BI303 - Exam 1
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
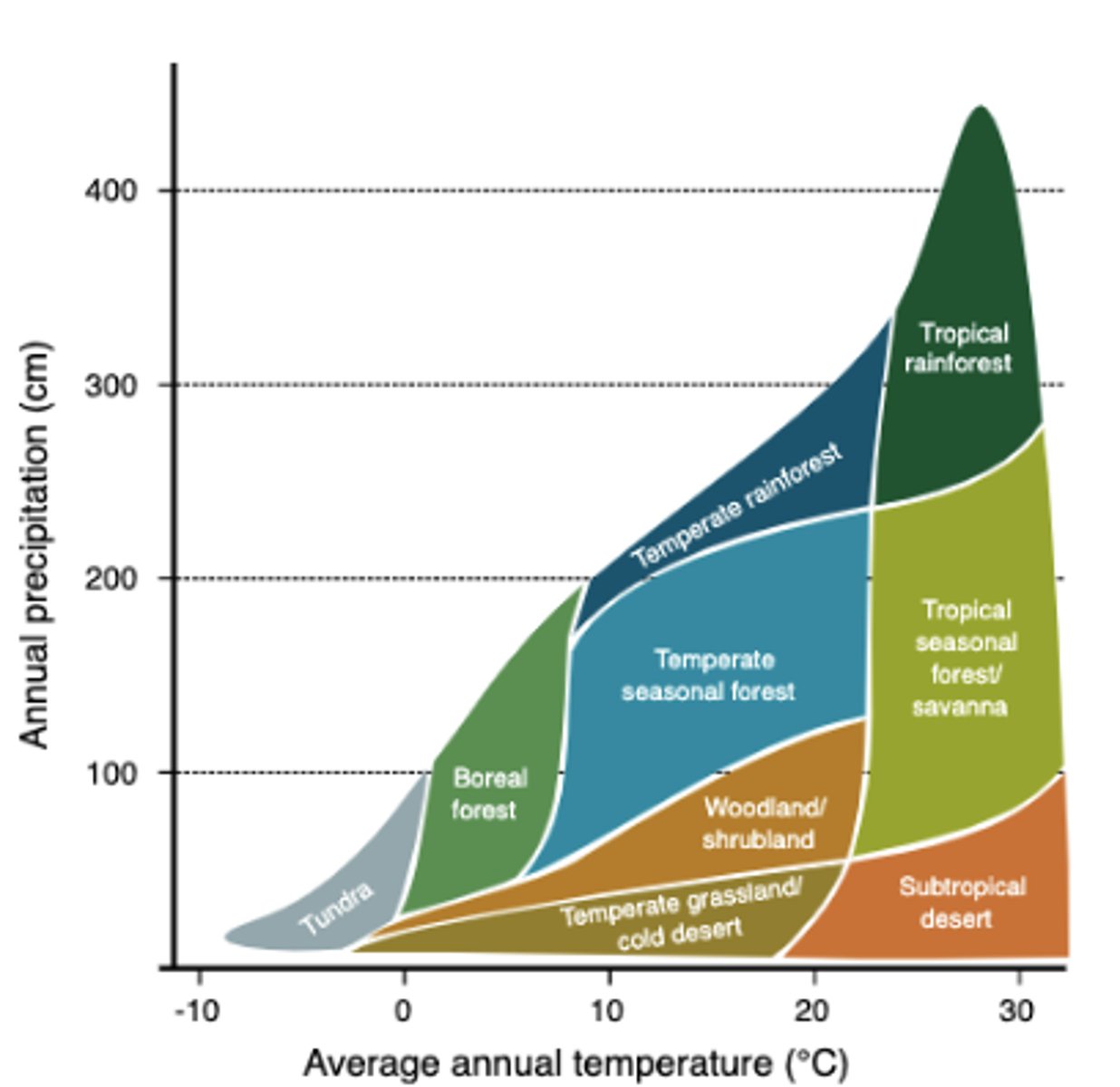
biome determination
temperature and precipitation
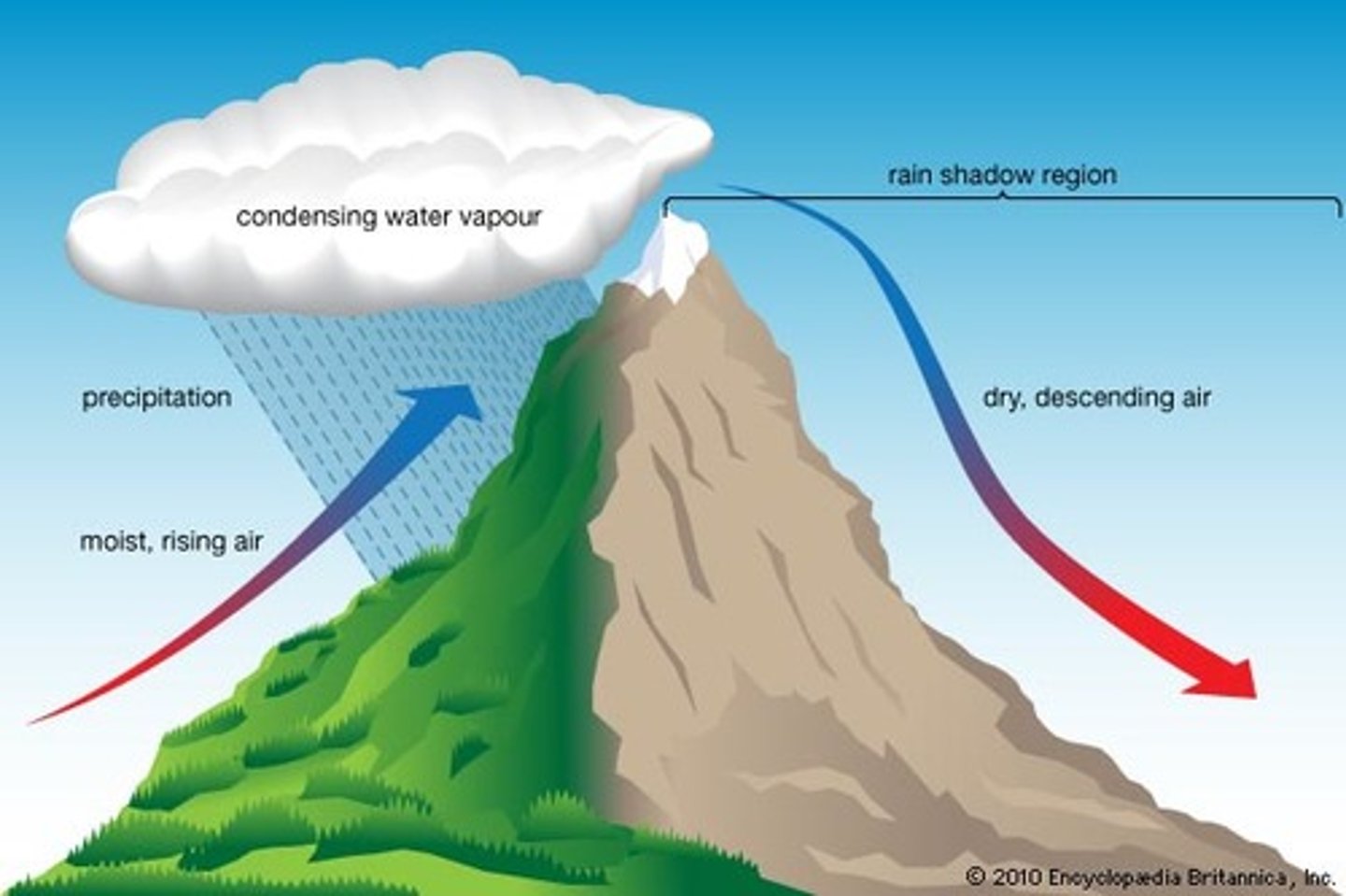
rain shadow effect
a phenomenon that occurs when a mountain range blocks rain-producing weather systems, creating a dry area on the downwind side.
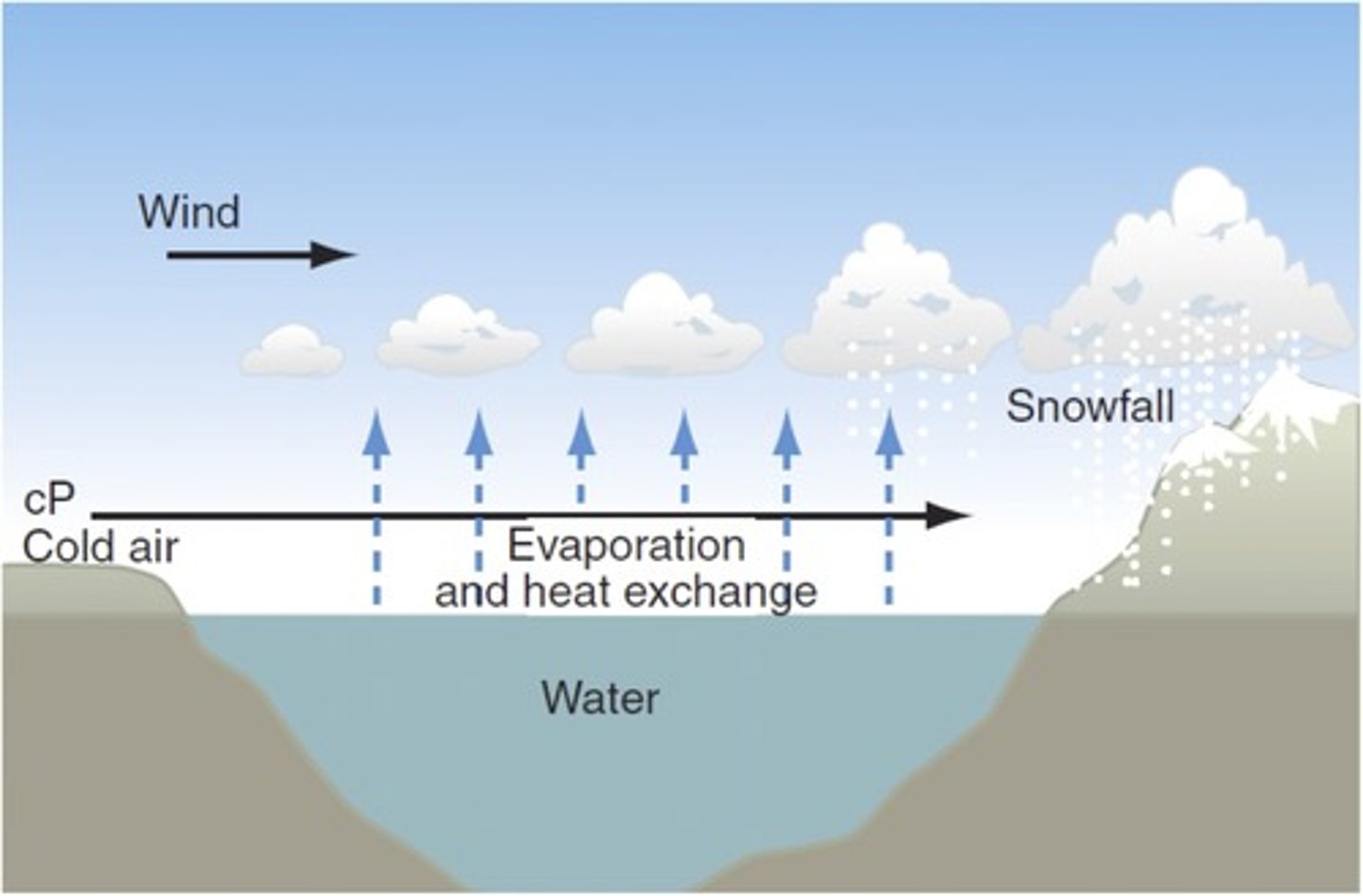
lake effect snow
Snow created when cold air flows over relatively warm water then over cold land
elevation effect on biome
biomes shift as elevation changes
tropical rainforest
Temp: High year-round
Precipitation: High year-round
Soil: Weathered, acidic, poor in nutrients
Plants: Adaptations to tolerate shade or find light quickly and easy, many epiphytes, parasites, and carnivorous plants.
tropical seasonal forest
Temp: High year-round
Precip: Seasonal (wet and dry seasons)
Soil: richer and less acidic than rainforest soil
Plants: many trees drought-deciduous (lose their leaves during dry season)
tropical savanna
Temp: High year-round
Precip: seasonal (short wet and long dry)
Soil: Productive, impermeable subsoils trap water
Plants: Grass dominated, along with hardy, drought-deciduous trees
hot desert
Temp: mostly hot, but high seasonal daily variation
Precip: very low (sometimes none)
Soil: low in nutrients, alkaline, sometimes saline, covered in biocrusts
Plants: defended against heat, UV, and herbivory
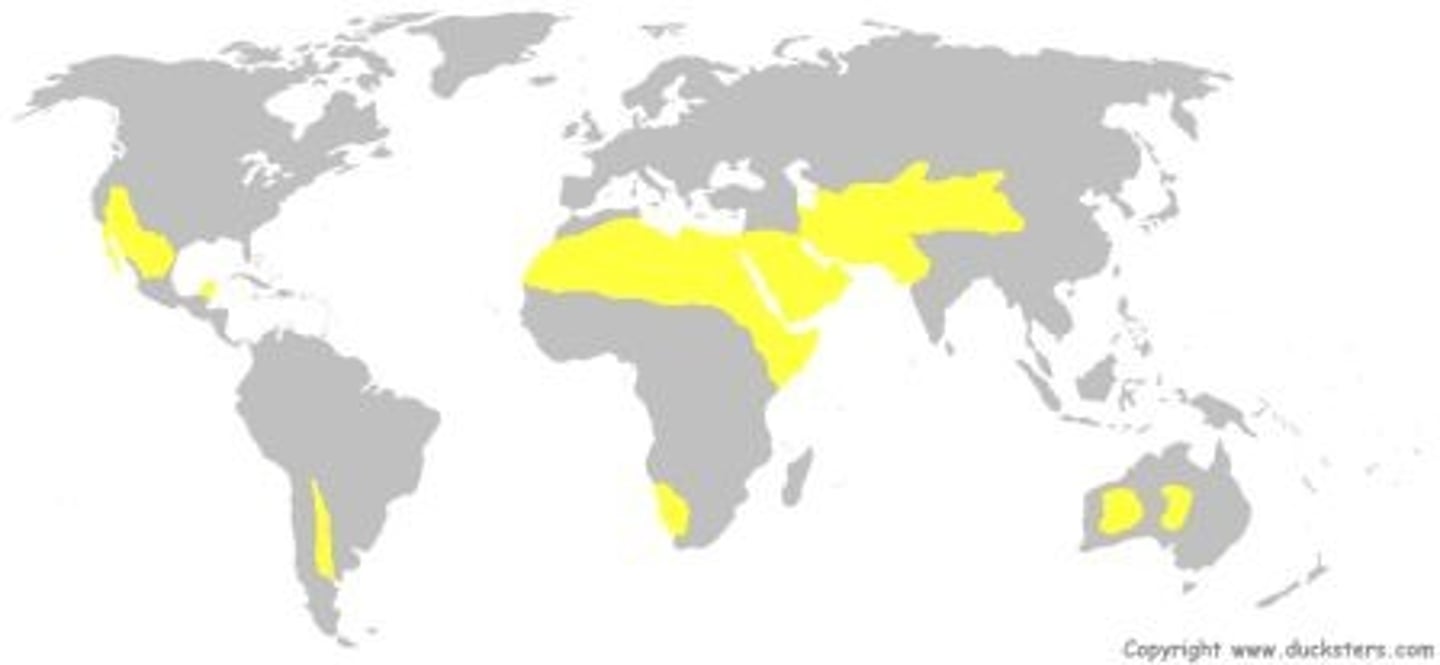
temperate grassland
Temp: temperate (warm summers, cold winters)
Precip: variable (generally wetter in the summer)
Soil: deep and very fertile
Plants: grasses and herbs, adapted to tolerate/benefit from fire and grazing
temperate forest
Temp: temperate, seasonal (warm summers, cold/mild winters)
Precip: moderate
Soil: thick, fertile, and rich in organic matter
Plants: cold-deciduous trees, some conifers
temperate shrubland
Temp: temperate, seasonal (warm summers, cold to mild winters)
Precip: seasonal (dry summers, wet winters)
Soil: dry, compacted, low fertility
Plants: many shrubs, small trees; adapted to drought and fire
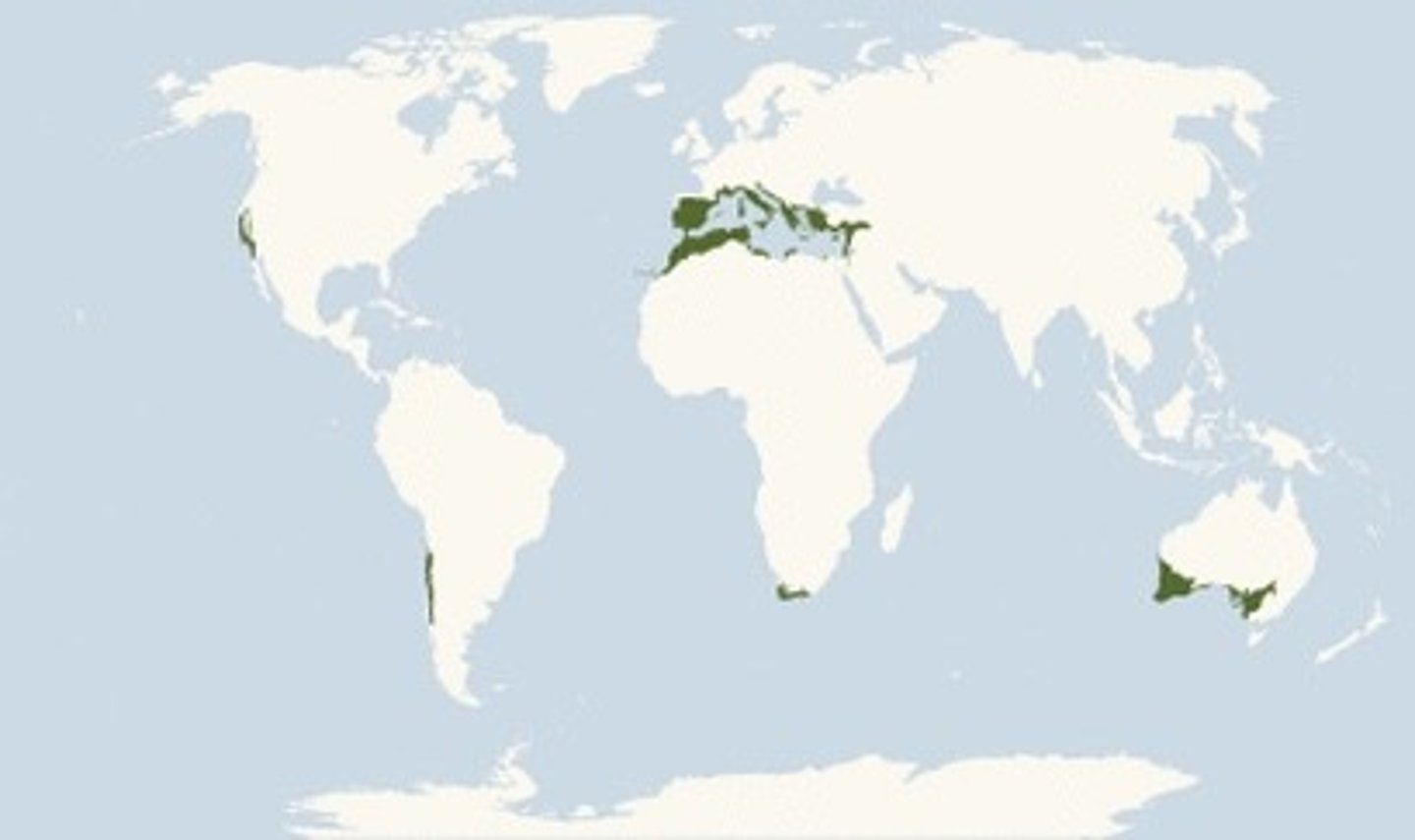
temperate rainforest
Temp: temperate, seasonal (cool summers, mild winters)
Precip: high (except during summer)
Soil: typically infertile
Plants: coniferous trees (including the largest on earths)
boreal forest
Temp: temperate, seasonal (warm summers, cold to mild winters)
Precip: moderate (but very little evaporation)
Soil: acidic, organic-rich, sometimes very thick and waterlogged
Plants: mostly evergreen conifers, deciduous trees, shrubs, fire-adapted
tundra
Temp: cold (subzero most of the year)
Precip: low (but little evaporation)
Soil: thick, defined by permafrost
Plants: moss, lichen, perennial grasses and herbs
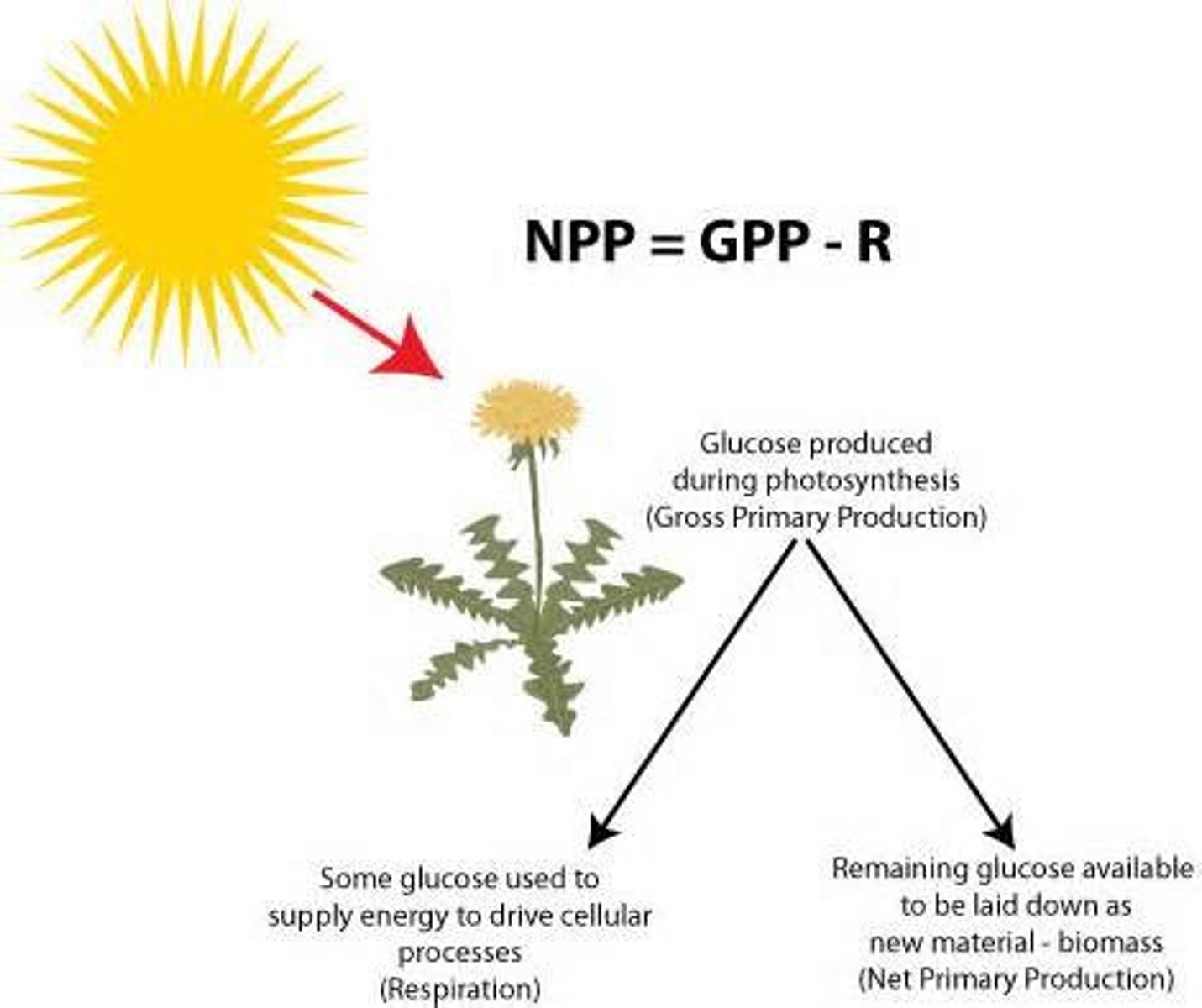
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
The energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire
Riparian area
areas of plants and trees that grow along the edges of rivers, streams and lakes. Can help prevent erosion and serve as filters for pollution.

allochthonous
where nutrients come from a terrestrial environment and enter into a river

Autochthonous
nutrients generated from WITHIN the river (algae, etc).
Lake "ingredients"
Water - from precipitation, snow/ice melt, rivers, and/or groundwater
A basin - formed by glaciers, tectonics, rivers, wind, karsts, volcanoes, animals, and/or humans
karsts
a type of landscape where the dissolving of the bedrock has created sinkholes, sinking streams, caves, springs, and other characteristic features

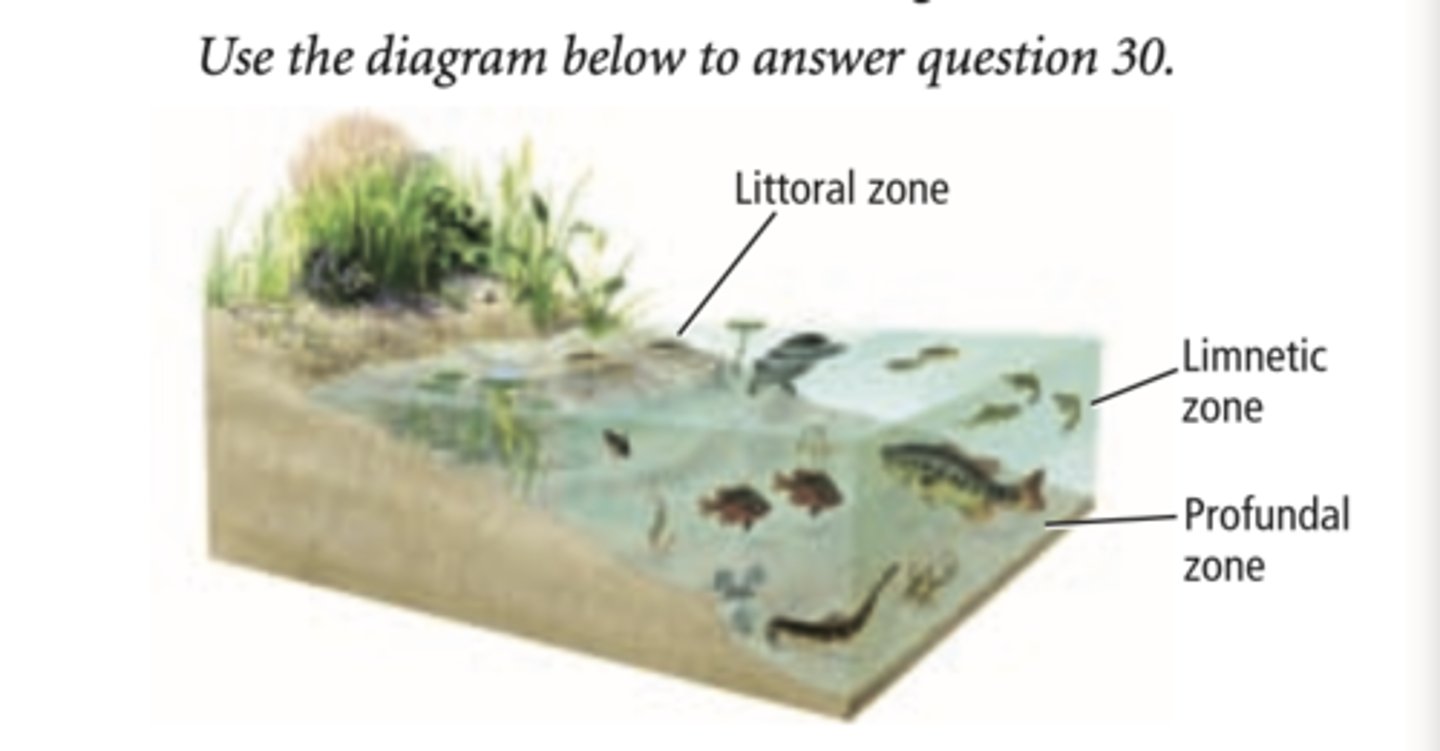
littoral zone (lake)
receives sunlight, near the shoreline, edge of the water
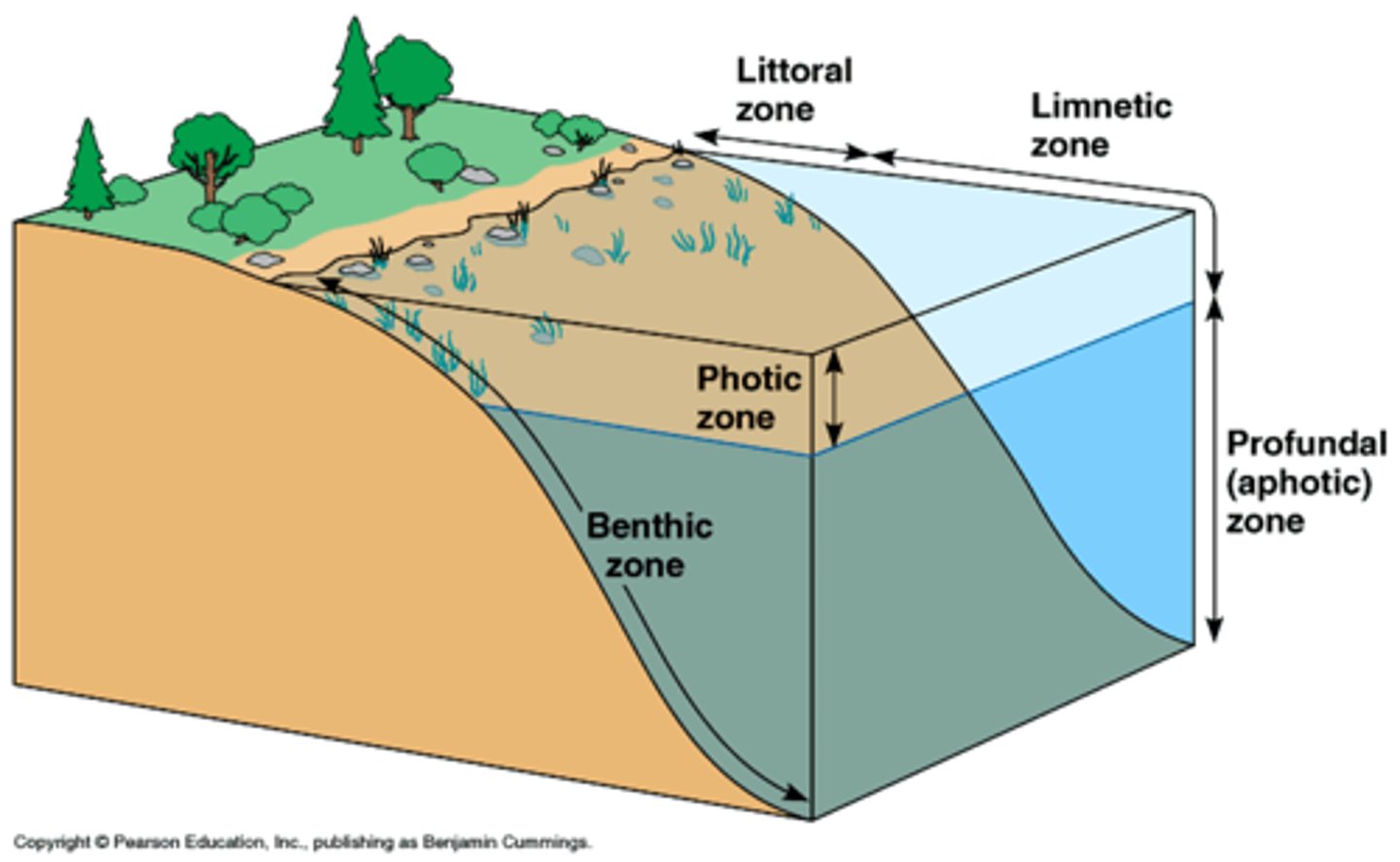
limnetic zone (lake)
receives sunlight that does not reach the bottom, high areas of photosynthesis
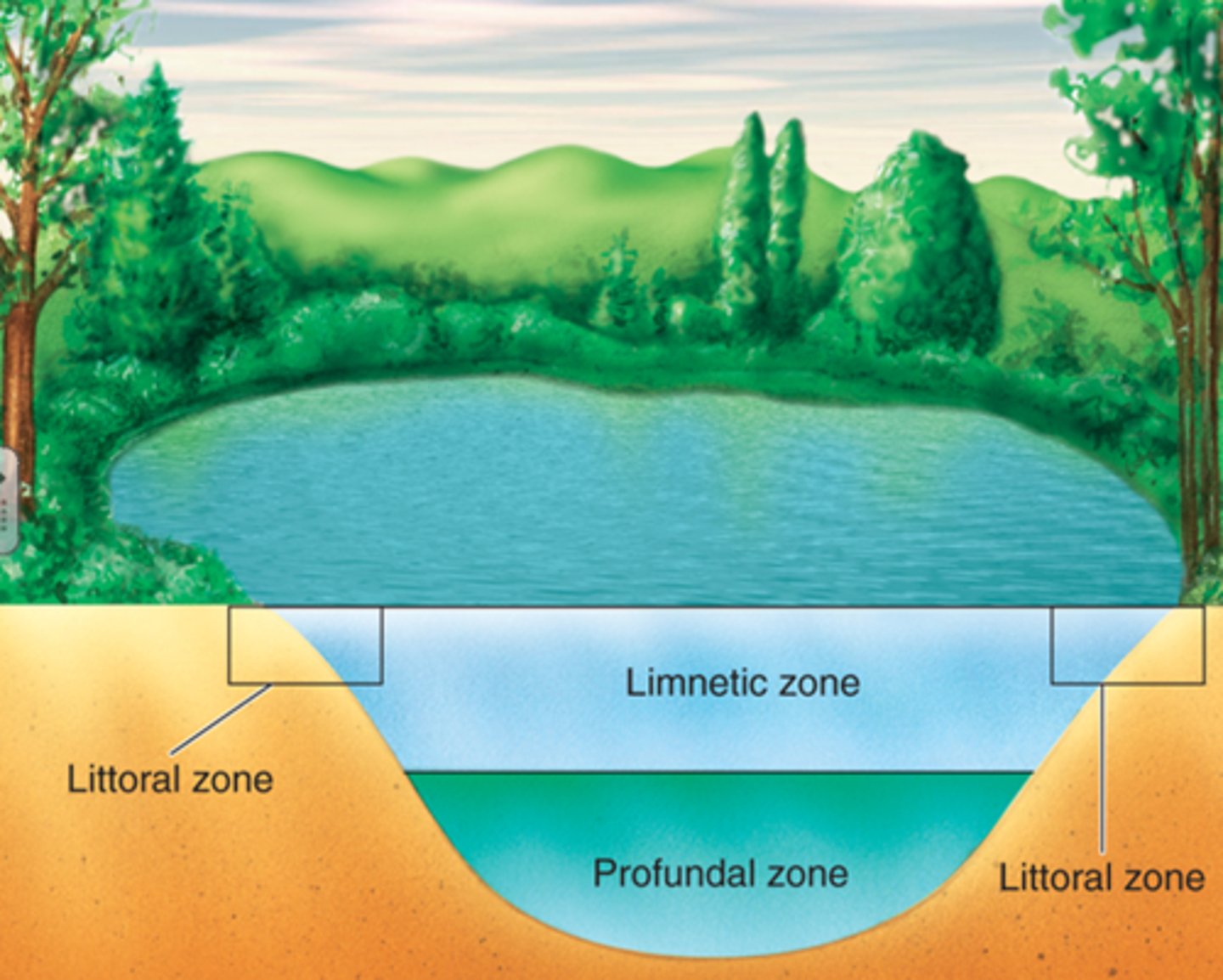
profundal zone (lake)
low levels of oxygen (anoxic), no producers, dominated by decomposers and predators

lake stratification
the layers of the lake that get mixed in turnover
meromitic
layers rarely mix
holomictic
layers mix at least once per year
monomictic
mixes once a year
dimitic
mixes twice a year
polymictic
mixes several times a year
oligotrophic
typically at a higher elevations and latitudes
Low in nutrients, low NPP, high oxygen levels
mesotrophic
wide distribution
Moderate nutrient levels, NPP dominated by plants, clear(ish) water, more tolerant fish to lower oxygenated water
eutrophic
found at lower latitudes and tend to be closer to humans
High nutrients, high NPP, low oxygen
Tend to be shallower and flat bottomed
Water clarity depends on dominant producers
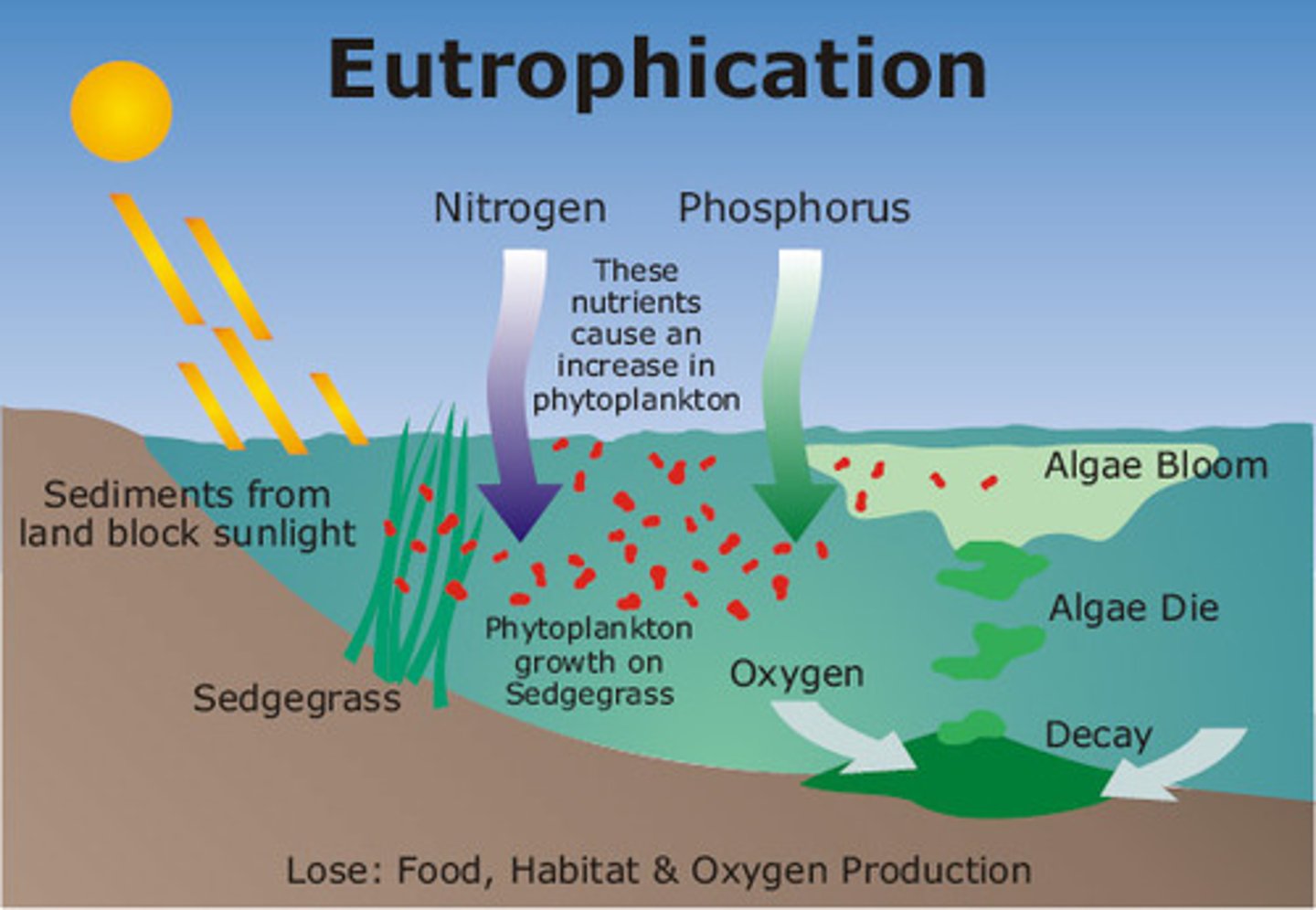
eutrophication
human-caused influx of nutrients (higher concentration of nitrogen, water is almost anoxic)
→ The removal of herbivorous fish adds to eutrophication (less fish to graze on producer)
neritic zones
-lies over the continental shelf
-not very deep
-plenty of nutrients and sunlight
-many organisms
kelp forest distribution
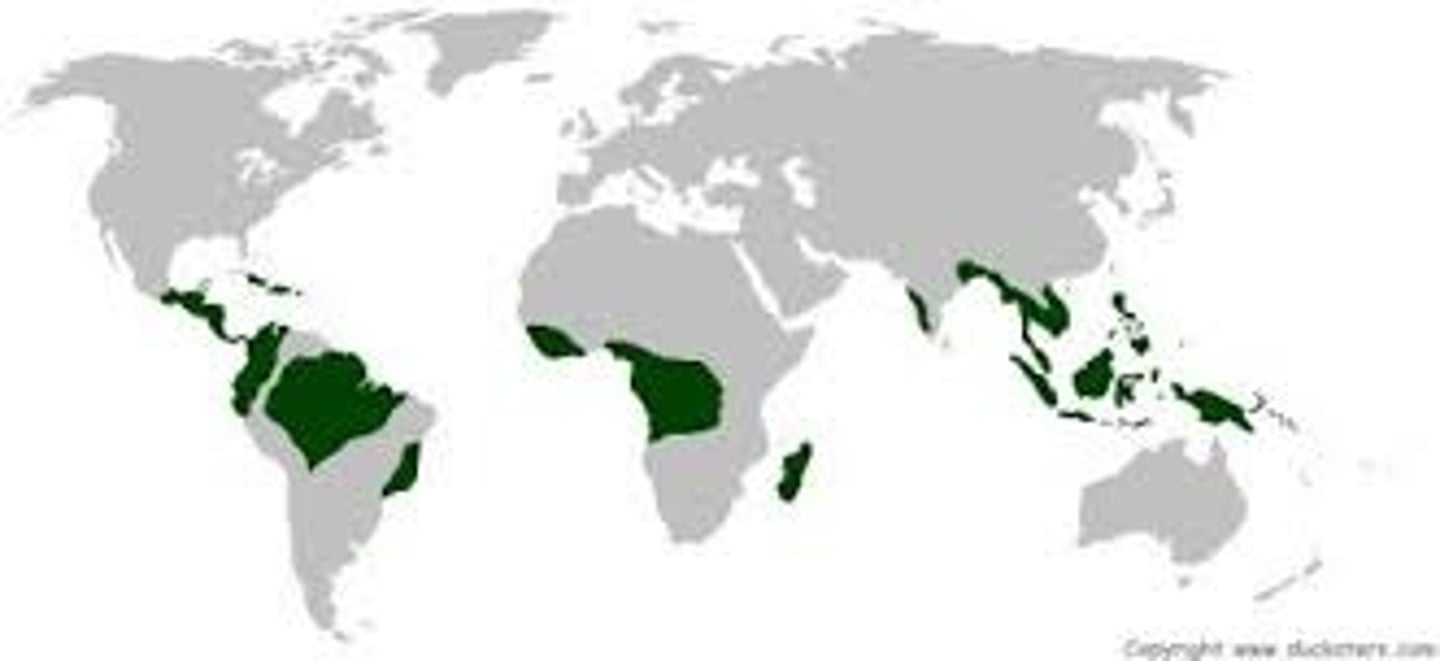
mangrove distribution
along tropical shores with limited wave action, a subtle slope (for sediment build up), high rate of sedimentation, and soil that's waterlogged, anoxic (no oxygen), and a high salt content.
oceanic zone
vast open ocean from the edge of the continental shelf outward

open ocean biome
The depth that light can penetrate in the open ocean is dependent on the amount of sediment and algae suspended in the water.
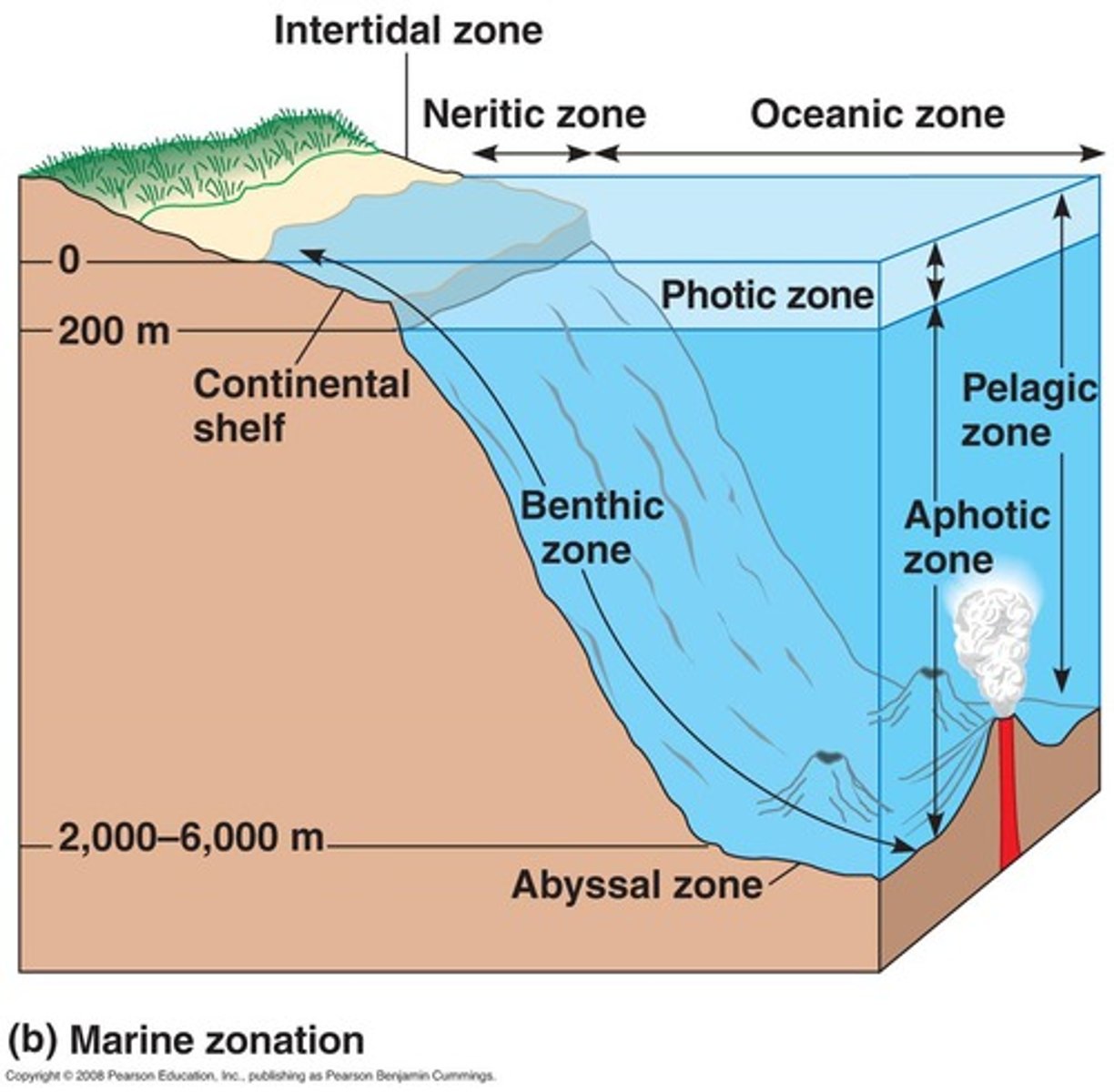
mesopelagic
known as the twilight zone, faint light
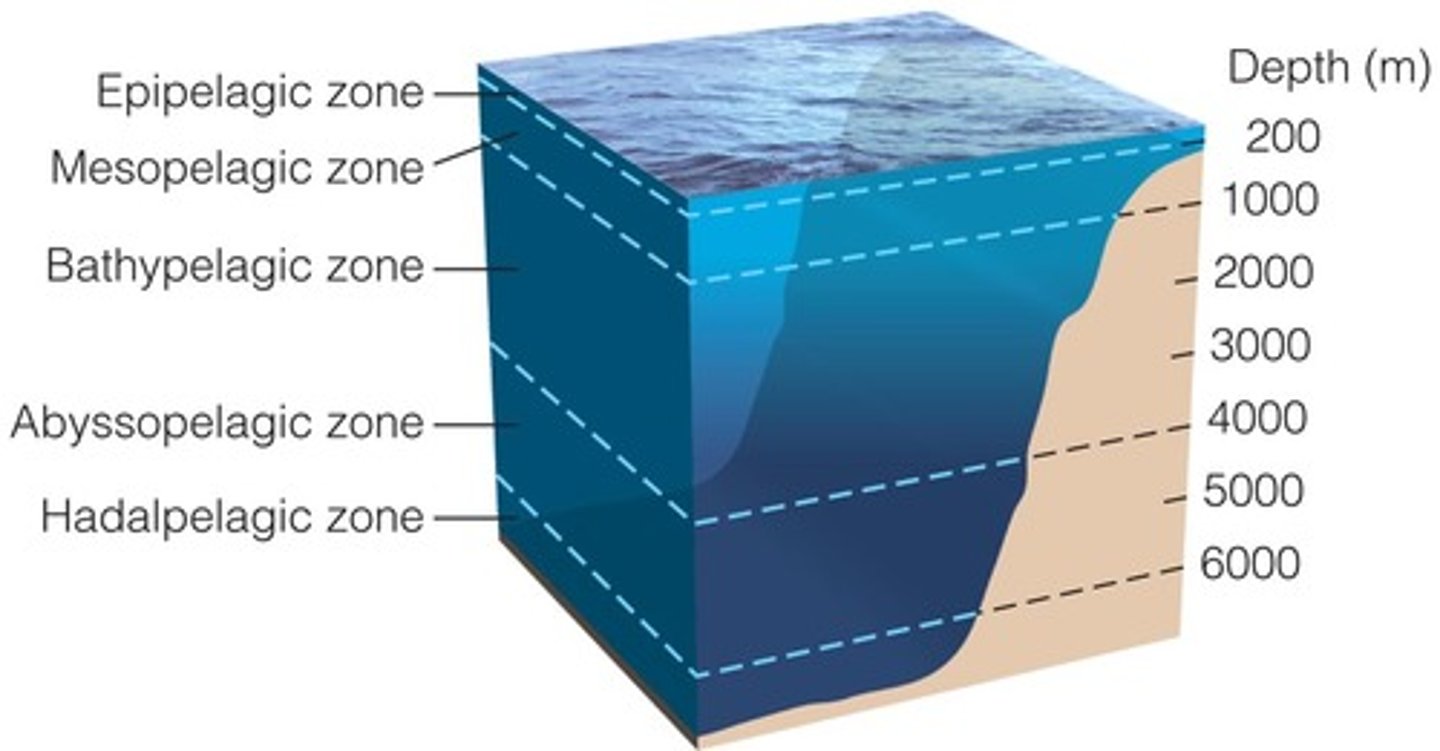
hydrothermal vents
spots on the ocean floor where hot gases and minerals escape from earth's interior into the water
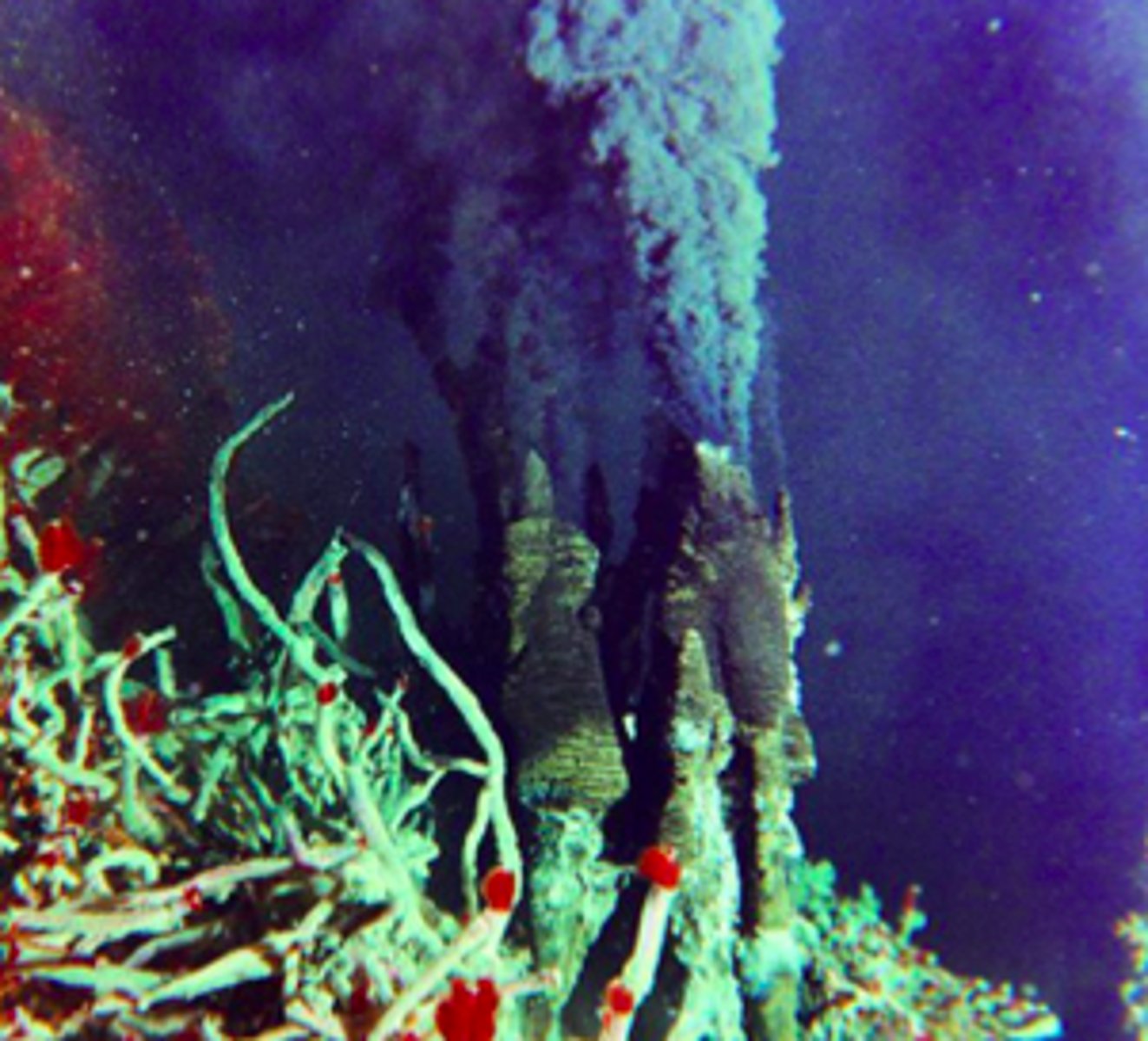

Chemoautotrophs
bacteria oxidize H2S from vents, form base of unique food web
evolution
change in allele frequencies in a population over time
genetic variation
Differences among individuals in the composition of their genes or other DNA segments

mutation
• Random changes to an allele (creating a new allele)
• Very rare
• Mostly neutral, or harmful, rarely beneficial
recombination
• Shuffling of alleles during sexual reproduction
• Creates new combinations of alleles (potentially, new phenotypes)
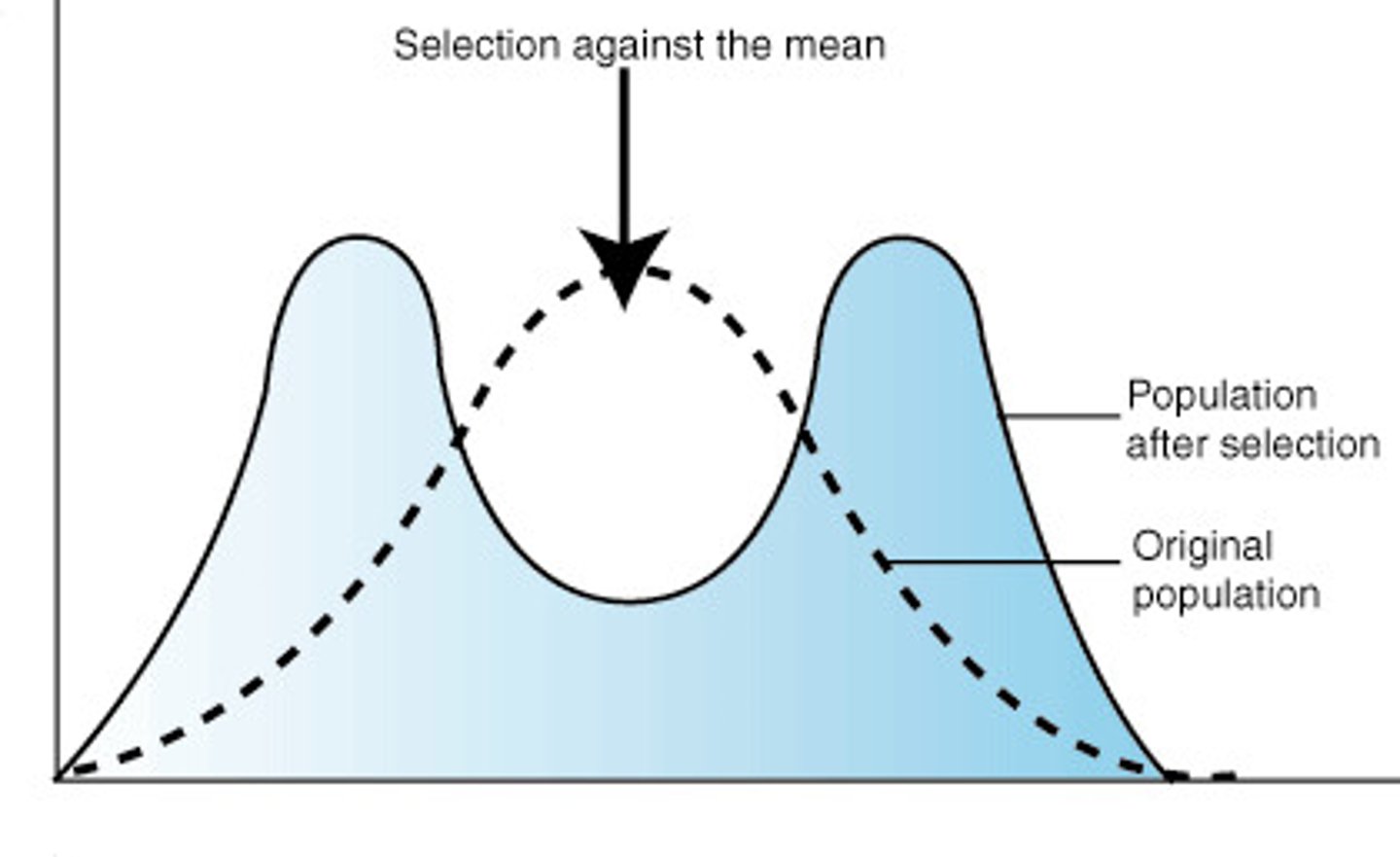
diversifying selection
a type of natural selection in which organisms with phenotypes at both extremes of the phenotypic range are favored by the environment
directional selection
Form of natural selection in which the entire curve moves; occurs when individuals at one end of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals in the middle or at the other end of the curve
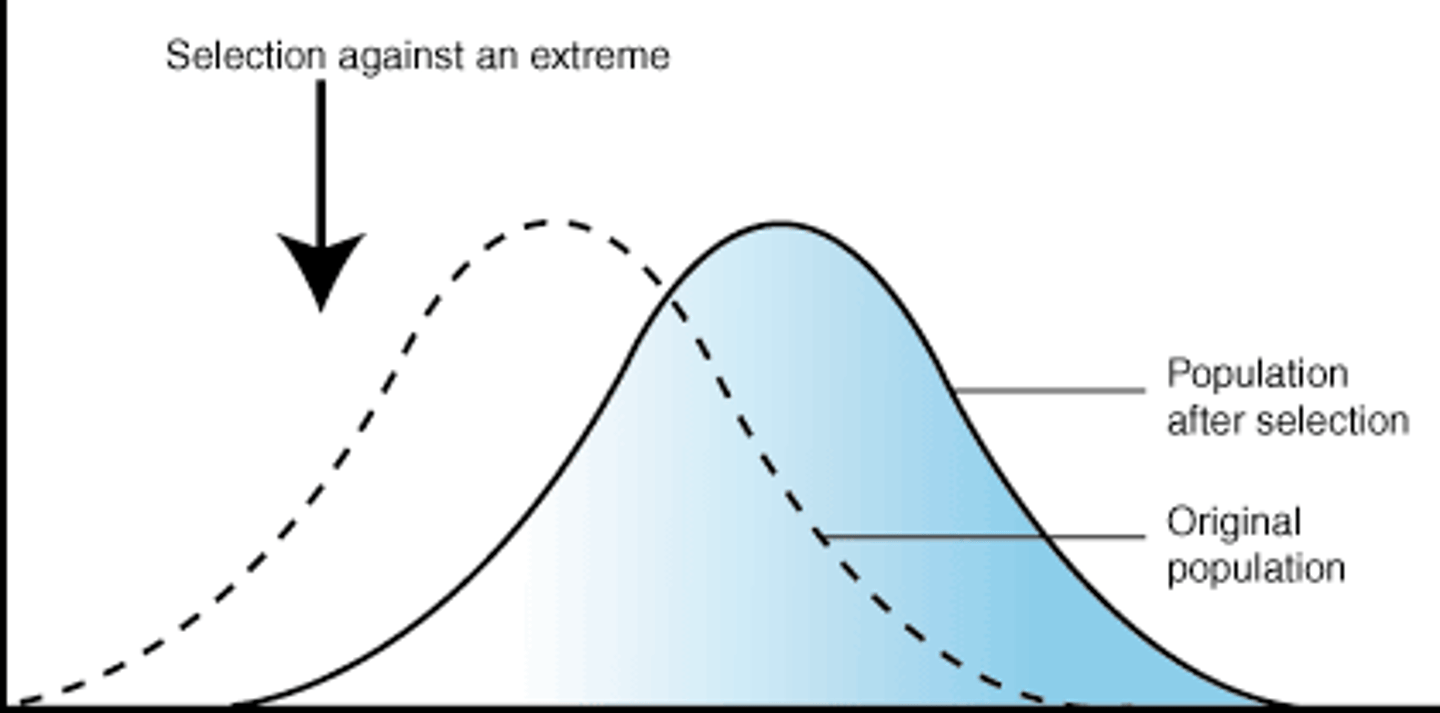
stabilizing selection
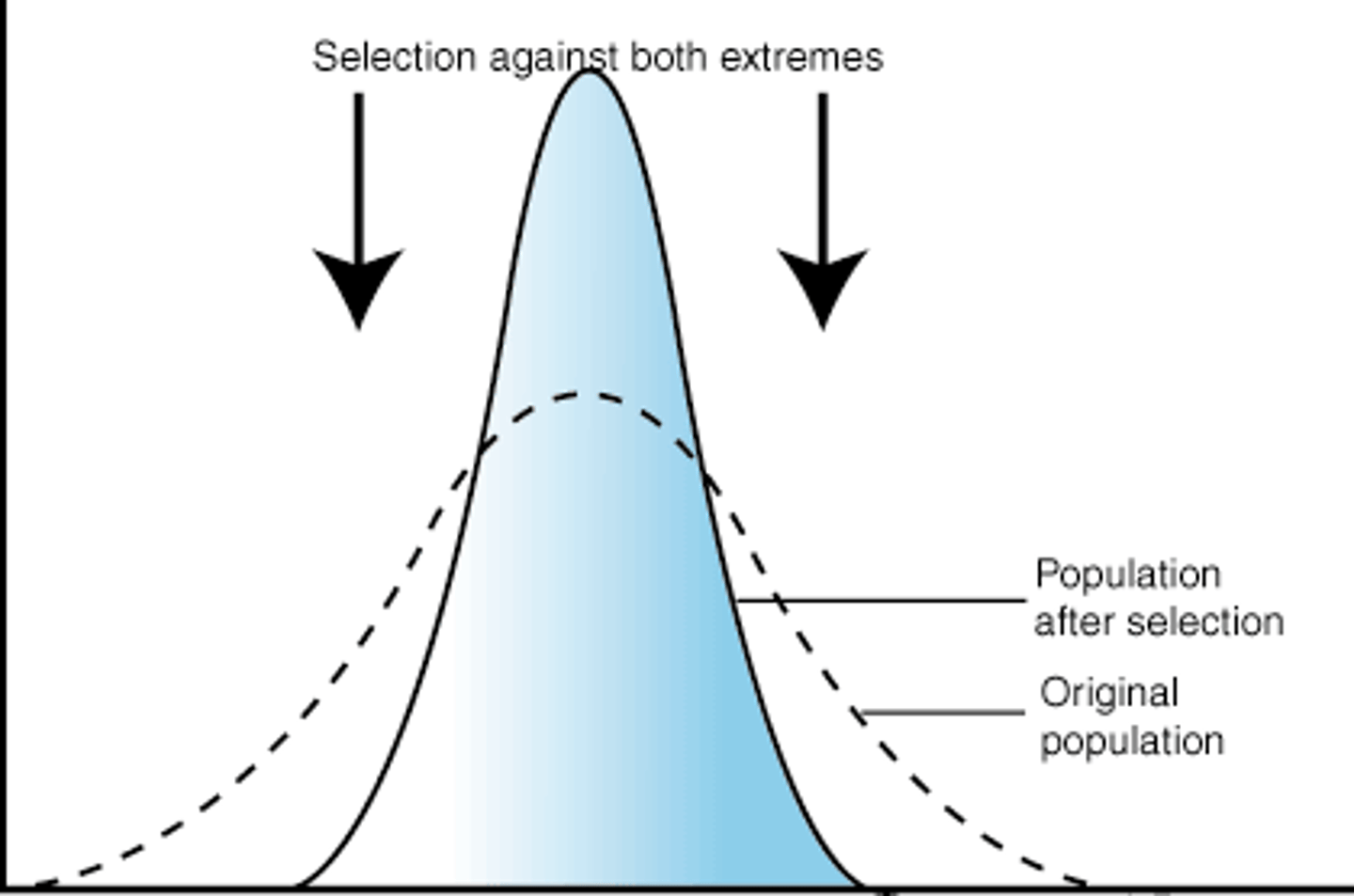
Natural selection that favors intermediate variants by acting against extreme phenotypes
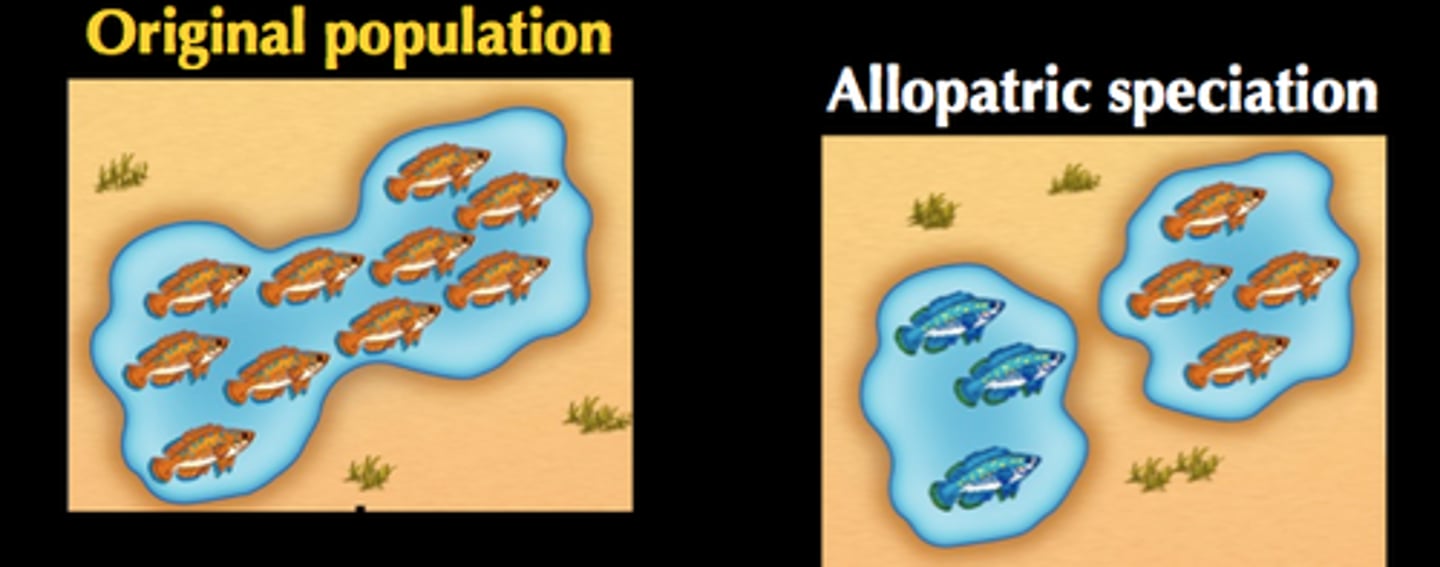
allopatric speciation
The formation of new species in populations that are geographically isolated from one another.
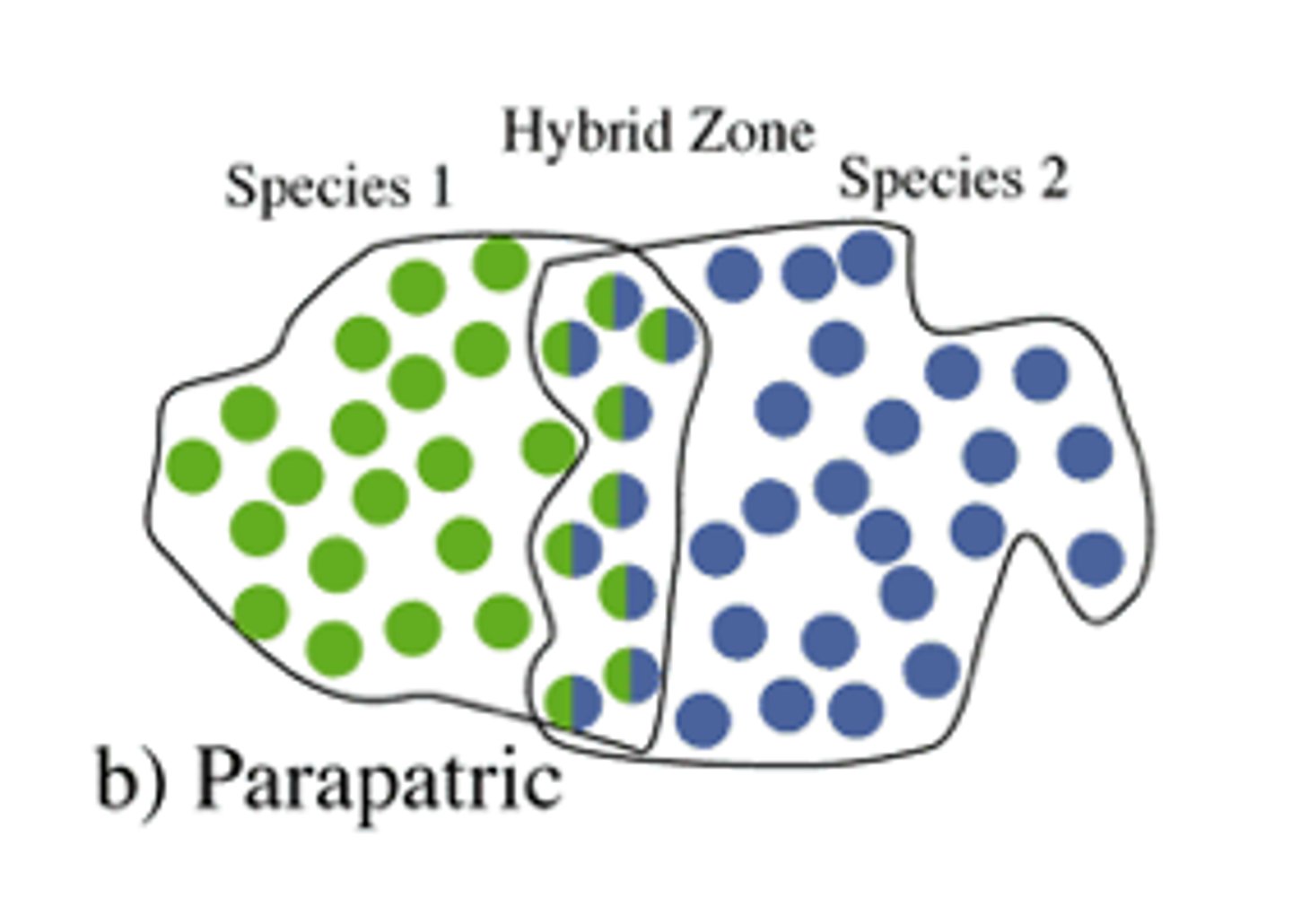
parapatric speciation
speciation pattern in which populations speciate while in contact along a common border
co-evolution
Process by which two species evolve in response to changes in each other

phenotypic plasticity
the ability of an organism to change its phenotype in response to changes in the environment.
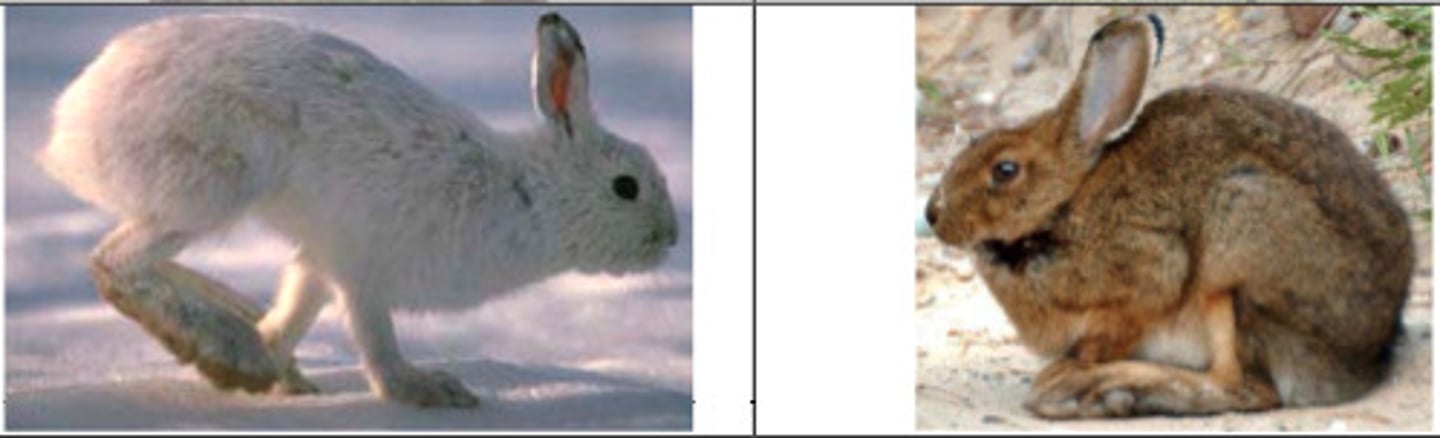

acclimation
an organism's change in response to a change in the organism's environment
developmental response
irreversible phenotypic change in response to environmental cues
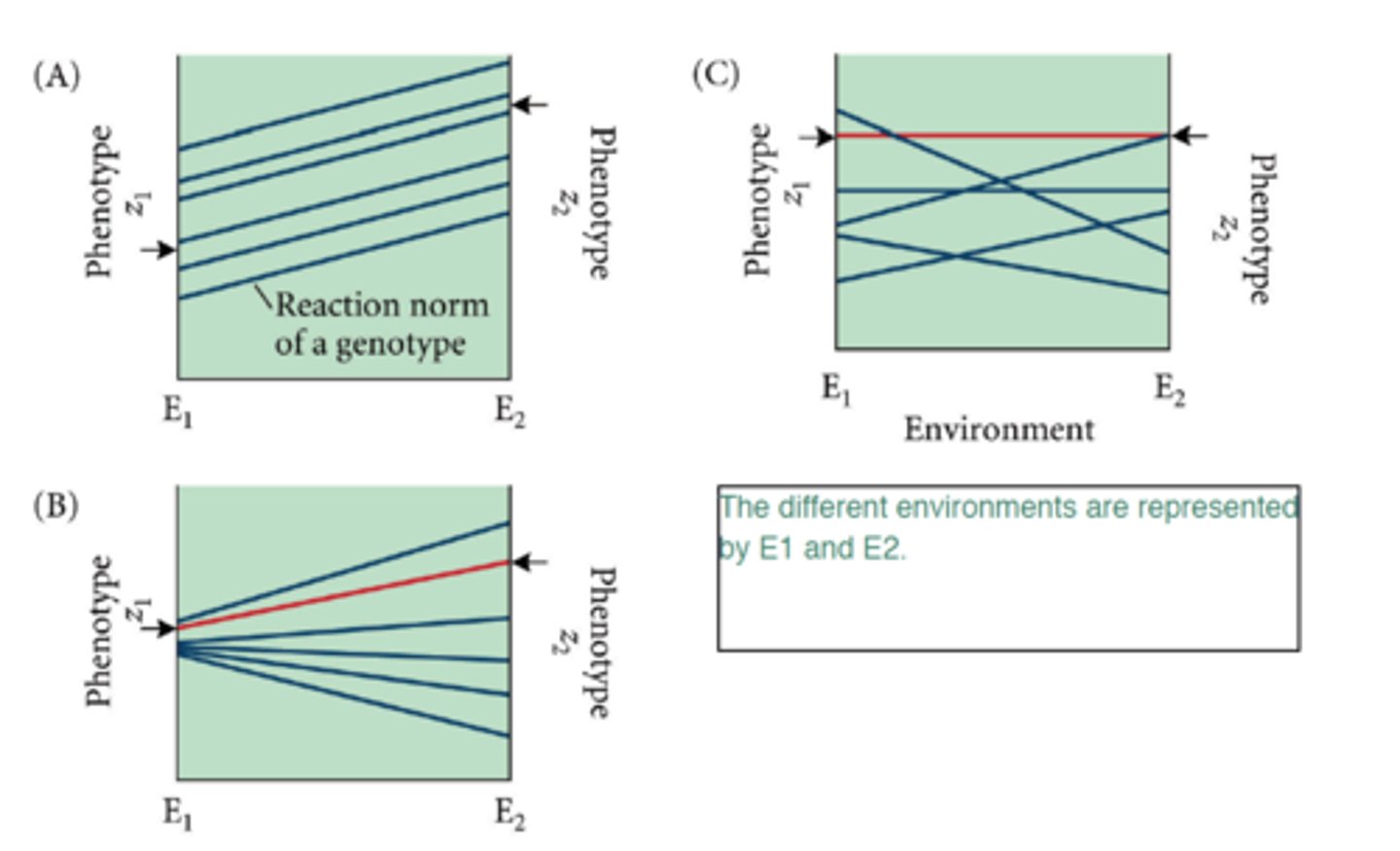
reaction norms
show a genotype's change in phenotype across a range of environments
niche partitioning
natural division of resources based on competitive advantages
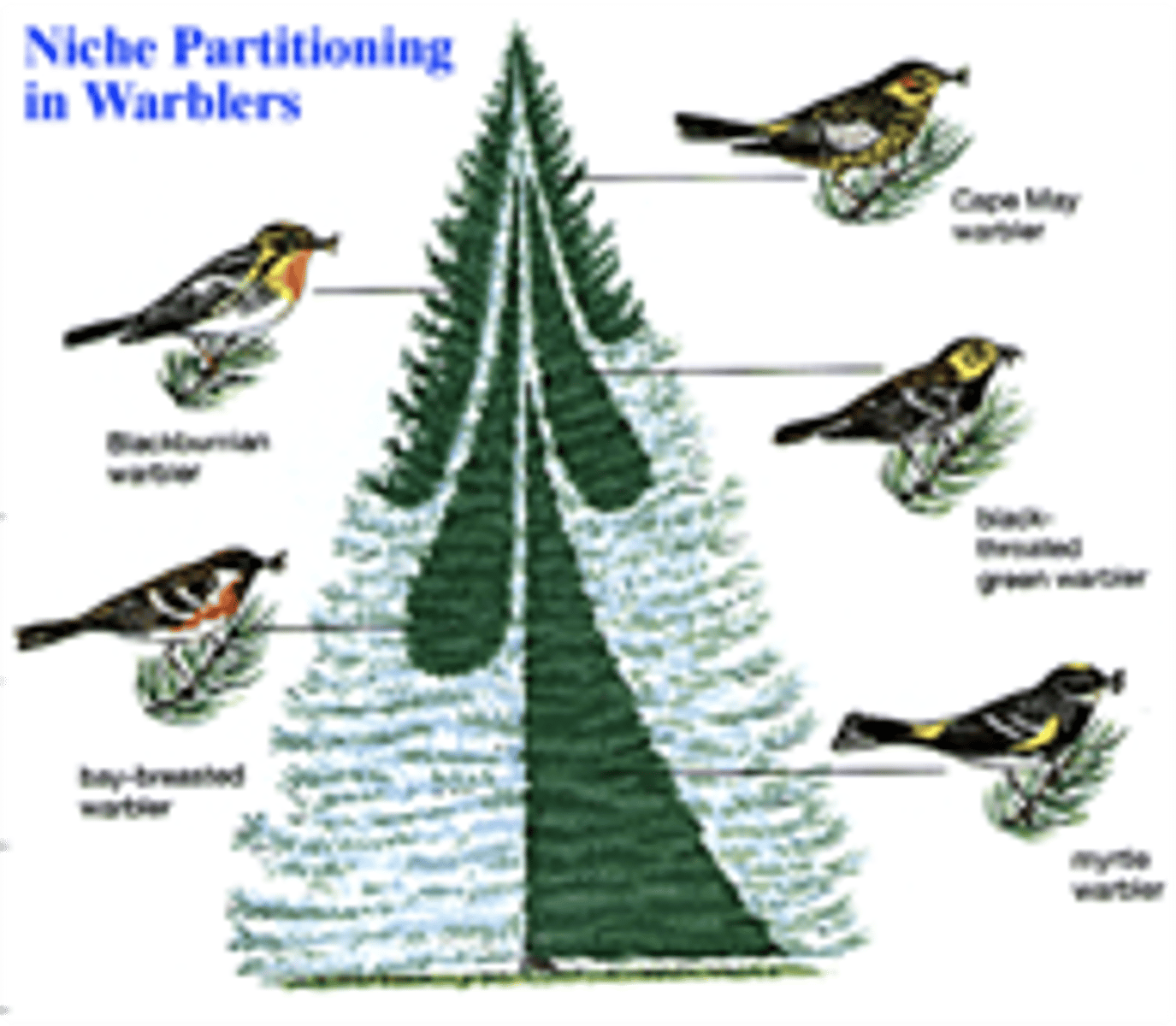
species distribution
areas of the world in which a species lives
niche
An organism's particular role in an ecosystem, or how it makes its living.
fundamental niche
environmental factors that permit a species to survive
• Defines conditions where a species might live, in the absence of interactions of other species
realized niche
the actual (observed) distribution of a species, as limited by ecological interactions such as competition, predation, disease and parasitism
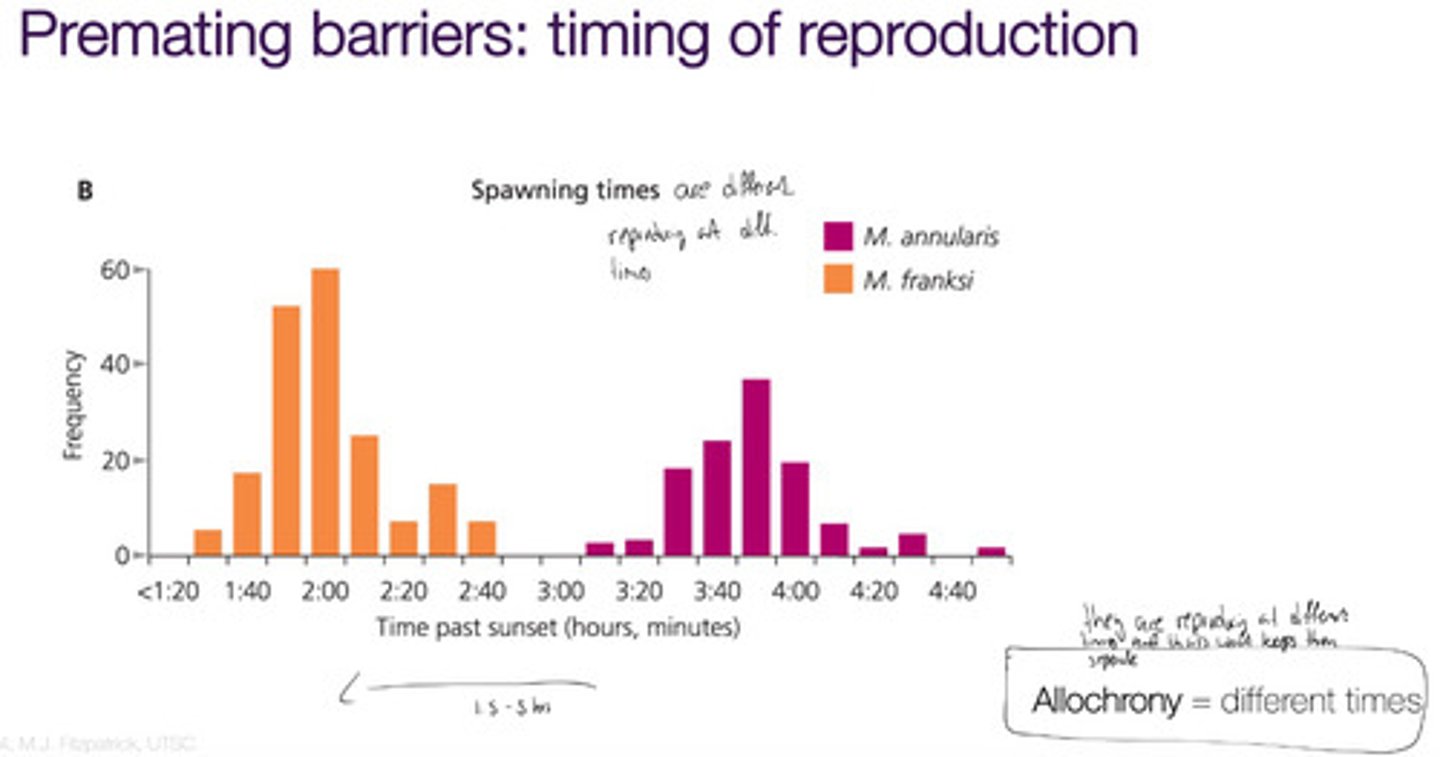
allochrony
species using the same area or resource, but at different times (includes different mating seasons)
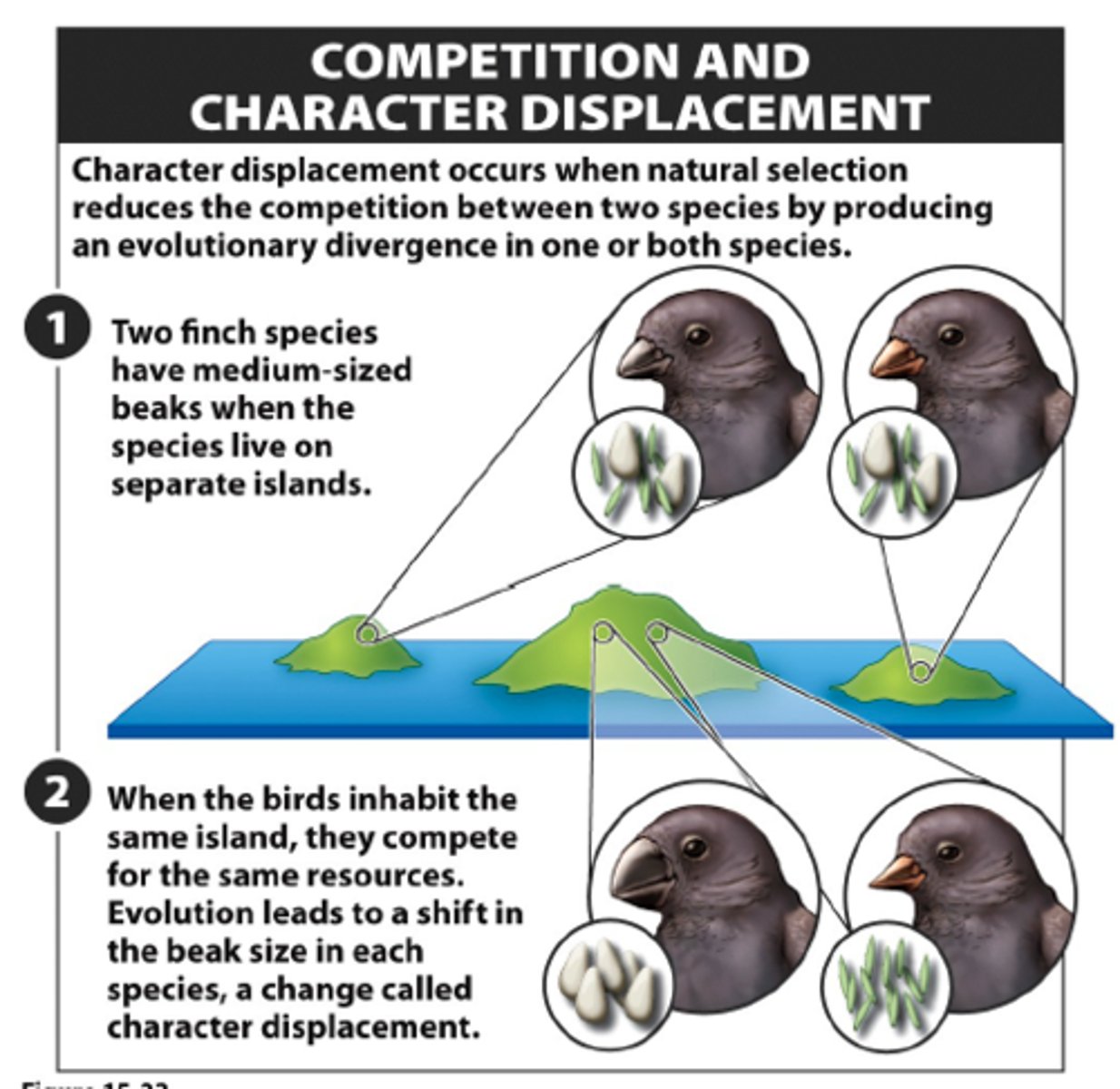
character displacement
Species evolve non-overlapping traits to avoid competition
extremophiles
species that have evolved to tolerate extreme conditions

homeotherms
Organisms that maintain a consistent body temperature

ectotherms
An animals that warms itself mainly by absorbing heat from its surroundings

poikilotherms
organisms that do not regulate their temperatures
food webs
A complex diagram representing the many energy pathways in an ecosystem
food chain
A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten
heterotrophs
An organism that obtains organic food molecules by eating other organisms or their by-products.
Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR)
wavelengths of light between 400 and 700 nm that photosynthetic organisms use as a source of energy
herbivores
Consumers that eat only plants
omnivores
eat both plants and animals
carnivores
Consumers that eat only animals
trophic levels
levels of nourishment in a food chain
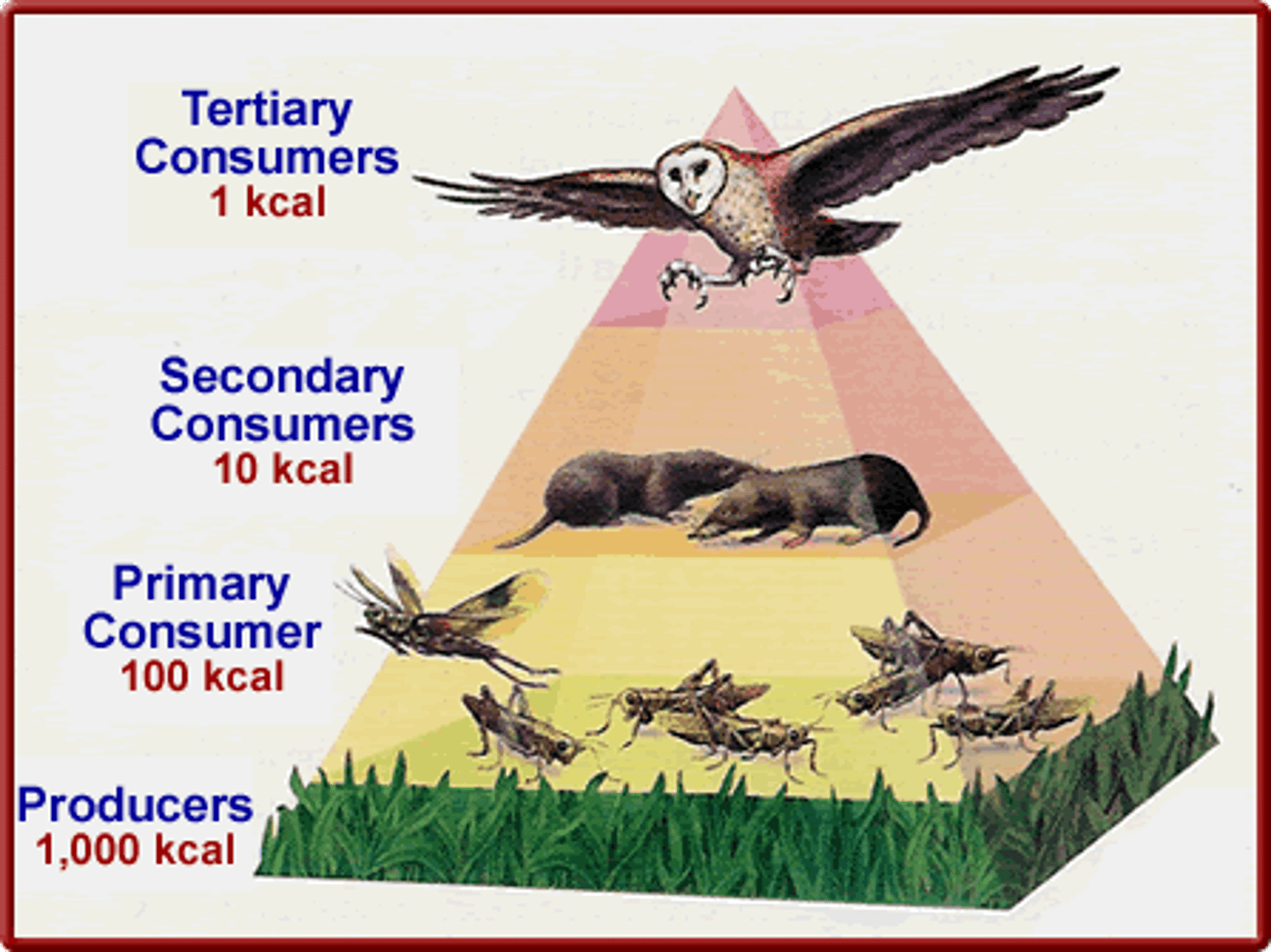
10% rule
Only 10% of the total energy produced at each trophic level is available to the next level. The amount of energy passed up to the levels of the food pyramid reduces as you go up.
optimal foraging
theory that states that natural selection will favor organisms that have behaviors that can gather the best food sources
OPT equation
(E/H+S)
nutritional ecology
the science of relating an animal to its environment through nutritional interactions
nutrition remobilization
the process by which plants relocate nutrients from older tissues to developing tissues, especially during periods of stress or senescence
sexual selection
A form of natural selection in which individuals with certain inherited characteristics are more likely than other individuals to obtain mates.
asexual reproduction
Process by which a single parent reproduces by itself
isogamy
gametes are equal in size
(lower chance of fertility = allows for more offspring)
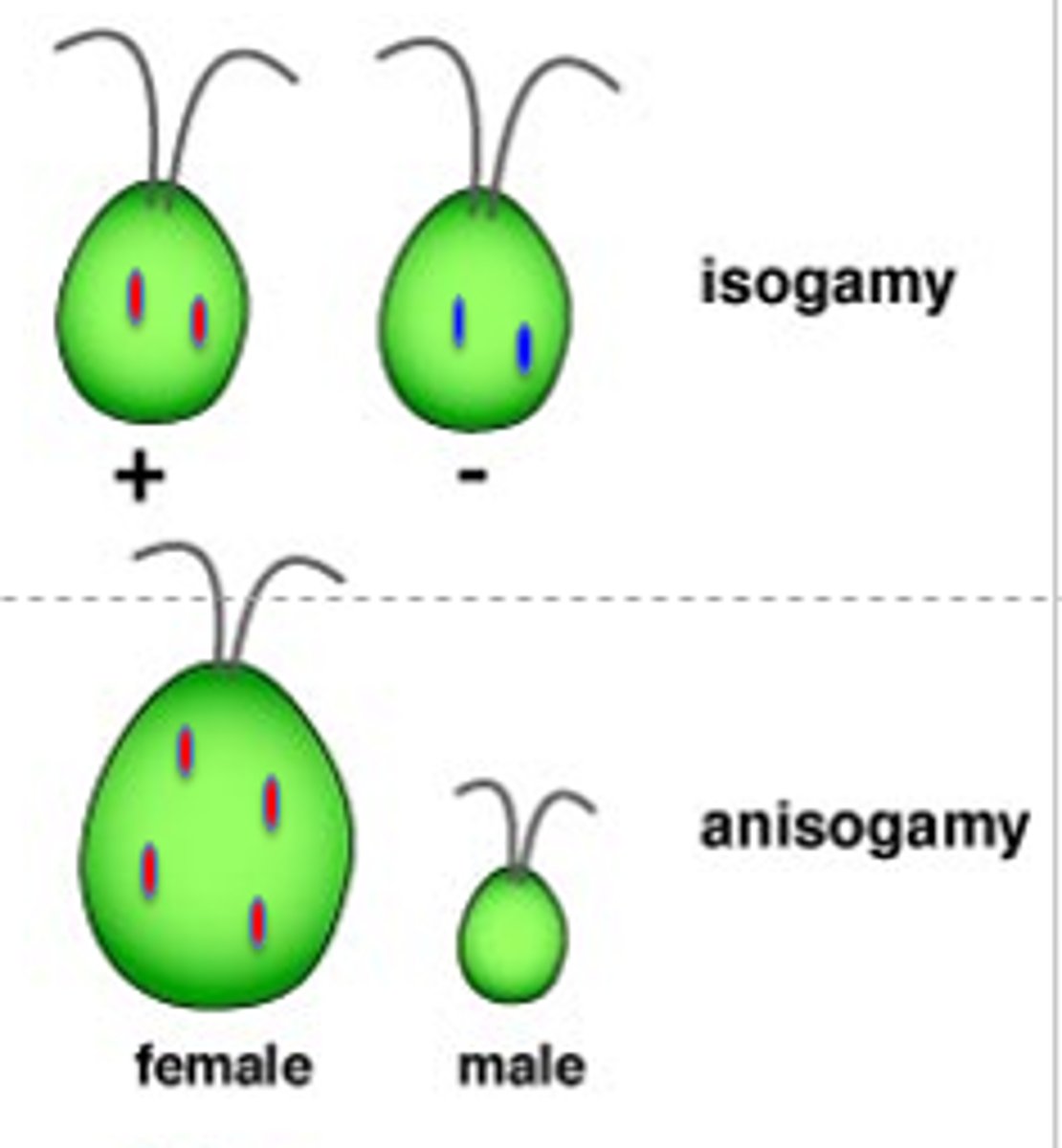
anisogamy
gametes are different in size, usually in the form of a larger egg
(higher chance of fertilization = less offspring)
gonochorism
a sexual system where each organism in a species is either male or female
Hermaphroditism
A condition in which an individual has both female and male gonads and functions as both a male and female in sexual reproduction by producing both sperm and eggs.
sexual dimorphism
Differences in physical characteristics between males and females of the same species.

intersexual selection
individuals of one sex are choosy in selecting their mates from the other sex (AKA mate choice)
intrasexual selection
A direct competition among individuals of one sex (usually the males in vertebrates) for mates of the opposite sex.
monogamy
pair bonding between a male and female, which exclusively mate with one another, raise offspring together and spend time together
polygamy
an organism may have multiple mating partners (polyandry and polygyny)
promiscuity
when multiple males and females mate with each other without forming pair bonds.
polygyny
a male will mate with several females
polyandry
a female will mate with several males
sociality
the preference for living in groups and interacting regularly with members of the same species
solitary
independent except for when mating
subsocial
mates and cares for own offspring but doesn't associate with other adults
parasocial
Co-habitate (live together) but care mostly for own young or related young
eusocial
organism population in which the role of each organism is specialized and not all of the organisms will reproduce
altruism
an individual will put themselves at risk of danger for the welfare of the rest of the pack (alarm calls, self-sacrifice, alloparenting)
Hamilton's rule of fitness
rB > C