Biology Ch. 8 - Biological Membranes
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Photosynthesis
The process of converting light into energy
Photoautotrophs
Organisms that perform photosynthesis
Ex) Plants, Algae
Integrins
Embedded in the membrane and are like long hands that stick to things and communicate
Heterotrophs
Consumes other organisms for energy
Ex) Animals, Humans
Peripheral Proteins (what do they do)
They help with structure and recognition sites, only located on the outside/inside of the membrane (never in the middle).
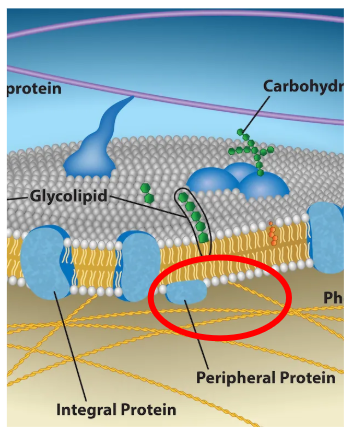
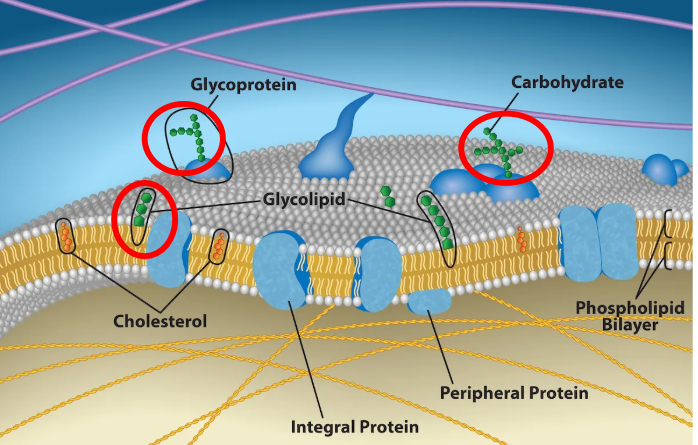
Carbohydrates
They are used for identification, located on the outside of proteins or lipids
Ex) They are like the fingerprints, cells look at the carbohydrate patterns
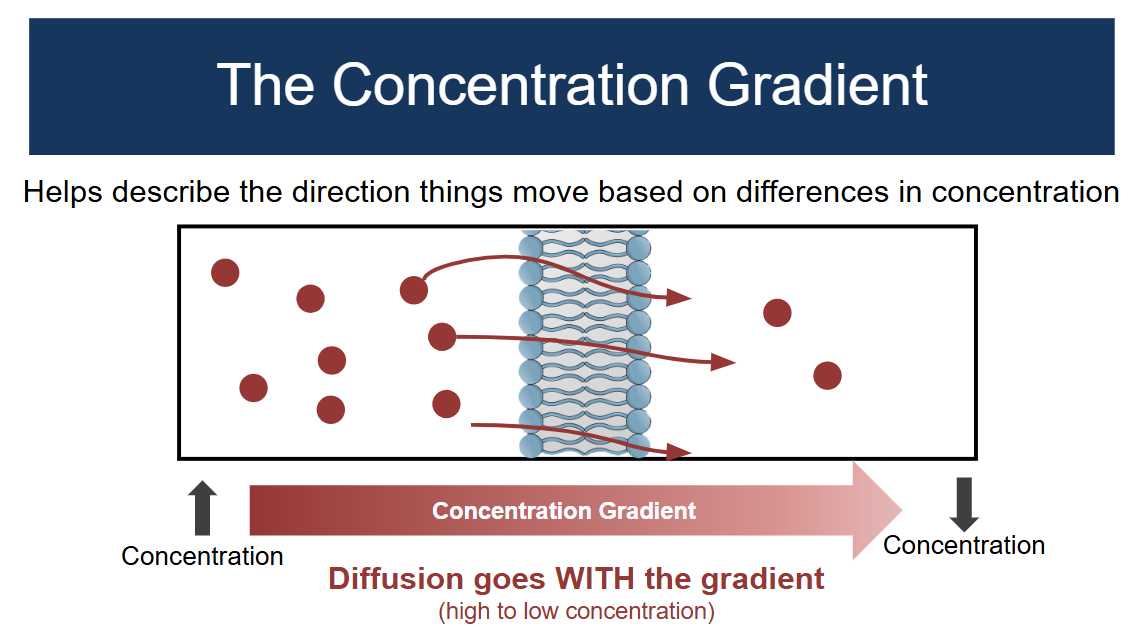
Selective Permeability
The ability to let specific things in and specific things out to keep the inside different from the outside
Things that move easily;
Nonpolar substances
Hydrophobic substances (Lipid-soluble substances)
Low molecular weight
Things that do not move easily;
Polar substances
Hydrophilic substances
High molecular weight
Charged ions
Chemoautotrophs
Organisms that consume inorganic compounds for energy
Ex) Bacteria that consumes heat for energy
Passive Transport
Doesn’t require energy, and things move with the grain via diffusion and concentration. They try to balance the two sides of the membrane
Active Transport
Does require energy and proteins to move things against the grain
Ex)
Concentration
How many things is in the cell
Tonicity
The solute concentrations in comparison to something else
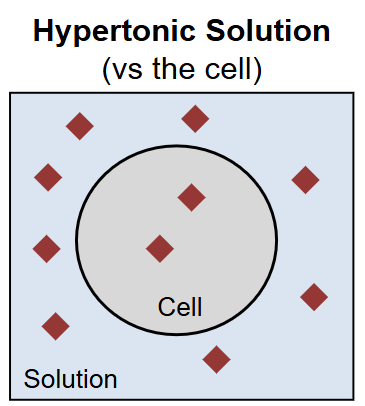
Hypertonic Solution
The solution is more concentrated than the cell
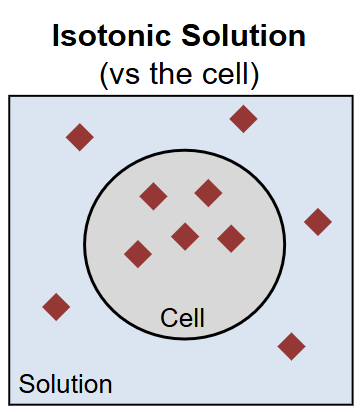
Isotonic
The solution is as concentrated as the cell
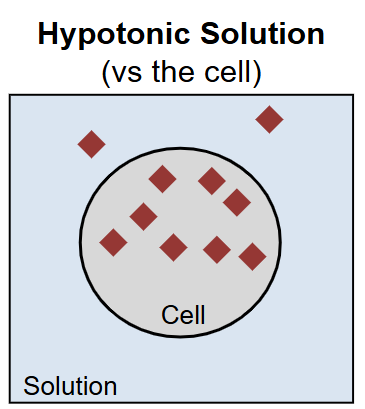
Hypotonic
The solution is less concentrated as the cell
Facilitated Diffusion
Things are aided to move with the help of proteins but still moves with the gradient
Ex) Carrier proteins or Channel proteins
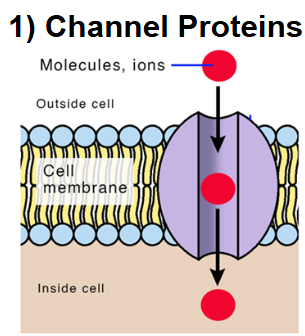
Channel Proteins
They make a channel/tunnel so the substance can flow right through
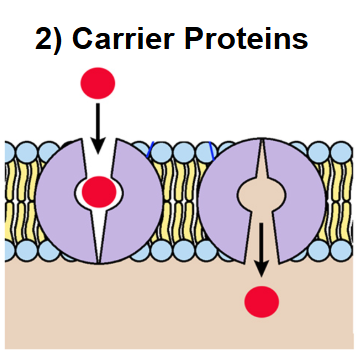
Carrier Proteins
They capture the substance within their sites and move them into the cell
Active Transport
Carrier proteins pump the substances in and out of the protein
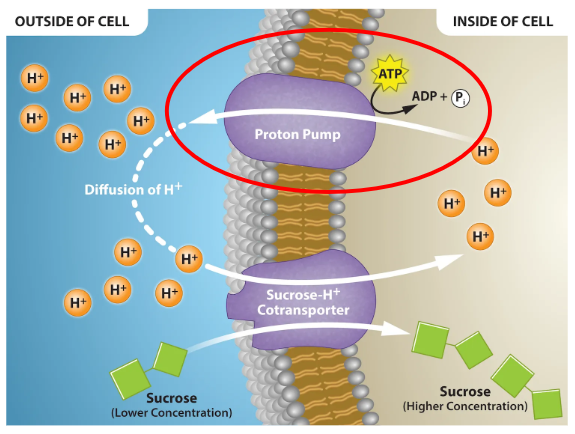
Primary Active Transport
Moves solutes against the gradient using ATP energy and protein transporters
Secondary Active Transport/Co-transport
Moves things using the changes in ions (electrochemical gradient) with protein transporters, not creating energy to do it but uses energy thats already there
Osmosis
Water moves from low concentration to high concentration
Membrane Components
Lipids, Proteins, and Carbohydrates
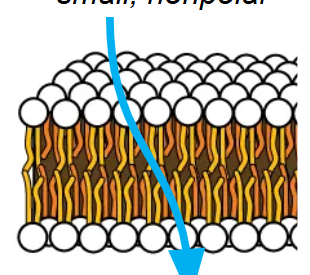
What moves across the membrane easily?
Substances that are nonpolar, hydrophobic (lipid-soluble), and have a low molecular weight
What do not move across the membrane easily?
Substances that are polar, hydrophilic (not lipid-soluble), have charged ions, and have a high molecular weight
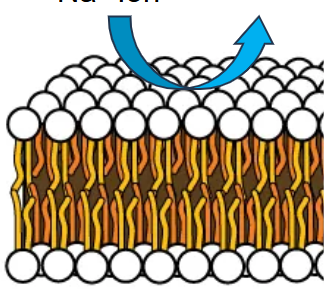
Diffusion
Does not require energy and works off using concentrations, moves from high concentration to low to make both sides equal
Electrochemical Gradient
Charge differences in the ions
Genome
A double strand DNA molecule
What are the properties inside the membrane
It’s made of fatty acids and is hydrophobic
What membrane component can be found on its surface
Proteins
How does water move in osmosis
From high concentration to low concentration
Does water move in an isotonic solution
Yes
Aquaporins
Proteins that create specific channels for water to easily move in and out of the cell
Crenated
Has a higher solute concentration outside of the cell compared to in the inside and this causes water to get drawn from out the cell, making the cell shrink in size
Lysed
Has a lower solute concentration outside the cell compared to the inside and this causes the cell to expand, making it bigger in size
Plasmolysed
In plant cells when there is a higher concentration outside than inside the cell, this causes water to move out, causing the cell to shrink.
Turgid
When a plant cell swells and expands because there is a lower concentration outside