Lab 6: Angiosperms
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Angiosperm term breakdown
angio = vessel
sperm = seed
Advantages of angiosperms
seeds protected
shorter generation times (natural selection)
more efficient pollination (rely on pollinators)
better seed dispersal (fruit)
more efficient vascular tissue
4 whorls of angiosperm structure
sepals
petals
stamen
carpel
Complete flower
all 4 whorls present
Incomplete flower
at least 1 whorl missing
In incomplete flower, sterile female is called
carpellate
In incomplete flower, sterile male is called
staminate
Monocot
flower parts in multiples of 3
leaves parallel veins
no secondary growth (girth)
vascular bundles randomly distributed
fibrous root
Eudicot
flower parts in multiples of 4-5
netted veins
secondary growth (vascular cambium)
vascular bundles as a ring
taproot system
Tepals are
when sepal and petal cannot be differentiated from each other
Superior Ovary is when
ovary occurs at same level or above the stamen (where anthers are connected)
Inferior Ovary is when
ovary occurs below the stamen (where anthers are connected)
Radial symmetry:
if you split the flower in half, it will be symmetrical in 2+ ways
Bilateral symmetry:
if you split the flower in half, it can only be symmetrical 1 way
Connation:
fusion of 1 whorl
Adnation
fusion of 2 different whorls (think about ADDing whorls)
Perfect monoecious plant:
has both stamens and carpels
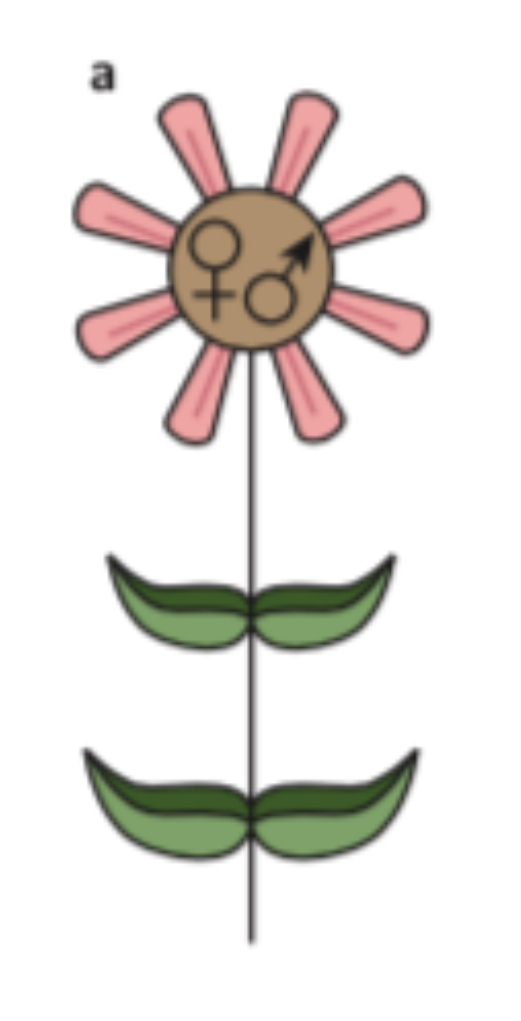
Identify the type of plant and what it signifies
Imperfect flower; has both stamens and carpels on one flower
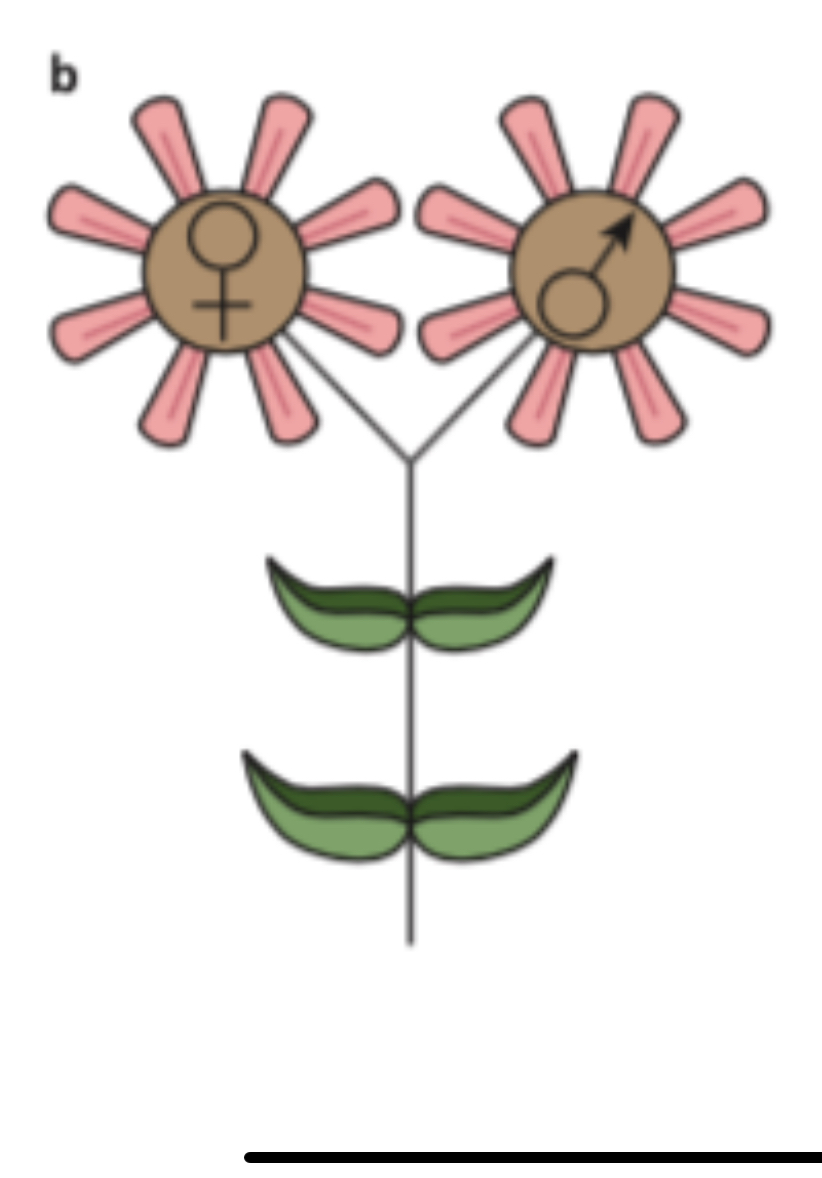
Identify the type of plant and what it signifies
Monoecious
(“one house”) has both male and female flowers on one plant
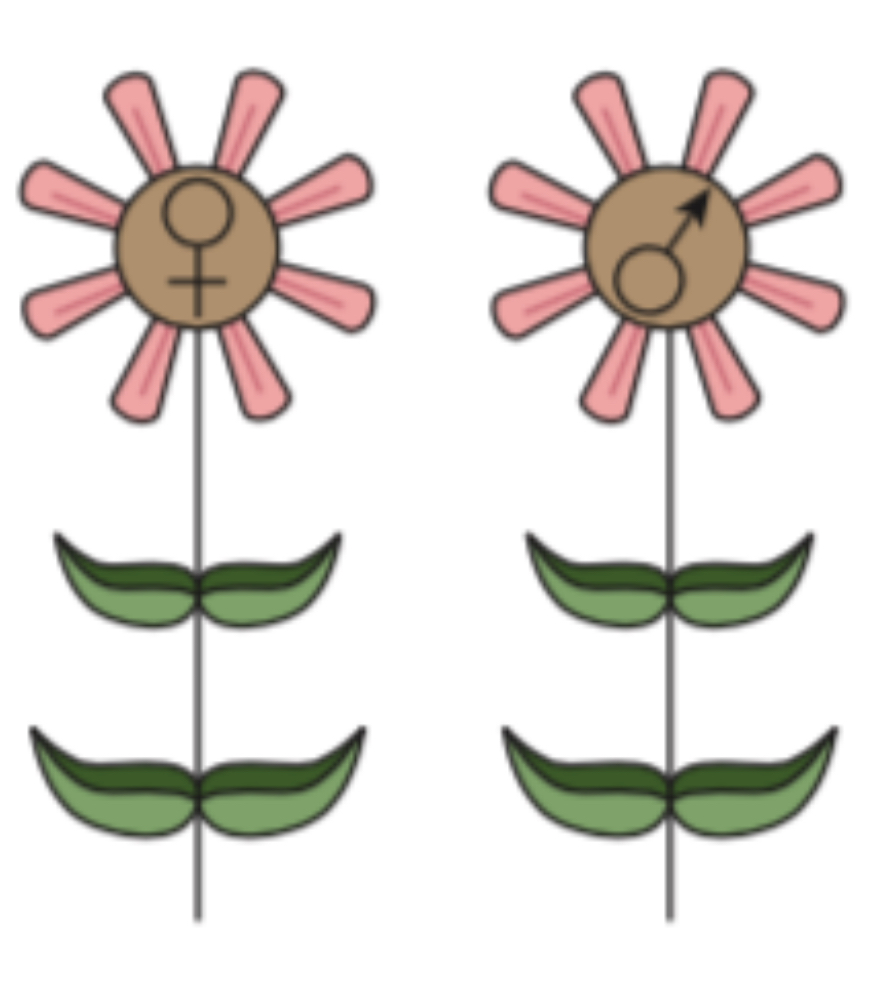
Identify the type of plant and what it signifies
Dioecious
(“two houses) has the male and female flowers found on different plants
What type of plant is corn?
Imperfect monoecious; Dicot
Inflorescence:
group of flowers attached to receptacle (ie. lots of flower on a single head. **no sepal)
Ray flowers:
Imperfect monoecious, often bilateral symmetry
Disk flowers:
Radially symmetric. Have all 4 whorls
Perfect flower
Traits of berries
More than 1 seed
fruit is fleshy/slimy
skin is thin
Traits of hesperidium
subtype of berry with skin you can peel
each segment contains more than 1 seed
Traits of pepo
subtype of berry with hard leathery rind
inside layers are fleshy, enclose many seeds
Traits of pome
flower has inferior ovary
flesh is primarily receptacle tissue
Traits of drupe
endocarp is hard
single seed inside
mesocarp is fleshy
exocarp is skin
Traits of aggregate fruits
From many ovaries on a single flower
Traits of multiple fruits
from ovaries of many flowers, fused together
Traits of dehiscents
fruit opens along 2 suture lines
pea pod is fruit
peas are the seeds
Traits of follicles
fruit opens along 1 suture
Traits of capsules
seeds released through multiple sutures/pores
Traits of samara
pericarp is thin and has a wing
Traits of nuts
pericarp is thick and hard
Traits of caryopsis
pericarp is thin and does not have a wing
seed coat is fused to pericarp
Traits of achenes
pericarp is thin and does not have a wing
seed coat is NOT fused to pericarp
Examples of berries
tomato, kiwi, blueberries, green pepperE
Examples of hesperidium
oranges and lemons
Examples of pepo
cucumber, squash, gourd
Example of pome
apple and pear
Example of drupe
cherry, coconut, avocado, plum
Examples of aggregate fruits
strawberry and raspberry
Example of multiple fruit
pineapple
Examples of legumes
pea family (peas, beans)
Examples of follicles
milkweed, columbine, larkspur
Examples of capsules
poppy, tulip, iris
Example of samaras
maple and ash
Examples of nut
acorn
Examples of caryopsis
grass family (wheat, rice, oats)
Examples of achenes
sunflower and dandelion
Define fleshy fruits
generally attractive to animals because of color and/or smell
Dry fruits are either ________ or ________
dehiscent, indehiscent
Define dehiscent fruits:
fruit splits open at maturity
Define indehiscent fruits:
fruit does not split open at maturity (something else is needed to release it)
How does a seed develop into zygote?
1) Zygote develops into embryo
2) Embryo surrounded by 3N endosperm
tissue
3) Ovary develops into fruit
4) Ovule develops into the seed