the spleen lecture slides
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
what is the largest lymphoid organ in the body?
spleen
The spleen is….
intraperitoneal
retroperitoneal
neither
intraperitoneal
The outer layer of capsule is peritoneum. It covers the entire organ except…
the hilum
What layer is fibroelastic and smooth muscle fiber capsule that surrounds the entire organ (allows it to expand and contract)?
middle layer
what layer of the capsule projects into the organ, forming partitions in the pulp?
inner layer
What is the spleen’s echogenicity compared to healthy liver tissue?
homogeneous and only slightly more echogenic
What is the spleen’s echo structure compared to kidney tissue?
hyperechoic
What is the normal spleen length?
<12 cm
what is the normal spleen width?
<7 cm
what is the normal spleen thickness?
<5 cm
True/False: The left lobe of the liver does not touch the spleen normally, if enlarged it may, as well as in 3rd trimester of pregnancy.
true
What are strands of connective tissue that project from the splenic capsule and divide the spleen into several compartments?
Trabeculae
what is cords of splenic tissue called?
cords of Billroth
What is white pulp (15%)?
clusters of lymphatic tissue called Malpighian corpuscles that form a sheath around the splenic artery and produce lymphocytes and is a major site for immunologic activity
What is is a major site for immunologic activity?
white pulp
What is the principle site of filtration, and performs major functions related to blood cells (These include the removal of macrophages of ruptured, worn out, or defective blood cells)?
red pulp
What are the functions of the spleen?
1.Blood filtration
2. Blood production: Glucocytes and plasma cells are produced
3. Blood destruction
4. Blood storage: Main storehouse of the blood
5. Storage of iron
Hemoglobin from the red blood cells is passed to where for storage and bile production?
the liver
What is found within this concavity and acts as an entry and exit route for the arterial, venous, and lymphatic vessels and nerves?
the splenic hilum
What are medial and anterior to splenic hilum?
Stomach fundus and lesser sac
What is inferior and medial to spleen?
Left kidney
What is anterior to UP of left kidney?
Pancreatic tail
Where is the spleen located?
The spleen is located in the left hypogastric quadrant of the abdomen and is fixed in its intra-peritoneal position beneath the 9th to 11th intercostal spaces by the spleno-renal, spleno-colic, spleno-gastric, and phrenico-splenic ligaments.
True/False: The splenic artery initially divides into two major branches before separating into several minor arterioles within the spleen. It is not important for the sonographer to remember that because there are no adequate anastomoses between arteries in the spleen, the organ is susceptible to infarction.
false, because it is important for the sonographer to remember this
What is the spleen susceptible to?
infarction
Blood from the arterioles flows into the venous sinusoids and then exits through
branches of the…
splenic vein
Where does the splenic vein originate?
at the splenic hilum
What courses posteroinferior to the pancreas body and tail?
splenic vein
Splenic vein joins with IMV, then SMV to form what?
MPV
What does the splenic vein drain?
stomach, spleen, and pancreas
What is the largest branch of the celiac axis?
splenic artery
What courses superior and anterior to the body and proximal tail of the pancreas?
splenic artery
What is low resistance and supplies the spleen, pancreas and fundus of the stomach?
splenic artery
What is considered the most tortuous artery in human body?
splenic artery
What are indications for US for the spleen?
1. Left upper quadrant pain 2.Splenomegaly
3. Anemia 4.Traumatic disorders
5. Congenital anomalies 6.Focal defects
7.Hematogenic and lymphogenic disorders
8.Liver disease 9. Metastases
What probe is best to use for examining the spleen?
2.5MHz to 6.5MHz adult probe
4MHz to 8MHz pediatric probe
Describe the spleen on US?
-Homogeneous texture
- Echogenicity the same as or slightly below the normal liver echogenicity
- Smooth border at diaphragm
- Intercostal coronal view used to obtain spleen length
- Average length 11-13cm; usually decreases in size with age
- Usually 2/3 size of the liver
- Deep inspiration usually necessary to evaluate the entire organ
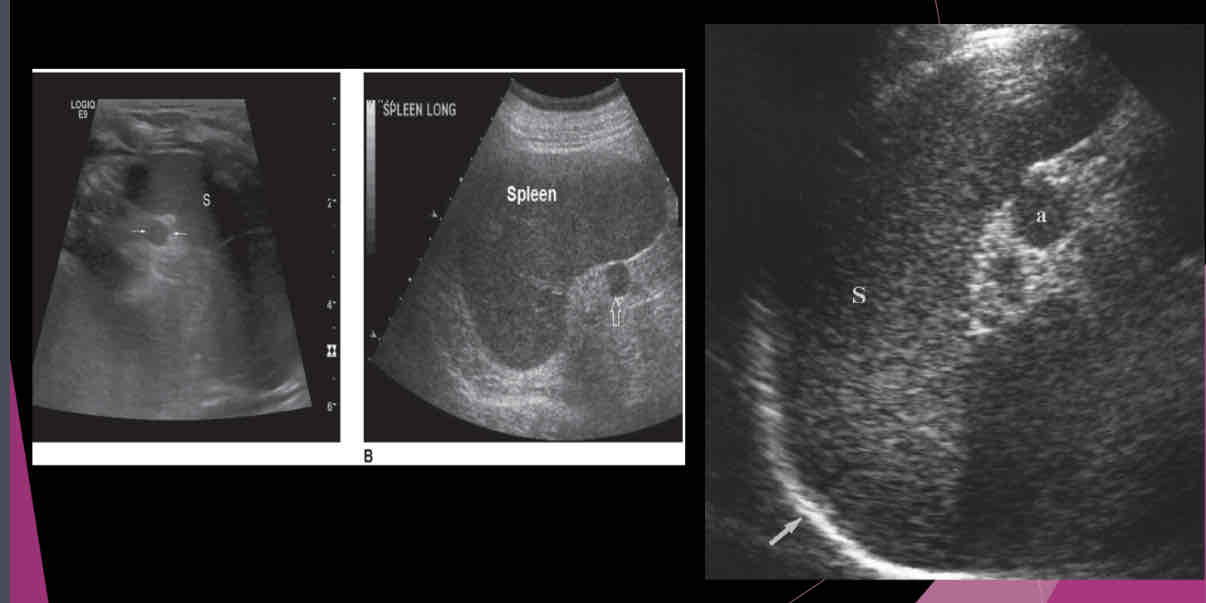
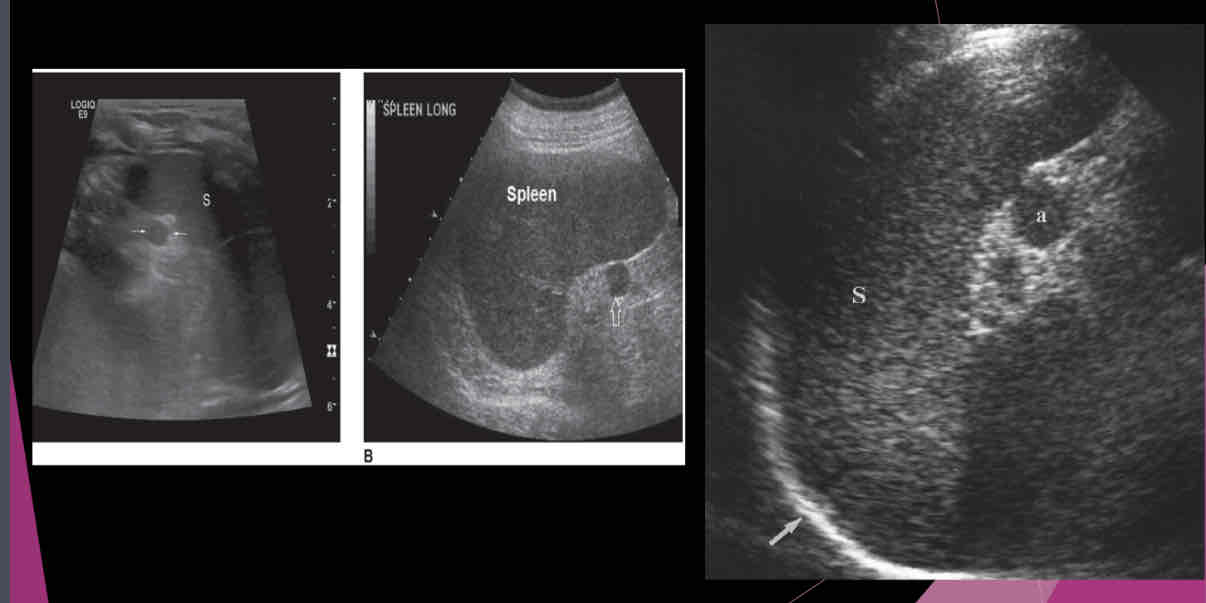
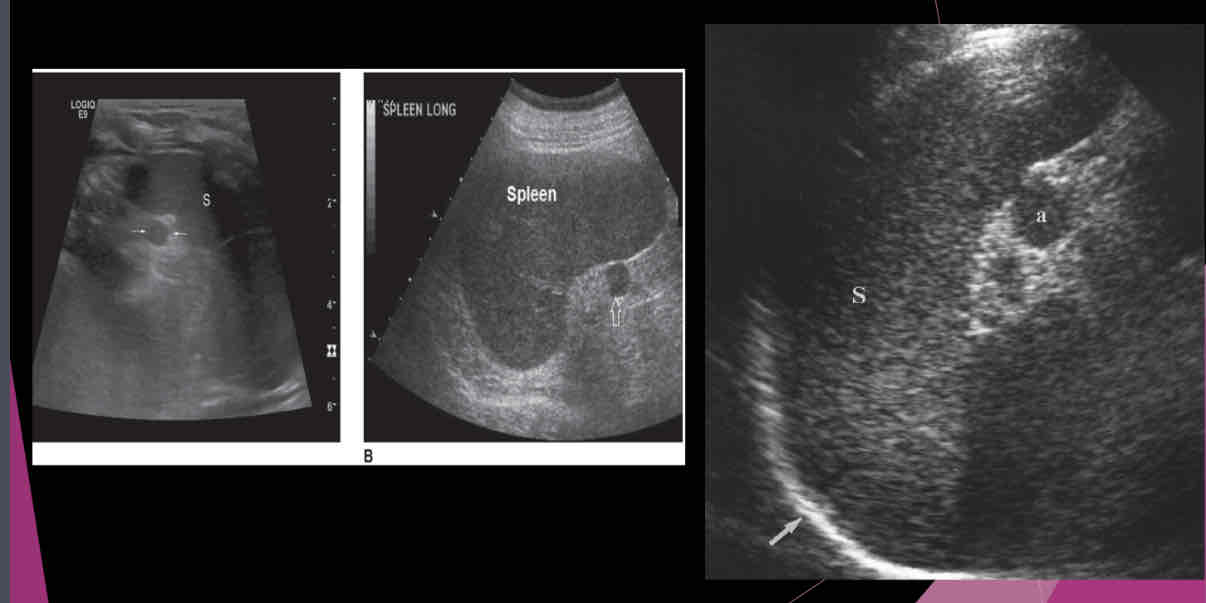
What is a relatively common anatomic variant?
accessory spleen (Splenule)
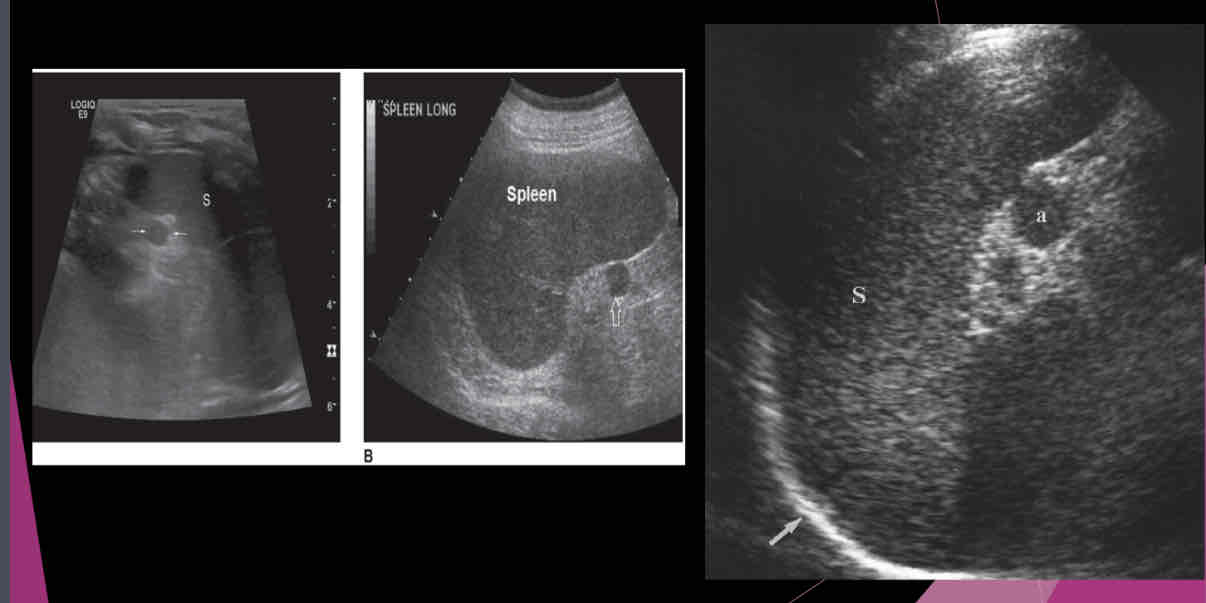
Most accessory spleens are small and measure between…
1.5 and 2.0 cm
True/False: Approximately 75% of accessory spleens are found near to the normal spleen within the splenic hilum or gastrosplenicligament omentum, rare locations for an accessory spleen include the pelvis or scrotum.
true
True/False: Following splenectomy, an accessory spleen may assume the function and size of the removed organ.
true
An accessory spleen or splenule is _______ to spleen
hypoechoic
Isoechoic
hyperechoic
heterogeneous
Isoechoic
What does the following describe?
-Absence of the spleen
-Very rare
-Usually occurs in cases of multiple congenital anomalies such as right sided aorta, midline liver, horseshoe kidneys and adrenal glands
-Congenital heart defects are common
Asplenia
What describes the following?
-Formation of multiple spleens
-Associated with biliary atresia, absence of the gallbladder, interrupted IVC, intestinal malrotation
-Congenital heart defects are common
Polysplenia
What is the disruption in the development of normal asymmetric arrangement of abdominal organs and vessels; Generic term meaning mis-arrangement of abdominal structures?
Heterotaxia or situs ambiguous
What can occur if the supporting ligaments are dysfunctional or lax?
Splenic ptosis aka wandering spleen
What does the following describe?
•Weak splenic ligaments lead to the organ migrating to unusual locations
•Mistaken for a mass
•Due to the abnormal location, it may undergo torsion resulting in pain .It may also undergo infarction
Splenic ptosis aka wandering spleen
The preferred treatment for wandering spleen is ____________ in which a surgeon repositions the spleen in the left upper quadrant in order to prevent torsion of splenic vessels and preserve splenic function.
splenopexy
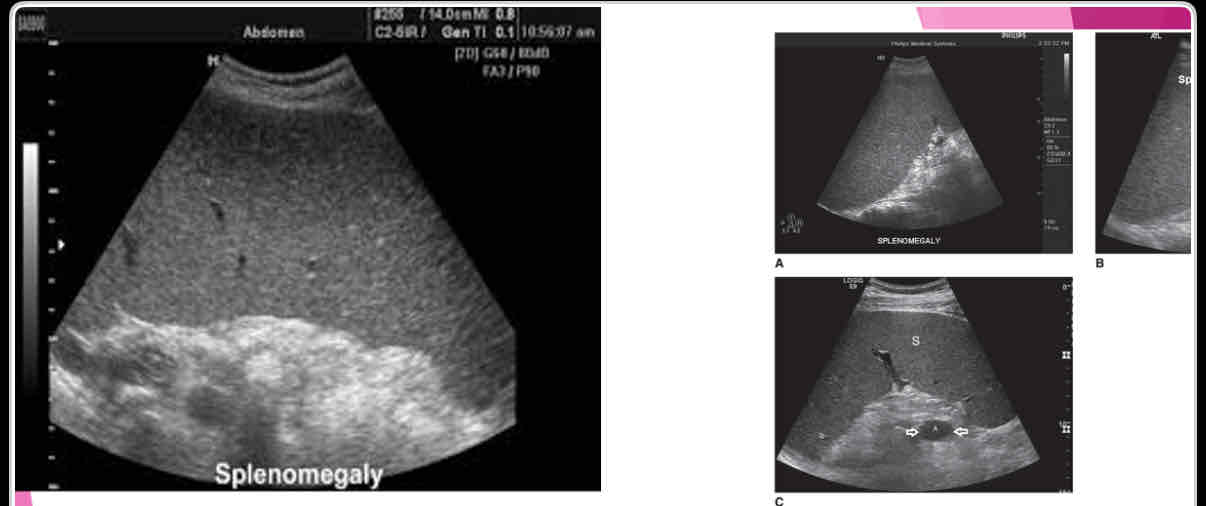
What is the measurement for enlarged spleen (splenomegaly)?
>13cm in length
What is the most common splenic abnormality observed sonographically?
enlargement (splenomegaly)
What is the most common cause of splenomegaly?
Portal hypertension due to cirrhosis is most common cause in adults
What is the most common malignant disease that affects the spleen?
lymphoma (Hodgkin disease and non-Hodgkin)
What is a blood disorder resulting from uncontrolled RBC production causing hyperviscosity and hypercoagulation; May be the cause of splenomegaly, Budd-Chiari syndrome, PV thrombosis and splenic infarcts?
Polycythemia Vera
The spleen suddenly enlarges and is accompanied by a sharp decrease in ______.
hematocrit
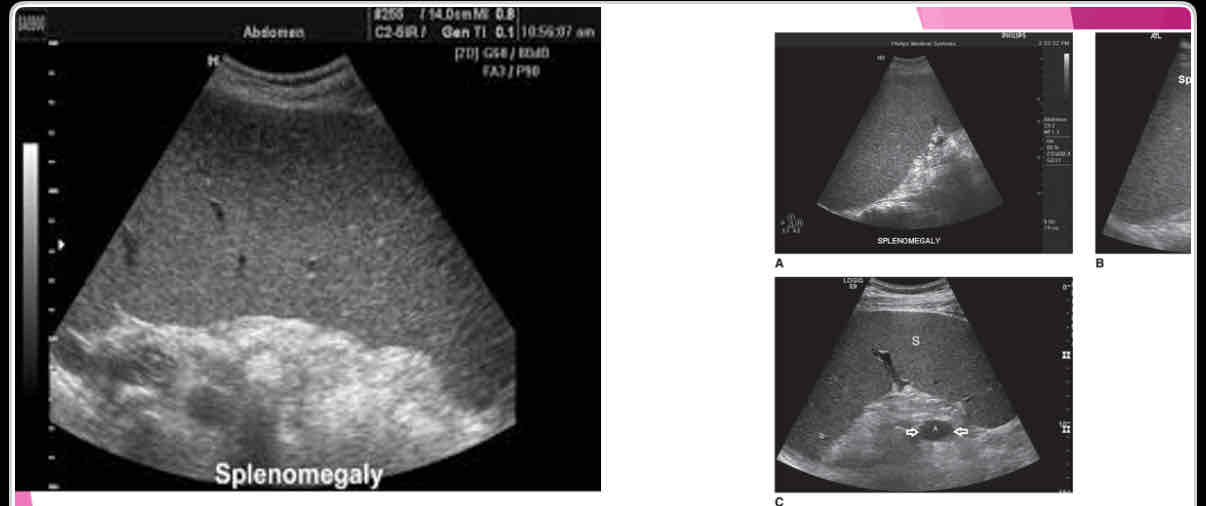
With splenomegaly: when enlarges, it extends
anteriorly, medially and inferiorly
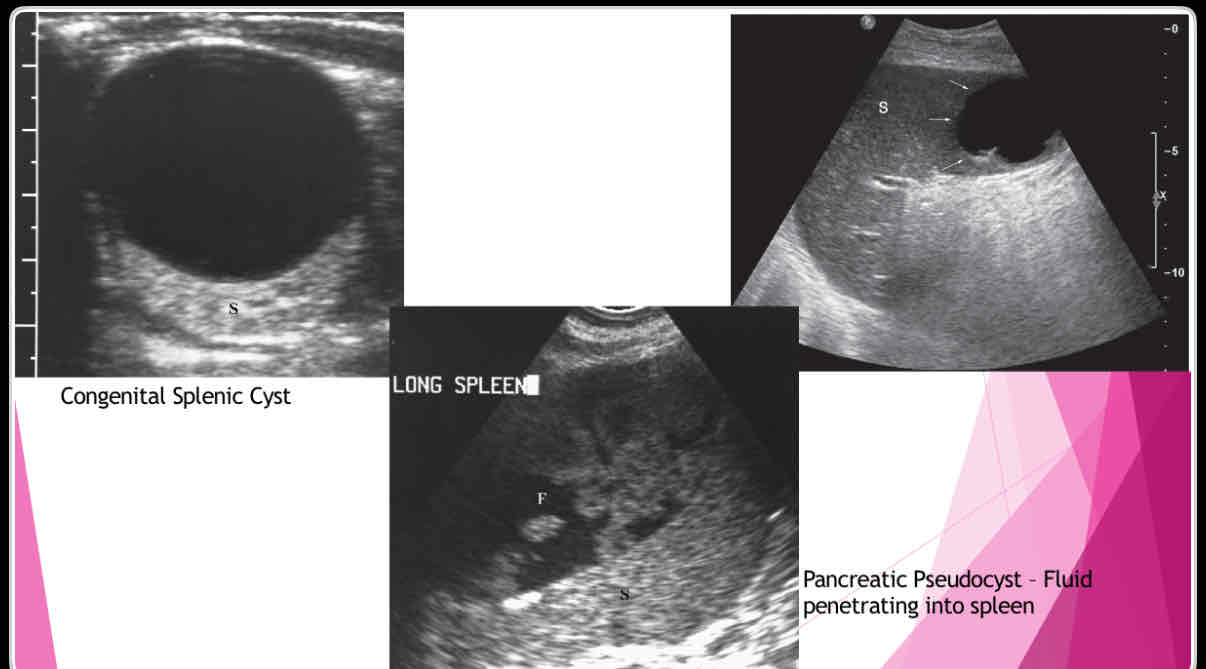
What does the following describe?
•Anechoic, well-defined walls, enhanced sound transmission
•Sharply demarcated wall, multilocular internal structure representing daughter cyst, mural calcifications
•Large cysts, dense, clearly defined walls May not have well-defined wall, mural calcifications Single or multiple simple cysts
splenic cysts
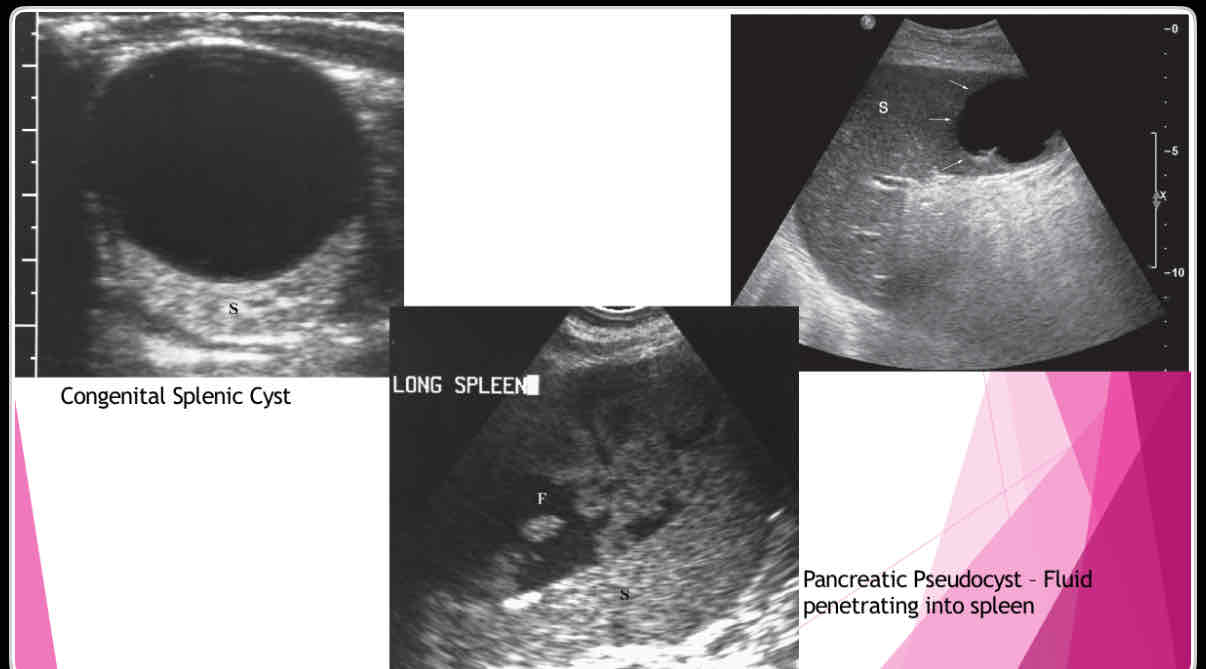
What are the different types of splenic cysts?
•Can be Congenital
•Can also be Acquired
• Echinococcal (hydatid)
•Epidermoid or epithelial
•Posttraumatic or postinflammatory pseudocysts
What does the following describe?
•True cysts lined by squamous epithelium
•Typically solitary, 10 cm
•Wall may be calcified and internal contents echogenic
Epidermoid or epithelial
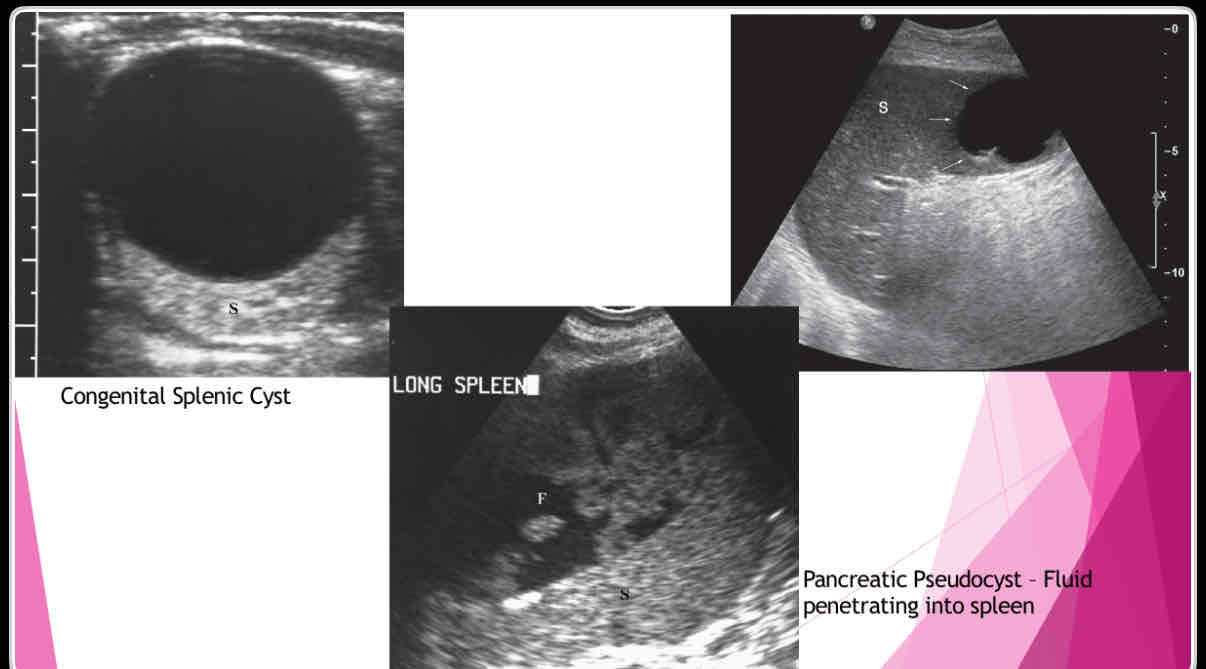
What does the following describe?
•Polycystic kidney disease lymphangioma,
•extension of pancreatic pseudocyst
-Erode into spleen due to proximity
-May weaken vessels causing pseudoaneurysms and bleeding into pseudocyst
Posttraumatic or postinflammatory pseudocysts
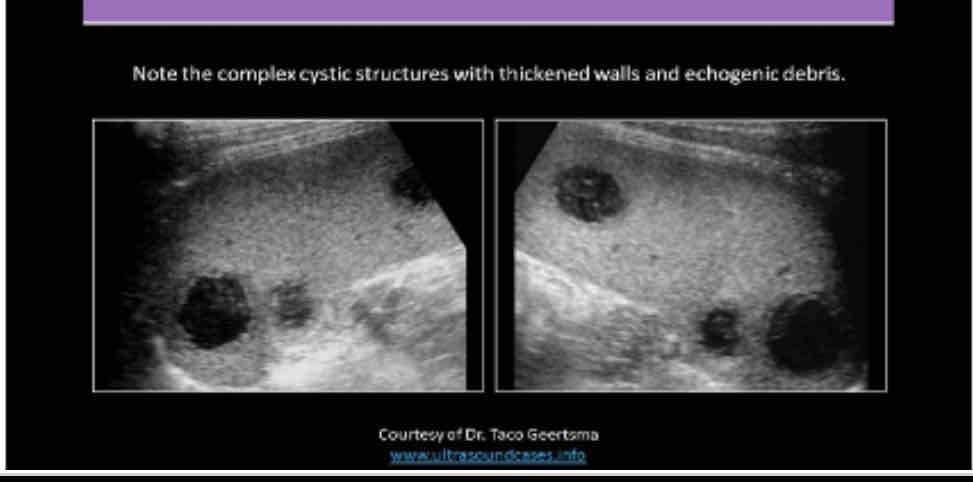
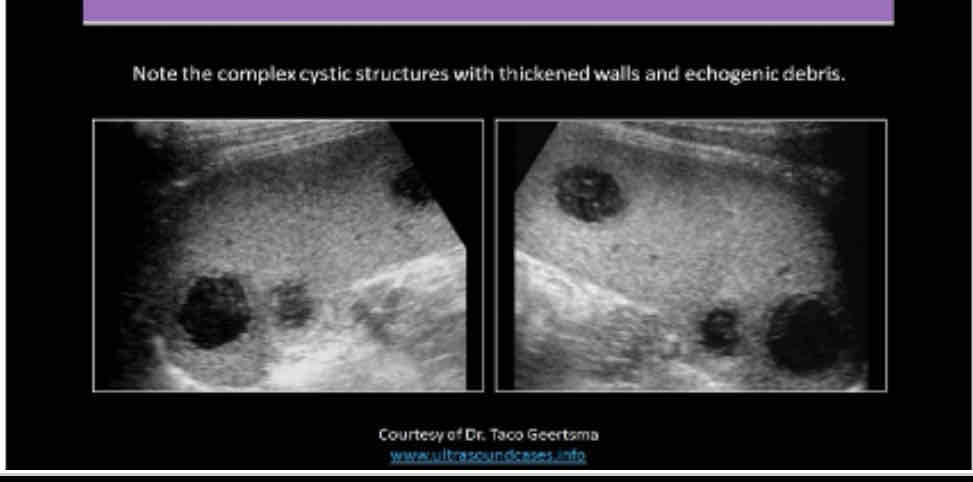
What does the following describe?
•It is rare. May be associated with endocarditis, septicemia and trauma
•May see them status post splenectomy
•Symptoms include pain, dizziness, faintness,
•Lab Testing: decreased hematocrit, fever, increased WBC and possible septicemia
splenic abscess
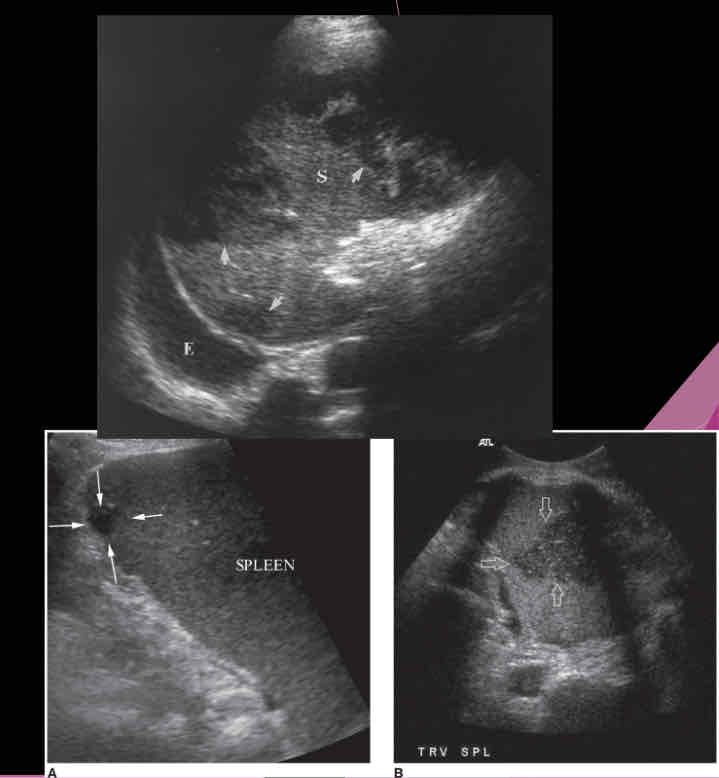
What does the following describe?
•Sonographically: Complex fluid collection with internal echoes
•Irregular borders
•May see septations and pleural effusion
•Dirty shadowing from gas producing organisms
splenic abscess
What does the following describe?
•Areas of tissue death, blood supply is cut off
•Found in patients with leukemia, sickle cell anemia, pancreatitis, bacterial endocarditis
•Calcification is last change
splenic infarct
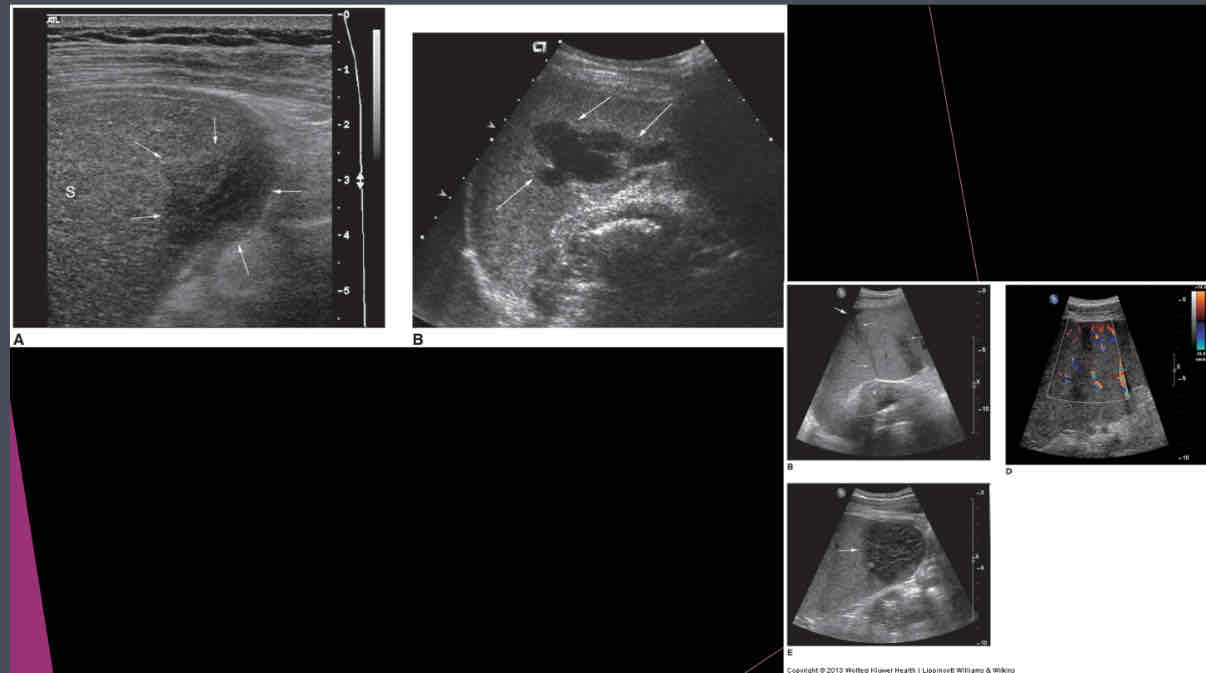
Focused assessment with Sonography for trauma (FAST) – used in ER to determine what?
if free fluid is in the peritoneal cavity
True/False: Fractured spleen may appear only as enlarging spleen with normal echogenicity; blood might be found in pelvis, flanks, Morrison pouch, lesser and greater sacs.
true
What is the condition of the capsule?
-intra-parenchymal or sub-capsular hematoma
-Subcapsular hematoma may appear as normal spleen, or hypoechoic, or echogenic mass adjacent to clearly defined capsule
capsule remains intact
What is the condition of the capsule?
-intraperitoneal or peri-splenic hematoma
-Fluid localized around spleen, but may spread within peritoneal cavity
-Pericapsular hematoma may efface smooth contour of splenic capsule
capsule ruptures
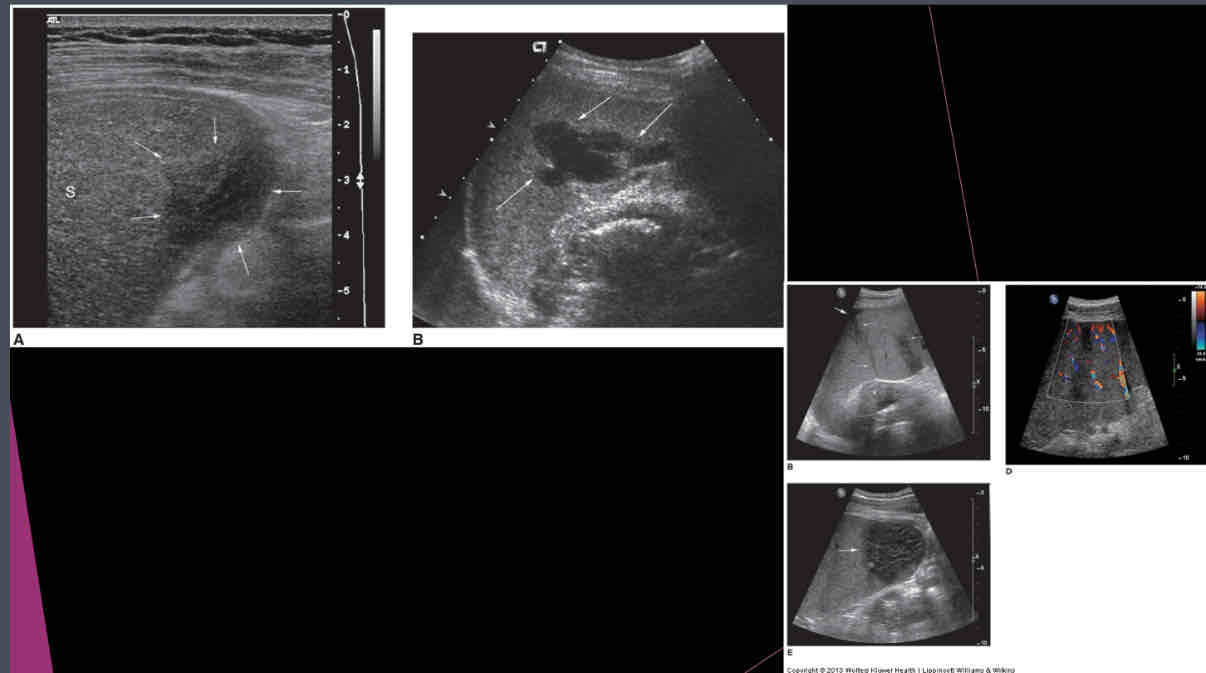
What can hematoma be due to?
•Trauma, coagulation disorder
•Ruptured spleen secondary to trauma or enlargement
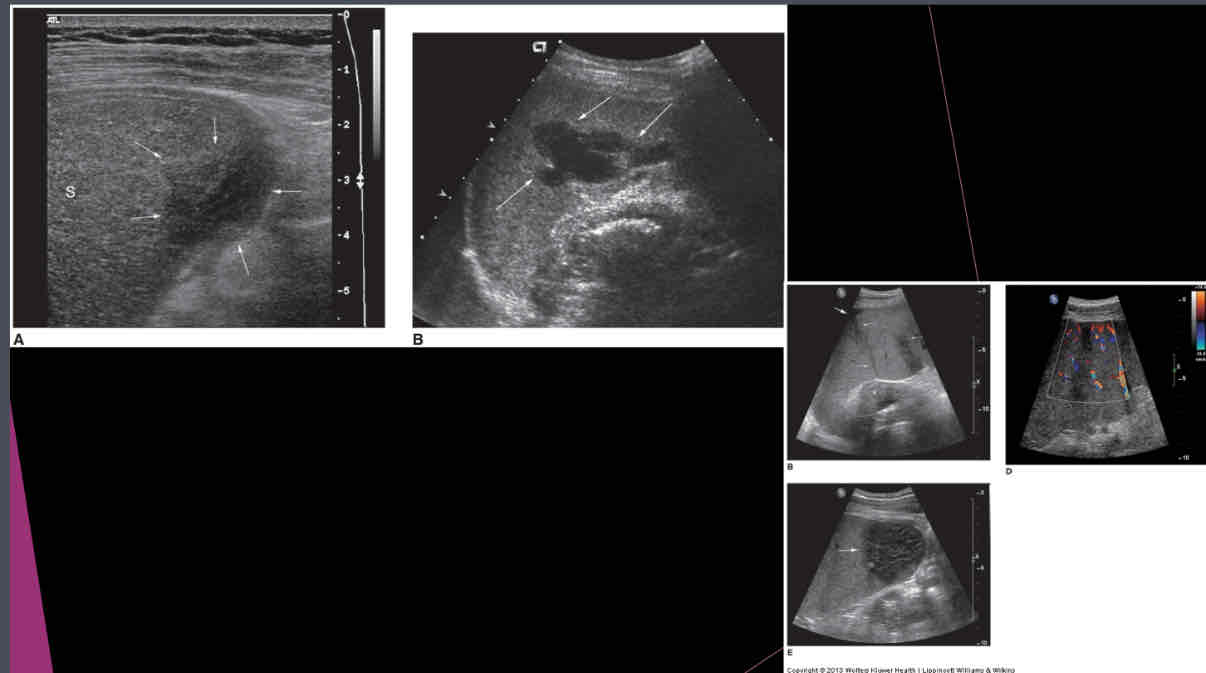
US appearance of intraperitoneal blood depends on what?
age, amount, and physical state of the clot
What is it called when a patient with rupture or surgery, splenic cells may implant throughout peritoneal cavity resulting in an ectopic spleen? (is often asymptomatic and may mimic other pathologies)
posttraumatic splenosis
What are focal lesions that are resulting from previous infection; most common causes are histoplasmosis and tuberculosis?
Granulomas
Other calcifications in spleen can be associated with?
•Splenic artery or splenic artery aneurysms
•Pneumocystis carinii infection
•Splenic infarcts (as it evolves)
True/False: Rarely splenic hemangiomas may contain calcifications.
true
What is a very rare benign splenic tumor?
Primary neoplasms
What are the most common benign primary neoplasm of spleen?
Hemangiomas
What is a malignant tumor of the spleen?
Lymphoma
What does the following describe?
•Tumor of lymphatic nodes
•Commonly involves the spleen
•Elevated alkaline phosphatase values
•Solid hypoechoic well circumscribed areas or can be nearly isoechoic
•Marked splenomegaly due to tumor formation
•Areas of cystic degeneration within the tumors
Lymphoma
What are the four sonographic patterns of lymphoma in the spleen?
•Diffuse, marked splenomegaly, patchy inhomogeneity
•Multiple small hypoechoic lesions
•Multiple large lesions
•Bulky solid mass lesions
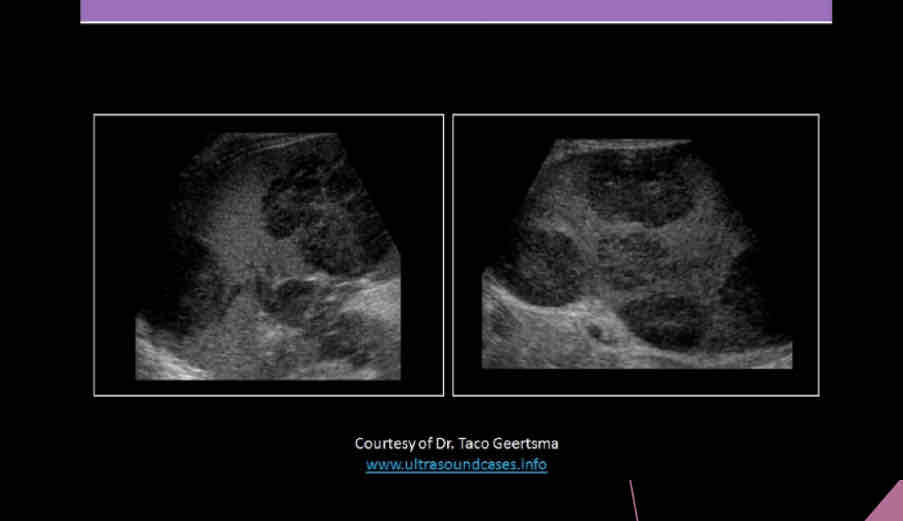
What is the most common type of lymphoma?
Hodgkin's disease
With lymphoma the sonographer should also evaluate for…
Evaluate the abdomen for lymphadenopathy; splenic and renal hilum areas, porta hepatis and para-aortic areas
metastases to the spleen seem relatively ________
common
uncommon
neither
uncommon
What do METS most commonly occur in?
malignant melanoma
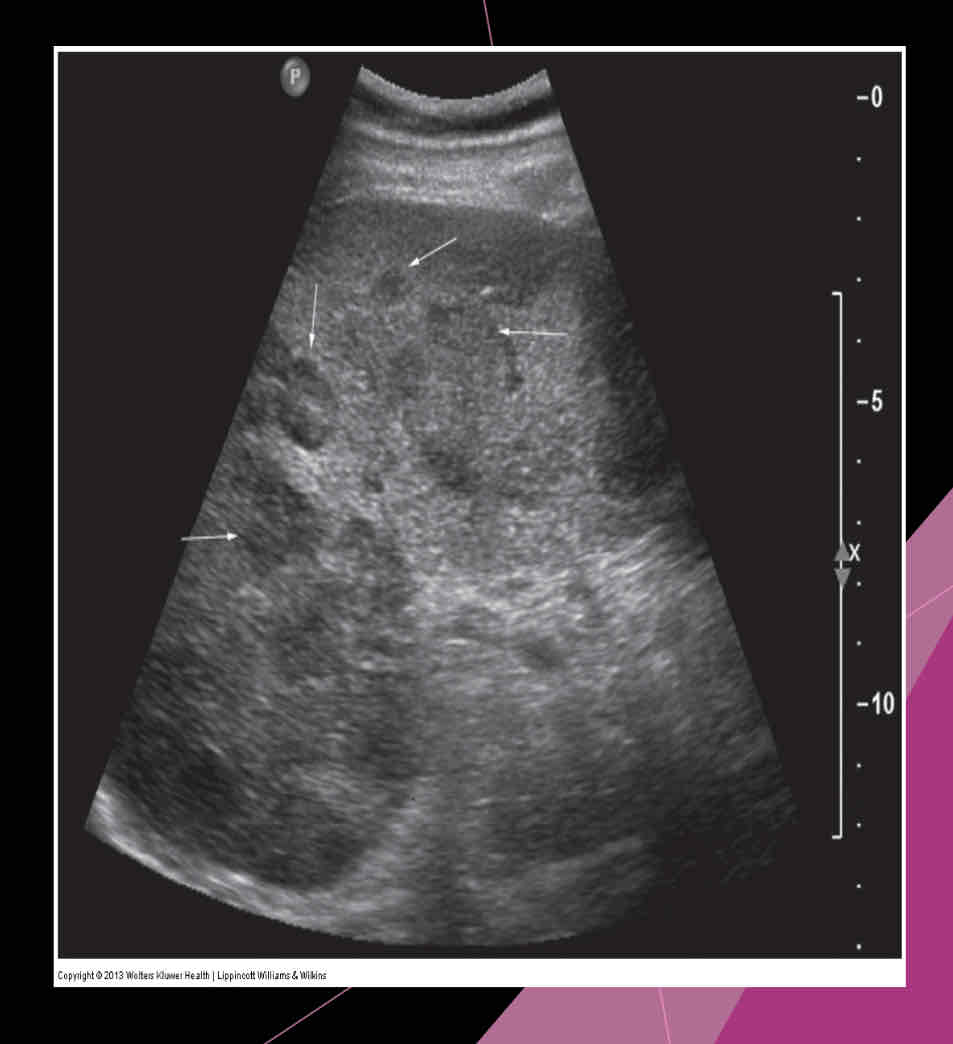
What may also occur with ovary, breast, lung, pancreas and stomach primaries, and Sonographically: hypoechoic is common, but it may vary?
Metastasis
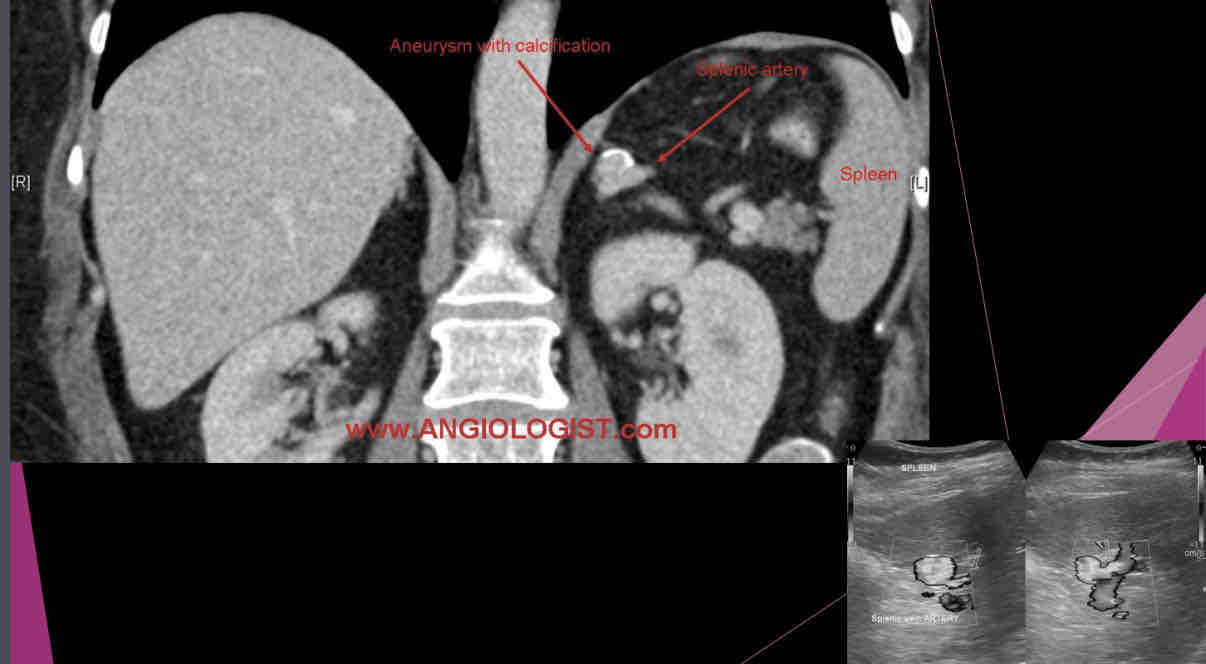
What describes the following?
•Those may be single or multiple and are most commonly involving the distal portion of the artery.
•Peripheral calcification is common, and mural thrombus may be present
•Usually, calcified circle seen in LUQ on X-ray and this is suspected
•Sonographically: may appear as cystic mass, or if calcified a hyperechoic shadow foci in area of artery
splenic artery aneurysm
Size of splenic artery aneurysms can range from…..
2 to 9 cm, but usually it is smaller than 3 cm
What are two characteristics of patients who have AIDS?
•Moderate splenomegaly in 50-70% of patients
•Splenomegaly noted more in patients with sexually transmitted HIV than in those acquiring the disease through IV drug use