water treatment and redox chemisty
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
steps in water purification
aeration
settling and precipitation
hardness removal
disinfection
aeration
removes volatiles and raises the Pe
→ for taste and odor
settling and precipitation
removes colloids by adding coagulates such as aluminum sulfate and ferric chloride to remove clay minerals and hume
→ improves turbidity (look of water)
hardness removal
add phosphate to precipitate calcium phosphate as Ca2+ is bad for pipes
disinfection
remove microbes to prevent disease
optional step
add ammonia and fluoride to adjust the pH and improve dental health respectively
why disinfect?
the spread of pathogenic microbes through water supply poses a serious health concern
3 types of disease causing microbes
bacteria → salmonella, ecoli, typhus
viruses → norwalk, polio, hep-A
protozoans → singe celled animals, giardia lamblia
water disinfection techniques
old methods = boiling and filtering through rocks and soil into deep aquifers (neither are practical on an industrial scale)
modern methods = filtration, reverse osmosis, UV radiation, chemical methods (ozonation, chlorination, bromination)
reverse osmosis
REQUIRES A MEMBRANE → made of an organic polymer
water is forced through a semipermeable membrane at high pressure, impact side becomes concentrated with contaminants that cant pass through
can be used to desalinate water, is very effective but is energy intensive, wasteful and creates saline discharge
ozonation
uses ozone gas which kills everything in its path and reacts with pollutants or generates radicals in water
just a 10 min contact with O3 destroys bacteria and viruses, but is energy intensive, has no lasting protection (short half life) and produces disinfection by products (trihalomethanes and haloacetic acids)
why are disinfection by products a big problem?
have potential to pose long term human health risks like increased cancer risk
usually caused by ozone reacting with Cl- and Br-
chlorination
uses hypochlorus acid HoCl- (can used other chlorine forms as well) as its readily reduced neutral therefore it can diffuse through cell walls and oxidize vital molecules
has lasting protection BUT can create disinfection by products
why treat wastewater?
eutrophication, disease, drugs, microbes, household chemicals, garbage, smell → wastewater is someone else’s drinking water
steps of waste water treatment
primary treatment
secondary treatment
tertiary treatment
primary treatment
physical treatment (can be chemically enchanted) for the settling of suspended particles (colloids) → sludge settles and grease floats
→ garbage can also be removed in this step
secondary treatment
biological process to convert organic matter to biomass (CO2) followed by settling of products (produces more sludge which poses a disposal problem)
→ reduces BOD by ~90%
tertiary treatment
a variety of advanced processes to remove specific contaminants or for disinfection
advanced chemical processes steps
lower phosphate content → to stop eutrophication
lower ammonium content → to stop eutrophication
remove Ca2+ added for phosphate removal
remove organic matter
blue baby syndrome
fertilizers increase nitrate (NO3) concentration in ground water and when humans are exposed it causes respiratory failure
→ NO3- is reduced to NO2- by anaerobic bacteria in the stomach → NO2- oxidizes Fe2+ in hemoglobin to Fe3+ therefore it cannot bind oxygen
drinking water guidelines
canada has guidelines with maximum acceptable concentrations measured in mg/L
→ some compounds like arsenic, cadmium and chromium found in drinking water have been established as carcinogens to humans
most powerful oxidant on earths surface
O2
redox reactions
chemical processes in which e- is transferred from one molecule to another → if something is reduced something else must be oxidized
*not the same as neutralization
most important biological redox reaction
aerobic environments = respiration
energy + CO2 + H2O —photosynthesis—> CH2O + O2
←-Respiration——
photosynthesis = driven by sun
respiration = driven by absence of sun
biological oxygen demand (BOD)
mg of O2 required to carry out oxidation of organic carbon in 1L of water
in aerobic environments respiration provides life supporting redox energy but O2 becomes depleted
in rivers it is replenished by contact with air
in standing water (lake,pond) dissolution of O2 in water is slow compared to microbically mediated decomposition of dead biomass
crucial reaction in carbon cycling
USES UP O2
CH2O + O2 → H2O +CO2
measurements of BOD
very clean = 1mg O2 / L (has very little organic matter in it)
fairly clean = 1-3mg O2/L
doubtful purity = 3-5mg O2/L
contaminated = >5mg O2/L
how to calculate BOD
incubate a sample at a specific temp in an air tight bottle for 5 days → dissolved O2 (DO) is measured before and after incubation → BOD is calculated from the difference between initial and final DO
O2 graph
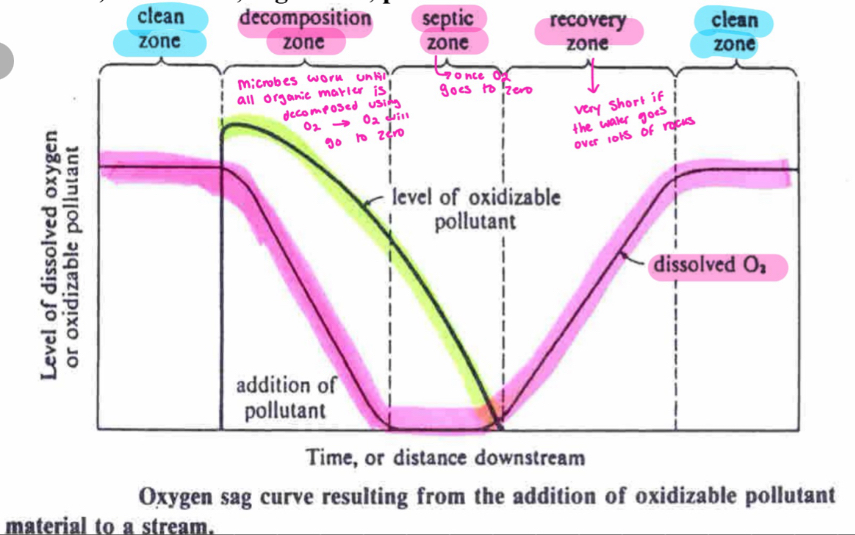
longitudinal analysis
used to detect pollution of oxidizable organic matter/pollution using [O2]
what happens when a lake/pond becomes depleted of O2
organisms that rely on aerobic respiration cannot survive → anaerobic bacteria takes over and uses oxidants other than O2 (these alternatives cannot produce as much energy as O2 but bacteria can still survive)
alternative oxidants for decomposing organic matter
used in decreasing order: NO3-, MNO2-, Fe(OH)3, SO42- and CO2
PE
used to characterize the extent to which natural waters are chemically reducing in nature
large negative PE
large value for e- activity in solution → REDUCING CONDITIONS → ANOXIC water bodies (anaerobic populations proliferate)
large positive PE
low e- activity in solution → OXIDIZING CONDITIONS → well AERATED surface water
what does dissolved O2 in water determine
the reduction of O2 to water determines e- activity
how does redox potential fall
In a stepwise pattern as BOD increases
PE/pH diagrams
a 2d plot with PE on the Y and pH on the X → water stability boundaries, H2O has a limited range of PE and pH values in which its stable
Region of stability for water
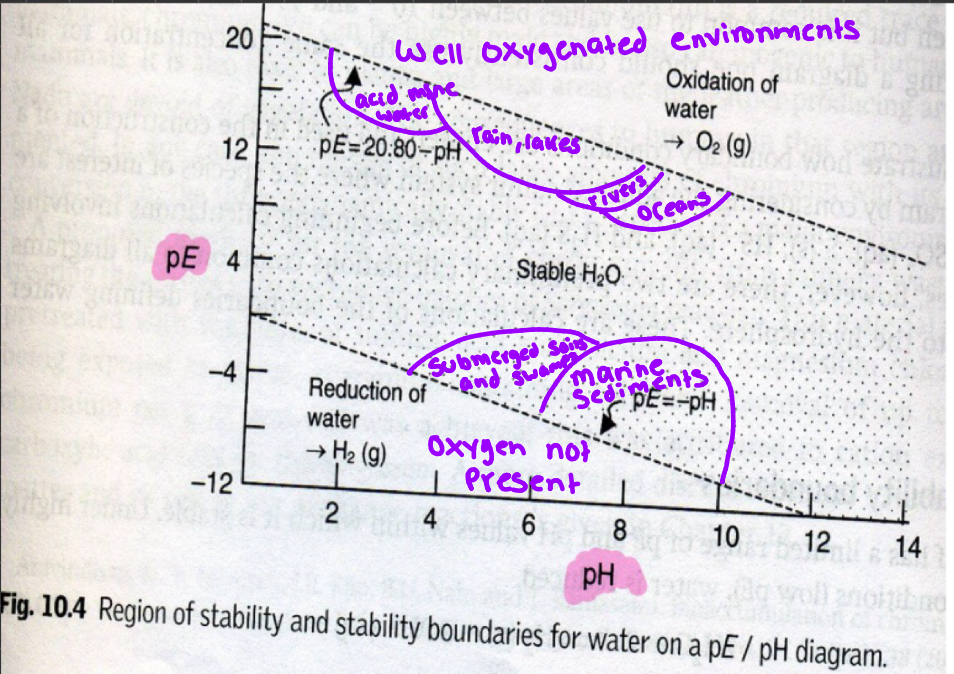
iron systems
equilibrium between dissolved Fe2+ and Fe3+ is only important for pH <3