WHOLE SECTION 1: SYSTEMS ARCHITECTURE, MEMORY, AND STORAGE
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What are the two groups for memory and storage?
Primary and Secondary storage
What is offline storage?
Storage devices which can be stored away from the computer
What is RAM?
Random Access Memory
Why do we need primary storage?
Act as a temporary storage for programs and data while the program is being executed
Why do we need main memory to store the programs currently being executed?
The computer would be really slow
What is virtual memory?
A portion of the hard disk designated to function as additional RAM
Volatile
Lose all contents?
Out of RAM and ROM which is volatile?
RAM
What is the bootstrap loader (booting)?
A small program that loads the operating system
What is ROM?
Read Only Memory
What are the characteristics of RAM?
- Volatile
- Stores user data which is currently in use
- Memory can be written to or read from
What are the characteristics of ROM?
- Non - volatile
- Used to store bootstrap loader
- Memory can only be read from and NOT written to
What are the main factors affecting CPU performance?
- Clock Speed
- Cache Size
- Number of cores
What is clock speed?
The speed at which a processor operates
What is clock speed measured in?
Hertz (Hz)
What is cache memory?
It is HIGH SPEED memory attached to the CPU
How much cache do we use?
Small amounts
Where is cache memory held?
Between main memory and the CPU
Why does cache improves processor performance?
Has data and instructions that can be held in cache and made available very quickly
How many levels of cache are there?
Level 1 = extremely fast but small (2 - 6KB)
Level 2 = fairly fast and medium sized (265KB - 2MB)
Level 3
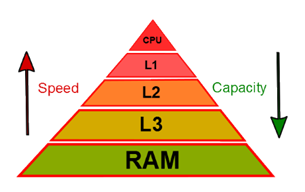
What is a dual - core processor?
Has two processing units within the CPU
Why is having many cores good?
Parallel processing can take place
Why is having many cores not good?
The computer may not be designed to use multiple cores therefore not faster
What is an embedded system?
A small computer built into a piece of equipment designed to perform a specific function
What are some examples of embedded systems?
Dishwashers
What are some characteristics of embedded systems?
- Reliability
- Minimal resources such as ROM etc.
- Limited operating system (only able to run one application)
- Simple user interface (buttons or no interface)
- Sensors designed to measure external stimuli and react accordingly
What are the three types of secondary storage?
Optical
What is magnetic storage?
Mechanical parts move over the disks surface to read and write data magnetically
What are the basic features of a hard disk (magnetic storage)?
- Disks contains concentric circles called tracks
- Each track is divided into sectors
- Disks heads mounted on mechanical arms read and write the data
Parts of a hard disk drive (magnetic)
components including platters, read/write heads, actuator arms, and spindle motor.
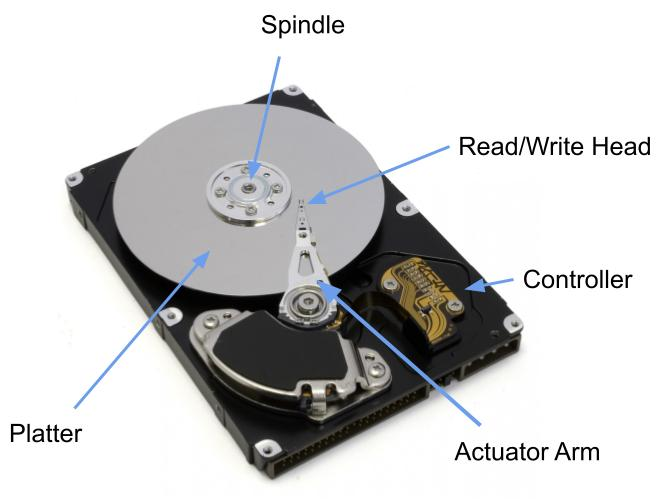
What storage capacity do hard disks have (magnetic)?
Very large storage capacity
How expensive is a hard disk drive (magnetic)?
They are a very cheap form of storage compared to solid state drives
How are portable hard disks (magnetic) connected to a computer?
Via a USB port
What was the primary magnetic secondary storage used at the beginning of the computer's creation?
Magnetic tape
Examples of magnetic storage
Floppy disk
What do cassettes require to be read?
A special tape-drive for reading and writing to the tape
How are magnetic tapes read? What order?
Magnetic tape is read/written sequentially
What is the speed of magnetic storage?
Slow when finding specific data stored on it but
has a Fast read/write speed when in the correct place to begin
How durable is magnetic storage?
When stored properly they are quite durable
What is optical storage?
Lasers read and write data using light
Examples of optical storage
CD
What formats can optical storage appear in?
ROM (read only memory)
How is data stored in optical storage?
Data is stored in pits
How do CD's work?
A laser beam passes over the pits and lands where the level of reflection is measured
What is the difference between CD's and Blu-rays?
A CD has bigger pits and lands as red light has a larger wavelength
The smaller Blu-ray pits and lands allow it to store more data and use a more precise wavelength
How expensive is optical storage?
Cheapest secondary storage
How durable is optical storage?
More durable than magnetic and less durable than solid state
How portable is optical?
Very portable
What kind of capacity does optical storage have?
50GB
What is solid state storage?
Data is recorded onto solid memory chips without any moving parts
How do solid state drives work?
A flow of electricity forcing electrons into floating gates between 2 oxide layers
This causes a change in the charge in the floating gate which can be measured as a 0 or 1
Oxide layers deteriorate over time
They have a limited number of read/write cycles
Examples of solid state
Memory sticks
What are the advantages of solid state storage?
- Very quick access to data
- No moving parts (durable and reliable)
- No noise (great for videoing)
- Low power (doesn't drain your phone battery)
- No need to defragment
What are the disadvantages of solid state storage?
- Limited number of read/write cycles
- More expensive per byte of storage than other types of storage
How expensive is solid state storage?
Very expensive
Is secondary storage volatile?
No
basic model of a computer system
What is Von Neumann architecture?
The idea of holding both programs and data in memory
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
hardware that executes programs and manages the rest of the hardware
Cache
very fast memory
What does the processor do to run the program?
Fetch
What does the control unit do?
- Controls the execution of instructions in the correct sequence
- Decodes instructions
- Regulates and controls processor timings using regular pulses from the system clock
- Sends and receives control signals to and from other devices within the computer
Arithematic Logic Unit (ALU)
- Logic operations (AND
Types of registers
MAR
What does the MAR do?
Memory Address Register - holds the address of the instruction or piece of data to be fetched or stored
What does the MDR do?
Memory Data Register - holds the data or a program instruction temporarily when it is fetched from memory or is to be sent to memory
What does the PC do?
Program Counter - holds the memory address of the next instruction to be processed
What does the ACC do?
Holds the results of calculations from the ALU
What are the main factors affecting CPU?
- Clock speed
- Cache size
- Number of cores