Crystalline Materials
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
what does amorphous mean
give a value
no long range structure
2nm is a reasonable measure of the cut-off
word describing a material with no long range structure
amorphous
how is a crystal defined
a material in which the atoms are organised in a regular, three-dimensional structure
what is a symmetry operation
an operation that can be performed to give no change in the appearance of an object
what are the 3 types of symmetry operations
rotation, reflection, inversion
what is rotational symmetry and what is its associated element
if an object can be rotated about an axis (which is the element) such that it appears unchanged
how is rotational symmetry described & calculated
n-fold rotation axis
fold = 360/degrees of rotation
angle = 360/fold
available rotations for crystal lattices + their angles
1-fold = 360 - every structure has this symmetry
3-fold = 120
4-fold = 90
6-fold = 60
no 5-fold
why is there no 5-fold rotation
with this type of rotation, the atoms cannot be close packed and the unit cell cannot be translated into 3 dimensions
what is mirror symmetry + its element
reflection of the structure in a mirror plane (the element) which reproduces the entire structure
what is inversion symmetry and how is it done
inversion through a point
lines are drawn from all points on the object through a point in the centre of the object (called the centre of symmetry, i)
the lines each have lengths that are equidistant from the original points
when the ends of the lines are connected, the original object is reproduced inverted from its original appearance
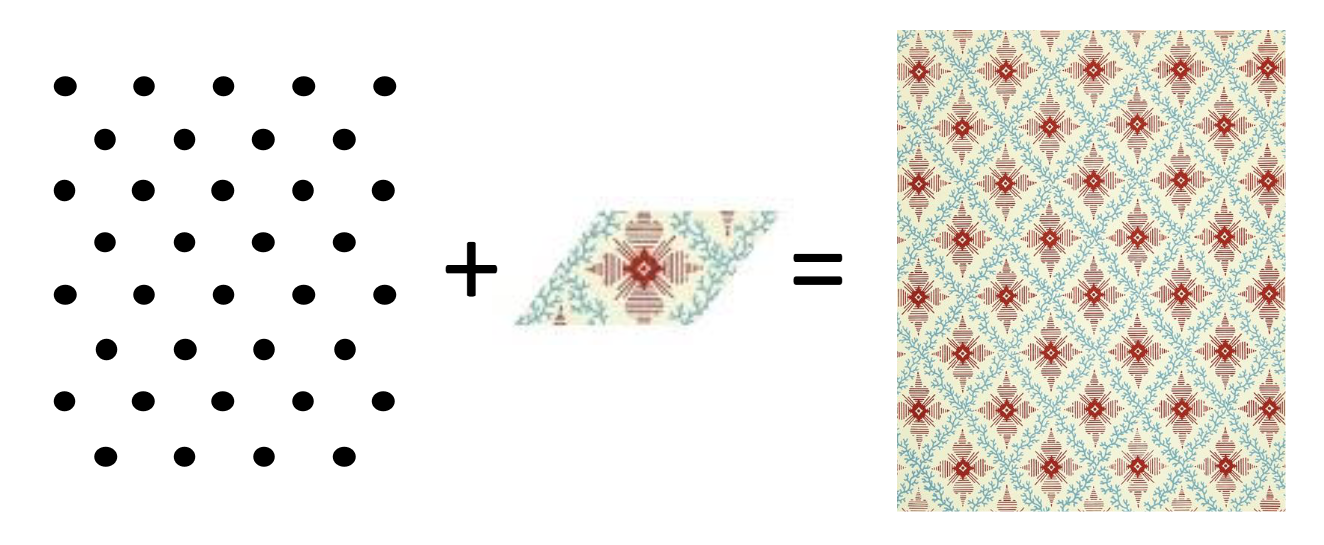
define a lattice
an infinite, regular arrangement of points, each of which has identical surroundings
define lattice points
points having identical surroundings in the crystal
could be 1 atom or a collection of atoms (which is more common)
what is a unit cell
the building block of the lattice
a parallelepiped (3D) or parallelogram (2D) with lattice points at its vertices, which when translated in all directions creates the lattice
what is needed to describe the whole structure of a crystal
lattice and motif
the motif is the arrangement of atoms associated with a lattice point