Receptors 3
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Affinity
How well the drug interacts with the receptor
can be measured using a binding assay. this is a direct measure of the physical interaction between a drug and a receptor
Specificity
how selective is drug binding to one type of receptors but not to other types of receptors
Efficacy
this tells us how effective a drug is at producing a particular receptor response
potency
this tells how much of the drug is required to produce an effect
Analyze radioligand binding data
a drug may bind to many biological targets
high affinity - specific binding
low affinity - nonspecific binding
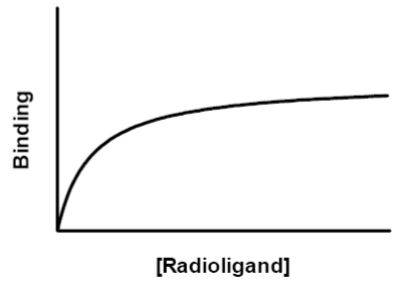
subtract non-specific binding from total binding to measure the amount of specific binding
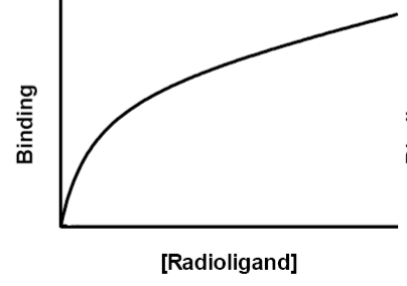
radioligand binding data - total binding
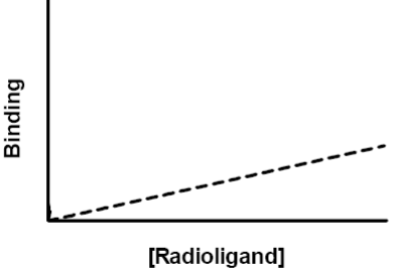
radioligand binding data - non specific binding
radioligand binding data - specific binding
receptor fractional occupancy
used in receptor-drug binding curves
= [Receptor bound with drug] / [(free receptor) + (receptor bound with drug)]
Kd - equations
equilibrium dissociation constant
= tendency of RD complex to dissociate / tendency of R&D to form RD complex
= [R] [D] / [RD]
Affinity = 1/Kd
Kd - definition
drug concentration when 50% of receptors are bound with the drug
Functional assay
a measure of the changes in the function of the receptor
used for evaluating potency and efficacy
EC50
the concentration of a drug that produces 50% of maximal response
measure of potency
higher potency = lower value
efficacy - graph evaluation
reflects the upper limit (maximal response) achieved by a drug on the dose-response curve
potency - graph evaluation
inversely correlated to EC50
Factors affecting a drug’s clinical effectiveness
potency
efficacy
ability to reach receptors (route of admin, absorption, distribution, clearance)
Agonist
binds to a receptor and activates it
shifts equilibrium towards active state
Antagonist
binds to a receptor but does not activate signaling
does not change equilibrium between active/inactive but can prevent agonist binding
inverse agonist
produces a response opposite that induced by a full agonist
shifts equilibrium towards inactive state
Partial agonist
produces a lower response than do full agonists
Chantix (Varenicline)
nicotinic AChR partial agonist
used as replacement therapy in smoking cessation
instead of nicotine - full agonist
Narcan (naloxone)
pure opioid receptor antagonist
no/little symptoms by itself
for Tx opioid OD induced respiratory depression, CNS depression
IM injection or nasal spray (effective after 2-5min)
competitive antagonists
compete for same binding site as agonist
shifts curve to the right
sufficiently high concentrations of agonists can overcome a given concentration of competitive antagonists
max response not changes, change in EC50
noncompetitive antagonist
bind to allosteric site on receptor and interferes with agonist binding or modifies receptor activity
can NOT be overcome by high concentrations of agonist
max response reduced (curve shorter)
EC50 may or may not change