Cell Structure and Function
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Which of the following is found in plant cells but not in animal cells?
Chloroplast, cell wall, permanent vacuole
The function of the mitochondria is to:
Produce energy through cellular respiration
What is the role of ribosomes in the cell?
Protein synthesis
The nucleus is surrounded by:
A nuclear envelope with pores
Which organelle packages and modifies proteins for transport?
Golgi apparatus
Why are cells generally very small in size?
A small size allows for a larger surface area to volume ratio

Which cell would be more efficient at exchanging materials with its environment? Explain why.
Cell A would be more efficient because it has a larger SA:V
Larger cells are less efficient than smaller cells. Suggest one way large organisms overcome this limitation while still having large overall size.
Large organisms are made up of many smaller cells to overcome this limitation smaller cells have large SA:V
Name three organelles found in both plant and animal cells
Nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes
Explain two key differences between plant and animal cells.
Plant cells have a cell wall animal cells do not, plant cells have chloroplast for photosynthesis animal cells do not, plant cells also have larger more permanent vacuoles.
Describe the function of the cell membrane and explain why it is important for the cell’s survival
Membrane acts as a barrier to the external environment, it controls what enters and exits the cell, making sure nutrients that are needed for survival can enter and wastes can leave
What is the surface area to volume ratio (SA:V)
It is the relationship between the surface area (plasma membrane) and the volume (internal environment for the cell)
Why is the SA:V important for a cell
The larger the SA to volume the more efficiently molecules can enter the cell

What is the SA:V of a
60:30 = 2:1 = 4:2

What is the surface area of b
96:64 = 3:2
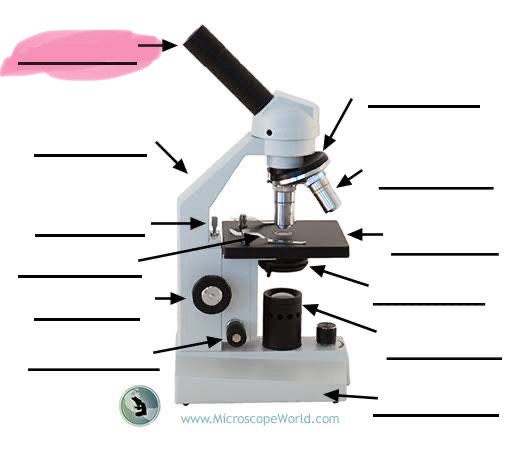
label the highlighted
eyepiece
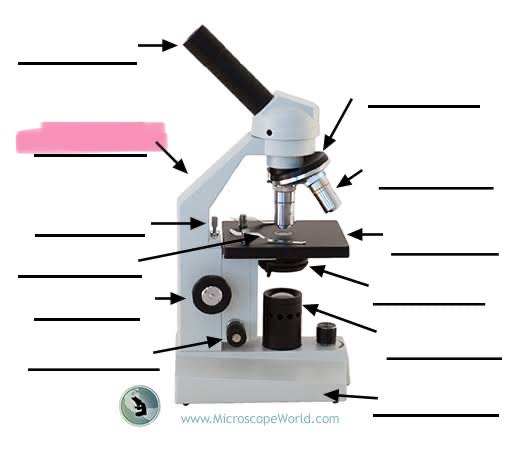
label the highlighted
arm
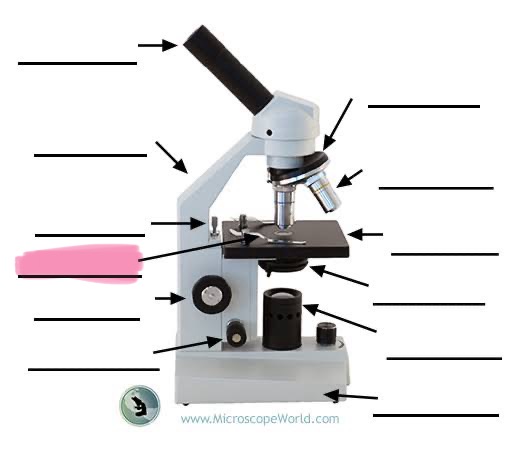
label the highlighted
stage clip
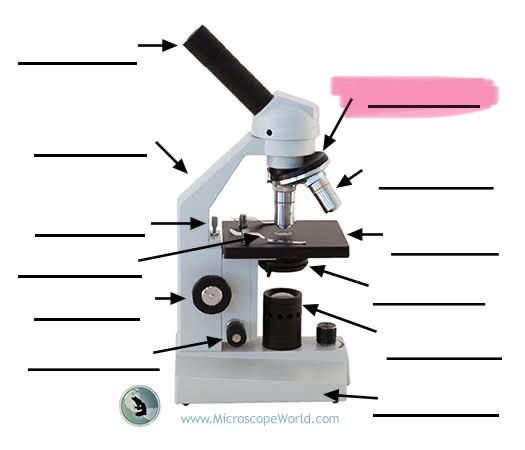
label the highlighted
nose piece
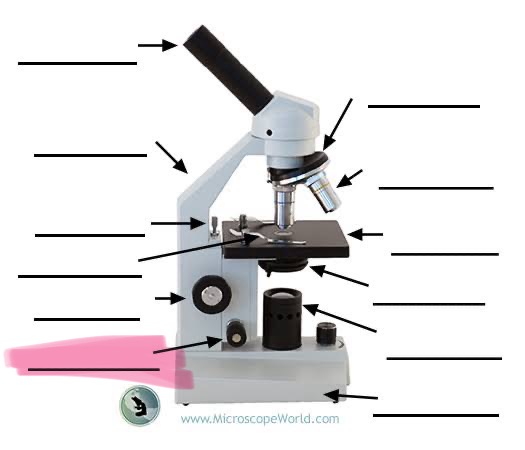
label the highlighted
fine focus
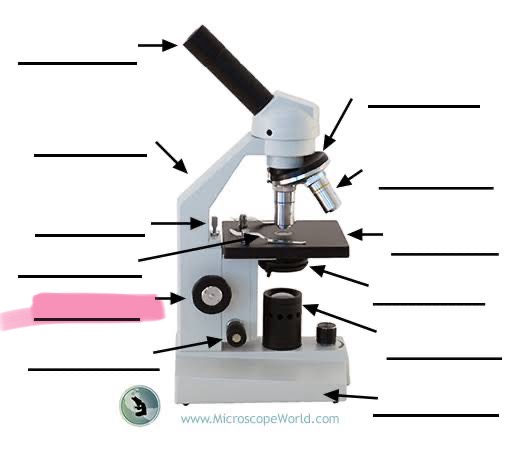
label the highlighted
coarse focus
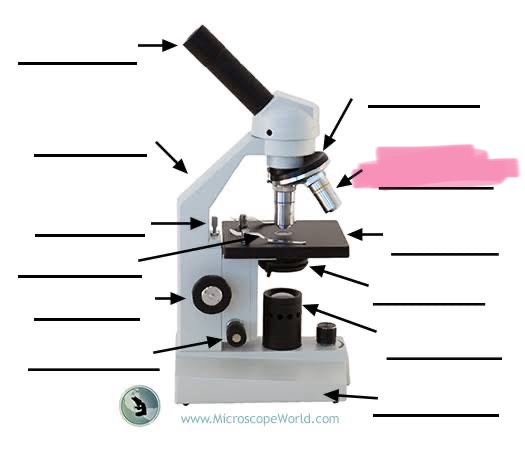
label the highlighted
objective lens
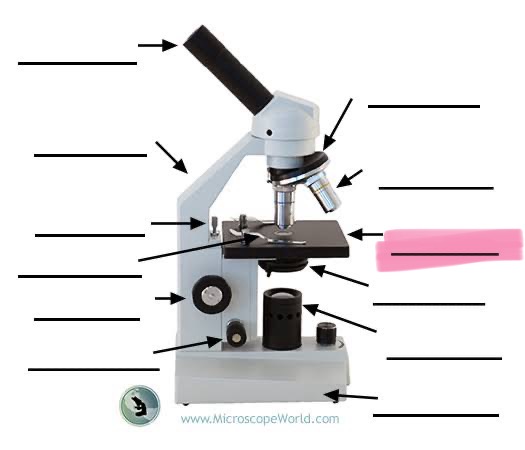
label the highlighted
stage
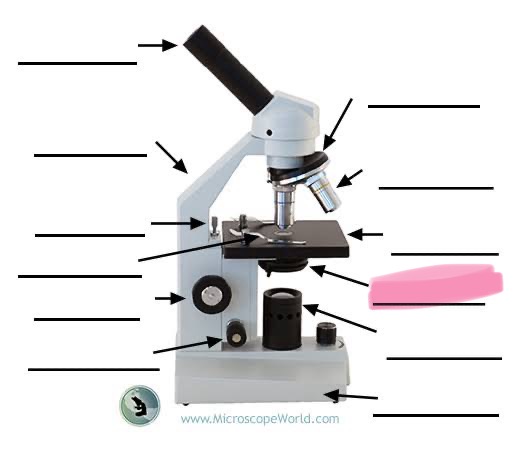
label the highlighted
diaphragm
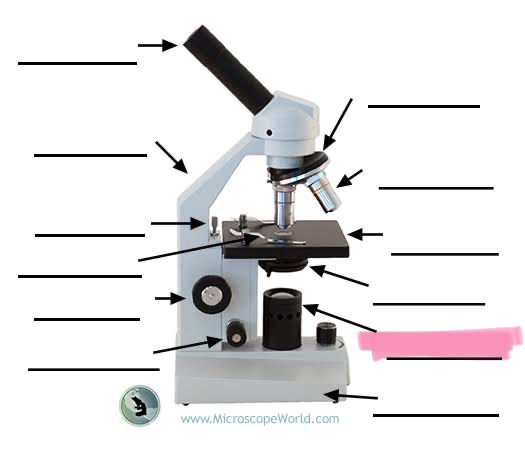
label the highlighted
Light source
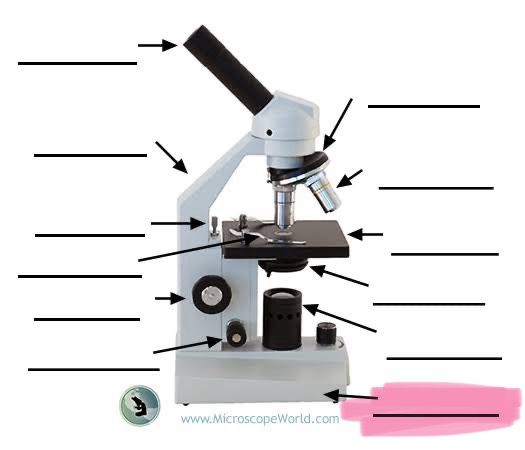
label the highlighted
base
Explain how magnification is calculated using the lens and eyepiece.
Multiply them together e.g. eyepiece 10, objective lens 10 magnification = 10 × 10 = 100
Steps to make a wet mount slide
collect glass slide, place specimen on slide, drop water or stain on specimen, place coverslip on top of specimen, place slide on microscope stage
Why are specimens often stained before being examined under the microscope?
To enhance features of the specimen so we can see them clearly under the microscope
Differences between prokaryote and eukaryote cells
Prokaryotes have no membrane bound organelles they are unicellular, Eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles can be multi or unicellular
Similarities between Eukaryote and Prokaryote cells
Both contain, cell membrane, genetic material, cytoplasm, ribosomes
Lysosome function
digesting invading cells, old, unwanted parts of cells and complex biomolecules
Chloroplast function
where photosynthesis takes place through a series of light dependent and independent reactions
Vacuole function
maintains osmotic pressure inside the cell and ensures that plant cells remain turgid
cell wall function
help maintain cell shape by providing structural support and protection from invading pathogens
Nucleus function
acts as the cell's control centre, housing the genetic material (DNA) and regulating cell activities, protein synthesis and ribosome production also take place in the nucleus
smooth er function
responsible for storing, synthesising and processing lipids
Rough er function
works with the ribosomes to process and produce 3d structures of protein, where glycoprotein is made
Plasma/cell membrane function
physical barriers preventing the movement of foreign bodies and other molecules into and out of the cell
Golgi Apparatus function
responsible for processing and packaging lipids and proteins it also produces lysosomes