INORG CHEM (CHEMICAL REACTION AND EQUATIONS
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
chemical reaction
is a process in which a substance is changed into two or more new substances
one new substance is produced as a result of chemical change
chemical equation
is a written statement that uses chemical symbols and formulas
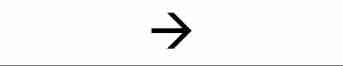
produce/yield

heat
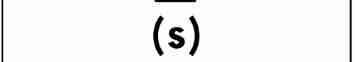
solid
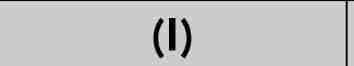
liquid
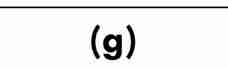
gas

gas product
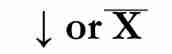
precipitate
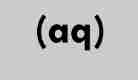
aqueous
reactant
a starting material in a chemical reaction
product
substance produced as a result of the chemical reaction
balanced chemical equation
same number of atoms of each element on each side of the equation
equation coeffecient
number that is placed to the left of the chemical formula
law of conservation of mass
only rearrangement of atoms occurs and that the product always contain the same number of atoms of each kind as do the reactants
5 chemical reactions
Combination reactions
Decomposition reactions
Displacement reactions
Exchange reactions
Combustion reactions
Combination reaction
a single product is produced from two or more reactions
Decomposition reaction
a single reactant is converted into two or more simpler substances
Displacement reaction
an atom or a molecule displace an atom or group of atoms from a compound
REACTIVITY SERIES (most to least)
P - lease (POTASSIUM)
S - END (SODIUM)
L - IONS (LITHIUM)
C - ATS (CALCIUM)
M - ONKEYS (MAGNESIUM)
A - and (ALUMINIUM)
Z - EBRAS (ZINC)
I - NTO (IRON)
L - OVELY (LEAD)
H - OT (HYDROGEN)
C - AGES ( COPPER)
M - ade of (MERCURY)
S - ILVER (SILVER)
G - OLD (GOLD)
P - LATEST (PLATINUM)
Exchange reaction
two substances exchange parts with one another and form two different substances
2 types of double displacement reactions
Ionic
Neutralization
Ionic reaction
at least one of the products is insoluble
Neutralization reaction
reaction of an acid with a base
Combustion reaction
substance and oxygen that evolves to heat and light
Hydrocarbons
binary compounds of carbon and hydrogen
most common type of compound that undergoes combustion
Oxidation reduction (REDOX)
there is a transfer of electrons from one reactant to another reactant
Non oxidation - reduction (NONREDOX)
NO transfer of electrons from one reactant to another reactant
bookkeeping system (oxidation numbers)
used to identify whether electron transfer ocurs in a chemical reaction
oxidation number
is a number that represents the charge an atom appears to have
4 KEY TERMS IN REDOX PROCESSES
oxidation
reduction
oxidizing agent
reducing agent
Oxidation
reactant in a chemical loses one or more electrons
Reduction
a reactant in a chemical reaction gains one or more electrons
VILEORA
VALENCE
INCREASE
LOSE
ELECTRONS
OXIDATION
REDUCING AGENT
VDGEROA
VALENCE
DECREASE
GAIN
ELECTRONS
REDUCTION
OXIDIZING AGENT
Oxidation
reactant in a redox reaction that causes oxidation
electrons gained
Reducing agent
reactant in a redox reaction that causes reduction of another reactant by providing electrons
electrons lost