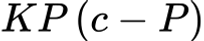Yellow Card Stuff to Know
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
sin(u)
cos(u)
cos(u)
-sin(u)
tan(u)
sec2(u)
cot(u)
-csc2(u)
sec(u)
sec(u)tan(u)
csc(u)
-csc(u)cot(u)
ln(u)
1/u
eu
eu
sin-1(u)
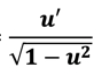
cos-1(u)
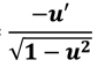
tan-1(u)
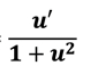
cot-1(u)
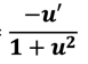
Limit from the left of f(x) as x → a
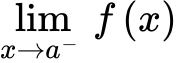
Limit from the right of f(x) as x → a
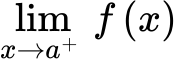
Definition of Continuity
f(a) is defined
Limit from left = limit from right
Overall limit = f(a)
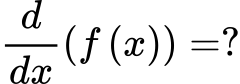
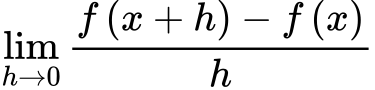
Chain rule
f’(u) * u’
Product Rule
uv’ + u’v
Quotient Rule
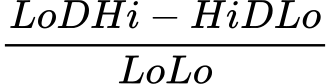
Intermediate Value Theorem
If f is continuous on the closed interval [a,b], where f(a) ≠ f(b) and k is a number between f(a) and f(b), then there is atleast one number c in (a, b) such that f(c) = k.
Mean Value Theorem
If f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] and differentiable on the open interval (a, b), then there exists a number c such that:
![<p>If <em>f</em> is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] and differentiable on the open interval (a, b), then there exists a number c such that: </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8ac2bc27-18f1-4f89-9f8a-0cdee141bf6f.png)
L’Hopital’s Rule
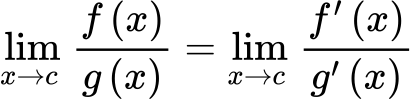
Critical Points
If f(x) is defined at x = c, then f(x) has a critical point at x = c if f’(c) = 0 OR f’(c) is undefined.
Global Minimum
f(c) < all other values of f(x)
Global Maximum
f(c) > all other values of f(x)
Extreme Value Theorem
If f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b], then f has both an absolute minimum value and absolute maximum in the interval.
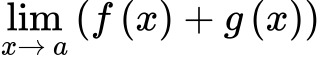
F + G
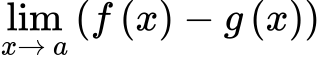
F - G
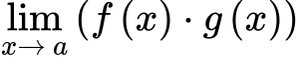
FG
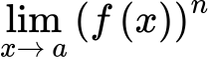
Fn
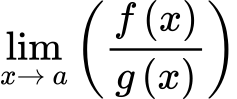
F/G
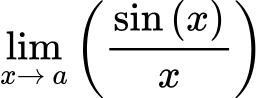
1
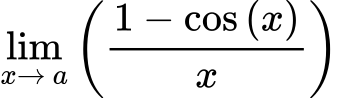
0
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
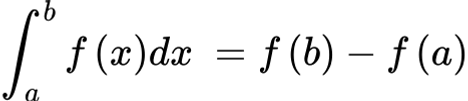
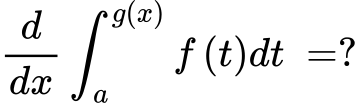
Corollary to FTC
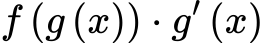
If continuous on [a, b] and x=c on (a, b) then…
(MVT/average value for integrals)
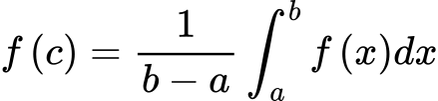
Disk Method
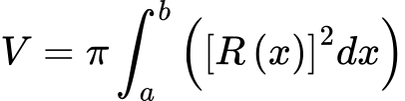
Washer Method
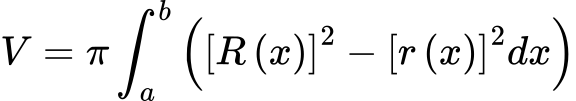
General volume equation
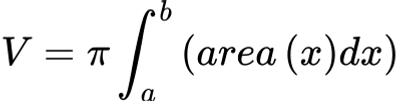
Arc Length (rectangular)
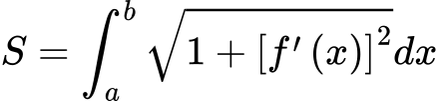
velocity
s’(t)
acceleration
s’’(t) = v’(t)
Speed (parametric and rectangular)
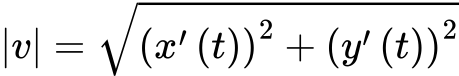
Displacement

Average velocity
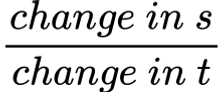
Euler’s Method

Integration By Parts
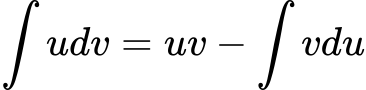
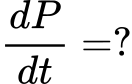
Logistics