Principles of Economics Macroeconomics Waseem Noor
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
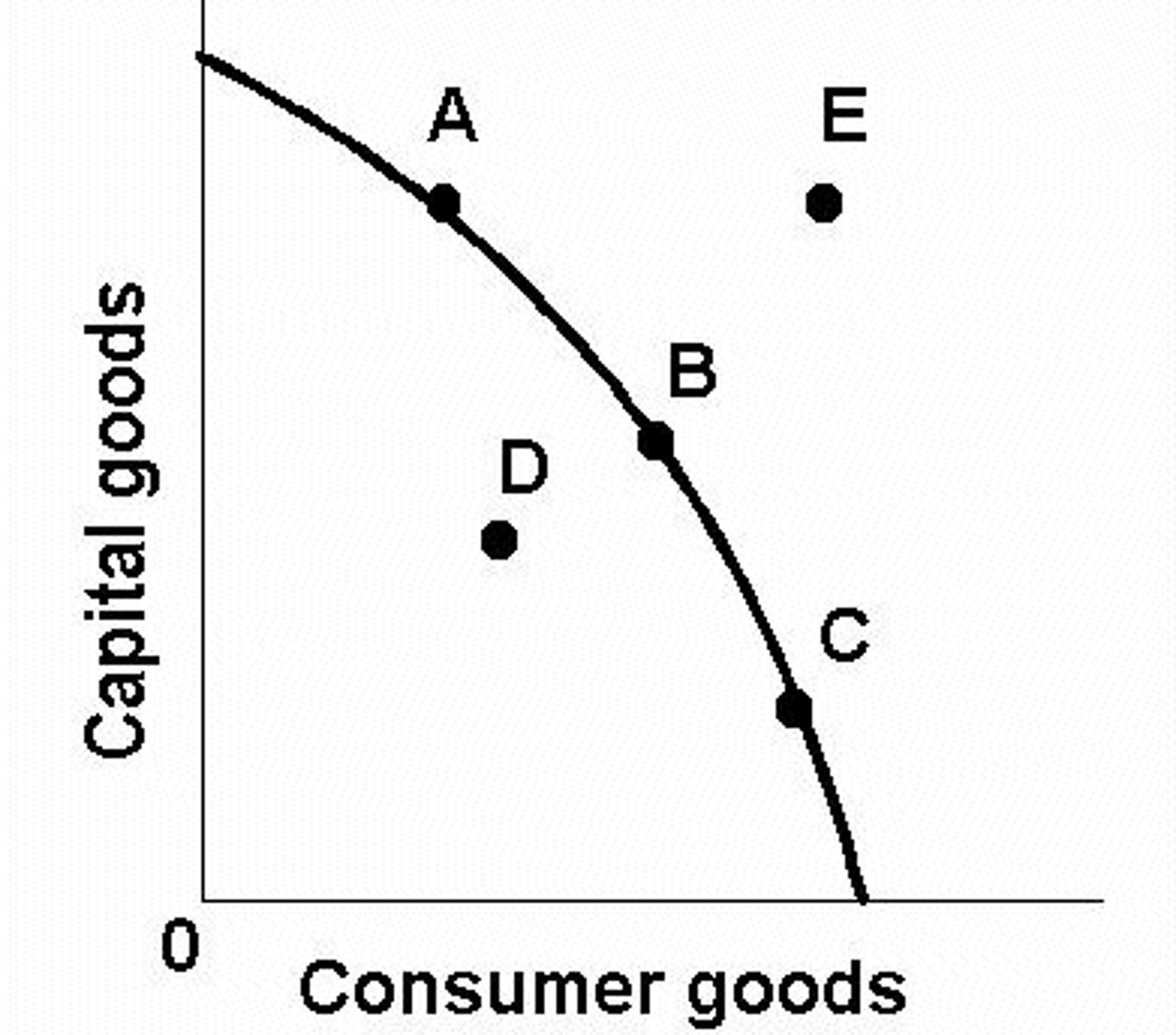
production possibilities curve
shows the relationship between the maximum production of one good for a given level of production of another good.
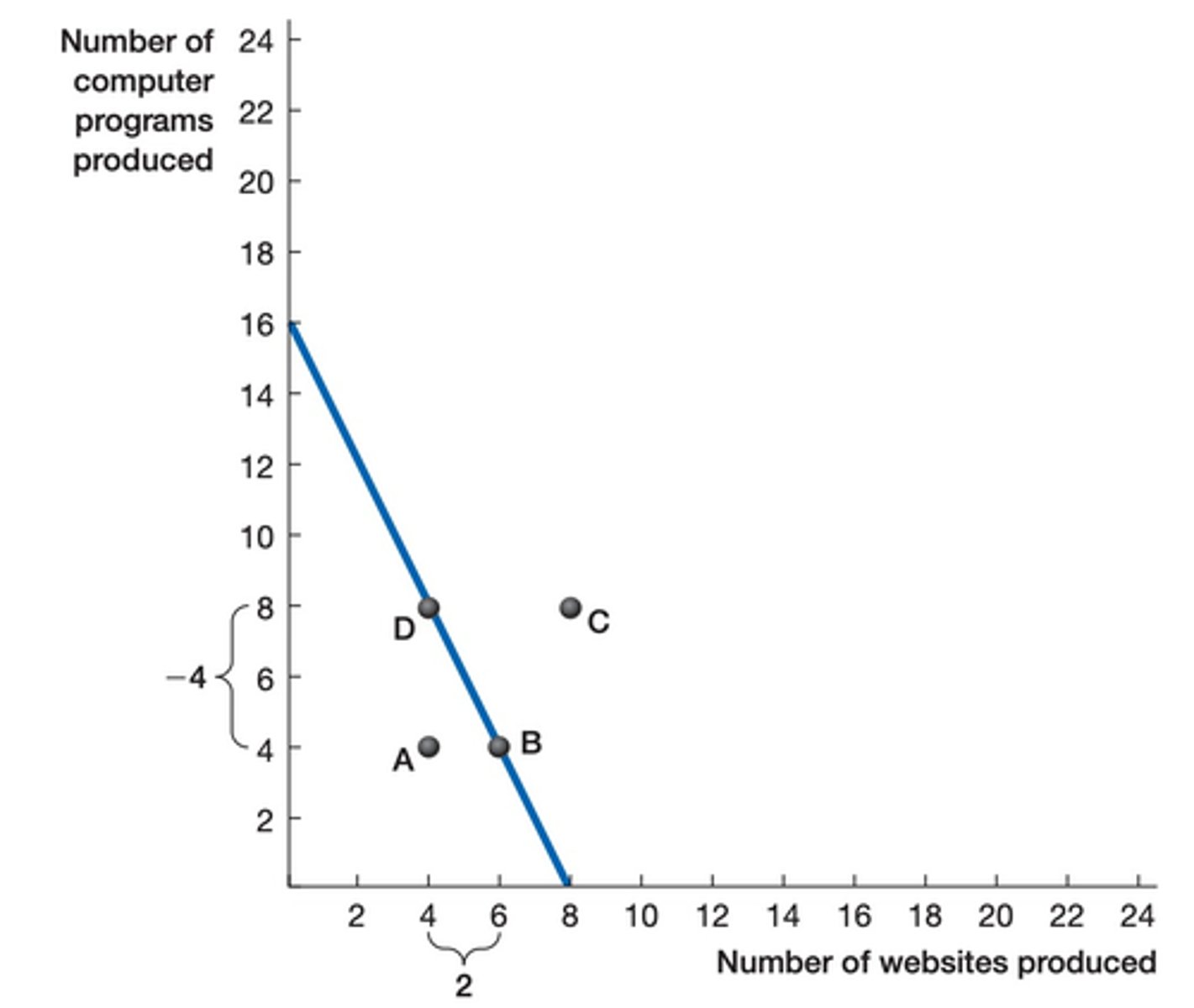
attainable and inefficient
Point A is?
attainable and efficient
Point B is?
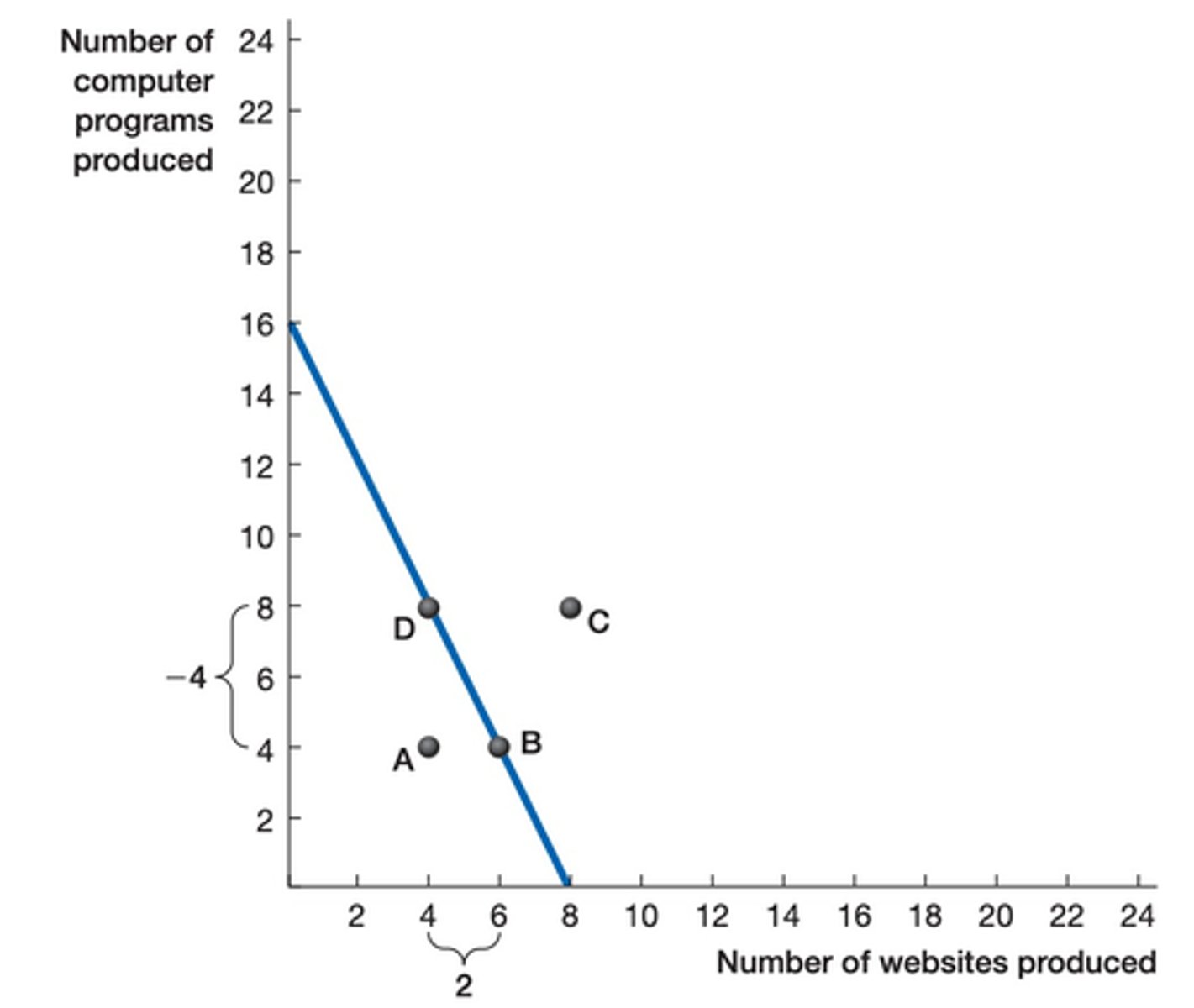
unattainable
Point E is?
give up/gain
opportunity cost formula (of other good/of good you are asked to compare)
3/4
if you lose 3 websites in order to gain the production of 4 computers what is the opportunity cost of computers produced?
comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer
specialization
occurs when someone produces only if they have a comparative advantage
absolute advantage
the ability of being able to produce more given the same resources
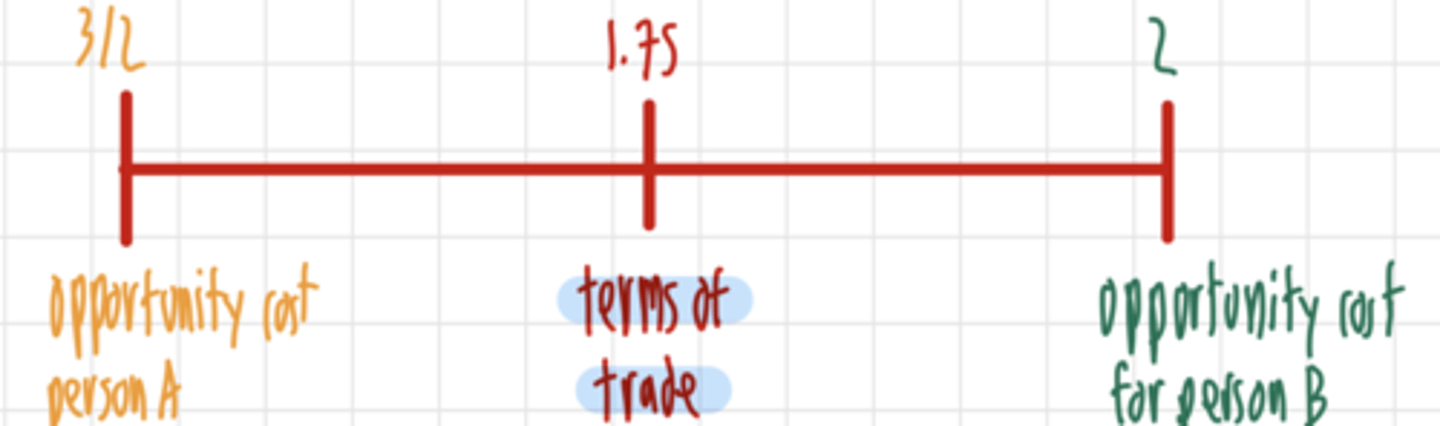
terms of trade
the negotiated exchange rate of goods for goods
fixed
In the short run the PPC is?
fluctuates
In the long run the PPC?
person B
If the opportunity cost is 1.76 who produces the good?
benefitial
trading is always
Exports
produced domestically and sold abroad (uppercase first letter)
Imports
goods produced abroad and sold domestically (uppercase first letter)
net importer
imports are worth more than exports over a given time period
free trade
the ability to trade without hindrance or encouragement from the government
world price
the price of a good that prevails in the world market for that good
domestic price
the price of a good or service within a country, determined by domestic demand and supply
Sellers win, buyers lose
If domestic price is below the world price the country becomes an exporter. What happens with sellers and buyers
Sellers lose, buyers win
If domestic price is above the world price the country becomes an importer. What happens with sellers and byuers?
Determinants of comparative advantage
Natural resources, techonology, education/labor force, abundance of labor and physical capital, capital
Arguments against free trade
1. National security concerns
2. Fear of the effects of globalization on a nation's culture
3. Environmental and resource concerns
4. Infant industry arguments
5. Potential negative effects on local wages and jobs
Protectionism
The idea that free trade can be harmful and that the goverment has to intervene. Raises price to consumers and lowers social surplus
Tarrifs
taxes levied against goods and services transported across political boundaries
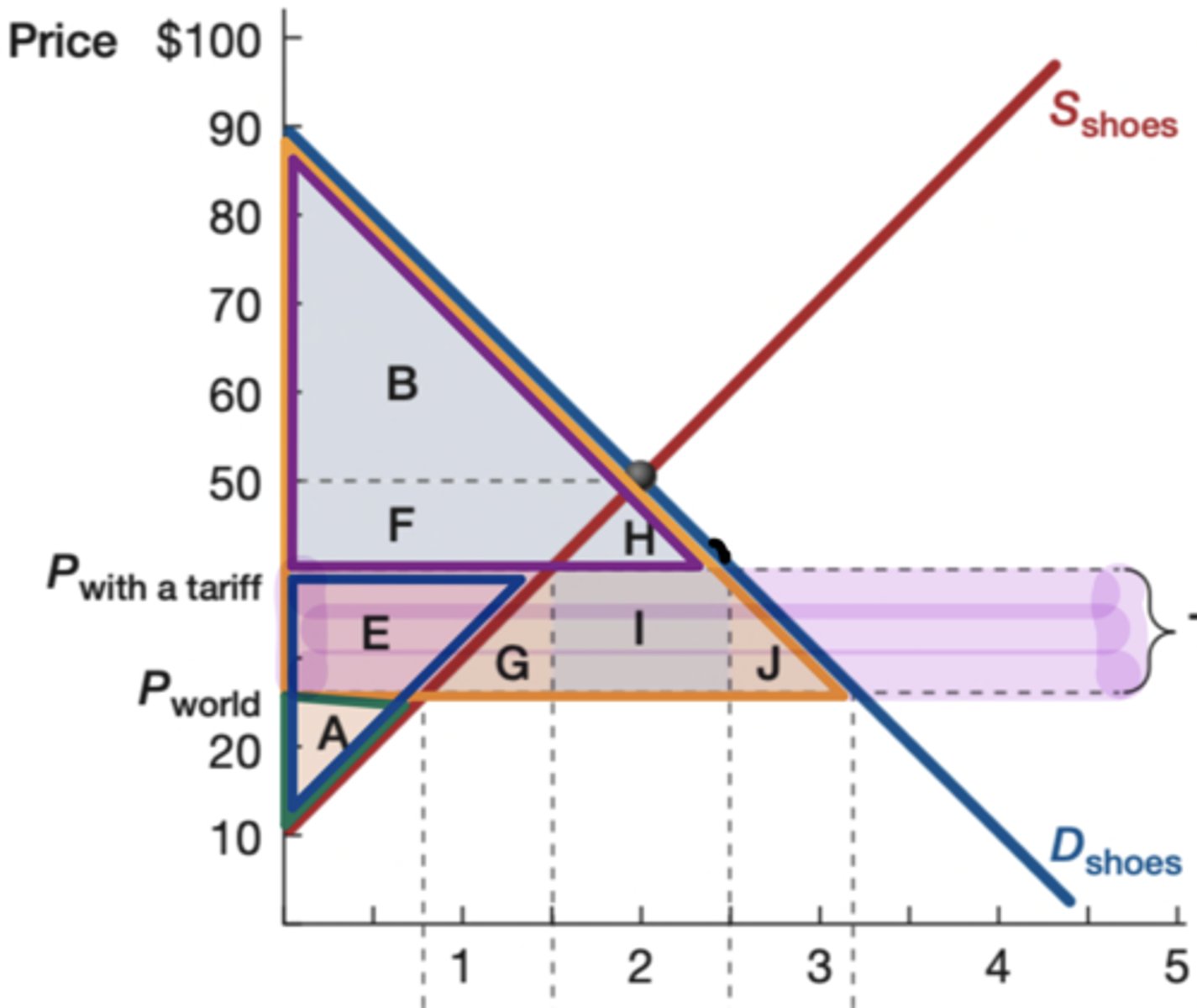
Orange
What is the color of the original consumer surplus?
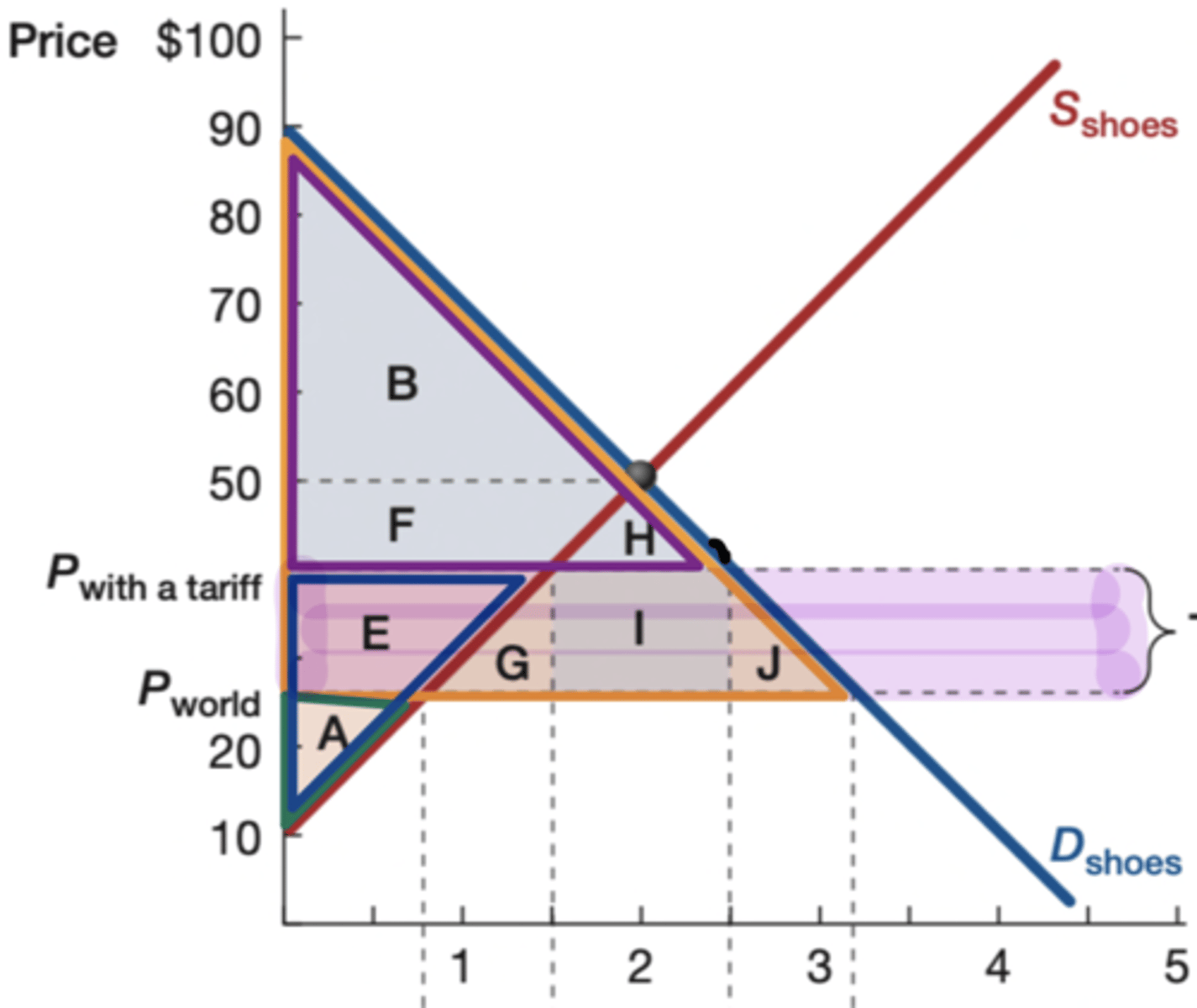
Purple
What is the color of the new consumer surplus?
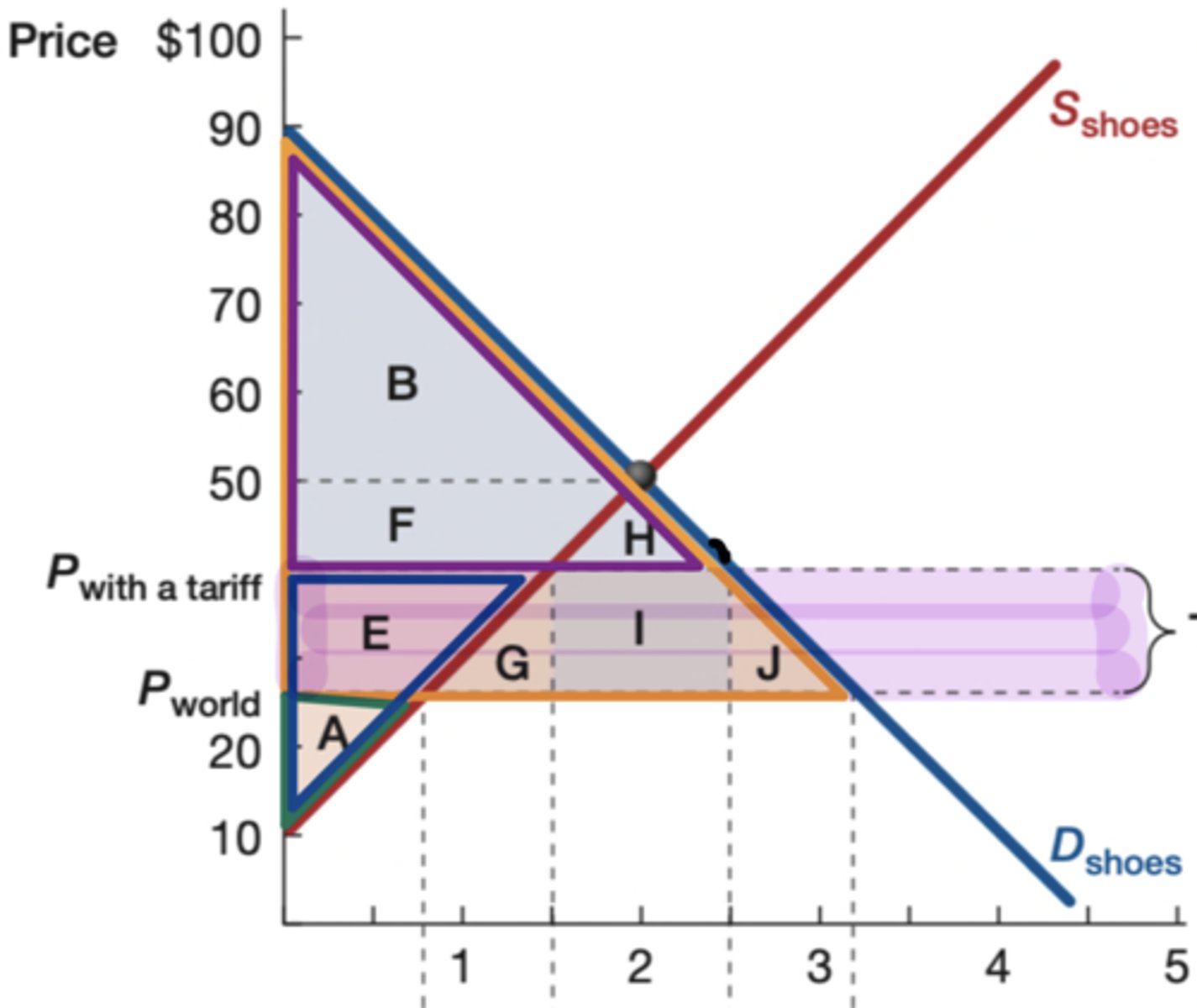
blue
What is the color of the new producer surplus?
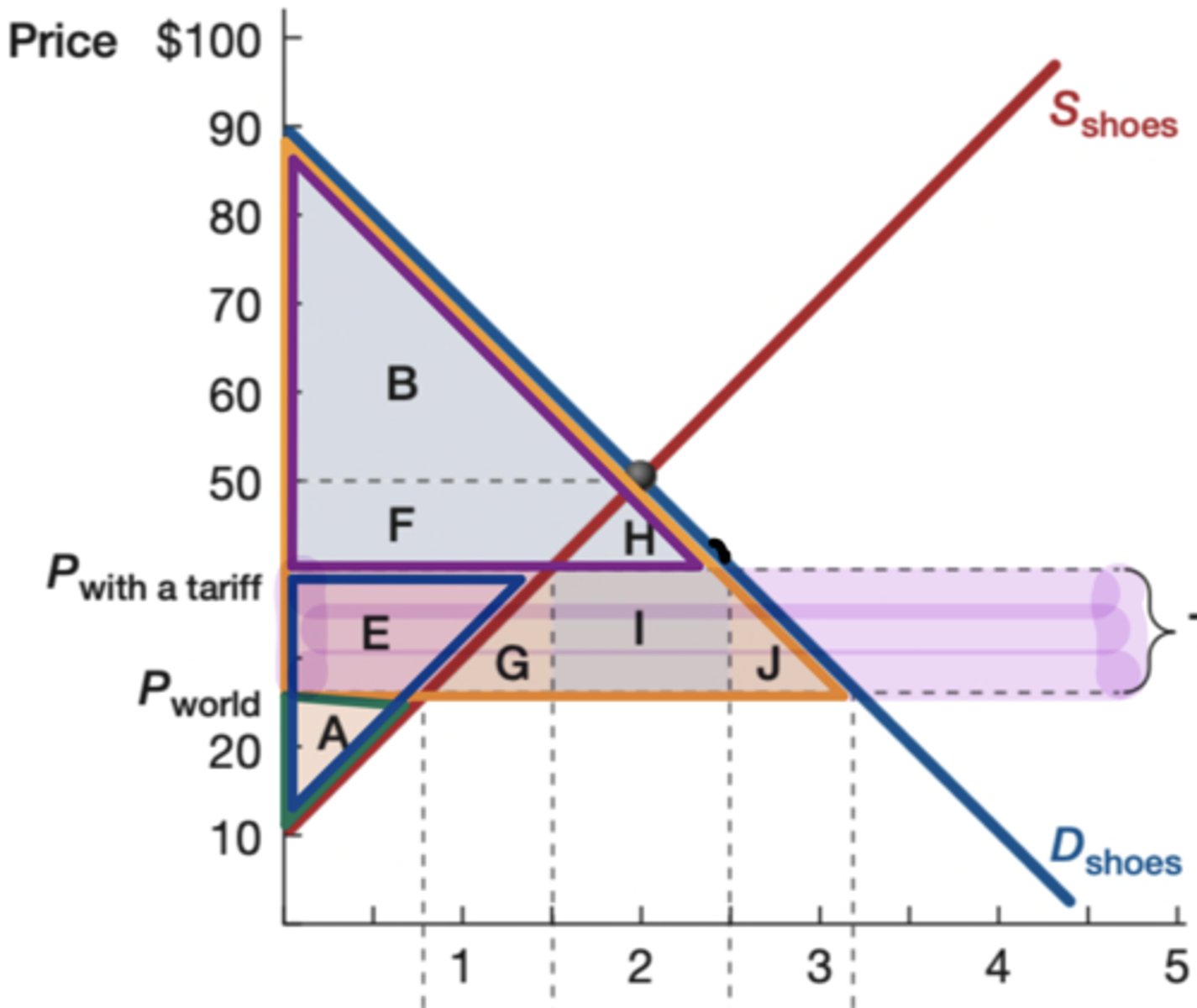
green
What is the color of the original producer surplus?
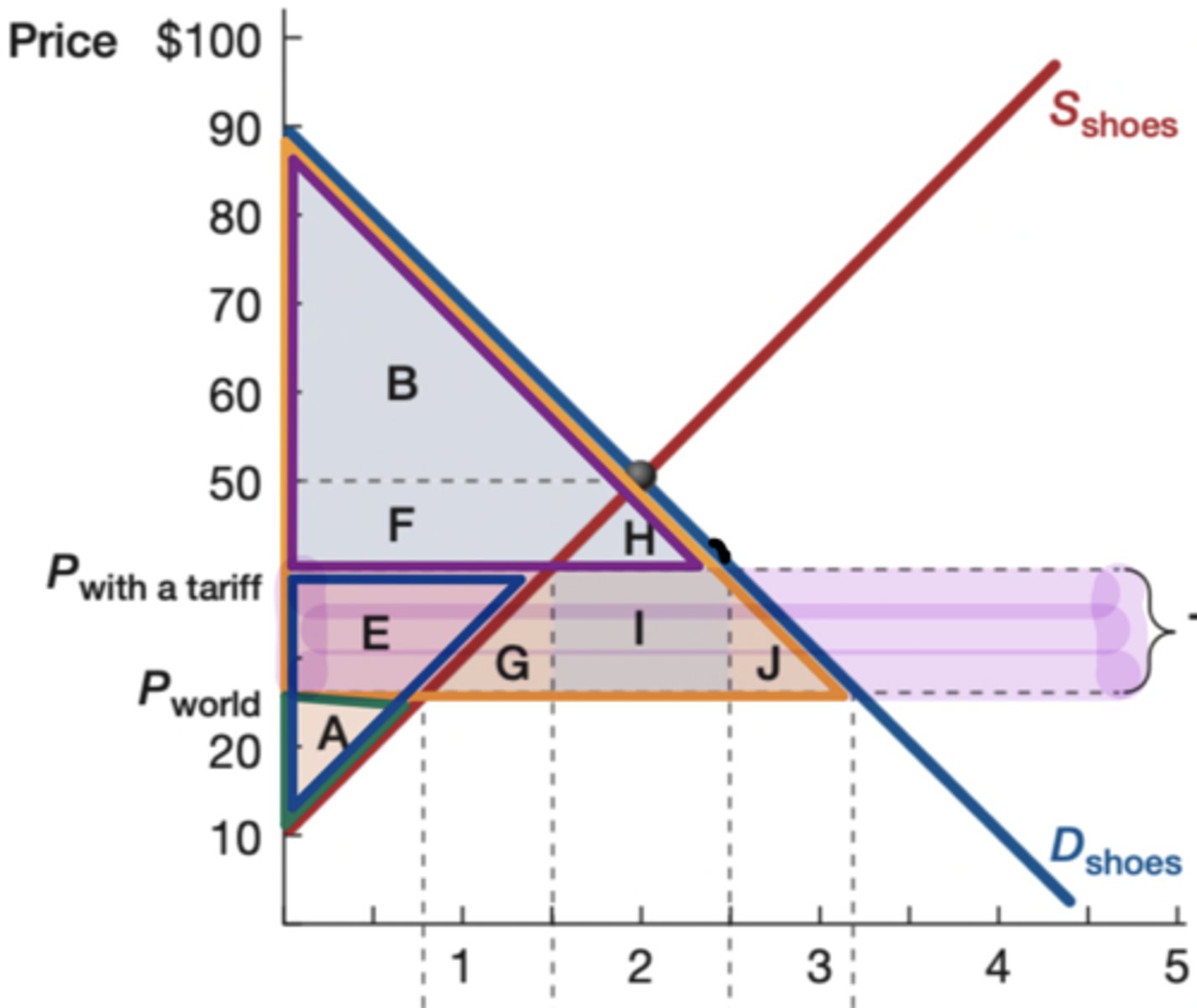
goverment earnings
What does rectangle I show
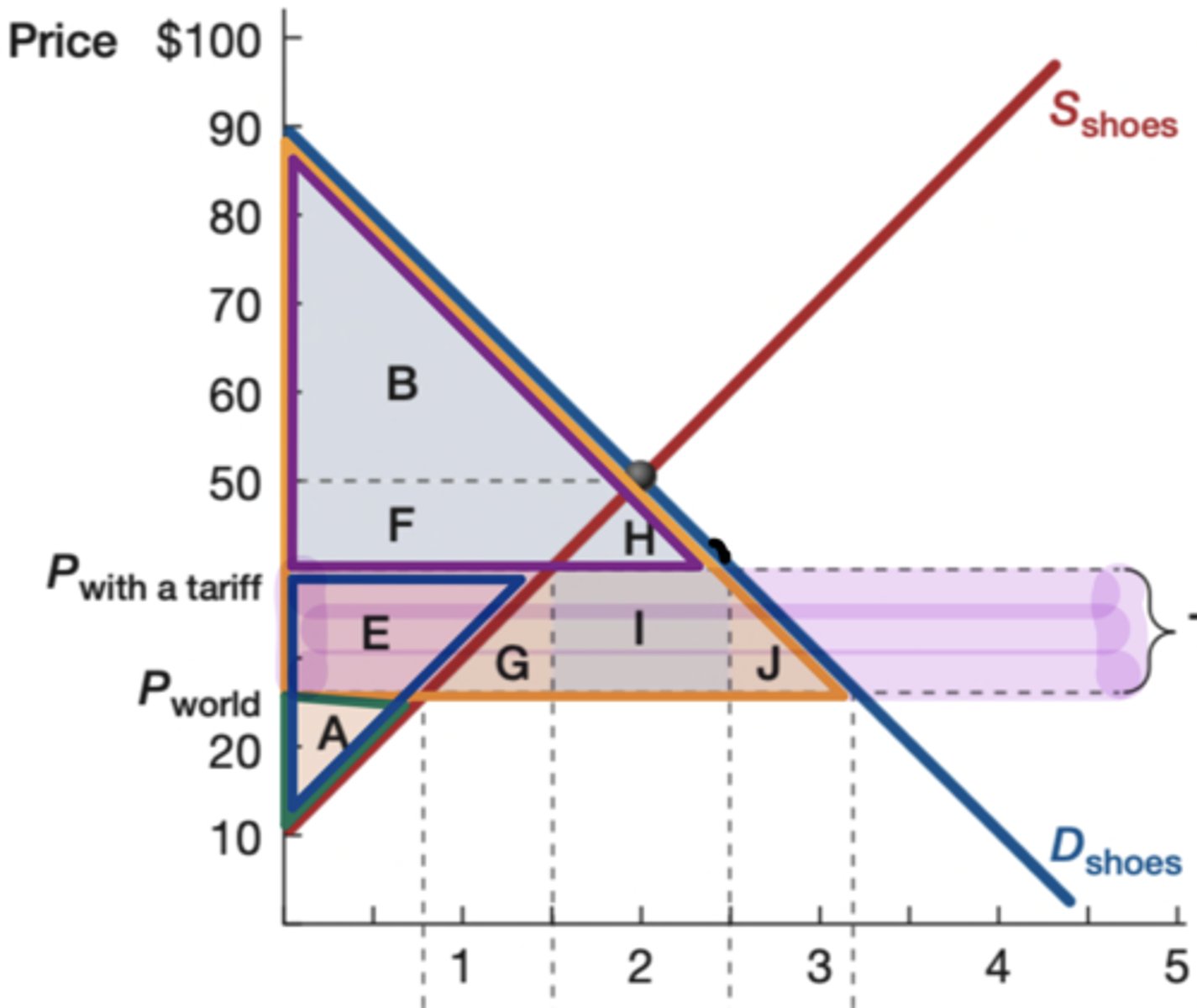
Yes (G and J)
Is there a deadweight loss on the following graph?
autorky
when a country makes things by itself
macroeconomics
economics as a whole, the aggregate economy
Income per capita (GDP per capita)
nation's aggregate income/number of people in the counrty
recession
a period lasting at least two quarters in which aggregate economic output falls
has no job
first condition of unemployment (has)
looked to get a job
first condition of unemployment (looked)
is currently available
first condition of unemployment (is)
unemployment rate
the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed expressed as a fraction
national income accounts
maeasured by the level of aggregate economic activity in a country
production=expenditure=income
Three things that are = to GDP
aggregate income
the total income received by all factors of production in a given period
factors of production
inputs of the production processes (capital, labor)
capital
land, factories and machines are an example of what type of factor of production
labor
oil is an example of what type of factor of production
households
who owns all factors of production
Production of goods and services
Purple line
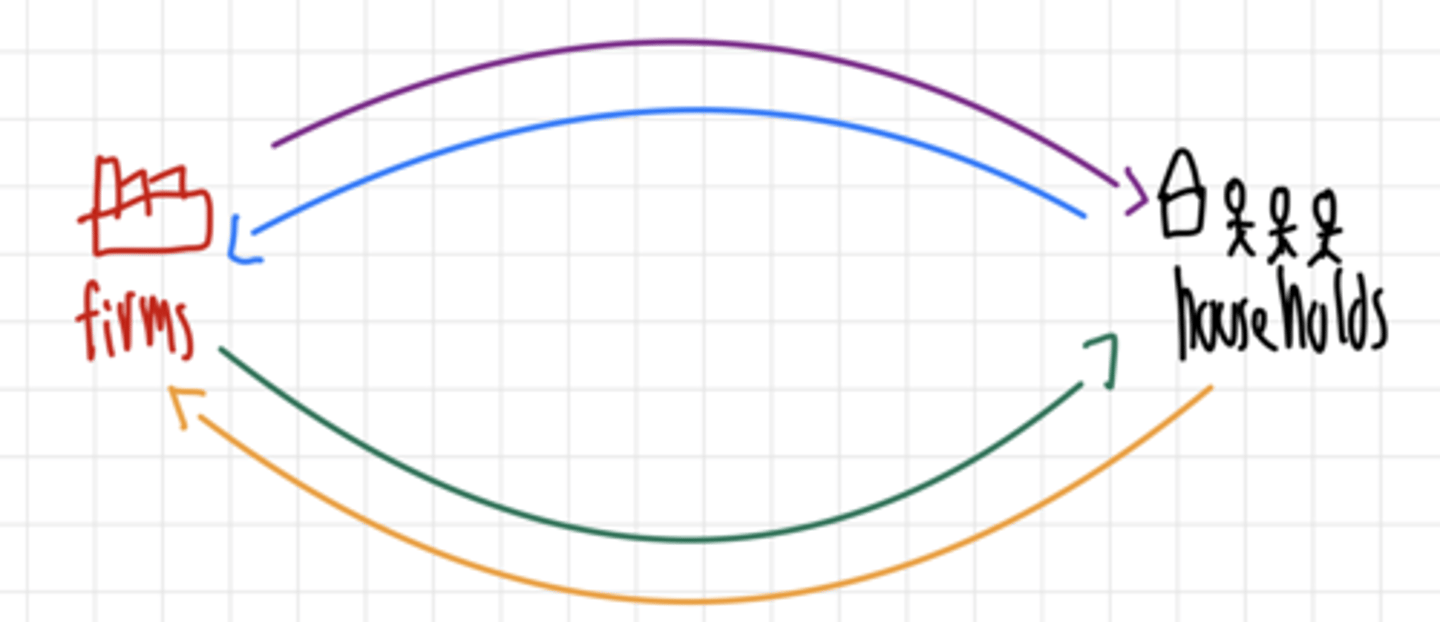
Expenditure on goods and services
Blue line
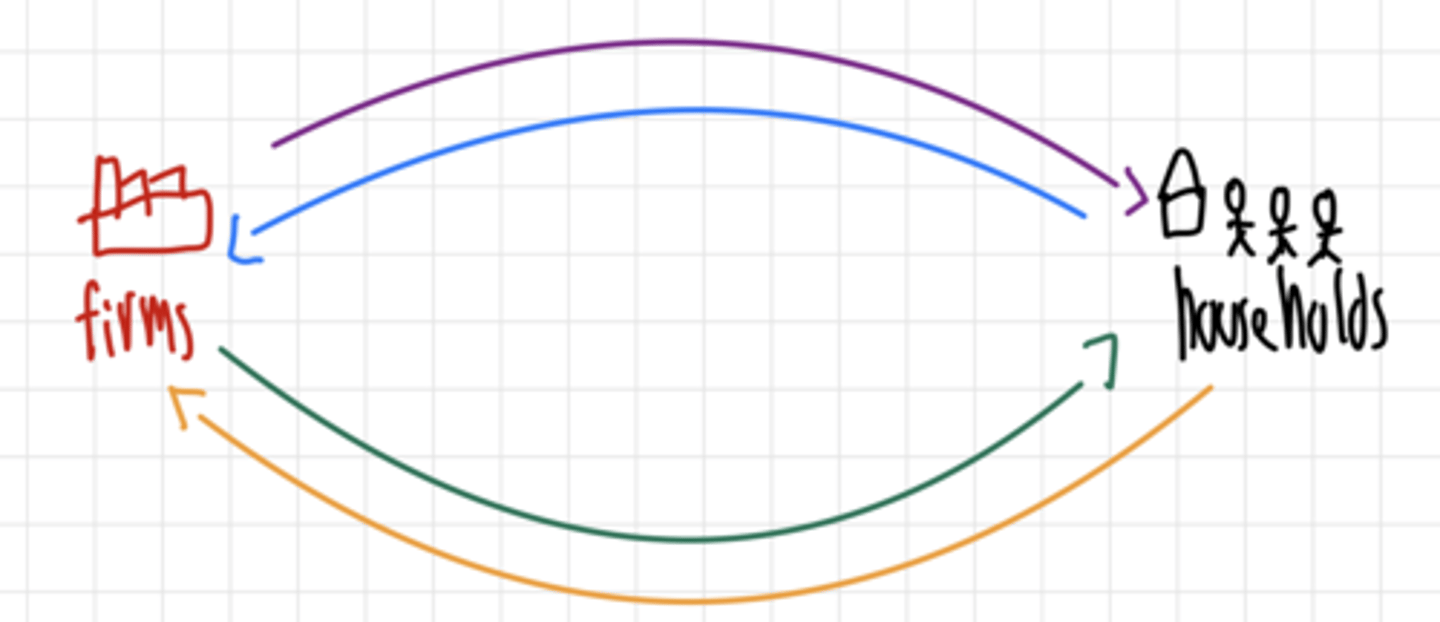
Income paid for factors of production
Grren line
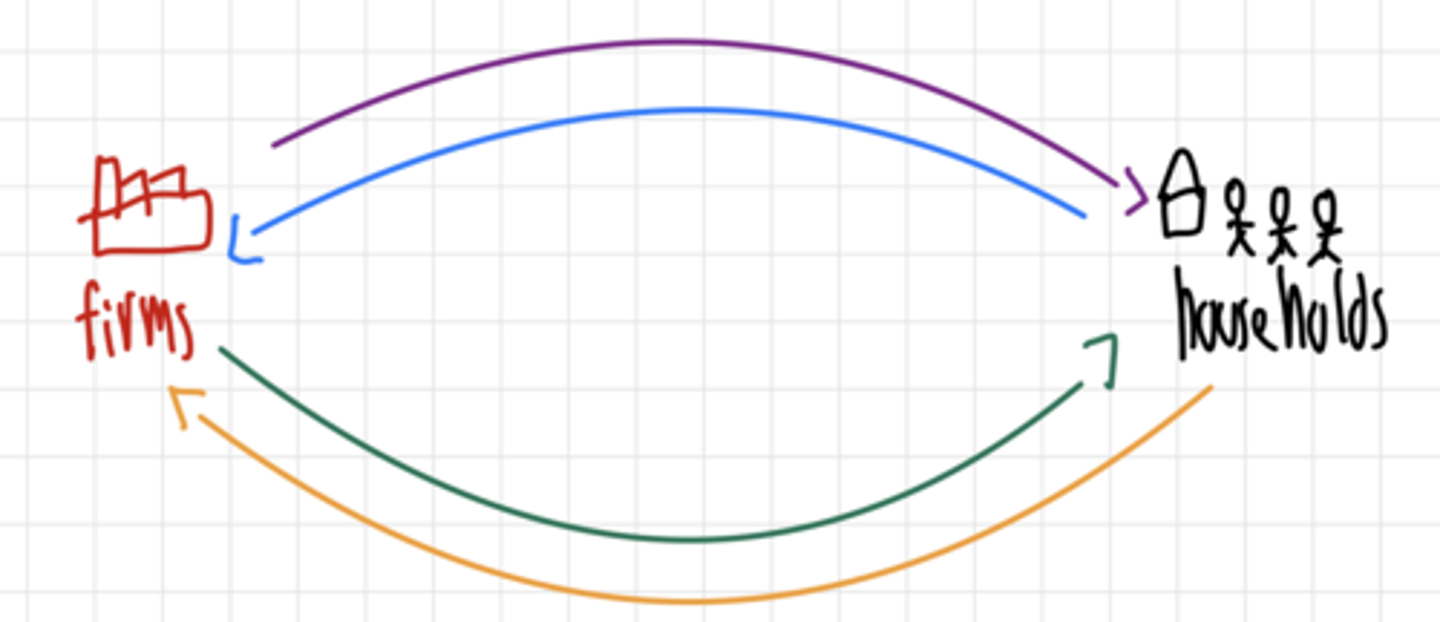
Factors of production
Orange line
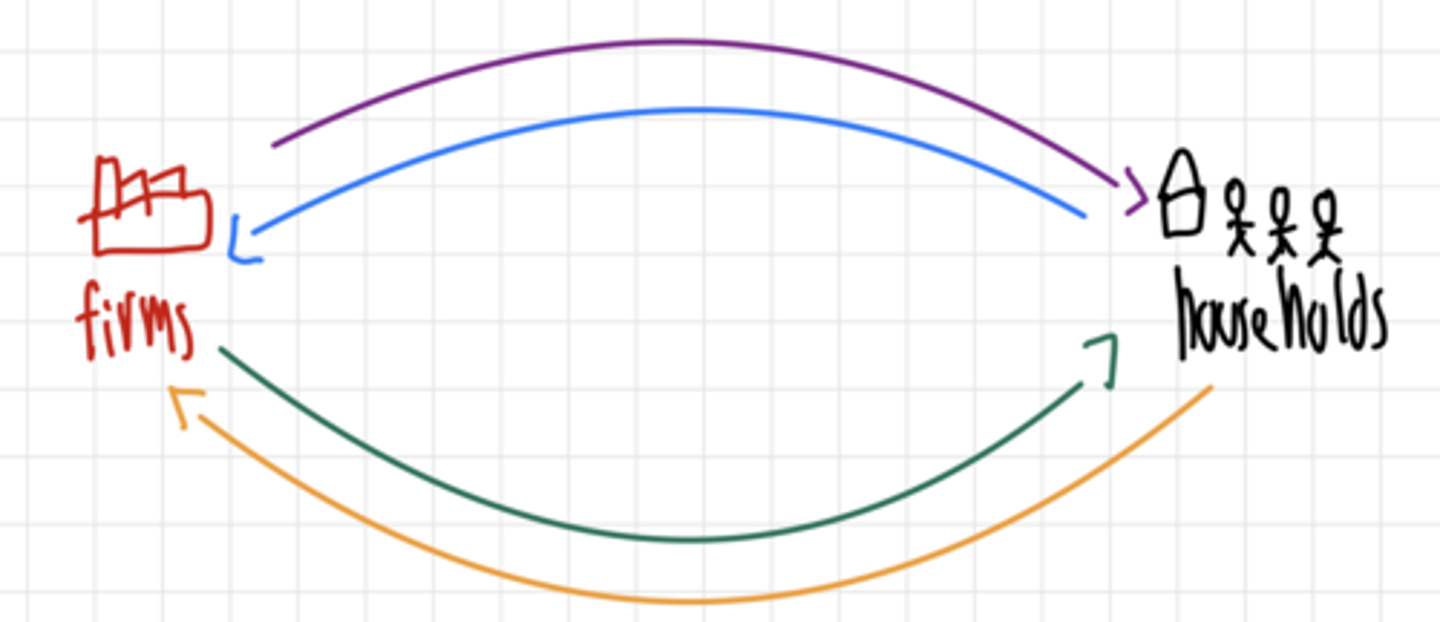
value added (adding all the value added by firms will sum up to the GDP)
the firms sale revenue minus its purchases of intermediate products from other firms
consumption
goods and services bought by domestic households
investment
market value of new physical capital that is bought by domestic households and firms. Purchase of only physical capital.
goverment expenditure
the market value of goverments or powers
exports
Market value of all domestically produced goods and servuces that are purchased by households, firms and goverments in foreign countries. Measured in value added.
imports
The market value of all foreign-produced goods and services that are sold to domestic households, domestic firms, and the domestic government.
C+I+G+X-M
formula for GDP or national income accounting identity
production
the creation of goods and services
expenditure
an expense; the amount needed to be paid out
income
money received, especially on a regular basis, for work or through investments.
Labor and capital
Two types of categories in which income payments come?
Investment
Savings is equal to