Week 5B: Depth perception and motion perception and eye movements
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
11 Depth cues
Occlusion, retinal size, perspective, familiarity, height in picture, blur, brightness, colour, shadow, motion parallax, stereo vision (disparity)
If objects of known size have different retinal sizes then they must be at (…). Familiarity and size.
Different distances
Explain the Ames room based on the depth cues
perspective (lines look parallel), relative size (left person looks smaller than the right one), and occlusion (the real shapes are hidden because of illusion)
Lens accommodation: For far objects the ciliary muscles are (…) and the lens is (…)
Relaxed, thin
Lens accommodation: For near objects the ciliary muscles are (…) and the lens is (…)
Tensed, thick
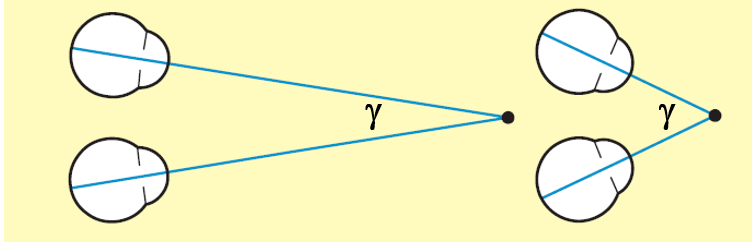
The state of the extraocular muscles offers a cue to vergence angle (gamma), and hence fixation distance. Large distance: (…) vergence angle
Small
Binocular disparity
Slight difference in the images seen by the left and right eyes due to their horizontal separation
When does crossed disparity happen
when an object is closer than the fixation point (The image of the object falls to the outer side (temporal side) of each retina, so to align them mentally, the brain has to "cross" the lines of sight inward.)
When does uncrossed disparity happen
when an object is farther than the fixation point (The image lands on the inner side (nasal side) of each retina, so the brain "uncrosses" the lines of sight outward to fuse them)
Vergence angle formula (binocular parallax)
beta - alpha
Version angle formula (binocular lattitude)
(beta + alpha)/2
Vieth-Muller circle
The curve of constant vergence angle is a circle through the fixation point and the nodal points of the eyes
How is stereo vision caused
Each eye having a slightly different image (horizontal disparity)
Why does stereo vision cause head-ache and eye-strain?
Your eyes are tricked into converging as if objects are at different depths, but the actual object is at a fixed distance, so accommodation doesn't match. This conflict between cues confuses the visual system and makes the eye muscles work harder to reconcile the mismatch
What is vergence
the inward or outward turning of the eyes to focus on objects at different distances.
How does a stereo viewer prevent eye-strain and headaches
Aligning the eye correctly to look at the different images by blocking the incorrect half-image
Random Dot Stereogram
A subset of dots in one image is shifted in position relative to the other images. The disparity between the images induces a sensation of depth.
What does a Random Dot Stereogram show
Disparity alone is sufficient to support an impression of depth and shape
What is the correspondence problem in stereopsis
Each point in one image can be matched in many ways with points in the other image
Cue integration
In stereograms, virtual reality cue conflicts occur. This is used in psychophysical experiments to determine how the human brain combines depth cues
Cue combination
The visual system combines cues to derive robust, reliable depth estimates
Monocular cues are available using (…) eye(s), while binocular cues require (…) eye(s).
one, two
Cue magnitude generally varies lawfully with (…) and varies most at depths (…)
a distance from fixation, close to fixation