Ch. 21: Antidepressants
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Which meds are SSRIs?
sertraline (Zoloft)
citalopram (Celexa)
escitalopram (Lexapro)
fluoxetine (Prozac)
paroxetine (Paxil)
What meds are SNRIs?
duloxetine (Cymbalta)
venlafaxine (Effexor)
What meds are TCAs?
- amitriptyline (Elavil)
- imipramine (Tofranil)
- clomipramine (Anafranil)
What are 'other' meds in this section?
- trazadone
- bupropion
- mirtazapine
What med is an MAOI?
tranylcypromine (Parnate)
What are the 2 general theories of why antidepressant meds work?
monamine hypothesis of mood: depression happens because of a deficiency of neurotransmitters, meds increase neurotransmitters
brain-derived neurotrophic factor theory: BDNF is a growth factor protein that may be disrupted in depression, meds may help the disruption
What 3 neurotransmitters are commonly influenced by antidepressants?
- 5HT --> serotoniin
- DA --> dopamine
- NE --> norepinephrine
What neurotranmitter is associated with sleep, cognition, sensory perception, mood, appetite, temp regulation, sexual behavior, and hormone secretion?
5HT/serotonin
What neurotransmitter is involved with reward, emotion, cognition, memory, and motor activity?
dopamine
What neurotransmitter is involved with alertness, energy, anxiety, attention?
norepinephrine
What causes serotonin syndrome?
Increased dose of a serotonergic drug or multiple serotonergic drugs being used at a time
Often happens with an SSRI/SNRI + MAOI or SSRI/SNRI with other serotonergic agent like opioids, buspirone, etc
What is the presentation of serotonin syndrome?
HARMED
- hyperthermia
- agitation/autonomic instability
- rigidity/reflexes increased
- myoclonus/tremors
- encephalopathy
- diaphoresis
also may have GI symptoms
How do you treat serotonin syndrome?
normally just supportive cares. however, if needed can treat with
- benzodiazepines for muscle rigitity/agitation
- dantrolene for hyperthermia d/t muscle contractions
- anticonvulscents
- cyproheptadine (5HT and H antagonist)
What is the BW for basically ALL antidepressants?
increased risk of suicidal behavior = thoughts/actions = suicidality
in studies no one complete suicide
affects children/adolescents/young adults but NOT adults >24 and reduced reduction in 65+
What has been the outcome of the BW for antidepressants?
use of antidepressants went down, and completed suicide rates increased
but now long term studies show a decrease in completed suicides if taking antidepressants
TL;DR - suicide behavior risk with antidepressants, but greater chance of completing suicide if NOT on antidepressant
What are common effect seen/things to monitor in antidepressant use?
- efficacy
- sedation/activation
- sexual dysfunction
- weight gain/loss
- serotonin syndrome
- behavior changes (suicidality, mania)
- seizures
- renal/hepatic function
- med adherence/withdrawl
What are less commonly seen/monitoring parameters for antidepressants?
- anticholingeric effects
- CV issues: hyper/hypotension, QT prolongation
- hyponatremia
- intraocular pressure/glaucoma
- other med specific ADRs
How does discontinuation syndrome happen?
if you abruptly discontinue medication, experience withdrawal
can last up to 2 weeks
taper med in order to avoid
What are the symptoms of discontinuation syndrome?
FINISH
- flu-like symptoms
- insomnia
- nausea
- imbalance
- sensory disturbances
- hyperarousal
may experience 'zaps' in brain, have issues sleeping, have psych symptoms reemerge
What antidepressant is the safest to use in pregnancy?
sertraline
What antidepressant is associated with cardiac septal defects?
paroxetine
T/F: antidepressants/SSRIs can be taken during pregnancy
TRUE
low risk of teratogenic effects
its considered less safe to have untreated depression vs. risk of taking med during pregnancy
What should you do with the antidepressant medications of a woman who is breastfeeding?
Nothing!
infant exposure to meds via breast milk is very negligible (even less exposure than in utero)
recommendation is not to change meds for the purpose of breastfeeding
What condition is fluoxetine used for?
PMDD
What non-depressive condition are escitalopram and paroxetine used for?
anxiety
What non-depression condition is fluvoxamine used for?
OCD
What antidepressant meds are recommended for use in PTSD?
sertraline
citalopram
How do antidepressants vary in their activating and sedating effects?
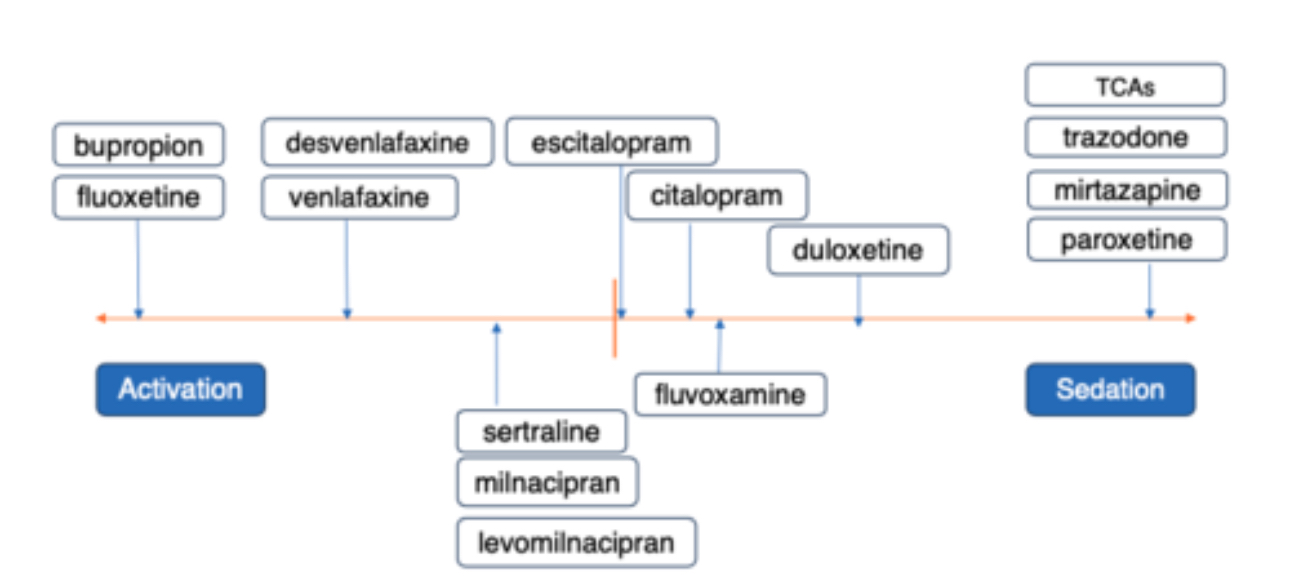
What are the main reasons why antidepressants don't work?
- not taking the med
- not taking high enough dose
- not taking med for long enough
- not actually treating the correct problem
How long do antidepressants take to work?
4-6 weeks
sometimes even up to 8 weeks for an adequate trial
T/F: Sometimes depression will feel worse before it gets better after starting meds
TRUE
What is the concept of antidepressant augmentation?
antidepressant combo therapy to help avoid risks of withdrawal or loss of benefit of first antidepressant
What meds classes are commonly used for antidepressant augmentation?
- other antidepressants like bupropion or mirtazepine
- buspirone
- 2nd gen antipsychotics
- lithium
- thyroid hormone
- anticonvulsants
- stimulants
How do SSRIs work?
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
serotonin reuptake is blocked so it stays in the synapse longer and exerts its effect for longer
T/F: some SSRIs and SNRIs have to be renally/hepatically dosed
TRUE
What classes of meds can you not use within 14 days of discontinuing an MAOI?
SSRIs
SNRIs
What are the 4 most common ADRs of SSRIs?
SSSS
- stomach upset
- sexual dysfunction
- serotonin syndrome
- suicidal thoughts
How common is sexual dysfunction/loss of libido in SSRI use?
30-40%! quite common
What risk is there of SSRI use in elderly?
hyponatremia and SIADH
What may SSRIs do to platelet aggregation?
it may impair it and cause increased bleeding risk
T/F: there are many DDIs with SSRIs
TRUE
lots of CYPs inhibited
Which SSRI has increased risk of diarrhea?
sertraline (zoloft)
What effect does sertraline (zoloft) have on energy?
neutral effect
Which SSRI has been most studied in pregnancy?
sertraline (zoloft)
What SSRI has the longest half life?
fluoxetine (Prozac)
4-6 day half life
What antidepressant med is also used for PMDD, bulimia/binge eating?
fluoxetine (Prozac)
Which SSRI has the shortest half life and therefore highest risk of discontinuation syndrome?
paroxetine (Paxil)
Which SSRI is known to cause weight gain?
paroxetine (Paxil)
What SSRI is also used for social anxiety/GAD?
Paroxetine (Paxil)
Which 2 SSRIs may cause EKG changes and/or QT prolongation?
Escitaopram (Lexapro) and Citalopram (Celexa)
Which SSRI causes headaches/zaps with discontinuation?
escitalopram (lexapro)
What is unique about the dosing of citalopram (Celexa)?
The EKG changes/QT prolongation is dependent on the dose. Avoid >40 mg
In 60+ individuals avoid >20 mg daily
Which 2 SSRIs are typically very well tolerated?
Escitalopram and citalopram
Which SSRI has higher risk for DDIs?
fluvoxamine (luvox)
How SSRIs compare with one another in terms of activation/weight loss and sedation/weight gain?
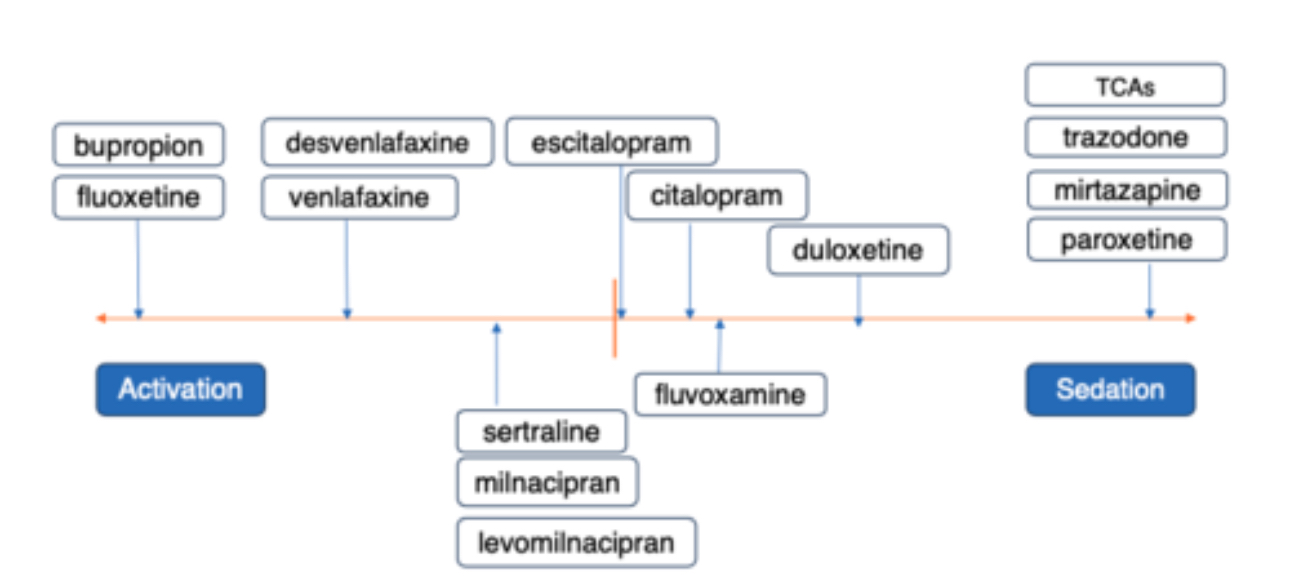
Which SSRI is more forgiving if a patient forgets a dose, and why?
fluoxetine
it has a longer half life
What are common adverse effects associated w/ SSRIs?
- stomach upset
- increased bleeding risk
- sexual dysfunction
How do SNRIs work?
they increase norepi and serotonin transmission as well as block the transporters so the neurotransmitters stay in the synapse for longer
What blood pressure issue is a precaution with the use of SNRIs?
orthostatic hypotension, and subsequent fall risk
Besides depression, what is venlafaxine (effexor) used for?
neuropathic pain and hot flashes
Besides depression, what is duloxetine (cymbalta) used for?
neuropathic pain
stress incontinence
What are the ADRs associated with SNRIs?
- sexual dysfunction
- insomnia
- constipation
- sweating
- headaches and nausea
What is trazodone a receptor antagonist to?
histamine and alpha adrenergic
What are the main ADRs of trazodone?
- sedation
- N/V
- xerostomia
- dizziness
- HA
- blurred vision
What is the BW of trazodone?
increased risk of suicidality in kids, adolescents, and young adults just like the antidepressants
What is the main contraindication and precaution of using bupropion as an antidepressant?
seizure
hypertension
What 3 conditions can bupropion be used for?
- can be combined with SSRI/SNRI to augment sexual dysfunction
- FDA approved for smoking cessation
- used in ADHD, bipolar depression
What are the main ADRs of bupropion?
- tachycardia
- diaphoresis
- insomnia
- agitation
- tremor
- blurred vision
- dizziness
- constipation
- headache
- n/v
- appetite suppression/wt loss
- xerostomia
- URI
Because of the seizure risk of bupropion what demographic should not take it?
eating disorder patients, more prone to seizures d/t electrolyte imbalances
Besides bupropion, what other med is considered to be an atypical antidepressant?
mirtazapine
What is the BW of mirtazapine?
same as the others - suicidality risk
What are the advantages/use for mirtazapine?
- no sexual dysfunction
- can be sedating, oddly at lower doses too
- can be used for atypical depression or augmentation
What blood work concern is related to mirtazapine use?
hyperlipidemia
What does mirtazapine do to appetite?
increases, so likely to cause weight gain
Besides weight gain and hyperlipidemia, what are other ADRs of mirtazapine?
- sedation
- xerostomia
- constipation
Why do TCAs cause sedation?
they block histamine
also block alpha adrenergic receptors which causes decrease in BP
What TCA is the standard treatment for OCD?
clomipramine (anafranil)
What TCA is also used for migraine prophylaxis, neuropathic pain, and sleep?
amitriptyline (Elavil)
Why are TCAs not used as commonly anymore?
overdose risk
What anticholinergic effects of TCAs affect the GU and GI system?
can cause impaired GI motility and urinary retention
What heart precaution is associated with TCAs?
risk of CV disease
T/F: TCAs share the same BW as the other antidepressants
TRUE
What class of med is associated with ADRs of hyperglycemia, fracture risk, orthostatic hypotension, and CV risks?
TCAs
CV risks include tachycardia, QT prolongation, and AV block
What are the 3 Cs of TCA overdose?
- convulsions
- coma
- cardiotoxicity
can be fatal
do not use TCAs in pt with hx of heart disease/MI/stroke, etc
How do MAOI medications work?
they irreversibly bind to MAO-A and B, which causes breakdown of NE, 5HT, and DA
nonselective of ALL 3
What medication class has a BW of consuming tyramine, and what will happen?
MAOIs
causing tyramine or other meds will cause a hypertensive crisis
What emerging area of medicine is helping us to understand peoples' varying metabolism of drugs?
pharamocogenomics
come people are fast/slow metabolizers