OOPD
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/130
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:48 PM on 1/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
1
New cards
Are objects and class the same thing?
No, every object has a class
2
New cards
Can the controller display things?
Yes such as buttons or input fields since that is directly related to input signals
3
New cards
Can there be multiple controllers?
Yes
4
New cards
Can there be multiple models?
No
5
New cards
Can there be multiple views?
Yes
6
New cards
Can we give type parameters their own type?
Yes. By assigning available types to the type parameter we can make assumptions about what type of type we are refering to.
7
New cards
Can you create an object that has type parameters without giving type arguments?
Yes! The type parameter becomes of the type Object which is a supertype to all objects. However you should always give a type argument!
8
New cards
Do buttons belong in the view of MVC?
No buttons and other things that are considered input should be handled by the controller
9
New cards
Do we always need implementation inheritance?
No, we don't need to do this to gain these benefits. We can use interfaces to gain the same benefits
10
New cards
Do we want high or low cohesion?
High Cohesion
11
New cards
Do we want high or low coupling?
Low coupling
12
New cards
Give an example of a literal
int - 10, 0x1a, 0b11010
double - 135.7, 3.0e5
boolean - true, false
char -, \\\\, \\', a
double - 135.7, 3.0e5
boolean - true, false
char -, \\\\, \\', a
13
New cards
Given that:
public class House;
public class Human;
public class Tom extends Human;
Can we write: House myHouse = new House(); ?
public class House
public class Human;
public class Tom extends Human;
Can we write: House
No we can't since House and House are considered their own unique types. This means that we can't write this since House is not a subtype of House even though Tom is a subtype to Human
14
New cards
How do dependencies work in MVC?
M should not depend on anything. V and C can depend on M.
C can depend on V, V can depend on C.
A usually depends on everything and nothing should depend on A
C can depend on V, V can depend on C.
A usually depends on everything and nothing should depend on A
15
New cards
How do we program defensively?
•Limit possible states and state changes. Strive for immutability
•Make expectations explicit.
Make it clear what "your" code takes responsibility for, and what responsibility it expects clients to take.
•Make it obvious as soon as possible when something breaks expectations Throw exceptions immediately (Close to the source)
•Make expectations explicit.
Make it clear what "your" code takes responsibility for, and what responsibility it expects clients to take.
•Make it obvious as soon as possible when something breaks expectations Throw exceptions immediately (Close to the source)
16
New cards
How do we represent a dependency in UML?

17
New cards
How do we represent an interface in a class diagram?
<> below the name of the class
18
New cards
How do we represent implementation of an interface in UML?

19
New cards
How do we represent subclassing in UML?

20
New cards
How do we show that a class has attributes that are objects of another class in UML?

21
New cards
How does variance work in java?
Methods are covariant in their return type and invariant in their argument types.
Essentially if the return type of a method is a subtype of the return type of the overriden method you're fine.
However if the argument type of a method is a subtypyte of the argument type of the overriden method it is considered overloading
Essentially if the return type of a method is a subtype of the return type of the overriden method you're fine.
However if the argument type of a method is a subtypyte of the argument type of the overriden method it is considered overloading
22
New cards
How should we handle checked exceptions?
They should always be caught and handled at some point in the program
23
New cards
How should we handle Errors?
We don't. Since we can't really do anything about them we don't handle them
24
New cards
How should we handle unchecked exceptions?
These should not be caught since they represent a bug made by the programmer. Instead we should let them crash the system
25
New cards
How should we use exceptions and assertions in relation to our contracts?
* Check that the pre-conditions are fulfilled - otherwise cast an unchecked exception immediately.
* After that use assertions generally to check your own code.
\- Assertions are not a defence mechanism - they are a tool to help you discover your own bugs.
* After that use assertions generally to check your own code.
\- Assertions are not a defence mechanism - they are a tool to help you discover your own bugs.
26
New cards
If B is a subclass of A then what type is class B
B is of type B but also of type A
27
New cards
If B is a subclass of class A, can a variable containing an object of class A have the type B? B b = new A();
No since A is not a subtype of B
28
New cards
Is a typecasting error a compile time error or a runtime error?
It is a runtime error that throws an exception ClassCastException
29
New cards
Is the @override annotation required when overriding methods in a subclass
No. As long as the method is of the same signature than it is overriden.
30
New cards
Is typecasting a code smell?
Yes
31
New cards
What are the 5 levels of abstraction in a modular design? (In order of largest to smallest)
System
Subsystem
Packages/subpackages
Classes
Methods
Subsystem
Packages/subpackages
Classes
Methods
32
New cards
What are the benefits of immutable objects?
It is easier to prove things about immutable objects.
Immutable objects are threadsafe.
No alias problem.
Working with immutable objects is "safer". Immutable objects have value semantics since they cannot change, they behave as data
Immutable objects are threadsafe.
No alias problem.
Working with immutable objects is "safer". Immutable objects have value semantics since they cannot change, they behave as data
33
New cards
What are the primitive types in Java?
boolean, byte, short, int, long, float, double, char
34
New cards
What are the SOLID principles
S - Single responsibility principle
O - Open closed Principle
L - Liskov substitution principle
I - Interface Segregation principle
D - Dependency inversion principle
O - Open closed Principle
L - Liskov substitution principle
I - Interface Segregation principle
D - Dependency inversion principle
35
New cards
What are type arguments?
They are the types that we send into a class when we make a new object of that class. These are the types that fill the type parameters
36
New cards
What are type parameters?
A type parameter is a variable that when filled holds a certain type. It is the same as parameters for methods. The variable is replaced with our argument. This way we can create general classes for multiple types
37
New cards
What characterizes a dynamic type?
This can change (hence the word dynamic), if the variable gets a new reference that points to another object with a different type it recieves a new dynamic type of the type it was assigned to
38
New cards
What characterizes a static type?
That type remains the same for the reference variable at all times
39
New cards
What code gains benefits by using subtype polymorphism?
Client code. Since we do not need to write duplicate client code for each type
40
New cards
What do we gain by using subtype polymorphism?
We can reuse a lot of code, we do not have to rewrite it, we can make it extensible.
41
New cards
What do we gain from implementation inheritance?
We gain the benefits of polymorphism and the reuse of superclass code, ●Define common methods in the superclass that can inherited by its subclass(es).
●Don’t repeat yourself (DRY), no cut-n-paste.
●Provides a single place for change when needed - maintainability.
●Don’t repeat yourself (DRY), no cut-n-paste.
●Provides a single place for change when needed - maintainability.
42
New cards
What does # mean in a class diagram?
protected
43
New cards
What does + mean in a class diagram?
Public
44
New cards
What does - mean in a class diagram?
private
45
New cards
What does a dependency mean in UML?
It means that one class uses or creates objects of another class
46
New cards
What does abstraction by contract benefit?
The team writing the method can then change the code however they want, as long as it still meets the specification.
The specification must therefore have sufficient information to provide the caller with meaningful guarantees.
The specification must therefore have sufficient information to provide the caller with meaningful guarantees.
47
New cards
What does abstraction by contract mean?
Anyone calling a method should only need to know its specification; not its implementation.
48
New cards
What does aggregation mean in UML?
An aggregation is a special kind of association indicated by a hollow diamond on one end of the icon. It indicates a “whole/part” relationship, in that the class to which the arrow points is considered a “part” of the class at the diamond end of the association.
49
New cards
What does client code mean?
Code that needs to use (i.e. call) a certain functionality.
50
New cards
What does defensive programming mean?
Designing your code with the thought that the developers of the executors (code that your code depends on), and clients (code that depends on your code), not only could make mistakes, but that they actively want to misuse your code (“malicious intent”).
51
New cards
What does executor code mean?
The code that provides the functionality that the client code needs.
52
New cards
What does high cohesion mean?
It means that all components of a module cooperate to handle the module's responsibilities without needing to call components from other modules.
53
New cards
What does implementation inheritance mean?
It is another word for subclassing. Essentially that a subclass inherits all of the attributes and methods from the super class. Except for constructors.
54
New cards
What does italics mean in a class diagram?
abstract class
55
New cards
What does liskov substitution principle say about contracts?
If S is a sublclass of T then:
* every object of type S must satisfy the specification of T
* every object of type S must fulfill the contract of T
* So in S: – Pre-conditions must be the same or weaker
* Post-conditions must be the same or stronger
* Invariants must be the same or stronger
* every object of type S must satisfy the specification of T
* every object of type S must fulfill the contract of T
* So in S: – Pre-conditions must be the same or weaker
* Post-conditions must be the same or stronger
* Invariants must be the same or stronger
56
New cards
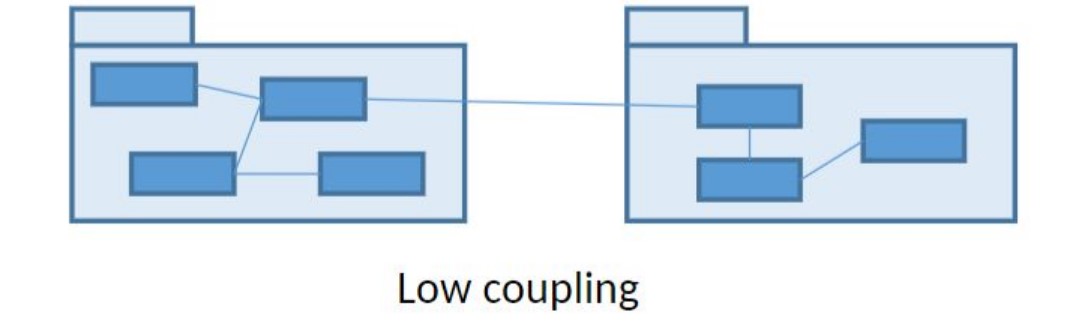
What does low coupling mean?
It means that the modules are very independent and that there is only a small number of dependecies between them
57
New cards
What does mutable mean?
It means that the objects can be changed. Instance attributes can be changed. Instance attributes point to other mutable objects
58
New cards
What does mutate-by-copy mean?
It means that when we want to mutate an object we instead return a copy of the object with the new mutated values
59
New cards
What does opaque pointer mean?
References (pointers) in Java are what’s called ”opaque” – you as a programmer can never see their values, only work with them (e.g. call methods through them).
60
New cards
What does the expression "Use only one dot" mean?
In another class, instead of calling
view.getFrame().repaint();
make a repaintFrame function in the view and call
view.repaintFrame();
view.getFrame().repaint();
make a repaintFrame function in the view and call
view.repaintFrame();
61
New cards
What does the expression design by contract mean?
Design by contract is a design philosophy where a method’s specification is considered as a contract between the client (caller) and the executor.
62
New cards
What does underlined names mean in a class diagram?
static
63
New cards
What does \~ mean in a class diagram?
none, i.e. usually a package
64
New cards
What enables dynamic binding?
Subtype polymorphism
65
New cards
What is a design pattern?
A general solution to a commonly occurring situation within software design.
66
New cards
What is a dynamic type?
A reference variable refers to an object in the heap. The object’s type is the variable’s dynamic type.
67
New cards
What is a literal?
An expression denoting a fixed value
68
New cards
What is a post-condition when designing by contract?
A predicate that must hold after the method has completed, given that the preconditions all held beforehand.
69
New cards
What is a precondition when designing by contract?
A predicate that must hold before the method can be called
70
New cards
What is a primitive type?
A type that points to a value, it is not considered an object and is immutable
71
New cards
What is a reference type?
All types that are not primitive types are reference types. That means that all classes and interfaces are reference types
72
New cards
What is a static type
A static type is the declared type of a reference variable. For example: Polygon p = new ___();
73
New cards
What is a UML class diagram
A diagram showing associations and dependencies between classes in an object oriented system
74
New cards
What is a UML object diagram
A diagram showing a state of the system. This encompasses objects, the stack, and instance variables
75
New cards
What is an alternative to defensive copying?
Immutable adapter. Using the adapter pattern to make immutable versions of objects through adaptations
76
New cards
What is an invariant when designing by contract?
A predicate that must apply for the object to be in a well-formed state. (Apply at all times)
77
New cards
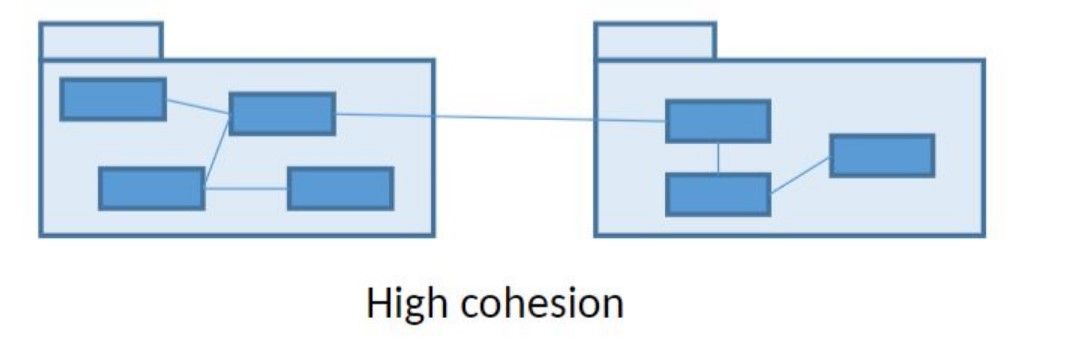
What is cohesion?
Cohesion (”sammanhållning”) is a measurement of the inner cohesion of a module (e.g. method, class, package, ...). How well do the components within the module cooperate?
78
New cards
What is composition in UML?
A composition is an aggregation indicating strong ownership of the parts. In a composition, the parts live and die with the owner because they have no role in the software system independent of the owner.
79
New cards
What is coupling?
Coupling (”sammanbindning”, ”koppling”) is a measurement of the strength of dependency between two separate modules.
80
New cards
What is defensive copying?
Defensive copying is returning a copy of an object when the client asks for the object or some value that the object holds. Usually by returning a new object of the same values
81
New cards
What is dynamic binding?
Dynamic binding (or dynamic dispatch) generally means that the choice between several possible implementations of a polymorphic method (ie overriding) is decided at runtime. This means that we can have mutliple methods of the same name for many different objects of different dynamic type but of the same static type.
For example:
for (Polygon p : polygons) {
p.paint(g); }
Now everything of static type Polygon but different dynamic type can run a method called paint
For example:
for (Polygon p : polygons) {
p.paint(g); }
Now everything of static type Polygon but different dynamic type can run a method called paint
82
New cards
What is dynamic type checking?
The dynamic type is used to determine which implementation of a method (signature) is actually running.
83
New cards
What is implementationsarv? (Implementation Inheritance)
När en klass övertar egenskaperna från en annan klass kallas det för implementationsarv. Vid implementationsarv ärvs (implementationen för) alla instansvariabler och klassvariabler (även privata), och alla ickeprivata metoder. Konstruktorer ärvs inte
84
New cards
What is important to note regarding reference variables
The object’s type does not change after it has been created. The reference does not change; it always points to the same object. The value of the variable is what changes, as it becomes a new reference.
85
New cards
What is M in MVC?
M is the Model (or domain) for the application. It is a representation of all the logic and data for the applications.
There is only one model and it must function independent from a view or controller i.e. should not be dependent on anything but the model.
There is only one model and it must function independent from a view or controller i.e. should not be dependent on anything but the model.
86
New cards
What is multiplicity in UML?
It is a number representing how many objects of that class that are related to the class on the other end of the relation.
87
New cards
What is Parametric Polymorphism for Specialization?

88
New cards
What is parametric polymorphism?
Parametric polymorphism: One type (or method) can be parameterized over another type. The parameterized type (method) defines a structure (algorithm) that is independent of the type it takes as an argument.
89
New cards
What is polymorphism?
Polymorphism is the name of the phenomenon that allows an entity (object, method, function, ...) to behave as if it had several different static types.
90
New cards
What is smart, dumb, thin, in MVC?
A model should be smart - handle all logic
A view should be dumb - only present the model, hence no logic
A controller should be thin - only be a thin layer between the interface and the model/view. Should do minimal work
A view should be dumb - only present the model, hence no logic
A controller should be thin - only be a thin layer between the interface and the model/view. Should do minimal work
91
New cards
What is static type checking?
This information is used only in the compilation, to ensure that everything will go right when the program is run, and to select the correct method signature.
92
New cards
What is subtype polymorphism
If S is a subtype of T, then an object O of type S can behave like an object of type T. O “has many forms”, one for every supertype.
Essentially objects of a subtype can behave like their supertype.
Essentially objects of a subtype can behave like their supertype.
93
New cards
What is the A in reference to MVC?
The application. The applications sets up the model, view, and controller and then sends a message for them to start running
94
New cards
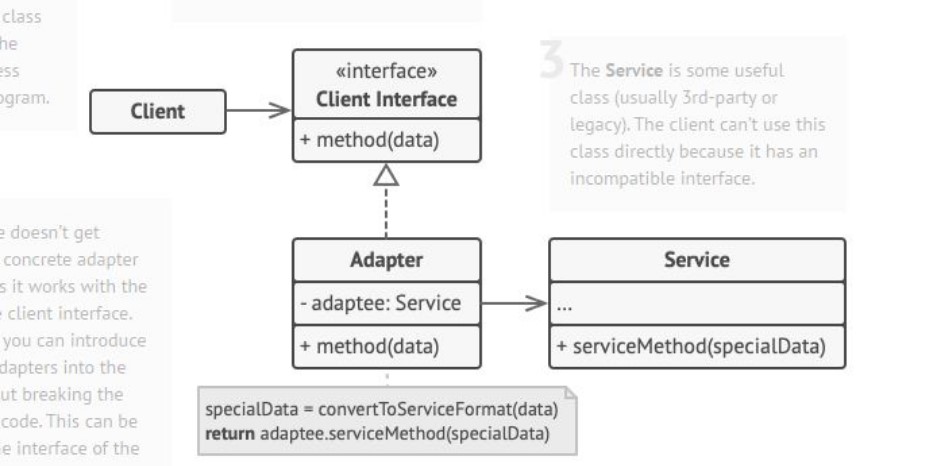
What is the adapter pattern?
Allow otherwise incompatible classes to work together by converting the interface of one class into an interface expected by the clients.
Typically used when code previously worked with components X, and now (also) needs to work with component Y which has a different interface.
Typically used when code previously worked with components X, and now (also) needs to work with component Y which has a different interface.
95
New cards
What is the bridge pattern?
When an aspect of an object can vary independently of the object itself: Create an interface with methods that represent the aspect; Use these methods within the object;
Define different concrete implementations of the aspect and use these with the object as necessary.
Bridge Pattern goes a step further than Template Method Pattern.
The variation is not bound to a specific subclass (context), but defines an independent interface. We can then define completely different behaviors as independent classes implementing this interface.
Define different concrete implementations of the aspect and use these with the object as necessary.
Bridge Pattern goes a step further than Template Method Pattern.
The variation is not bound to a specific subclass (context), but defines an independent interface. We can then define completely different behaviors as independent classes implementing this interface.
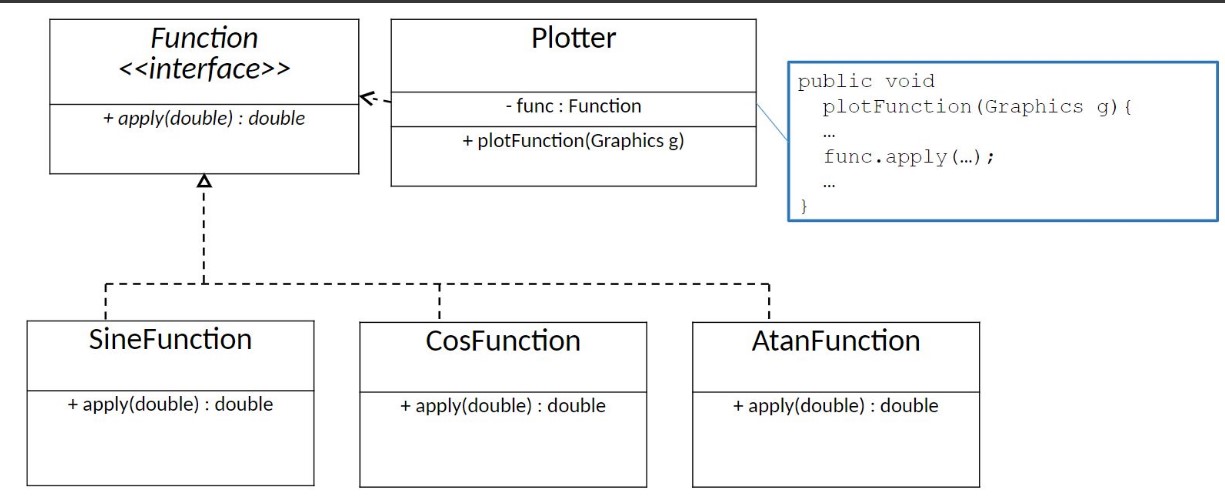
96
New cards
What is the C in MVC?
The Controller. The controller sends signals to the model and the view based on input.
97
New cards
What is the dependency inversion principle?
Depend on abstractions, not on concrete implementations. This means that classed should depend on abstractions which include but are not limited to abstract classes and interfaces. They should not depend on the classes that implement these abstractions. The result of this is following the OCP and making extendable code.
For example: A musicplayer should depend on the interface Instrument that the concrete implementation (Guitar, Piano, etc.) implement, instead of depending on Guitar and Piano itself
For example: A musicplayer should depend on the interface Instrument that the concrete implementation (Guitar, Piano, etc.) implement, instead of depending on Guitar and Piano itself
98
New cards
What is the difference between subtype and parametric polymorphism?
Subtype polymorphism is about concrete objects behaving in the same way and therefore can be used in place of each other.
Parametric polymorphism is about defining code that is independent of an underlying type. This code can then be reused in all concrete instances of the type.
Parametric polymorphism is about defining code that is independent of an underlying type. This code can then be reused in all concrete instances of the type.
99
New cards
What is the difference between the state and strategy patterns?
The state pattern is about switching to a different state for different behaviour. Strategy is about choosing an implementation or using an algorith regardless of implementation.
100
New cards
What is the facade pattern?
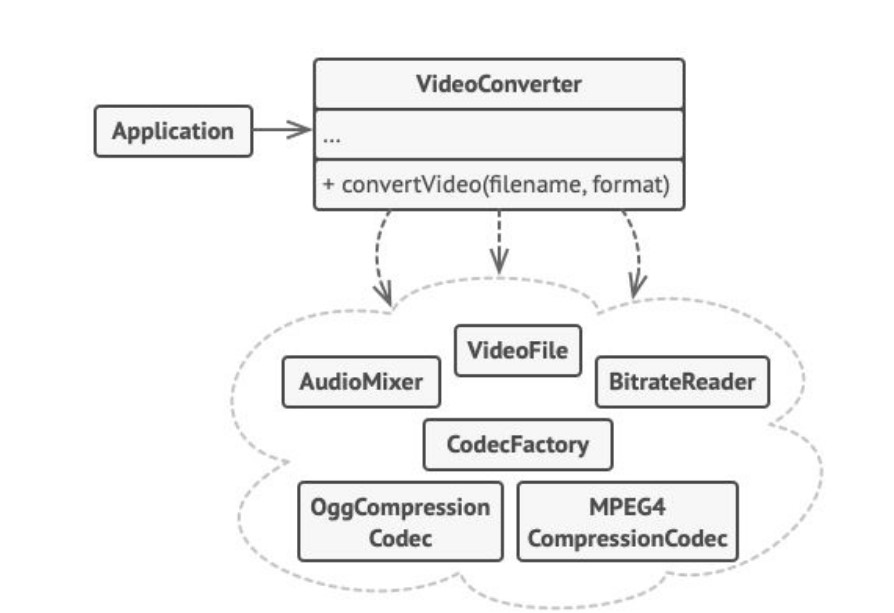
A facade is a class that provides a simple interface to a complex subsystem which contains lots of moving parts. A facade might provide limited functionality in comparison to working with the subsystem directly. However, it includes only those features that clients really care about.