BIO MID TERMS
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/100
Last updated 3:37 AM on 1/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
1
New cards
Define Biology
study of life and living things
2
New cards
What are the 4 characteristics of living things ?
RGDA - reproduce, grow, DNA, adapt
3
New cards
What from of energy our cells use to do work?
ATP
4
New cards
What is the indirect and direct source of energy for most life on earth?
The sun
5
New cards
Chemical equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + H2O + light energy \------\> O2+C6H12O6
6
New cards
chemical equation for cellular respiration
O2 + C6H12O6 --\> CO2 + H2O + ATP
7
New cards
Photosynthesis reactants
CO2 , H2O
8
New cards
Photosynthesis products
O2+C6H12O6
9
New cards
What does photosynthesis do?
They are responsible for oxygen gas in our atmosphere and gives it to us
10
New cards
In which organelle does photosynthesis occur ?
Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts
11
New cards
cellular respiration reactants
O2 , C6H12O6
12
New cards
Do plants need oxygen to survive ?
Yes they need oxygen to convert food into energy and need it for cellular respiration
13
New cards
cellular respiration products
CO2, H2O, ATP
14
New cards
A Calorie is a measure of how much \_____________ is in your food.
Energy
15
New cards
What does cellular respiration do?
puts carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere, and uses oxygen to release energy from food (ATP)
16
New cards
Where does cellular respiration happen?
mitochondria
17
New cards
Define autotroph
Organism that can produce its own food using light, water, carbon, other chemicals
18
New cards
Define heterotroph
An organism that eats other plants and animals for energy
19
New cards
Define producer
(autotroph) are typically plants
20
New cards
Define primary consumer
An organism that eats producers (herbivore) and is second trophic level
21
New cards
Define secondary consumer
An organism that eats primary consumers (carnivore)
22
New cards
Define tertiary consumer
eats secondary consumers
23
New cards
Define Quaternary consumer
top carnivores and majorly prey on animals below them
24
New cards
Define herbivore
Organisms that eat only plants.
25
New cards
Define carnivore
eats only meat
26
New cards
Define omnivore
eats both plants and animals
27
New cards
Define decomposer
organism that breaks down and obtains energy from dead organic matter
28
New cards
Define population
a group of organisms of the same species who live in the same area at the same time
29
New cards
Define ecology
The study of interactions between organisms and their environment
30
New cards
Define community
The populations of different species living in a habitat
31
New cards
Define ecosystem
includes the biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) features of an organism's environment
32
New cards
Define abiotic
Non-living things
33
New cards
Define biotic
Living things
34
New cards
Most of the air you breathe is what type of gas?
nitrogen gas
35
New cards
What nutrient cycle involves fossil fuels?
The carbon cycle
36
New cards
What organisms can fix nitrogen?
nitrogen can fix bateria
37
New cards
What types of plants have nitrogen-fixing organism in their roots nodules?
bean plants have nitrogen-fixings organism
38
New cards
What is nitrogen fixation?
Nitrogen from the atmosphere is converted into a usable form of nitrogen for plants and others
39
New cards
Commensalism (+/0)
Help/No effect
40
New cards
Parasitism (+/-)
help/harm
41
New cards
Mutualism (+/+)
help/help
42
New cards
What type of bond forms within a molecule of water?
Polar Covalent
43
New cards
What type of bond forms between water molecules?
hydrogen bond
44
New cards
Substance A is non polar. Will it dissolve in water?
NO
45
New cards
Substance B is polar. Will it dissolve in water?
YES
46
New cards
How is water able to defy gravity and move up a tree?
Capillary action helps bring water up into the root
47
New cards
What are the four different types of macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, nucleic acids, , proteins , lipids
48
New cards
What element do all organic compounds contain?
Carbon atoms
49
New cards
What does the perfix "macro" mean?
Large , thick
50
New cards
What 6 elements make up all living things?
CHNOPS
51
New cards
What are the two main types of nucleic acids?
deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid
52
New cards
What are they important to living things?
They are important because they carry genetic material
53
New cards
What type of macromolecules are most enzyme?
protein
54
New cards
What is the name for the molecule to which an enzyme binds-to and acts upon?
substrate
55
New cards
Is the shape of an enzyme important?
Yes because an enzymes shape will only allow it to work on a molecule that can fit it and has a effect on it's catalyzes recation.
56
New cards
What happens if an enzyme denatures or loses its shape?
They wont be able to function
57
New cards
What is an enzyme?
enzymes are proteins
58
New cards
What do enzymes do?
speed up chemical reactions
59
New cards
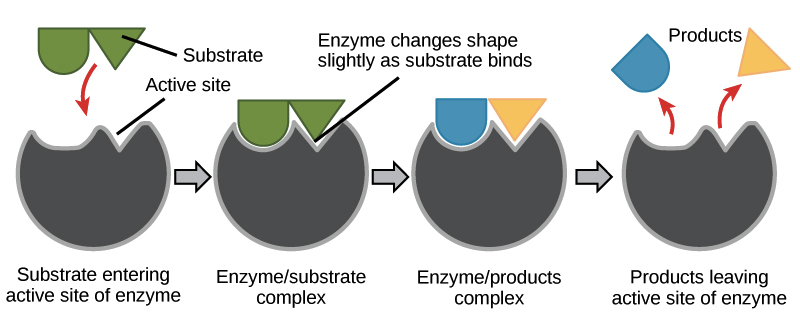
What is the name of pocket label 2 diagram below
active site
60
New cards
What is the smallest unit of life?
cell
61
New cards
Why are small cells more efficient than large cells?
small cells give u more surface area for nutrients and wastes can enter and exit the cell faster
62
New cards
How can we see most cells?
microscopes
63
New cards
Eukaryotic cells have a \___________.
nucleus
64
New cards
Prokaryotic are \_____________.
all bacteria
65
New cards
Eukaryotic have \_________________ such as mitochondria.
membrane-enclosed organelles
66
New cards
Eukaryotic cells include \_________________.
algae, humans, dogs, mushrooms, yeast, trees, fish, frogs.
67
New cards
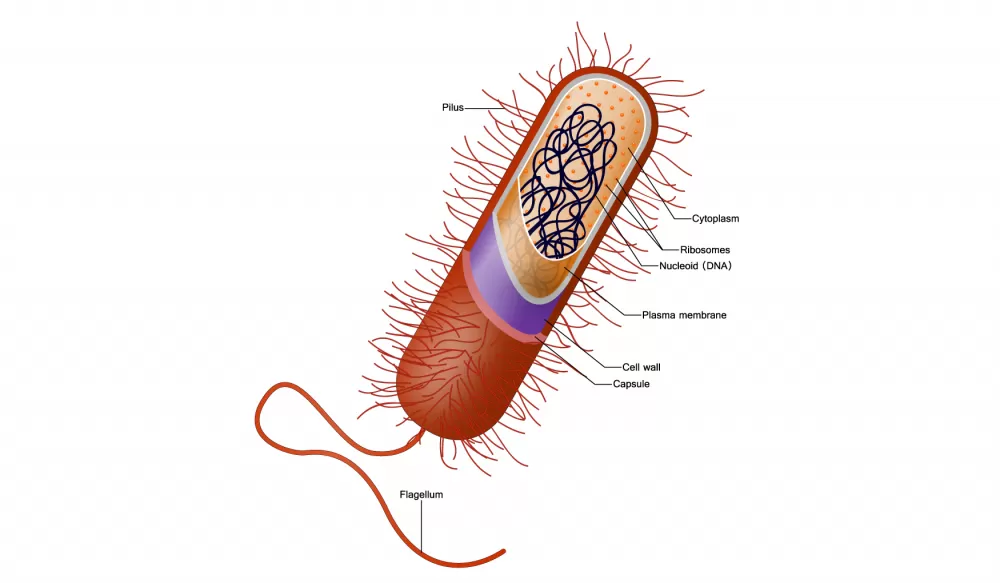
Is the above cell a prokaryote or eukaryote?
Prokaryote
68
New cards
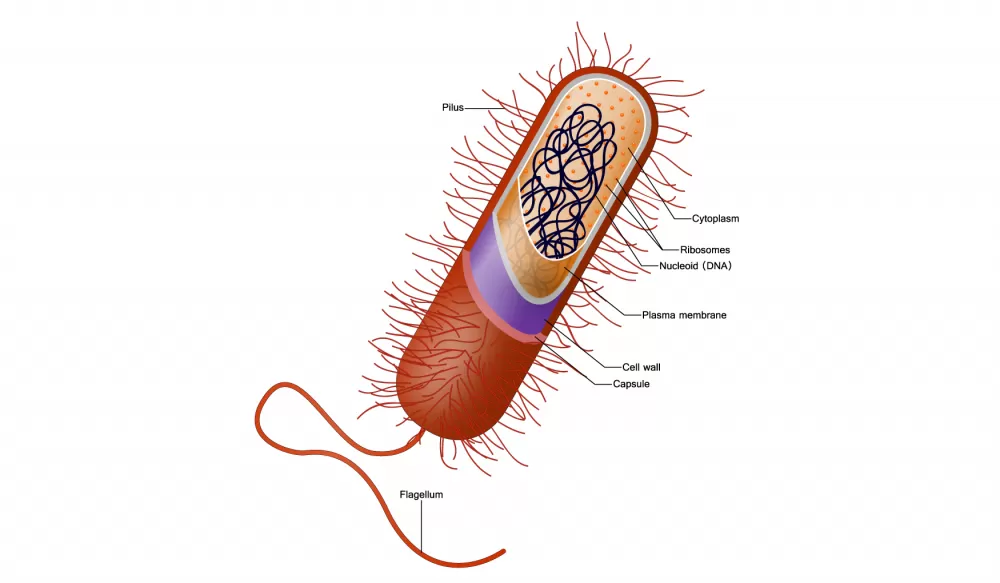
is the cell above from an animal, a plant, or a bacteria cell?
bacteria cell
69
New cards
Is DNA single or double stranded?
double
70
New cards
Is RNA single or double stranded?
single
71
New cards
what type of monomers is DNA and RNA made of?
nucleotides
72
New cards
What type of sugar is found in DNA?
deoxyribose
73
New cards
what type of sugar is found in RNA?
ribose
74
New cards
what are the bases of DNA?
A-T C- G
75
New cards
What are the bases of RNA?
A-U C-G
76
New cards
What type of macromolecule does DNA contain the instructions for making?
nucleic acids
77
New cards
Which types of macromolecules are listed on nutrition labels?
Lipids, Carbonhydrates, proteins, nucleic acids
78
New cards
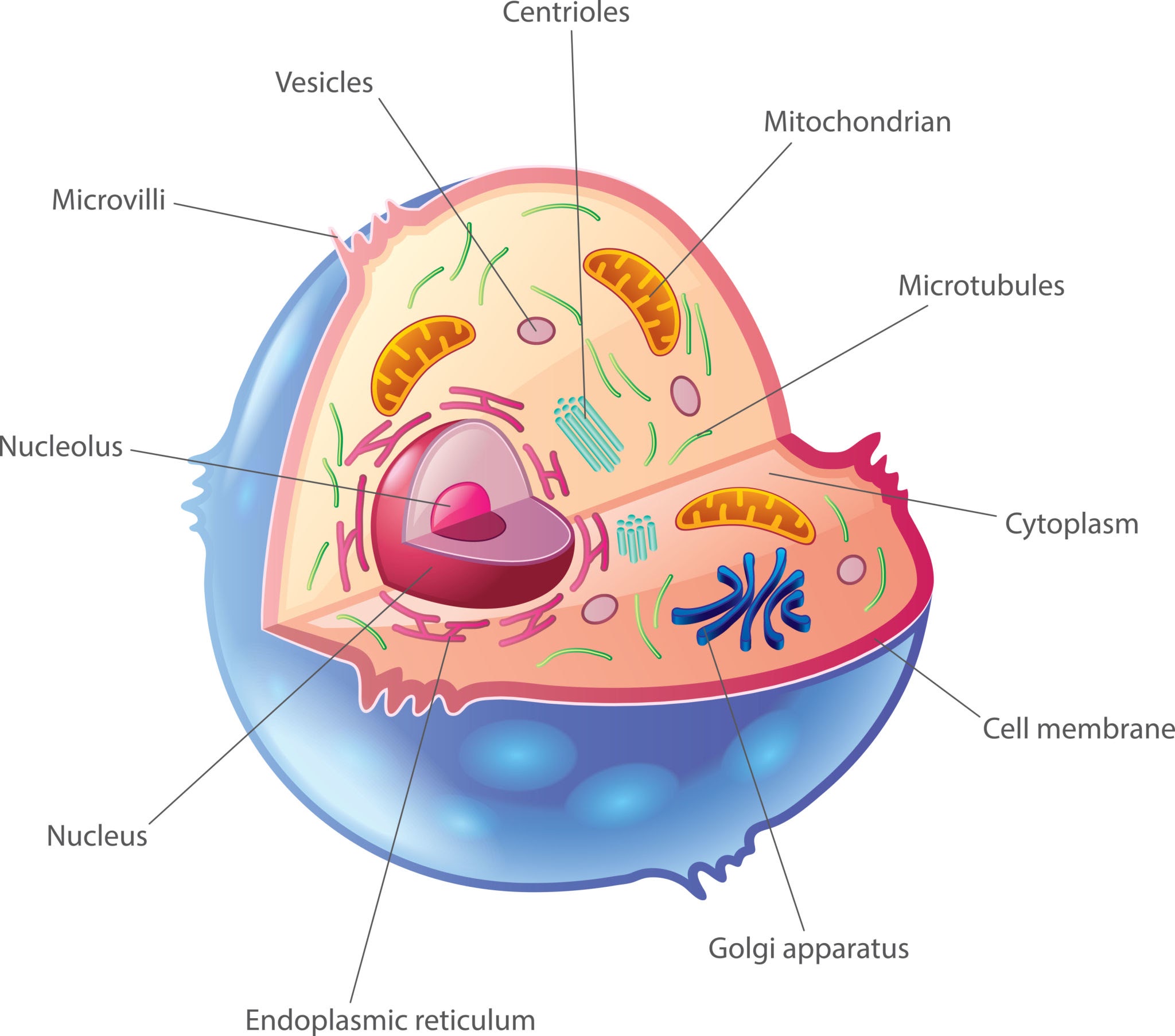
Is the cell below a prokaryote or eukaryote?
Eukaryotic
79
New cards
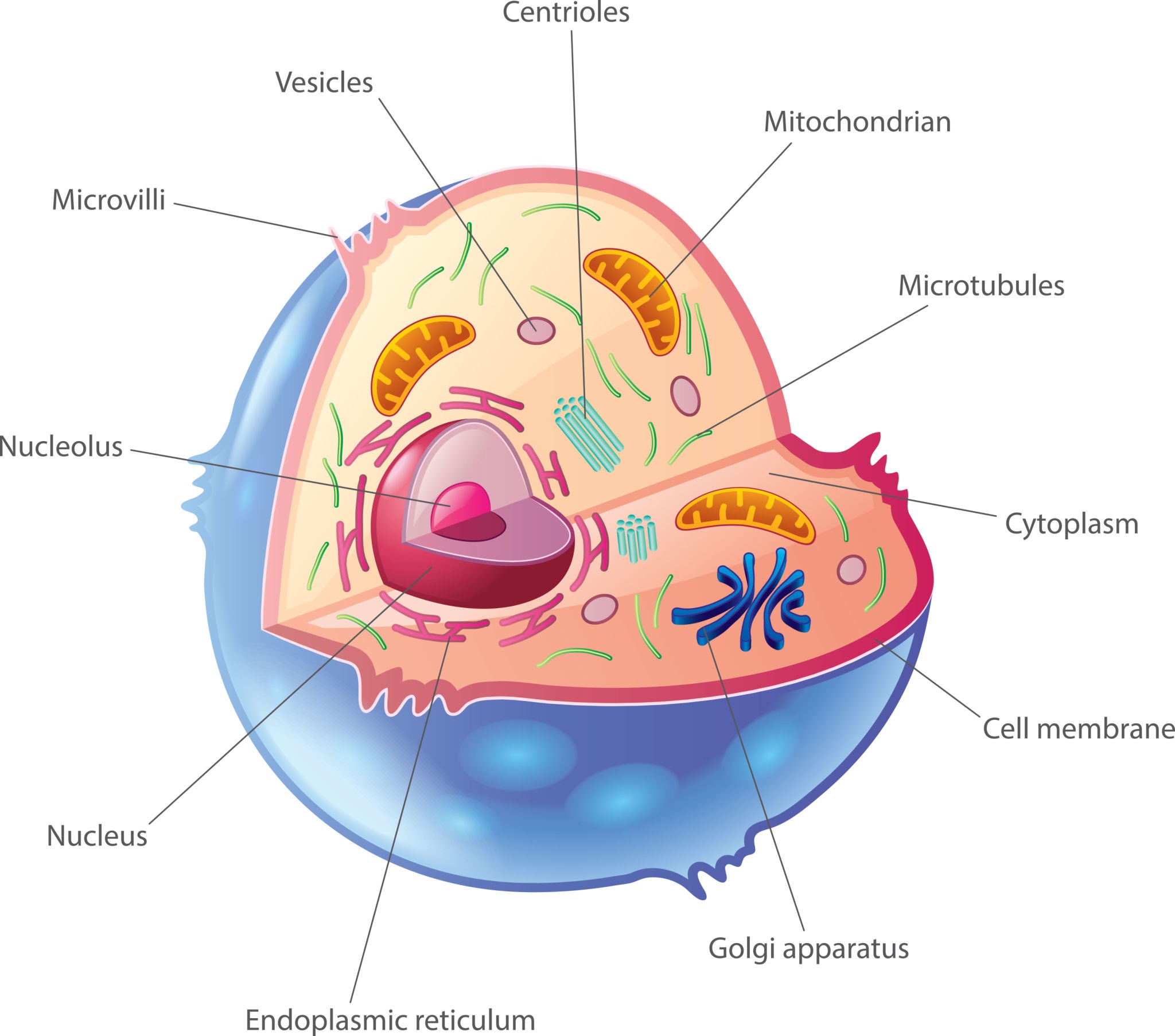
Is the cell an animal cell, plant cell, or bacteria cell?
animal cell
80
New cards
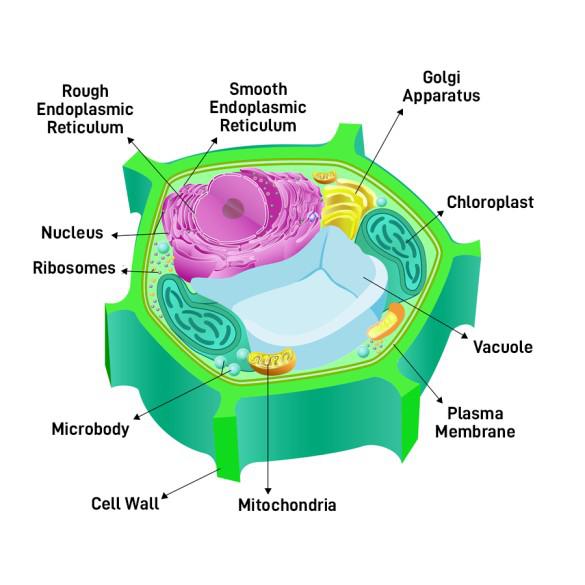
Is the cell below from a prokaryote or eukaryote? Is it an animal cell or bacteria or plant?
Eukaryotic PLANT CELL
81
New cards
Plant cell has a large \______________.
central vacuole
82
New cards
plant cell has a cell \____________.
WALL
83
New cards
Both plant and animal cells have \______________.
mitochondria
84
New cards
Define nucleus
brain of the cell , genetic material
85
New cards
Define rough ER
make proteins and has ribosomes
86
New cards
Define smooth ER
makes carbohydrates and lipids-no ribisosmes
87
New cards
Define Golgi Apparatus
Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release
88
New cards
Define ribosomes
Makes proteins
89
New cards
Define lysosomes
organelle that breaks down organelles that are no longer useful and has enzymes
90
New cards
Define mitocondria
produces ATP and site cellular respiration
91
New cards
Define chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis
92
New cards
Define cell wall
Support and protects the cell
93
New cards
Define plasma membrane
boundary of the cell, monitors what enters and leaves
94
New cards
Define flagella
movement
95
New cards
Why aren't viruses considered living things?
Viruses are not made out of cells, they can't keep themselves in a stable state, they don't grow, and they can't make their own energy a virus isn't considered living because it doesn't need to consume energy to survive, nor is it able to regulate its own temperature.
96
New cards
What is the permeability of the plasma membrane?
semi-permeable
97
New cards
What does semi-permeable mean?
some things can go through, some things cannot.
98
New cards
True or False: All cells have a plasma membrane.
TRUE
99
New cards
What is the function of cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
stabilization of the phospholipids and supports
100
New cards
What is the function of carbohydrates in the plasma membrane?
they identify the chemical signals "cell to cell communication " allow cells to be recognized by other cells.