auto immune hemolytic anemia pt 1 - cold reacting auto abs
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Immune hemolytic anemia: shortened RBC survival
mediated through the immune response, specifically
by _____ antibody
humoral
what are the 3 broad categories of immune hemolytic anemias
alloimmune
autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AHA)
drug induced immune hemovtic anemia
what is autoimmune hemolytic anemia
shortening of time RBCd survive in circulation (less than 90 to 120 days)
pathophysiology of immune hemolysis: ______: destruction on RBCs within the blood
vessels. This type of hemolysis is rare.
intra vascular
what is a classic example of an intravascular immune hemolysis
serious ABO incompatibility ( anti a or -b are destorying rbcs in the blood vessels)
pathophysiology of immune hemolysis: ______: destruction of RBCs that occurs after
sensitized cells are removed from circulation by the spleen via the reticuloendothelial system
Extra-vascular
which type of in vivo hemolysis is more common
extravascular
which causative agent(s) is/are most frequently associated w extravascular hemolysis
IgG
which causative agent(s) is/are associated w both intra or extra vascular hemolysis
Complement
which pathophysiology of immune hemolysis is less frequent
intravascular hemolysis
in what conditions is intravascular hemolysis most seen
ABO mismatch
paroxysmal hemoglobin hematuria (PNH)
what are lab indicators for intravascular hemolysis 5
hemoglobinemia (plasma pink or red)
hemoglobinuria (pee pink, red, brown, or almost black)
decreased serum haptoglobin (theres lots of free hb therefore all the haptoglobin is bound to it)
elevated LDH (enzyme present in rbcs have spilled out)
RBC are schistocytes (fragments)
what are the lab indicators for extravascular hemolysis 5
increase serum bilirubin (rbcs being destroyed)
spherocytes (due to spleen sequestering out cells w IgG)
agglutination
increased reticulocytes (bone marrow trying to compensate therefore is pushing out red cells prematurely)
dec hb and hct
how do u diagnose hemolytic anemia
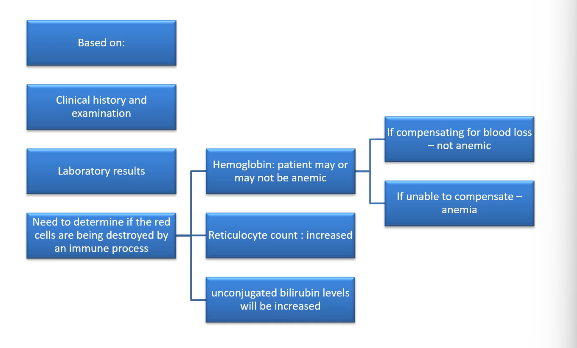
t/f a pos DAT proves autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA)
F( THO IT IS a v good guide, it isnt definitive)
if autocontrol is pos, it may detect ___ sensitization
in vitro sensitization
t/f when auto control is pos, dat is pos
f ( dat may be neg if ac is pos)
t/f DAT detects in vitro sensitization while AC detect s in vivo sensitization
f; DAT detects in vivo sensitization (a/c can detect both)
t/f majority of individuals with hemolytic anemia are DAT pos
t (83%)
majority of DAT, when eluate is run are reactive t/f
f (79% of positive
DAT are nonreactive eluate)
what are the 3 major types of autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA)
COLD autoimmune hemolytic anemia
WARM (WAIHA)
drug in duced
which autoimmune HA: The antibodies
react optimally at 4C. May also react at room temperature.
cold
what type of AIHA: The
antibodies react optimally at 37C.
WAIHA
what type of AIHA: Patient produces antibody to
a particular drug or drug complex which causes damage to
patient’s RBCs
drug induced
list from lowest incidence to highest the autoimmune hemolytic anemias
drug induced
cold
waiha
what antibodies are cold autoimmune hemolytic anemias associated w
cold auto abs
t/f someone w a cold hemolytic anemia, their anemia gets worse in the winter
t
what i the most common benighn cold auto antibody
anti-I
T/F benign cold auto abs are present in the serum of most healthy individuals
t
what are the rare benign cold auto antibodies
anti IH and anti-i
t/f benign cold abs are non red cell immune
t
whaat type of abs are benign cold abs
IgM
are benign cold abs clinically significnt
typically no
if you perform a serial dilution on a sample w benign cold autoabs, what wuld their titer be
low (Patient produces antibody to
a particular drug or drug complex which causes damage to
patient’s RBCsless than 64)
if you think you have a benign cold ab, what do u do to make it react stronger
enzyme treat it
benign cold autoabs react w ____ cells but not w ____ cells
adult cells; cord cells
why are cold benign autoantibodies a problem
if reacting at RT can mask significant abs
whats an easy way to stop cold auto abs for interfering
pre warm sample
DAT done on ___ samples to avoid false pos
EDTA
during ABO typing, how can cold autoantibodies interfere
Cells heavily coated with cold agglutinin cause spontaneous
agglutination (evth pos even Rh ctrll)
Cells heavily coated with cold agglutinin cause spontaneous
agglutination. whats the sltn
-wash cells 2x with warm saline
-incubate at 37C for at least 1 hour , then wash with warm
saline
-thiol reagent e.g. dithiothreitol can be used (DTT)
-auto adsorption technique
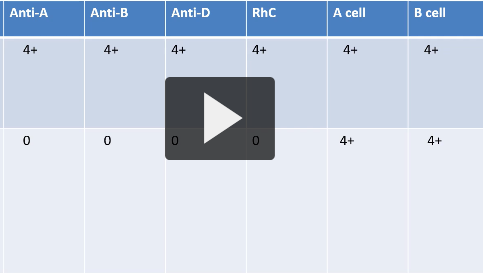
THIS IS THE SAME SAMPLE, WHAT DOES THIS MEAN
there was a cold auto antibody present. it was warmed/ washed w warm saline and spat out the reult on the bottom
if everyth is pos during abo/ rh testing, what direction does it point you in
sampe has a cold auto ab
t/f cold antibodies can cause false pos in wk d if clotted sample and polyspecific rgt is used
t
cold antibodies can cause false pos in wk d if clotted sample and ______ rgt is used
polyspecific
how do you stop cold auto ab from causing false rxns during Rh typing
use monoclonal rgts
- warm saline wash w thiol rgts
Cold agglutinins found in the sera of group A1
and A1B individuals (and occasionally group B)
may have anti-____specificity.
anti-H
which ABO groups have the largest amt of H antigen nd will therefore react the best with anti H and anti-IH
group O and A2
which ABO groups have the least amt of H antigen nd will therefore react the weakest with anti H and anti-IH
Group A1 and A1B
Less commonly encountered cold autoagglutinins
have been described, such as
anti-Pr
-Gd
-Sdx
-Rx
Anti-IH and anti-H give weaker
reactions with group ___ and ___,
stronger with group ___
A, B, O (much more H ag on O cells)
pathologic cold autoagglutinins may cause mild to life threatening _____
acute intravascular lysis
what causes pathologic cold autoagglutinins
idiopathic (primary)
not associated w any demonstratable underlying disease
acute, transient (secondatry)
associated w a primary disease state
mycoplasmo pneumoniae
anit-I
hemolysis rare but rapid onset may occur usually 2-3rd week of illness
infectious mono
anti-I
wide thermal range
what is the diagnosis that has auto anti-I
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
what is the diagnosis that has auto anti-i
infectious mononucleosis
in which population is cold hemagglutinin disease most common (CHD)
ppl over 50 yo
what is typically the cold auto ab present in cold hemagglutinin disease (CHD)
anti-I
when is cold hemagglutinin disease usually displayed
winter (triggered when body temp goes below 28 deg c)
CHD: antibody agglutinates the red cells, fixing complement causing auto-
agglutination and signs of ____ also known as ______
phenomenon.
acrocyanosis ; Raynaud
if CHD id rlly bad what are the characteristic signs that are displayed (chronic anemia)
weakness
pallor
weight loss
why is DAT pos in CHD
DUE TO COMPLEMENT****
what are the lab findings of CHD 4
reticulocytosis (bone marrow trying to compensate for anemia)
pos DAT
peripheral slide: agglutination, polychromasia
autoagglutination of sample (automated CBC difficult)
what does a peripheral slide have if pt has CHD
agglutination
polychromasia
why is CHD a problem during surgeries
some surgeries u need to cool the body down therefore must do special testing
treatment for CHD 4
keep pt warm
pt move to warmer climate
plasmapheresis
must transfuse w washed red cells
paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria (PCH) affects mostly who?
children and young adults w viral illnesses such as
measles
mumps
chicken pox
infectious mono
what is the main characteristic of paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria
intermittent, recurring episodes of hemoglobinuria after being exposed to cold
what are the symptoms of PCH 6
hemoglobinuria after exposed to cold
sudden onset of fever
shaking cills
malaise
tummy cramp
back pain
Red cell destruction in PCH is caused by a cold autoantibody called a
biphasic autohemolysin
what does a biphasic autohemolysin do
• Binds to patient’s red cells at low temperatures and fixes complement
• Hemolysis occurs when body temperature rises to 37 ̊C
what is the classic biphasic autohemolysin antibody produced during PCH*****
donath landsteiner ab
donath landsteiner antibody has ____ specificity and is ____
autoanti-P specificity; IgG
Lab findings of PCH 5
severe and rapid anemia (as low as 40 g/L)
polychromasia
nrbcs
poikilocytosis
donath landsteiner positive test for confirmation
what is the treatment for chronic and acute PCH
chronic: must protect from cold
acute: most infection end once underlying infection is treated
what are the rgts for the donath landsteineer test
freshly collected pooled normal plasma
50% group O P1 positive washed cells
when is the donath lanndsteiner test considered pos
when pt serum w or w/o complement causes hemolysis in the tubes that were incubated first in melting ice then at 37 C and there was NO hemolysis in any tubes kept j at 37 or melting ice only.
donath-landsteiner test: A3, B3 , C3 tubes serve as a ____ of the normal sera complement source and should manifest no hemolysis
control
wht is the diff between benign and pathological auto antibodies
benign reacts only w adult cells but not cord cells. pathological react w both adult and cord cells