GI system
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Anorexia
loss of appetite or desire for food
Nausea
subjective, unpleasant sensation that precede V, caused by distention anywhere in the GI tract or stimulated by higher brain center
vomiting
reflex mediated by vomiting center in medulla, in response to excessive distention or irritation of the stomach or duodenum, chemical stimulation, or pain. Projectile vomiting happens with increase ICP
acute diarrhea
frequent passage of loose stools persisting 3-5 days that are not bloody, purulent, or greasy. Lasts less than 2 weeks
Secretory diarrhea
secretory processes of the bowel are increased, more acute infectious diarrhea
osmotic diarrhea
water is pulled into the bowel by the hyperosmotic nature of its content
constipation
stools less than once every 3 days, caused by dehydration, delayed gastric motility, sedentary lifestyle, hypothyroidism, low fiber diet, psychogenic, drug side effect
Parietal pain
caused by stimulation of pain receptors in parietal peritoneum, pain is localized, sharp, intense, and lateralized
Visceral pain
caused by stimulation of abdominal organs, pain is vague, diffuse, and dull
Referred pain
felt at a distance from the affected tissue, localized at some point along the afferent nerve pathway of tissue
Hematochezia
bright red stools
Melena
black or tarry stools, foul-smelling caused by digestion of blood in GI tract
Hematemesis
bloody vomit, either fresh, bright red blood or dark grainy digested blood with “coffee ground” appearance
Occult bleeding
trace amounts of blood in normal-appearing stools or gastric secretions, detectable only with positive fecal occult test
Dysphagia
difficulty swallowing
Achalasia
loss of inhibitory neurons in the myenteric plexus with smooth muscle atrophy in the middle and lower portions of the esophagus
(7) s/s of dysphagia
stabbing pain at level of obstruction, discomfort after swallowing, regurgitation of undigested food, unpleasant taste sensation, vomiting, aspiration, weight loss
(4) physiologic factors of GERD
decreased lower esophageal sphincter tone, esophageal mucosal irritation from HCL acid and pepsin, delayed esophageal peristalsis, delayed gastric emptying
(7) s/s of GERD
heartburn (pyrosis), regurgitation of fluid/food particles, retrosternal aching or burning occurring 30-60 min after eating, chest heaviness, pressure radiating to neck, jaw, or shoulders, chronic cough, laryngitis
Hiatal Hernia
stomach protrudes through the diaphragm into the thorax
(2) s/s of Hiatal Hernia
asymptomatic or cause GERD symptoms
(5) complications of hiatal hernia
GERD, esophagitis, gastritis, ulcer formation, strangulation
Gastroparesis
delayed gastric emptying in the absence of a mechanical gastric outlet obstruction
mechanical intestinal obstruction
Mechanical is caused by anything that affects lumen of bowel, tumor, adhesion, and severe constipation. Severe cases can lead to ischemia of bowel, acidosis, perforation, shock, sepsis, and death.
nonmechanical intestinal obstruction
Nonmechanical is ileus. Ileus is the non-mechanical block of small and large intestine. It can be caused by surgery, disruption to blood supply to abdomen, and meds.
(8) s/s of intestinal obstructional
pain, distention of bowel, N/V, anorexia, diarrhea, reduced bowel sounds, abdominal tenderness, fever
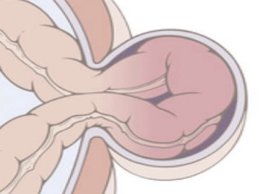
herniation intestinal obstruction
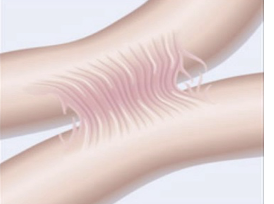
adhesions intestinal obstruction
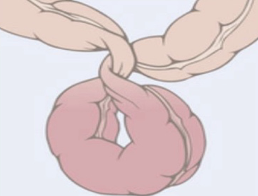
valvulus intestinal obstruction
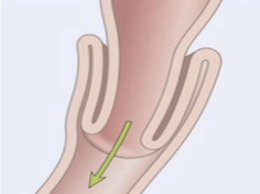
intussusception intestinal obstruction
what causes actue gastritis
caused by injury of the protective mucosal barrier
what are types of chronic gastritis
type A – chronic fundal gastritis (immune) and type B – chronic antral gastritis (nonimmune)
(4) risk factors of peptic ulcer disease
advancing age, use for warfarin and NSAIDS, corticosteroid use, and smoking
patho of peptic ulcer disease
excessive acid leads to ulceration in the mucosa of stomach or duodenum -> break allows mucosa to be subjected to acidic or alkaline environment -> autodigestion occurs
Duodenal ulcer
happens in pt 25-75 y, epigastric burning 2-3 hr post meal, relief with food, awakening at 1-2am is common w/ symptoms, has periods of feeling well
Gastric ulcer
more common in NSAID users, 55-65 yrs, pain reported w/ or immediately after meals, N/V and weight loss are common
(6) s/s of peptic ulcer disease
dyspepsia, pain depending on ulcer type, hematemesis, melena, severe cases lead to perforation and hemorrhage
patho of dumping syndrome
too rapid movement of stomach contents and acid into duodenum overwhelms protective layer -> causes fluid shift from intravascular compartment into lumen into small intestine -> sudden loss of intravascular volume triggers set of vasomotor responses that include hypotension, tachycardia, dizziness, sweating -> as intestine fills up, individual develops sensation of intestinal fullness accompanied by cramping, N/V, and diarrhea
(8) s/s of dumping syndrome
early (hypotension, tachycardia, dizziness, sweating) late (cramping, N/V/D)
ulcerative colitis patho
autoimmunity leads to inflammatory ulceration in large intestine with mucosal erythema, edema, and friability -> mucosal ulceration and edema lead to narrowing of colonic lumen, D, and hematochezia = Begins in rectum, goes up to colon without skipping parts of mucosa, higher risk of cancer
patho of Chrohn’s disease
same as UC but has skip lesions, ulcerations can produce fissures that extend into lymphatics
(5) s/s of ulcerative colitis
cramping, abdominal pain and dehydration, 10 to 20 stools per day, bleeding can cause anemia
(11) s/s of chron’s disease
N/V, farting, colicky pain in RLQ, malabsorption, 3-5 semisolid foul-smelling stools/day, mucosa in stools possible with pus, intermittent nonbloody diarrhea, urgency to defecate at night, weight loss, hypoalbuminemia, perianal abscesses and fistulas
patho of diverticulitis
asymptomatic presence of poopball, associated with increased intracolonic pressure and abdominal intestinal mobility
patho of Diverticulosis
increased intraluminal pressure causes poopball to rupture -> bacterial invasion of weakened area -> local ischemia
(6) s/s of diverticulitis
steady and severe abdominal pain in LLQ, abdominal guarding and rebound, constipation more usual than D, pain increased with pooping, lower grade fever
(8) s/s of appendicitis
periumbilical or epigastric pain that localizes to RLQ, anorexia, N/V, leukocytosis, tenderness at McBurney’s point (pressing on appendix point), Rovsing sign (RLQ pain when palpating LLQ), Psoas sign (pain with right thigh extension), Obturator sign (pain with internal rotation of flexed right thigh)
patho of Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder occurring acutely or chronically, often secondary to previously asymptomatic gallstones
Cholelithiasis leading to Cholecystitis
· when a stone becomes impacted in the cystic duct, inflammation develops behind the obstruction
· if not relieved, pressure builds up in the gallbladder and leads to distention, ischemic changes, gangrene, and perforation with subsequent abscess formation and less frequently generalized peritonitis
Acute cholecystitis s/s (6)
· abdominal pain (sudden onset, intense, in epigastrium or RUQ, radiates to back or shoulder), “biliary colic” (pain that starts out from mild to steadily increasing in intensity and is present for more than 20 min )
· N/V, recurrent attacks following fatty meals 1-6 hrs later, local tenderness in epigastric and RUQ aras, positive Murphy’s sign (tenderness on palpating RUQ)
(4) s/s of common duct stone
jaundice, fever and chills, mild to marked hepatomegaly
(2) s/s of chronic cholecystitis
asymptomatic, mild dyspepsia following fatty meals
(3) types of pancreatitis
acute, biliary tract obstructions, and alcohol abuse
(3) s/s of Pancreatitis
LUQ pain, N/V, Cullen’s sign (bruising around the belly button)
Pancreatitis dx
serum amylase and lipase and CT
cause of Peritonitis
perforation of gut/organ into perineal space
(6) s/s of peritonitis
pain (over inflamed area and rebound in nature), N/V, rigid abdomen, tachycardia, fever, increased WBC
Preicteric stage
first stage before jaundice, flu-like symptoms (malaise, fatigue), anorexia, N/V/D, pain (headaches, muscle aches, polyarthritis), serum. Bilirubin and enzymes levels are elevated
Icteric stage
includes appearance of jaundice, dark-or-tea colored urine, clay-colored stools, pruritus, decreased in preicteric phase symptoms
Posticteric stage
jaundice decreased, color of urine and stool goes to normal, energy levels increase, pain subsides, GI symptoms are minimal to absent, serum bilirubin and enzyme levels return to normal
mode of transmission of Hep A
fecal-contaminated drinking water and food
mode of transmission of Hep B
exchange of body fluids (Sexual contact, IVDU with needle sharing, occupational exposure in health care workers), course of illness is 2-3 weeks
mode of transmission of Hep C
· exchange of blood and body fluids (sexual transmission is low, maternal-fetus transmission is uncommon and is limited to women with high circulation HCV levels
· Incubation period is 6-7 weeks
Hep A prevention
vaccine to pt who reside or travel to areas where disease is endemic, food handles, day care and long-term care workers AND Prevent infection through water and food safety, immunization, and post exposure immune globulin use
Hep B prevention
universal precautions, clean needle exchange, immunizations, and safer sex, Hep B vaccine does not contain live virus (most develop HbsAb after 3 doses which means you have protection for the virus), HBsAb testing to confirm the development of HBV protection in those with high risk as well as those at risk for poor immune responses
Laennec’s Cirrhosis
alcohol-induced, nutrition, portal cirrhosis, cellular necrosis causes eventual widespread scar tissue with fibrotic infiltration of liver
Postnecrotic Cirrhosis
occurs after massive liver necrosis, results as a complication of acute viral hepatitis or exposure to hepatotoxins, scar tissue causes destruction of liver lobules and entire lobes
Biliary Cirrhosis
develops from chronic biliary obstruction, bile stasis, and inflammation resulting in severe obstructive jaundice
Cardiac cirrhosis
associated with severe, right-sided congestive heart failure and results in an enlarged, edematous, congested liver. The liver becomes anoxic, resulting in liver cell necrosis and fibrosis
patho of cirrhosis
cellular injury -> fibrosis (leukocyte infiltration, release of inflammatory mediators, activation of fibrotic processes) -> structural changes (altered biliary channels and blood flow, formation of shunts, disrupted regeneration process) -> liver architecture distortion (formation of fibrous bands and regenerating nodules, cobbly appearance of liver)
(13) s/s of cirrhosis
jaundice, abdominal pain/tenderness, ascites, peripheral edema, dry skin and rashes, petechiae or ecchymosis, spider angiomas on the nose, cheeks, upper thorax, and shoulders, hepatomegaly, protruding umbilicus, dilated abdominal veins, fetor hepaticus (fruity, musty breath odor of chronic liver disease), asterixis (course tremor characterized by rapid, nonrhythmic extension and flexions in the wrist and fingers, delirium (accumulate NH3)
hepatic encephalopathy early s/s (6)
subtle changes in personality, memory loss, irritability, disinhibition, lethargy, and sleep disturbances
(7) s/s of late hepatic encephalopathy
disorientation to time and space, flapping tremor of the hands, slow speech, bradykinesia, stupor, convulsions, and coma