Exam 1
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
prototype drug
The first drug in a drug class to be developed
Penicillin is the prototype of its drug class
generic vs trade names
Generic name > Brand name
Either name could be used for a prescription or dispensing however it can cause confusion
generic
chemical/official name of the drug independent of the manufacturer- it can also indicate the drug group
Ibuprofen
trade
manufacture's chosen name for a drug under a patent
Advil
controlled substances
DEA enforces the Controlled Substances Act registers individuals and companies legally empowered to handle controlled substances and regulates the documentation and handling of controlled substances
Narcotics, depressants, Stimulants, hallucinogens, Anabolic steroids
categorized by federal law due to the potential for abuse
Limitations on how much and when a pt can get the drug
categories of drugs
schedule I-V
schedule I
no medical use/high abuse: Heroin
schedule II
high abuse opioids/stimulants: Oxycodone
schedule III
less abuse but risk of dependence: steroids, ketamine, codeine
schedule IV
some abuse potential- benzodiazepines / phentermine
schedule V
contain a controlled in the product but small amount- Tylenol with codeine syrup, Lomotil
safeguards
Main goal of drug laws/standards is to protect the public, making sure drugs are safe and effective
The Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FDA) of 1938 requires that official drugs meet standards of purity and strength.
Regulates manufacturing, distribution, advertising and labeling of drugs
The Durham-Humphrey Amendment designates which medications must be prescribed by a health care professional and dispensed by a pharmacist
Gives the FDA power to enforce this
Public Health service regulates biologic products and the Federal Trade Commission controls OTC products
pharmacology
study of drugs that alter functions of living organisms
pharmacotherapy
use of drugs to prevent, diagnose, or treat signs, symptoms, and disease processes
includes lifelong therapy
drug safe administration
Regulated by:
Quality and Safety Education for Nurses (QSEN) competencies
National Patient Safety Goals from the Joint Commission
The Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP)
post marketing
Black Box Warning
High alert medications with serious side effects, example: Accutane
Additional steps involved to ensure safety
Look-alike drug errors
Beer’s criteria: Geriatric focused adverse effects
Lots of drugs that have adverse effects in >65 years old
Pregnancy warnings
X = no
10 rights of drug administration
Right drug
Right patient
Right route
Right dose
Right time
Right reason
Right documentation
Right patient education
Right evaluation
Right to refuse
drug development process
Phase 1- healthy volunteers: determines dose, route, toxicity, absorption, metabolism, excretion
Phase 2- few doses to those with the disease and compared to healthy people
Phase 3- expands research pool to different populations, different doses (double-blind placebo-controlled and other methods) determines benefits vs risk
Phase 4/Post-Marketing-drug is on the market with reporting on a larger scale, this is where you can find bigger issues
prescription
ordered in writing by licensed provider
over the counter
available for purchase without prescription
drug classification
Groups of medications are based on their effects on the body, their therapeutic use and chemical characteristics
ligand-gated ion channels
Amlodipine (Ca2+ channel blocker)
Antihypertensive
Channel opens or closes after ligand binds to the channel
Ca is important second messenger
GPCRs
Losartan (Ang-11 receptor antagonist)
G protein coupled receptors
G protein in cytosol become activated and go down their resepctive pathways for response
Biggest class of drug protein targets (50-60% of small molecule drug targets)
Enzyme coupled receptors
Abrocitinib CIBINQO (tyrosine kinase inhibitor)
Enzymatic activity after binding
nuclear receptors
Activated vitamin-D (i.e., calcitriol)
Fat soluble (lipophilic) so it can travel through the membrane
Within the cell
Near the nucleus and when bound it goes into the nucleus and code for proteins that do something
VDR – vitamin D receptor
pharmacokinetics
How the body processes a drug over time through different processes
getting the drug to the site of action
Kinetic – move
Drug moves through the body at different rates at the same time
Monitor PK through drug plasma concentrations
What the body does to the drug
Pharmacodynamics
How a drug affects the body at site(s) of action over time through different intensities
drug is at the site of action and how much is needed for the desired outcome
What the drug does to the body
At what dose do you see this specific response
Clinical pharmacokinetics
The use of pharmacokinetics principles to ensure safe and effective therapeutic management of drugs in patients
Increase efficacy and reduce toxicity
emax
Parameter of efficacy
At a plasma concentration of 12 mg/L there is the maximum efficacy of the drug
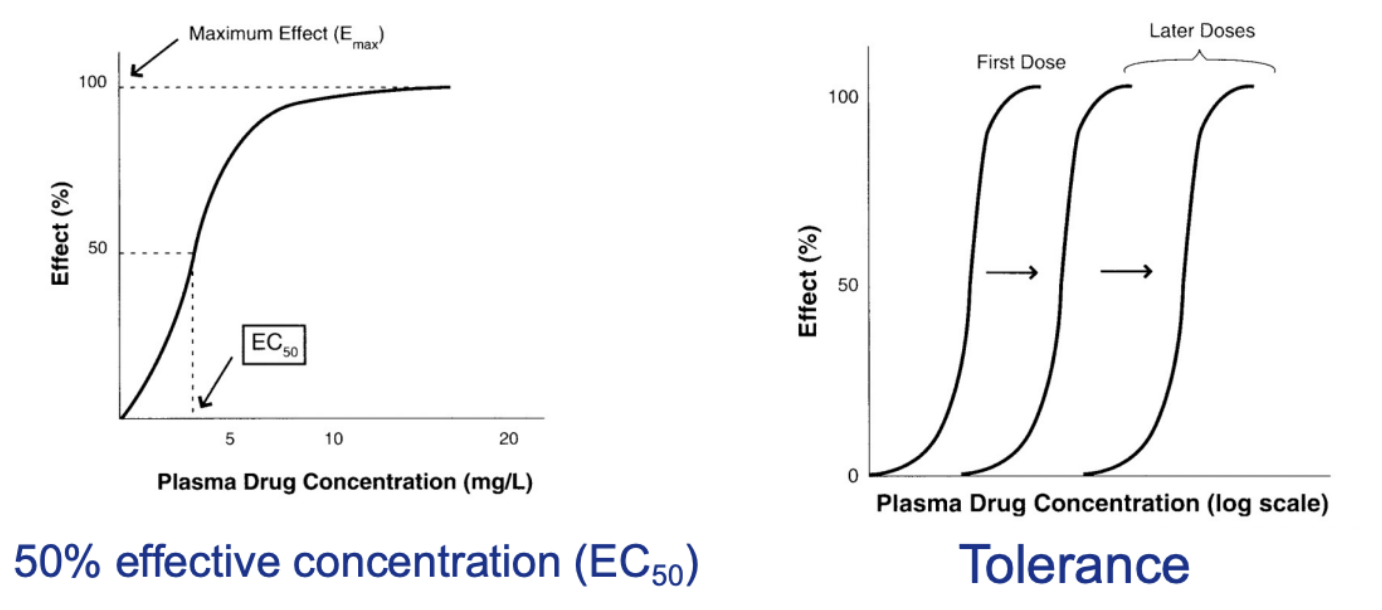
ec50
Effective concentration
Parameter of drug potency
That dose at that concentration produces 50% of the response of that drug
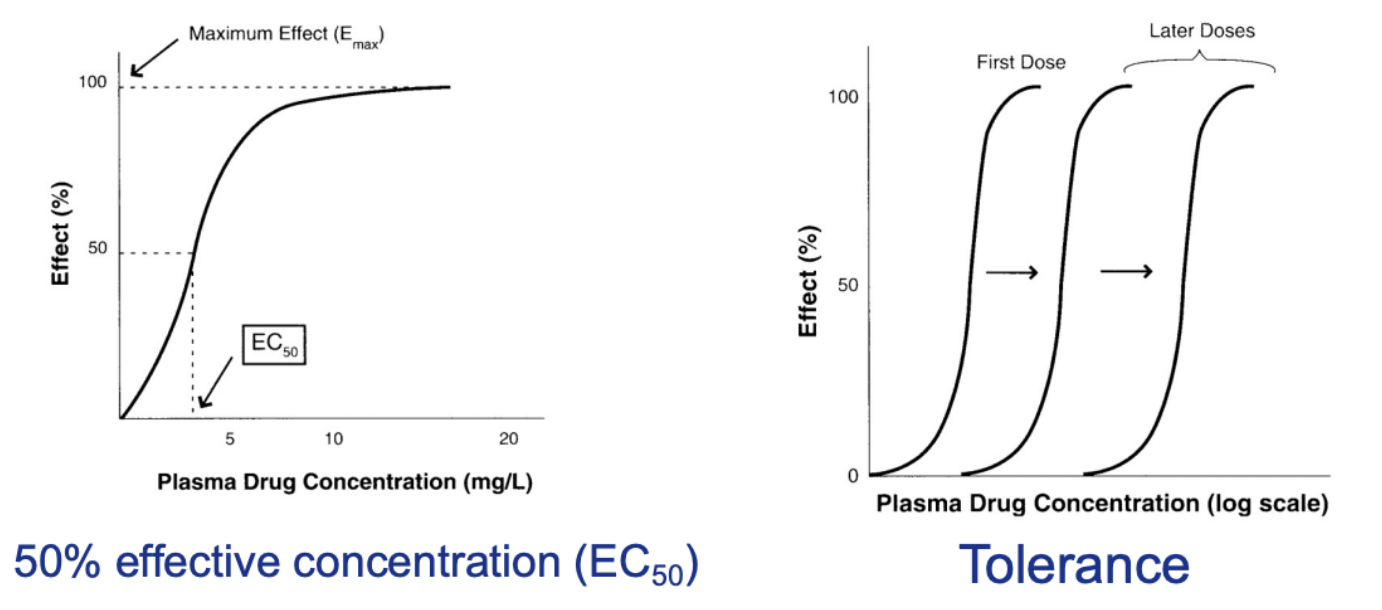
tolerance
Pharmacologic mechanism where cells become overstimulated due to chronic repeated stimulation from drugs
Opioids
Oxycodone tolerance develops quickly
Right shift in the curves illustrates the increasing tolerance to a drug
You need a higher and higher dose to get the therapeutic effects
Stimulants
Ethanol (alcohol)
Hepatocytes turn on transcription to make more alcohol dehydrogenase to breakdown the alcohol
absorption
How is it getting to the plasma
Most oral drug absorption occurs in the small intestine (high SA and permeable membrane)
Two primary processes
Active transport
Done by a protein
Goes against a gradient
Passive diffusion
High to low concentration
Not required when a med is given IV
factors affecting absorption
Surface area
Larger area -> higher drug absorption
Nature of epithelial membranes
Transport proteins can prevent absorption or kick out meds
Presence of bile and mucus
Thicker mucus -> lower absorption
Blood perfusion
Higher perfusion -> higher absorption
Differences in luminal pH along the GI tract
Stomach (pH 1—2), duodenum (pH5-6), small intestine (pH ~7.5) and colon (pH 7-8)
Ionized drug will not travel as fast as its unionized form
distribution
In plasma where does it go
Out of vasculature?
What rate?
To what extent does it extend out the vasculature
The volume of distribution (Vd) = how large an area in the body the drug has been distributed into after the dose is given
Based on the properties of the drug
NOT ACTUAL VOLUME OF DRUGS OR TISSUES
Factors that affect distribution

factors affecting distribution
Physical and chemical properties
Lipophilicity: lipophilic vs hydrophilic
Lipophilic easily go through the membrane and leave vasculature easily
Will be drawn away from aqueous vasculature and be drawn to lipids especially into adipose tissue
Small lipophilic drugs can penetrate the brain
“Sticky icky” = lipophilic
Molecular weight: low vs high
How big it is
Solubility: high aqueous solubility vs low aqueous solubility
Does it have to go into a solution before absorption
Ionization status: ionization vs unionization
Interactions with membranes and tissues
Extent of protein binding
Low protein binding vs. High protein binding
Albumin binding drugs will not leave vasculature
metabolism
Drug can accumulate in body if not metabolized
Increases likelihood of side effect
CYP3A4
Grapefruit juice can compete with medications
Process by which a drug is converted from its original chemical structure (parent drug) into other forms (metabolites)
Wants to keep the drug into the plasma so it can be excreted and no accumulate in the body
Gut and liver are primary sites for metabolism as they contain many metabolizing enzymes
First pass metabolism
Blood from the stomach travels to the liver before it reaches the rest of the body
Occurs in the liver
Contains transporters and metabolizing enzymes that catalyze major reactions (i.e., oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, conjugation)
Dramatically reduces the bioavailability of oral drugs
Certain drugs with extensive first pass metabolism can bypass by given non-oral routes
phase 1 enzymes
Conversion of parent drug to a more polar metabolite
Reactions
Oxidation
Reduction
Hydrolysis (prodrug to active drug)
Catalyzed by cytochrome p450s, flavin containing monooxygenases, and epoxide hydrolases
Introduce functional groups to increase water solubility and drastically alter pharmacological activity
CYP450 enzymes
Superfamily with families and subfamilies with increasing gene sequence similarities
Work together with drug transporters to influence systemic bioavailability
CYP3A4/5 family is involved in the majority of Phase 1 metabolism
phase 2 enzymes
After phase 1
The metabolites need to have oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur atoms to accept hydrophilic moiety
UGT and CYP3A4/5 are involved in the metabolism of more than 75% of drugs
elimination
Irreversible removal of drugs from the body
Excretion
Pee or fecal elimination
Exhalatory elimination
Sweat elimination
More drug -> faster rate of elimination
Up to a certain point
Rate of elimination will stop (point of saturation) -> accumulation in the body
clearance
rate of drug removal in a certain volume of plasma over a certain amount of time

bioavailibility
Extent to which a drug is absorbed into the systemic circulation
Fraction of a dose PO that reaches systemic circulation
Percentage of drug absorbed from extravascular relative to IV administration
Drugs with good absorption = high bioavailability (> 70%)
Drugs with poor absorption = low bioavailability
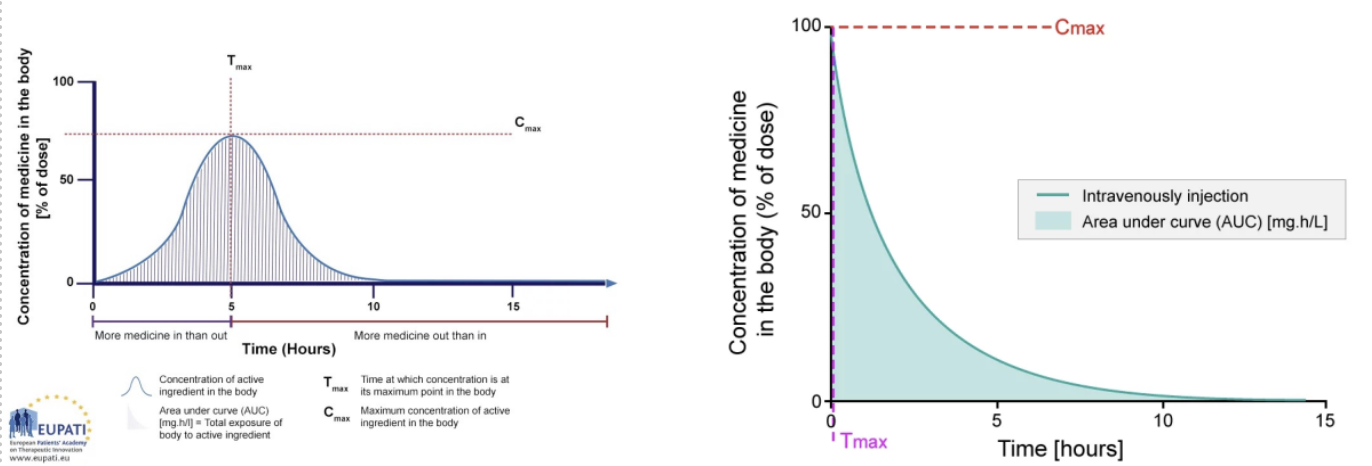
Area under the curve (AUC) = most reliable measurement of a drugs bioavailability
Represents the amount of the drug that has reached the systemic circulation
plasma concentration
AUC = area under the curve
total exposure measures bioavailability
Cmax = maximum concentration of drug in the body
Tmax = time at which the drug concentration is at its maximum
There can be a lag time with oral meds
Above minimum effective concentration and below minimum toxic concentration is the therapeutic window
Extended-release Cmax is lower and Tmax is later
Immediate release Cmax is higher and Tmax is quicker
glomerular filtration
Affects all solutes of appropriate size
Influenced by protein binding
Passive and unidirectional
secretion
Occurs mostly in the proximal tubule
Requires a carrier protein to bring drugs out
Saturable process
Not influences by protein binding
reabsorption
Occurs all along nephron
Passive by nature & active
Favors lipid soluble, unionized drugs
Weak acids & weak base depend on the urine pH and the pKa of the drug
zero order elimination
The rate of drug elimination is independent of drug concentration
The concentration does not affect how long it will take to leave
eg if 5mL takes 1 hour to leave 10mL will take one hour
Dangerous
Alcohol zero order processes is vomiting (protective mechanism)
first order elimination
The rate of drug elimination is dependent of drug concentration
eg if 5mL takes 1 hour to leave then 10mL will take 2 hours
produces higher concentration
ANS
It regulates involuntary physiologic processes:
Heart rate
Blood pressure
Pupil diameter
Respiration
Digestion & Excretion
Glandular activity
Renal function
Conversion of glycogen to glucose
Not under direct conscious control
Some features include:
High-level integration in the brain
The ability to influence processes in distant regions of the body
Extensive use of negative feedback
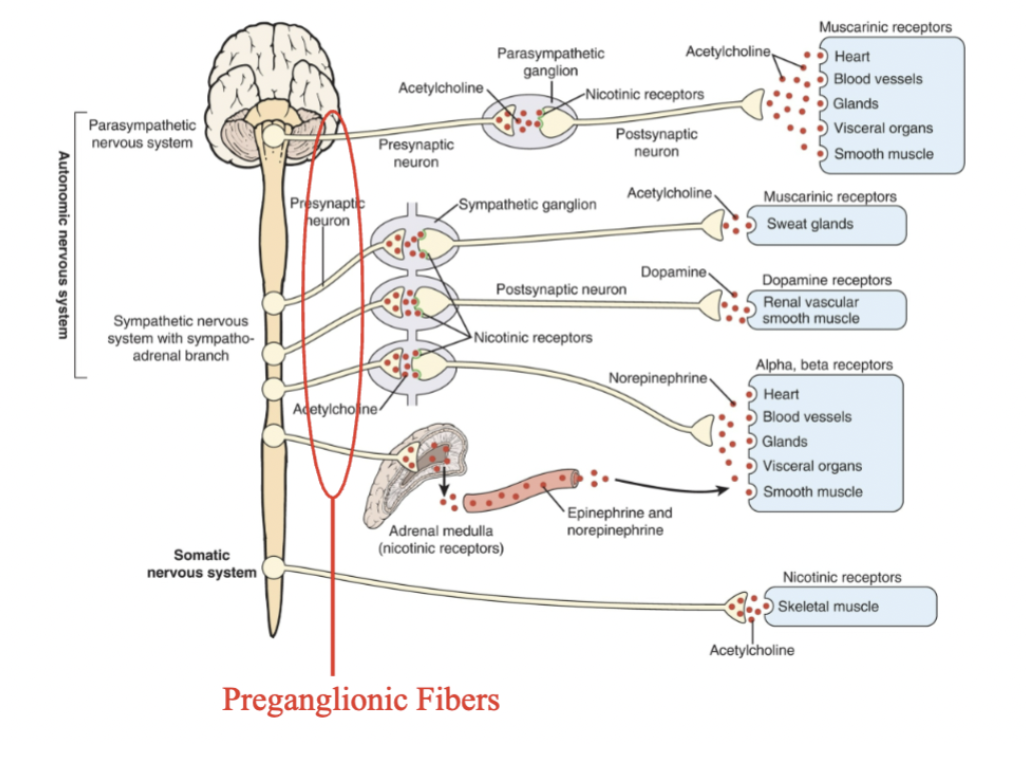
preganglionic fibers
Located outside the CNS + exit from areas of the spinal cord
Preganglionic fibers originate from cell located in the brainstem or spinal cord and project to a ganglion
Apart of SNS and PNS
All preganglionic fibers use acetylcholine (ACh) as their neurotransmitter
The ACh acts on nicotinic receptors located on the ganglion cells.
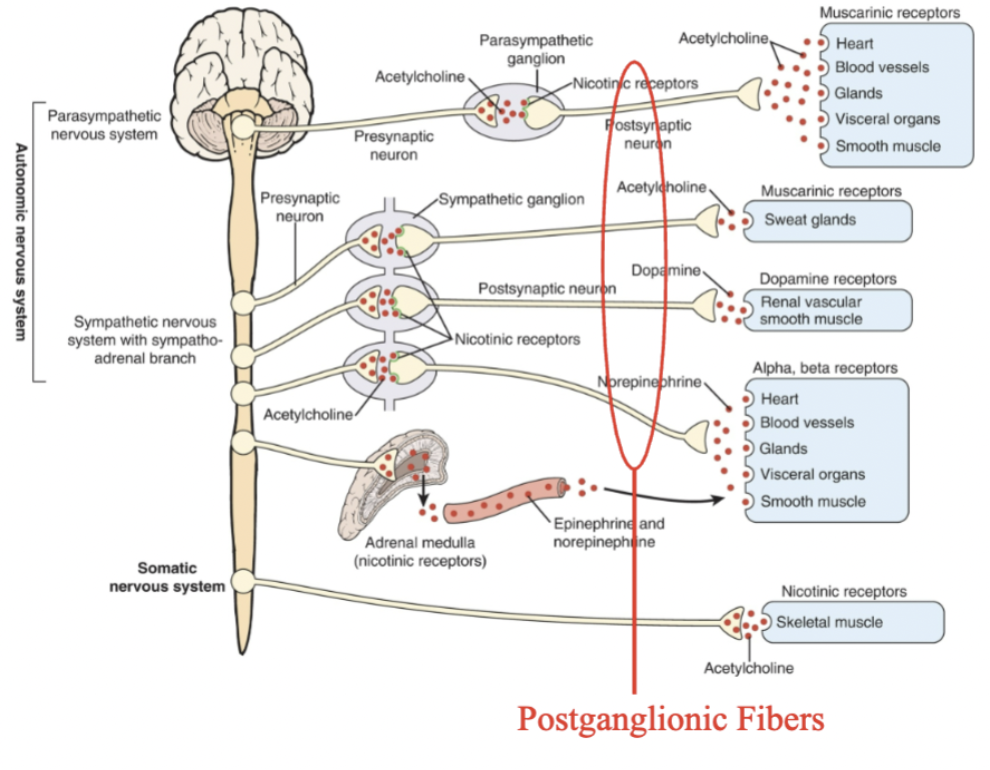
post ganglionic fibers
Postganglionic fibers of the sympathetic NS
originate from ‘ganglia’ located either in a ‘chain’ next to the spinal cord (paravertebral) or located along the midline in front of the heart and spinal column (prevertebral).
These fibers project to the end organs.
Heart, stomach, etc.
Postganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic NS originate from cells located near the end organ
Neurotransmitters released determine the kind of response
Most postganglionic fibers of the SNS use norepinephrine (NE) as their neurotransmitter.
NE acts on adrenergic receptors located in the end organs.
One exception is SNS innervation of sweat glands which uses ACh
Postganglionic fibers of the PNS use ACh as their neurotransmitter
The ACh acts on muscarinic receptors located in the end organs
ionotropic receptors
Form ion channel
Activation alters membrane conductance.
metabotropic receptors
Act through G-proteins.
Can activate or inhibit second messenger systems. Also can be associated with an ion channel
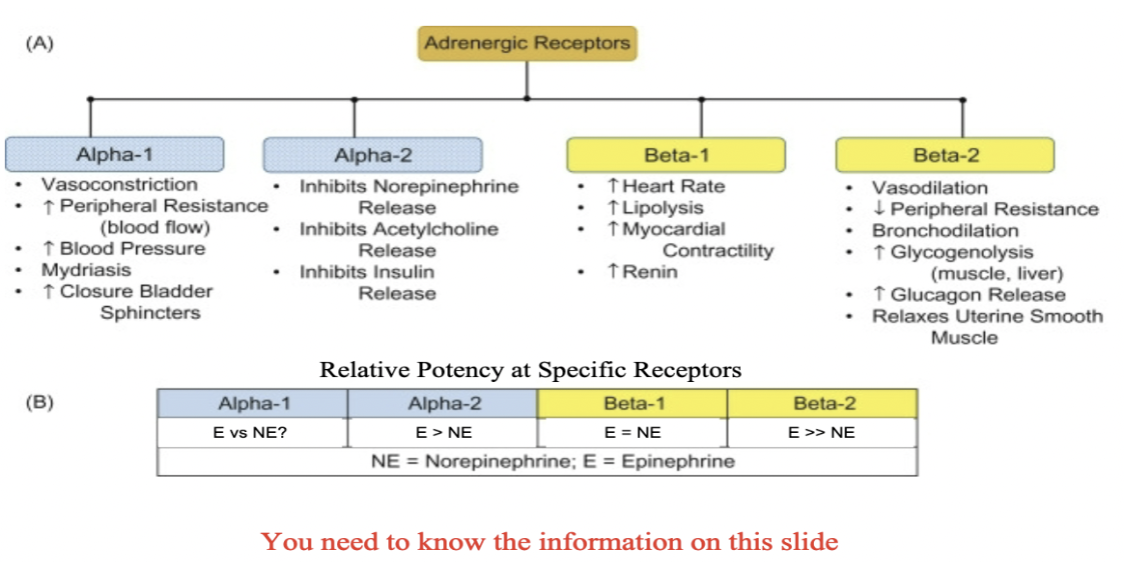
adernergic receptors
All of the adrenergic receptors are metabotropic receptors.
Both adrenergic and cholinergic receptors have multiple receptor subtypes
Adrenaline (epinephrine) or norepinephrine are receptor ligands to either a1, a2, or ß adrenergic receptors
Anything that stimulates a1 causes increase of BP and inhibition causes decrease in BP
increased intracellular Ca2+ and subsequent
smooth muscle contraction when stimulated
B1 causes HR to increase which increases BP
B2 in bronchial tubes – causes muscle relaxation (b2 agonist causes bronchial to relax and dilates blood vessels)
Opposes a1 effect
cholinergic receptors
Most of the cholinergic receptors are metabotropic receptors except the nicotinic receptors
All nicotinic receptors are ionotropic.
muscarinic are metabotropic
Both adrenergic and cholinergic receptors have multiple receptor subtypes
Receptors also are classified as nicotinic or muscarinic, based on whether they have high affinity for nicotine or muscarine
sympathomimetic agents
mimic activation of the SNS by increasing adrenergic receptor activity.
Direct Agonists- Directly interact with and activate adrenoceptors (e.g., NE, Epi, clonidine (⍺ 2), isoproterenol (ß), albuterol (ß2), etc...)
Indirect Agonists - Dependent on ability to enhance the actions of endogenous catecholamines
By enhancing release from nerve terminals (e.g., reserpine, amphetamines, tyramine)
By blocking re-uptake/removal of the transmitter (cocaine, methylphenidate)
By preventing enzymatic degradation of the neurotransmitter (MAOIs, COMT inhibitors)
sympatholytic agents
reduce activation of the SNS by reducing adrenergic receptor activity, by blocking the actions of NE and Epi on adrenergic receptors.
Beta blockers (propranolol, metoprolol, atenolol)
⍺1 (e.g., prazosin (Minipress®)) and ⍺ 2 (e.g., yohimbine) antagonist
effects of SNS activation
Increased heart rate, arterial blood pressure, and cardiac output
Increased blood flow to brain, heart, and skeletal muscles
Increased blood glucose
Pupil dilation
Increased sweating
Increased rate of cellular metabolism
Increased rate and depth of respiration
Reduced saliva production
Reduced gut motility and urine flow
nicotinic receptors
Nicotinic receptors are ionotropic and pentomeric
Primarily act as sodium channels.
Can also increase permeability to Ca2+
in skeletal muscle
muscarinic receptors
There are 2 subtypes, M1 (includes M1, M3 and M5 receptors) and M2 (includes M2 and M4 receptors).
In the tissues
Ach acts on them
anti-muscarinic drugs = dries out pt
parasympathomimetic agents
mimic activation of the PNS by increasing muscarinic cholinergic receptor activity.
Direct Agonists- Directly interact with and activate muscarinic cholinergic receptors (e.g., ACh, methacholine, bethanechol, muscarine, pilocarpine, etc...)
Indirect Agonists – Enhance ACh effects by inhibiting cholinesterase thereby blocking degradation (e.g., neostigmine, physostigmine, donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine, etc...
parasympatholytic agents
reduce activation of the PNS by:
Blocking the actions of ACh on muscarinic receptors (e.g., atropine, scopolamine, and other muscarinic receptor antagonists)
Block cholinergic effects
effects of PNS
Decreased heart rate, arterial blood pressure, and cardiac output
Decreased blood glucose
Pupil constriction
Increased sweating & tearing
Increased saliva production
Increased gut motility and urine flow
Decreased rate of cellular metabolism
Bronchoconstriction
prefrontal cortex
Regulates thought in terms of short-term and long-term decision making
Allows humans to plan and create strategies, and to adjust actions and reactions to situations
Connects emotions with decision-making
Allows humans to pull together disparate but related strands of thought when learning or evaluating complex concepts or tasks
Houses active, working memory, a form of short-term memory in which trial- unique events are temporarily stored and manipulated in consciousness
Essential for tasks in which memory for recent events is used in decision-making
Executes social judgements
Helps to focus thoughts
Enables humans to pay attention, learn, and concentrate on goals
D
A nurse practitioner (NP) has just changed a patient’s medication from an oral form to a patch formulation to avoid the first-pass effect. The NP has explained it to the patient, but the patient still has questions and asks the nurse to explain again what is meant by the first-pass effect. The nurse would be most correct in explaining that this has to do with how
A. drugs initially bind to plasma proteins
B. initial renal function is involved in drug excretion
C. the way drugs first reach their target cells
D. initial metabolism of an oral drug occurs before it reaches the systemic circulation
C
A nurse is reading a research report about use of a medication that describes the pharmacokinetics of a particular medication that a patient is taking. Pharmacokinetics involves
A. drug effects on human cells
B. drug binding with receptors
C. drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination
D. drug stimulation of normal cell functions
C
A nurse is caring for a man who has worsening liver disease. In monitoring his medication, it is important to know that a patient with liver disease may have impaired drug
A. absorption
B. distribution
C. metabolism
D. excretion
D
A nurse is looking up information about the effects of a drug on different receptors. Characteristics of receptors include which of the following?
A. They are carbohydrates located in cell membranes or inside cells
B. They are constantly synthesized and degraded in the body
C. They bind with molecules of any drug circulating in the bloodstream
D. They regulate the actions of all drugs.
B
A patient with an overdose of an oral drug usually receives which of the following?
specific antidote
activated charcoal
syrup of ipecac
strong laxative
D
The mother of a 14-month-old girl calls a nurse working in a pediatric clinic and reports that her daughter ingested an unknown number of sleeping pills about 4 hours ago and is now drowsy. The mother asks what she should do. The best response to give the mother is
“Administer a dose of syrup of ipecac to ensure vomiting”
“Call the Poison Control Center immediately”
“Administer a strong laxative and observe for a response”
“Call 911 to transport your daughter to the nearest emergency department”
A, B, C
Differences in CYP-450 drug-metabolizing enzymes are known to cause genetic variation in the drug metabolism of certain drugs that increase the risk of adverse effects. These include which of the following? (Select all that apply.)
CYP2D6 metabolism of several antidepressant, antipsychotic, and beta-adrenergic blocker drugs that increases the risk of drug accumulation and adverse effects.
CYP2D6 metabolism of codeine in individuals who are ultrarapid metabolizers. The conversion of codeine to morphine occurs quickly and poses a risk of serious adverse effects, such as respiratory depression.
CYP2C19 metabolism in some individuals of Asian descent. This may cause decreased drug metabolism of diazepam, omeprazole, and some antidepressants leading to adverse effects.
Individuals with a deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, who may have hemolytic anemia when given antimalarial drugs, sulfonamides, analgesics, antipyretics, and other drugs.
B
A physician writes an order using the abbreviation MS. The order states “MS 10 mg IV push every 6 hours as needed for pain.” According to The Joint Commission’s “Do Not Use” list, what is the potential problem in this order?
A. The order does not include a dosage.
B. The drug could be magnesium sulfate or morphine sulfate.
C. The potential problem is minimal, and the order is clear
D. The order does not include the route.
C, D
2. A prescriber has written an order for an oral antihypertensive medication for a patient who is in rehabilitation following a stroke. Prior to administering the medication, which of the following nursing interventions is most important? (Select all that apply.)
A. allowing the patient to take the medication with thickened liquids
B. placing the patient in the sitting position
C. assessing the patient’s blood pressure
D. assessing the patient’s ability to swallow
A
A prescriber has written an order for levothyroxine sodium 50 mg/day by mouth. The nurse knows that the standard dose is 50 mcg. What action should the nurse take?
A. Call the prescriber and question the order.
B. Administer 50 mcg instead.
C. Consult the pharmacist about the order.
D. Ask the patient what he or she usually takes.
C
4. The nurse is administering the first dose of an anti-infective agent. Which of the following assessments should the nurse make prior to administering the anti-infective agent?
A. Assess the patient’s temperature.
B. Assess the patient’s level of consciousness.
C. Assess whether the patient is allergic to any anti-infective agent.
D. Assess whether the patient has taken the medication previously.
D
5. Which of the following nursing actions will prevent adverse drug events?
A. Use only the trade name when documenting medications.
B. Crush long-acting medications if the patient has dysphagia.
C. After receiving a verbal order, administer the medication and then write down the order.
D. Use bar code technology according to institutional policy
C
A nurse is administering an elixir. Which of the following measures is appropriate?
A. microgram
B. milligram
C. milliliter
D. kilogram
A
The nurse has administered lacosamide to the wrong patient. What is the first action the nurse should take?
A. Assess the patient’s vital signs and level of consciousness.
B. Notify the physician.
C. Fill out an incident report.
D. Call the respiratory therapist for administration of oxygen.
C
A patient is to receive lamotrigine 300 mg by mouth two times per day. The pharmacy has delivered 50-mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer each time?
A. 2 tablets
B. 4 tablets
C. 6 tablets
D. 8 tablets
D
9. A nurse is preparing to administer a subcutaneous injection. What size needle should the nurse use to administer the injection?
A. 18 gauge
B. 20 gauge
C. 23 gauge
D. 25 gauge
B
10. A patient is to receive an intramuscular injection of ketorolac. Which of the following muscles should be avoided?
A. deltoid
B. Dorso gluteal
C. ventrogluteal
D. vastus lateralis
B, D
The patient receives regular insulin 5 units subcutaneously. To what degree is the syringe held for the injection? (Select all that apply.)
A. 30 degrees
B. 45 degrees
C. 60 degrees
D. 90 degrees
D
How is a medication delivered by piggyback administered?
A. It is pushed into the IV line.
B. It is retrograded into the IV line.
C. It is injected intramuscularly after another medication.
D. It is mixed with 50 to 100 mL of IV fluid in a separate container.
A
During an initial nursing assessment, the patient reports that he is allergic to a particular medicine. What should the nurse ask the patient?
A. What symptoms occurred when you had the allergic reaction?
B. Did you need to take epinephrine (Adrenalin)?
C. Did your physician think this information needed to be communicated?
D. Have you ever overdosed on this medication?
C
14. How do nursing interventions increase safety and effectiveness of drug therapy?
A. by avoiding the use of nondrug measures during drug therapy
B. by using multiple drugs to relieve most symptoms or problems
C. by teaching patients about their drug therapy
D. by avoiding excessive instructions
B
What should the nurse keep in mind when evaluating a patient’s response to drug therapy?
A. Few drugs cause adverse effects.
B. Drugs may cause virtually any symptom or problem.
C. Patients always report adverse effects.
D. Therapeutic effects are more important than adverse effects.
B
What should the nurse keep in mind when evaluating a patient’s response to drug therapy?
A. Few drugs cause adverse effects.
B. Drugs may cause virtually any symptom or problem.
C. Patients always report adverse effects.
D. Therapeutic effects are more important than adverse effects.
A, B, C
Activation of the sympathetic nervous system will result in which of the following? (Select all that apply.)
A. increased rate and depth of respiration
B. pupil dilation to aid vision
C. increased blood pressure and heart rate
D. increased urine output
A
2. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous systems?
A. Acetylcholine activates muscarinic receptors.
B. Activation of the sympathetic nervous system causes a decrease in blood pressure.
C. Acetylcholine activates adrenergic receptors.
D. Norepinephrine activates cholinergic receptors.
A
3. The sympathetic nervous system is also called the
A. fight-or-flight system
B. eat-drink-and-rest system
C. autonomic nervous system
D. somatic nervous system
A, B, C
A drug that has the same effects on the human body as stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system is called which of the following? (Select all that apply.)
A. sympathomimetic agent
B. adrenergic drug
C. beta-adrenergic agonist drug
D. alpha-adrenergic blocking agent
A, B
When the body is exposed to high concentrations of substances that stimulate their function, the resulting decrease in beta-adrenergic responsiveness is called which of the following? (Select all that apply.)
A. desensitization
B. downregulation
C. fight or flight
D. norepinephrine reuptake
A
During a teaching session for a patient who is receiving a respiratory inhaler that stimulates beta2 receptors in the respiratory tract, the patient asks why he needs to take the inhaler. The best response by the nurse is that the effect of a beta2 receptor is
A. prevention of bronchospasm
B. reduction of sputum production
C. maintenance of respiratory rate
D. suppression of cough
A, B, D
Functions stimulated by the parasympathetic nervous system include which of the following? (Select all that apply.)
A. digestion
B. excretion
C. catabolism
D. anabolism
A
8. A drug that has the same effects on the body as stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system is described as
A. cholinergic
B. sympatholytic
C. antiadrenergic
D. parasympatholytic
A, B, C, D
Activation of the parasympathetic system will result in which of the following? (Select all that apply.)
A. dilation of blood vessels in the skin
B. decreased heart rate
C. increased motility of the gastrointestinal tract
D. constriction of smooth muscle of bronchi
when prefrontal cortex is damaged
very susceptible to damage
Personality can change drastically
For example, someone who had been outgoing can become quiet and withdrawn after suffering injury to the pre-frontal cortex
Can negatively impact someone’s ability to assess situations or perform tasks, especially if they have a moral or ethical aspect to them
Can be unable to discern appropriate behavior, may experience reduced inhibitions, or may experience extreme emotional distress, such as paranoia, anxiety, euphoria, and irritability
Can produce impairments of working memory (i.e., ability to hold information online and use in decision-making)
primary motor cortex
precentral gyrus
Part of the Pyramidal Motor System
Provides direct innervation of motor neurons in spinal cord, brainstem, and cranial nerve nuclei
Is responsible for initiation of voluntary movements
Is a crossed system – cells on the right side of the brain control muscles on the left side of the body
Damage causes paresis or paralysis on the opposite side of the body
extrapyramidal motor system (EMS)
Second motor system in the brain (unconscious system)
Subcortical
Involves multiple structures
Responsible for modulating voluntary and involuntary movements
Postural adjustments
Fine-tuning motor movements
Motor learning (i.e., procedural memory)
Some extrapyramidal projections are crossed, and some are uncrossed
EMS damage
Some drugs can cause these symptoms
Antipsychotic medications (more common with first generation)
Damage to EPS can result in very debilitating movement disorders
Tremors
Rigidity
Loss of gait
Uncontrolled movements (dyskinesias)
Inability to make postural adjustments
Disruption of autonomic functions
hippocampus
Located in medial temporal lobe
Required for declarative memory consolidation and the formation of long-term declarative memories
Implicated in maintenance of cognitive maps for navigation
Damage is associated with a profound anterograde amnesia (inability to learn new information)
Declarative memory
Names, dates of exams, categories of things
amygdala
Two almond-shaped masses of neurons on either side of the thalamus at the lower end of the hippocampus
Involved in perceptions of fear and anxiety, defensive behaviors, emotional learning, and in social functions such as mating.
Heavily interconnected with hippocampus, hypothalamus, sensory nerves, and with insular cortex
Damage causes dysregulation of emotions and is associated with depression, aggression, anxiety, etc