3 - Endocrine System
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What are endocrine glands?
epithelial tissue
secrete hormones into blood vessel from basal surface
may or may not have lumen
slower signalling, but often larger effects, than nervous system signalling
What are hormones?
signalling moleucles that affect metabolic processes by traveling through blood to a target tissue
What are the endocrine organs?
Pineal
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Gland
Thyroid
Parathryoid
Thymus - create immune structures to help develop T cells
Adrenal Glands - secrete 4 hormones, dual function
Pancreas - dual function (hormones and exocrine secretion to GI tract)
gonads - ovary/tests, make gametes as well
What two systems communicate together to maintain homeostasis? Which is faster?
nervous and endocrine system
nervous system is faster
What are the chemical classes of hormones, including their hydrophillicity?
amino acid based hormones - usually hydrophilic
steroids - usually hydrophobic
Describe the amino acid based class of hormones
small amino acid derivatives - slightly modified single aa; ex. adrenalin
small peptides - ex. oytocin
large polypeptide chains - ex. insulin
usually hydrophilic - dissolve easily in blood/H20, but can’t get through cell lipid bi layer
stored in vesicles
faster release then steroids (already made)
Describe the steroid class of hormones
cholesterol derived
made on demand, so slower release then amino acid based hormones
hydrophobic - can diffuse across cell membrane, so can’t make ahead of time; lipid soluble
ex. testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, cortisol
Describe free vs bound hormone concentratinos
hydrophobic hormones are bound to plasma proteins to help keep them in the blood (like a raft)
only so much availability to bind to receptors
What are the different ways to stimulate the release of a hormone? Describe them
humoral stimulus - responds to amount of a substance in the blood, causing a gland to secrete/stop secreting hormones
Neural stimulus - brain detects signal/change, stimulates a neuron to stimulate endocrine glands to release hormones
Hormonal Stimulus - hormones trigger hormone release; hormone travels through blood to stimulate release of a another hormone form a gland
Describe humoral stimulus of a hormone. Include an example
gland responds to amount of a substance in the blood, causing a gland to secrete/stop secreting hormones
ex. pancreas detects high glucose, releases insulin, which tells body to lower blood glucose
Describe neural stimulus of a hormone. Include an example
brain detects signal/change, stimulates a neuron to stimulate endocrine glands to release hormones
ex. stress signal, brain signals adrenal gland to release adrenalin
Describe hormonal stimulus of a hormone. Include an example
hormones trigger hormone release; hormone travels through blood to stimulate release of a another hormone form a gland
ex. Hypothalamus releases F- inhibiting hormone into portal system, travels to anterior pituitary, tells anterior pituitary to release less FSH
How do peptide/protein hormones signal target cells?
dissolve freely into blood (hydrophilic)
bind to membrane receptors that bring them to the target cell
second messengers inside cell act (can amplify and cause many effects in one cell)
How do steroids/lipid-soluble hormones signal target cells?
carried by proteins in blood
travel through cell membrane and bind to intracellular receptors
affects gene inscription directly inside cell (ex. bind to DNA)
What can hormones affect in target cells?
membrane permeability of a cell
protein synthesis
enzyme activity
secretory activity
mitotic activity
What kind of hormone interactions are there? Describe them.
permissiveness - permissive hormone has no effect on target molecule, but allows OTHER hormone to have a large (instead of usual small) effect
synergism - both hormones have an effect on a cell, but have much larger overall effects when combines
antagonism - hormones have opposite effects
What is a permissive hormone and an example?
hormone that has no affect on a target molecule, but allows other hormones to have a large effect
ex. Thyroid hormones
Describe the hypothalamus and pituitary glands from most superior to inferior
hypothalamus
infundibulum
anterior pituitary gland (epithelial tissue)
posterior pituitary gland (neural tissue)
What is the hypothalamus?
main control center for maintaining homeostasis
integrates info from brain
neurally signals posterior pituitary gland, hormonally signals anterior pituitary gland
What hormones does the posterior pituitary gland produce and what do they do?
oxytocin - affects mammary glands and uterus, affects brain (ex. mother-child bond); hydrophilic peptides
vasopressin (ADH) - constricts blood vessels to raise blood pressure, signals kidneys to lower urine production; hydrophilic peptides
How are oxytocin and ADH signalled/released?
neural signalling in posterior pituitary
hypothalamic neurons produce oxytocin or ADH
hormones transported down axon to axon terminal in posterior pituitary gland
oxytocin/ADH released into blood vessel in posterior pituitary gland when neurons fire
How are hormones in the anterior pituitary gland signalled/released?
hormonal signalling
hypothalamic neurons produce either releasing or inhibiting hormones
hormones released into portal system
hormones travel through portal system directly to anterior pituitary gland
RH/IH affect cells in anterior pituitary gland to make hormones (FLAT PG)
What is the portal system and how is it used in endocrinology?
A specialized vascular arrangement in which blood passes through two capillary beds in sequence
Allows substances to be transported directly and efficiently from one organ or tissue to another without dilution in the systemic circulation.
Capillaries in the hypothalamus collect releasing and inhibiting hormones.
Blood flows through portal veins to a second capillary bed in the anterior pituitary.
What hormones are released by the Anterior Pituitary Gland and what do they do?
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) - affects gonads to produce testosterone and estrogen
Luteinizing Hormone (LH) - affects gonads to produce testosterone and estrogen
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) - affects adrenal glands release cortisol
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) - affects thyroid gland to produce TH
Prolactin (PRL) - affects mammary glands/uterus, usually constantly secreting unless told not to
Growth Hormone (GH) - affects bones, muscle, liver, etc. to produce Growth Factor (GF)
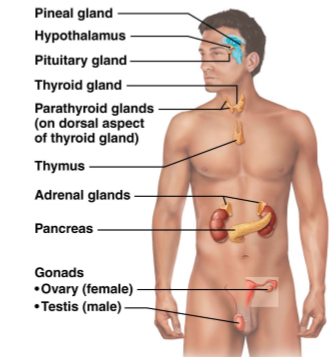
Describe the endocrine glands not associated with the hypothalamus & pituitary glands
pineal gland
pancreas
parathyroid/thyroid
thymus
pineal gland - helps regulate circadian rhythms
pancreas - regulates blood glucose
parathyroid/thyroid - regulates blood calcium
thymus - regulates lymphocyte production/maturation
What does the pineal gland do in the endocrine system?
helps regulate circadian rhythms
What does the pancreas do in the endocrine system?
regulates blood glucose
What does the parathyroid/thyroid do in the endocrine system?
regulates blood calcium
What does the thymus do in the endocrine system?
regulates lymphocyte production/maturation
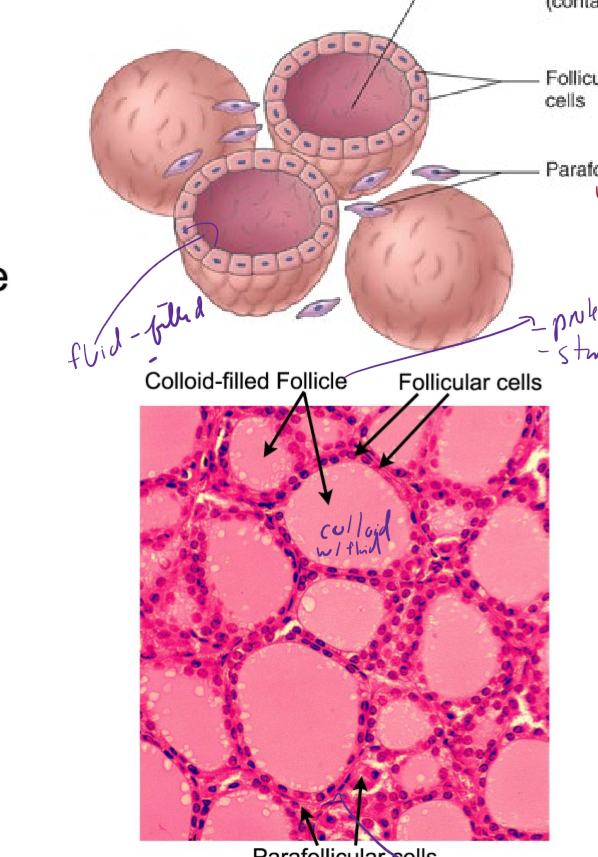
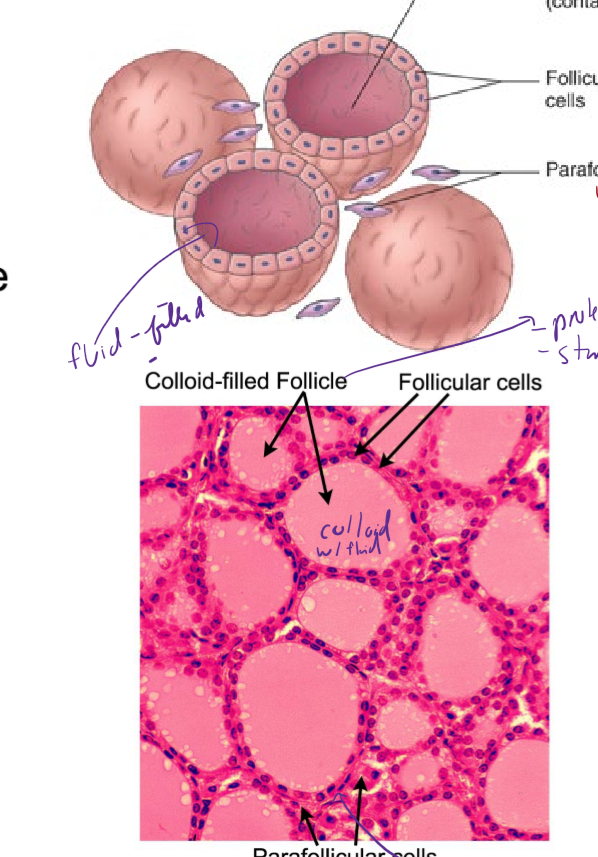
Describe the structure of the thyroid gland
contains colloid-filled follicle with thyroglobulin inside (where t3 and t4 are attached); thyroid hormone made in here
surrounded by follicular cells that make thyroid hormone
parafollicular cells in between follicles make calcitonin for Calcium homeostasis
What does the thyroid do?
produces T3 and T4
metabolic actions: stimulate ATPase pumps (affects nearly all cells in body); promotes glucose and lipid breakdown for energy
Growth and development: essential for normal CNS development, promotes normal muscle and skeletal growth
permissive effects for other hormones (ex. epinephrine, GH, steroids)
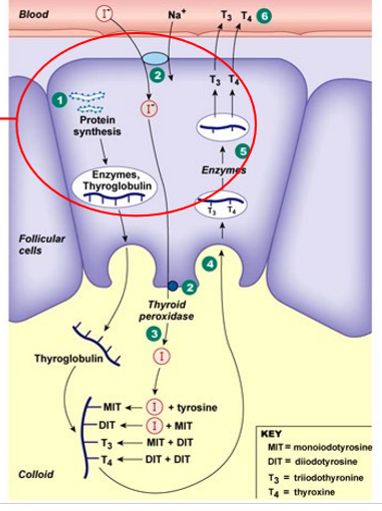
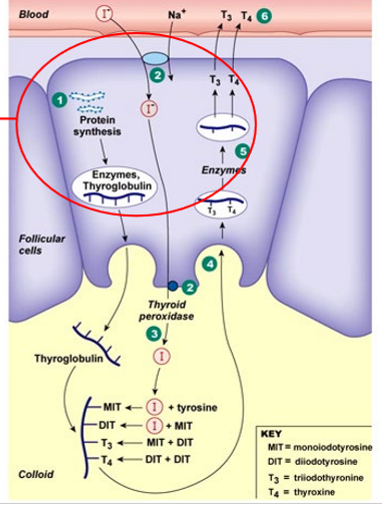
How is thyroid hormone synthesized?
thyroid follicular cells stimulated by TSH to make thyroglobulin protein and thyroid peroxidase to secrete into follicle
thyroid peroxidase attaches iodine to tyrosine (amino acid) on thyroglobulin to make T3 and T4
T3 and T4 still attached to thyroglubin
when TSH arrives, enzymes cleave off T3 and T4
T3 and T4 (lipid-soluble) diffuse out of cell
What kind of hormones are T3 and T4 and are they hydrophobic or hyrdophilic?
amino acid derivates
hydrophobic
Why does an iodine insufficiency cause a goiter?
low iodine prevents making of T3 and T4, causing high TSH/TRh levels
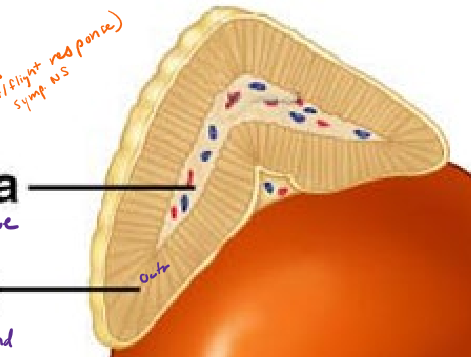
What hormones does the adrenal MEDULLA produce? What class of molecules are they? How are they stimulated?
norepinephrine and epinephrine (neural tissue)
amino acid derivative
nerually stimulated
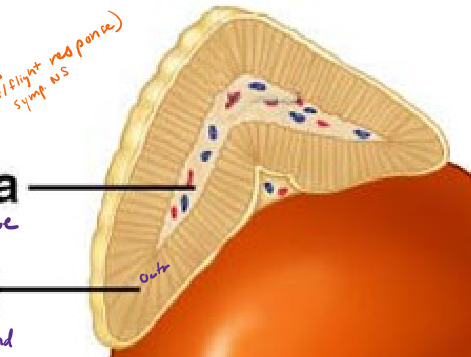
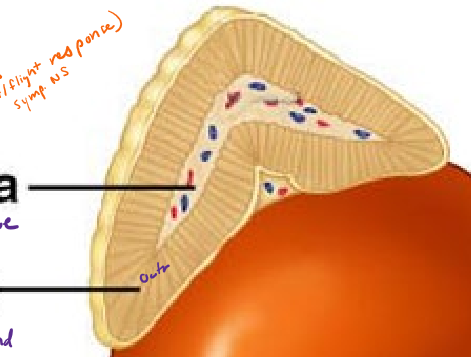
Describe the structure of the adrenal glands
above kidneys
cortex (outside) of gland made of epithelial tissue
medulla (inside) of gland made of nervous tissue
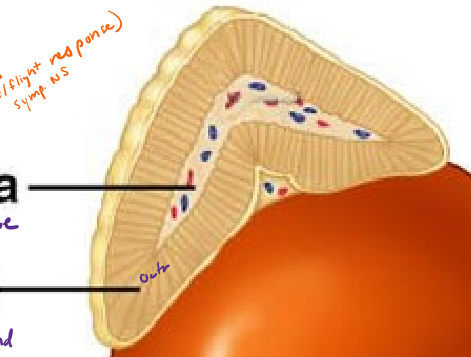
What hormones does the adrenal CORTEX produce? What class of molecules are they? How are they stimulated?
cortisol (follows circadian rhythm), aldosterone, androgen
steroids
hormonally stimulated by ACTH
stress/circadian —> CRH —> ACTH —→ cortisol
What releases cortisol? What does cortisol do?
released by adrenal cortex
increases plasma glucose
permissive for many metabolic and developmental functions
anti-inflammatory/anti-immune
promotes bone breakdown
Describe the pathway that leads to the release of cortisol
stress or circadian rhythm
CRH released from hypothalamus
ACTH released from anterior pituitary gland
cortisol released from adrenal cortex
describe the 2 stress responses mediated by the adrenal gland
fast: neurally stimulated adrenal medula, releases NE and epinephrine to act throughout body (increase HR, BP, metabolic rate, etc.) ; effect goes away faster
slow: hormonally stimulated adrenal cortex, releases steroid cortisol to increase blood glucose levels, suppress immune system; longer lasting effects