peripheral nervous system
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
Last updated 2:56 AM on 11/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
peripheral
along the outside
2
New cards
what makes up the peripheral nervous system
all the nervous tissue structures except the brain and spinal cord
3
New cards
difference between central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
peripheral nervous system is not protected by bone
4
New cards
nerves of the peripheral nervous system
12 cranial nerves and 31 spinal nerves pairs
5
New cards
how long are spinal nerves
extremely short in length and course laterally for 1-5 millimeters
6
New cards
where do spinal nerves exit
intervertebral foramina located between each vertebral segment level
7
New cards
Number of cervical nerves
8 pairs (C1-C8)
8
New cards
how do cervical spinal nerves course?
above the numbered cranial vertebrae (except C8)
9
New cards
throacic nerves
12 pairs (T1-T12) and correspond to the thoracic vertebrae above it
10
New cards
lumbar nerves
5 pairs (L1-L5) and corresponds to the lumbar vertebrae above it
11
New cards
End of the spinal cord (the conus medullaris)
where sacral and coccygeal nerves emerge
12
New cards
sacral spinal nerves
5 pairs that emerge through the pelvic and dorsal sacral foramina and sacral hiatus of the sacrum
13
New cards
coccygeal spinal nerves
1 pair emerge through the sacral hiatus above the coccyx
14
New cards
dorsal rami
supply structures on the back
small branches that course posteriorly and innervate the deep back muscles and give cutaneous innervation to the skin of the back
small branches that course posteriorly and innervate the deep back muscles and give cutaneous innervation to the skin of the back
15
New cards
ventral rami
supply structures on the front of the torso and the extremities
also give rise to the nerve plexuses that innervate the upper and lower extremities
also give rise to the nerve plexuses that innervate the upper and lower extremities
16
New cards
Which rami are larger?
ventral
17
New cards
nerve plexus
braiding or twining together of nervous tissue
18
New cards
4 major plexus systems
cervical plexus, brachial plexus, lumbar plexus and sacral plexus
19
New cards
cervical plexus (ventral rami C1-C4)
supplies motor innervation to some muscles of the neck region
responsible for the cutaneous innervation to the skin of the neck and sides of the head
responsible for the cutaneous innervation to the skin of the neck and sides of the head
20
New cards
major nerves in the cervical plexus
phrenic nerve
21
New cards
Phrenic Nerve
innervates the diaphragm C3-C5
22
New cards
Brachial Plexus (ventral rami C5- T1)
supplies the musculature of the entire upper limb with the exception of the trapezius muscle (CN XI) and levator scapula (C3 and C4 spinal nerves)
also gives cutaneous innervation to the majority of the upper limb except for the skin over the upper medial portion of the arm and part of the upper shoulder
In total, gives off a total of 16 nerves (32 for right and left)
also gives cutaneous innervation to the majority of the upper limb except for the skin over the upper medial portion of the arm and part of the upper shoulder
In total, gives off a total of 16 nerves (32 for right and left)
23
New cards
brachial plexus breakdown
roots, trunks, divisions (3 posterior, 3 anterior), cords (lateral, posterior and medial) , branches
24
New cards
terminal branches of brachial plexus
Musculocutaneous Nerve
Radial Nerve
Median Nerve
Ulnar Nerve
Radial Nerve
Median Nerve
Ulnar Nerve
25
New cards
musculocutaneous nerve
formed from the ventral rami C5-C7 and is a derived from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus
26
New cards
innervation of the musculocutaneous nerve
anterior upper arm (coracobrachialis, biceps brachii and brachialis)
27
New cards
lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve
musculocutaneous nerve as it courses lateral to the tendon of insertion of the biceps brachii muscle
supplies cutaneous innervation to the skin on the lateral forearm
supplies cutaneous innervation to the skin on the lateral forearm
28
New cards
median nerve
made from the ventral rami of spinal nerves C5-T1 is derived from the medial and lateral roots of the brachial plexus
courses through the medial surface of the arm within the neurovascular compartment
courses through the medial surface of the arm within the neurovascular compartment
29
New cards
innervations of the median nerve
supply the majority of muscles in the anterior forearm and give cutaneous innervation to portions of the hand
30
New cards
what is special about the median nerve
only nerve to pass deep to the flexor retinaculum and thus lies within the carpal tunnel
31
New cards
potion of the hand the median nerve innervates
the lateral surface of the palm and the distal ends of digits 1, 2, 3 and the lateral half of digit 4
32
New cards
ulnar nerve
derived from the ventral rami of spinal nerves C8 and T1 and is a continuation of the medial cord of the brachial plexus
courses through the medial surface of the arm within the neurovascular compartment
courses through the medial surface of the arm within the neurovascular compartment
33
New cards
Location of the median nerve
lies posterior to the medial epicondyle of the humerus (along the groove for the ulnar nerve) and continues distally along the medial surface of the forearm
34
New cards
innervation of the median nerve
supplies 1 ½ muscles in the anterior forearm and the majority of hand muscles
35
New cards
hand innervations of the ulnar nerve
Superficial Branch of the Ulnar Nerve innervates the skin on the medial surface of the palm and dorsum of the hand
It also innervates the distal end of digit 5 and the medial half of digit 4
It also innervates the distal end of digit 5 and the medial half of digit 4
36
New cards
carpal tunnel syndrome
results from significant compression of the ulnar nerve against the medial epicondyle
37
New cards
radial nerve
derived from the ventral rami of spinal nerves C5-T1 and is a continuation of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus
38
New cards
innervation of the radial nerve
innervate all the posterior forearm muscles
39
New cards
innervation to the hand radial nerve
superficial branch of the radial nerve innervates the skin on the lateral dorsal surface of the hand and lateral palmar surface of the thenar area
40
New cards
lumbosacral plexus (ventral rami L1-S4)
supplies muscular and cutaneous innervation to the entire lower limb
41
New cards
how can the lumbosacral plexus be divided?
lumbar plexus and sacral plexus
42
New cards
lumbar plexus (ventral rami L1- upper L4)
supplies the tissue and musculature of the anterior, medial and lateral thigh
43
New cards
location of lumbar plexus
the posterior wall of the abdomen within the substance of the psoas major muscle
44
New cards
major nerves of lumbar plexus
femoral and obturator
45
New cards
femoral nerve
L2, L3 and the upper division of ventral ramus L4
Macular distribution: Iliopsoas, Sartorius, Pectineus, Quadriceps Femoris
Macular distribution: Iliopsoas, Sartorius, Pectineus, Quadriceps Femoris
46
New cards
obturator nerve
Derived from the Ventral Rami of spinal nerves L2, L3 and the upper division of ventral ramus of L4
Transverses through the obturator foramen
Muscular Distribution: Gracilis , Adductor Longus, Adductor Brevis, Adductor part of Adductor Magnus
Transverses through the obturator foramen
Muscular Distribution: Gracilis , Adductor Longus, Adductor Brevis, Adductor part of Adductor Magnus
47
New cards
sacral plexus (Lower L4, L5- S4)
supplies tissues and musculature of the pelvis, gluteal region, posterior thigh, the entire leg and all the foot
48
New cards
location of sacral plexus
along the lateral walls of the pelvis, medial to the piriformis muscle
49
New cards
major nerves of sacral plexus
superior gluteal nerve
inferior gluteal nerve
nerve to piriformis
nerve to superior gemellus and obturator internus
nerve to inferior gemellus and quadratus femoris
pudendal nerve
posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
sciatic nerve (common fibular nerve, tibial nerve, medial and lateral plantar nerves, superficial and deep fibular nerves)
inferior gluteal nerve
nerve to piriformis
nerve to superior gemellus and obturator internus
nerve to inferior gemellus and quadratus femoris
pudendal nerve
posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
sciatic nerve (common fibular nerve, tibial nerve, medial and lateral plantar nerves, superficial and deep fibular nerves)
50
New cards
superior gluteal nerve
Originates from the lower division of the ventral ramus of L4 and the ventral rami of L5 and S1
Muscular distribution: Gluteus Medius , Gluteus Minimus, Tensor Fasciae Latae
Muscular distribution: Gluteus Medius , Gluteus Minimus, Tensor Fasciae Latae
51
New cards
inferior gluteal nerve
L5, S1 and S2
muscular innervation: Gluteus Maximus
muscular innervation: Gluteus Maximus
52
New cards
Nerve to piriformis
ventral ramus of spinal nerve S2
53
New cards
Nerve to superior gemellus and obturator internus
ventral rami of spinal nerves L5, S1 and S2
54
New cards
Nerve to Inferior Gemellus and Quadratus Femoris
lower division of the ventral ramus of L4 and the ventral rami L5 and S1
55
New cards
pudendal nerve
ventral rami of spinal nerves S2, S3 and S4
responsible for innervating the male and female genitalia and plays a role in the sexual stimulatory response
responsible for innervating the male and female genitalia and plays a role in the sexual stimulatory response
56
New cards
posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
Ventral rami of spinal nerves S1, S2 and S3
Largest cutaneous nerve in the body
Provides cutaneous innervation to the skin on the posterior surface of the thigh
Largest cutaneous nerve in the body
Provides cutaneous innervation to the skin on the posterior surface of the thigh
57
New cards
sciatic nerve
Largest nerve in the body
Lower division of the ventral ramus of L4 and the ventral rami of L5, S1, S2 and S3
Courses through the greater sciatic notch and enters the gluteal region inferior to the piriformis muscle
Lower division of the ventral ramus of L4 and the ventral rami of L5, S1, S2 and S3
Courses through the greater sciatic notch and enters the gluteal region inferior to the piriformis muscle
58
New cards
common epineurium
a connective tissue surrounding the individual nerves
59
New cards
nerves within the common epineurium
Tibial Nerve and Common Fibular Nerve
60
New cards
course of the sciatic nerve
courses distally along the posterior surface of the thigh between the adductor magnus and the long head of biceps femoris
61
New cards
sciatic nerve muscle innervation
Extensor Part of Adductor Magnus
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Long and Short Heads of Biceps Femoris
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Long and Short Heads of Biceps Femoris
62
New cards
tibial nerve muscle innervation
Gastrocnemius
Soleus
Plantaris
Tibialis Posterior
Flexor Hallucis Longus
Flexor Digitorum Longus
(posterior leg muscles)
Soleus
Plantaris
Tibialis Posterior
Flexor Hallucis Longus
Flexor Digitorum Longus
(posterior leg muscles)
63
New cards
2 divisions of the tibial nerve
Medial and Lateral Plantar Nerves
64
New cards
medial and lateral plantar nerves
supply the majority of the musculature on the plantar surface of the foot
65
New cards
branches of the common fibular nerve
bifurcates at the neck of the fibula into Superficial and Deep Fibular (Peroneal) Nerves
66
New cards
deep fibular nerve
courses inferiorly with the anterior tibial artery on the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane
67
New cards
muscular distribution of deep fibular nerve
tibialis anterior
extensor hallucis longus
extensor digitorum longus
Peroneus tertius
extensor digitorum brevis
(anterior leg)
extensor hallucis longus
extensor digitorum longus
Peroneus tertius
extensor digitorum brevis
(anterior leg)
68
New cards
muscular distribution of superficial fibular nerve
peroneus longus
peroneus brevis
(lateral leg)
peroneus brevis
(lateral leg)
69
New cards
intercostal nerves
derived from the ventral rami of spinal nerves T1- T11
70
New cards
innervation of intercostal nerves
intercostal muscles located between the ribs
cutaneous innervation to the skin on the lateral and anterior thoracic walls
cutaneous innervation to the skin on the lateral and anterior thoracic walls
71
New cards
subcostal nerves
derived from the ventral rami of spinal nerves T12
72
New cards
innervation of subcostal nerves
the muscles of the abdominal wall (Rectus Abdominis, Internal and External Obliques and Transversus Abdominis)
Cutaneous branches of the subcostal nerves also innervate the skin on the lateral abdominal wall
Cutaneous branches of the subcostal nerves also innervate the skin on the lateral abdominal wall
73
New cards
Foramina of cranial base
where cranial nerves enter and exit the cranial cavity
74
New cards
what kinds of neurons can cranial nerves have
motor, sensory or both
75
New cards
foramina of the cribriform plate
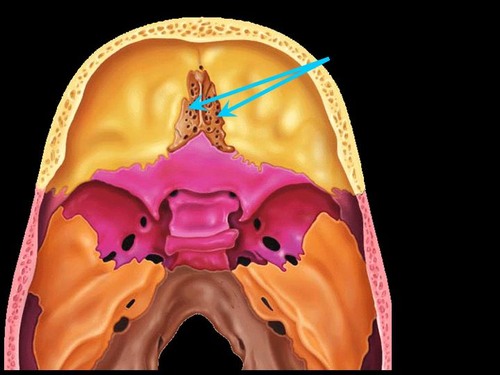
76
New cards
optic canal
77
New cards
superior orbital fissure
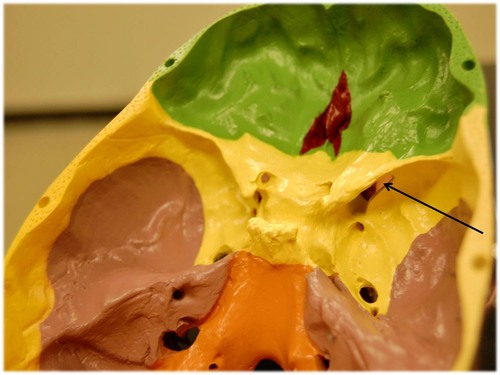
78
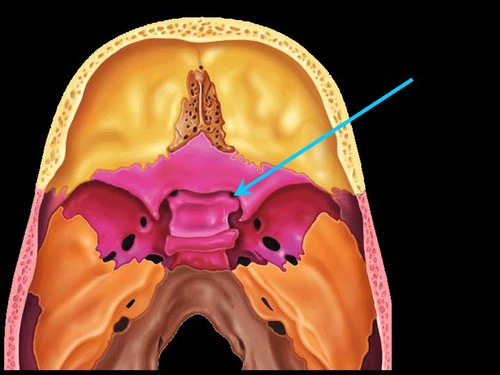
New cards
foramen rotundum
79
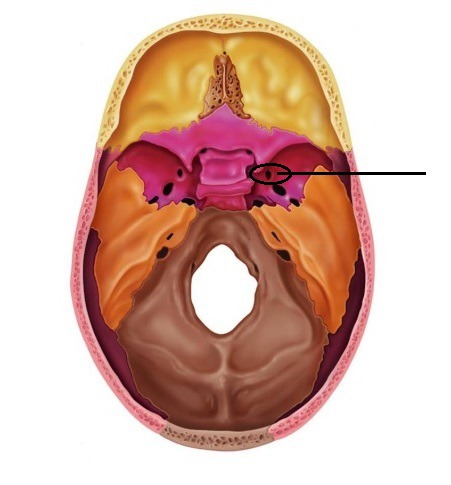
New cards
foramen ovale
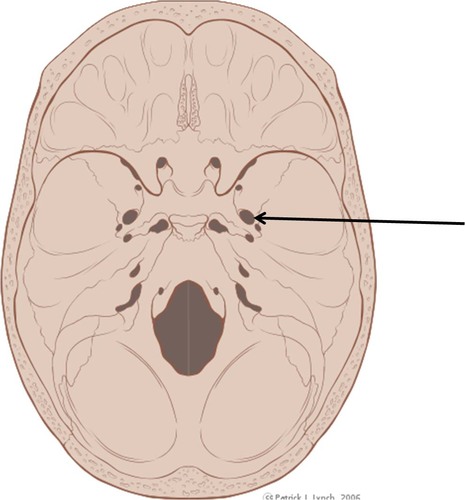
80
New cards
internal accoustic meatus
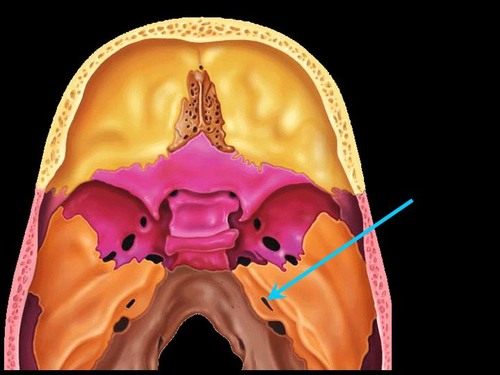
81
New cards
jugular foramen
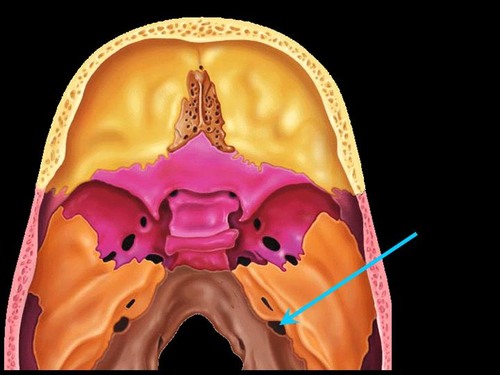
82
New cards
hypoglossal canal
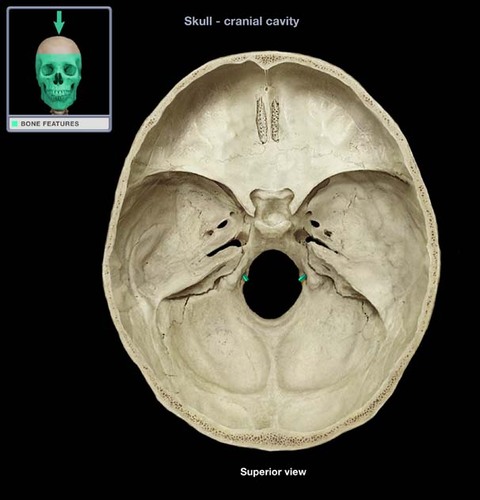
83
New cards
Olfactory Nerve
CN 1
afferent/ sensory in nature
enters cranial cavity foramina of the cribriform plate
conveys smell by nerve endings in superior nasal mucosa
afferent/ sensory in nature
enters cranial cavity foramina of the cribriform plate
conveys smell by nerve endings in superior nasal mucosa
84
New cards
path of olfactory sense
olfactory nerve fibers "synapse" in the olfactory bulb and extend posteriorly as the olfactory tracts
olfactory nerves lead to the temporal lobes of the brain which contain the primary olfactory cortex for interpretation of smell
olfactory nerves lead to the temporal lobes of the brain which contain the primary olfactory cortex for interpretation of smell
85
New cards
optic nerve
CN 11
afferent in nature
conveying sensory information to the brain for the interpretation of visual stimuli
optic canal
afferent in nature
conveying sensory information to the brain for the interpretation of visual stimuli
optic canal
86
New cards
optic nerve path to the brain
optic nerves course posteriorly, "synapsing" on the thalamus and then continue as the optic radiations which lead to the occipital lobe of the brain (the primary visual cortex) for interpretation of the sense of sight
87
New cards
Oculomotor (III) Nerve
efferent in nature
innervates intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of eye movement
exits through the superior orbital fissure
innervates intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of eye movement
exits through the superior orbital fissure
88
New cards
extrinsic eye muscles innervated by oculomotor nerve
Medial rectus
Superior rectus
Inferior rectus
Inferior oblique
Superior rectus
Inferior rectus
Inferior oblique
89
New cards
intrinsic eye muscles
involved with dilation and contraction of the iris
90
New cards
Trochlear Nerve (IV)
efferent in nature
exits the cranial cavity through the superior orbital fissure
extrinsic eye movement: Superior oblique
exits the cranial cavity through the superior orbital fissure
extrinsic eye movement: Superior oblique
91
New cards
Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
both motor and sensory nerve fibers
3 branches: Ophthalmic nerve, Maxillary nerve, Mandibular nerve
3 branches: Ophthalmic nerve, Maxillary nerve, Mandibular nerve
92
New cards
Opthalmic Nerve (V1)
exits through the superior orbital fissure
supply the lacrimal glands and give cutaneous innervation to the skin of the forehead, nose and upper eyelids.
supply the lacrimal glands and give cutaneous innervation to the skin of the forehead, nose and upper eyelids.
93
New cards
maxillary nerve (V2)
exits the cranial cavity through the foramen rotundum
supply the superior dental plexus, lateral scalp, cheek, lower eyelid, lateral nose and upper lip
supply the superior dental plexus, lateral scalp, cheek, lower eyelid, lateral nose and upper lip
94
New cards
mandibular nerve (V3)
exits the cranial cavity through the foramen ovale
gives off the inferior alveolar nerve which supplies the inferior dental plexus,
Other branches supply sensation to the skin and mucosa of the cheek, the anterior 2/3 of the tongue (for general sensation) and the muscles of mastication
gives off the inferior alveolar nerve which supplies the inferior dental plexus,
Other branches supply sensation to the skin and mucosa of the cheek, the anterior 2/3 of the tongue (for general sensation) and the muscles of mastication
95
New cards
abducent nerve (VI)
exits the cranial cavity through the superior orbital fissure
innervates a single extrinsic muscle of eye movement: Lateral rectus
innervates a single extrinsic muscle of eye movement: Lateral rectus
96
New cards
Facial Nerve (VII)
exits the cranial cavity through the internal acoustic meatus
both motor and sensory in nature
anterior 2/3 of the tongue for taste supply sensory innervation to the side of the face and motor innervation to the muscles of facial expression
both motor and sensory in nature
anterior 2/3 of the tongue for taste supply sensory innervation to the side of the face and motor innervation to the muscles of facial expression
97
New cards
Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
afferent in nature
conveys sensory information for hearing and balance to the brain
enters the cranial cavity through the internal acoustic meatus
conveys sensory information for hearing and balance to the brain
enters the cranial cavity through the internal acoustic meatus
98
New cards
2 parts of vestibulocochlear nerve
vestibular branch and cochlear branch
99
New cards
vestibular branch of vestibulocochlear nerve
courses from the semicircular canals and is responsible for balance
100
New cards
cochlear branch of vestibulocochlear nerve
courses from the cochlea and is responsible for the sense of hearing