Unit 1.2: EM
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
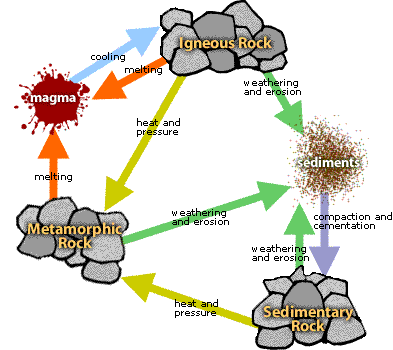
Rock cycle
The rock cycle describes the processes through which the three main rock types transform from one type into another.
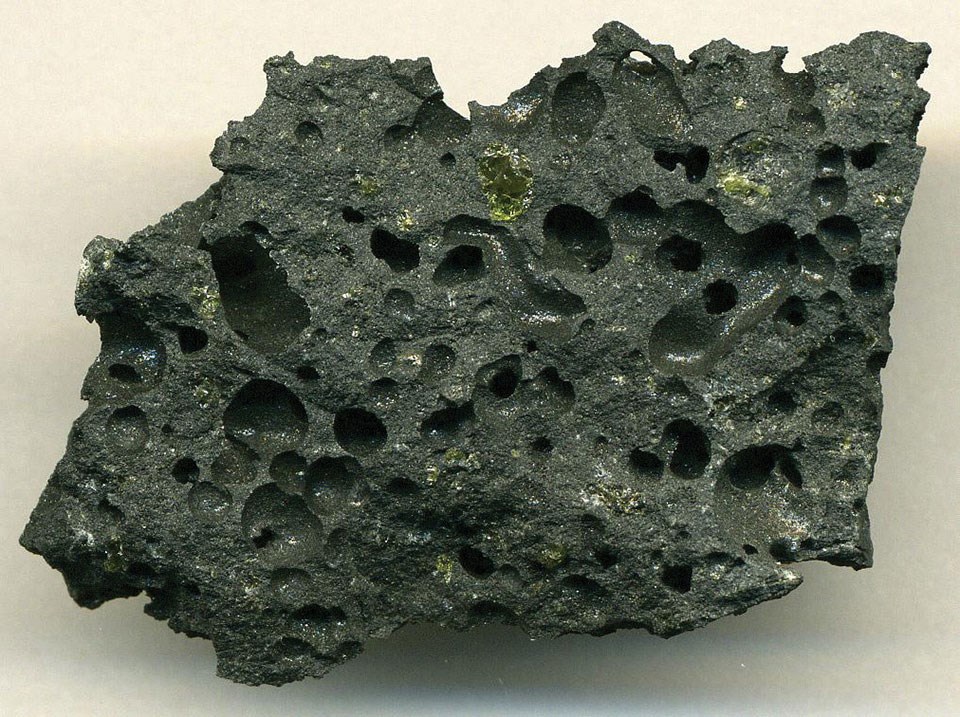

Igneous rocks
Igneous rocks are made from liquid magma
Magma cools to form solid rock
Mineral crystal sometimes present, size depends on cooling
No fossil present
What are the three types of igneous rocks?
Extrusive, Intrusive, Plutonic
Examples of igneous rocks
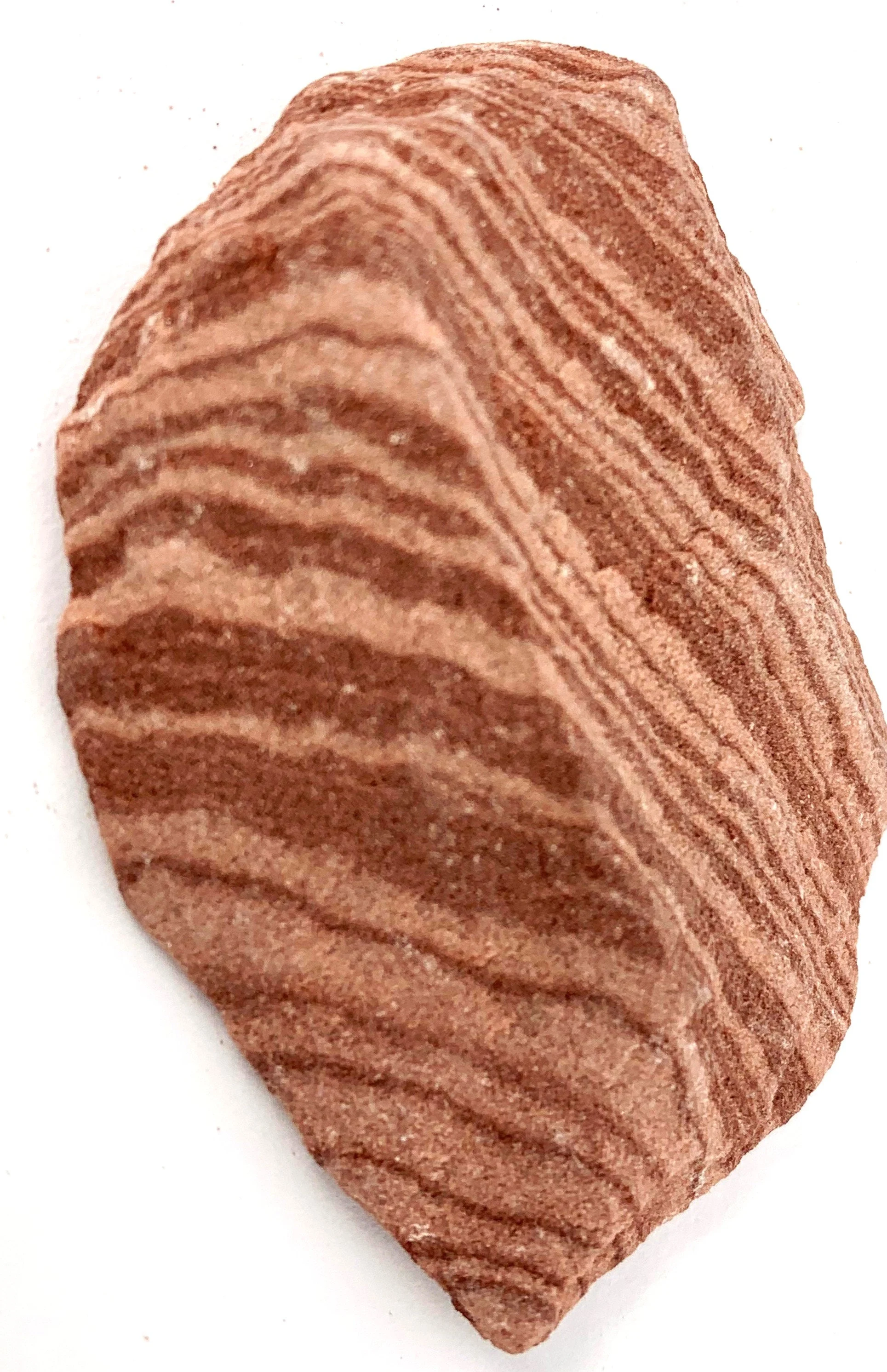


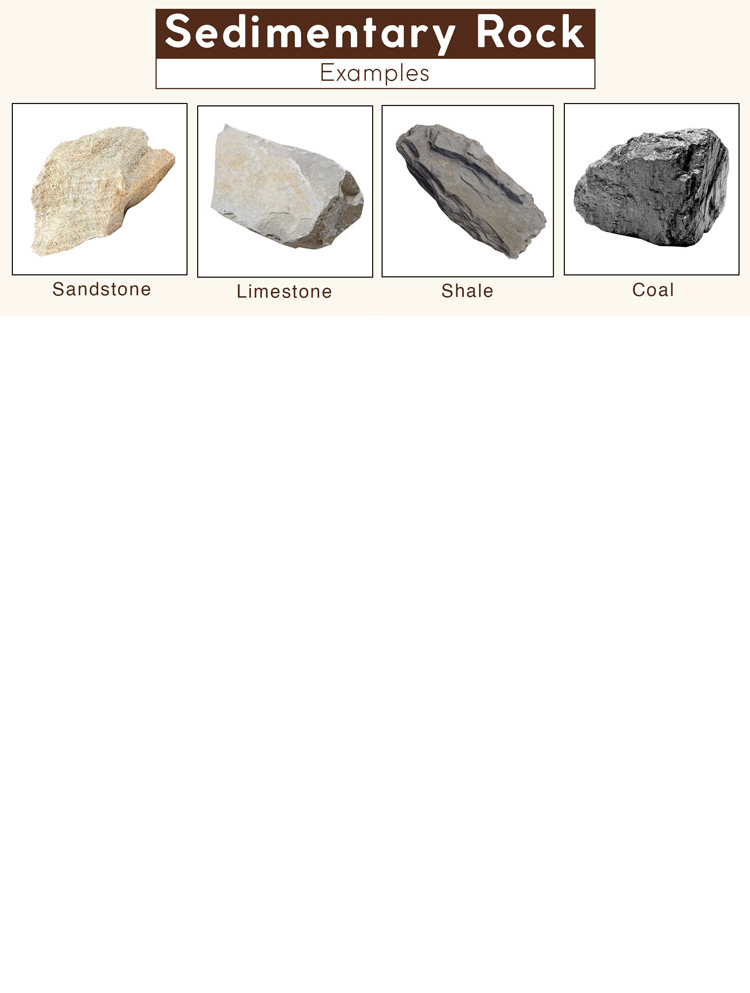
Sedimentary Rock
Made from other rock fragments
Rock fragments become buried and increased pressure forms a rock
No crystal
Fossil maybe present
Examples of sedimentary rocks

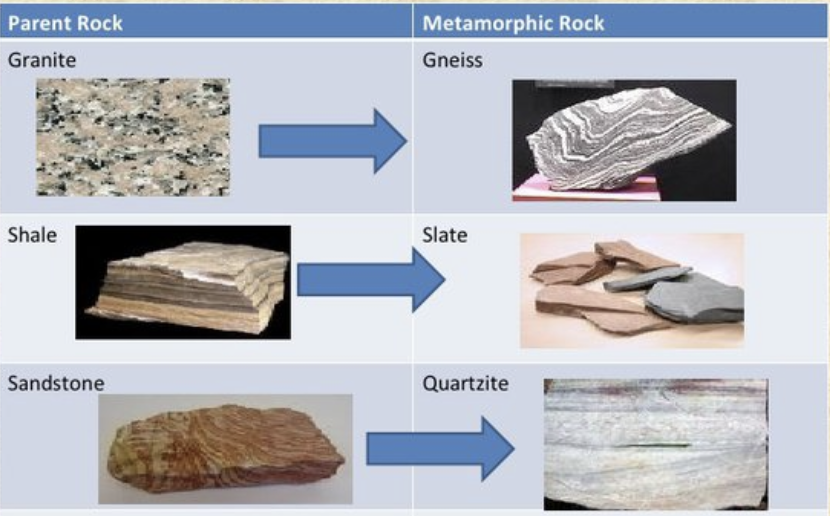
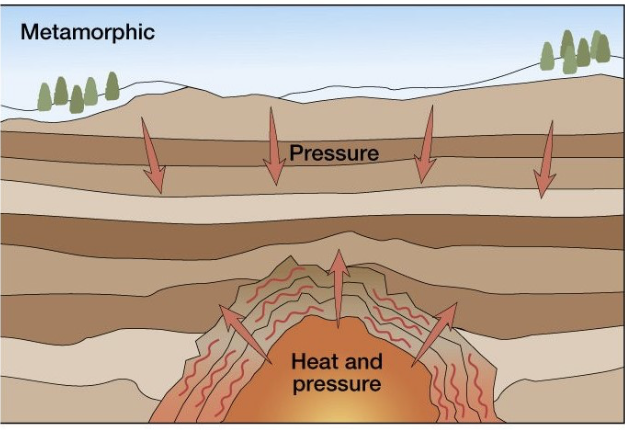
Metamorphic rocks
Metamorphic rocks are created by existing rocks when heat or pressure
Mineral crystals are present
No fossils
Examples of metamorphic rocks

Common metamorphic rocks

Lava
Magma that reaches the earth’s surface
Question 1: What stone results when magma cools and crystallizes slowly within the Earth's crust?
Plutonic or intrusive rocks
Question 2: What rocks are metamorphic rocks built or created from?
From existing rocks
Why are sedimentary rocks very compact and hard
Due to the sediments being buried deeply layer by layer.
minerals vs rocks
Minerals have the same chemical composition throughout. ( Graphite – C ).
Rocks are simply a combination of 2 or more of different minerals.
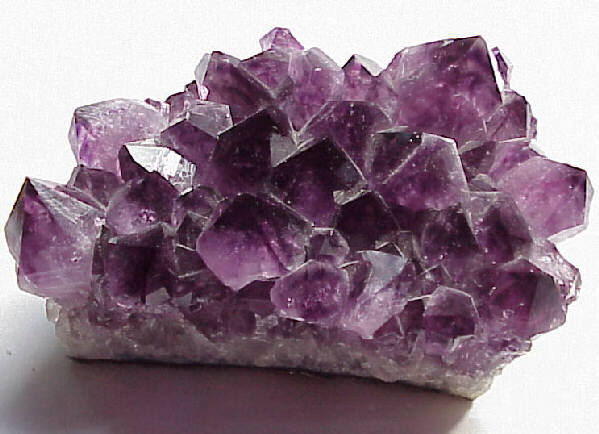

Mineral
Naturally formed, inorganic solid that has a definite crystalline structure
Question: What is in magma?
Minerals
Magma composition
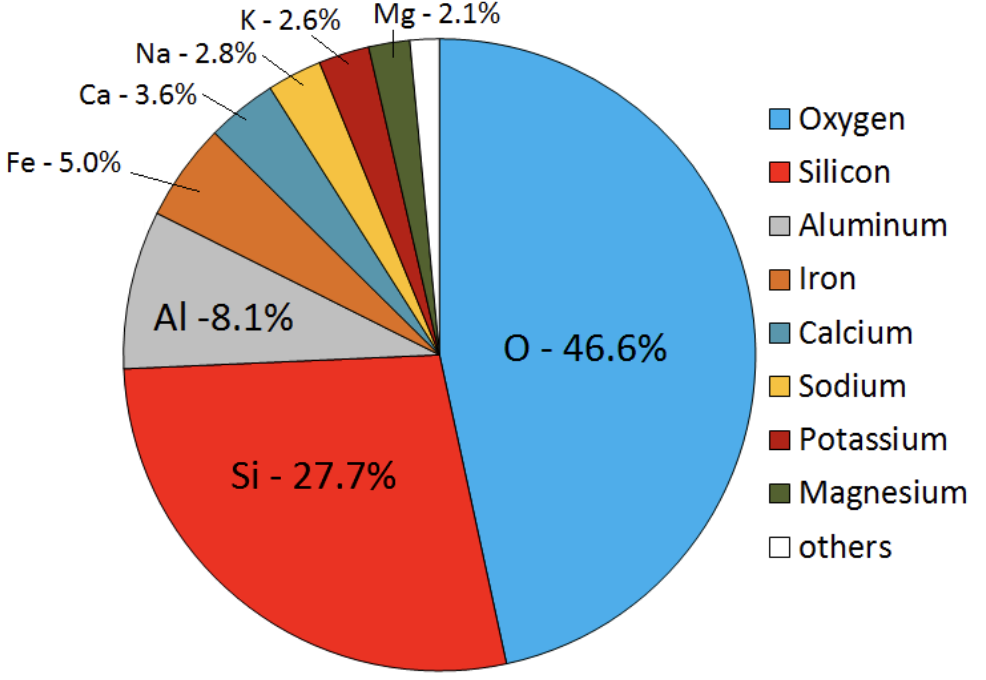
Silicates
Minerals that are made of a silicon—oxygen bond. 90% of all minerals are silicates.
e.g. quartz, mica and feldspar
Earth’s most common minerals
Feldspar, quartz, mica
Feldspar
Makes up 60% of the Earth’s crust.
Hardness = 6
Pearly luster.
Usually pink or white.
Quartz
2nd most common mineral.
Hardness = 7
Glassy luster.
Many colors, usually white.
Mica
Breaks in sheets.
Hardness = 2.5
Flat, shiny sheets
Mineral must be:
Naturally occurring made from non-living things,
(Fossils come from dead organisms, so they aren’t minerals.)Not man-made
Minerals must be: (cont.)
Solid
Have a fixed shape and volume
Never living- inorganic
Minerals must be: (cont.)
Have a definite crystal structure
particles line up in a regular, repeating pattern.
flat sides called faces, that meet at sharp edges and corners.
Minerals must be: (cont.)
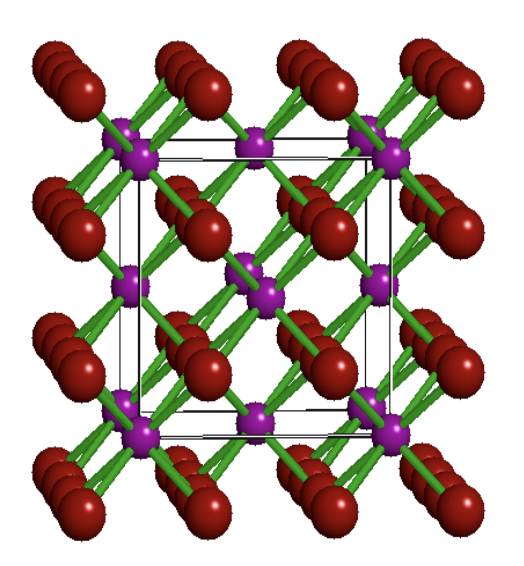
A definite chemical composition
Always contains certain elements in the same proportion.
❖ Almost all minerals are compounds, (two or more different elements chemically joined).
Basic mineral requirements
All minerals must:
Occur naturally in nature
Inorganic solid
Crystal structure
Definite chemical composition

Question 1: Are pearls minerals?
Pearls are not minerals because it does not have a distinctive crystal structure and it is formed by the action of a living organism.
Question 2: Is coal a mineral
Coal is not a mineral because it comes from organic materials.
Coal forms when dead plants and animals are compressed underground for millions of years.
Question 3: Is salt a mineral?
Salt a crystalline mineral that is composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl); a chemical compound.
Properties used to identify minerals
Color — what color is it?
Luster — way a mineral shines
Streak — does it leave a streak if rubbed on a white tile?
Hardness — use Mohs’ Hardness scale from 1 to 10.
Cleavage — how does it break?
mnemonic: Cats Like Soft Hairy Couches
Color
Most easily observed property.
Least useful for ID.
Minerals can have impurities or come in a variety of colors.
Helpful for elimination.
Luster
The way a mineral reflects light.
Either metallic or nonmetallic.𝑵𝒐𝒏-𝒎𝒆𝒕𝒂𝒍𝒊𝒄:
Vitreous — Glassy.
Pearly — like a pearl
Resinous — Waxy, plastic
Adamantine — very hard to break
Dull — no reflection
.𝒎𝒆𝒕𝒂𝒍𝒊𝒄:
Metallic — like a metal
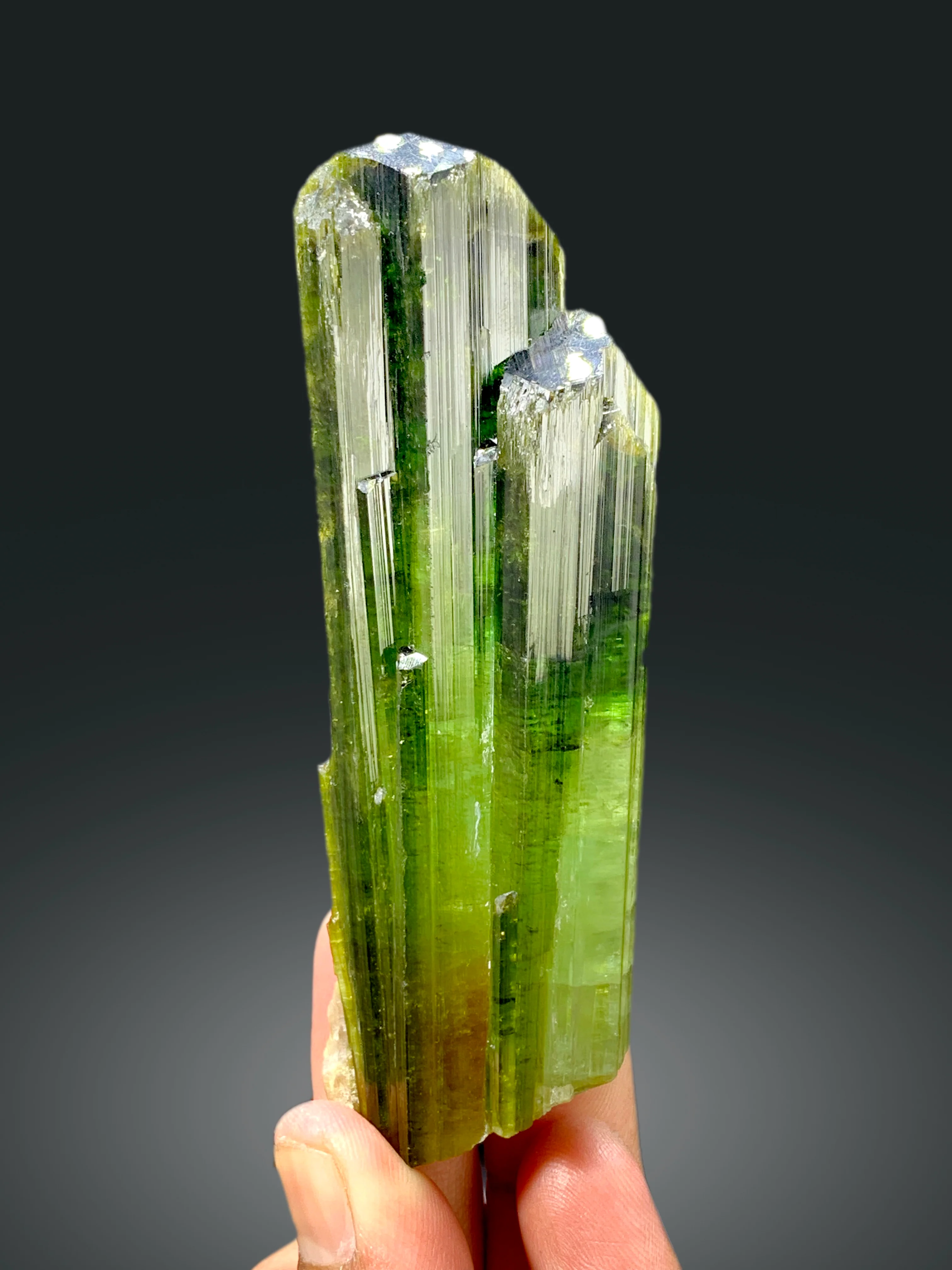

Streak
The color of its powder
Rub on white tile to find the streak
Streak of metallic mineral is usually the color of the mineral.
Streak of non-metallic mineral is usually colorless or white.

Hardness
A measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched
Hardest mineral
diamond
Softest mineral
talc

Mohs Hardness Scale

Cleavage
The way a mineral breaks.
May be none, 1, 2, 3, 4, or 6 dir
Or an absence of cleavage is called fracture.
Fracture
Absense of cleavage

Properties of Minerals
Density
Minerals will have a certain density regardless of the size of the sample.
Each mineral has its own density called specific gravity
Acid Test
Putting acid on the mineral to see if there is a reaction (effervescing).

Special Properties
Magnetism
Glowing under UV light
Double refraction
Double refraction
Splits lines in two

Question 1: Are bricks rocks
No, bricks are not rocks. Rocks are formed naturally through erosion and weathering.
Question 2: Are glaciers rocks?
Yes, glaciers are rocks. They are naturally occurring (not man-made), solid, and they can form large deposits. Snow, lake ice, and glaciers fit the definition
Rocks classification
Texture
Grain
Minerals
Color
Origin of rocks
mnemonic: Tough Granite Makes Cool Objects
Texture
Texture is how a rock looks and feels
texture in rocks is determined by the size, shape, and pattern of a rocks grains.
Grain
Size, is it large or small?
Shape, smooth, rough, round, jagged?
Pattern – rows, waves, swirls, beads or random patterns
Mineral composition
Rocks are made up of more than one mineral
Color
Color rocks come in all sorts of colors
How are rocks formed
magma
erosion and layering
heat and pressure

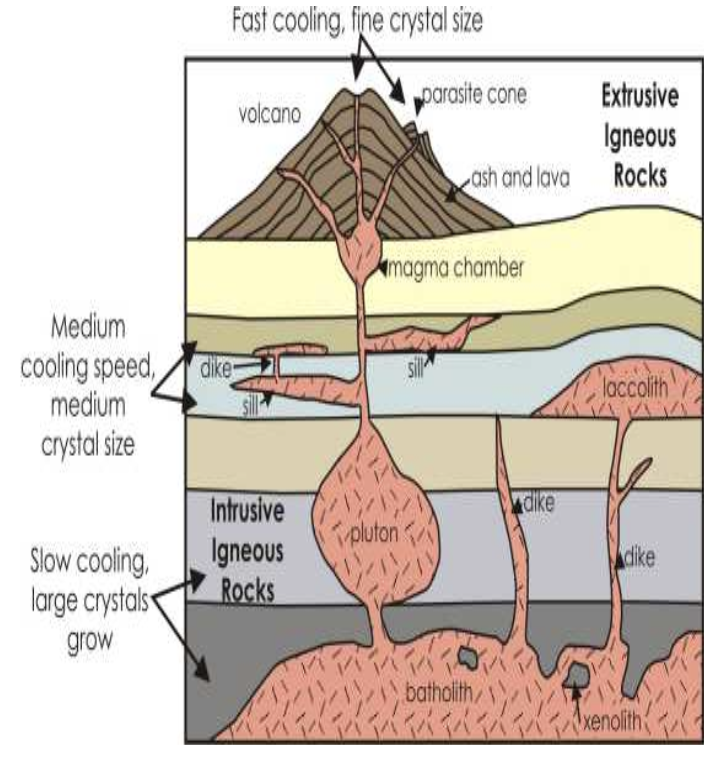
Origin of igneous rocks
Igneous rocks are formed from the cooling of magma or lava
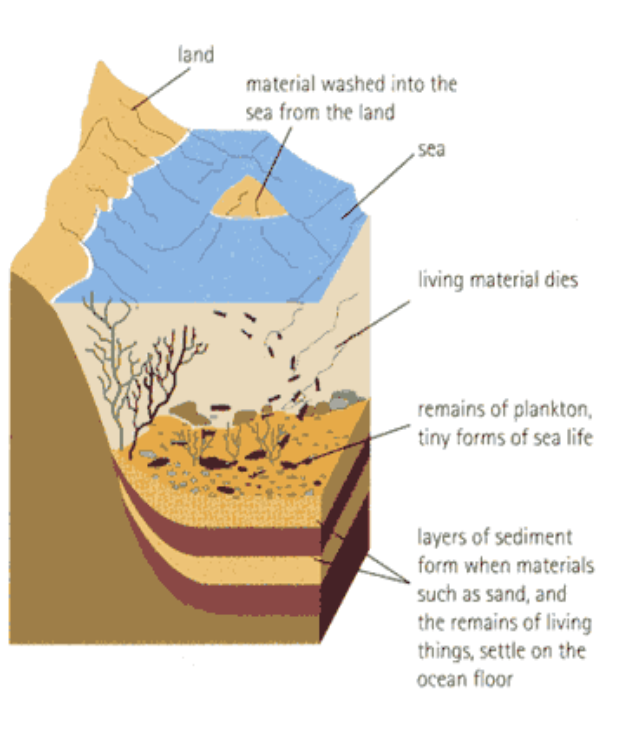
Origin of sedimentary rocks
Sedimentary rocks are formed from other rocks that are broken into small particles and moved by erosion (wind or water)
The particles are squeezed or cemented together
Rocks are layered
Origin of metamorphic rocks
Metamorphic rocks are formed from other rocks
Rocks have been pushed deep into the earth’s crust
Pressure from the earth above and heat from the mantle below cause them to change shape, color, grain and crystal structure
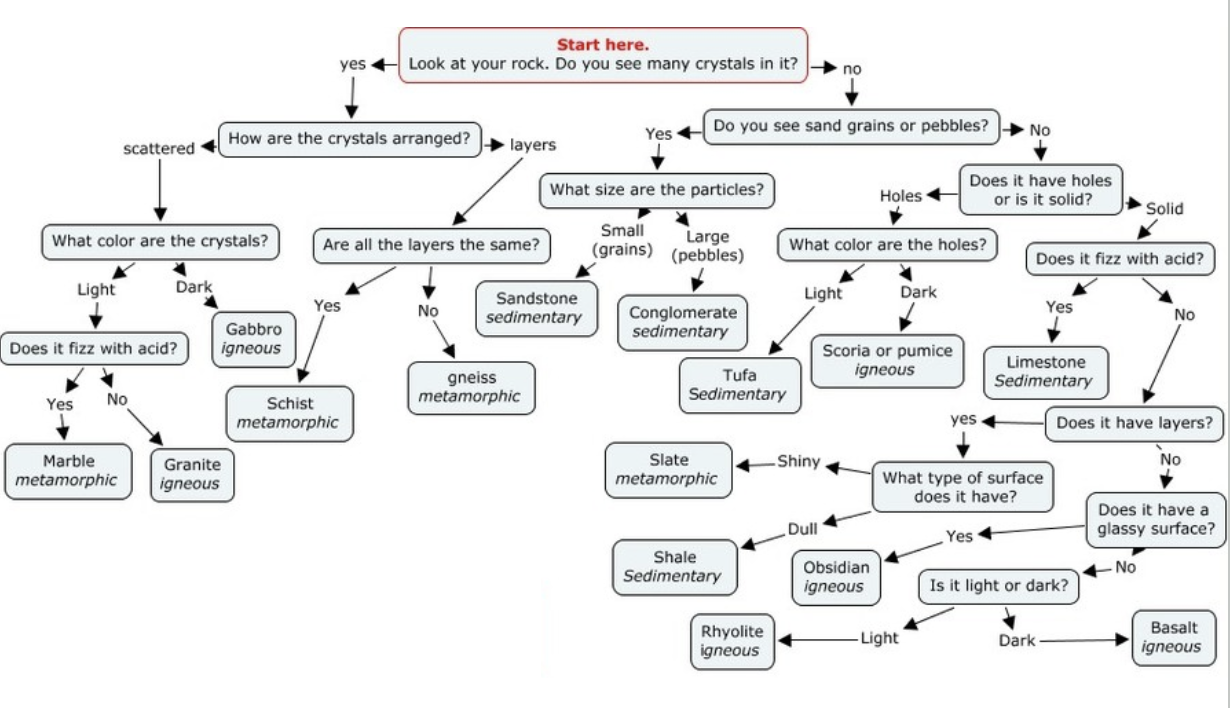
Rock identification chart