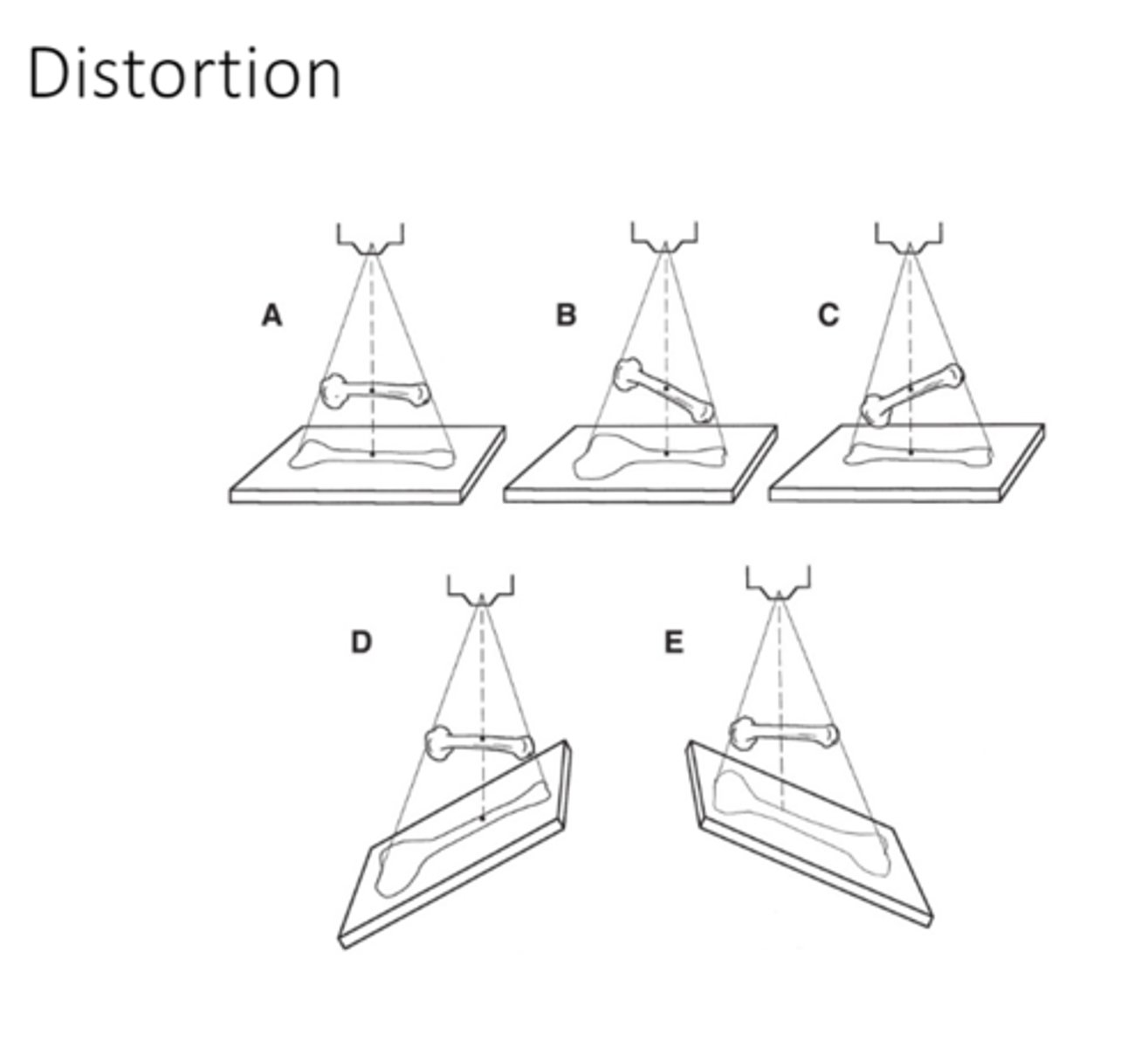
if an object is father from the X-ray tube and very close to the image receptor what is the result
the image will be LESS distorted and magnified
and the image will appear sharper because it is close to the image receptor
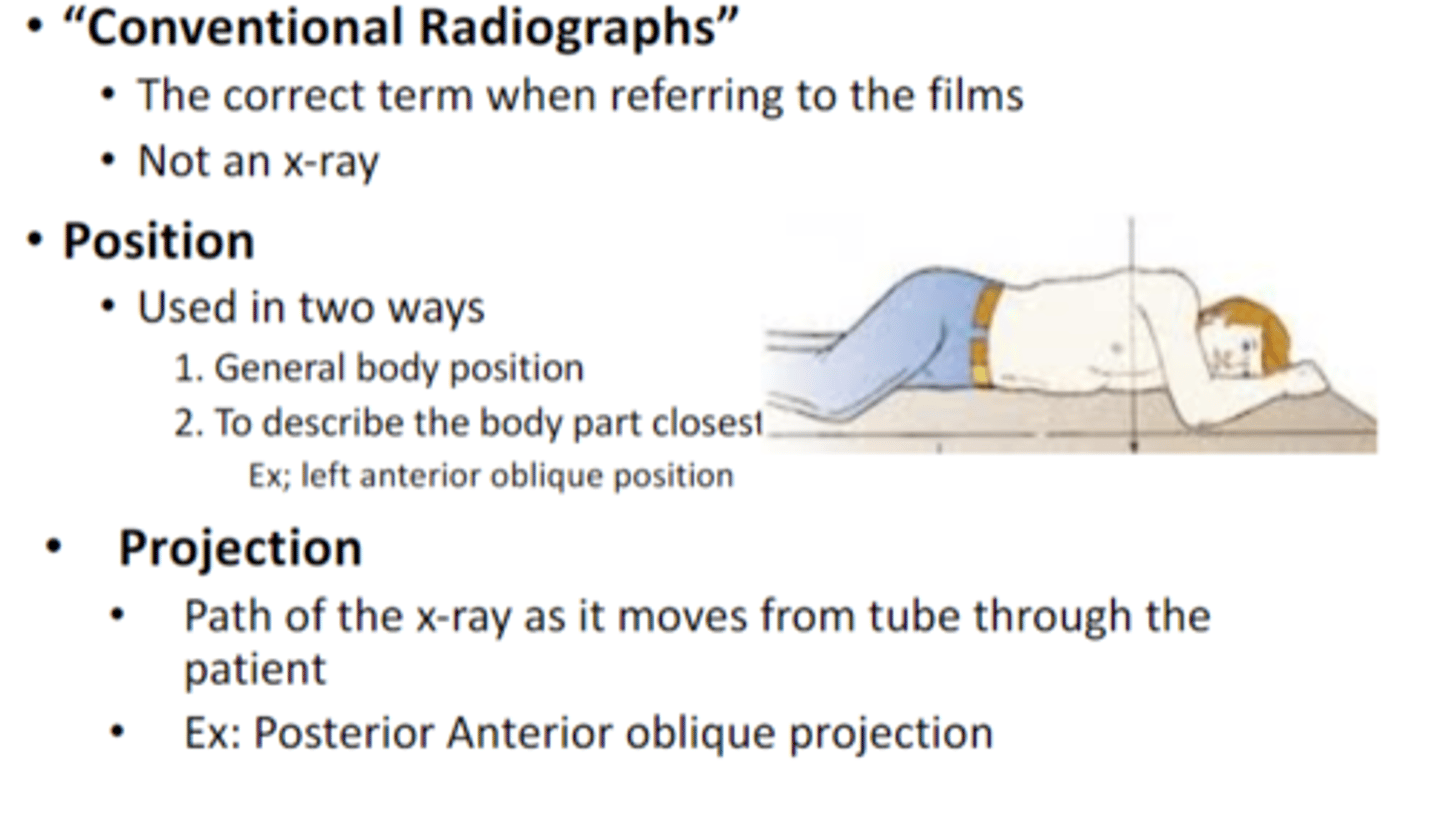
is a conventional radiograph the same as an X ray
no

what are the two ways position is described
1. General body position
2. To describe the body part closest to the image receptor
Ex; left anterior oblique position
how is projection described
Path of the x-‐ray as it moves from tube through the patient
•Ex: Posterior Anterior oblique projection
what is the angle of projection
The angle that the x-‐ray enters the body will influence the radiodensity of the object.
(three images of cheese)
when viewing x-ray film what will hands and feet look like?
the toes and fingers will face upward
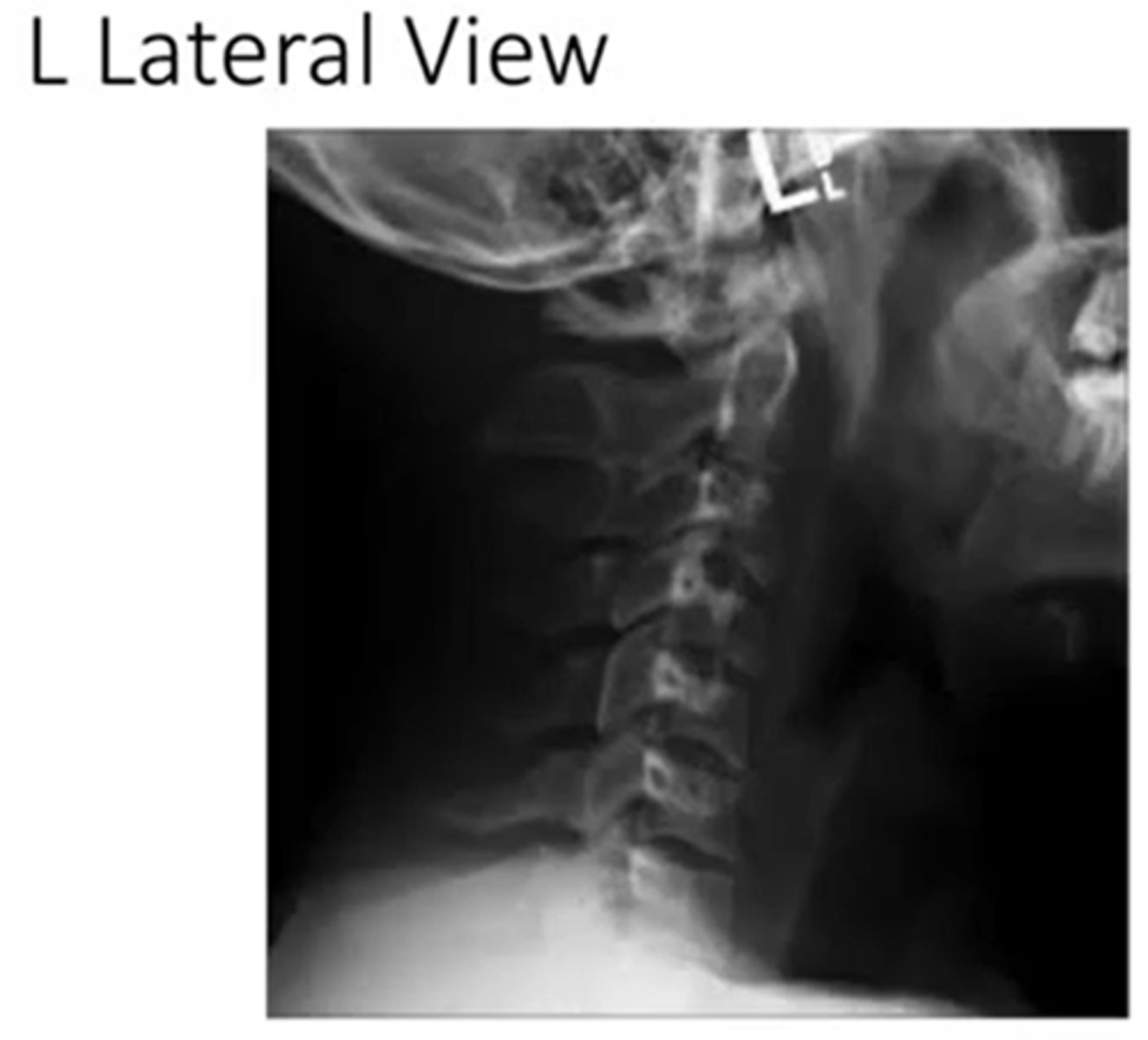
when viewing a lateral view x-ray, what is the perspective
perspective of the x-ray beam
(in this picture its a left view, if it was a right the person would be facing the opposite direction)
what does a right anterior to posterior view of the ankle look like
this is a right ankle facing you in anatomical position
what are the ABCS of radiologic evaluation
Alignment
Bony Density
Cartilage spaces
Soft tissues

using the ABCs of radiologic evals what does the A consist of
correct number of bones
the size of bones
bone abnormalities
developmental deformities (growth plate not closed)
contour of bones
cortical bone outline
bone spurs
what may you see at muscle attachments
or where two bones rub
example Achilles tendon
bone spurs
in regards to bone density is sclerotic bone abnormal when looking at X-ray, whats an example
no, it can be both normal or abnormal depending on the area
normal is bone healing
abnormal is OA
what does a trabeculae abnormality look like
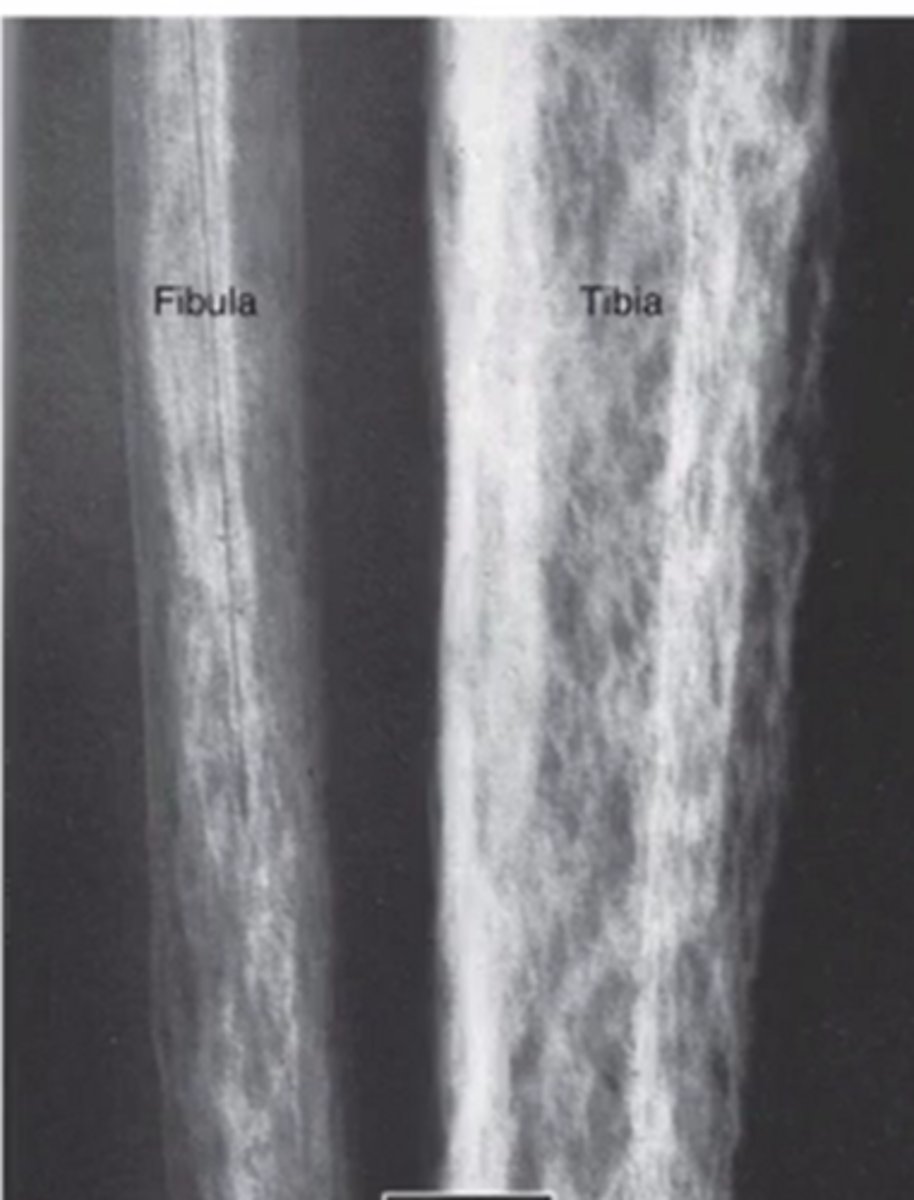
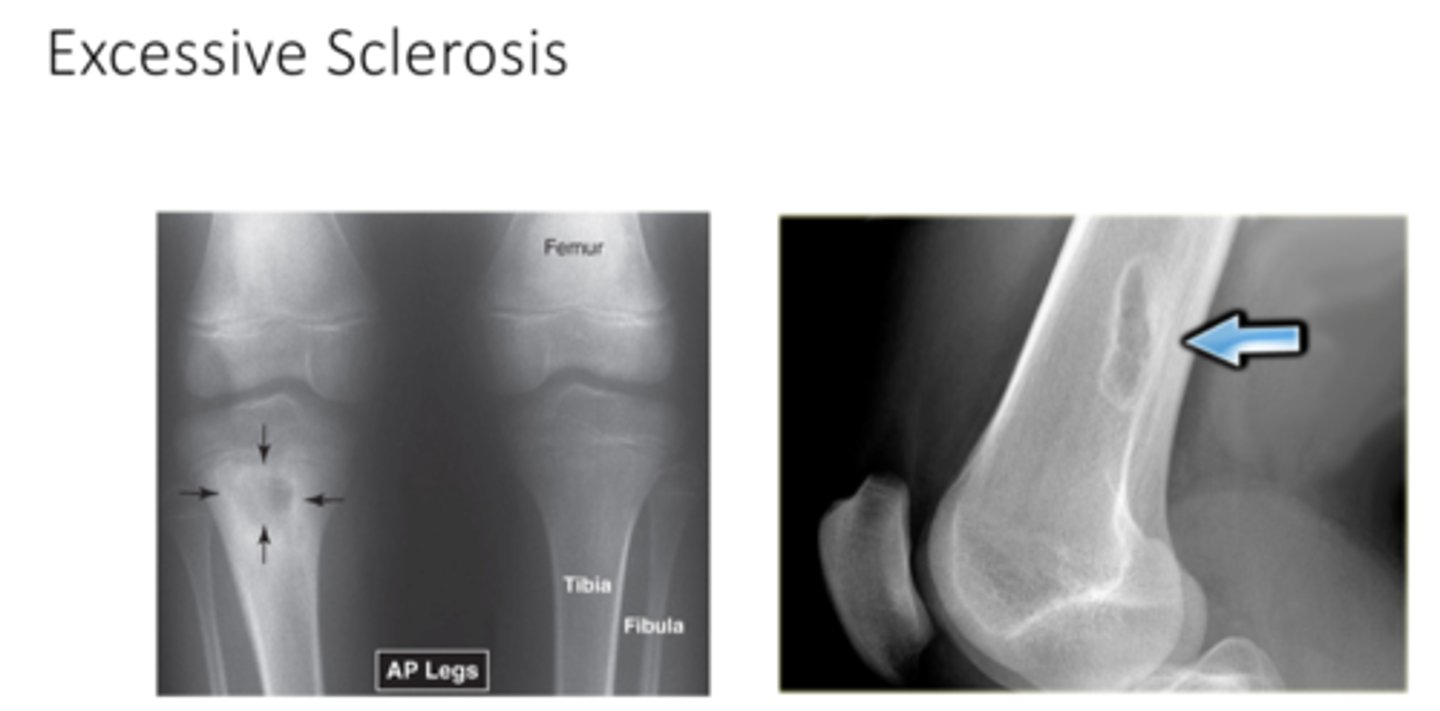
what is sclerosis as it relates to bone
increase in bone density
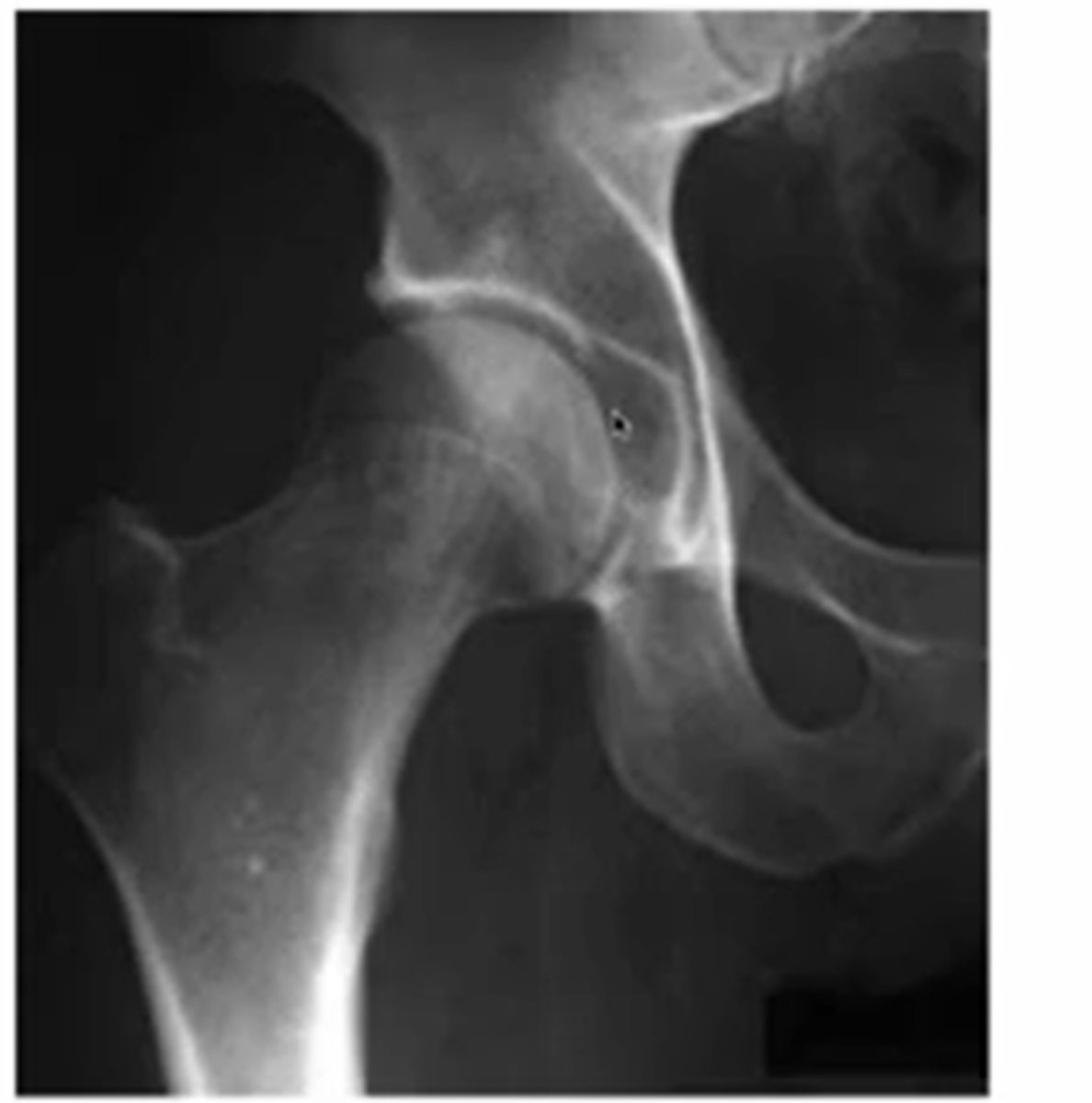
what does normal sclerosis at the hip look like and why
the whiter parts of the acetabulum
(because of WB)
what does knee OA look like
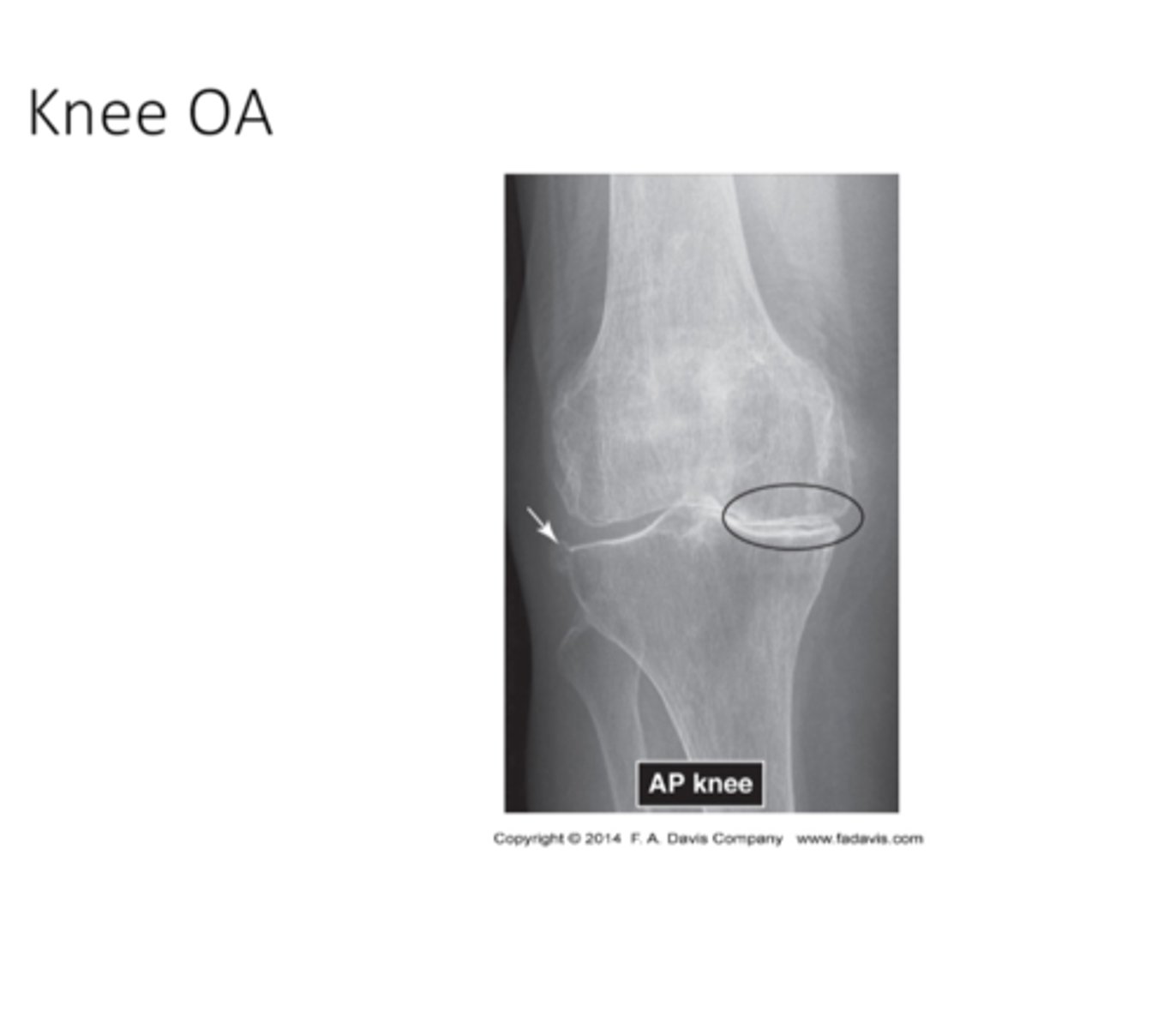
what does Excessive Sclerosis look like
when looking at the cartilage spaces what are you looking for
joint space width
subchondral bone
-erosions
epiphyseal plates
-disruption
-sclerotic bone
-the size of the plate is related to age
what does gout look like
increased radiolucency
will got be more radiodense or radiolucent
Subchondral bone erosions
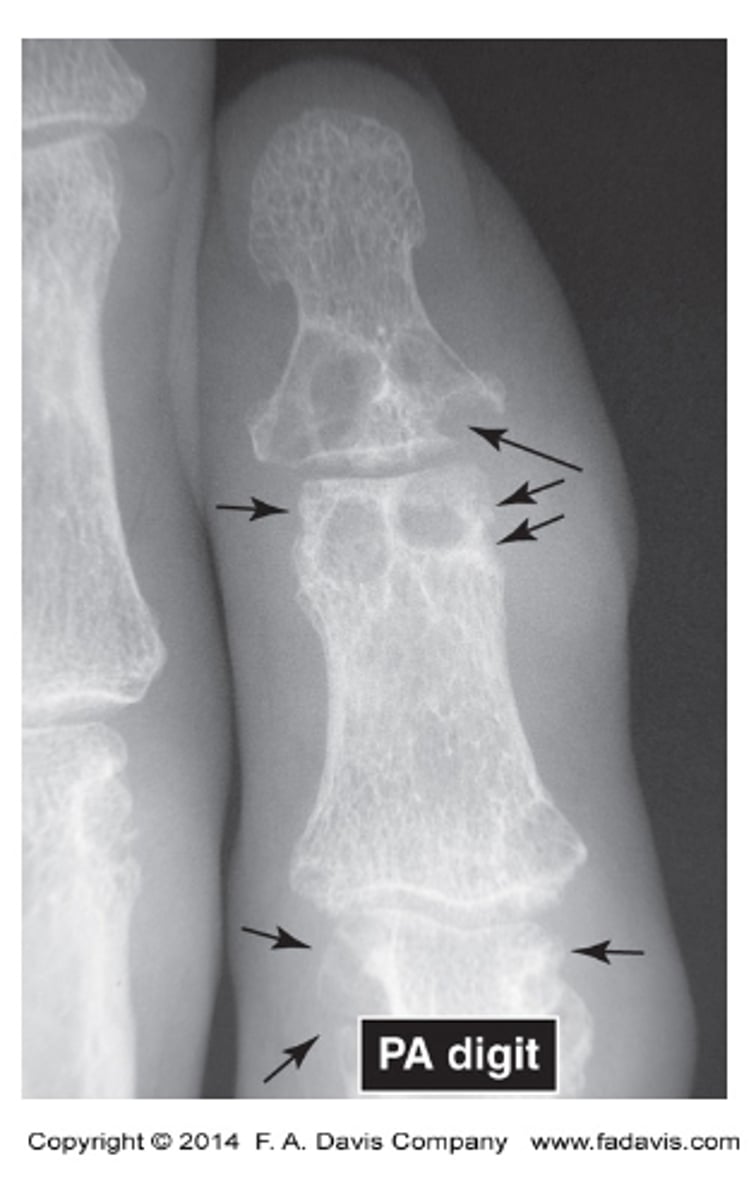
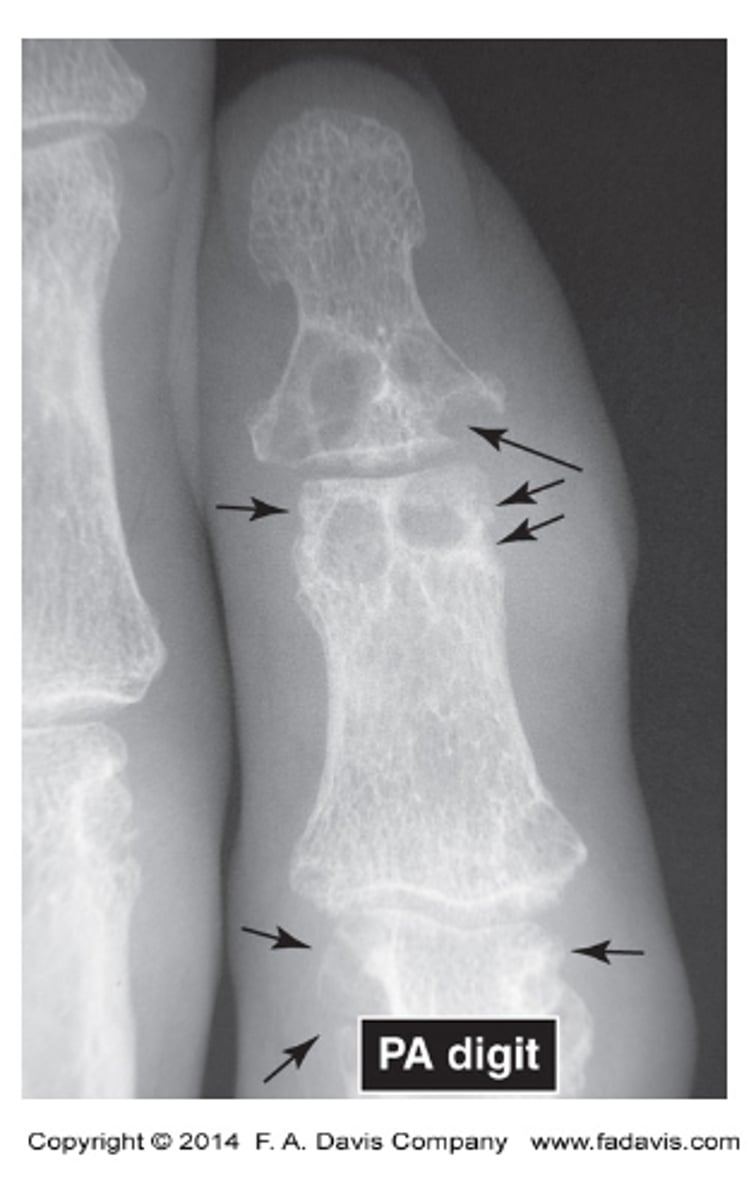
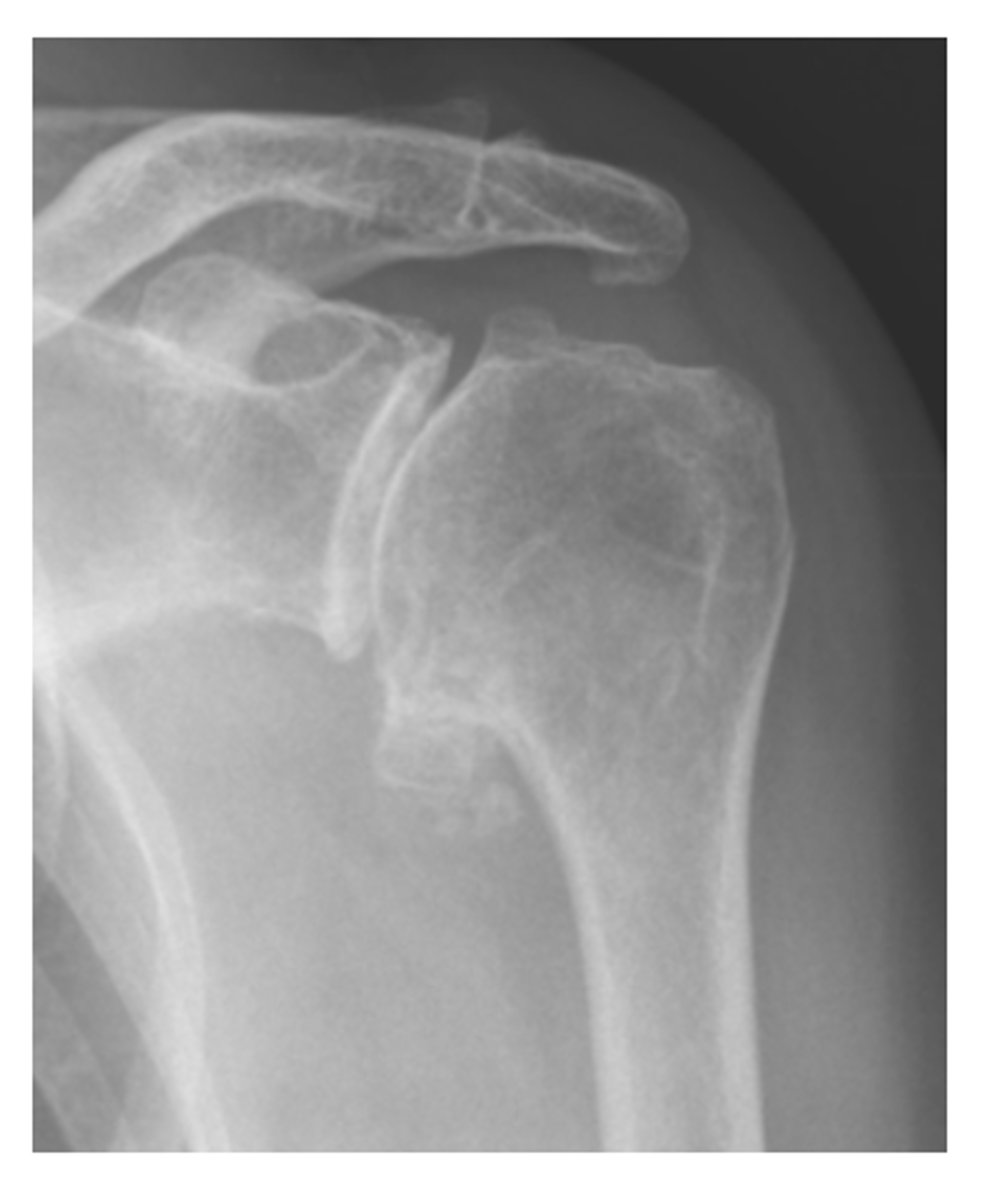
what does normal epiphyseal plates look like
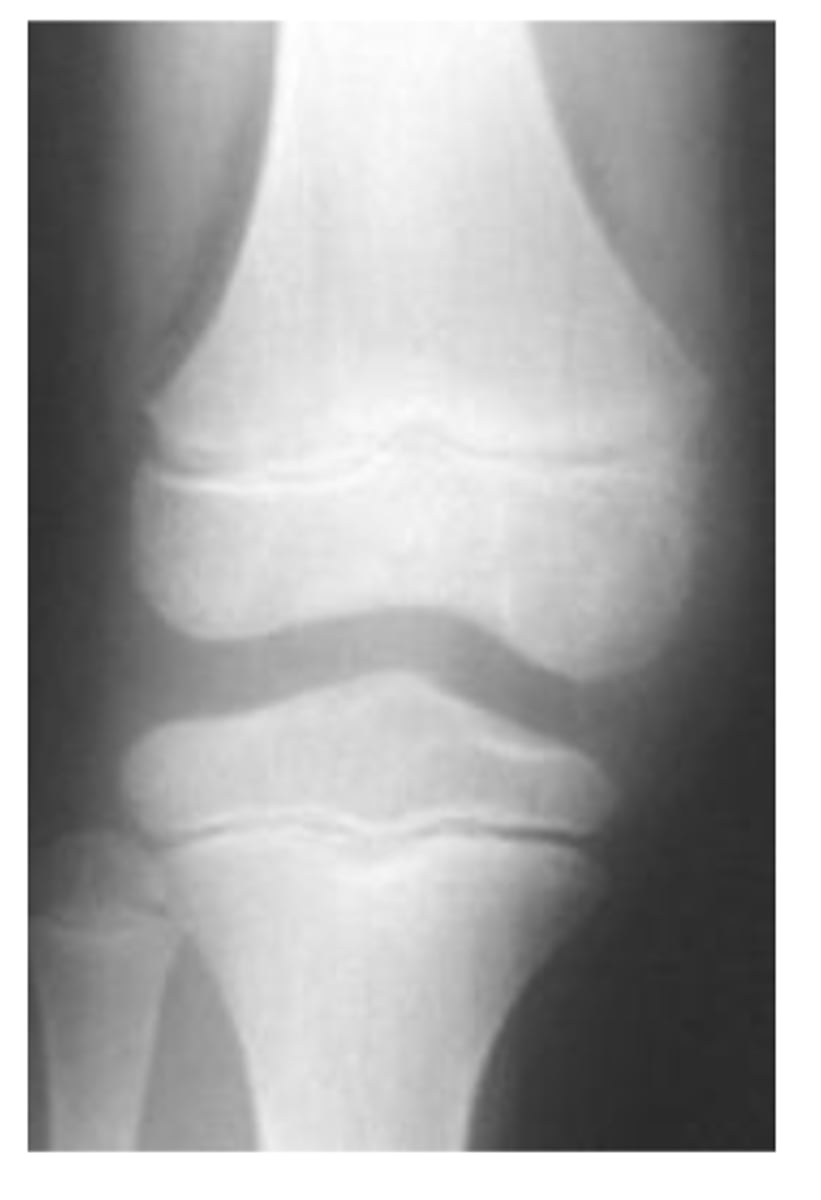
are there any abnormalities in this image
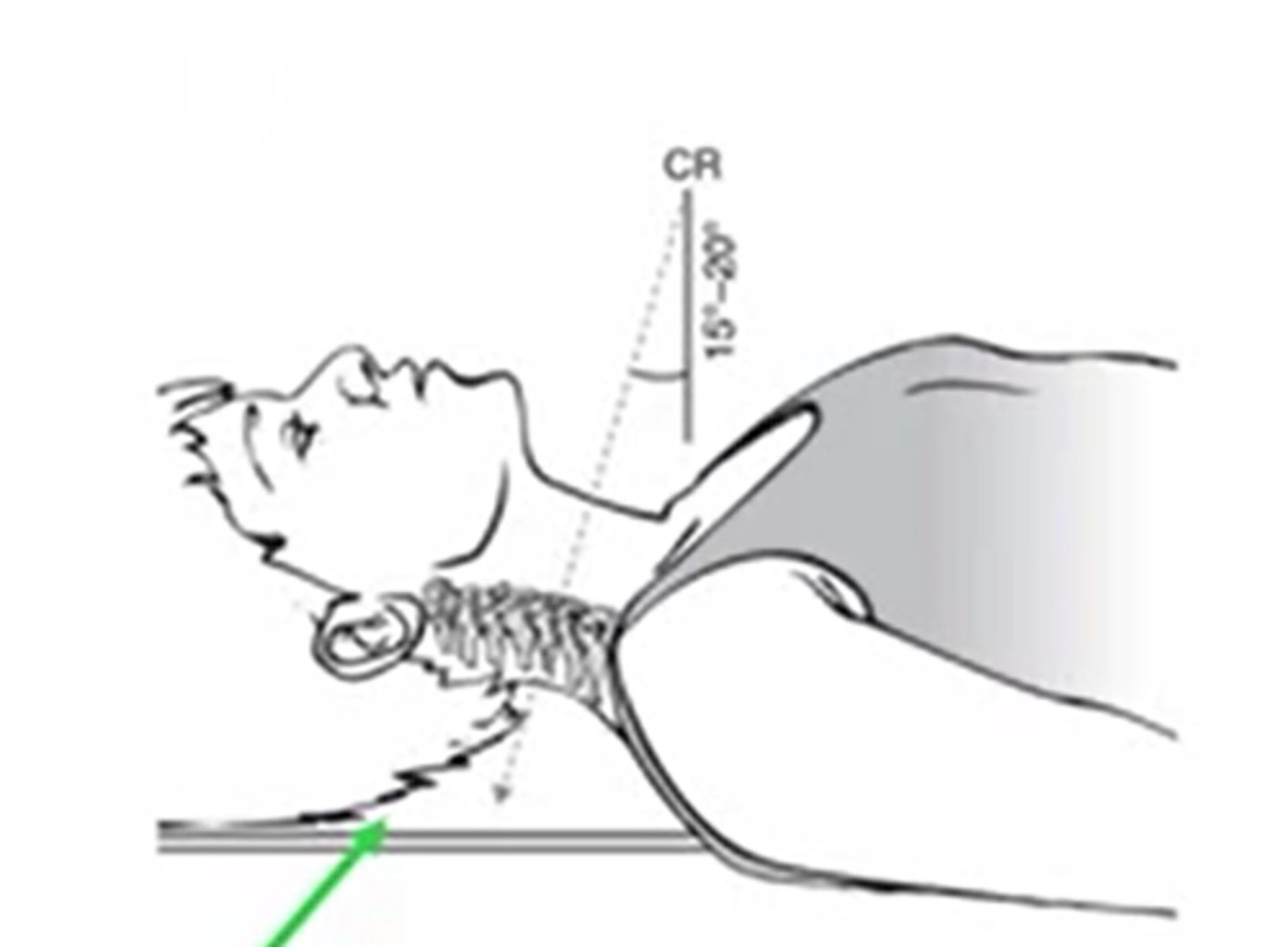
at what angle is the ap cs taken?
15-20 deg
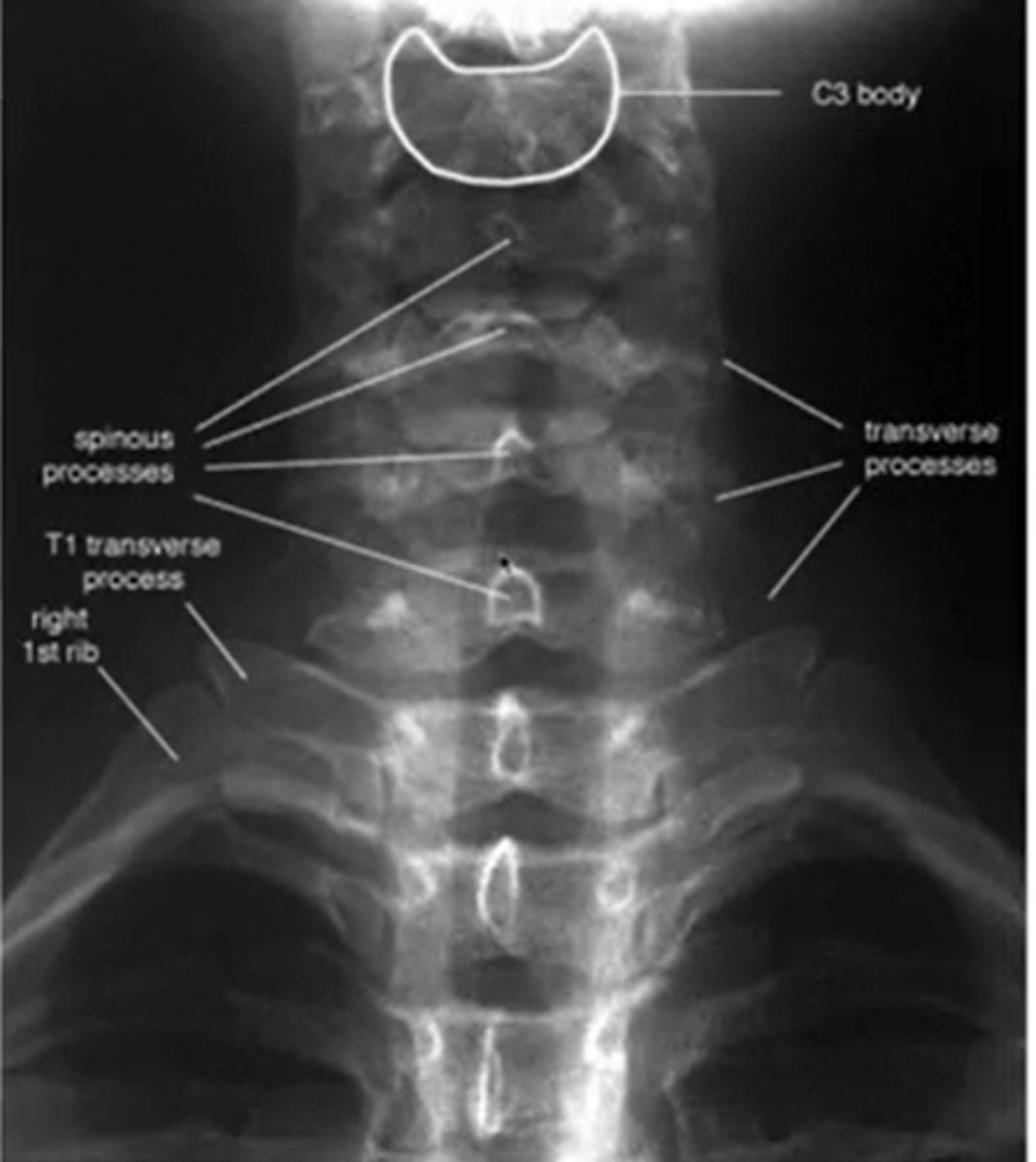
what does a normal AP cs look like
when looking at the c/s what is the better view to see the disc height
lateral
what view of the c/s can you see the pedicles?
AP
what are you looking for during AP view of CS

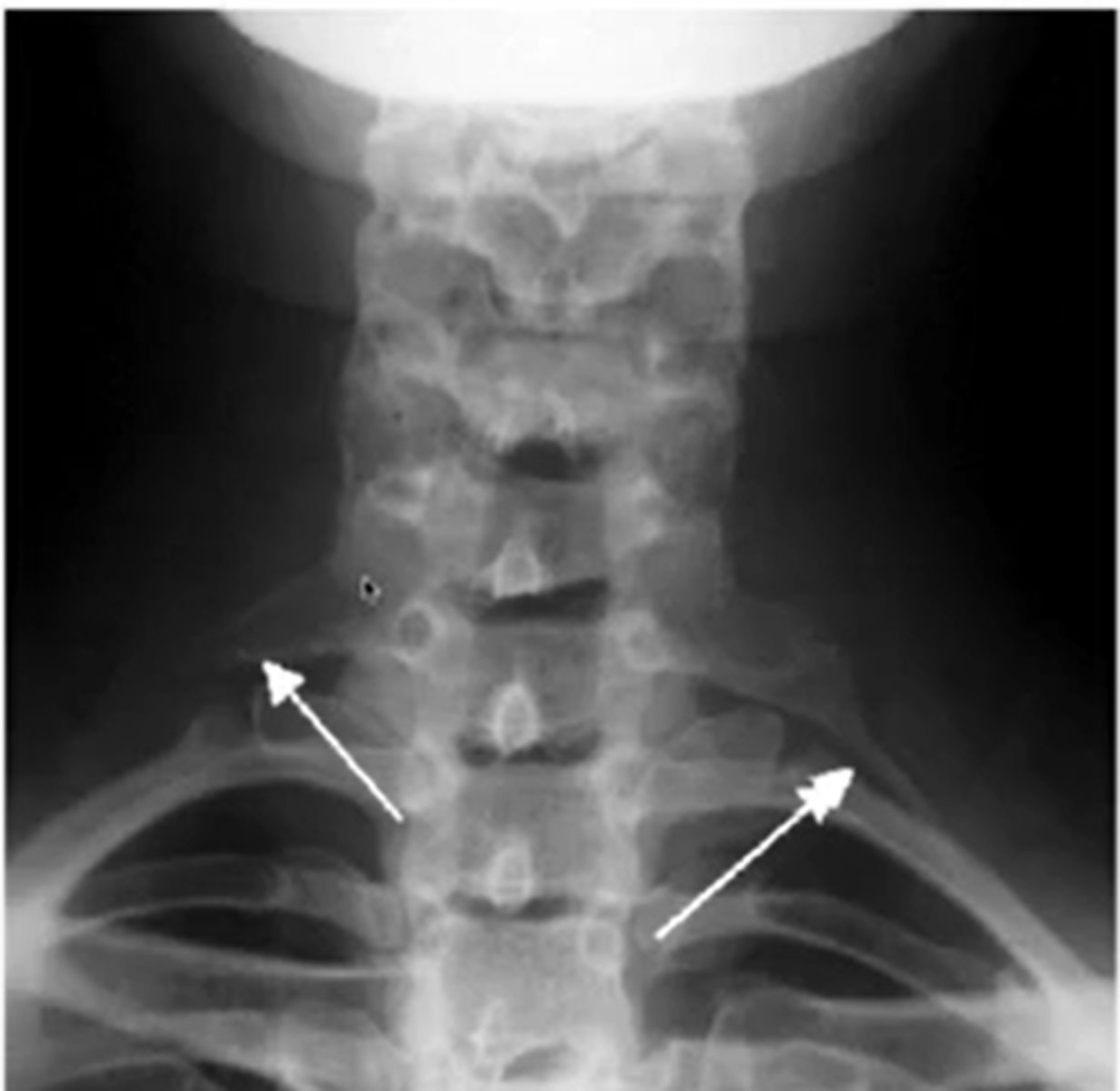
after a trumatic event to the C/S what image will you expect them to take
AP open mouth view
what does a normal AP x-ray of C1-2 look like
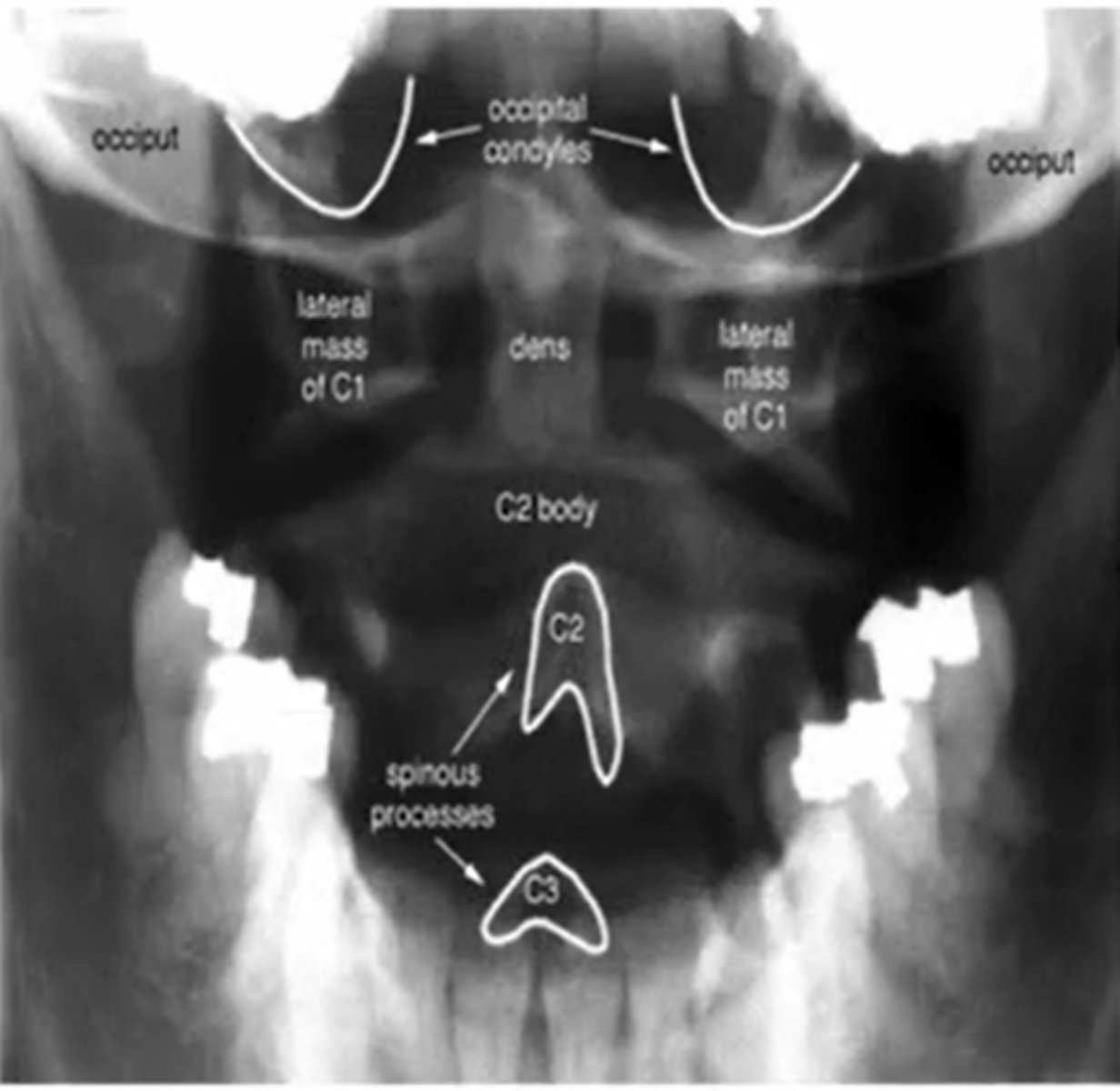
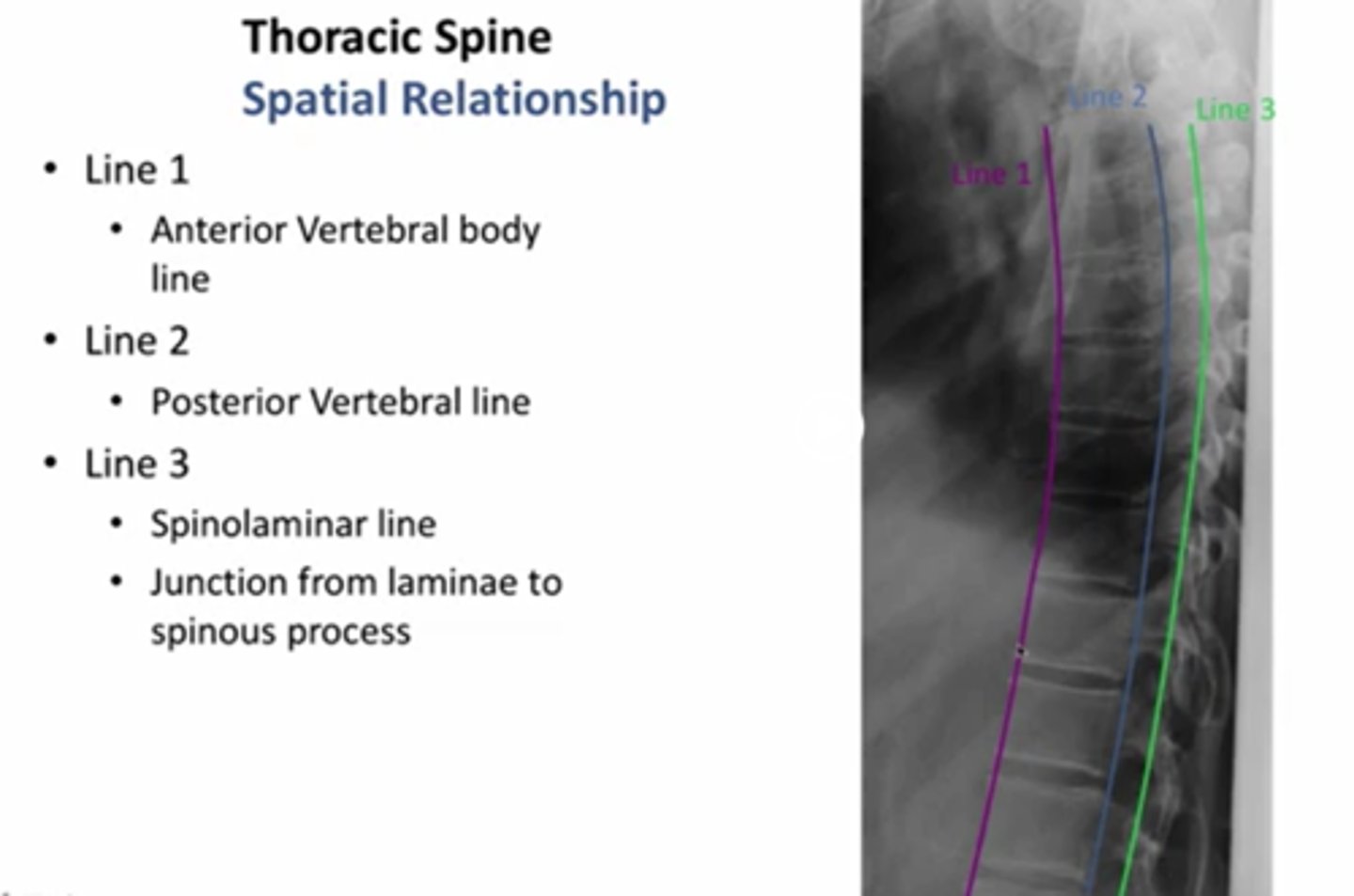
what does the spinolaminar line, anterior and posterior vertebral line look like
purple anterior
posterior: blue
spinolaminar line: green
between blue and green is the spinal cord
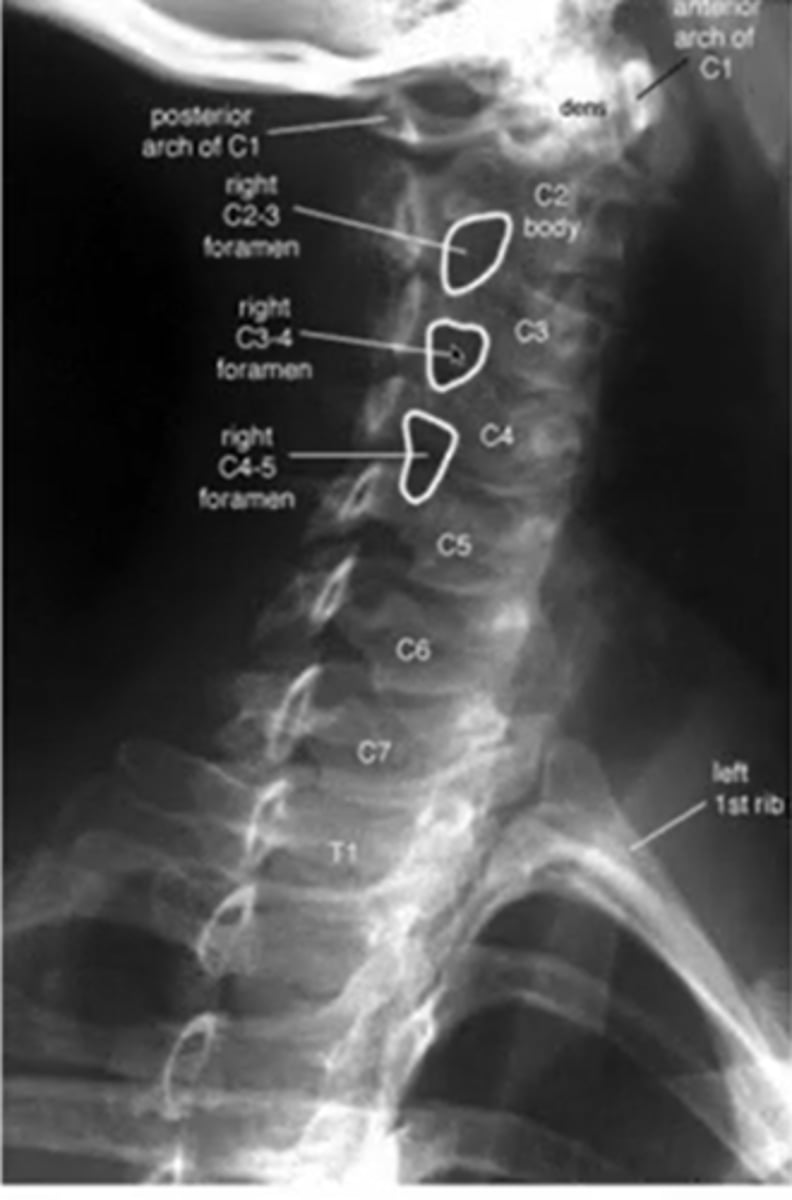
what does a left oblique cs image look like
(it says right but its really left)
when looking at the thoracic spine
what view should you choose to see
vertebral bodies
AP
when looking at the thoracic spine
what view should you choose to see
transverse process
AP
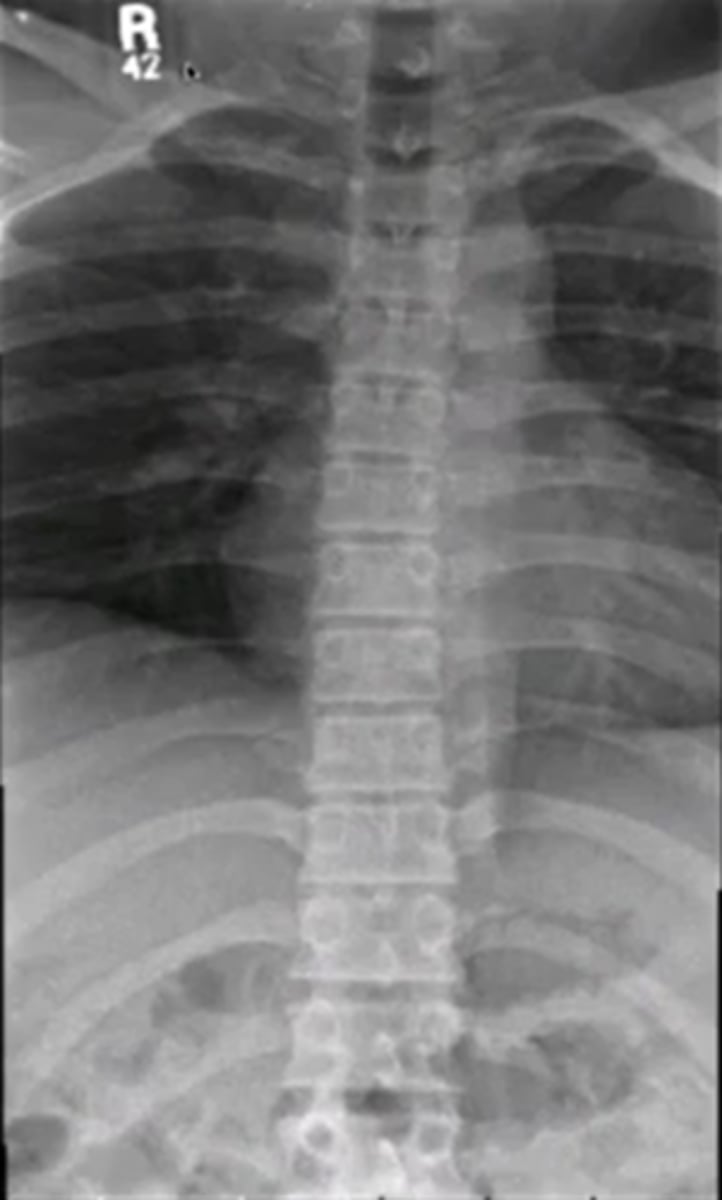
when looking at the thoracic spine
what view should you choose to see
spinous process
AP
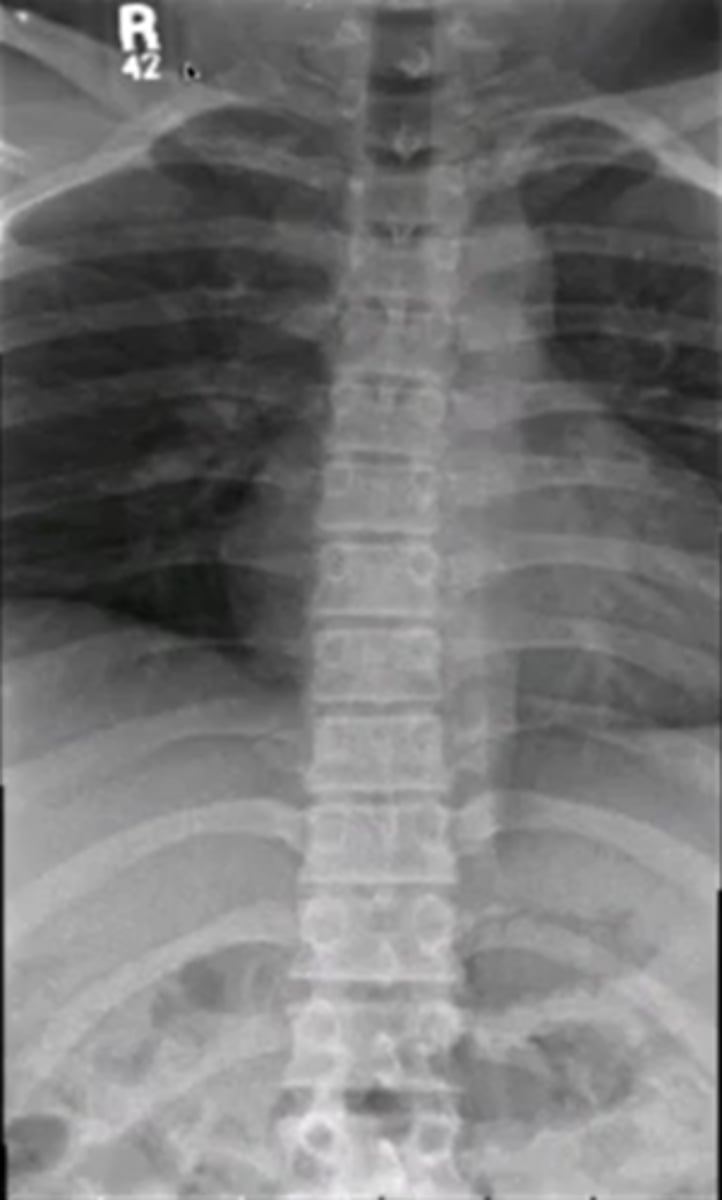
when looking at the thoracic spine
what view should you choose to see
pedicles
AP
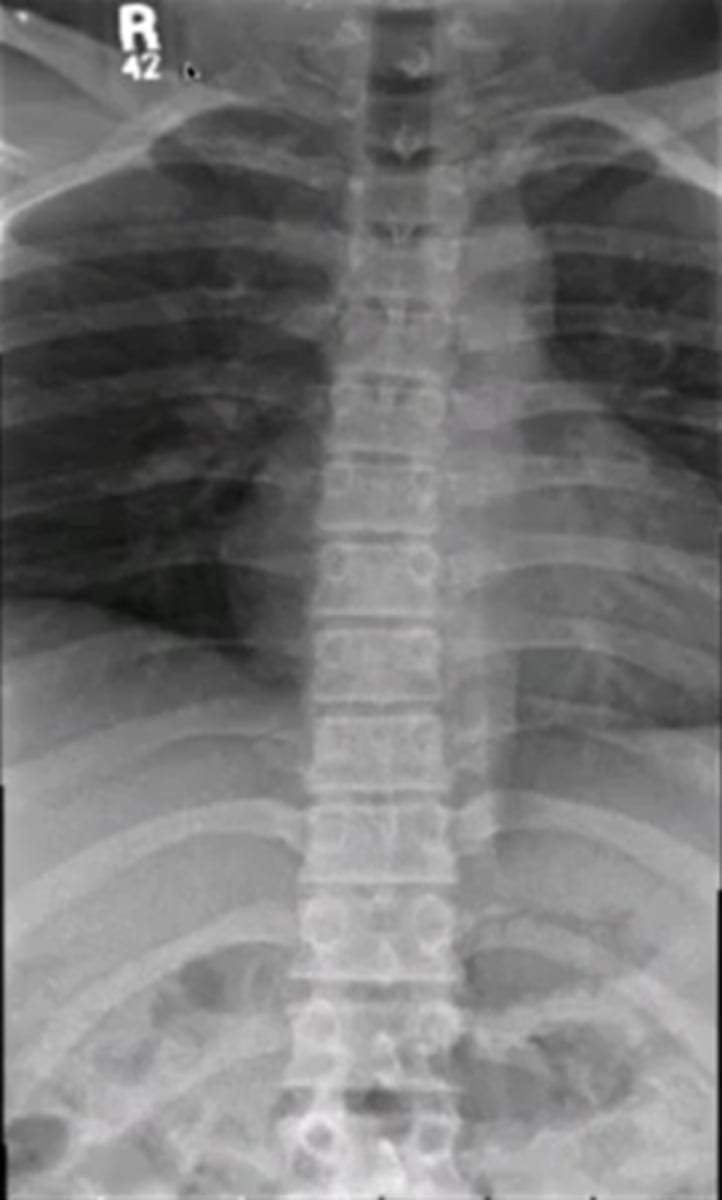
when looking at the thoracic spine
what view should you choose to see
vertebral bodies
lateral
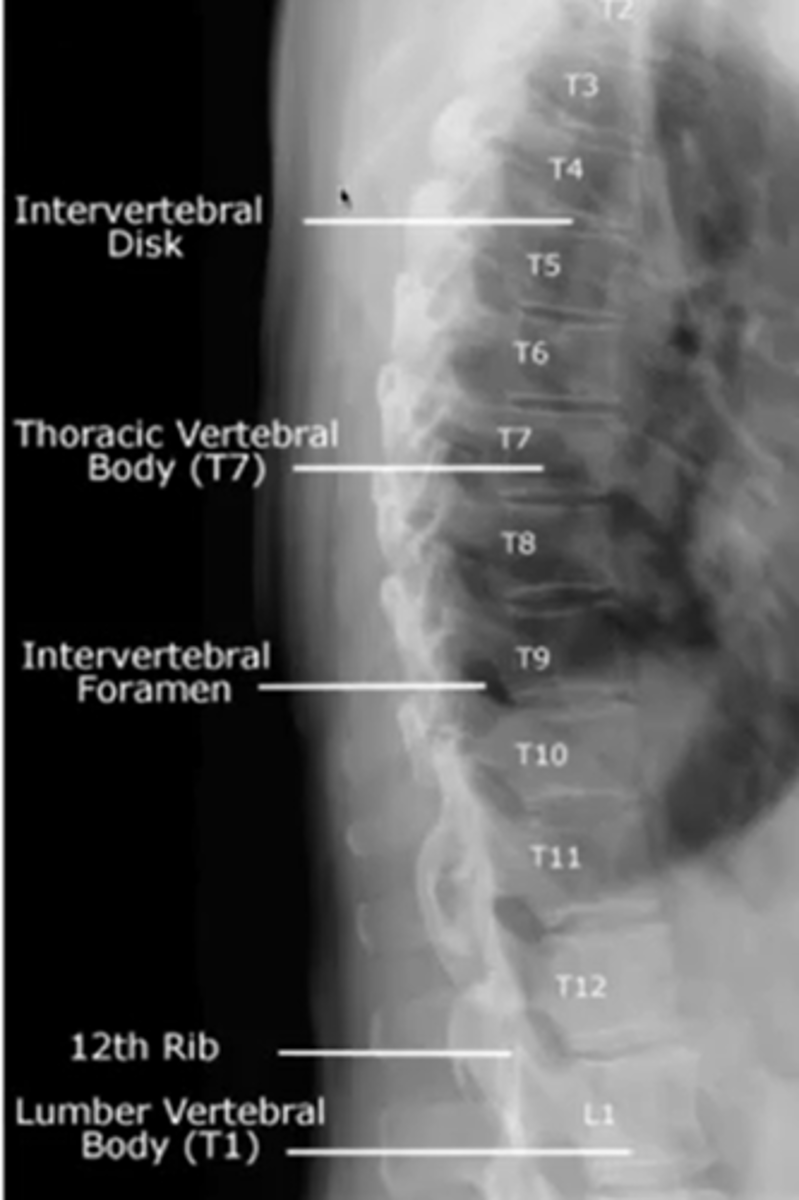
when looking at the thoracic spine
what view should you choose to see
intervertebral disc height
lateral
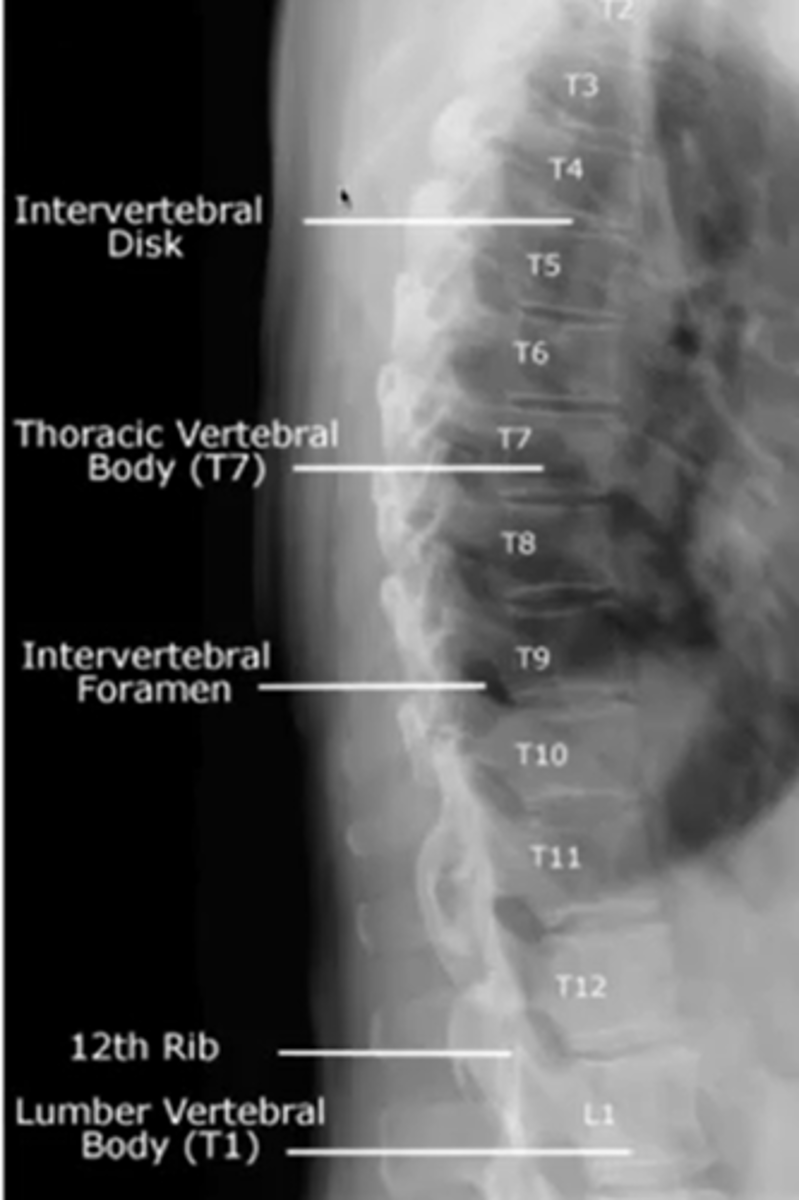
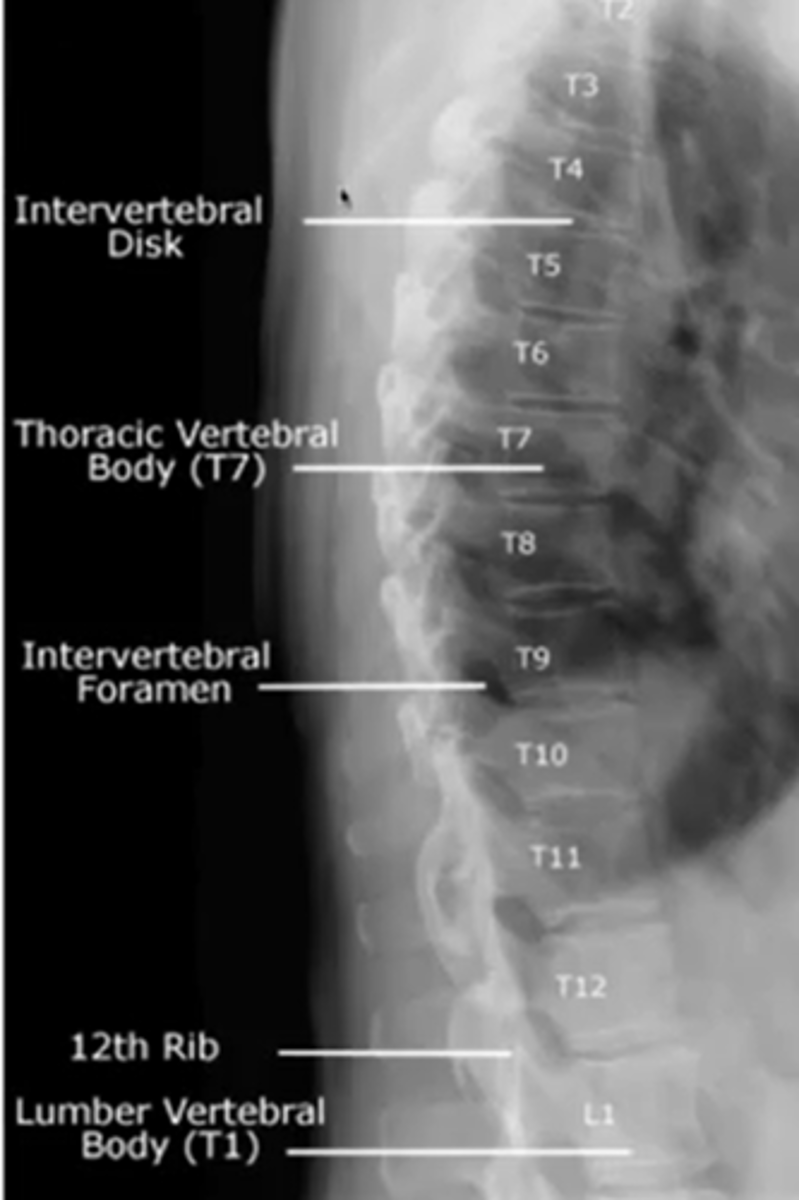
when looking at the thoracic spine
what view should you choose to see
intervertebral foramina
lateral
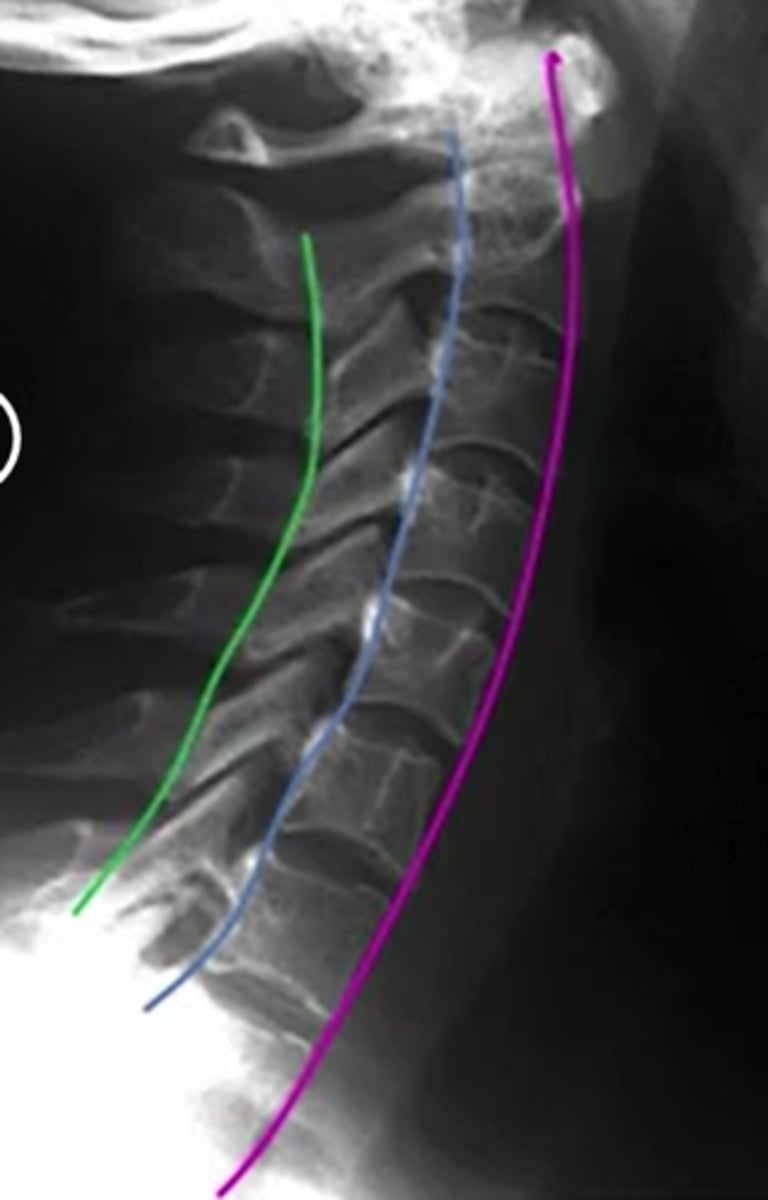
what are the three lines for the thoracic spine
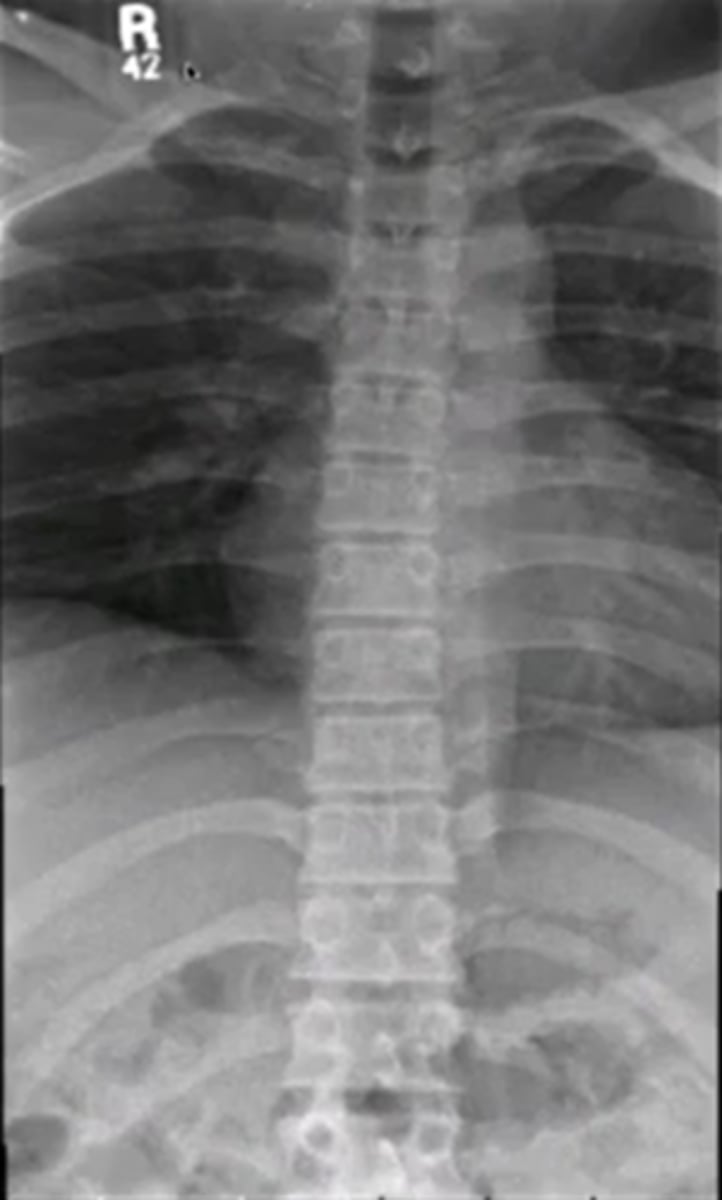
for a chest xray what kind of view will they take
PA
because you want the heart furthest away from the xray beam and closer to the IR
during a chest xray what kind of contrast should you use to view soft tissue
low
true or false you can use a chest xray to view lungs, vascular system and metastatic disease
true
what does a normal lumbar AP look like
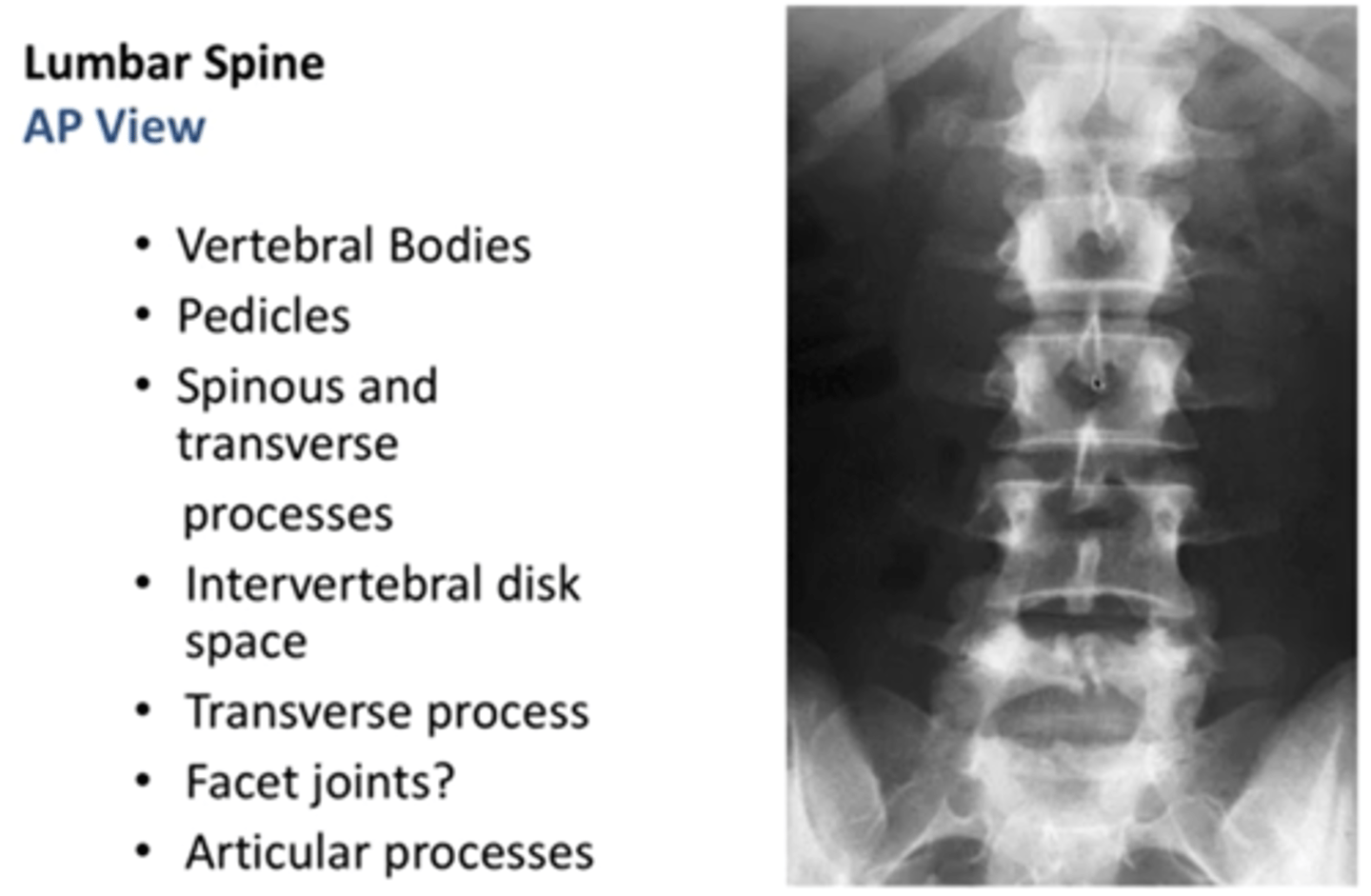
what does lumbar spina bifida look like
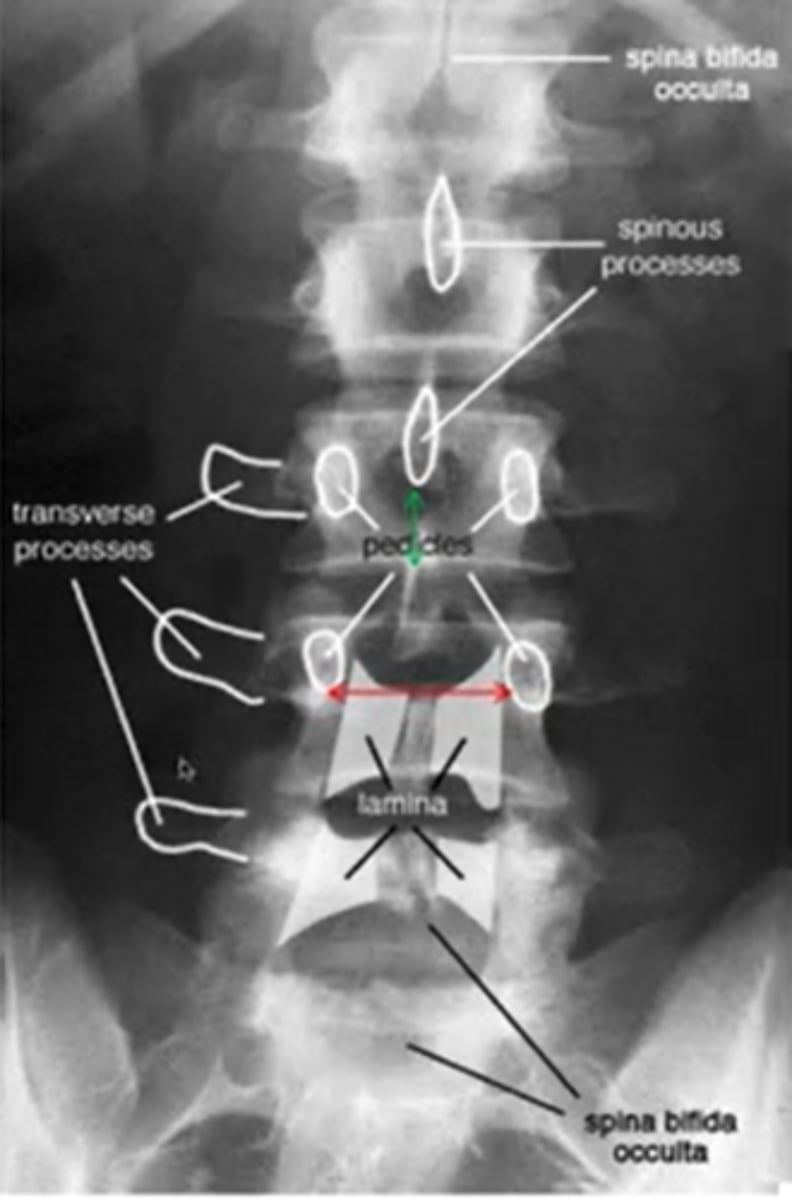
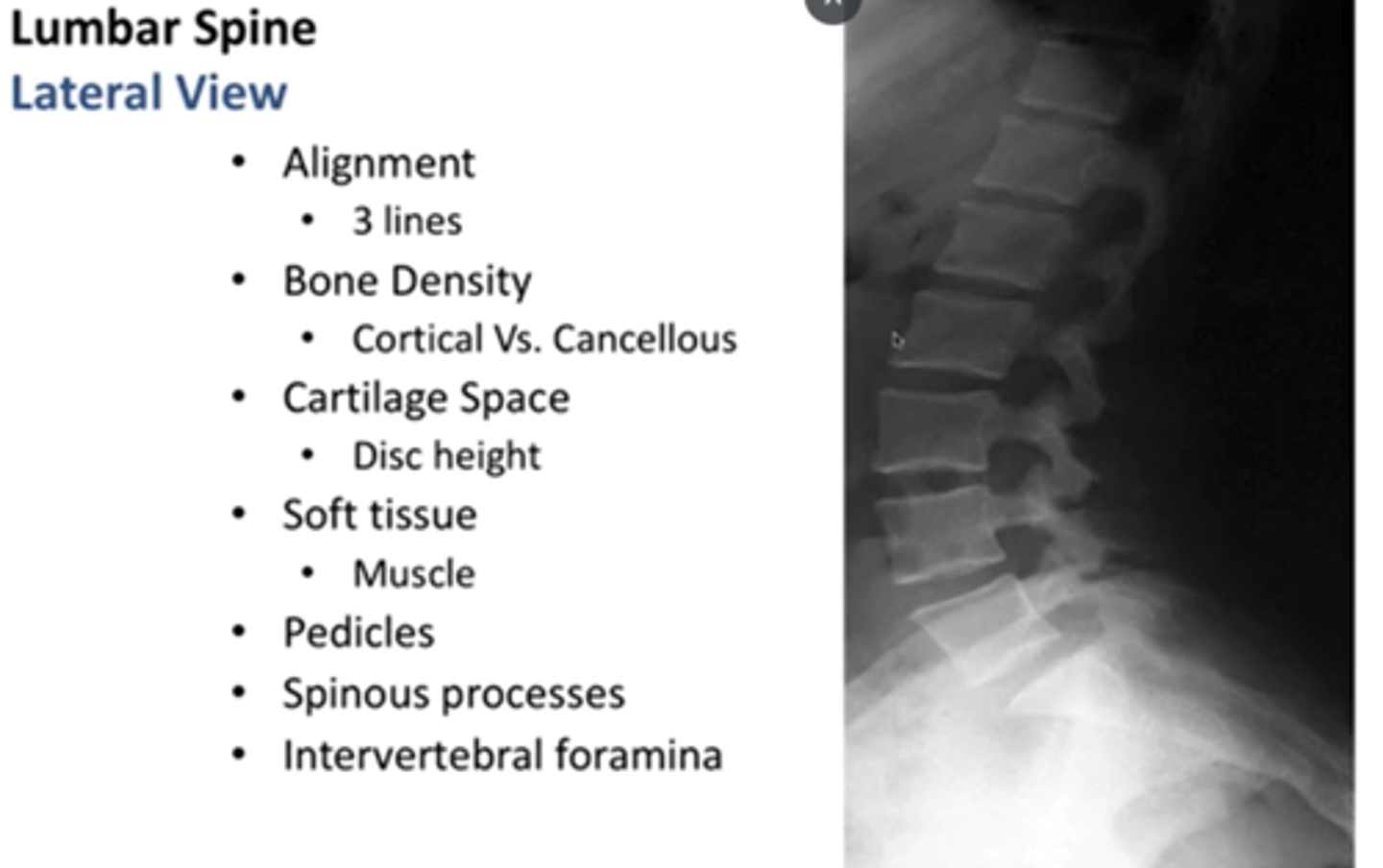
what does a lateral view of the lumbar spine
when looking at an oblique image for the lumbar spine, which side are you looking at whether its right or left?
the side closest to the image receptor or the side that is labeled
(posterior)
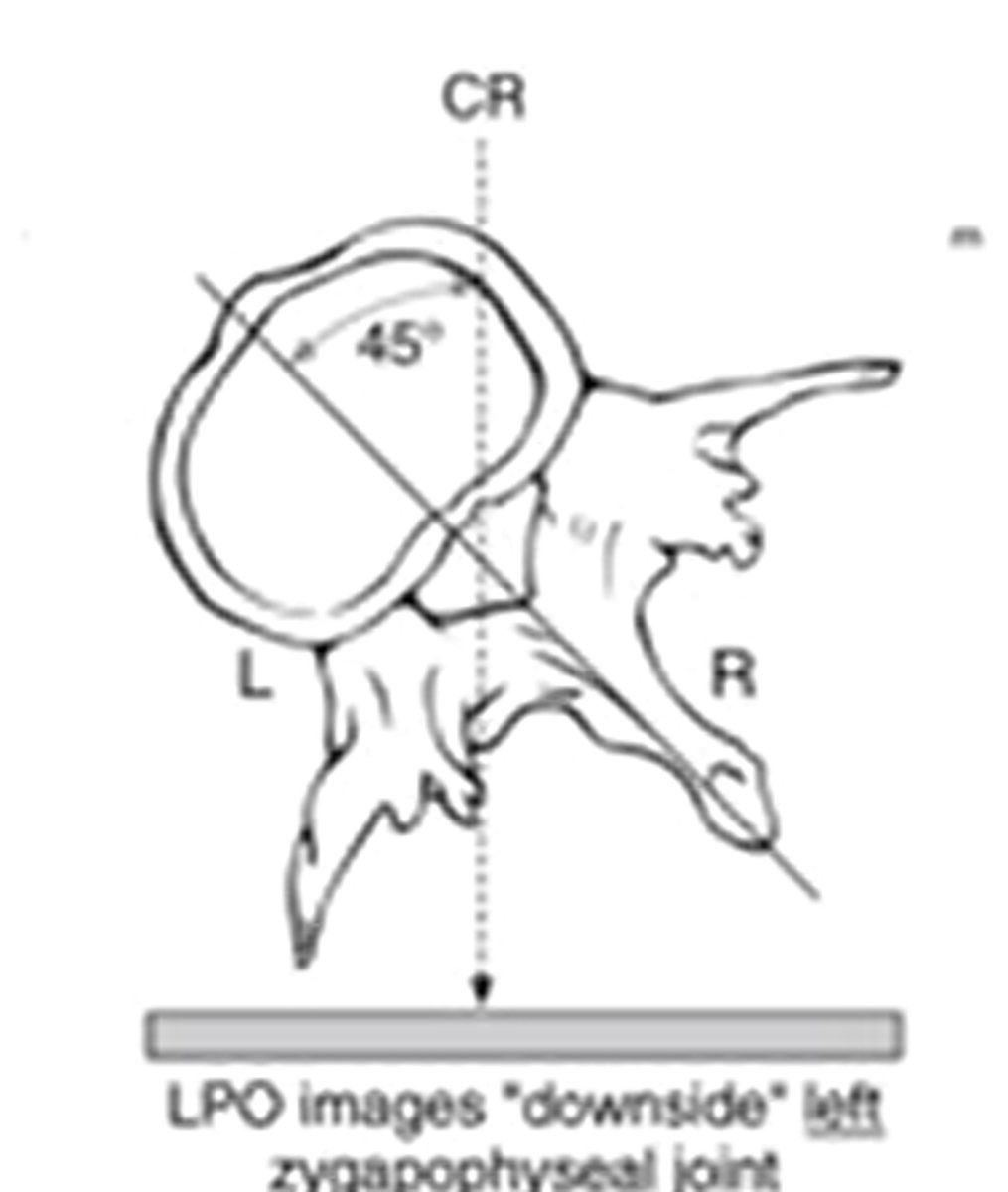
what is the most common reason for taking a oblique image of the lumbar spine
to see if there is a fracture of the pars interarticularis
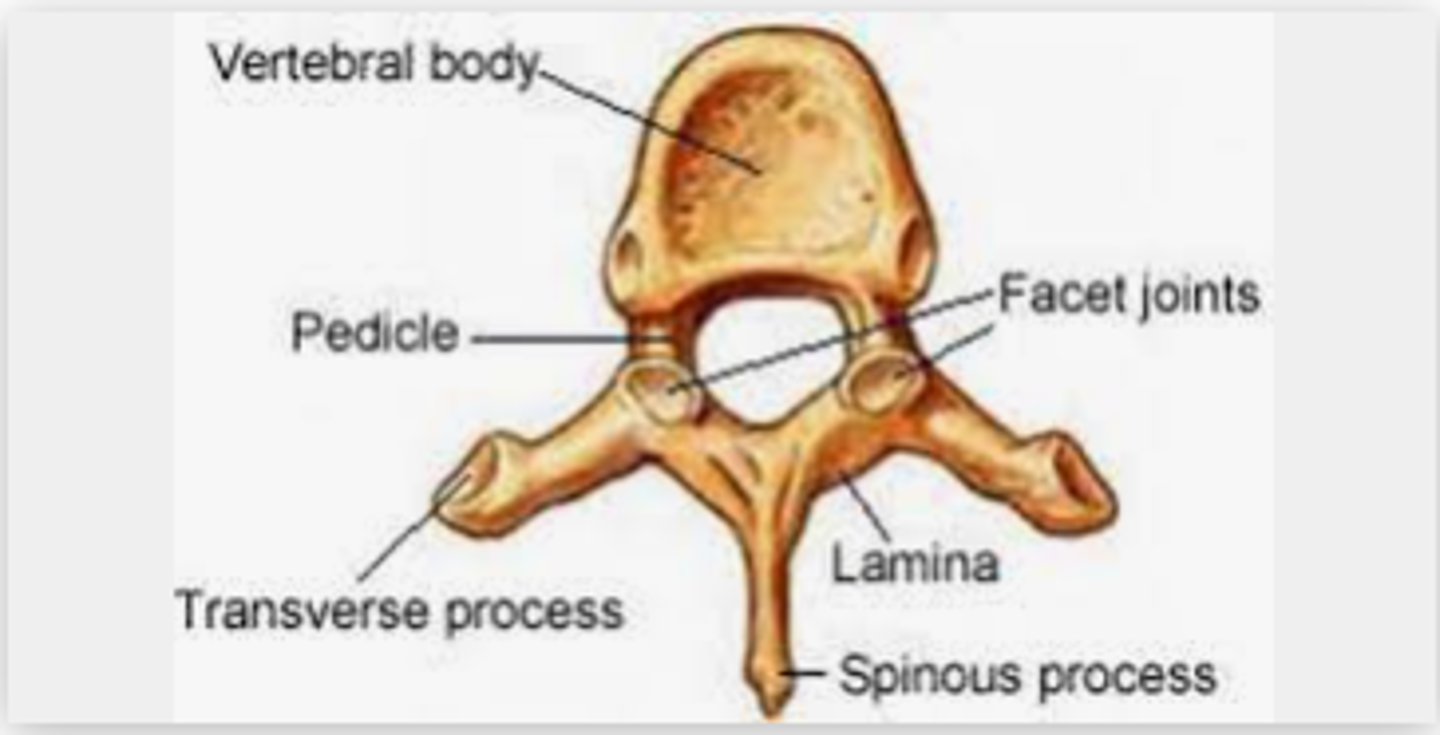
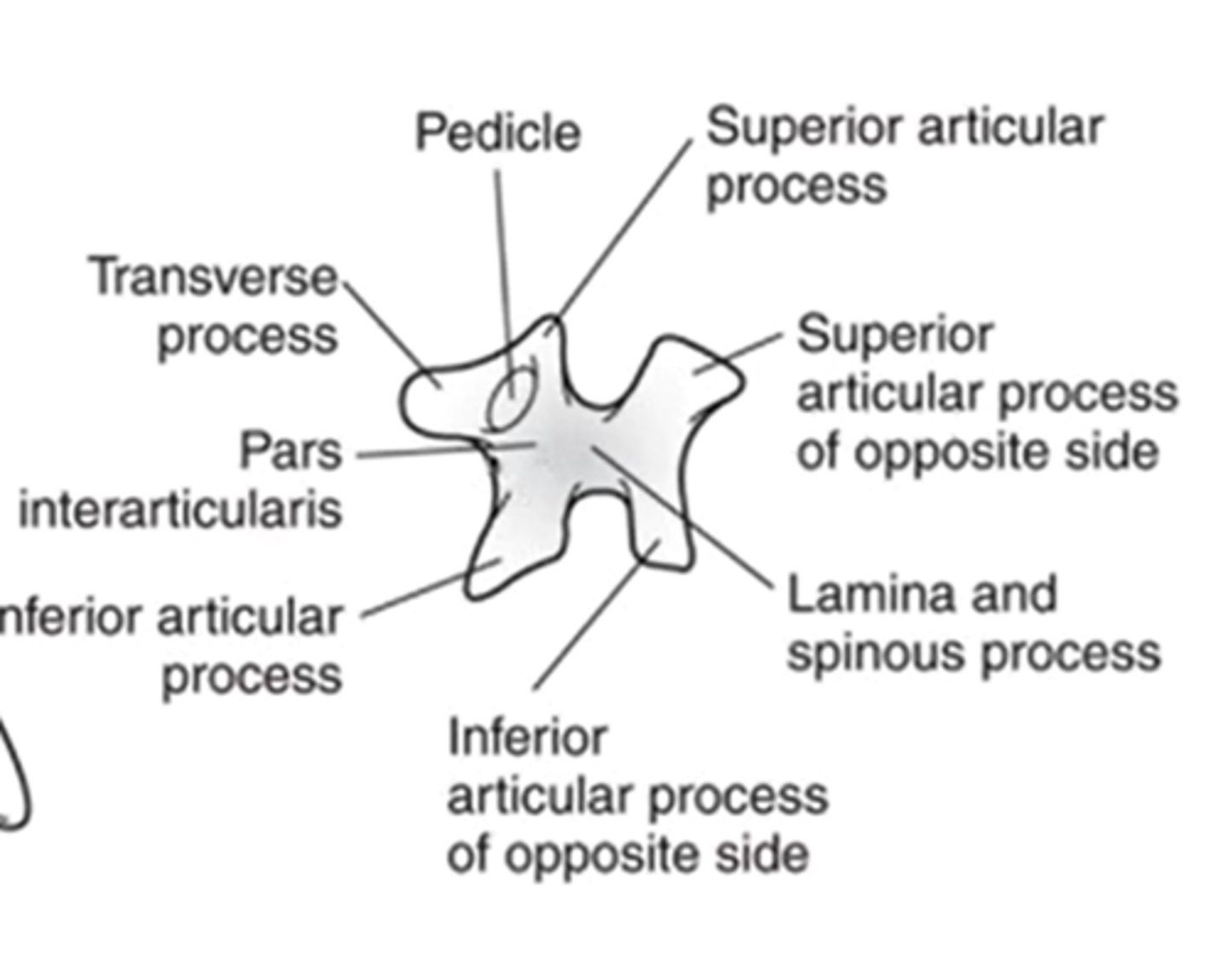
what is a pedicle
the segment between the transverse process and the vertebral body
what kind of image will show a scotty dog?
lumbar oblique view
what part of the scotty dog is the neck?
pars interarticularis
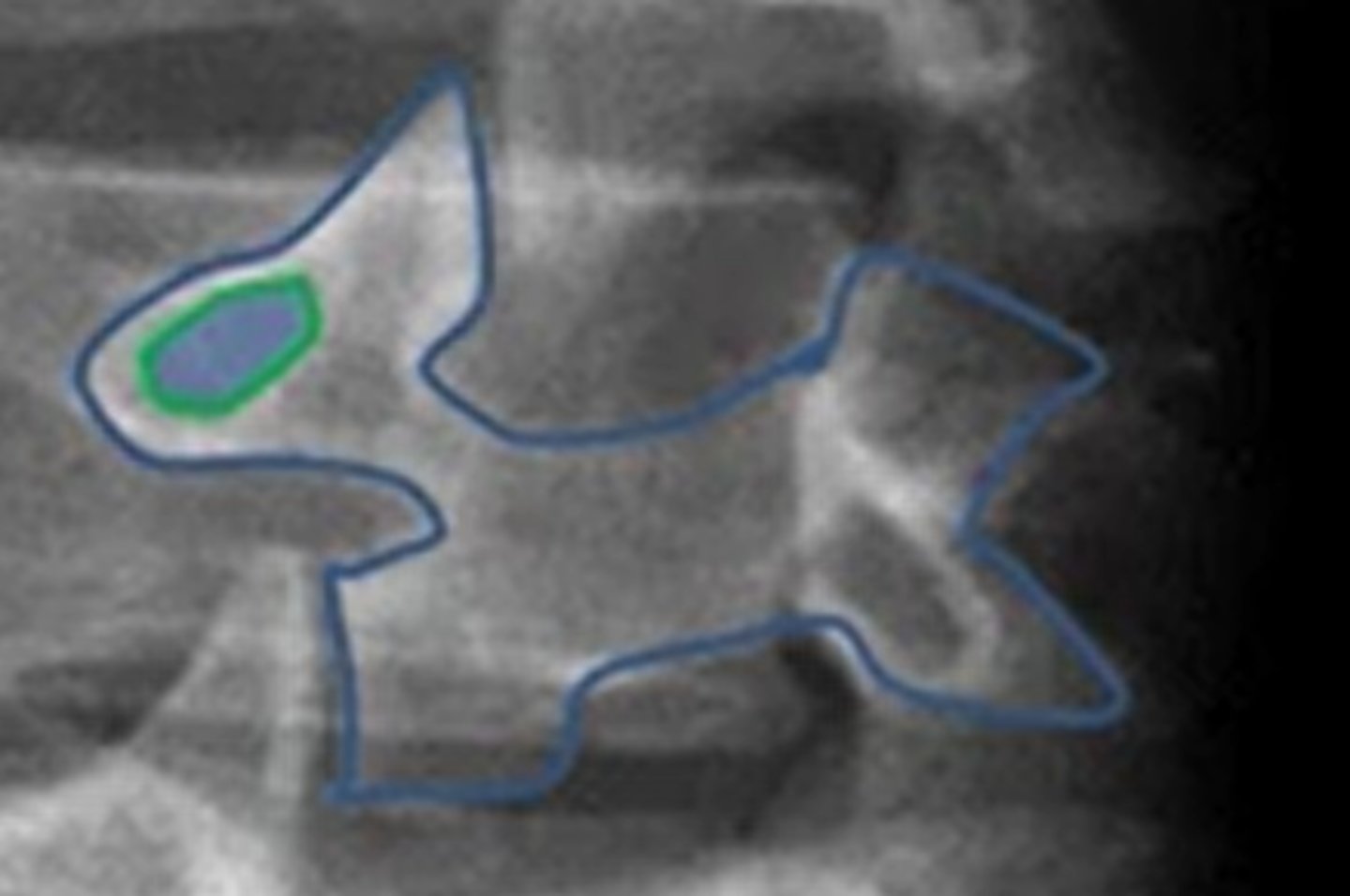
label the scotty dog
what are the two views of the SIJ
(what are you looking for in each view)
AP (looking at the joint surface)
R/L oblique ( joint space)
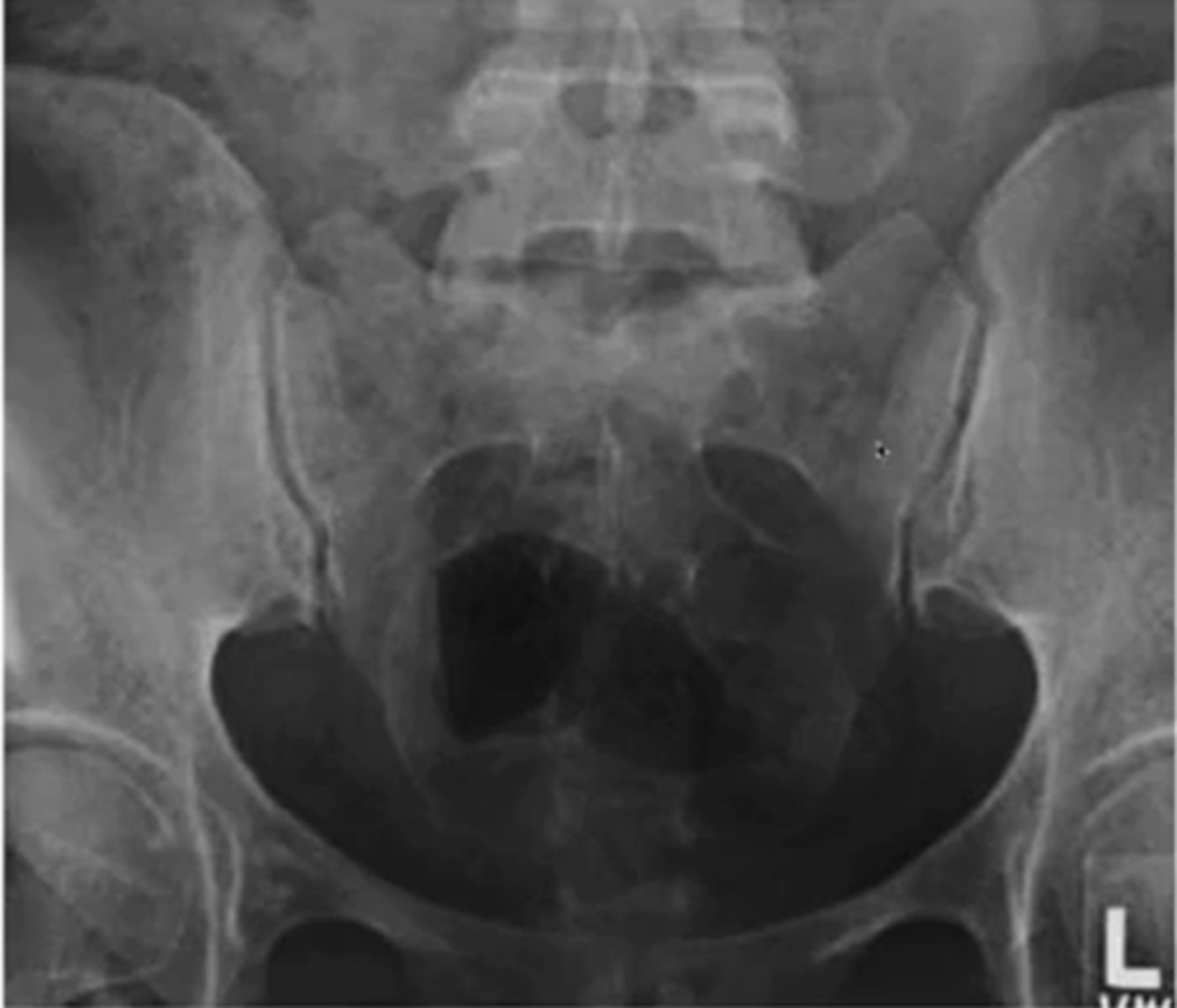
when looking at a R oblique of the SIJ what side are you looking at
the left
what kind of angle is the CR shot for an AP SIJ xray
inferior to superior 30-35 degrees
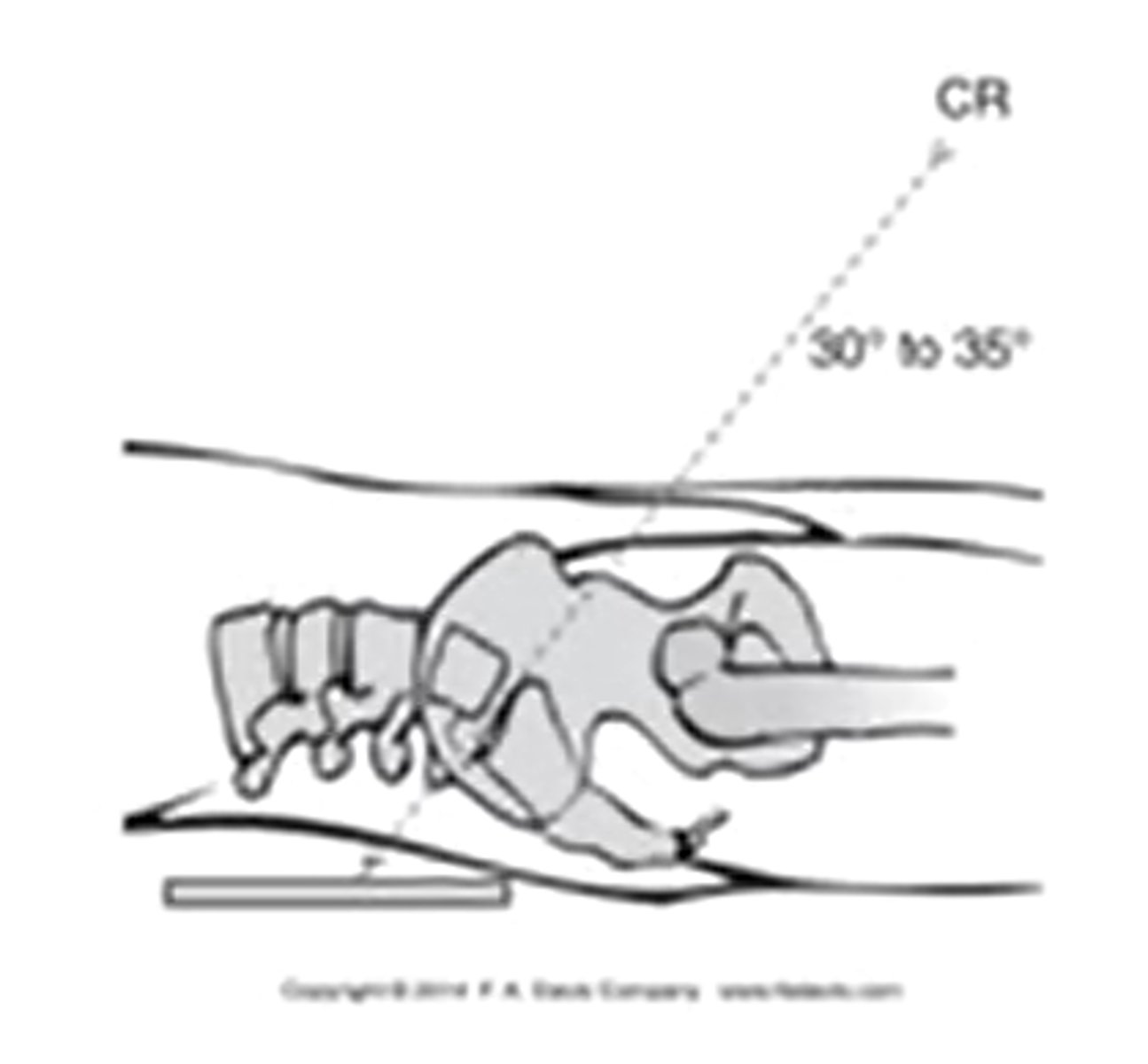
what is an example of an oblique image of the SIJ
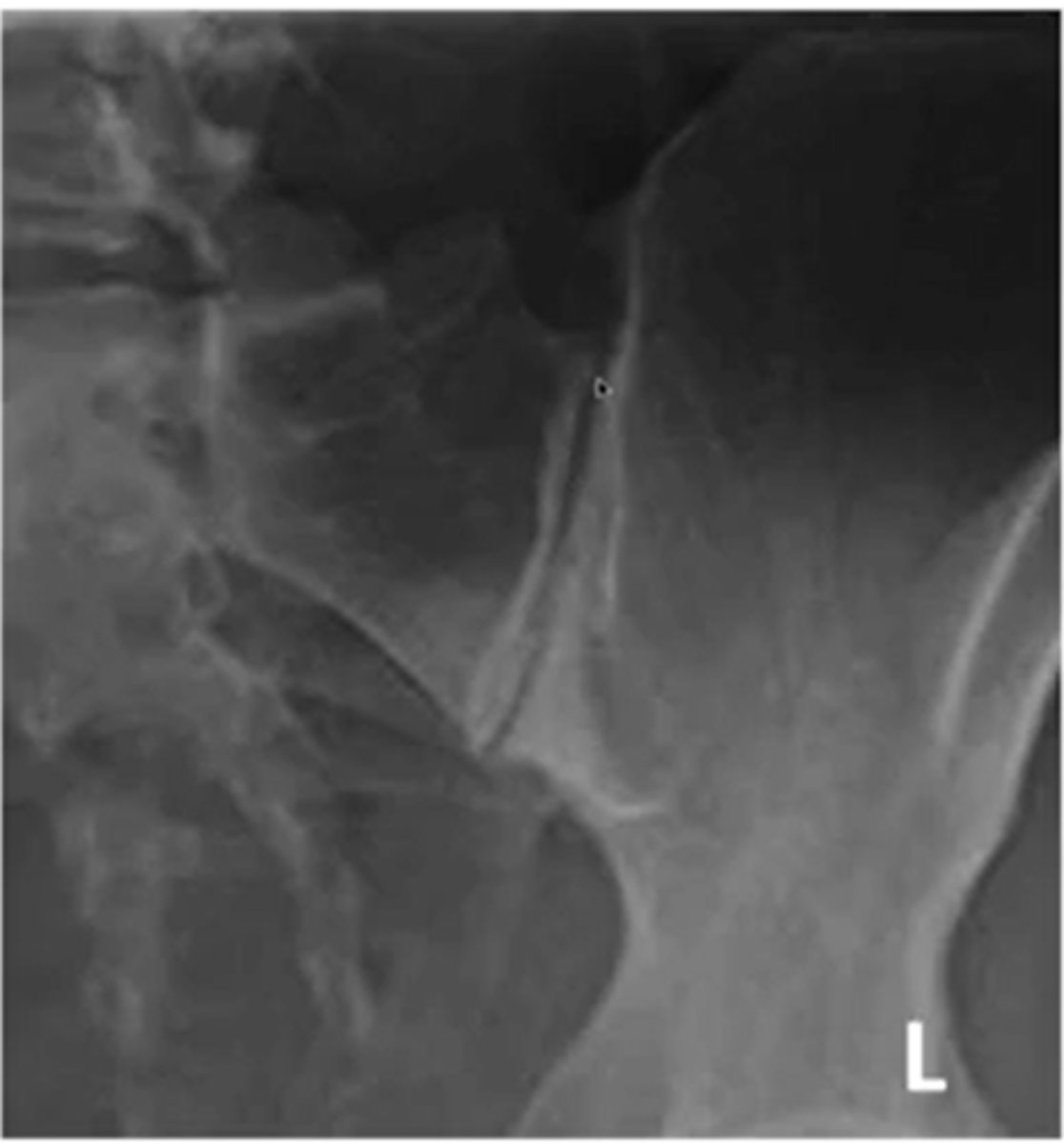
for the SIJ would you use a AP or an oblique view for joint space
oblique
what are the three indications for hip radiograph
hip pain
avascular necrosis
stress fractures
for the pelvis what position is the hips for an AP view
IR 15-20 degrees
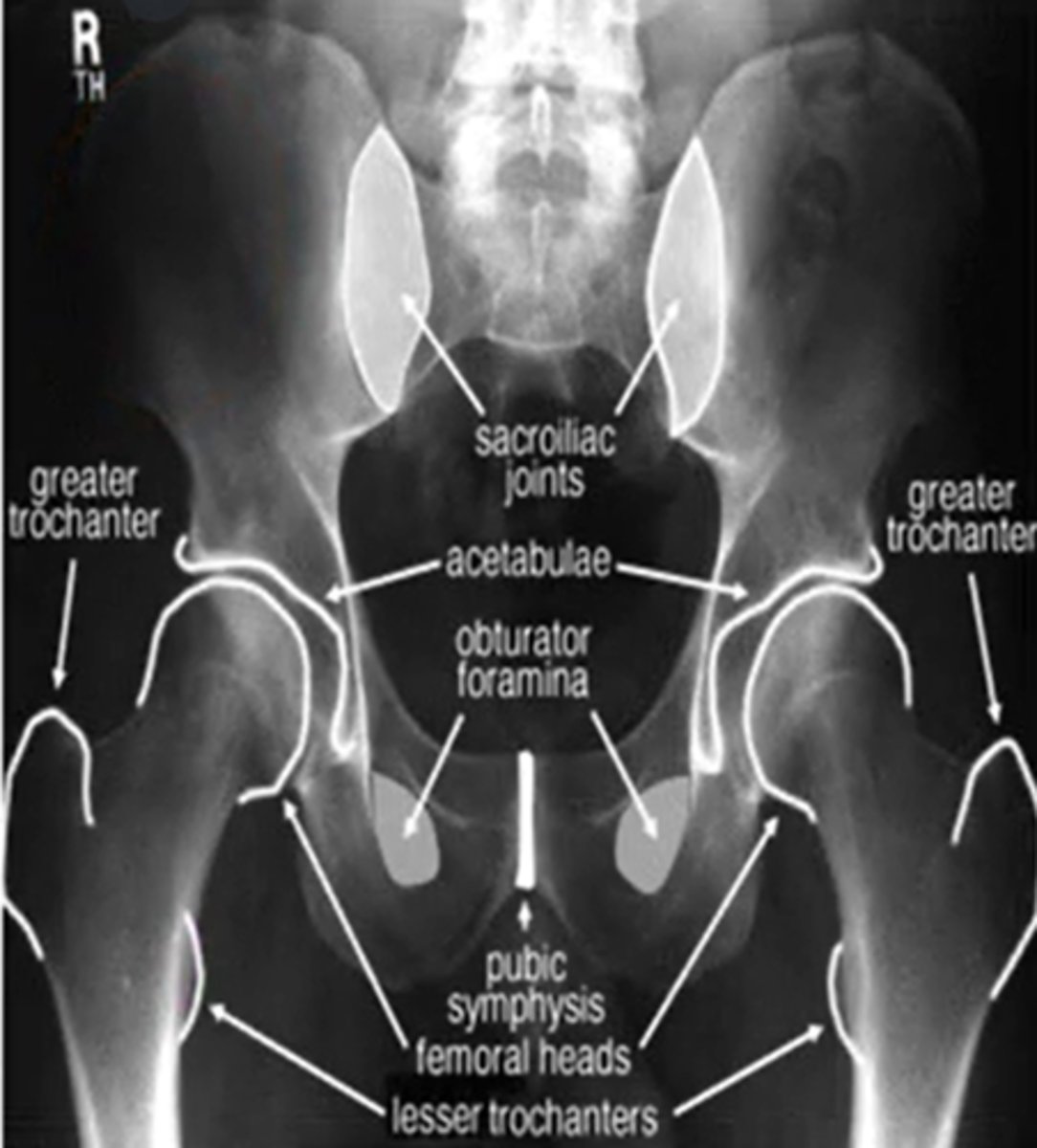
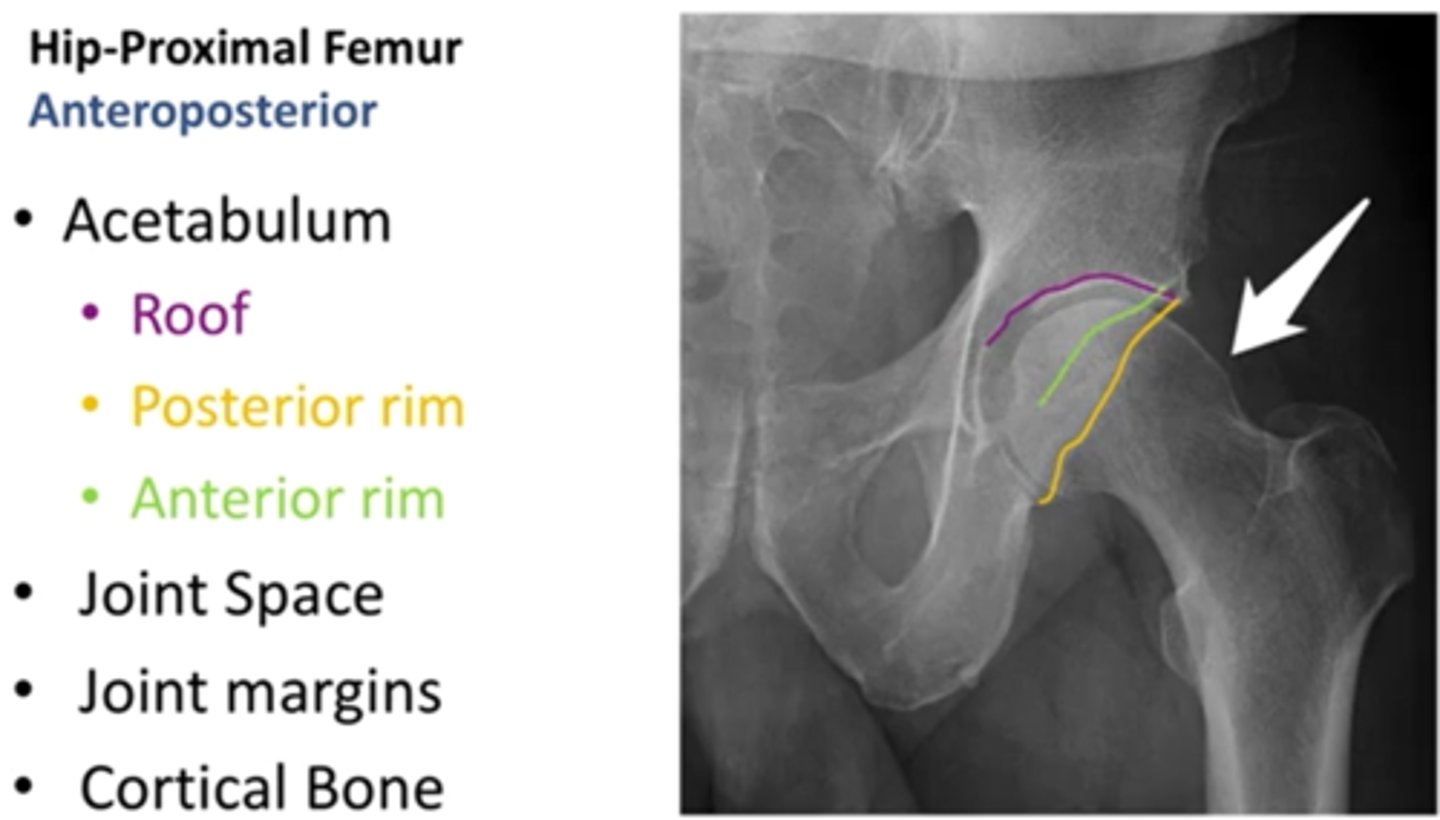
what are the three important portions of the acetabulum (ap view)
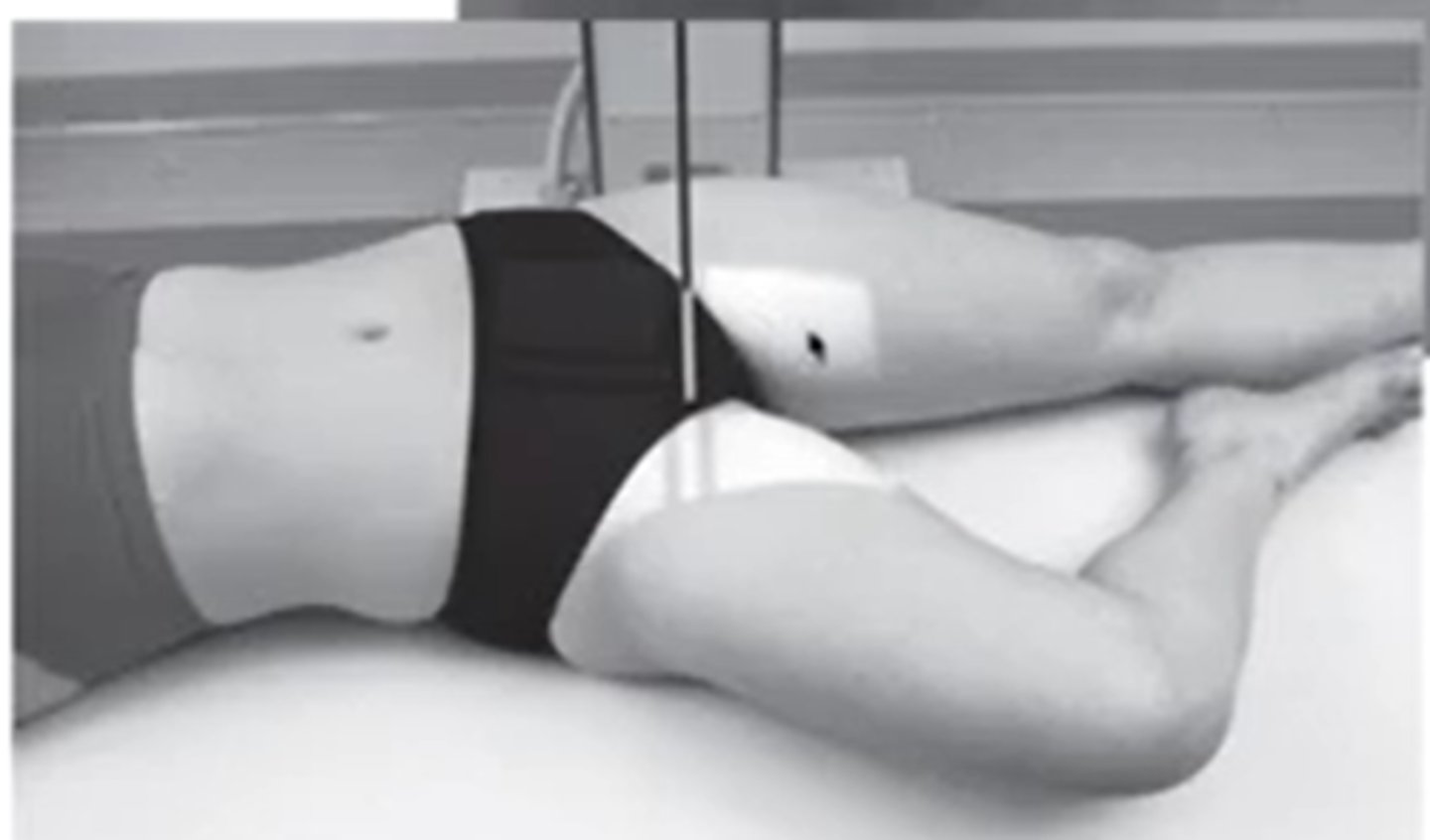
what position will the hip be if you want to see the medial portion of the femur (AP view)
frog leg
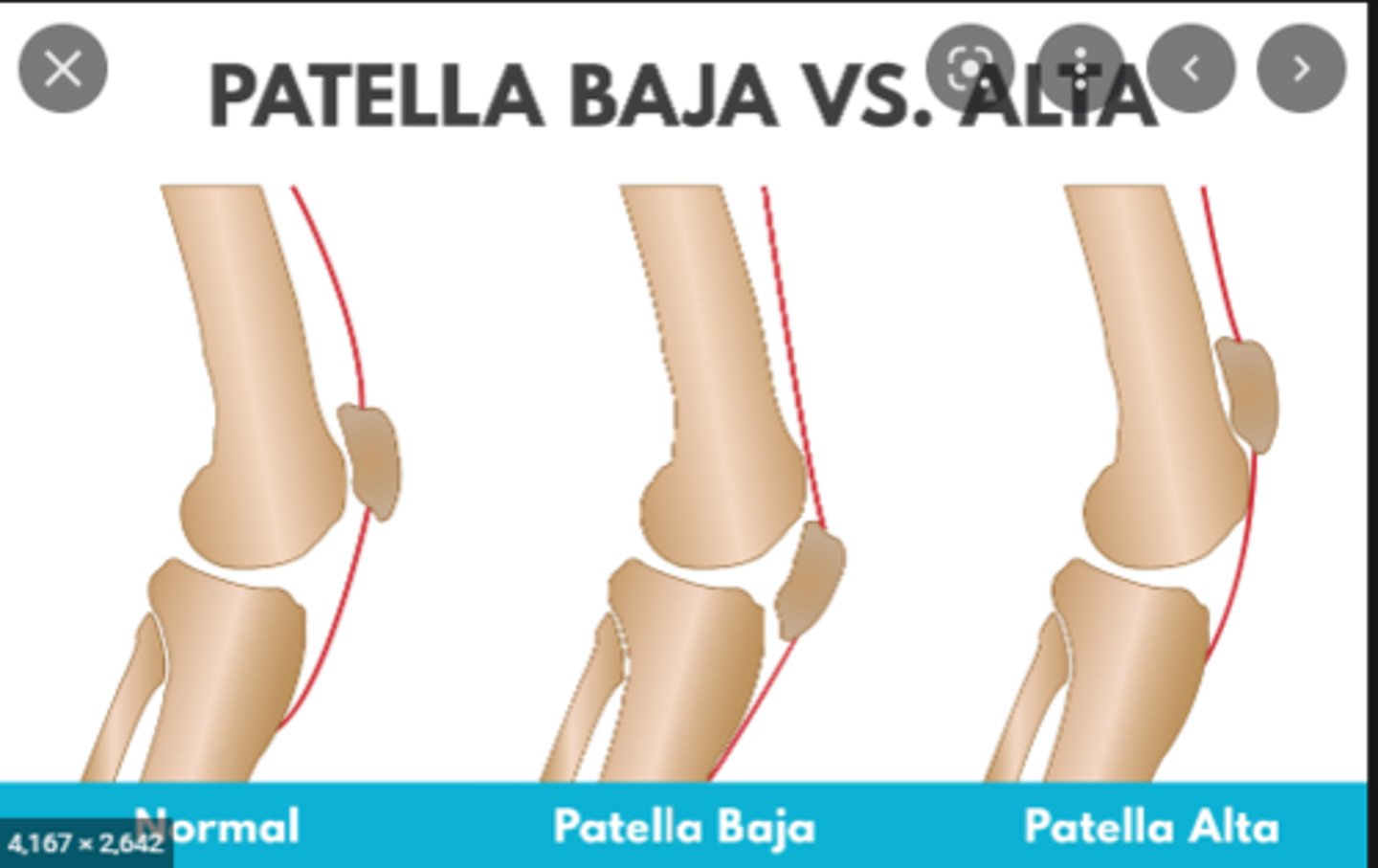
what is the difference between patella alta and baja
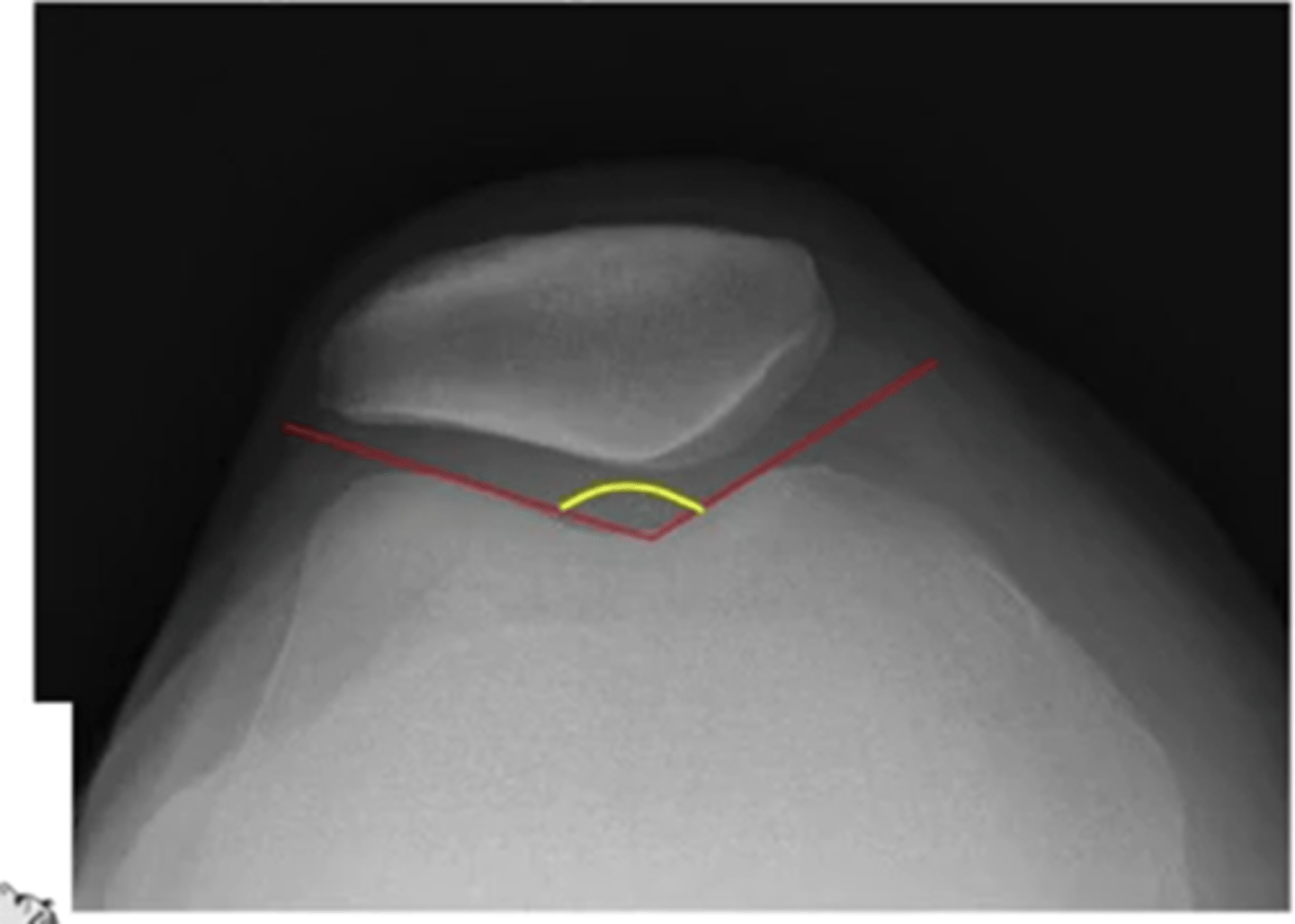
what is the sulcus angle at the knee
the greater the angle = greater chance of dislocation
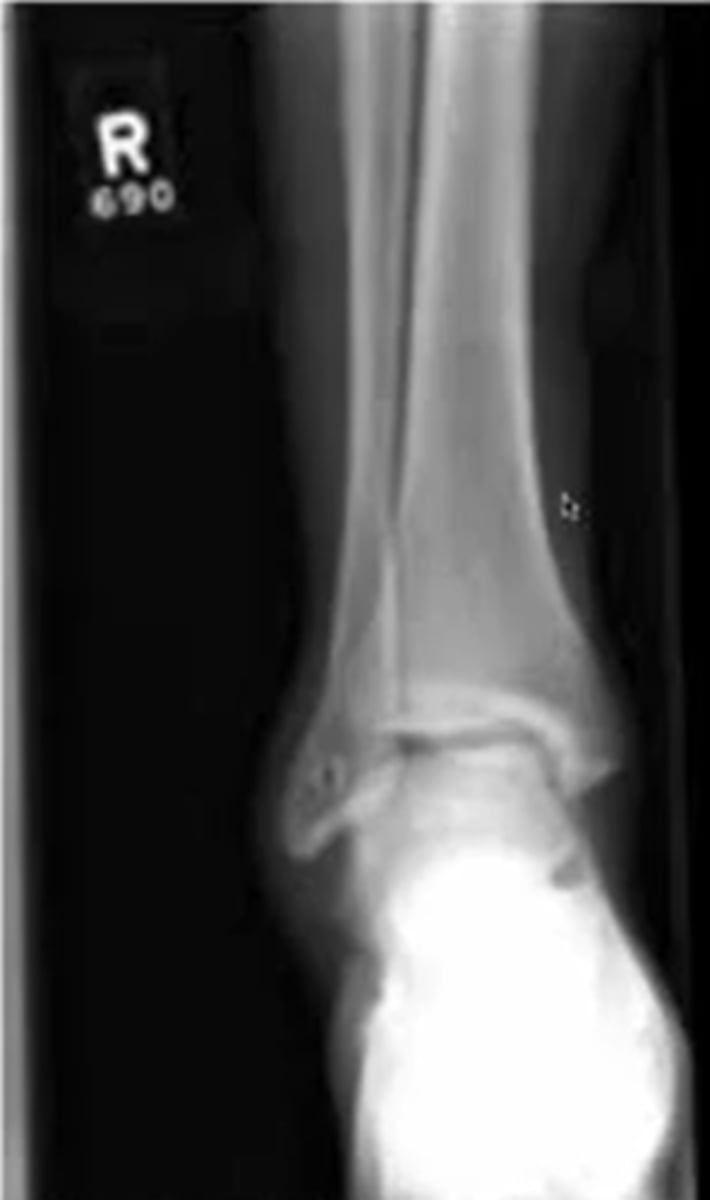
on an xray AP of the ankle what will you see with ankle instability
shortened fibula or fibular displacement